生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (9): 1821-1830.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.09.006
孙雪娇1,2( ), 李吉玫1,2,*(
), 李吉玫1,2,*( ), 张毓涛1,2, 李翔1,2, 芦建江1,2, 佘飞3
), 张毓涛1,2, 李翔1,2, 芦建江1,2, 佘飞3
收稿日期:2021-01-15
出版日期:2021-09-18
发布日期:2021-12-08
通讯作者:
*李吉玫(1980年生),女,研究员,主要研究方向为森林生态研究。E-mail: jimeili@126.com作者简介:孙雪娇(1993年生),女(土家族),助理研究员,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为森林生态研究。E-mail: 1594468536@qq.com
基金资助:
SUN Xuejiao1,2( ), LI Jimei1,2,*(
), LI Jimei1,2,*( ), ZHANG Yutao1,2, LI Xiang1,2, LU Jianjiang1,2, SHE Fei3
), ZHANG Yutao1,2, LI Xiang1,2, LU Jianjiang1,2, SHE Fei3
Received:2021-01-15
Online:2021-09-18
Published:2021-12-08
摘要:
植被格局对森林水文过程具有显著影响,量化分析不同植被类型的产流产沙特征很有必要。为探究天山北坡山地森林产流产沙特征及其影响因素,依托天山森林生态系统定位研究站,依据植被类型、林龄、郁闭度、人工林管理方式设置坡面径流观测场14个,对产流产沙量进行了6年的观测,结果表明,(1)各样地的产流产沙量在年际间随降雨量有较大差异,降雨量与产流产沙量相关性显著,并呈多项式分布(P=0—2.952×10-7,r2=0.464—0.698)。(2)裸地的径流系数和土壤侵蚀模数显著高于其他植被类型(P<0.001);天然林中,径流系数和土壤侵蚀模数随着林龄的增加逐渐降低,而土壤侵蚀模数在不同林龄间无显著差异(P=0.089—0.984);郁闭度为0.2和0.4的天然中龄林的径流系数和土壤侵蚀模数显著大于郁闭度为0.6和0.8的天然中龄林(P=0.008—0.021);人工林不同管理方式间产流产沙量无显著差异(P=0.657—0.992)。(3)通过径流系数、侵蚀模数与其影响因素的冗余分析和相关性分析,平均株高、郁闭度、冠层活枝高,土壤饱和含水量、枯落物厚度与径流系数和土壤侵蚀模数呈现负相关关系(r= -0.592— -0.842)。研究结果表明在天山北坡山地森林植被覆盖会减小森林地表径流量,而乔木林具有良好的减沙效果。
中图分类号:
孙雪娇, 李吉玫, 张毓涛, 李翔, 芦建江, 佘飞. 天山北坡山地森林林地产流产沙特征及其影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(9): 1821-1830.
SUN Xuejiao, LI Jimei, ZHANG Yutao, LI Xiang, LU Jianjiang, SHE Fei. Characteristics and Influence of Runoff and Sediment Yield in Mountain Forest on the North Slope of Tianshan Mountains[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(9): 1821-1830.
| 编号 Plot number | 类型 Types | 植被情况 Vegetation situation | 布设时间Deployment time/ a | 林分密度 Forest density/ (plant∙hm-2) | 郁闭度Canopy density/ % | 平均株高Average plant height/m | 坡度Slope gradient/ (°) | 枯落物厚度 Litter thickness/ cm | 冠层活枝高Living branch height of canopy/m | 草本盖度Herbaceous coverage/ % | 土壤饱和 含水量 Soil saturated water content/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 裸地 Bare land | 少量草本A few herbs | 2010 | — | — | 0.1 | 16 | 0 | — | 30 | 42.1 |
| 2 | 草地 Grass land | 天山羽衣草 Alchemilla tianschanica Juz., 羊角芹 Aegopodium podagraria L. et al. | 2010 | — | — | 0.3 | 18 | 0.6 | — | 100 | 45.2 |
| 3 | 灌木林 Shrubbery | 黑果小檗 Berberis heteropoda Schrenk, 密刺蔷薇 Rosa spinosissima L. | 2012 | 2625 | 0.8 | 1.8 | 22 | 0.6 | — | 40 | 53.2 |
| 4 | 幼龄林 Young forest | 天山云杉 Picea schrenkiana Fisch. et Mey., 黑果小檗 Berberis heteropoda Schrenk | 2009 | 1455 | 0.5 | 4 | 25 | 1 | 3.3 | 60 | 54.5 |
| 5 | 中龄林 (0.2) Middle aged forest (0.2) | 天山云杉 Picea schrenkiana Fisch. et Mey. | 2010 | 420 | 0.2 | 10 | 14 | 1.2 | 5 | 50 | 53.1 |
| 6 | 中龄林 (0.4) Middle aged forest (0.4) | 天山云杉 Picea schrenkiana Fisch. et Mey. | 2009 | 525 | 0.4 | 8 | 15 | 1.7 | 6 | 40 | 50.1 |
| 7 | 中龄林 (0.6) Middle aged forest (0.6) | 天山云杉 Picea schrenkiana Fisch. et Mey. | 2009 | 1110 | 0.6 | 14 | 18 | 2.4 | 10.5 | 30 | 67.2 |
| 8 | 中龄林 (0.8) Middle aged forest (0.8) | 天山云杉 Picea schrenkiana Fisch. et Mey. | 2009 | 1695 | 0.8 | 11 | 20 | 2.8 | 4.5 | 10 | 66.9 |
| 9 | 近熟林 Near mature forest | 天山云杉 Picea schrenkiana Fisch. et Mey. | 2009 | 1215 | 0.7 | 16 | 15 | 5.2 | 12 | 10 | 64.3 |
| 10 | 成熟林 Near mature forest | 天山云杉 Picea schrenkiana Fisch. et Mey. | 2009 | 600 | 0.9 | 16 | 21 | 4.5 | 12 | 0 | 65.5 |
| 11 | 混交人工林 Mixed planted forest | 天山云杉 Picea schrenkiana Fisch. et Mey., 新疆落叶松 Larix sibirica Ledeb. | 2012 | 2250 | 0.8 | 12 | 11 | 1.5 | 7 | 45 | 60.9 |
| 12 | 未抚育人工林 No tenging planted forest | 天山云杉 Picea schrenkiana Fisch. et Mey. | 2012 | 5745 | 1 | 10 | 11 | 2.2 | 9.7 | 0 | 48.7 |
| 13 | 修枝抚育人工林Tenging planted forest | 天山云杉 Picea schrenkiana Fisch. et Mey. | 2012 | 2100 | 0.8 | 8.1 | 20 | 2.1 | 5.6 | 40 | 61.1 |
| 14 | 间伐人工林 Thining plantedcforest | 天山云杉 Picea schrenkiana Fisch. et Mey. | 2012 | 1800 | 0.65 | 8.7 | 16 | 2.2 | 4.3 | 50 | 58.4 |
表1 径流观测场布设信息
Table 1 Information of runoff field
| 编号 Plot number | 类型 Types | 植被情况 Vegetation situation | 布设时间Deployment time/ a | 林分密度 Forest density/ (plant∙hm-2) | 郁闭度Canopy density/ % | 平均株高Average plant height/m | 坡度Slope gradient/ (°) | 枯落物厚度 Litter thickness/ cm | 冠层活枝高Living branch height of canopy/m | 草本盖度Herbaceous coverage/ % | 土壤饱和 含水量 Soil saturated water content/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 裸地 Bare land | 少量草本A few herbs | 2010 | — | — | 0.1 | 16 | 0 | — | 30 | 42.1 |
| 2 | 草地 Grass land | 天山羽衣草 Alchemilla tianschanica Juz., 羊角芹 Aegopodium podagraria L. et al. | 2010 | — | — | 0.3 | 18 | 0.6 | — | 100 | 45.2 |
| 3 | 灌木林 Shrubbery | 黑果小檗 Berberis heteropoda Schrenk, 密刺蔷薇 Rosa spinosissima L. | 2012 | 2625 | 0.8 | 1.8 | 22 | 0.6 | — | 40 | 53.2 |
| 4 | 幼龄林 Young forest | 天山云杉 Picea schrenkiana Fisch. et Mey., 黑果小檗 Berberis heteropoda Schrenk | 2009 | 1455 | 0.5 | 4 | 25 | 1 | 3.3 | 60 | 54.5 |
| 5 | 中龄林 (0.2) Middle aged forest (0.2) | 天山云杉 Picea schrenkiana Fisch. et Mey. | 2010 | 420 | 0.2 | 10 | 14 | 1.2 | 5 | 50 | 53.1 |
| 6 | 中龄林 (0.4) Middle aged forest (0.4) | 天山云杉 Picea schrenkiana Fisch. et Mey. | 2009 | 525 | 0.4 | 8 | 15 | 1.7 | 6 | 40 | 50.1 |
| 7 | 中龄林 (0.6) Middle aged forest (0.6) | 天山云杉 Picea schrenkiana Fisch. et Mey. | 2009 | 1110 | 0.6 | 14 | 18 | 2.4 | 10.5 | 30 | 67.2 |
| 8 | 中龄林 (0.8) Middle aged forest (0.8) | 天山云杉 Picea schrenkiana Fisch. et Mey. | 2009 | 1695 | 0.8 | 11 | 20 | 2.8 | 4.5 | 10 | 66.9 |
| 9 | 近熟林 Near mature forest | 天山云杉 Picea schrenkiana Fisch. et Mey. | 2009 | 1215 | 0.7 | 16 | 15 | 5.2 | 12 | 10 | 64.3 |
| 10 | 成熟林 Near mature forest | 天山云杉 Picea schrenkiana Fisch. et Mey. | 2009 | 600 | 0.9 | 16 | 21 | 4.5 | 12 | 0 | 65.5 |
| 11 | 混交人工林 Mixed planted forest | 天山云杉 Picea schrenkiana Fisch. et Mey., 新疆落叶松 Larix sibirica Ledeb. | 2012 | 2250 | 0.8 | 12 | 11 | 1.5 | 7 | 45 | 60.9 |
| 12 | 未抚育人工林 No tenging planted forest | 天山云杉 Picea schrenkiana Fisch. et Mey. | 2012 | 5745 | 1 | 10 | 11 | 2.2 | 9.7 | 0 | 48.7 |
| 13 | 修枝抚育人工林Tenging planted forest | 天山云杉 Picea schrenkiana Fisch. et Mey. | 2012 | 2100 | 0.8 | 8.1 | 20 | 2.1 | 5.6 | 40 | 61.1 |
| 14 | 间伐人工林 Thining plantedcforest | 天山云杉 Picea schrenkiana Fisch. et Mey. | 2012 | 1800 | 0.65 | 8.7 | 16 | 2.2 | 4.3 | 50 | 58.4 |
| 样地编号 Plot number | 类型 Type | 年份Year | 平均值 Average value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | |||
| 1 | 裸地Bare land | — | 25.41 | 47.57 | 14.18 | 44.80 | 18.81 | 45.66 | 32.74 |
| 2 | 草地 Grass land | — | 18.21 | 16.75 | 9.93 | 16.23 | 10.2 | 31.6 | 17.15 |
| 3 | 灌木林Shrubbery | — | 4.92 | 20.72 | 5.48 | 20.69 | 12.88 | 34.74 | 16.57 |
| 4 | 幼龄林Young forest | 31.54 | 17.52 | 18.30 | 5.05 | 10.81 | 7.19 | 24.06 | 16.35 |
| 5 | 中龄林 (0.2) Middle aged forest (0.2) | — | 14.95 | 21.05 | 6.73 | 15.30 | 10.68 | 27.13 | 15.97 |
| 6 | 中龄林 (0.4) Middle aged forest (0.4) | 23.98 | 11.36 | 22.10 | 7.95 | 19.76 | 15.39 | 23.37 | 17.70 |
| 7 | 中龄林 (0.6) Middle aged forest (0.6) | 20.19 | 6.07 | 12.03 | 3.16 | 11.64 | 2.05 | 19.46 | 10.66 |
| 8 | 中龄林 (0.8) Middle aged forest (0.8) | 26.17 | 4.67 | 11.25 | 3.12 | 12.99 | 1.45 | 21.44 | 11.58 |
| 9 | 近熟林 Near mature forest | 25.71 | 8.27 | 11.73 | 2.86 | 5.23 | 1.38 | 19.33 | 10.64 |
| 10 | 成熟林 Near mature forest | 12.60 | 6.80 | 10.63 | 2.95 | 7.54 | 0.92 | 17.35 | 8.40 |
| 11 | 混交人工林 Mixed planted forest | — | — | — | 3.26 | 12.35 | 3.13 | 22.31 | 10.26 |
| 12 | 未抚育人工林 No tenging planted forest | — | — | — | 5.96 | 9.57 | 4.93 | 24.25 | 11.18 |
| 13 | 修枝抚育人工林 Tenging planted forest | — | — | — | 3.55 | 14.15 | 3.68 | 19.72 | 10.28 |
| 14 | 间伐人工林 Thining plantedcforest | — | — | — | 4.27 | 16.01 | 3.14 | 18.30 | 10.43 |
| 平均值 Average values | 23.37 | 11.82 | 19.21 | 5.60 | 15.51 | 6.85 | 24.91 | ||
| 降雨量 Rainfall/mm | 281.71 | 140.72 | 202.62 | 169.78 | 211.36 | 101.67 | 276.72 | 197.80 | |
表2 各年份的产流总量
Table 2 Total runoff yield in each year m3∙hm-2
| 样地编号 Plot number | 类型 Type | 年份Year | 平均值 Average value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | |||
| 1 | 裸地Bare land | — | 25.41 | 47.57 | 14.18 | 44.80 | 18.81 | 45.66 | 32.74 |
| 2 | 草地 Grass land | — | 18.21 | 16.75 | 9.93 | 16.23 | 10.2 | 31.6 | 17.15 |
| 3 | 灌木林Shrubbery | — | 4.92 | 20.72 | 5.48 | 20.69 | 12.88 | 34.74 | 16.57 |
| 4 | 幼龄林Young forest | 31.54 | 17.52 | 18.30 | 5.05 | 10.81 | 7.19 | 24.06 | 16.35 |
| 5 | 中龄林 (0.2) Middle aged forest (0.2) | — | 14.95 | 21.05 | 6.73 | 15.30 | 10.68 | 27.13 | 15.97 |
| 6 | 中龄林 (0.4) Middle aged forest (0.4) | 23.98 | 11.36 | 22.10 | 7.95 | 19.76 | 15.39 | 23.37 | 17.70 |
| 7 | 中龄林 (0.6) Middle aged forest (0.6) | 20.19 | 6.07 | 12.03 | 3.16 | 11.64 | 2.05 | 19.46 | 10.66 |
| 8 | 中龄林 (0.8) Middle aged forest (0.8) | 26.17 | 4.67 | 11.25 | 3.12 | 12.99 | 1.45 | 21.44 | 11.58 |
| 9 | 近熟林 Near mature forest | 25.71 | 8.27 | 11.73 | 2.86 | 5.23 | 1.38 | 19.33 | 10.64 |
| 10 | 成熟林 Near mature forest | 12.60 | 6.80 | 10.63 | 2.95 | 7.54 | 0.92 | 17.35 | 8.40 |
| 11 | 混交人工林 Mixed planted forest | — | — | — | 3.26 | 12.35 | 3.13 | 22.31 | 10.26 |
| 12 | 未抚育人工林 No tenging planted forest | — | — | — | 5.96 | 9.57 | 4.93 | 24.25 | 11.18 |
| 13 | 修枝抚育人工林 Tenging planted forest | — | — | — | 3.55 | 14.15 | 3.68 | 19.72 | 10.28 |
| 14 | 间伐人工林 Thining plantedcforest | — | — | — | 4.27 | 16.01 | 3.14 | 18.30 | 10.43 |
| 平均值 Average values | 23.37 | 11.82 | 19.21 | 5.60 | 15.51 | 6.85 | 24.91 | ||
| 降雨量 Rainfall/mm | 281.71 | 140.72 | 202.62 | 169.78 | 211.36 | 101.67 | 276.72 | 197.80 | |
| 样地编号 Plot number | 类型 Type | 年份 Year | 平均值 Average value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | |||
| 1 | 裸地Bare land | 0.248 | 0.072 | 0.259 | 0.120 | 0.445 | 0.229 |
| 2 | 草地 Grass land | 0.063 | 0.037 | 0.079 | 0.055 | 0.069 | 0.061 |
| 3 | 灌木林Shrubbery | 0.033 | 0.065 | 0.068 | 0.203 | 0.093 | |
| 4 | 幼龄林Young forest | 0.074 | 0.031 | 0.059 | 0.019 | 0.092 | 0.055 |
| 5 | 中龄林 (0.2) Middle aged forest (0.2) | 0.105 | 0.034 | 0.073 | 0.072 | 0.104 | 0.078 |
| 6 | 中龄林 (0.4) Middle aged forest (0.4) | 0.107 | 0.036 | 0.067 | 0.016 | 0.087 | 0.063 |
| 7 | 中龄林 (0.6) Middle aged forest (0.6) | 0.038 | 0.016 | 0.082 | 0.012 | 0.070 | 0.044 |
| 8 | 中龄林 (0.8) Middle aged forest (0.8) | 0.042 | 0.017 | 0.056 | 0.011 | 0.019 | 0.029 |
| 9 | 近熟林 Near mature forest | 0.039 | 0.017 | 0.048 | 0.008 | 0.067 | 0.036 |
| 10 | 成熟林 Near mature forest | 0.042 | 0.020 | 0.046 | 0.006 | 0.044 | 0.032 |
| 11 | 混交人工林 Mixed planted forest | 0.019 | 0.051 | 0.024 | 0.082 | 0.044 | |
| 12 | 未抚育人工林 No tenging planted forest | 0.027 | 0.045 | 0.033 | 0.091 | 0.049 | |
| 13 | 修枝抚育人工林 Tenging planted forest | 0.017 | 0.056 | 0.024 | 0.076 | 0.043 | |
| 14 | 间伐人工林 Thining plantedcforest | 0.019 | 0.054 | 0.024 | 0.072 | 0.042 | |
| 平均值 Average values | 0.084 | 0.028 | 0.074 | 0.035 | 0.109 | 0.064 | |
表3 各年份土壤侵蚀模数
Table 3 Total erosion modulus in each year t∙hm-2∙a-1
| 样地编号 Plot number | 类型 Type | 年份 Year | 平均值 Average value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | |||
| 1 | 裸地Bare land | 0.248 | 0.072 | 0.259 | 0.120 | 0.445 | 0.229 |
| 2 | 草地 Grass land | 0.063 | 0.037 | 0.079 | 0.055 | 0.069 | 0.061 |
| 3 | 灌木林Shrubbery | 0.033 | 0.065 | 0.068 | 0.203 | 0.093 | |
| 4 | 幼龄林Young forest | 0.074 | 0.031 | 0.059 | 0.019 | 0.092 | 0.055 |
| 5 | 中龄林 (0.2) Middle aged forest (0.2) | 0.105 | 0.034 | 0.073 | 0.072 | 0.104 | 0.078 |
| 6 | 中龄林 (0.4) Middle aged forest (0.4) | 0.107 | 0.036 | 0.067 | 0.016 | 0.087 | 0.063 |
| 7 | 中龄林 (0.6) Middle aged forest (0.6) | 0.038 | 0.016 | 0.082 | 0.012 | 0.070 | 0.044 |
| 8 | 中龄林 (0.8) Middle aged forest (0.8) | 0.042 | 0.017 | 0.056 | 0.011 | 0.019 | 0.029 |
| 9 | 近熟林 Near mature forest | 0.039 | 0.017 | 0.048 | 0.008 | 0.067 | 0.036 |
| 10 | 成熟林 Near mature forest | 0.042 | 0.020 | 0.046 | 0.006 | 0.044 | 0.032 |
| 11 | 混交人工林 Mixed planted forest | 0.019 | 0.051 | 0.024 | 0.082 | 0.044 | |
| 12 | 未抚育人工林 No tenging planted forest | 0.027 | 0.045 | 0.033 | 0.091 | 0.049 | |
| 13 | 修枝抚育人工林 Tenging planted forest | 0.017 | 0.056 | 0.024 | 0.076 | 0.043 | |
| 14 | 间伐人工林 Thining plantedcforest | 0.019 | 0.054 | 0.024 | 0.072 | 0.042 | |
| 平均值 Average values | 0.084 | 0.028 | 0.074 | 0.035 | 0.109 | 0.064 | |
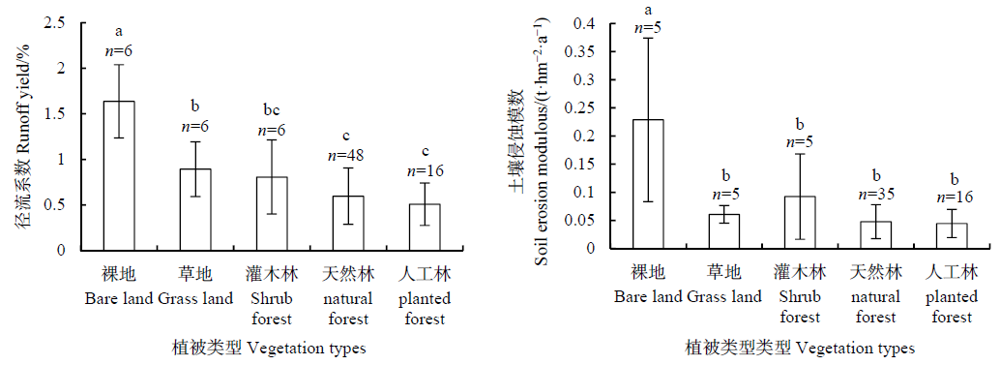
图2 不同植被类型的径流系数和土壤侵蚀模数 图中不同小写字母a、b、c表示P<0.05水平下差异显著,下同
Fig. 2 Runoff coefficient and soil erosion modulus of different vegetation types The different letters in the figure represent significant differences at P<0.05 level, The same below
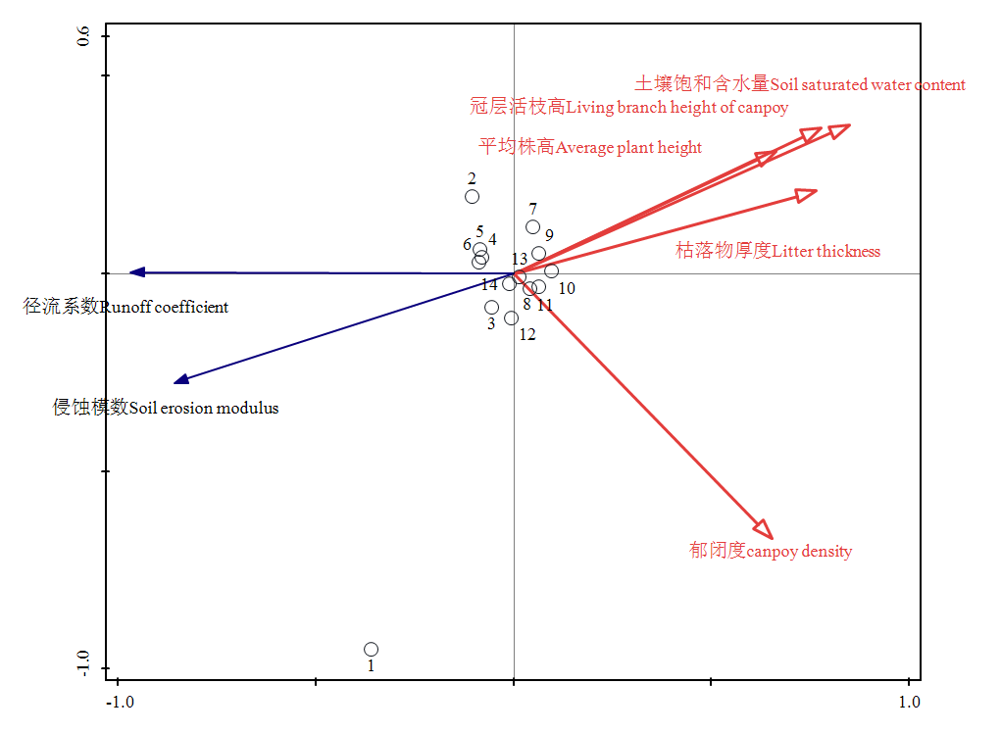
图6 产流产沙特征与环境因子的二维排序图 箭头及排序轴之间的夹角表示各指标与排序轴之间相关性的正负,小于90°,为正相关,等于90°,无相关性,大于90°,为负相关。箭头线段在排序轴和另一箭头线段及其延长线上的投影表示二者相关性的大小,投影越大,相关性越强。图中○表示各样地的位置,序号代表的样地类型与表1相同
Fig. 6 Two-dimensional sequence diagram of RDA analysis between runoff coefficient, soil erosion modulus and and environmental factors The angle between the arrows and the axis indicated the positive and negative correlation between index and the axis. If it is less than 90°, it is a positive correlation; if it is equal to 90°, it is no correlation, and if it is greater than 90°, it is a negative correlation. The projection of the arrow line on the axis and another arrow line represented their correlation. The larger the projection, the stronger the correlation.○ indicates the location of the plots, and the sample plot type represented by serial number is the same as that in table 1
| 影响因子 Influence factor | 林分密度 Forest density/ (plant∙hm-2) | 郁闭度 Canopy density/% | 平均株高 Average plant height/m | 枯落物厚度 Litter thickness/ cm | 坡度 Slope gradient/ (°) | 冠层活枝高 Living branch height of canopy/m | 草本盖度 Herbaceous coverage/% | 土壤饱和含水量 Soil saturated water content/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 径流系数 Runoff coefficient | -0.099 | -0.634* | -0.787** | -0.738** | -0.136 | -0.704** | 0.349 | -0.842** |
| 侵蚀模数 Soil erosion modulus | 0.112 | -0.375 | -0.663** | -0.618* | -0.118 | -0.592* | 0.106 | -0.724** |
表4 产流产沙特征与环境因子间的相关性分析
Table 4 Correlation analysis between runoff coefficient, soil erosion modulus and and environmental factors
| 影响因子 Influence factor | 林分密度 Forest density/ (plant∙hm-2) | 郁闭度 Canopy density/% | 平均株高 Average plant height/m | 枯落物厚度 Litter thickness/ cm | 坡度 Slope gradient/ (°) | 冠层活枝高 Living branch height of canopy/m | 草本盖度 Herbaceous coverage/% | 土壤饱和含水量 Soil saturated water content/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 径流系数 Runoff coefficient | -0.099 | -0.634* | -0.787** | -0.738** | -0.136 | -0.704** | 0.349 | -0.842** |
| 侵蚀模数 Soil erosion modulus | 0.112 | -0.375 | -0.663** | -0.618* | -0.118 | -0.592* | 0.106 | -0.724** |
| [1] |
BHATTA B, SHRESTHA S, SHRESTHA P K, et al., 2019. Evaluation and application of a SWAT model to assess the climate change impact on the hydrology of the Himalayan River Basin[J]. Catena, DOI: 10.1016/j.catena.2019.104082.
DOI |
| [2] | CARROL C, MERTON L, BURGER P, 2000. Impact of vegetative cover and slope on runoff, erosion, and water quality for field plots on a range of soil and spoil materials on central Queensland coal mines[J]. Australian Journal of Soil Research, 38(2): 313-328. |
| [3] |
COMINO J R, ISERLOH T, LASSU T, et al., 2016. Quantitative comparison of initial soil erosion processes and runoff generation in Spanish and German vineyards[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 565: 1165-1174.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
LUCEY J T D, REAGER J T, LOPEZ S R, 2020. Global partitioning of runoff generation mechanisms using remote sensing data[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 24(3): 1415-1427.
DOI URL |
| [5] | RAN Q H, SU D Y, LI P, et al., 2012. Experimental study of the impact of rainfall characteristics on runoff generation and soil erosion[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 424(6): 99-111. |
| [6] |
TADESSE L, SURYABHAGAVAN K V, SRIDHAR G, et al., 2017. Land use and land cover changes and Soil erosion in Yezat Watershed, North Western Ethiopia[J]. International Soil and Water Conservation Research, 5(2): 85-94.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
ZHANG H, WANG B, LIU D L, et al., 2020. Using an improved SWAT model to simulate hydrological responses to land use change: A case study of a catchment in tropical Australia[J]. Journal of Hydrology, DOI: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.124822.
DOI |
| [8] | 阿茹∙苏里坦, 常顺利, 张毓涛, 2019. 天山林区不同群落土壤水分入渗特性的对比分析与模拟[J]. 生态学报, 39(24): 94-101. |
| ARU S L T, CHANG S L, ZHANG Y T, 2019. Comparative analysis and simulation of soil moisture infiltration characteristics in different communities in the forest of Tianshan Mountains, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(24): 94-101. | |
| [9] | 陈鹏, 张铁钢, 董智, 等, 2020. 灌草格局对砒砂岩区产流产沙特征的影响[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 34(9): 116-121. |
| CHEN P, ZHANG T G, DONG Z, et al., 2020. Effects of different shrub-grass patterns on runoff and sediment characteristics in Pisha sandstone area[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 34(9): 116-121. | |
| [10] | 成向荣, 渠勇建, 虞木奎, 等, 2017. 植被覆盖变化对衢江流域水文效应的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 26(11): 1829-1835. |
| CHENG X R, QU Y J, YU M K, et al., 2017. Hydrological effects of vegetation cover change in Qujiang Basin[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 26(11): 1829-1835. | |
| [11] | 窦小东, 黄玮, 易琦, 等, 2019. LUCC及气候变化对龙川江流域径流的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(1): 7-15. |
| DOU X D, HUANG W, YI Q, et al., 2019. Effects of LUCC and climate change on the runoff in Longchuan River Watershed[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 28(1): 7-15. | |
| [12] | 高光耀, 傅伯杰, 吕一河, 等, 2013. 干旱半干旱区坡面覆被格局的水土流失效应研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 33(1): 12-22. |
| GAO G Y, FU B J, LV Y H, et al., 2013. The effect of land cover pattern on hillslope soil and water loss in the arid and semiarid region: A review[J]. Acta Eeologica Sinica, 33(1): 12-22. | |
| [13] | 韩春, 陈宁, 孙杉, 等, 2019. 森林生态系统水文调节功能及机制研究进展[J]. 生态学杂志, 38(7): 2191-2199. |
| HAN C, CHEN N, SUN S, et al., 2019. A review on hydrological mediating functions and mechanisms in forest ecosystems[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 38(7): 2191-2199. | |
| [14] | 郝帅, 张毓涛, 刘端, 等, 2009. 不同郁闭度天山云杉林林冠截留量及穿透雨量特征研究[J]. 干旱区地理, 32(6): 917-923. |
| HAO S, ZHANG Y T, LIU D, et al., 2009. Characteristics of canopy interception and through fall of Picea schrenkiana var. tianschanica (Rupr.) Chen et Fu[J]. Arid Land Geography, 32(6): 917-923. | |
| [15] | 何玉广, 信忠保, 余新晓, 等, 2017. 模拟降雨条件下侧柏林地枯落物对坡面产流产沙的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 31(3): 27-32, 38. |
| HE Y G, XIN Z B, YU X X, et al., 2017. Influence of litter layer of Pltaycladus orientalis forests on runoff and sediment yield of the slope under simulated rainfall[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 31(3): 27-32, 38. | |
| [16] | 何志斌, 杜军, 陈龙飞, 等, 2016. 干旱区山地森林生态水文研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 31(10): 1078-1089. |
| HE Z B, DU J, CHEN L F, et al., 2016. Review on montane forest eco-hydrology in arid area[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 31(10): 1078-1089. | |
| [17] | 贺亮亮, 张淑兰, 于澎涛, 等, 2017. 泾河流域的降水径流影响及其空间尺度效应[J]. 生态环境学报, 26(3): 415-421. |
| HE L L, ZHANG S L, YU P T, et al., 2017. Spatial scale effect of the precipitation influence on runoff in Jinghe Basin[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 26(3): 415-421. | |
| [18] | 胡建, 郭太龙, 卓慕宁, 等, 2013. 华南红壤坡面产流产沙过程模拟降雨试验研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 22(5): 787-791. |
| HU J, GUO T L, ZHUO M N, et al., 2013. Erosion processes on red soil slope in south China under simulated rainfall system[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 22(5): 787-791. | |
| [19] | 胡沁梅, 谢炎敏, 2020. 长汀县水土保持措施下径流小区的产流产沙及其对降水量和植被覆盖度的响应[J]. 亚热带水土保持, 32(3): 14-19. |
| HU Q M, XIE Y M, 2020. Runoff and sediment yield and responses to rainfall and vegetation cover in runoff plots with different soil and water conservation measures in the Changting county[J]. Subtropical Soil and Water Conservation, 32(3): 14-19. | |
| [20] | 姜亮亮, 包安明, 刘海隆, 等, 2015. 玛纳斯流域生态需水变化与景观格局的响应关系研究[J]. 水土保持研究, 22(3): 143-149. |
| JIANG L L, BAO A M, LIU H L, et al., 2015. Study on the repones relationship between ecological water requirement and landscape pattern in Manas River Basin[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 22(3): 143-149. | |
| [21] | 李宗勋, 李启艳, 侯晓龙, 等, 2020. 不同自然降雨等级下不同郁闭度马尾松林的水土流失特征[J]. 水土保持学报, 34(1): 27-33. |
| LI Z X, LI Q Y, HOU X L, et al., 2020. Characteristics of soil and water loss under different natural rainfall grades of Pinus Massoniana forest with different canopy density[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 34(1): 27-33. | |
| [22] | 廖轶群, 2012. 基于GIS的新疆地区植被生态需水量研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学. |
| LIAO Y Q, 2012. Study on ecological water requirrment of vegetation in Xinjiang Region based on GIS[D]. Yangling: Northwest A & F University. | |
| [23] | 林艺, 秦凤, 郑子成, 等, 2015. 不同降雨条件下垄作坡面地表微地形及土壤侵蚀变化特征[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 13(3): 32-38. |
| LIN Y, QIN F, ZHENG Z C, et al., 2015. Characteristics of variations in soil surface micro-topography and soil erosion on the cross ridge slope under different rainfall conditions[J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 13(3): 32-38. | |
| [24] | 刘柏玲, 蔡强国, 史志华, 等, 2016. 模拟降雨条件下塿土的溅蚀特征试验研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 30(5): 29-33. |
| LIU B L, CAI Q G, SHI Z H, et al., 2016. Rain-simulated experiment study on the splash erosion characteristics of lou soil[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 30(5): 29-33. | |
| [25] | 吕刚, 王磊, 张卓, 等, 2019. 辽西低山丘陵区不同年龄荆条冠层截留降雨模拟实验研究[J]. 生态学报, 39(17): 190-198. |
|
LV G, WANG L, ZHANG Z, et al., 2019. Simulated and experimental study on rainfall interception of different aged Vitex negundo var. heterophylla canopies in the low mountains and hills of western Liaoning[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(17): 190-198.
DOI URL |
|
| [26] | 吕锡芝, 康玲玲, 左仲国, 等, 2015. 黄土高原吕二沟流域不同植被下的坡面径流特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 24(7): 1113-1117. |
| LV X Z, KANG L L, ZUO Z G, et al., 2015. Characteristics of slope runoff under different vegetation conditions in Lvergou Watershed of the Loess Plateau[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 24(7): 1113-1117. | |
| [27] | 马鹏嫣, 王智超, 李晴, 等, 2018. 秦皇岛市北戴河区森林生态系统服务功能价值评估[J]. 水土保持通报, 38(03): 286-292. |
| MA P Y, WANGA Z C, LI Q, et al., 2018. Evaluation of forest ecosystem services in Beidaihe District of Qihuangdao City[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 38(03):286-292. | |
| [28] | 史佳良, 王秀茹, 李淑芳, 等, 2016. 次降雨过程中北京市不同土地利用方式下土壤养分流失特征[J]. 水土保持学报, 30(5): 58-63. |
| SHI J L, XU Y X, LI S F, et al., 2016. Characteristics of Soil Nutrients Loss under Different Land Use Patterns in Beijing during Course of Rain[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 30(5): 58-63. | |
| [29] | 王荣嘉, 高鹏, 李成, 等, 2019. 模拟降雨下麻栎林地表径流和壤中流及氮素流失特征[J]. 生态学报, 39(8): 2732-2740. |
| WANG R J, GAO P, LI C, et al., 2019. Characteristics of surface flow and intertlow and nitrogen loss in Quercus acutissima forest land under simulated rainfall[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(8): 2732-2740. | |
| [30] | 魏霞, 李勋贵, 2015. 交替冻融对坡面产流产沙的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 31(13): 157-163. |
| WEI X, LI X G, 2015. Impacts of freeze-thaw cycles on runoff and sediment yield of slope land[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 31(13): 157-163. | |
| [31] | 谢林妤, 白玉洁, 张风宝, 等, 2017. 沙层厚度和粒径组成对覆沙黄土坡面产流产沙的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 54(1): 60-72. |
| XIE L S, BAI Y J, ZHANG F B. et al., 2017. Effects of Thickness and Particle Size Composition of Overlying Sand Layer on Runoff and Sediment Yield on Sand-covered Loess Slopes[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 54(1): 60-72. | |
| [32] | 谢锦, 常顺利, 张毓涛, 等, 2016. 天山北坡植物土壤生态化学计量特征的垂直地带性[J]. 生态学报, 36(14): 4363-4372. |
| XIE J, CHANG S L, ZHANG Y T, et al., 2016. Plant and soil ecological stoichiometry with vertical zonality on the northern slope of the middle Tianshan Mountains[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36(14): 4363-4372. | |
| [33] | 严友进, 戴全厚, 伏文兵, 等, 2017. 喀斯特裸坡产流产沙过程试验研究[J]. 生态学报, 37(6): 2067-2079. |
| YAN Y J, DAI Q H, FU W B, et al., 2017. Runoff and sediment production processes on a Karst bare slope[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37(6): 2067-2079. | |
| [34] | 张洪亮, 张毓涛, 张新平, 等, 2011. 天山中部天然云杉林凋落物层水文生态功能研究[J]. 干旱区地理, 34(2): 271-277. |
| ZHANG H L, ZHANG Y T, ZHANG X P, et al., 2011. Eco-hydrological characteristics of litter of artificial spruce forest in the middle part of Tianshan Mountains[J]. Arid Land Geography, 34(2): 271-277. | |
| [35] | 张思毅, 梁志权, 谢真越, 等, 2016. 白三叶不同部位减沙效应及其对径流水动力学参数的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 25(8): 1306-1314. |
| ZHANG S Y, LIANG Z Q, XIE Z Y, et al., 2016. Effects of different parts of Trifolium repens L. on sediment reduction and runoff hydrodynamic parameters[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 25(8): 1306-1314. | |
| [36] | 张兴奇, 顾礼彬, 张科利, 等, 2015. 坡度对黔西北地区坡面产流产沙的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 29(4): 18-22. |
| ZHANG X Q, GU L B, ZHANG K L, et al., 2015. Impact of slope gradient on runoff and sediment in northwest Guizhou[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 29(4): 18-22. | |
| [37] | 张云云, 张毓涛, 师庆东, 等, 2019. 天山北坡中段草地、林地积雪消融过程的定量化分析[J]. 水土保持学报, 33(3): 108-114. |
| ZHANG Y Y, ZHANG Y T, SHI Q D, et al., 2019. Quantitative analysis of snow melting process in grassland and forest land on the middle section of northern slope of Tianshan Mountain[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 33(3): 108-114. | |
| [38] | 仲亚婷, 2017. 植被及土壤类型对坡面产流产沙特征的影响[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆农业大学. |
| ZHONG Y T, 2017. Influence of Vegetation and Soil Types on the Characteristics of Hillslope Runoff and Sediment Yield[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University. | |
| [39] | 周宏飞, 王大庆, 马健, 等, 2009. 新疆天池自然保护区春季融雪产流特征分析[J]. 水土保持学报, 23(4): 68-71. |
| ZHOU H F, WANG D Q, MA J, et al., 2009. Analysis of snowmelt runoff formation regularity during the spring in the natural conservation area of Tianchi Lake in Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 23(4): 68-71. |
| [1] | 张立进, 杜虎, 曾馥平, 黄国勤, 宋敏, 宋同清. 喀斯特峰丛洼地植被恢复过程中生产力与多样性关系探讨[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 26-35. |
| [2] | 马辉英, 李昕竹, 马鑫钰, 贡璐. 新疆天山北麓中段不同植被类型下土壤有机碳组分特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1124-1131. |
| [3] | 喻阳华, 吴银菇, 宋燕平, 李一彤. 不同林龄顶坛花椒林地土壤微生物浓度与生物量化学计量特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1160-1168. |
| [4] | 杨虎, 王佩瑶, 李小伟, 王继飞, 杨君珑. 贺兰山东坡不同植被类型的土壤真菌多样性及其群落结构[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 239-247. |
| [5] | 张淑兰, 韩勇, 杨盼, 闫育盈, 刘昭雪, 李卓瑶. 汉江上游不同林龄麻栎林枯落物的水文功能评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 44-51. |
| [6] | 张洋洋, 周清慧, 许骄阳, 魏鸣, 陈继豪, 何伟, 王鹏程, 晏召贵. 林龄对马尾松人工林林下植物与土壤种子库多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(11): 2121-2129. |
| [7] | 郑诗禹, 张绿水, 郭晓敏, 黄子峻, 肖以华. 不同森林郁闭度环境内空气负氧离子的时空变化及环境影响要素研究——以广州帽峰山为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(11): 2204-2212. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
