Ecology and Environment ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (3): 535-545.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.03.012
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHU Xu( ), LI Haimei*(
), LI Haimei*( ), LI Yanhua, SUN Yingkun, TIAN Yuan
), LI Yanhua, SUN Yingkun, TIAN Yuan
Received:2021-12-01
Online:2022-03-18
Published:2022-05-25
Contact:
LI Haimei
通讯作者:
李海梅
作者简介:朱旭(1997年生),女,硕士研究生,主要从事城市生态学研究。E-mail: 787261006@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
ZHU Xu, LI Haimei, LI Yanhua, SUN Yingkun, TIAN Yuan. Physiological Responses of Eight Shrubs to Atmospheric Particulate Matter Pollution[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 535-545.
朱旭, 李海梅, 李彦华, 孙迎坤, 田园. 8种灌木对大气颗粒物污染的生理响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 535-545.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.03.012
| 树种 Tree species | 科 Family | 属 Genus | 生活型 Life form |
|---|---|---|---|
| 火棘 Pyracantha fortuneana | 蔷薇科 Rosaceae | 火棘属 Pyracantha | 常绿灌木 |
| 大叶黄杨 Euonymus japonicus | 黄杨科 Buxaceae | 黄杨属 Buxus | 常绿灌木 |
| 红叶石楠 Photinia frasery | 蔷薇科 Rosaceae | 石楠属 Photinia | 常绿灌木 |
| 小叶黄杨 Buxus sinica | 黄杨科 Buxaceae | 黄杨属 Buxus | 常绿灌木 |
| 金叶女贞 Ligustrum vicaryi | 木犀科 Oleaceae | 女贞属 Ligustrum | 落叶灌木 |
| 紫叶小檗 Berberis thunbergii cv. atropurpurea | 小檗科 Berberidaceae | 小檗属 Berberis | 落叶灌木 |
| 蔷薇 Rosa multifolora | 蔷薇科 Rosaceae | 蔷薇属 Rosa | 落叶灌木 |
| 紫荆 Cercis chinensis | 豆科 Leguminosae | 紫荆属 Cercis | 落叶灌木 |
Table 1 Tested plant species
| 树种 Tree species | 科 Family | 属 Genus | 生活型 Life form |
|---|---|---|---|
| 火棘 Pyracantha fortuneana | 蔷薇科 Rosaceae | 火棘属 Pyracantha | 常绿灌木 |
| 大叶黄杨 Euonymus japonicus | 黄杨科 Buxaceae | 黄杨属 Buxus | 常绿灌木 |
| 红叶石楠 Photinia frasery | 蔷薇科 Rosaceae | 石楠属 Photinia | 常绿灌木 |
| 小叶黄杨 Buxus sinica | 黄杨科 Buxaceae | 黄杨属 Buxus | 常绿灌木 |
| 金叶女贞 Ligustrum vicaryi | 木犀科 Oleaceae | 女贞属 Ligustrum | 落叶灌木 |
| 紫叶小檗 Berberis thunbergii cv. atropurpurea | 小檗科 Berberidaceae | 小檗属 Berberis | 落叶灌木 |
| 蔷薇 Rosa multifolora | 蔷薇科 Rosaceae | 蔷薇属 Rosa | 落叶灌木 |
| 紫荆 Cercis chinensis | 豆科 Leguminosae | 紫荆属 Cercis | 落叶灌木 |
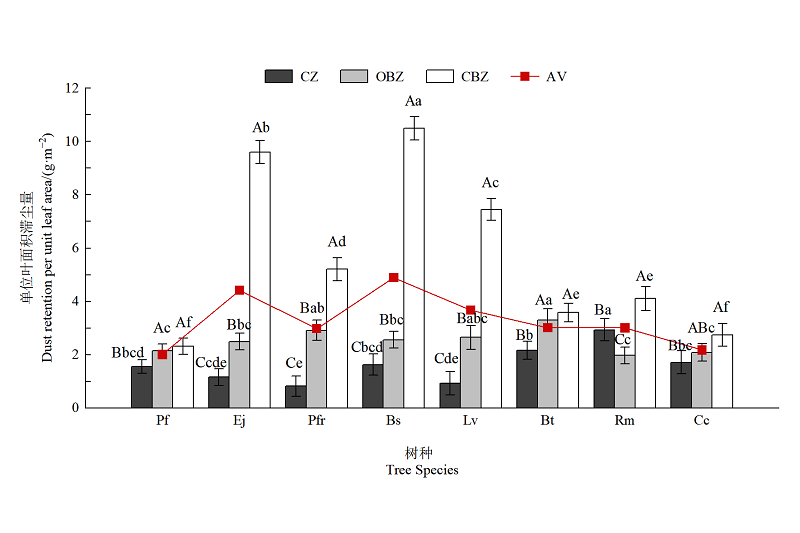
Figure 1 Dust retention of shrubs with different particle sizes Mean±standard deviation, n=3; Pyracantha fortuneana, Pf; Euonymus japonicus, Ej; Photinia frasery, Pfr; Buxus sinica, Bs; Ligustrum vicaryi, Lv; Berberis thunbergii cv. Atropurpurea, Bt; Rosa multifolora, Rm; Cercis chinensis, Cc. The same below===Different small letters indicate that there is a significant difference in dust retention between different plants in the same dust source area (P<0.05), and different capital letters indicate that there is a significant difference in dust retention between different dust source areas of the same plant (P<0.05)
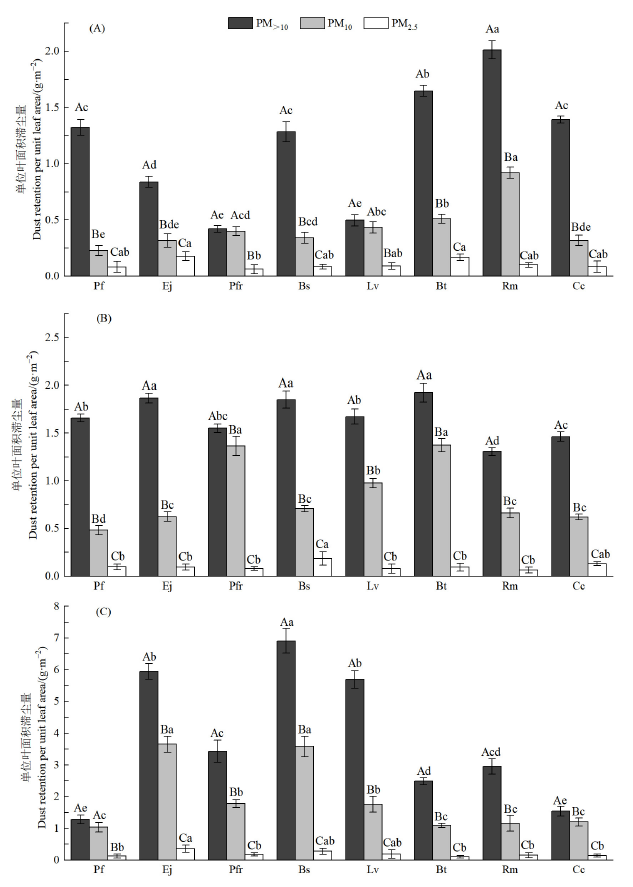
Figure 2 Dust retention of eight shrubs with different particle sizes A: Clean zone; B: Oil burning zone; C: Coal burning zone. Different lowercase letters indicate that there are significant differences in dust retention of different plants under the same index (PM10, PM5, PM2.5) (P<0.05)
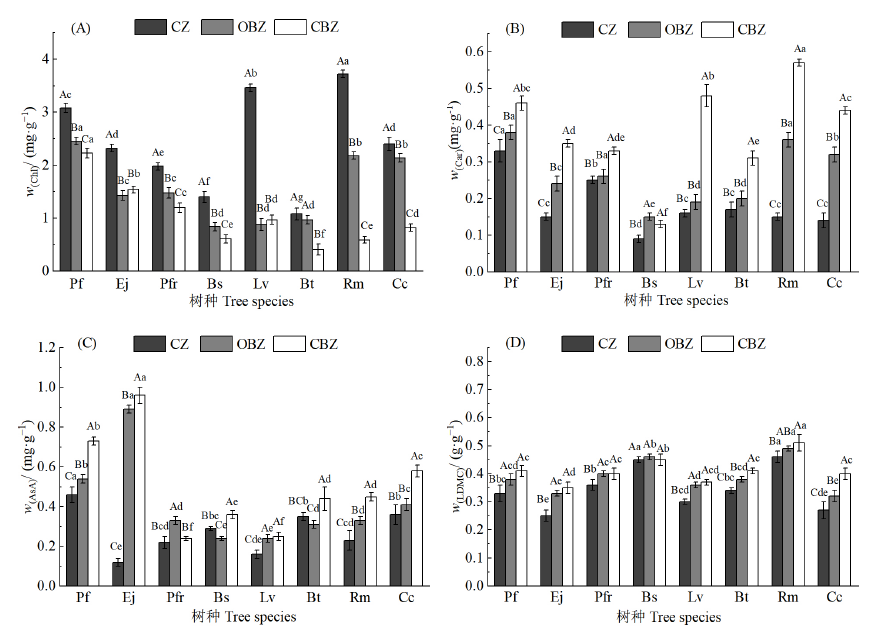
Figure 3 Physiological indexes of shrubs Different small letters indicate that there are significant differences in physiological indexes of different plants in the same dust source area (P<0.05), and capital letters indicate that there are significant differences in physiological indexes between different dust source areas of the same plant (P<0.05)
| 指标 Index | 叶片滞尘量 Amount of dust on leaves | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pf | Ej | Pfr | Bs | Lv | Bt | Rm | Cc | |
| Chl | -0.795* | -0.521 | -0.917** | -0.770* | -0.675* | -0.672* | -0.516 | -0.776* |
| Car | 0.679* | 0.936** | 0.862** | 0.265 | 0.979** | 0.603 | 0.512 | 0.730* |
| AsA | 0.775* | 0.673* | 0.092 | 0.795* | 0.616 | 0.474 | 0.483 | 0.803** |
| LDMC | 0.634 | 0.717* | 0.664 | -0.065 | 0.755* | 0.825** | 0.528 | 0.800** |
Table 2 Correlation coefficients between dust retention and physiological indexes of leaves of various tree species
| 指标 Index | 叶片滞尘量 Amount of dust on leaves | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pf | Ej | Pfr | Bs | Lv | Bt | Rm | Cc | |
| Chl | -0.795* | -0.521 | -0.917** | -0.770* | -0.675* | -0.672* | -0.516 | -0.776* |
| Car | 0.679* | 0.936** | 0.862** | 0.265 | 0.979** | 0.603 | 0.512 | 0.730* |
| AsA | 0.775* | 0.673* | 0.092 | 0.795* | 0.616 | 0.474 | 0.483 | 0.803** |
| LDMC | 0.634 | 0.717* | 0.664 | -0.065 | 0.755* | 0.825** | 0.528 | 0.800** |
| [1] | AMULYA, HEMANTH KNK, JAGANNATH S, 2015. Air pollution impact on micromorphological and biochemical response of Tabernaemontana divaricata L. (Gentianales: Apocynaceae) and Hamelia patens Jacq. (Gentianales: Rubiaceae)[J]. Brazilian Journal of Biological Sciences, 2(4): 287-294. |
| [2] |
ANIL K R, BALA C, 2011. Effect of vehicular pollution on Duranta repens L. in Jammu City[J]. Journal of Applied and Natural Science, 3(2): 211-218.
DOI URL |
| [3] | BANDARA W A R T W, DISSANAYAKE C T M, 2021. Most tolerant roadside tree species for urban settings in humid tropics based on Air Pollution Tolerance Index[J]. Urban Climate, 37: 1-10. |
| [4] | COLAPICCHION V, MOSCA S, GUERRIERO E, et al., 2020. Environmental impact of co-combustion of polyethylene wastes in a rice husks fueled plant: Evaluation of organic micropollutants and PM emissions[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 716(3): 1-27. |
| [5] |
DZIERZANOWSKI K, POPEK R, GAWRONSKA, et al., 2011. Deposition of particulate matter of different size fractions on leaf surfaces and in waxes of urban forest species[J]. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 13(10): 1037-1046.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
ETESAMI H, JEONG B R, SILICON, 2018. Silicon (Si): Review and future prospects on the action mechanisms in alleviating biotic and abiotic stresses in plants[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 147: 881-896.
DOI URL |
| [7] | GEETA N, 2014. Effect of air pollution on the photosynthetic pigments of selected plant species along roadsides in Jamshedpur, Jharkhand[J]. Research in Plant Biology, 4(5): 65-68. |
| [8] |
GHAFARI S, KAVIANI B, SEDAGHATHOOR S, et al., 2021. Correction to: Assessment of air pollution tolerance index (APTI) for some ornamental woody species in green space of humid temperate region (Rasht, Iran)[J]. Environ Dev Sustain, 23(3): 4747-4748.
DOI URL |
| [9] | GUPTA G P, KUMAR B, SINGH S, et al., 2016. Deposition and impact of urban atmospheric dust on two medicinal plants during different seasons in NCR Delhi[J]. Aerosol & Air Quality Research, 16(11): 2920-2932. |
| [10] |
HANSLIN HM, PRZYBYSZ A, SLIMESTAD R, et al., 2017. Stress acclimation and particulate matter accumulation in Pinus sylvestris saplings affected by moderate combinations of urban stressors[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 593-594: 581-591.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
JOSHI P C, SWAMI A, 2007. Physiological responses of some tree species under roadside automobile pollution stress around city of Haridwar, India[J]. Environmentalist, 27(3): 365-374.
DOI URL |
| [12] | KAMBLE P, BODANE PS, BEIG G, et al., 2021. Impact of transport sector emissions on biochemical characteristics of plants and mitigation strategy in Pune, India[J]. Environmental Challenges, 4(1): 1-8. |
| [13] | KARMAKAR D, PADHY P K, 2019. Air pollution tolerance, anticipated performance, and metal accumulation indices of plant species for greenbelt development in urban industrial area[J]. Chemosphere, 237: 1-12. |
| [14] |
KAUR M, NAGPAL A K, 2017. Evaluation of air pollution tolerance index and anticipated performance index of plants and their application in development of green space along the urban areas[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 24(23): 18881-18895.
DOI URL |
| [15] | LI M, HUANG D M, ZHOU Y H, et al., 2021. The legacy effects of PM2.5 depositon on Nerium Oleander L.[J]. Chemosphere, 281: 1-8. |
| [16] |
LIU L, GUAN D S, PEART M R, et al., 2013. The dust retention capacities of urban vegetation: A case study of Guangzhou, South China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 20(9): 6601-6610.
DOI URL |
| [17] | LU T, LIN X T, CHEN J, et al., 2019. Atmospheric particle retention capacity and photosynthetic responses of three common greening plant species under different pollution levels in Hangzhou[J]. Global Ecology and Conservation, 20: 1-11 |
| [18] | MOLNÁR V É, SIMON E, TOTHMERESZ B, et al., 2020. Air pollution induced vegetation stress - The Air Pollution Tolerance Index as a quick tool for city health evaluation[J]. Ecological Indicators, 113: 1-8. |
| [19] |
NIEVES-CORDONES M, LOPEZ-DELACALLE M, RODENAS R, et al., 2019. Critical responses to nutrient deprivation: A comprehensive review on the role of ROS and RNS[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 161: 74-85.
DOI URL |
| [20] | RAI P K, 2016. Impacts of particulate matter pollution on plants: Implications for environmental biomonitoring[J]. Ecotoxicology & Environmental Safety, 129: 120-136. |
| [21] |
SHAHID MA, BALAL RM, KHAN N, et al., 2019. Selenium impedes cadmium and arsenic toxicity in potato by modulating carbohydrate and nitrogen metabolism[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 180: 588-599.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
WU H T, YANG C, CHEN J, et al., 2018. Effects of green space landscape patterns on particulate matter in Zhejiang Province, China[J]. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 9(5): 923-933.
DOI URL |
| [23] | ZHOU S J, CONG L, LIU Y, et al., 2021. Rainfall intensity plays an important role in the removal of PM from the leaf surfaces[J]. Ecological Indicators, 128(10):1-9 |
| [24] |
阿丽亚∙拜都热拉, 玉米提∙哈力克, 塔依尔江∙艾山, 等, 2014. 阿克苏市5种常见绿化树种滞尘规律[J]. 植物生态学报, 38(9): 970-977.
DOI |
|
ALIYA B, UMUT H, TAYIERJIANG A, et al., 2014. Patterns of dust retention by five common tree species for urban greening in Aksu City, Northwest China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 38(9): 970-977.
DOI URL |
|
| [25] | 安婷婷, 黄帝, 张一, 等, 2021. 植物对镉胁迫的生理生化响应及其机制的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 56(3): 347-362. |
| AN T T, HUANG D, ZHANG Y, et al., 2021. Research advances in plant physiological and biochemical mechanisms in response to cadmium stress[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 56(3): 347-362. | |
| [26] | 曹宇坤, 温天雪, 张小玲, 等, 2021. 华北典型农业区PM2.5组分分析与来源解析[J]. 大气科学, 45(4): 819-832. |
| CAO Y K, WEN T X, ZHANG X L, et al., 2021. Component and source analyses of PM2.5 in typical agricultural regions of North China[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 45(4): 819-832. | |
| [27] | 陈玮, 何兴元, 张粤, 等, 2003. 东北地区城市针叶树冬季滞尘效应研究[J]. 应用生态学报, 14(12): 2113-2116. |
| CHEN W, HE X Y, ZHANG Y, et al., 2003. Dust absorption effect of urban conifers in Northeast China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 14(12): 2113-2116. | |
| [28] | 樊宝莲, 王晓云, 2021. 转录因子调控植物类胡萝卜素合成途径的研究进展[J]. 分子植物育种, 19(13): 4401-4408. |
| FAN B L, WANG X Y, 2021. Research progress of transcription factors regulating carotenoid synthesis pathway in plant[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 19(13): 4401-4408. | |
| [29] | 房瑶瑶, 王兵, 牛香, 2015. 叶片表面粗糙度对颗粒物滞纳能力及洗脱特征的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 29(4): 110-115. |
| FANG Y Y, WANG B, NIU X, 2015. Effects of surface roughness on leaf particulate matter capturing capability and rain wash-off characteristics[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 29(4): 110-115. | |
| [30] | 耿天召, 朱余, 魏帧, 等, 2020. 基于多种源解析技术的合肥市环境空气PM2.5来源解析[J]. 合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版), 43(6): 830-838. |
| GENG T Z, ZHU Y, WEI Z, et al., 2020. Study on source apportionment of PM2.5 in Hefei City based on multiple technologies[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology (Natural Science), 43(6): 830-838. | |
| [31] | 李朝梅, 王军梦, 王腾飞, 等, 2021. 郑州市常见公园绿化植物的滞尘能力及叶片性状分析[J]. 西北林学院学报, 36(2): 123-129. |
| LI C M, WANG J M, WANG T F, et al., 2021. Dust-retention capability and leaf traits of common park greening plant species in Zhengzhou city[J]. Journai of Northwest Forestry University, 36(2): 123-129. | |
| [32] | 李海梅, 党宁, 禹靓倩, 等, 2021. 5个园林树种滞尘能力与叶表形态及颗粒物粒径的关系[J]. 林业科学研究, 34(4): 84-94. |
| LI H M, DANG N, YU L Q, et al., 2021. The relationships between the dust-holding capacity and the leaf surface structure & particle size in five evergreen tree species locates in Hangzhou[J]. Forest Research, 34(4): 84-94. | |
| [33] | 李娟霞, 何靖, 孙一梅, 等, 2020. 10种园林植物功能性状对大气污染的生理生态响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(6): 1205-1214. |
| LI J X, HE J, SUN Y M, et al., 2020. Physiological and ecological responses of ten garden plant functional traits to air pollution[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 29(6): 1205-1214. | |
| [34] | 李诗瑶, 牛玉斌, 樊瑾, 等, 2021. 基于叶面微结构的火电厂周边绿化树种的滞尘能力分析[J]. 生态学杂志, 40(2): 604-614. |
| LI S Y, NIU Y B, FAN J, et al., 2021. Analysis on dust retention capability of greening tree species surrounding coal-fired power plant based on leaf surface micro-structure[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 40(2): 604-614. | |
| [35] | 李玉洁, 赵娜, 曹月娥, 等, 2018. 露天煤矿煤粉沉降对矿区周边主要植物的生理影响[J]. 生态学报, 38(22): 8129-8138. |
| LI Y J, ZHAO N, CAO Y E, et al., 2018. Effects of coal dust deposition on the physiological properties of plants in an open-pit coal mine[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(22): 8129-8138. | |
| [36] | 刘建新, 刘瑞瑞, 贾海燕, 等, 2021. 硫化氢对盐碱胁迫下裸燕麦叶片抗坏血酸-谷胱甘肽循环的调控效应[J/OL]. 应用生态学报, 1-9 [2021-10-22]. https://doi.org/10.13287/j.1001-9332.202111.023. |
| LIU J X, LIU R R, JIA H Y, et al., 2021. Regulation effects of hydrogen sulfide on ascorbate-glutathione cycle in naked oat leaves under saline-alkali stress[J/OL]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 1-9 [2021-10-22]. https://doi.org/10.13287/j.1001-9332.202111.023. | |
| [37] | 刘威, 陈珍, 李孝乾, 等, 2018. 台州椒江不同植物滞尘能力分析[J]. 台州学院学报, 40(6): 30-37, 49. |
| LIU W, CHEN Z, LI X Q, et al., 2018. Analysis of dust retention capacity of different plants in Jiaojiang, Taizhou[J]. Journal of Taizhou University, 40(6): 30-37, 49. | |
| [38] | 罗佳, 周小玲, 田育新, 等, 2019. 长沙市不同污染程度区域桂花和香樟叶表面PM2.5吸附量及其影响因素[J]. 应用生态学报, 30(2): 503-510. |
| LUO J, ZHOU X L, TIAN Y X, et al., 2019. PM2.5 adsorption capacity of Osmanthus fragrans and Cinnamomum camphora leaf surface and influencing factors under different pollution levels in Changsha, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 30(2): 503-510. | |
| [39] | 彭长连, 温达志, 孙梓健, 等, 2002. 城市绿化植物对大气污染的响应[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报, 10(4): 321-327. |
| PENG C L, WEN D Z, SUN Z J, et al., 2002. Response of some plants for municipal greening to air pollutants[J]. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 10(4): 321-327. | |
| [40] | 淑敏, 敖敦格日乐, 胡和珠拉, 等, 2020. 辽西北部主要绿化树种对粉尘污染的生理响应研究[J]. 西北植物学报, 40(10): 1740-1750. |
| SHU M, AO Dungerile, HU Hezhula, et al., 2020. Physiological response of main greening tree species to dust pollution in Northwest of Liaoning Province[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 40(10): 1740-1750. | |
| [41] | 孙晓丹, 李海梅, 郭霄, 等, 2017. 10种灌木树种滞留大气颗粒物的能力[J]. 环境工程学报, 11(2): 1047-1054. |
| SUN X D, LI H M, GUO X, et al., 2017. Atmospheric particulates-retaining capacity of ten shrubs species[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 11(2): 1047-1054. | |
| [42] | 孙晓丹, 李海梅, 孙丽, 等, 2016. 8种灌木滞尘能力及叶表面结构研究[J]. 环境化学, 35(9): 1815-1822. |
| SUN X D, LI H M, SUN L, et al., 2016. Dust-retaining capability and micro morphology structure of leaves of eight shrubs[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 35(9): 1815-1822. | |
| [43] | 王琴, 冯晶红, 黄奕, 等, 2020. 武汉市15种阔叶乔木滞尘能力与叶表微形态特征[J]. 生态学报, 40(1): 213-222. |
| WANG Q, FENG J H, HUANG Y, et al., 2020. Dust-retention capability and leaf surface micromorphology of 15 broad-leaved tree species in Wuhan[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(1): 213-222. | |
| [44] | 王书恒, 朱晓宇, 田如男, 等, 2021. 南京市6种常见园林植物滞尘效益的综合分析[J]. 中国园林, 37(6): 111-116. |
| WANG S H, ZHU X Y, TIAN R N, et al., 2021. Comprehensive analysis of dust retention efficiency of six common garden plants in Nanjing[J]. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 37(6): 111-116. | |
| [45] | 王松, 康红梅, 王晋, 等, 2021. 山西太原常绿植物滞尘能力差异性及叶面微结构[J]. 北方园艺, 2021(14): 80-86. |
| WANG S, KANG H M, WANG J, et al., 2021. Dust catching property and leaf surface micro-structure of evergreen plants in Taiyuan, Shanxi[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2021(14): 80-86. | |
| [46] | 王学奎, 黄见良, 2015. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M]. 第3版. 北京: 高等教育出版社: 131-133, 268-271. |
| WANG X K, HUANG J L, 2015. Principles and techniques of plant physiological and biochemical experiments[M]. Third edition. Beijing: Higher Education Press: 131-133, 268-271. | |
| [47] | 吴天忠, 蔡寅潮, 管文轲, 2020. 乌鲁木齐市4种绿化树种叶片滞尘量对叶片光合气体交换参数的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学, 48(19): 128-130, 135. |
| WU T Z, CAI Y C, GUAN W K, 2020. Effects of leaf dust removal on leaf photosynthetic gas exchange parameters of four greening tree species in Urumqi City[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 48(19): 128-130, 135. | |
| [48] | 肖致美, 毕晓辉, 冯银厂, 等, 2012. 宁波市环境空气中PM10和PM2.5来源解析[J]. 环境科学研究, 25(5): 549-555. |
| XIAO Z M, BI X H, FENG Y C, et al., 2012. Source apportionment of ambient PM10 and PM2.5 in urban area of Ningbo City[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 25(5): 549-555. | |
| [49] | 谢滨泽, 王会霞, 杨佳, 等, 2014. 北京常见阔叶绿化植物滞留PM2.5能力与叶面微结构的关系[J]. 西北植物学报, 34(12): 2432-2438. |
| XIE B Z, WANG H X, YANG J, et al., 2014. Retention capability of PM2.5 and it's explanation by leaf surface micro-structure of common broad-leaved plant species in Beijing[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali- Occidentalia Sinica, 34(12): 2432-2438. | |
| [50] | 谢元博, 陈娟, 李巍, 2014. 雾霾重污染期间北京居民对高浓度PM2.5持续暴露的健康风险及其损害价值评估[J]. 环境科学, 35(1): 1-8. |
|
XIE Y B, CHEN J, LI W, 2014. An assessment of PM2.5 related health risks and impaired values of Beijing residents in a consecutive high-level exposure during heavy haze days[J]. Environmental Science, 35(1): 1-8.
DOI URL |
|
| [51] | 闫倩, 徐立帅, 段永红, 等, 2021. 20种常用绿化树种叶面滞尘能力及滞尘粒度特征[J/OL]. 生态学杂志, 1-12 [2021-09-01]. https://doi.org/10.13292/j.1000-4890.202110.027. |
| YAN Q, XU L S, DUAN Y H, et al., 2021. Dust retention ability and dust retention size characteristics of 20 commonly used greening tree species[J/OL]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 1-12 [2021-09-01]. https://doi.org/10.13292/j.1000-4890.202110.027. | |
| [52] | 晏增, 赵蓬晖, 杨淑红, 等, 2021. 冬季郑州市12个常绿树种的光合特性及滞尘能力[J]. 广西植物, 41(9): 1433-1442. |
| YAN Z, ZHAO P H, YANG S H, et al., 2021. Photosynthetic characteristics and dust retention capacities of 12 evergreen tree species in Zhengzhou City during winter[J]. Guihaia, 41(9): 1433-1442. | |
| [53] | 杨佳, 王会霞, 谢滨泽, 等, 2015. 北京9个树种叶片滞尘量及叶面微形态解释[J]. 环境科学研究, 28(3): 384-392. |
| YANG J, WANG H X, XIE B Z, et al., 2015, Accumulation of particulate matter on leaves of nine urban greening plant species with different micromorphological structures in Beijing[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 28(3): 384-392. | |
| [54] | 张曦, 王振南, 陆姣云, 等, 2016. 紫花苜蓿叶性状对干旱的阶段性响应[J]. 生态学报, 36(9): 2669-2676. |
| ZHANG X, WANG Z N, LU J Y, et al., 2016. Responses of leaf traits to drought at different growth stages of alfalfa[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36(9): 2669-2676. | |
| [55] | 赵松婷, 李新宇, 李延明, 2014. 园林植物滞留不同粒径大气颗粒物的特征及规律[J]. 生态环境学报, 23(2): 271-276. |
| ZHAO S T, LI X Y, LI Y M, 2014. The characteristics of deposition of airborne particulate matters with different size on certain plants[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 23(2): 271-276. | |
| [56] | 赵松婷, 李新宇, 李延明, 2016. 北京市常用园林植物滞留PM2.5能力的研究[J]. 西北林学院学报, 31(2): 280-287. |
| ZHAO S T, LI X Y, LI Y M, 2016. Capability of common garden plants in Beijing to retain PM2.5[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 31(2): 280-287. | |
| [57] | 郑瑶瑶, 李晓燕, 2019. 不同城市11种常用绿化树种滞尘能力研究[J]. 贵州师范大学学报 (自然科学版), 37(4): 56-62, 73. |
| ZHENG Y Y, LI X Y, 2019. Study on dust-retention ability of 11 common greening tree species in different cities[J]. Journal of Guizhou Normal University (Natural Sciences), 37(4): 56-62, 73. | |
| [58] | 朱济友, 徐程扬, 覃国铭, 等, 2019. 3种典型绿化植物叶功能性状对大气污染的响应及其叶经济谱分析--以北京市为例[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 39(3): 91-98. |
| ZHU J Y, XU C Y, QIN G M, et al., 2019. Responses of leaf functional characters of three typical greening plants to air pollution and leaf economic spectrum analysis: A Beijing City as the study case[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 39(3): 91-98. | |
| [59] | 朱济友, 于强, 刘亚培, 等, 2018. 植物功能性状及其叶经济谱对城市热环境的响应[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 40(9): 72-81. |
| ZHU J Y, YU Q, LIU Y P, et al., 2018. Response of plant functional traits and leaf economics spectrum to urban thermal environment[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 40(9): 72-81. |
| [1] | QIN Hao, LI Mengai, GAO Jin, CHEN Kailong, ZHANG Yinbo, ZHANG Feng. Composition and Diversity of Soil Bacterial Communities in Shrub at Different Altitudes in Luya Mountain [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 459-468. |
| [2] | ZHANG Li, LI Cheng, TAN Haoze, WEI Jiayi, CHENG Jiong, PENG Guixiang. Reduction Effect and Influencing Factors of Typical Urban Woodlands on Atmospheric Particulate Matter in Guangzhou [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(2): 341-350. |
| [3] | WANG Zhanyong, CHEN Xin, HU Xisheng, HE Hongdi, CAI Ming, PENG Zhongren. Mechanism and Research Methods of Roadside Green Barriers Affecting the Distribution of Atmospheric Particulate Matter: A Review [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(5): 1047-1058. |
| [4] | LIU Mei, MA Zhiliang. Effects of Warming and Plant Removal on Soil Nitrogen Contents in An Alpine Shrubland of Eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 470-477. |
| [5] | WANG Xiaona, XU Danghui, WANG Xiejun, FANG Xiangwen. Changes of Shrub Community Structure with Altitudinal Gradient and Longitude in Qilian Mountains [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(2): 231-238. |
| [6] | WANG Hao, CHEN Yongjin, LIU Jiazhen, WAN Bo, ZHANG Li. Effects of Three Types Tamarix Shrubs Communities on Spatial Distribution of Soil Organic Carbon in the New Wetland of the Yellow River Delta [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(1): 9-16. |
| [7] | ZHAO Xiaoliang, GUO Meng, LV Meiting, ZHAO Xueying, JIANG Guiguo, HUANG Yuanyuan, WANG Fan, JI Yaqin. Study on Retention Capacity of Green Tree Species to Atmospheric Particulate Matter and Heavy Metals in Fuxin [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(8): 1662-1671. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
