生态环境学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (2): 212-221.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.02.005
曹晓霭1( ), 张睿1, 温云浩1, 王建1, 徐智超1, 田雅婷4, 王立新1,2,3, 刘华民1,2,3,*(
), 张睿1, 温云浩1, 王建1, 徐智超1, 田雅婷4, 王立新1,2,3, 刘华民1,2,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-10-19
出版日期:2024-02-18
发布日期:2024-04-03
通讯作者:
*刘华民。E-mail: Liuhmimu@aliyun.com作者简介:曹晓霭(1993年生),博士研究生,研究方向为环境生态学。E-mail: 1062695375@qq.com
基金资助:
CAO Xiaoai1( ), ZHANG Rui1, WEN Yunhao1, WANG Jian1, XU Zhichao1, TIAN Yating4, WANG Lixin1,2,3, LIU Huamin1,2,3,*(
), ZHANG Rui1, WEN Yunhao1, WANG Jian1, XU Zhichao1, TIAN Yating4, WANG Lixin1,2,3, LIU Huamin1,2,3,*( )
)
Received:2023-10-19
Online:2024-02-18
Published:2024-04-03
摘要:
土壤酶活性是土壤生态系统物质循环和能量流动的重要参与者,其活性大小对土壤养分和生化反应过程有明显指示作用。北方高纬度湿地经常受到冻融作用的影响,由于土壤温度的变化,土壤酶活性会发生变化。然而,春季冻融对土壤酶活性的影响机制仍不清楚。为探讨春季冻融过程对河滨带湿地土壤理化性质和土壤酶活性的影响,以及土壤理化性质与土壤酶活性间的关系,选取锡林河河滨带分布最广泛的芦苇(Phragmites australis)和灰脉苔草(Carex appendiculata)这2种典型湿地植物群落为研究对象,分析春季冻融期间土壤脲酶、蔗糖酶、过氧化氢酶活性的变化及其影响因素。在冻结期,河滨带湿地土壤酶活性均保持较高活性,土壤脲酶和蔗糖酶活性在冻融期均出现迅速增高而后降低的趋势,并在土壤融化期又升高,然而土壤过氧化氢酶对冻融作用的响应较小。在冻融过程中,芦苇覆盖下土壤蔗糖酶和过氧化氢酶活性显著高于灰脉苔草群落且表现出明显的空间异质性。通径分析结果表明,春季冻融期河滨带湿地土壤脲酶活性与土壤温度、总碳、总氮显著正相关,土壤蔗糖酶与总碳、总氮呈显著正相关;过氧化氢酶活性除与土壤温度没有显著相关性,与其他理化因子均有显著相关性。冻融期不同植物群落下土壤酶活性与河滨带湿地碳、氮含量密切相关,频繁的冻融对土壤酶活性以及河滨带湿地土壤物质循环产生重要影响。该研究探讨了3种土壤酶活性对春季冻融过程的响应及在植物群落间的差异,为河滨带湿地生态系统碳、氮等营养物质的循环提供理论依据。
中图分类号:
曹晓霭, 张睿, 温云浩, 王建, 徐智超, 田雅婷, 王立新, 刘华民. 春季冻融过程对河滨带湿地土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(2): 212-221.
CAO Xiaoai, ZHANG Rui, WEN Yunhao, WANG Jian, XU Zhichao, TIAN Yating, WANG Lixin, LIU Huamin. Effect of Spring Freeze-thaw Process on Soil Enzyme Activities in Riparian Wetland[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(2): 212-221.
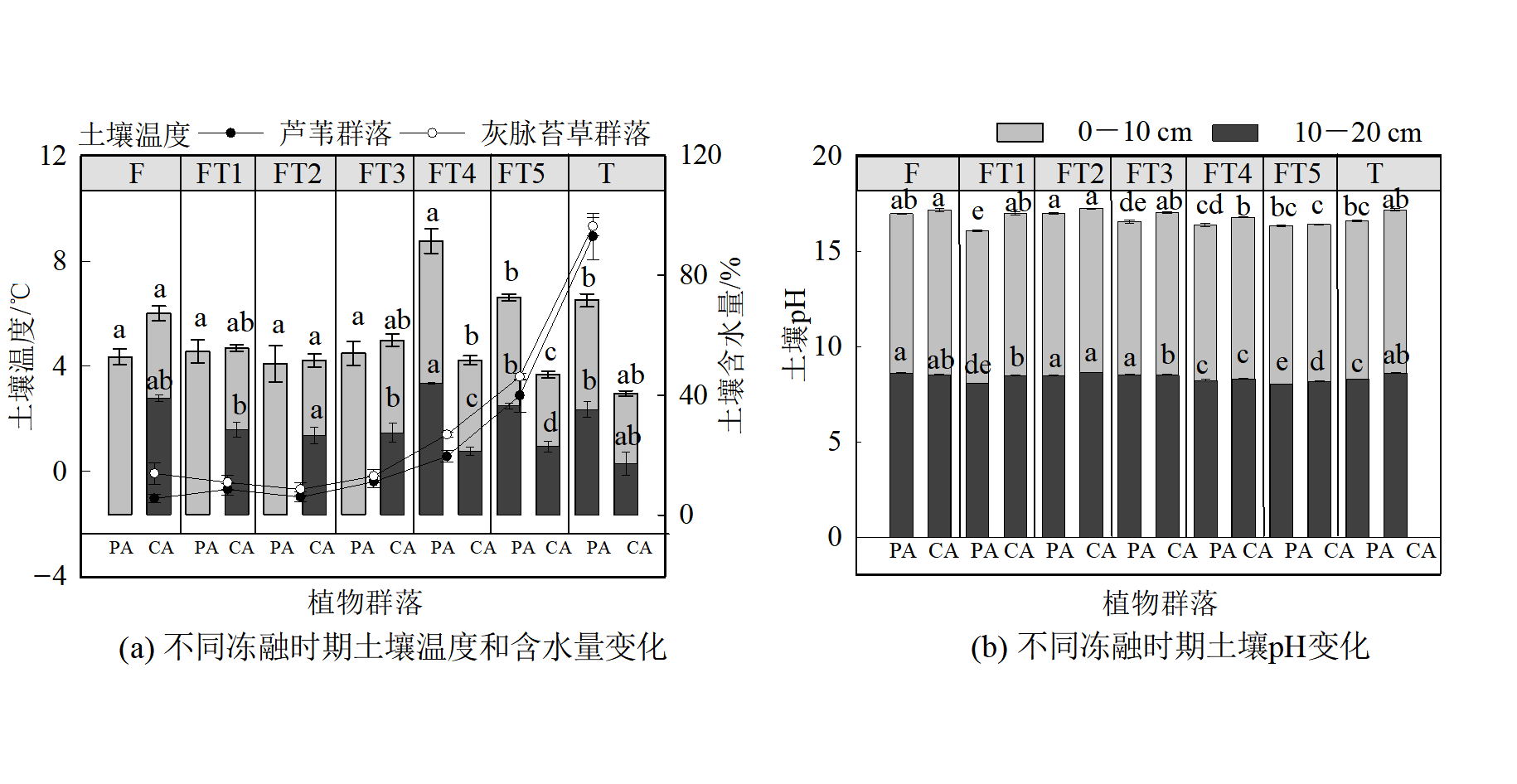
图2 河滨带湿地不同冻融时期土壤温度、土壤含水量和土壤pH变化 不同小写字母表示不同冻融时期差异性显著,n=5;PA代表芦苇群落,CA代表灰脉苔草群落;下同
Figure 2 Change of soil temperature, soil water content and soil pH in different freeze-thaw periods of riparian wetlands
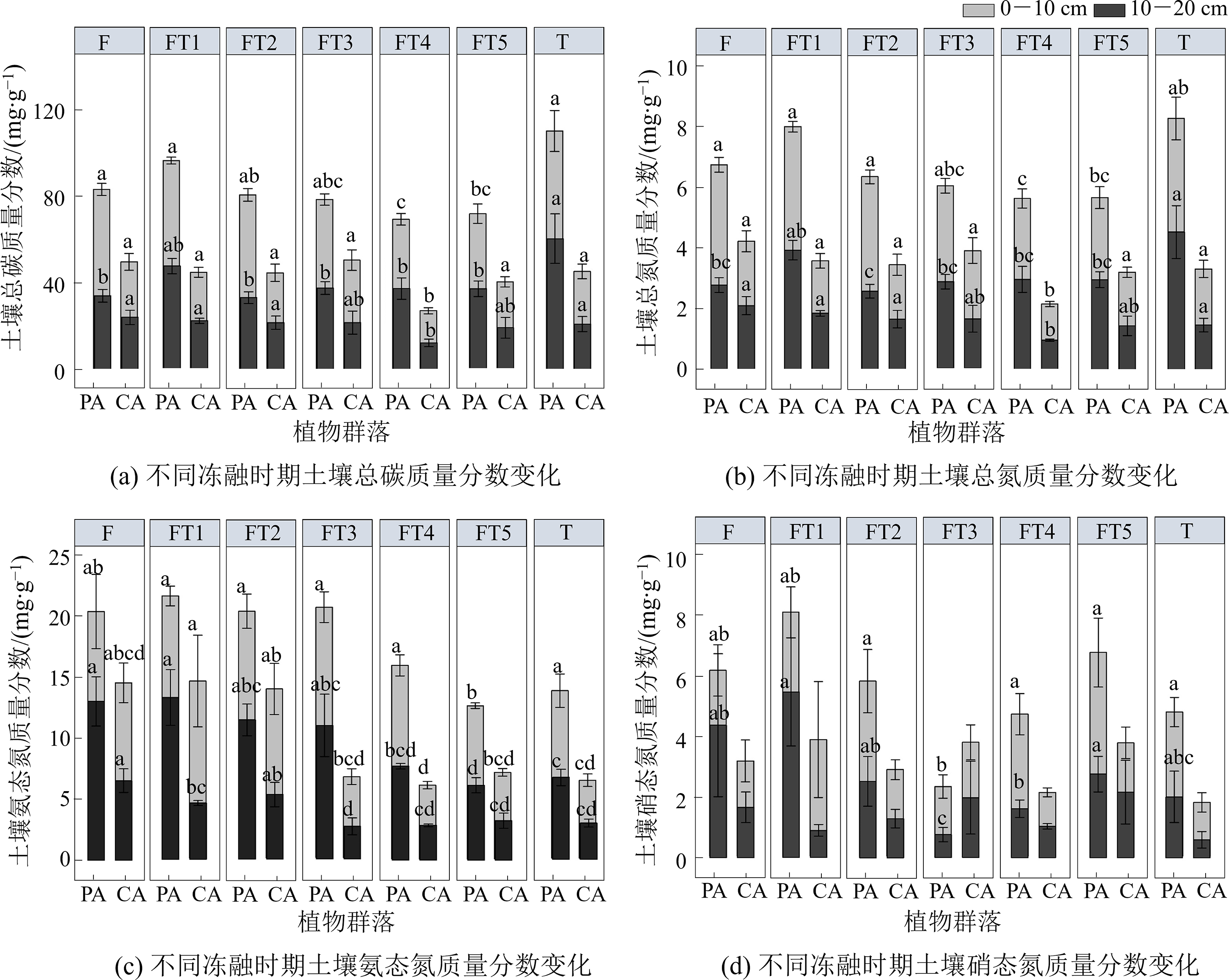
图3 河滨带湿地不同冻融时期土壤总碳、总氮、氨态氮和硝态氮含量变化
Figure 3 Change of soil total carbon, total nitrogen, ammonia nitrogen and nitrate nitrogen contents in different freeze-thaw periods of riparian wetlands
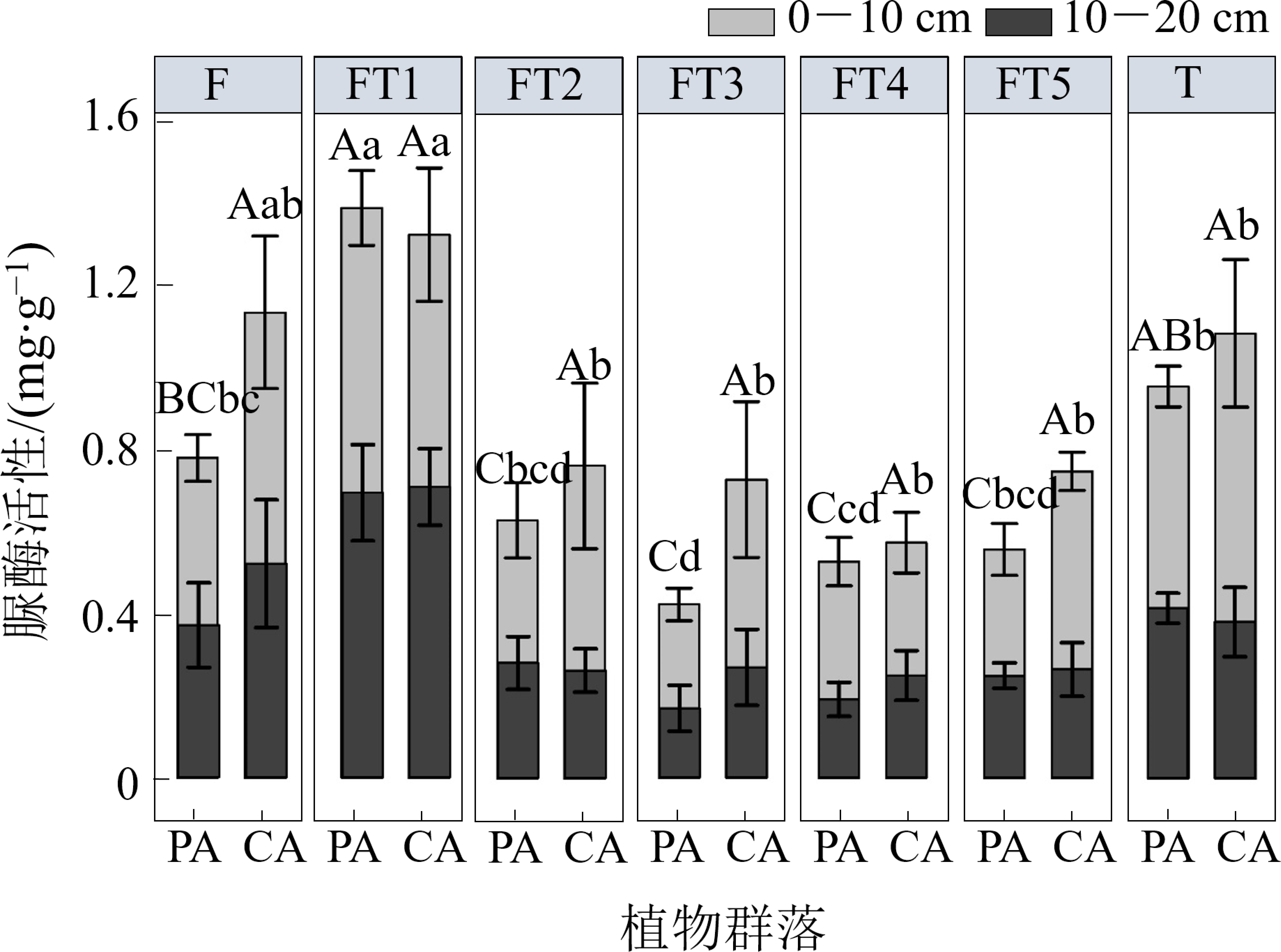
图4 春季冻融期2种植物群落土壤脲酶活性变化 不同大写字母和小写字母分别代表0-10 cm和10-20 cm土层不同采样时期数据差异显著(P<0.05)
Figure 4 Changes of soil urease activity in two plant communities during spring freezing-thawing period
| 酶类型 | 芦苇群落 | 灰脉苔草群落 |
|---|---|---|
| 脲酶 | 0.374±0.025a | 0.451±0.037a |
| 蔗糖酶 | 23.466±0.903a | 19.497±0.909b |
| 过氧化氢酶 | 1.162±0.012a | 0.945±0.021b |
表1 采样期不同植物群落土壤酶活性
Table 1 Soil enzyme activities in different plant communities during the sampling period
| 酶类型 | 芦苇群落 | 灰脉苔草群落 |
|---|---|---|
| 脲酶 | 0.374±0.025a | 0.451±0.037a |
| 蔗糖酶 | 23.466±0.903a | 19.497±0.909b |
| 过氧化氢酶 | 1.162±0.012a | 0.945±0.021b |
| 因子 | 土壤酶类型 | df | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 植被 | 脲酶 | 1 | 3.936 | 0.050 |
| 蔗糖酶 | 1 | 14.967 | 0.000 | |
| 过氧化氢酶 | 1 | 87.611 | 0.000 | |
| 时期 | 脲酶 | 6 | 8.007 | 0.000 |
| 蔗糖酶 | 6 | 5.439 | 0.000 | |
| 过氧化氢酶 | 6 | 3.354 | 0.004 | |
| 深度 | 脲酶 | 1 | 8.328 | 0.005 |
| 蔗糖酶 | 1 | 8.336 | 0.005 | |
| 过氧化氢酶 | 1 | 8.437 | 0.004 | |
| 植被*时期 | 脲酶 | 6 | 0.479 | 0.823 |
| 蔗糖酶 | 6 | 1.532 | 0.174 | |
| 过氧化氢酶 | 6 | 0.928 | 0.478 | |
| 植被*深度 | 脲酶 | 1 | 0.899 | 0.345 |
| 蔗糖酶 | 1 | 5.462 | 0.021 | |
| 过氧化氢酶 | 1 | 0.132 | 0.717 | |
| 时期*深度 | 脲酶 | 6 | 0.663 | 0.679 |
| 蔗糖酶 | 6 | 2.936 | 0.011 | |
| 过氧化氢酶 | 6 | 1.292 | 0.267 | |
| 植被*时期*深度 | 脲酶 | 6 | 0.313 | 0.929 |
| 蔗糖酶 | 6 | 4.961 | 0.000 | |
| 过氧化氢酶 | 6 | 1.022 | 0.415 |
表2 植被类型、冻融时期和土层深度交互作用下土壤酶活性的多因素方差分析
Table 2 Multivariate variance analysis of soil enzyme activity under the interaction of vegetation type, freeze-thaw period and soil depth
| 因子 | 土壤酶类型 | df | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 植被 | 脲酶 | 1 | 3.936 | 0.050 |
| 蔗糖酶 | 1 | 14.967 | 0.000 | |
| 过氧化氢酶 | 1 | 87.611 | 0.000 | |
| 时期 | 脲酶 | 6 | 8.007 | 0.000 |
| 蔗糖酶 | 6 | 5.439 | 0.000 | |
| 过氧化氢酶 | 6 | 3.354 | 0.004 | |
| 深度 | 脲酶 | 1 | 8.328 | 0.005 |
| 蔗糖酶 | 1 | 8.336 | 0.005 | |
| 过氧化氢酶 | 1 | 8.437 | 0.004 | |
| 植被*时期 | 脲酶 | 6 | 0.479 | 0.823 |
| 蔗糖酶 | 6 | 1.532 | 0.174 | |
| 过氧化氢酶 | 6 | 0.928 | 0.478 | |
| 植被*深度 | 脲酶 | 1 | 0.899 | 0.345 |
| 蔗糖酶 | 1 | 5.462 | 0.021 | |
| 过氧化氢酶 | 1 | 0.132 | 0.717 | |
| 时期*深度 | 脲酶 | 6 | 0.663 | 0.679 |
| 蔗糖酶 | 6 | 2.936 | 0.011 | |
| 过氧化氢酶 | 6 | 1.292 | 0.267 | |
| 植被*时期*深度 | 脲酶 | 6 | 0.313 | 0.929 |
| 蔗糖酶 | 6 | 4.961 | 0.000 | |
| 过氧化氢酶 | 6 | 1.022 | 0.415 |
| 因变量 | 自变量 | r | 温度X1 | pH X2 | 含水量X3 | 总碳X4 | 总氮X5 | 氨态氮X6 | 硝态氮X7 | 间接通径系数和IPC Sum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 脲酶 | X1 | 0.268**1) | 0.253 | 0.003 | 0.089 | −0.066 | −0.004 | −0.013 | 0.005 | 0.015 |
| X2 | 0.123 | 0.014 | 0.060 | 0.153 | −0.094 | −0.007 | −0.005 | 0.003 | 0.063 | |
| X3 | −0.101 | −0.072 | −0.029 | −0.314 | 0.293 | 0.019 | 0.012 | −0.010 | 0.214 | |
| X4 | 0.193* 2) | −0.038 | −0.013 | −0.212 | 0.434 | 0.026 | 0.012 | −0.016 | −0.241 | |
| X5 | 0.168* | −0.036 | −0.016 | −0.213 | 0.406 | 0.028 | 0.013 | −0.014 | 0.141 | |
| X6 | −0.032 | −0.097 | −0.009 | −0.116 | 0.163 | 0.011 | 0.033 | −0.017 | −0.065 | |
| X7 | 0.041 | −0.033 | −0.005 | −0.081 | 0.173 | 0.010 | 0.015 | −0.039 | 0.080 | |
| 蔗糖酶 | X1 | 0.142 | 0.088 | 0.005 | −0.014 | 0.016 | 0.273 | 0.007 | −0.002 | 0.285 |
| X2 | 0.086 | 0.005 | 0.092 | 0.087 | −0.007 | −0.096 | 0.061 | 0.004 | 0.054 | |
| X3 | 0.047 | −0.025 | −0.045 | −0.308 | −0.010 | −0.176 | 0.023 | 0.003 | −0.229 | |
| X4 | 0.367** | −0.013 | −0.020 | −0.208 | 0.044 | 0.462 | −0.059 | −0.009 | 0.153 | |
| X5 | 0.402** | −0.012 | −0.024 | −0.209 | 0.041 | 0.681 | −0.060 | −0.014 | −0.277 | |
| X6 | −0.045 | −0.034 | −0.014 | −0.114 | 0.017 | 0.273 | −0.159 | −0.012 | 0.116 | |
| X7 | 0.063 | −0.011 | −0.007 | −0.080 | 0.018 | 0.247 | −0.071 | −0.034 | 0.096 | |
| 过氧化氢酶 | X1 | −0.163 | −0.068 | −0.005 | −0.076 | −0.015 | −0.042 | 0.050 | −0.007 | −0.095 |
| X2 | −0.306** | −0.004 | −0.088 | −0.130 | −0.022 | −0.077 | 0.019 | −0.004 | −0.218 | |
| X3 | 0.565** | 0.019 | 0.043 | 0.267 | 0.068 | 0.203 | −0.048 | 0.014 | 0.298 | |
| X4 | 0.562** | 0.010 | 0.019 | 0.181 | 0.100 | 0.280 | −0.049 | 0.022 | 0.462 | |
| X5 | 0.573** | 0.010 | 0.023 | 0.181 | 0.094 | 0.299 | −0.052 | 0.020 | 0.275 | |
| X6 | 0.189* | 0.026 | 0.013 | 0.099 | 0.038 | 0.120 | −0.130 | 0.024 | 0.319 | |
| X7 | 0.229* | 0.009 | 0.007 | 0.069 | 0.040 | 0.109 | −0.058 | 0.054 | 0.175 |
表3 土壤酶活性和土壤理化性质相关性分析及通径分析
Table 3 Correlation analysis and path analysis of soil enzyme activity and soil physical and chemical properties
| 因变量 | 自变量 | r | 温度X1 | pH X2 | 含水量X3 | 总碳X4 | 总氮X5 | 氨态氮X6 | 硝态氮X7 | 间接通径系数和IPC Sum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 脲酶 | X1 | 0.268**1) | 0.253 | 0.003 | 0.089 | −0.066 | −0.004 | −0.013 | 0.005 | 0.015 |
| X2 | 0.123 | 0.014 | 0.060 | 0.153 | −0.094 | −0.007 | −0.005 | 0.003 | 0.063 | |
| X3 | −0.101 | −0.072 | −0.029 | −0.314 | 0.293 | 0.019 | 0.012 | −0.010 | 0.214 | |
| X4 | 0.193* 2) | −0.038 | −0.013 | −0.212 | 0.434 | 0.026 | 0.012 | −0.016 | −0.241 | |
| X5 | 0.168* | −0.036 | −0.016 | −0.213 | 0.406 | 0.028 | 0.013 | −0.014 | 0.141 | |
| X6 | −0.032 | −0.097 | −0.009 | −0.116 | 0.163 | 0.011 | 0.033 | −0.017 | −0.065 | |
| X7 | 0.041 | −0.033 | −0.005 | −0.081 | 0.173 | 0.010 | 0.015 | −0.039 | 0.080 | |
| 蔗糖酶 | X1 | 0.142 | 0.088 | 0.005 | −0.014 | 0.016 | 0.273 | 0.007 | −0.002 | 0.285 |
| X2 | 0.086 | 0.005 | 0.092 | 0.087 | −0.007 | −0.096 | 0.061 | 0.004 | 0.054 | |
| X3 | 0.047 | −0.025 | −0.045 | −0.308 | −0.010 | −0.176 | 0.023 | 0.003 | −0.229 | |
| X4 | 0.367** | −0.013 | −0.020 | −0.208 | 0.044 | 0.462 | −0.059 | −0.009 | 0.153 | |
| X5 | 0.402** | −0.012 | −0.024 | −0.209 | 0.041 | 0.681 | −0.060 | −0.014 | −0.277 | |
| X6 | −0.045 | −0.034 | −0.014 | −0.114 | 0.017 | 0.273 | −0.159 | −0.012 | 0.116 | |
| X7 | 0.063 | −0.011 | −0.007 | −0.080 | 0.018 | 0.247 | −0.071 | −0.034 | 0.096 | |
| 过氧化氢酶 | X1 | −0.163 | −0.068 | −0.005 | −0.076 | −0.015 | −0.042 | 0.050 | −0.007 | −0.095 |
| X2 | −0.306** | −0.004 | −0.088 | −0.130 | −0.022 | −0.077 | 0.019 | −0.004 | −0.218 | |
| X3 | 0.565** | 0.019 | 0.043 | 0.267 | 0.068 | 0.203 | −0.048 | 0.014 | 0.298 | |
| X4 | 0.562** | 0.010 | 0.019 | 0.181 | 0.100 | 0.280 | −0.049 | 0.022 | 0.462 | |
| X5 | 0.573** | 0.010 | 0.023 | 0.181 | 0.094 | 0.299 | −0.052 | 0.020 | 0.275 | |
| X6 | 0.189* | 0.026 | 0.013 | 0.099 | 0.038 | 0.120 | −0.130 | 0.024 | 0.319 | |
| X7 | 0.229* | 0.009 | 0.007 | 0.069 | 0.040 | 0.109 | −0.058 | 0.054 | 0.175 |
| [1] |
ALLISON S D, TRESEDER K K, 2010. Warming and drying suppress microbial activity and carbon cycling in boreal forest soils[J]. Global Change Biology, 14(12): 2898-2909.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
BAI E, LI S L, XU W H, et al., 2013. A meta-analysis of experimental warming effects on terrestrial nitrogen pools and dynamics[J]. New Phytologist, 199(2): 441-451.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
HAO F, LAI X, OUYANG W, et al., 2012. Effects of Land Use Changes on the Ecosystem Service Values of a Reclamation Farm in Northeast China[J]. Environmental Management, 50(5): 888-899.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
HENRY H A L, 2012. Soil extracellular enzyme dynamics in a changing climate[J]. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 47: 53-59.
DOI URL |
| [5] | HENTSCHEL K, BORKEN W, MATZNER E, 2008. Repeated freeze-thaw events affect leaching losses of nitrogen and dissolved organic matter in a forest soil[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition & Soil Science, 171(5): 699-706. |
| [6] |
KIVLIN S N, HAWKES C V, 2020. Spatial and temporal turnover of soil microbial communities is not linked to function in a primary tropical forest[J]. Ecology, 101: e02985.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
LEI H, GAO X, LIU M, et al., 2012. Correlation among soil microorganisms, soil enzyme activities, and removal rates of pollutants in three constructed wetlands purifying micro-polluted river water[J]. Ecological Engineering, 46(3): 98-106.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
LI W B, WU J B, BAI E, et al., 2016. Response of terrestrial nitrogen dynamics to snow cover change: A meta-analysis of experimental manipulation[J]. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 100: 51-58.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
LU M, ZHOU X H, YANG Q, et al., 2013. Responses of ecosystem carbon cycle to experimental warming: A meta-analysis[J]. Ecology, 94(3): 726-738.
PMID |
| [10] | LU R, 1999. Soil and agro-chemical analytical methods[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press:146- 195. |
| [11] |
MIKAN C J, SCHIMEL J P, DOYLE A P, 2002. Temperature controls of microbial respiration in arctic tundra soils above and below freezing[J]. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 34(11): 1785-1795.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
SCHINNER F, MERSI W V, 1990. Xylanase-, CM-cellulase- and invertase activity in soil: An improved method[J]. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 22(4): 511-515.
DOI URL |
| [13] | LEI T Z, SI G C, WANG J, et al., 2017. Microbial communities and associated enzyme activities in alpine wetlands with increasing altitude on the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Wetlands the Journal of the Society of Wetland Scientists, 37(3): 401-412. |
| [14] |
THERIOT J M, CONKLE J L, REZA PEZESHKI S, et al., 2013. Will hydrologic restoration of Mississippi River riparian wetlands improve their critical biogeochemical functions[J]. Ecological Engineering, 60: 192-198.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
VIKLANDER P, 2016. Permeability and volume changes in till due to cyclic freeze/thaw[J]. Revue Canadienne De Géotechnique, 35(3): 471-477.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
WALLENSTEIN M D, MCMAHON S K, SCHIMEL J P, 2009. Seasonal variation in enzyme activities and temperature sensitivities in Arctic tundra soils[J]. Global Change Biology, 15(7): 1631-1639.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
WATANABE T, TATENO R, IMADA S, FUKUZAWA K, et al., 2019. The effect of a freezethaw cycle on dissolved nitrogen dynamics and its relation to dissolved organic matter and soil microbial biomass in the soil of a northern hardwood forest[J]. Biogeochemistry, 142(3): 319-338.
DOI |
| [18] |
YANG Z P, GAO J X, YANG M, et al., 2016. Effects of freezing intensity on soil solution nitrogen and microbial biomass nitrogen in an alpine grassland ecosystem on the Tibetan Plateau, China[J]. Journal of Arid Land, 8(5): 749-759.
DOI |
| [19] | ZHANG X R, BAI W, GILLIAM F S, et al., 2011. Effects of in situ freezing on soil net nitrogen mineralization and net nitrification in fertilized grassland of northern China[J]. Grass & Forage Science, 66(3): 391-401. |
| [20] |
ZHAO H T, ZHANG X L, XU S T, et al., 2010. Effect of freezing on soil nitrogen mineralization under different plant communities in a semiarid area during a non-growing season[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 45(3): 187-192.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
边雪廉, 赵文磊, 岳中辉, 等, 2016. 土壤酶在农业生态系统碳、氮循环中的作用研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 32(4): 171-178.
DOI |
|
BIAN X L, ZHAO W L, YUE Z H, et al., 2016. Research process of soil enzymes effect on carbon and nitrogen cycle in agricultural ecosystem[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 32(4): 171-178.
DOI |
|
| [22] | 曹晓霭, 2019. 草原区河流河滨带湿地融冻期温室气体排放通量研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学. |
| CAO X A, 2019. Study on greenhouse gas emission fluxes during thawing and freezing period of riverfront wetland in grassland area[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University. | |
| [23] | 陈鸽, 王璐, 宫雨薇, 等, 2019. 季节性冻融期长白山森林溪流中凋落叶N、P的释放动态[J]. 生态与环境学报, 28(12): 2341-2348. |
| CHEN G, WANG L, GONG YW, et al., 2019. Release dynamics of nitrogen and phosphorus of leaf litter in a forest stream of the Changbai Mountains during seasonal freezing-thawing period[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 28(12): 2341-2348. | |
| [24] | 陈子豪, 张晓蓉, 谭波, 等, 2020. 冻融循环对川西亚高山森林土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 40(8): 161-168. |
| CHEN Z H, ZHANG X R, TAN B, et al., 2020. Effects of freeze-thaw cycle on soil enzyme activity in subalpine forest in western Sichuan[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(8): 161-168. | |
| [25] | 樊子豪, 张瑞香, 冯雪琦, 等, 2023. 河滨湿地不同植物群落根系分布特征与土壤理化性状的关系——以黄河中游荥阳段为例[J]. 生态学报, 43(1): 4772-4781. |
| FAN Z H, ZHANG R X, FENG X Q, et al., 2023. Characteristics of root distribution and soil physical and chemical properties of different vegetation communities in tidal flat wetland: A case study of Xingyang section of Zhengzhou in the middle reaches of the Yellow River[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 43(11):4772-4781. | |
| [26] | 范昊明, 黄东浩, 周丽丽, 等, 2014. 季节性冻融作用对黑土坡面磷素流失的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 28(1): 152-155. |
| FAN H M, HUANG D H, ZHOU L L, et al., 2014. Effects of seasonal freeze-thaw action on phosphorus loss on black soil slope[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 28(1): 152-155. | |
| [27] | 高珊, 辛贵民, 赵清竹, 等, 2020. 循环冻融过程对6种温带森林土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 51(3): 668-676. |
| GAO S, XIN G M, ZHAO Q Z, et al., 2020. Effects of cyclic freeze-thaw processes on soil enzyme activities of six temperate forest species[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 51(3): 668-676. | |
| [28] | 缑倩倩, 屈建军, 王国华, 等, 2015. 中国干旱半干旱地区湿地研究进展[J]. 干旱区研究, 32(2):213-220. |
| GOU Q Q, QU J G, WANG G H, et al, 2015. Progress of wetland researches in arid and semi-arid regions in China[J]. Arid Zone Research, 32(2):213-220. | |
| [29] | 关松荫, 1986. 土壤酶及其研究法[M]. 北京: 农业出版社. |
| GUAN S Y, 1986. Soil enzymes and their research methods[M]. Beijing: Agriculture Press. | |
| [30] |
郭冬楠, 臧淑英, 赵光影, 2017. 冻融交替对不同年代排水造林湿地土壤微生物活性及有机碳密度的影响[J]. 冰川冻土, 39(1): 175-184.
DOI |
| GUO D N, ZANG S Y, ZHAO G Y, 2017. Effects of freeze-thaw alternations on soil microbial activity and organic carbon density in different years of drainage afforestation wetland[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 39(1): 175-184. | |
| [31] | 郭彤, 孙嘉鸿, 徐志伟, 等, 2022. 冻融作用对金川泥炭沼泽土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2(12): 5348-5359. |
| GUO T, SUN J H, XU Z W, et al., 2022. Effects of freezing and thawing on soil enzyme activities in Jinchuan peatlands[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42(13): 5348-5359. | |
| [32] | 韩冰雪, 赵光影, 臧淑英, 等, 2018. 大兴安岭多年冻土区森林湿地土壤碳氮含量及酶活性研究[J]. 安徽农业科学, 46(13): 136-140. |
| HAN B X, ZHAO G Y, ZANG S Y, et al., 2018. Soil carbon and nitrogen content and enzyme activity in forest wetland in the permafrost region of the Greater Khingan Mountains[J]. Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 46(13): 136-140. | |
| [33] | 和文祥, 朱铭莪, 张一平, 2000. 土壤酶与重金属关系的研究现状[J]. 土壤与环境, 9(2): 139-142. |
| HE W X, ZHU M E, ZHANG Y P, 2000. Research status of the relationship between soil enzymes and heavy metals[J]. Soil and Environmental Sciences, 9(2): 139-142. | |
| [34] | 华璐, 于晓菲, 王啟光, 等, 2020. 冻融作用对植物生理生态的影响[J]. 土壤与作物, 9(1): 13-21. |
| HUA L, YU X F, WANG Q G, et al., 2020. Effects of soil freezing thawing on plant ecophysiological characteristics[J]. Soils and Crops, 9(1): 13-21. | |
| [35] | 李凤霞, 王学琴, 郭永忠, 等, 2013. 宁夏引黄灌区不同盐化程度土壤酶活性及微生物多样性研究[J]. 水土保持研究, 20(1): 61-65. |
| LI F X, WANG X Q, GUO Y Z, et al., 2013. Study on soil enzyme activity and microbial diversity with different salinity levels in the Yellow River irrigation area of Ningxia[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 20(1): 61-65. | |
| [36] | 李富, 臧淑英, 刘赢男, 等, 2019. 冻融作用对三江平原湿地土壤活性有机碳及酶活性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 39(21): 149-160. |
| LI F, ZANG S Y, LIU Y N, et al., 2019. Effects of freeze-thaw effects on soil active organic carbon and enzyme activities in Sanjiang Plain wetland[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(21): 149-160. | |
| [37] |
李红琴, 徐海燕, 马小亮, 等, 2017. 马衔山多年冻土与季节冻土区土壤微生物量及酶活性的季节动态[J]. 冰川冻土, 39(2): 421-428.
DOI |
| LI H Q, XU H Y, MA X L, et al., 2017. Seasonal dynamics of soil microbial biomass and enzyme activities in permafrost and seasonal frozen soil in Maxian Mountain[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 39(2): 421-428. | |
| [38] | 李龙, 尹航, 黄世臣, 等, 2018. 春季解冻期3种温带森林土壤酶活性动态变化[J]. 土壤通报, 49(3): 609-615. |
| LI L, YIN H, HUANG S C, et al., 2018. Dynamic Changes of Soil Enzyme Activities in ThreeTypes of Temperate Forest during Spring Thawing Period[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 49(3): 609-615. | |
| [39] | 刘帅, 于贵瑞, 浅沼顺, 等, 2009. 蒙古高原中部草地土壤冻融过程及土壤含水量分布[J]. 土壤学报, 46(1): 48-53. |
| LIU S, YU G R, QIAN Z S, et al., 2009. Soil freeze-thaw process and soil water content distribution in grassland in central Mongolia Plateau[J]. Journal of Soil Science, 46(1): 48-53. | |
| [40] | 刘心宇, 2023. 内蒙古锡林河河滨带湿地碳排放和碳储藏影响机制研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学. |
| LIU X Y, 2023. Study on the mechanism of carbon emission and carbonstorage in the Xilin River riparian wetlands in Inner Mongolia[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University. | |
| [41] | 马晓飞, 楚新正, 马倩, 2015. 艾比湖地区冻融作用对梭梭群落土壤酶活性及微生物数量的影响[J]. 干旱区地理, 38(6): 1190-1201. |
| MA X F, CHU X Z, MA Q, 2015. Effects of freeze-thaw action on soil enzyme activity and microbial population of Haloxel community in Ebi Lake area[J]. Arid Land Geography, 38(6): 1190-1201. | |
| [42] | 彭振阳, 黄介生, 曾文治, 等, 2011. 季节性冻融土壤水分运动规律[J]. 武汉大学学报(工学版), 44(6): 696-700. |
| PENG Z Y, HUANG J S, ZENG W Z, et al., 2011. Seasonal freeze-thaw soil water movement[J]. Journal of Wuhan University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 44(6): 696-700. | |
| [43] | 宋阳, 于晓菲, 邹元春, 等, 2016. 冻融作用对土壤碳、氮、磷循环的影响[J]. 土壤与作物, 5(2): 78-90. |
| SONG Y, YU X F, ZOU Y C, et al., 2016. Effects of freeze-thaw on soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus cycles[J]. Soil and Crops, 5(2): 78-90. | |
| [44] | 田雅婷, 2021. 放牧对锡林河河滨带湿地甲烷生成-氧化潜力及甲烷氧化菌的影响研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学. |
| TIAN Y T, 2021. Study on the effects of grazing on methang production and oxidation protential and methanotrophs of XiLin River riparian wetland[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University. | |
| [45] |
万红云, 陈林, 庞丹波, 等, 2021. 贺兰山不同海拔土壤酶活性及其化学计量特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 32(9): 3045-3052.
DOI |
| WAN H Y, CHEN L, PANG D B, et al., 2021. Soil enzyme activities and their stoichiometry at different altitudes in Helan Mountains Northwest China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 32(9): 3045-3052. | |
| [46] | 王娇月, 2014. 冻融作用对大兴安岭多年冻土区泥炭地土壤有机碳的影响研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院研究生院(东北地理与农业生态研究所). |
| WANG J Y, 2014. Effect of freeze-thaw on soil organic carbon in peatland in permafrost region of Greater Khingan Mountains[D]. Changchun: Northeast Institute of Geography and AgroEcology, Graduate School of Chinese Academy of Sciences. | |
| [47] | 王立新, 2012. 内蒙古草原区河流河滨带湿地植被分布格局、过程与功能研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学. |
| WANG L X, 2012. The spatial distribution of wetland vegetation and its ecological process and function on riparian zone of riverscape in Inner Mongolia grassland[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University. | |
| [48] | 王振芬, 2019. 三江平原湿地不同土地利用方式对土壤养分及酶活性的影响[J]. 水土保持研究, 26(2): 43-48. |
| WANG Z F, 2019. Effects of different land uses on soil nutrients and enzyme activities in Sanjiang Plain wetland[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 26(2): 43-48. | |
| [49] | 杨小林, 李义玲, 朱波, 等, 2013. 紫色土小流域不同土地利用类型的土壤氮素时空分异特征[J]. 环境科学学报, 33(10): 2807-2813. |
| YANG X L, LI Y L, ZHU B, et al., 2013. Spatial and temporal differences of soil nitrogen in different land use types in purple soil small watershed[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 33(10): 2807-2813. | |
| [50] | 袁霞, 何斌, 2004. 八角林地土壤酶活性和养分的分布特点及其相关分析[J]. 经济林研究, 22(2): 13-16. |
| YUAN X, HE B, 2004. Distribution characteristics of soil enzyme activities and nutrients in anise forest and their correlation analysis[J]. Economic Forest Research, 22(2): 13-16. | |
| [51] | 苑鹏云, 2019. 内蒙古草原区河流河滨带湿地植物性状对不同环境梯度的响应[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学. |
| YAUN P Y, 2019. Response of wetland plant traits to different environmental gradients in the riverside zone of the Inner Mongolia grassland[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University. | |
| [52] | 张少良, 沈庆松, 王曜, 等, 2016. 不同冻结强度下容重和含水量对黑土剖面水分变化特征影响[J]. 东北农业大学学报, 47(12): 48-55. |
| ZHANG S L, SHEN Q S, WANG Y, et al., 2016. Effects of bulk density and water content on water change characteristics of black soil profiles under different freezing intensities[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 47(12): 48-55. | |
| [53] | 周丽丽, 马世伟, 米彩红, 等, 2017. 冻融条件下土壤水分和速效磷垂直迁移规律[J]. 水土保持研究, 24(3): 70-74. |
| ZHOU L L, MA S W, MI C H, et al., 2017. Vertical migration of soil moisture and available phosphorus under freeze-thaw conditions[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 24(3): 70-74. |
| [1] | 盛美君, 李胜君, 杨昕玥, 王蕊, 李洁, 李刚, 修伟明. 华北潮土农田土壤酶活性对土地利用强度的响应特征探讨[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 299-308. |
| [2] | 周世强, Vanessa HULL, 张晋东, 刘巅, 谢浩, 黄金燕, 张和民. 野生大熊猫与放牧家畜利用生境的特征比较[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 309-319. |
| [3] | 袁佳宝, 宋艳宇, 刘桢迪, 朱梦圆, 程小峰, 马秀艳, 陈宁, 李晓宇. 松嫩平原芦苇湿地土壤酶活性剖面分布特征及其微生物养分限制指示作用[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(12): 2141-2153. |
| [4] | 李萍, 白小明, 陈鑫, 李娟霞, 冉福, 陈辉, 杨小妮, 康瑞卿. 白三叶入侵对禾本科草坪土壤特性和植物群落的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 70-79. |
| [5] | 蒋恬田, 杨纯, 廖炜, 胡力, 刘欢瑶, 任勃, 李小马. 城市绿地景观格局影响地表温度的通径分析——以长沙市为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 18-25. |
| [6] | 段文军, 李达, 李冲. 5种不同林龄尾巨桉人工林林下植物多样性及其影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 857-864. |
| [7] | 王占永, 陈昕, 胡喜生, 何红弟, 蔡铭, 彭仲仁. 植物屏障影响路边大气颗粒物分布机理及研究方法的进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 1047-1058. |
| [8] | 李春环, 王攀, 韩翠, 许艺馨, 黄菊莹. 硫氮沉降下西北荒漠煤矿区周边土壤性质的变化特点[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 170-180. |
| [9] | 王瑞, 宋祥云, 柳新伟. 黄河三角洲不同植被类型土壤酶活性的季节变化[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 62-69. |
| [10] | 李欣, 陈小华, 顾海蓉, 钱晓雍, 沈根祥, 赵庆节, 白玉杰. 典型农田土壤酶活性分布特征及影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1634-1641. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
