Ecology and Environment ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (10): 1822-1832.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.10.011
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Longfei1,2( ), WEI Ying1,2, ZHAO Jiannan1,2, DONG Jing1,2, ZHANG Jingxiao1,2, GAO Xiaofei1,2, ZHANG Man1,2, YUAN Huatao1,2, GAO Yunni1,2,*(
), WEI Ying1,2, ZHAO Jiannan1,2, DONG Jing1,2, ZHANG Jingxiao1,2, GAO Xiaofei1,2, ZHANG Man1,2, YUAN Huatao1,2, GAO Yunni1,2,*( ), LI Xuejun1,2
), LI Xuejun1,2
Received:2023-05-12
Online:2023-10-18
Published:2024-01-16
Contact:
GAO Yunni
李龙飞1,2( ), 魏颖1,2, 赵建南1,2, 董静1,2, 张景晓1,2, 高肖飞1,2, 张曼1,2, 袁华涛1,2, 高云霓1,2,*(
), 魏颖1,2, 赵建南1,2, 董静1,2, 张景晓1,2, 高肖飞1,2, 张曼1,2, 袁华涛1,2, 高云霓1,2,*( ), 李学军1,2
), 李学军1,2
通讯作者:
高云霓
作者简介:李龙飞(1998年生),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为水域生态学。E-mail: llf619@outlook.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
LI Longfei, WEI Ying, ZHAO Jiannan, DONG Jing, ZHANG Jingxiao, GAO Xiaofei, ZHANG Man, YUAN Huatao, GAO Yunni, LI Xuejun. The Inhibition of Microcystis by the Three Submerged Hydrocharitaceae Species and the Response of Periphytic Algae[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(10): 1822-1832.
李龙飞, 魏颖, 赵建南, 董静, 张景晓, 高肖飞, 张曼, 袁华涛, 高云霓, 李学军. 3种沉水植物对微囊藻的抑制作用及其周丛藻类响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(10): 1822-1832.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.10.011
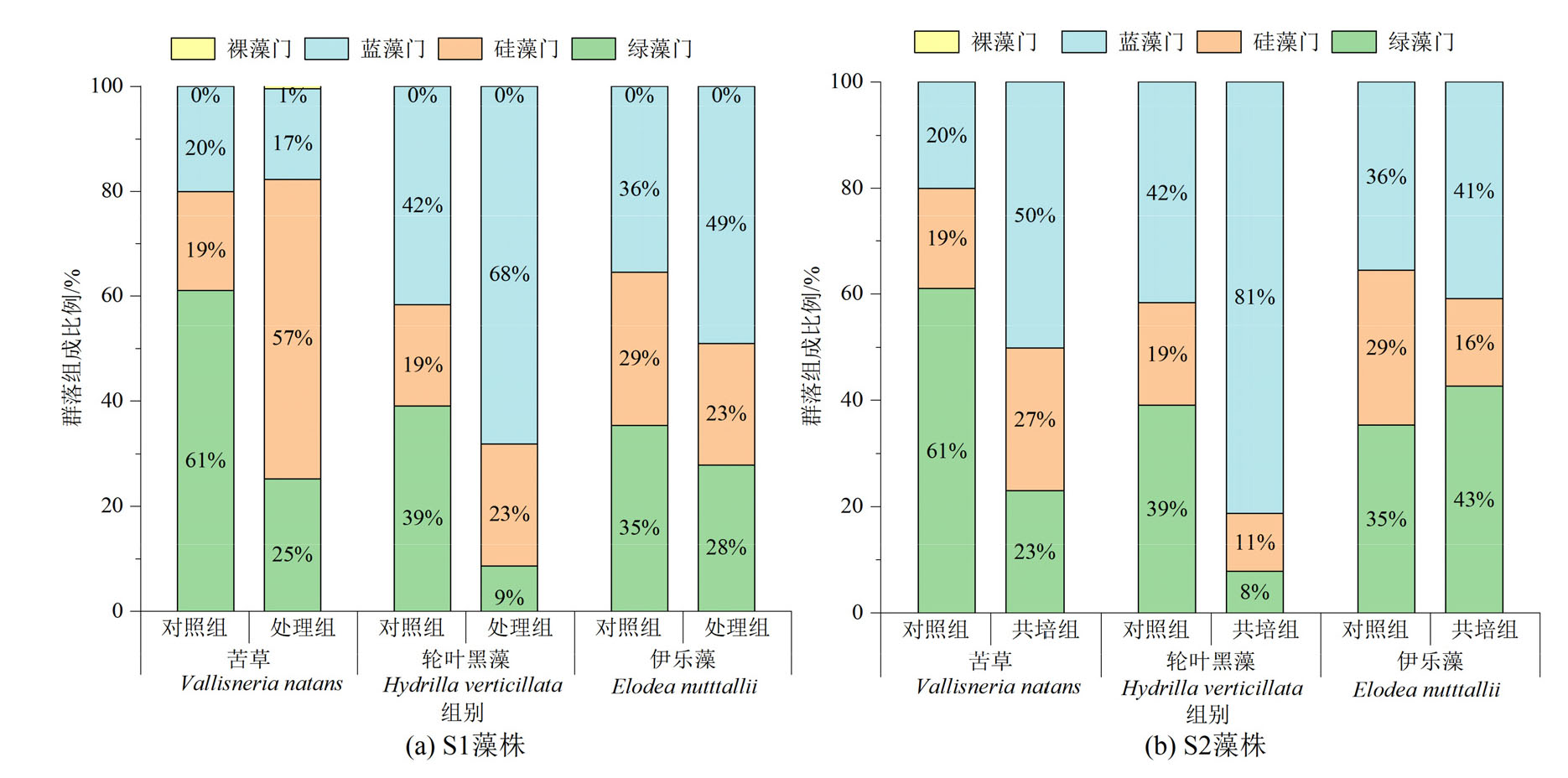
Figure 4 Community composition of periphytic algae at phylum level in monoculture controls of V. natans, H. verticillata and E. nutttallii and co-culture groups with Microcystis
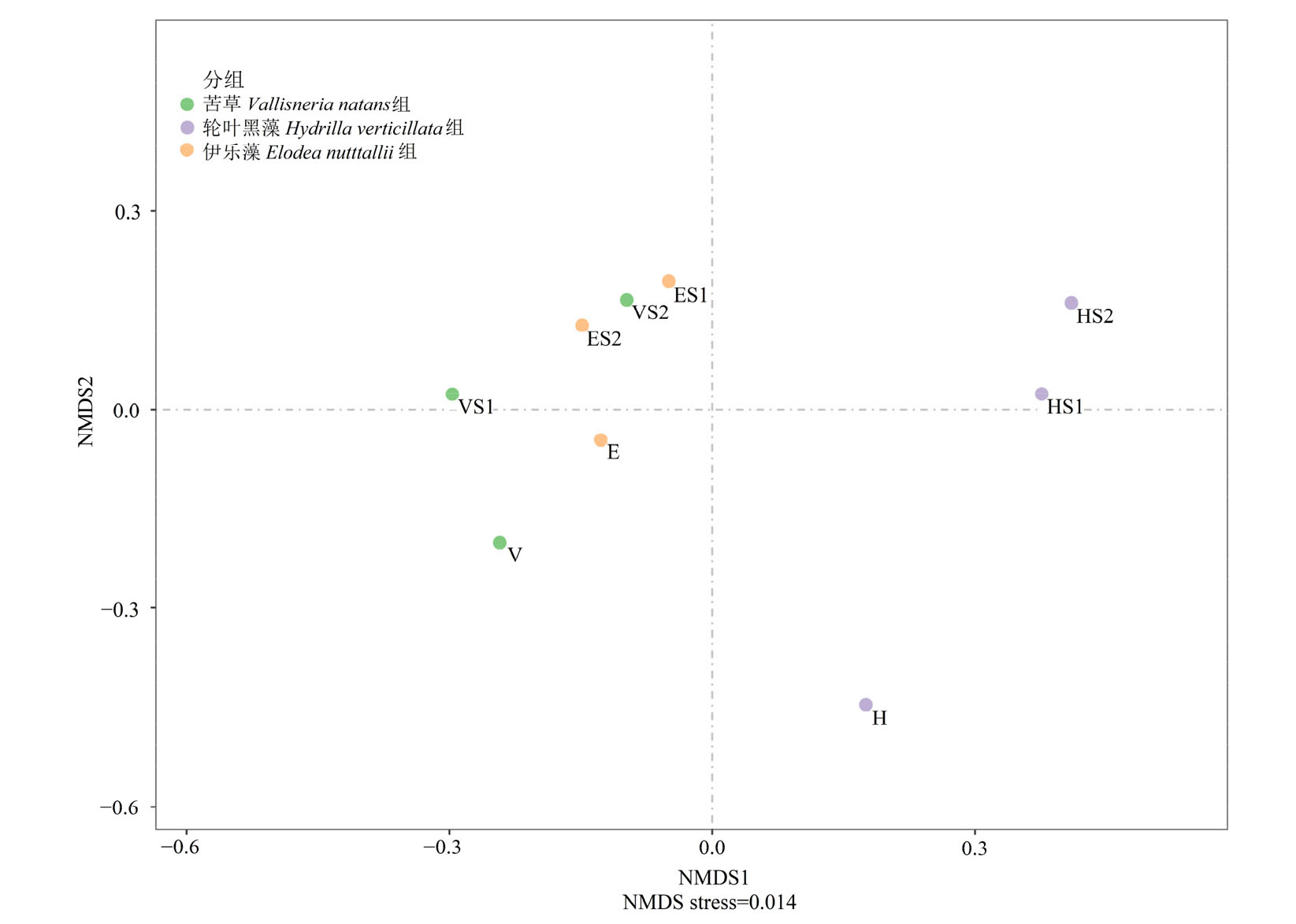
Figure 5 Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) diagram of periphytic algae in monoculture controls of V. natans, H. verticillata and E. nutttallii and co-culture groups with Microcystis
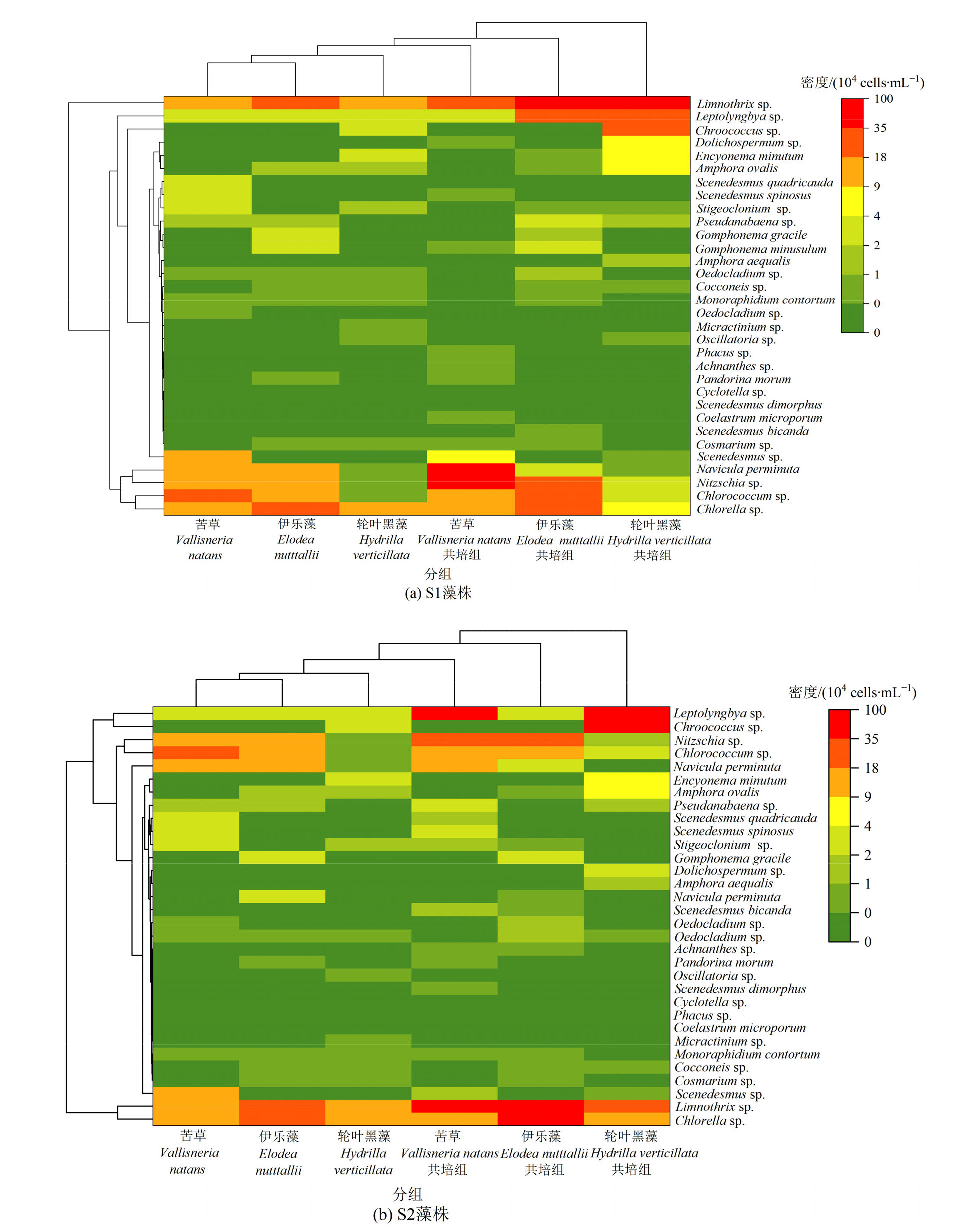
Figure 6 Community composition of periphytic algae at genus level in monoculture controls of V. natans, H. verticillata and E. nutttallii and co-culture groups with Microcystis
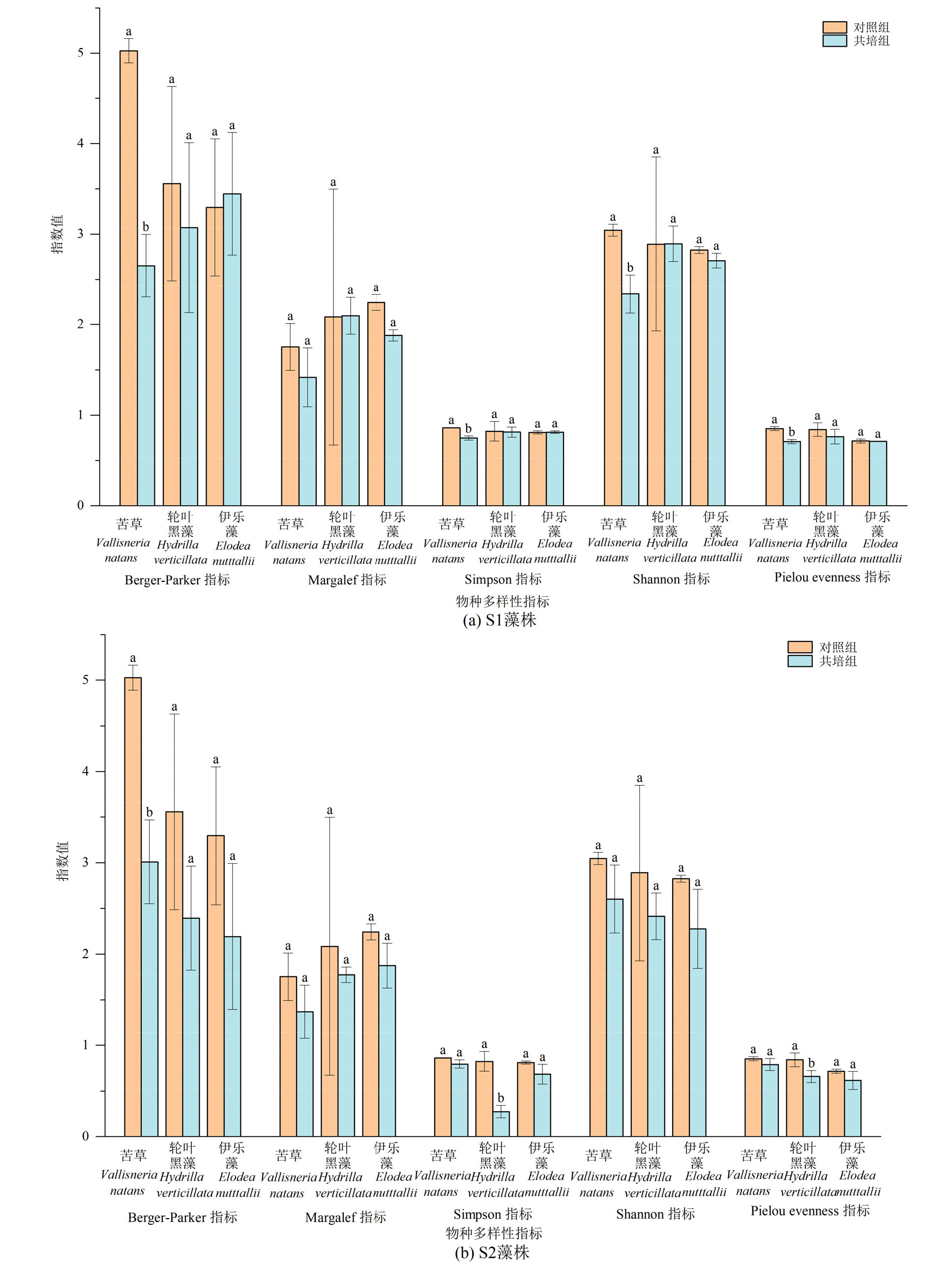
Figure 7 Diversity indices of periphytic algae in monoculture controls of V. natans, H. verticillata and E. nutttallii and co-culture groups with Microcystis
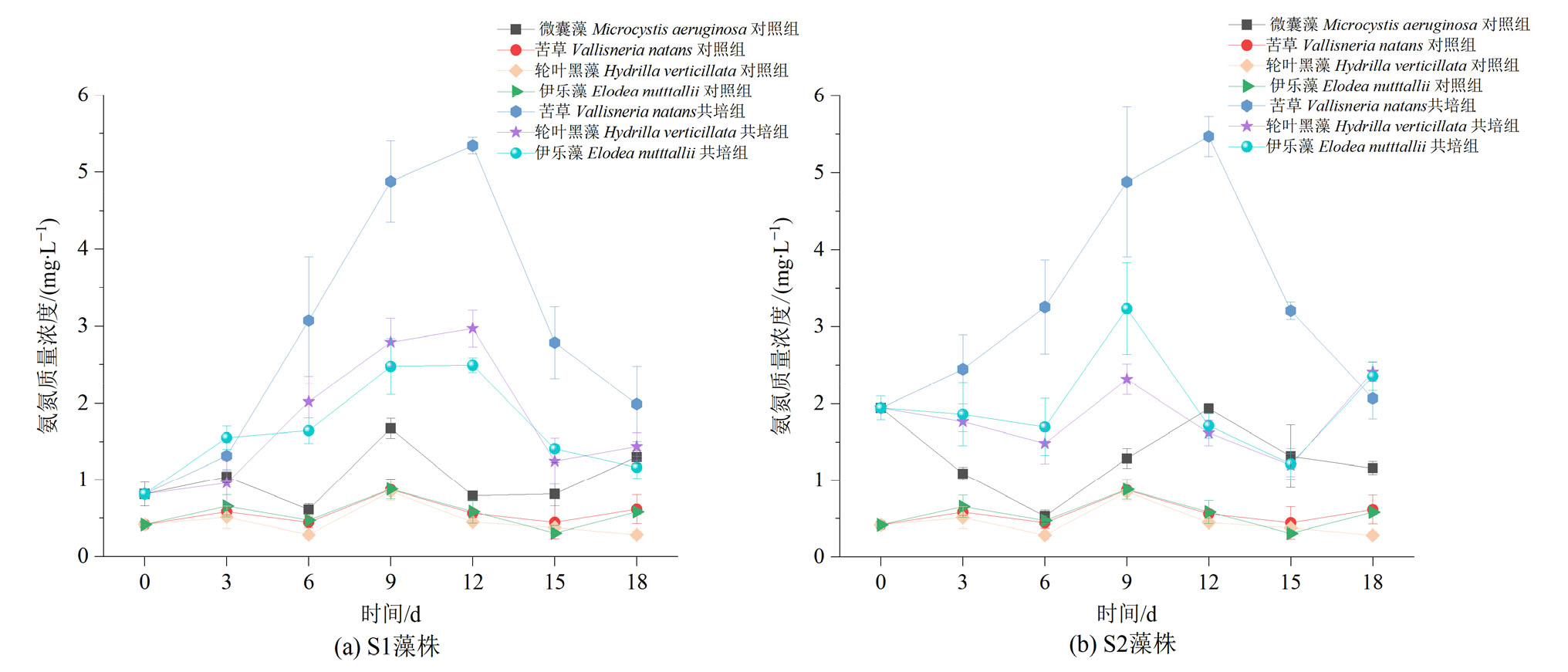
Figure 8 Dynamic changes in ammonia concentrations in monoculture controls of V. natans, H. verticillata and E. nutttallii and co-culture groups with Microcystis
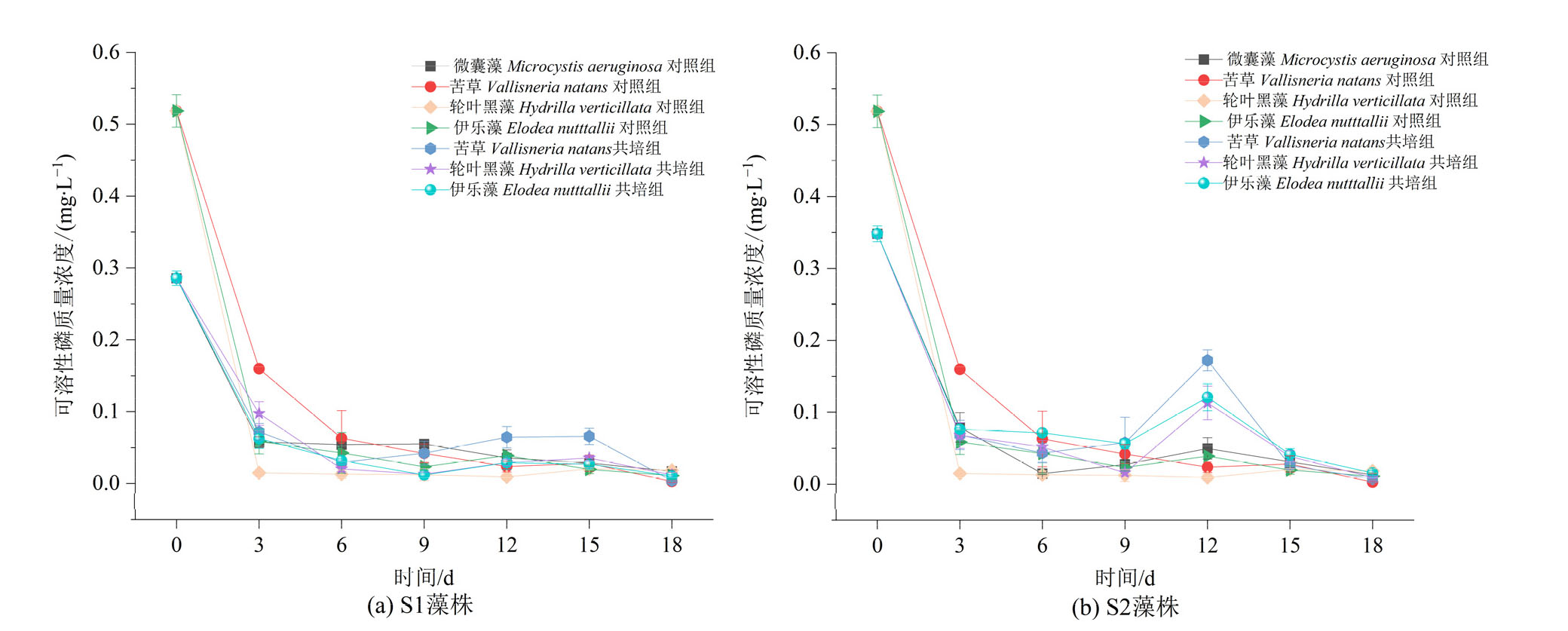
Figure 9 Dynamic changes in phosphate concentrations in monoculture controls of V. natans, H. verticillata and E. nutttallii and co-culture groups with Microcystis
| [1] |
BAI G, ZHANG Y, YAN P, et al., 2020. Spatial and seasonal variation of water parameters, sediment properties, and submerged macrophytes after ecological restoration in a long-term (6 year) study in Hangzhou west lake in China: Submerged macrophyte distribution influenced by environmental variables[J]. Water Research, 186: 116379.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
DAVIS T W, GOBLER C J, 2016. Preface for special issue on “Global expansion of harmful cyanobacterial blooms: Diversity, ecology, causes, and controls”[J]. Harmful Algae, 54: 1-3.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
GAGET V, HUMPAGE A R, HUANG Q, et al., 2017. Benthic cyanobacteria: A source of cylindrospermopsin and microcystin in Australian drinking water reservoirs[J]. Water Research, 124: 454-464.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
GAO Y N, GE F J, ZHANG L P, et al., 2017. Enhanced toxicity to the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa by low-dosage repeated exposure to the allelochemical N-phenyl-1-naphthylamine[J]. Chemosphere, 174: 732-738.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
GAO Y N, YANG H, GAO X F, et al., 2022. Ecological damage of submerged macrophyte Myriophyllum spicatum by cell extracts from microcystin (MC)- and non-MC-producing cyanobacteria, Microcystis [J]. Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 40: 1732-1749.
DOI |
| [6] |
GAO Y N, YANG H, LI L F, et al., 2023. Higher resistance of a microcystin (MC)-producing cyanobacterium, Microcystis, to the submerged macrophyte Myriophyllum spicatum[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30(23): 63941-63952.
DOI |
| [7] |
GUZZON A, BOHN A, DIOCIAIUTI M, et al., 2008. Cultured phototrophic biofilms for phosphorus removal in waste water treatment[J]. Water Research, 42(16): 4357-4367.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
GUBELIT Y I, GROSSART H P, 2020. New methods, new concepts: What can be applied to freshwater periphyton?[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 11: 1275.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
HARKE M J, STEFFEN M M, GOBLER C J, et al., 2016. A review of the global ecology, genomics, and biogeography of the toxic cyanobacterium, Microcystis spp.[J]. Harmful Algae, 54: 4-20.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
HE Y, ZHOU Q H, LIU B.Y., et al., 2016. Programmed cell death in the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa induced by allelopathic effect of submerged macrophyte Myriophyllum spicatum in co-culture system[J]. Journal of Applied Phycology, 28(5): 2805-2814.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
JONES J I, SAYER C D, 2003. Does the fish-invertebrate-periphyton cascade precipitate plant loss in shallow lakes[J]. Ecology, 84(8): 2155-2167.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
MOHAMED Z A, AL SHEHRI A M, 2010. Differential responses of epiphytic and planktonic toxic cyanobacteria to allelopathic substances of the submerged macrophyte Stratiotes aloides[J]. International Review of Hydrobiology, 95(3): 224-234.
DOI URL |
| [13] | NICKLISCH A, KOHL J G, 1989. The influence of light on the primary production of two planktic blue-green algae[J]. Arch Hydrobiol Beih Ergebn Limnol, 33: 451-455. |
| [14] |
O’DRISCOLL C, EYTO D E, RODGERS M, et al., 2012. Diatom assemblages and their associated environmental factors in upland peat forest rivers[J]. Ecological Indicators, 18: 443-451.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
ROBERTS E, KROKER J, KÖRNER S, et al., 2003. The role of periphyton during the re-colonization of a shallow lake with submerged macrophytes[J]. Hydrobiologia, 506-509: 525-530.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
ROMO S, MIRACLE M R, VILLENA M J, et al., 2004. Mesocosm experiments on nutrient and fish effects on shallow lake food webs in a Mediterranean climate[J]. Freshwater Biology, 49(12): 1593-1607.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
WIJEWARDENE L, WU N, FOHRER N, et al., 2022. Epiphytic biofilms in freshwater and interactions with macrophytes: Current understanding and future directions[J]. Aquatic Botany, 176: 103467.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
WU Y H, HE J Z, YANG L, 2010. Evaluating adsorption and biodegradation mechanisms during the removal of Microcystin-RR by periphyton[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 44(16): 6319-6324.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
WU Y, LIU J, YANG L, et al., 2011. Allelopathic control of cyanobacterial blooms by periphyton biofilms[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 13(3): 604-615.
DOI PMID |
| [20] | WU Z B, GAO Y N, WANG J, et al., 2009. Allelopathic effects of phenolic compounds present in submerged macrophytes on Microcystis aeruginosa [J]. Allelopathy Journal, 23(2): 403-410. |
| [21] |
SCHEFFER M, RINALDI S, GRAGNANI A, et al., 1997. On the dominance of filamentous cyanobacteria in shallow, turbid lakes[J]. Ecology, 78(1): 272-282.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
SOREN B, YVONNE V, PAUL S, 2016. Benthic algae compensate for phytoplankton losses in large aquatic ecosystems[J]. Global Change Biology, 22(12): 3865-3873.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | STEWART P M, PRATT J R, CAIRNS J, et al., 1985. Diatom and protozoan species accrual on artificial substrates in lentic habitats[J]. Microscopical Society, 104(4): 369-377. |
| [24] |
VADEBONCOEUR Y, STEINMAN A D, 2002. Periphyton function in lake ecosystems[J]. The Scientific World Journal, 2: 1449-1468.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
XIAO M, LI M, REYNOLDS C S, et al., 2018. Colony formation in the cyanobacterium Microcystis[J]. Biological Reviews, 93(3): 1399-1420.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
XU Y, WANG G X, YANG W B, et al., 2010. Dynamics of the water bloom-forming Microcystis and its relationship with physicochemical factors in Lake Xuanwu (China)[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 17(9): 1581-1590.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
YAN L Y, ZHANG S H, LIN D, et al., 2018. Nitrogen loading affects microbes, nitrifiers and denitrifiers attached to submerged macrophyte in constructed wetlands[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 622-623: 121-126.
DOI URL |
| [28] | YANG C T, SHEN X B, SHI X Y, et al., 2023. Impact of submerged macrophytes on growth and 2-MIB release risk of Pseudanabaena sp.: From field monitoring to cultural experiments[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 442: 130052. |
| [29] |
YU J L, XIA M L, HE H, et al., 2021. Species-specific responses of submerged macrophytes to the presence of a small omnivorous bitterling Acheilognathus macropterus[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 753: 141998.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
ZHANG L, LIU B Y, GE F J, et al., 2019. Interspecific competition for nutrients between submerged macrophytes (Vallisneria natans, Ceratophyllum demersum) and filamentous green algae (Cladophora oligoclona) in a co-culture system[J]. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 28(3): 1483-1494.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
ZHANG L, PENG X, LIU B Y, et al., 2018. Effects of the decomposing liquid of Cladophora oligoclona on Hydrilla verticillata turion germination and seedling growth[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 157: 81-88.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
ZHANG W Z, SHEN H, ZHANG J, et al., 2020. Physiological differences between free-floating and periphytic filamentous algae, and specific submerged macrophytes induce proliferation of filamentous algae: A novel implication for lake restoration[J]. Chemosphere, 239: 124702.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
ZHANG X F, LIU Z W, JEPPESEN E, et al., 2016. Effects of benthic-feeding common carp and filter-feeding silver carp on benthic-pelagic coupling: Implications for shallow lake management[J]. Ecological Engineering, 88: 256-264.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
ZHAO Y H, ZHANG Y, GUO J S, et al., 2023. Shifts in periphyton research themes over the past three decades[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30(3): 5281-5295.
DOI |
| [35] | 胡鸿钧, 魏印心, 2006. 中国淡水藻类-系统、分类及生态[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| HU H J, WEI Y X, 2009. Freshwater Algae in China- Systematics, Taxonomy and Ecology[M]. Beijing: Science Press. | |
| [36] | 何月, 2015. 底栖藻类在浅水湖泊稳态转换中的作用[D]. 武汉: 中南民族大学:39-40. |
| HE Y, 2015. The role of periphyton regime shifts in shallow lakes[D]. Wuhan: South-Central University for Nationalities:39-40. | |
| [37] | 邱东茹, 吴振斌, 刘保元, 1997. 武汉东湖水生植被的恢复试验研究[J]. 湖泊科学, 9(2): 168-174. |
|
QIU D R, WU Z B, LIU B Y, 1997. Ecological restoration of aquatic vegetation in a eutrophic shallow lake, Donghu lake, Wuhan[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 9(2): 168-174.
DOI URL |
|
| [38] | 尚媛媛, 2013. 蓝藻降解对大型沉水植物种群生长的影响[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学:18-19. |
| SHANG Y Y, 2013. The influence of cyanobacteria degradation on the submersed plant population growth[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology:18-19. | |
| [39] | 王立新, 2005. 黑藻对水华的抑制及其机制的研究[D]. 南京: 南京师范大学:30-31. |
| WANG L X, 2005. Study on the inhibition of water bloom by black algae and its mechanism[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Normal University:30-31. | |
| [40] | 王涛, 2021. 富营养化水体中底栖藻类生长和沉水植物响应的机制研究[D]. 武汉: 中南民族大学:54-56. |
| WANG T, 2021. Study on the mechanism of benthic algae growth and submerged macrophytes response in eutrophic water[D]. Wuhan: South-Central Minzu University:54-56. | |
| [41] | 吴婷婷, 刘国锋, 韩士群, 等, 2015. 蓝藻水华聚集对水葫芦生理生态的影响[J]. 环境科学, 36(1): 114-120. |
| WU T T, LIU G F, HAN S Q, et al., 2015. Impacts of algal blooms accumulation on physiological ecology of water hyacinth[J]. Environmental Science, 36(1): 114-120. | |
| [42] | 吴振斌, 等, 2011. 水生植物与水体生态修复[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| WU Z B, et al., 2011. Aquatic plant and ecological restoration of water environment[M]. Beijing: Science Press. | |
| [43] | 吴振斌, 邱东茹, 贺锋, 等, 2001. 水生植物对富营养水体水质净化作用研究[J]. 武汉植物学研究, 19(4): 299-303. |
| WU Z B, QIU D R, HE F, et al., 2001. Studies on eutrophicated water quality provement by means of Aquatic Macrophytes[J]. Journal of Wuhan Botanical Research, 19(4): 299-303. | |
| [44] | 张兵之, 2008. 伊乐藻对铜绿微囊藻的化感作用研究[D]. 武汉: 中国科学院研究生院(水生生物研究所):66-67. |
| ZHANG B Z, 2008. Studies on The Allelopathy of Elodea nuttallii on Microcystis aeruginosa [D]. Wuhan: Chinese Academy of Sciences (Institute of Hydrobiology): 66-67. |
| [1] | HE Wenxuan, LI Lei, SUN Siyu, LI Chang, LI Jiuyi, TIAN Xiujun. Distribution Characteristics of Microplastics in Water, Sediment and Fish in Beiyun River [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(11): 1901-1912. |
| [2] | LI Wenjing, HUANG Yuequn, HUANG Liangliang, LI Xiangtong, SU Qiongyuan, SUN Yangyan. Distribution Characteristics and Risk Assessment of Microplastics in Beibu Gulf Marine Fish [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(11): 1913-1921. |
| [3] | HAN Qian, ZHANG Yujiao, LAI Chengyue, YANG Luyao, MENG Xu. Pollution Characteristics and Ecological Risk Assessment of Tetracycline and Quinolone Antibiotics in Rivers of Chengdu [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(11): 1922-1932. |
| [4] | GAO Xiaoyu, WANG Lei. The Accumulation, Transfer and Elimination of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Soil: A Review [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(11): 2062-2071. |
| [5] | HOU Dongmei, ZHANG Lan, LI Chuncheng, CHEN Lutong, WANG Panpan, ZOU Jianping. Enhanced Removal of Sb(III) and Sb(V) Using Biological Iron and Manganese Oxides Modified Chitosan: Performance and Mechanism Study [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(10): 1842-1853. |
| [6] | LI Xuan, QIAN Xiuwen, HUANG Juan, WANG Mingyu, XIAO Jun. Responses of Operating Performance and Microbial Community in Constructed Wetlands to NiO NPs Exposure [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(10): 1833-1841. |
| [7] | LIANG Chuan, YANG Yanfang, YU Shanshan, ZHOU Li, ZHANG Jingwei, ZHANG Xiujuan. Differences of Microbial Biomass and Community Structure Characteristics in Sediments under Net-pen and Pond Fish Farming [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(10): 1802-1810. |
| [8] | ZHOU Jiacheng, SONG Zhibin, MIAO Peng, TAN Lu, TANG Tao. Differences in Benthic Macroinvertebrate Communities and Their Driving Forces between the Edge and Center Positions of the Liujiang River Network [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(10): 1794-1801. |
| [9] | ZHAO Yanchu, WANG Fei, WU Dan, HUANG Xin, CHEN Jialin, ZHOU Linpu, KONG Fanqing. Health Assessment of Haihe River Basin Based on Benthic Index of Biotic Integrity [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(10): 1785-1793. |
| [10] | FAN Yanxiang, LEI Sheping, XIE Jiancang. Comprehensive Evaluation and Differentiation Characteristics of Eutrophication in River Waters of Guangdong Province: Based on Game Theory Combined Empowerment Method and VIKOR Model [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(10): 1811-1821. |
| [11] | CHEN Hongzhan, OU Hui, YE Sihua, ZHANG Qianhua, ZHOU Shujie, MAI Lei. Spatial-temporal Distribution and Ecological Risk Assessment of Microplastics in the Guangzhou Section of the Pearl River [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(9): 1663-1672. |
| [12] | LU Yanbo, CHEN Zhanfeng, LI Xiaofang. A Study on Water Quality Prediction Model of Cross-boundary Sections in Guangdong Province Based on GRU Improved with Particle Swarm Optimization [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(9): 1673-1681. |
| [13] | LIANG Chuan, YANG Yanfang, YU Shanshan, ZHOU Li, ZHANG Jingwei, ZHANG Xiujuan. Differences of Microbial Biomass and Community Structure Characteristics in Sediments under Net-pen and Pond Fish Farming [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(8): 1487-1495. |
| [14] | LI Jiaman, WANG Xiaoming, HU Xinrui, XIE Yingying, WEN Zhen. Effects of Fe-S Ratio on the Microstructure and Cr Adsorption Properties of Schwertmannite [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(8): 1478-1486. |
| [15] | WANG Yuanzhe, HUA Chunlin, ZHAO Li, FAN Min, LIANG Xiaoying, ZHOU Lele, CAI Can, YAO Jing. Study on Water Quality Evaluation and Prediction of Major Rivers in Mountainous City: A Case Study of Mianyang City [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(8): 1465-1477. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
