Ecology and Environment ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (2): 341-350.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.02.014
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Li1,2( ), LI Cheng2, TAN Haoze2,3, WEI Jiayi4, CHENG Jiong2, PENG Guixiang1,*(
), LI Cheng2, TAN Haoze2,3, WEI Jiayi4, CHENG Jiong2, PENG Guixiang1,*( )
)
Received:2022-11-28
Online:2023-02-18
Published:2023-05-11
Contact:
PENG Guixiang
张莉1,2( ), 李铖2, 谭皓泽2,3, 韦家怡4, 程炯2, 彭桂香1,*(
), 李铖2, 谭皓泽2,3, 韦家怡4, 程炯2, 彭桂香1,*( )
)
通讯作者:
彭桂香
作者简介:张莉(1997年生),女(土家族),硕士研究生,研究方向为土壤学和景观生态学。E-mail: 2279290378@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
ZHANG Li, LI Cheng, TAN Haoze, WEI Jiayi, CHENG Jiong, PENG Guixiang. Reduction Effect and Influencing Factors of Typical Urban Woodlands on Atmospheric Particulate Matter in Guangzhou[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(2): 341-350.
张莉, 李铖, 谭皓泽, 韦家怡, 程炯, 彭桂香. 广州典型城市林地对大气颗粒物的削减效应及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 341-350.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.02.014
| 公园名称 | 样地 | 林内外 | 经度 | 纬度 | 距离污染源的最近距离/m | 林内外监测点的距离/m | 林分类型 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 华南国家植物园 | a1 | 林内 | 113.3667 | 23.1835 | 229.16 | 208.57 | 火力楠-灰木莲 Michelia macclurel-Manglietia glauca |
| a2 | 林外 | 113.3647 | 23.1831 | 363.09 | |||
| b1 | 林内 | 113.3587 | 23.1871 | 229.09 | 31.72 | 白千层 Melaleuca leucadendron L. | |
| b2 | 林外 | 113.3584 | 23.1871 | 212.45 | |||
| 白云山风景区 | c1 | 林内 | 113.3055 | 23.1884 | 1159.45 | 139.48 | 湿地松-山油柑-柯 Pinus elliottii-Acronychia pedunculata (L.) Miq.-Lithocarpus glaber (Thunb.) Nakai |
| c2 | 林外 | 113.3041 | 23.1883 | 1276.07 | |||
| 华南国家植物园 | d1 | 林内 | 113.3604 | 23.1800 | 518.70 | 176.70 | 尾叶桉 Eucalyptus urophylla S.T. Blake |
| d2 | 林外 | 113.3621 | 23.1805 | 416.51 | |||
| 白云山风景区 | e1 | 林内 | 113.2985 | 23.1844 | 1711.20 | 99.06 | 锥-木荷 Schima superba Gardn. et Champ.-Castanopsis chinensis (Sprengel) Hance |
| e2 | 林外 | 113.2985 | 23.1835 | 1696.63 |
Table 1 Overview of the sample sites in our study
| 公园名称 | 样地 | 林内外 | 经度 | 纬度 | 距离污染源的最近距离/m | 林内外监测点的距离/m | 林分类型 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 华南国家植物园 | a1 | 林内 | 113.3667 | 23.1835 | 229.16 | 208.57 | 火力楠-灰木莲 Michelia macclurel-Manglietia glauca |
| a2 | 林外 | 113.3647 | 23.1831 | 363.09 | |||
| b1 | 林内 | 113.3587 | 23.1871 | 229.09 | 31.72 | 白千层 Melaleuca leucadendron L. | |
| b2 | 林外 | 113.3584 | 23.1871 | 212.45 | |||
| 白云山风景区 | c1 | 林内 | 113.3055 | 23.1884 | 1159.45 | 139.48 | 湿地松-山油柑-柯 Pinus elliottii-Acronychia pedunculata (L.) Miq.-Lithocarpus glaber (Thunb.) Nakai |
| c2 | 林外 | 113.3041 | 23.1883 | 1276.07 | |||
| 华南国家植物园 | d1 | 林内 | 113.3604 | 23.1800 | 518.70 | 176.70 | 尾叶桉 Eucalyptus urophylla S.T. Blake |
| d2 | 林外 | 113.3621 | 23.1805 | 416.51 | |||
| 白云山风景区 | e1 | 林内 | 113.2985 | 23.1844 | 1711.20 | 99.06 | 锥-木荷 Schima superba Gardn. et Champ.-Castanopsis chinensis (Sprengel) Hance |
| e2 | 林外 | 113.2985 | 23.1835 | 1696.63 |
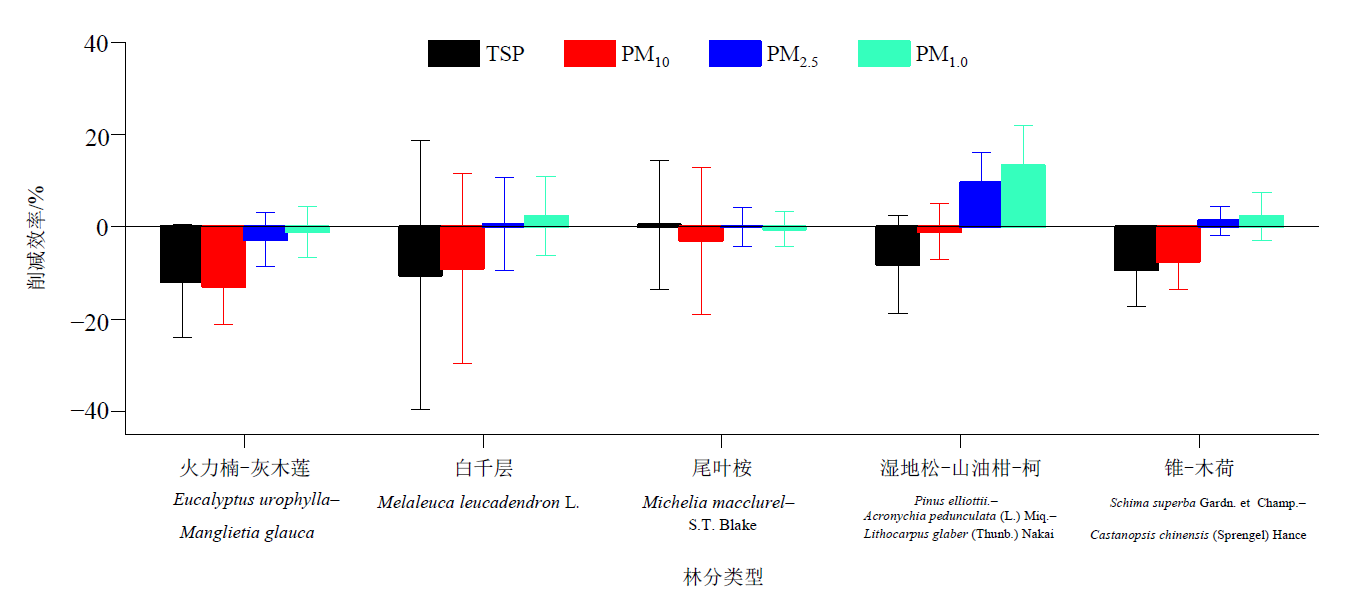
Figure 2 Mean values (columns) and standard deviations (error bars) of reduction efficiencies of atmospheric particulate matter by different woodland types
| 大气颗粒物削减率/质量浓度 | 颗粒物类型 | 温度 | 相对湿度 | 风速 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大气颗粒物削减率/ % | TSP | 0.08 | -0.12 | -0.19** |
| PM10 | -0.01 | 0.03 | -0.31** | |
| PM2.5 | 0.15** | -0.11 | -0.26** | |
| PM1.0 | 0.21** | -0.10 | -0.23** | |
| 林内大气颗粒物质量浓度/ (μg·m-3) | TSP | -0.36** | 0.56** | -0.22** |
| PM10 | -0.35** | 0.60** | -0.22** | |
| PM2.5 | -0.36** | 0.63** | -0.24** | |
| PM1.0 | -0.30** | 0.54** | -0.25** | |
| 林外大气颗粒物质量浓度/ (μg·m-3) | TSP | -0.38** | 0.58** | -0.29** |
| PM10 | -0.39** | 0.65** | -0.29** | |
| PM2.5 | -0.36** | 0.65** | -0.27** | |
| PM1.0 | -0.30** | 0.57** | -0.28** |
Table 2 Spearman correlation coefficients between the reduction rate/mass concentrations of atmospheric particulate matter and meteorological factors
| 大气颗粒物削减率/质量浓度 | 颗粒物类型 | 温度 | 相对湿度 | 风速 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大气颗粒物削减率/ % | TSP | 0.08 | -0.12 | -0.19** |
| PM10 | -0.01 | 0.03 | -0.31** | |
| PM2.5 | 0.15** | -0.11 | -0.26** | |
| PM1.0 | 0.21** | -0.10 | -0.23** | |
| 林内大气颗粒物质量浓度/ (μg·m-3) | TSP | -0.36** | 0.56** | -0.22** |
| PM10 | -0.35** | 0.60** | -0.22** | |
| PM2.5 | -0.36** | 0.63** | -0.24** | |
| PM1.0 | -0.30** | 0.54** | -0.25** | |
| 林外大气颗粒物质量浓度/ (μg·m-3) | TSP | -0.38** | 0.58** | -0.29** |
| PM10 | -0.39** | 0.65** | -0.29** | |
| PM2.5 | -0.36** | 0.65** | -0.27** | |
| PM1.0 | -0.30** | 0.57** | -0.28** |
| 颗粒物类型 | 林外大气颗粒物质量浓度/(μg·m-3) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSP | PM10 | PM2.5 | PM1.0 | |
| TSP | 0.04 | -0.02 | -0.10 | -0.09 |
| PM10 | 0.00 | 0.01 | -0.02 | -0.00 |
| PM2.5 | -0.25** | -0.21** | -0.22** | -0.21** |
| PM1.0 | -0.29** | -0.23** | -0.22** | -0.21** |
Table 3 Spearman correlation coefficients between the reduction rate of atmospheric particulate matter and its mass concentrations outside the woodland
| 颗粒物类型 | 林外大气颗粒物质量浓度/(μg·m-3) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSP | PM10 | PM2.5 | PM1.0 | |
| TSP | 0.04 | -0.02 | -0.10 | -0.09 |
| PM10 | 0.00 | 0.01 | -0.02 | -0.00 |
| PM2.5 | -0.25** | -0.21** | -0.22** | -0.21** |
| PM1.0 | -0.29** | -0.23** | -0.22** | -0.21** |
| 尺度 | 颗粒物 类型 | 冠幅1 | 冠幅2 | 平均 树高 | 优势种 密度 | 叶面积 指数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 半小时 (n=205) | TSP | -0.14* | -0.12 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.22** |
| PM10 | -0.31** | -0.30** | -0.05 | 0.02 | 0.30** | |
| PM2.5 | -0.32** | -0.35** | -0.11 | -0.03 | 0.27** | |
| PM1.0 | -0.31** | -0.34** | -0.13 | -0.03 | 0.19** | |
| 日 (n=14) | TSP | -0.03 | 0.06 | -0.07 | -0.07 | 0.15 |
| PM10 | -0.21 | -0.18 | -0.21 | -0.13 | 0.27 | |
| PM2.5 | -0.36 | -0.44 | -0.24 | -0.10 | 0.25 | |
| PM1.0 | -0.50 | -0.58* | -0.16 | 0.02 | 0.31 | |
| 林地 (n=5) | TSP | 0.03 | 0.17 | -0.09 | 0.03 | 0.26 |
| PM10 | -0.20 | -0.06 | -0.20 | 0.09 | 014 | |
| PM2.5 | -0.31 | -0.58 | -0.49 | -0.26 | 0.09 | |
| PM1.0 | -0.43 | -0.73 | -0.54 | -0.20 | 0.03 |
Table 4 Spearman correlation coefficients between the reduction efficiency of atmospheric particulate matter and the vegetation characteristics of woodlands at different scales
| 尺度 | 颗粒物 类型 | 冠幅1 | 冠幅2 | 平均 树高 | 优势种 密度 | 叶面积 指数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 半小时 (n=205) | TSP | -0.14* | -0.12 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.22** |
| PM10 | -0.31** | -0.30** | -0.05 | 0.02 | 0.30** | |
| PM2.5 | -0.32** | -0.35** | -0.11 | -0.03 | 0.27** | |
| PM1.0 | -0.31** | -0.34** | -0.13 | -0.03 | 0.19** | |
| 日 (n=14) | TSP | -0.03 | 0.06 | -0.07 | -0.07 | 0.15 |
| PM10 | -0.21 | -0.18 | -0.21 | -0.13 | 0.27 | |
| PM2.5 | -0.36 | -0.44 | -0.24 | -0.10 | 0.25 | |
| PM1.0 | -0.50 | -0.58* | -0.16 | 0.02 | 0.31 | |
| 林地 (n=5) | TSP | 0.03 | 0.17 | -0.09 | 0.03 | 0.26 |
| PM10 | -0.20 | -0.06 | -0.20 | 0.09 | 014 | |
| PM2.5 | -0.31 | -0.58 | -0.49 | -0.26 | 0.09 | |
| PM1.0 | -0.43 | -0.73 | -0.54 | -0.20 | 0.03 |
| [1] |
BUCCOLIERI R, GROMKE C, SABATINO S D, et al., 2009. Aerodynamic effects of trees on pollutant concentration in street canyons[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 407(19): 5247-5256.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
BUCCOLIERI R, SALIM S M, LEO L S, et al., 2011. Analysis of local scale tree-atmosphere interaction on pollutant concentration in idealized street canyons and application to a real urban junction[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 45(9): 1702-1713.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
BURNETT R, CHEN H, SZYSZKOWICZ M, et al., 2018. Global estimates of mortality associated with long-term exposure to outdoor fine particulate matter[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of the United States of America, 115(38): 9592-9597.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
CHEN L, GAO S, ZHANG H, et al., 2018. Spatiotemporal modeling of PM2.5 concentrations at the national scale combining land use regression and Bayesian maximum entropy in China[J]. Environment International, 116: 300-307.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
GROMKE C, BUCCOLIERI R, SABATINO S D, et al., 2008. Dispersion study in a street canyon with tree planting by means of wind tunnel and numerical investigations-Evaluation of CFD data with experimental data[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 42(37): 8640-8650.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
GROMKE C, JAMARKATTEL N, RUCK B, 2016. Influence of roadside hedgerows on air quality in urban street canyons[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 139: 75-86.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
GROMKE C, RUCK B, 2007. Influence of trees on the dispersion of pollutants in an urban street canyon-Experimental investigation of the flow and concentration field[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 41(16): 3287-3302.
DOI URL |
| [8] | HUANG D S, XU J H, ZHAN S Q, 2012. Valuing the health risks of particulate air pollution in the Pearl River Delta, China[J]. Environmental Science & Policy, 15(1): 38-47. |
| [9] |
LARKIN A, DONKELAAR A V, GEDDES J A, et al., 2016. Relationships between changes in urban characteristics and air quality in east asia from 2000 to 2010[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 50(17): 9142-9149.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
LUO X S, BING H J, LUO Z X, et al., 2019. Impacts of atmospheric particulate matter pollution on environmental biogeochemistry of trace metals in soil-plant system: A review[J]. Environmental Pollution, 255(Part 1): 113138.
DOI URL |
| [11] | PUGH T A, MACKENZIE A R, WHYATT J D, et al., 2012. Effectiveness of green infrastructure for improvement of air quality in urban street canyons[J]. Environmental Science & Techology, 46(14): 7692-7699. |
| [12] |
SHI W Z, WONG M S, WANG J Z, et al., 2012. Analysis of airborne particulate matter (PM2.5) over Hong Kong using remote sensing and GIS[J]. Sensors, 12(6): 6825-6836.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
TURNER J, POND G R, TREMBLAY A, et al., 2021. Risk perception among a lung cancer screening population[J]. Chest, 160(2): 718-730.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
VOS P E, MAIHEU B, VANKERKOM J, et al., 2013. Improving local air quality in cities: to tree or not to tree?[J]. Environmental Pollution, 183: 113-122.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
包红光, 王成, 郄光发, 等, 2016. 城市公园外侧防护林结构对外源PM2.5的消减作用[J]. 生态环境学报, 25(6): 987-993.
DOI |
| BAO H G, WANG C, QIE G F, et al., 2016. The effect of forest shelter belt on subduction of PM2.5 in urban parks[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 25(6): 987-993. | |
| [16] | 陈尖, 黎明, 2011. 广东让森林挺进城市[J]. 中国林业 (4): 18-21. |
| CHE J, LI M, 2011. Let the forest advance into the city in Guangdong[J]. Forest of China (4): 18-21. | |
| [17] | 陈上杰, 牛健植, 韩旖旎, 等, 2015. 道路绿化带内大气PM2.5质量浓度变化特征[J]. 水土保持学报, 29(2): 100-105. |
| CHEN S J, NIU J Z, HAN Y N, et al., 2015. Characteristics of mass concentration variations of PM2.5 in the road greenbelts[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 29(2): 100-105. | |
| [18] | 杜志坚, 2017. 华南植物园迁地植物害虫多样性分析[D]. 广州: 仲恺农业工程学院: 6-7. |
| DU Z J, 2017. Analysis on the diversity of pests of ex situ plants in Southern China Botanical Garden[D]. Guangzhou: ZhongKai University of Agriculture and Engineering: 6-7. | |
| [19] | 冯海英, 2018. 北京市大气颗粒物浓度与植被空间分布相关性研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学:68-69. |
| FENG H Y, 2018. Study on correlation between particulate concentration and spatial distribution of vegetation in Beijing[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University:68-69. | |
| [20] | 郭二果, 2008. 北京西山典型游憩林生态保健功能研究[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院:36-66. |
| GUO E G, 2008. Ecological health effects of typical recreation forests in west mountain of Beijing[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry:36-66. | |
| [21] | 郭二果, 王成, 郄光发, 等, 2013. 北方地区典型天气对城市森林内大气颗粒物的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 33(7): 1185-1198. |
| GUO E G, WANG C, QIE G F, et al., 2013. Influence of typical weather conditions on the airborne particulate matters in urban forests in northern China[J]. China Environmental Science, 33(7): 1185-1198. | |
| [22] | 黄俊彪, 2013. 广州市典型森林土壤多环芳烃分布及其吸附性能研究[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院:15-16. |
| HUANG J B, 2013. Distribution and absorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in tipical forest soil of Guangzhou[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry:15-16. | |
| [23] |
蒋燕, 陈波, 鲁绍伟, 等, 2016. 北京城市森林PM2.5质量浓度特征及影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 25(3): 447-457.
DOI |
| JIANG Y, CHEN B, LU S W, et al., 2016. Analysis on characteristics and influential factors of PM2.5 mass concentration in Beijing’s urban forest[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 25(3): 447-457. | |
| [24] | 赖乃揆, 翟月明, 贺紫兰, 等, 1982. 广州市部分地区空气中花粉及其致敏性的初步调查[J]. 广州医学院学报 (3): 1-11. |
| LAI N K, ZHAI Y M, HE Z L, et al., 1982. Pollen in air in some areas of Guangzhou preliminary investigation of its sensitization[J]. Academic Journal of Guangzhou Medical College (3): 1-11. | |
| [25] | 李惠玲, 何秉宇, 玉米提·哈力克, 等, 2020. 干旱区城市森林大气颗粒物浓度变化特征及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 江苏农业科学, 48(18): 294-299. |
| LI H L, HE B Y, YU M T·H L G, et al., 2020. Characteristics of atmospheric particulate concentrations in urban forests in arid areas and its relationship with environmental factors[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 48(18): 294-299. | |
| [26] | 粟莉圆, 2021. 火力楠种子园开花动态与繁育系统研究[D]. 南宁: 广西大学: 3-4. |
| LI L Y, 2021. Study on the flowering dynamics and breeding system in seed orchard of Michelia macclurei[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University: 3-4. | |
| [27] | 李少宁, 刘斌, 鲁笑颖, 等, 2016. 北京常见绿化树种叶表面形态与PM2.5吸滞能力关系[J]. 环境科学与技术, 39(10): 62-68. |
| LI S N, LIU B, LU X Y, et al., 2016. Relationship between leaf surface morphology and PM2.5 adsorption capacity of common greening tree species in Beijing[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 39(10): 62-68. | |
| [28] | 李新宇, 赵松婷, 李延明, 等, 2014. 北京市不同主干道绿地群落对大气PM2.5浓度消减作用的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 23(4): 615-621. |
| LI X Y, ZHAO S T, LI Y M, et al., 2014. Subduction effect of urban arteries green space on atmospheric concentration of PM2.5 in Beijing[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 23(4): 615-621. | |
| [29] | 廖莉团, 苏欣, 李小龙, 等, 2014. 城市绿化植物滞尘效益及滞尘影响因素研究概述[J]. 森林工程, 30(2): 21-24, 28. |
| LIAO L T, SU X, LI X L, et al., 2014. Review on the purification effects of urban landscape plants and factors affecting detaining dust[J]. Forest Engineering, 30(2): 21-24, 28. | |
| [30] | 刘斌, 鲁绍伟, 李少宁, 等, 2016. 北京大兴6种常见绿化树种吸附PM2.5能力研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 39(2): 31-37. |
| LIU B, LU S W, LI S N, et al., 2016. Study on adsorption ability of PM2.5 about six common landscape plants in Daxing District, Beijing[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 39(2): 31-37. | |
| [31] | 刘浩栋, 陈亚静, 李清殿, 等, 2020. 城市道路林对细颗粒物 (PM2.5) 的阻滞作用解析[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 37(3): 397-406. |
| LIU H D, CHEN Y J, LI Q D, et al., 2020. Analysis of blocking effects of urban roadside forests on PM2.5[J]. Journal of Zhejiang A & F University, 37(3): 397-406. | |
| [32] | 刘旭辉, 2016. 北京地区典型人工林对空气颗粒物浓度的影响[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学:19-20. |
| LIU X H, 2016. Influence of plantation ecosystems on atmospheric particles concentration in Beijing region[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University:19-20. | |
| [33] | 刘一超, 王萌, 梁琼, 等, 2018. 北京通州不同树种滞纳大气颗粒物的能力[J]. 北京农学院学报, 33(1): 84-88. |
| LIU Y C, WANG M, LIANG Q, et al., 2018. Study on the atmospheric particulate matter adsorption capacity of different tree species in Tongzhou District of Beijing[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Agriculture, 33(1): 84-88. | |
| [34] | 卢万鸿, 罗建中, 曹加光, 2010. 不同树龄、种源尾叶桉的开花结实情况调查[J]. 桉树科技, 27(2): 39-42. |
| LU W H, LUO J Z, CAO J G, 2010. Investigation on florescence and seeding of different provenances and ages of Eucalyptus urophylla[J]. Eucalypt Science & Technology, 27(2): 39-42. | |
| [35] | 罗传秀, 苏翔, 杨艺萍, 2017. 广州市孢粉致敏病学研究与预报[R]. 广东省, 中国科学院南海海洋研究所: 1-2. |
| LUO C X, SU X, YANG Y P, 2017. Study and prediction of sporopollen allergies in Guangzhou[R]. Institute of Oceanology Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangdong Province: 1-2. | |
| [36] | 鲁绍伟, 蒋燕, 陈波, 等, 2017. 北京城市植被区PM2.5浓度时空变化及影响因素分析[J]. 环境科学与技术, 40(1): 180-187. |
| LU S W, JIANG Y, CHEN B, et al., 2017. Analysis on spatial-temporal variation and influential factors of PM2.5mass concentration in Beijing’s urban forest[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 40(1): 180-187. | |
| [37] | 潘丽琴, 郝建, 徐建民, 等, 2018. 灰木莲花期物侯观测及生殖构件分布[J]. 林业科学研究, 31(2): 92-97. |
| PAN L Q, HAO J, XU J M, et al., 2018. Flowering phenology and reproductive modules distribution of Manglietia glance blune[J]. Forest Research, 31(2): 92-97. | |
| [38] | 舒德远, 丁访军, 刘延惠, 等, 2017. 贵阳市城郊常绿落叶阔叶混交林对大气颗粒物的影响[J]. 贵州林业科技, 45(1): 15-21. |
| SHU D Y, DING F J, LIU Y H, 2017. Impact of evergreen and deciduous broad-leaved mixed forest on atmospheric particulates in suburb of Guiyang City[J]. Guizhou Forestry Science and Technology, 45(1): 15-21. | |
| [39] | 谭超, 郑慧梓, 马艺天, 2022. 绿色发展享誉世界[N]. 南方日报, [2022-07-12]. AA4. |
| TAN C, ZHENG H Z, MA Y T, 2022. Green development is world-renowned[N]. Southern Daily, [2022-07-12]. AA4. | |
| [40] | 王兵, 张维康, 牛香, 等, 2015. 北京10个常绿树种颗粒物吸附能力研究[J]. 环境科学, 36(2): 408-414. |
| WANG B, ZHANG W K, NIU X, et al., 2015. Particulate matter adsorption capacity of 10 evergreen species in Beijing[J]. Environmental Science, 36(2): 408-414. | |
| [41] | 王科朴, 张语克, 刘雪华, 2020. 北京城市绿地对大气颗粒物的削减量计算[J]. 环境科学与技术, 43(4): 121-129. |
| WANG K P, ZHANG Y K, LIU X H, 2020. Modeled particulate matters removal by urban green lands in Beijing[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 43(4): 121-129. | |
| [42] | 王磊, 黄利斌, 万欣, 等, 2016. 城市森林对大气颗粒物 (尤其PM2.5) 调控作用研究进展[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 40(5): 148-154. |
| WANG L, HUANG L B, WAN X, et al., 2016. Progress on the regulating effects of urban forest vegetation on atmospheric particulate matter (especially PM2.5)[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 40(5): 148-154. | |
| [43] | 王萌, 刘一超, 梁琼, 等, 2018. 北京城市森林公园不同树种吸附大气颗粒物能力[J]. 北京农学院学报, 33(1): 79-83. |
| WANG M, LIU Y C, LIANG Q, et al., 2018. Study on the atmospheric particulate matters adsorption capacity of different tree species in urban forest park of Beijing[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Agriculture, 33(1): 79-83. | |
| [44] | 王忠, 欧阳婵娟, 罗燕燕, 等, 2007. 乡土植物在广州城市园林绿化中的应用[J]. 亚热带植物科学, 36(4): 33-37. |
| WANG Z, OUYANG C J, LUO Y Y, et al., 2007. Application of indigenous plants to urban landscap in Guangzhou[J]. Subtropical Plant Scienc, 36(4): 33-37. | |
| [45] | 王轶浩, 凯旋, 谢双喜, 2016. 重庆铁山坪森林植被调控下的大气PM2.5和PM10特征[J]. 四川林业科技, 37(6): 54-58. |
| WANG Y H, KAI X, XIE S X, 2016. Characteristics of atmospheric PM2.5 and PM10 regulated by forest vegetation in the Tieshanping forest park of Chongqing[J]. Journal of Sichuan Forestry Science and Technology, 37(6): 54-58. | |
| [46] | 肖小军, 谢雄杰, 康敏雄, 等, 2011. 深圳市春季气传致敏花粉的调查[J]. 免疫学杂志, 27(10): 837-839, 844. |
| XIAO X J, XIE X J, KANG M X, et al., 2011. Investigation on airborne pollen in spring of Shenzhen[J]. Immunological Journal, 27(10): 837-839, 844. | |
| [47] | 杨期和, 黄楚琪, 王燕华, 2018. 粤东山区山茶科植物资源及其开发利用初探[J]. 中国野生植物资源, 37(3): 56-63. |
| YANG Q H, HUANG C Q, WANG Y H, 2018. A preliminary study on the exploitation and utilization of theaceae plant resources in the mountainous area of eastern Guangdong[J]. Chinese Wild Plant Resources, 37(3): 56-63. | |
| [48] | 杨伟儿, 张乔松, 周先武, 2006. 广州城市绿地生物多样性的现状与展望[J]. 广东园林, 28(2): 47-51, 55. |
| YANG W E, ZHANG Q S, ZHOU X W, 2006. Gurrent status and prospects of iodiversity in Guangzhou urban green space[J]. Guangdong Landscape Architecture, 28(2): 47-51, 55. | |
| [49] | 喻明美, 谢正生, 2011. 广州市白云山五种森林类型的土壤渗透性研究[J]. 水土保持研究, 18(1): 153-156. |
| YU M M, XIE Z S, 2011. Study on soil permeability capability of five forest types in Baiyunshan scenic spot of Gangzhou[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 18(1): 153-156. | |
| [50] |
张刘东, 郭建曜, 万家隆, 等, 2021. 泰山景区不同林型空气颗粒物浓度研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 37(19): 100-105.
DOI |
|
ZHANG L D, GUO J Y, WAN J L, et al., 2021. Study on ambient particulate matter concentration of different forest types in Mountain Tai Scenic Area[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 37(19): 100-105.
DOI |
|
| [51] | 张雅慧, 廖景平, 张容妹, 等, 2020. 华南植物园藤本植物专类园规划设计[J]. 中国园林, 36(10): 92-97. |
| ZHANG Y H, LIAO J P, ZHANG R M, et al., 2020. The planning and design of the specialized gardenfor vine plants in South China Botanical Garden[J]. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 36(10): 92-97. | |
| [52] | 张志国, 2016. 森林城市群让广东更美丽[J]. 绿色中国 (23): 18-23. |
| ZHANG Z G, 2016. Forest city group make more beautiful in Guangdong[J]. Green China (23): 18-23. | |
| [53] | 赵云阁, 鲁笑颖, 刘斌, 等, 2016. 夏季绿化树种滞留PM2.5与叶片微形态特征研究[J]. 水土保持研究, 23(6): 52-58. |
| ZHAO Y G, LU X Y, LIU B, et al., 2016. Study on four kinds of greening tree retention PM2.5 and leaf surface morphology during summer in Beijing, China[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 23(6): 52-58. | |
| [54] | 郑铭浩, 2017. 重庆主城区常见树种及植物群落对空气颗粒物的调控作用研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学:57-61. |
| ZHENG M H, 2017. Study on the regulation of common tree species and plant communities on atmospheric particle in urban areas of Chongqing[D]. Chongqing: Master Thesis of Southwest University:57-61. | |
| [55] | 朱书银, 2019. 新乡市主城区大气颗粒物的变化特征及来源解析[D]. 新乡: 河南师范大学: 1-2. |
| ZHU S Y, 2019. Variation characteristics and source apportionment of atmosphere particul atematterin the main urban area of Xinxiang[D]. Xinxiang: Henan Normal University: 1-2. | |
| [56] | 邹杰, 2011. 湿地松种子园花粉散发特性研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学: 1-2. |
| ZOU J, 2011. Studies on pollen dispersal characteristic in seed orchard of Pinus elliottii[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University: 1-2. |
| [1] | DONG Jiefang, DENG Chun, ZHANG Zhongwu. Spatio-temporal Evolution and Population Exposure Risk to PM2.5 in the Weihe River Basin [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(6): 1078-1088. |
| [2] | LI Jianhui, DANG Zheng, CHEN Lin. Spatial-temporal Characteristics of PM2.5 and Its Influencing Factors in the Yellow River Jiziwan Metropolitan Area [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 697-705. |
| [3] | ZHANG Lin, QI Shi, ZHOU Piao, WU Bingchen, ZHANG Dai, ZHANG Yan. Study on Influencing Factors of Soil Organic Carbon Content in Mixed Broad-leaved and Coniferous Forests Land in Beijing Mountainous Areas [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 450-458. |
| [4] | HE Yanhu, GONG Zhenjie, WU Haibin, CAI Yanpeng, YANG Zhifeng, CHEN Xiaohong. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Urban Eco-efficiency and Its Influencing Factors in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 469-480. |
| [5] | HAO Jinhu, WEI Wei, LI Shengnan, MA Muyuan, LI Xiaoxia, YANG Hongguo, JIANG Qiyu, CHAI Peidong. GEE Based Evaluation of the Spatial-temporal Pattern and Drivers of Long-term Water Body in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 556-566. |
| [6] | YUAN Linjiang, LI Mengbo, LENG Gang, ZHONG Bingbing, XIA Dapeng, WANG Jinghua. Synergistic Effect of Sulfate Reduction and Ammonia Oxidation in Anaerobic Environment [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(1): 207-214. |
| [7] | JIANG Ming, ZHANG Ziyang, LI Tingting, LIN Boji, ZHANG Zhengen, LIAO Tong, YUAN Luan, PAN Suhong, LI Jun, ZHANG Gan. Source Apportionment of Ammonium in Atmospheric PM2.5 in the Pearl River Delta Based on Nitrogen Isotope [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(9): 1840-1848. |
| [8] | SU Yongsong, SONG Song, CHEN Ye, YE Ziqiang, ZHONG Runfei, WANG Zhaoyao. Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of Net Anthropogenic Nitrogen Input and Its Influencing Factors in the Pearl River Delta [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(8): 1599-1609. |
| [9] | WEI Xiaofeng, HAN Hong, YAN Xuejun, WANG Zaifeng, LI Shengzeng, TIAN Yong, LIANG Di, MA Mingliang, ZHANG Guiqin. Source Apportionment of PM2.5 during Heavy Pollution Process in Ji'nan Based on Satellite Remote Sensing and CMB Model [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(6): 1175-1183. |
| [10] | WANG Zhanyong, CHEN Xin, HU Xisheng, HE Hongdi, CAI Ming, PENG Zhongren. Mechanism and Research Methods of Roadside Green Barriers Affecting the Distribution of Atmospheric Particulate Matter: A Review [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(5): 1047-1058. |
| [11] | JIANG Peng, QIN Mei’ou, LI Rongping, MENG Ying, YANG Feiyun, WEN Rihong, SUN Pei, FANG Yuan. Seasonal Variability of GPP and Its Influencing Factors in the Typical Ecosystems in China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(4): 643-651. |
| [12] | WANG Wei, CHENG Xinyue. Analysis of Temporal and Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of PM2.5 and PM10 in Different Functional Street Canyons in Hefei City [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 524-534. |
| [13] | ZHU Xu, LI Haimei, LI Yanhua, SUN Yingkun, TIAN Yuan. Physiological Responses of Eight Shrubs to Atmospheric Particulate Matter Pollution [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 535-545. |
| [14] | ZHAO Rui, ZHAN Liping, ZHOU Liang, ZHANG Junke. Identification of Driving Factors of PM2.5 Based on Geographic Detector Combined with Geographically Weighted Ridge Regression [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(2): 307-317. |
| [15] | JIANG Bin, CHEN Duohong, ZHANG Tao, YUAN Luan, ZHOU Yan, SHEN Jing, ZHANG Chunlin, WANG Boguang. Characteristics and Sources of Carbonaceous Aerosols during the Crop Straw Burning Seasons in Southern China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(12): 2358-2366. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
