Ecology and Environment ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (7): 1400-1408.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.07.012
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
JI Bingjing1,2,3( ), LIU Yi4, WU Yang1,2, GAO Shutao1,2, ZENG Xiangying1,2,*(
), LIU Yi4, WU Yang1,2, GAO Shutao1,2, ZENG Xiangying1,2,*( ), YU Zhiqiang1,2
), YU Zhiqiang1,2
Received:2022-01-24
Online:2022-07-18
Published:2022-08-31
Contact:
ZENG Xiangying
吉冰静1,2,3( ), 刘艺4, 吴杨1,2, 高淑涛1,2, 曾祥英1,2,*(
), 刘艺4, 吴杨1,2, 高淑涛1,2, 曾祥英1,2,*( ), 于志强1,2
), 于志强1,2
通讯作者:
曾祥英
作者简介:吉冰静(1992年生),女,博士研究生,主要从事新型有机污染物方面的研究。E-mail: 1531776535@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
JI Bingjing, LIU Yi, WU Yang, GAO Shutao, ZENG Xiangying, YU Zhiqiang. Occurrence, Source and Potential Ecological Risk of Parent and Oxygenated Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Sediments of Yangtze River Estuary and Adjacent East China Sea[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(7): 1400-1408.
吉冰静, 刘艺, 吴杨, 高淑涛, 曾祥英, 于志强. 长江口及邻近东海沉积物中多环芳烃和含氧多环芳烃的分布特征、来源及生态风险[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1400-1408.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.07.012
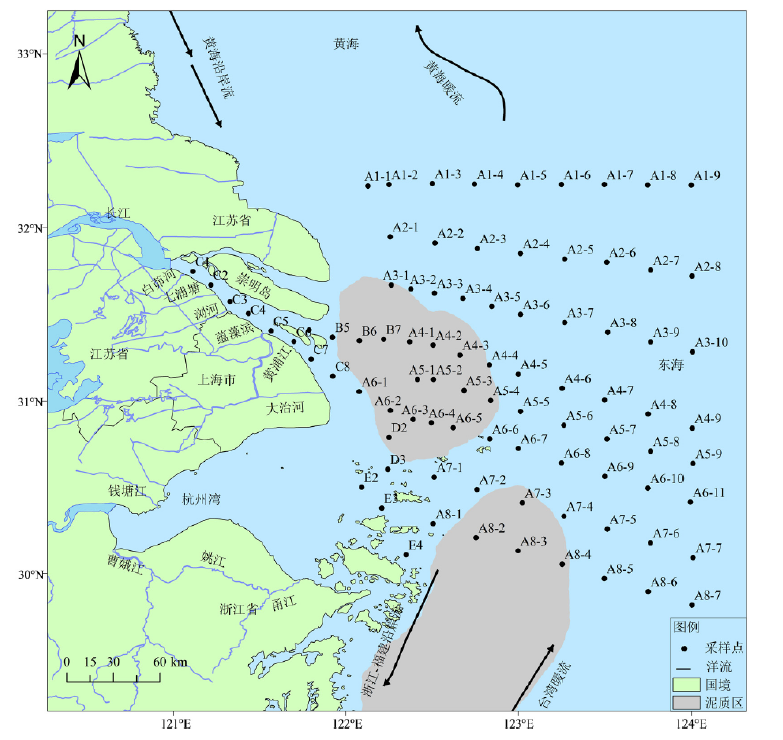
Figure 1 Map of the sampling sites in Yangtze River Estuary and adjacent East China Sea Upper: the Yangtze River Estuary Mud Zone; lower: Zhejiang-Fujian Coastal Mud Zone
| 化合物 Compound | 美国USA | 加拿大Canada | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 影响范围低值ERL | 影响范围中值ERM | 初始效应阈值TEL | 可能效应值PEL | ||
| 苊烯 Acy | 44 | 640 | 5.87 | 128 | |
| 苊 Ace | 16 | 500 | 6.71 | 88.9 | |
| 芴 Fl | 19 | 540 | 21.2 | 144 | |
| 菲 Phe | 240 | 1500 | 86.7 | 544 | |
| 蒽 Ant | 85.3 | 1100 | 46.9 | 245 | |
| 荧蒽 Flu | 600 | 5100 | 113 | 1494 | |
| 低分子量多环芳烃 ΣLMW-PAHs | 552 | 3160 | — | — | |
| 芘 Pyr | 665 | 2600 | 153 | 1398 | |
| 苯并[a]蒽 BaA | 261 | 1600 | 74.8 | 693 | |
| 䓛 Chr | 384 | 2800 | 108 | 846 | |
| 苯并[b]荧蒽 BbF | — | — | — | — | |
| 苯并[k]荧蒽 BkF | — | — | — | — | |
| 苯并[a]芘 BaP | 430 | 1600 | 88.8 | 763 | |
| 茚并[1, 2, 3-cd]芘 InP | — | — | — | — | |
| 二苯并[a,h]蒽 DBA | 63.4 | 260 | 6.22 | 135 | |
| 苯并[g, h, i]苝 BgP | 85 | 330 | — | — | |
| 高分子量多环芳烃 ΣHMW-PAHs | 1700 | 9600 | — | — | |
| 多环芳烃 ΣPAHs | 4022 | 44792 | — | — | |
Table 1 Sediment quality guidelines of PAHs ng·g-1 (by dry mass)
| 化合物 Compound | 美国USA | 加拿大Canada | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 影响范围低值ERL | 影响范围中值ERM | 初始效应阈值TEL | 可能效应值PEL | ||
| 苊烯 Acy | 44 | 640 | 5.87 | 128 | |
| 苊 Ace | 16 | 500 | 6.71 | 88.9 | |
| 芴 Fl | 19 | 540 | 21.2 | 144 | |
| 菲 Phe | 240 | 1500 | 86.7 | 544 | |
| 蒽 Ant | 85.3 | 1100 | 46.9 | 245 | |
| 荧蒽 Flu | 600 | 5100 | 113 | 1494 | |
| 低分子量多环芳烃 ΣLMW-PAHs | 552 | 3160 | — | — | |
| 芘 Pyr | 665 | 2600 | 153 | 1398 | |
| 苯并[a]蒽 BaA | 261 | 1600 | 74.8 | 693 | |
| 䓛 Chr | 384 | 2800 | 108 | 846 | |
| 苯并[b]荧蒽 BbF | — | — | — | — | |
| 苯并[k]荧蒽 BkF | — | — | — | — | |
| 苯并[a]芘 BaP | 430 | 1600 | 88.8 | 763 | |
| 茚并[1, 2, 3-cd]芘 InP | — | — | — | — | |
| 二苯并[a,h]蒽 DBA | 63.4 | 260 | 6.22 | 135 | |
| 苯并[g, h, i]苝 BgP | 85 | 330 | — | — | |
| 高分子量多环芳烃 ΣHMW-PAHs | 1700 | 9600 | — | — | |
| 多环芳烃 ΣPAHs | 4022 | 44792 | — | — | |
| 化合物 Compound | 范围 Range | 均值 Mean | 中值 Median | 检出率 DF% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 多环芳烃PAHs | 苊烯 Acy | 0.127-1.38 | 0.407 | 0.371 | 100 |
| 苊Ace | 0.188-4.92 | 0.656 | 0.496 | 100 | |
| 芴 Fl | 0.441-10.0 | 2.94 | 2.51 | 100 | |
| 菲 Phe | 0.737-29.9 | 10.2 | 8.91 | 100 | |
| 蒽 Ant | 0.177-9.44 | 1.87 | 1.24 | 100 | |
| 荧蒽 Flu | 0.875-34.7 | 9.08 | 6.93 | 100 | |
| 芘 Pyr | 0.894-48.0 | 10.5 | 6.92 | 100 | |
| 苯并[a]蒽 BaA | 0.246-79.4 | 11.4 | 7.55 | 100 | |
| 䓛 Chr | 0.169-47.7 | 7.26 | 4.28 | 100 | |
| 苯并[b]荧蒽BbF | 0.354-73.2 | 13.1 | 8.64 | 100 | |
| 苯并[k]荧蒽BkF | 0.152-32.1 | 7.19 | 5.40 | 100 | |
| 苯并[a]芘BaP | ND-51.7 | 7.59 | 3.23 | 86 | |
| 茚并[1, 2, 3-cd]芘 InP | 0.255-22.0 | 6.20 | 4.09 | 100 | |
| 二苯并[a, h]蒽 DBA | ND-12.9 | 2.29 | 1.16 | 87 | |
| 苯并[g, h, i]苝 BgP | 0.404-40.4 | 7.83 | 3.77 | 100 | |
| 15种多环芳烃 ∑15PAHs | 5.53-415 | 98.5 | 68.1 | ||
| 含氧 多环芳烃 O-PAHs | 9-芴酮 9-Fl | 0.945-13.6 | 4.80 | 4.35 | 100 |
| 4H-环戊二烯并[d, e, f]-4-酮 PheO | 0.146-4.27 | 1.34 | 0.875 | 100 | |
| 蒽醌 AQ | 6.51-123 | 29.2 | 22.9 | 100 | |
| 2-甲基蒽醌 2-MAQ | 0.269-11.4 | 1.41 | 0.946 | 100 | |
| 苯并[a]芴-11-酮 BaF-11-one | 0.171-5.40 | 1.92 | 1.47 | 100 | |
| 苯并蒽酮 BezO | ND-1.76 | 0.164 | ND | 49 | |
| 苯并蒽-7, 12-二酮 BaA-7, 12-D | ND-5.02 | 1.66 | 1.22 | 99 | |
| 7种含氧多环芳烃 ∑7O-PAHs | 8.93-158 | 40.5 | 33.5 | ||
| 总有机碳含量TOC% | 0.072-0.518 | 0.253 | 0.232 | ||
Table 2 Concentrations of PAHs and O-PAHs and their compound in sediments (ng·g-1, by dry mass) from Yangtze River Estuary and adjacent East China Sea
| 化合物 Compound | 范围 Range | 均值 Mean | 中值 Median | 检出率 DF% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 多环芳烃PAHs | 苊烯 Acy | 0.127-1.38 | 0.407 | 0.371 | 100 |
| 苊Ace | 0.188-4.92 | 0.656 | 0.496 | 100 | |
| 芴 Fl | 0.441-10.0 | 2.94 | 2.51 | 100 | |
| 菲 Phe | 0.737-29.9 | 10.2 | 8.91 | 100 | |
| 蒽 Ant | 0.177-9.44 | 1.87 | 1.24 | 100 | |
| 荧蒽 Flu | 0.875-34.7 | 9.08 | 6.93 | 100 | |
| 芘 Pyr | 0.894-48.0 | 10.5 | 6.92 | 100 | |
| 苯并[a]蒽 BaA | 0.246-79.4 | 11.4 | 7.55 | 100 | |
| 䓛 Chr | 0.169-47.7 | 7.26 | 4.28 | 100 | |
| 苯并[b]荧蒽BbF | 0.354-73.2 | 13.1 | 8.64 | 100 | |
| 苯并[k]荧蒽BkF | 0.152-32.1 | 7.19 | 5.40 | 100 | |
| 苯并[a]芘BaP | ND-51.7 | 7.59 | 3.23 | 86 | |
| 茚并[1, 2, 3-cd]芘 InP | 0.255-22.0 | 6.20 | 4.09 | 100 | |
| 二苯并[a, h]蒽 DBA | ND-12.9 | 2.29 | 1.16 | 87 | |
| 苯并[g, h, i]苝 BgP | 0.404-40.4 | 7.83 | 3.77 | 100 | |
| 15种多环芳烃 ∑15PAHs | 5.53-415 | 98.5 | 68.1 | ||
| 含氧 多环芳烃 O-PAHs | 9-芴酮 9-Fl | 0.945-13.6 | 4.80 | 4.35 | 100 |
| 4H-环戊二烯并[d, e, f]-4-酮 PheO | 0.146-4.27 | 1.34 | 0.875 | 100 | |
| 蒽醌 AQ | 6.51-123 | 29.2 | 22.9 | 100 | |
| 2-甲基蒽醌 2-MAQ | 0.269-11.4 | 1.41 | 0.946 | 100 | |
| 苯并[a]芴-11-酮 BaF-11-one | 0.171-5.40 | 1.92 | 1.47 | 100 | |
| 苯并蒽酮 BezO | ND-1.76 | 0.164 | ND | 49 | |
| 苯并蒽-7, 12-二酮 BaA-7, 12-D | ND-5.02 | 1.66 | 1.22 | 99 | |
| 7种含氧多环芳烃 ∑7O-PAHs | 8.93-158 | 40.5 | 33.5 | ||
| 总有机碳含量TOC% | 0.072-0.518 | 0.253 | 0.232 | ||
| [1] |
ABBAS I, BADRAN G, VERDIN A, et al., 2018. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon derivatives in airborne particulate matter: sources, analysis and toxicity[J]. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 16(2): 439-475.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
BANSAL V, KUMAR P, KWON E E, et al., 2017. Review of the quantification techniques for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in food products[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 57(15): 3297-3312.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
BARAKAT A O, MOSTAFA A, WADE T L, et al., 2011. Distribution and characteristics of PAHs in sediments from the Mediterranean coastal environment of Egypt[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 62(9): 1969-1978.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
BI C J, WANG X P, JIA J P, et al., 2018. Spatial variation and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons influenced by intensive land use in an urbanized river network of East China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 627: 671-680.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
CAI M, ZHAO Z, YANG H, et al., 2012. Spatial distribution of per- and polyfluoroalkyl compounds in coastal waters from the East to South China Sea[J]. Environmental Pollution, 161: 162-169.
DOI URL |
| [6] | CANADIAN COUNCIL OF MINISTERS OF THE ENVIRONMENT, 2002. Canadian Sediment Quality Guidelines for the Protection of Aquatic Life, Summary Tables Update 2002 [EB/OL]. Canada: Government of Canada Public Works & Government Services, [2022-01-23]. https://ccme.ca/en/summary-table. |
| [7] |
CHEN Y Y, ZHU L Z, ZHOU R B, 2007. Characterization and distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon in surface water and sediment from Qiantang River, China[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 141(1): 148-155.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
DICKHUT R M, CANUEL E A, GUSTAFSON K E, et al., 2000. Automotive sources of carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons associated with particulate matter in the Chesapeake Bay region[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 34(21): 4635-4640.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
GAO S H, CHEN J, SHEN Z Y, et al., 2013. Seasonal and spatial distributions and possible sources of polychlorinated biphenyls in surface sediments of Yangtze Estuary, China[J]. Chemosphere, 91(6): 809-816.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
GUAN Y F, WANG J Z, NI H G, et al., 2007. Riverine inputs of polybrominated diphenyl ethers from the Pearl River Delta (China) to the coastal ocean[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 41(17): 6007-6013.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
HUANG B, LIU M, BI X H, et al., 2014. Phase distribution, sources and risk assessment of PAHs, NPAHs and OPAHs in a rural site of Pearl River Delta region, China[J]. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 5(2): 210-218.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
IDOWU O, CARBERY M, O'CONNOR W, et al., 2020. Speciation and source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic compounds (PACs) in sediments of the largest salt water lake of Australia[J]. Chemosphere, DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125779.
DOI |
| [13] |
JOHNSEN S, GRIBBESTAD I S, JOHANSEN S, 1989. Formation of chlorinated PAH-a possible health hazard from water chlorination[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 81-82: 231-238.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
KEITH L H, TELLIARD W A, 1979. Priority Pollutants I-a Perspective View[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 13(4): 416-423.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
KURAL G, BALKS N A, AKSU A, 2018. Source identification of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the urban environment of İstanbul[J]. International Journal of Environment and Geoinformatics, 5(1): 53-67.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
LI D, YUN Y, GAO R, 2019. Oxygenated Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (Oxy-PAHs) facilitate lung cancer metastasis by epigenetically regulating the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT)[J]. Environmental Pollution, 255(Part 2): 113261.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
LI W, WANG C, SHEN H Z, et al., 2015. Concentrations and origins of nitro-polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and oxy-polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in ambient air in urban and rural areas in northern China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 197: 156-164.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
LIN T, GUO Z G, LI Y Y, et al., 2015. Air-Seawater Exchange of Organochlorine Pesticides along the Sediment Plume of a Large Contaminated River[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 49(9): 5354-5362.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
LIU L Y, WANG J Z, WEI G L, et al., 2012. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in continental shelf sediment of China: implications for anthropogenic influences on coastal marine environment[J]. Environmental Pollution, 167: 155-162.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
LONG E R, MACDONALD D D, SMITH S L, et al., 1995. Incidence of Adverse Biological Effects within Ranges of Chemical Concentrations in Marine and Estuarine Sediments[J]. Environmental Management, 19(1): 81-97.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
LÜ M, LUAN X L, LIAO C Y, et al., 2020. Human impacts on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon distribution in Chinese intertidal zones[J]. Nature Sustainability, 3(10): 878-884.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
MONTUORI P, AURINO S, GARZONIO F, et al., 2016. Distribution, sources and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water and sediments from Tiber River and estuary, Italy[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 566-567: 1254-1267.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
MOTELAY-MASSEI A, GARBAN B, TIPHAGNE-LARCHER K, et al., 2006. Mass balance for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the urban watershed of Le Havre (France): transport and fate of PAHs from the atmosphere to the outlet[J]. Water Research, 40(10): 1995-2006.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
PICHLER N, MARIA DE SOUZA F, FERREIRA DOS SANTOS V, et al., 2021. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in sediments of the amazon coast: Evidence for localized sources in contrast to massive regional biomass burning[J]. Environmental Pollution, 268(Part B): 115958.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
QIAO M, CAO W, LIU B C, et al., 2017. Simultaneous detection of chlorinated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 409(13): 3465-3473.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
QIAO M, QI W X, LIU H J, et al., 2013. Simultaneous determination of typical substituted and parent polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water and solid matrix by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 1291: 129-136.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
SARKAR A, BHAGAT J, SAHA SARKER M, et al., 2017. Evaluation of the impact of bioaccumulation of PAH from the marine environment on DNA integrity and oxidative stress in marine rock oyster (Saccostrea cucullata) along the Arabian sea coast[J]. Ecotoxicology, 26(8): 1105-1116.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
SHEN M, YU Y J, ZHENG G J, et al., 2006. Polychlorinated biphenyls and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in surface sediments from the Yangtze River Delta[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 52(10): 1299-1304.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
SUN X, YIN R S, HU L M, et al., 2020. Isotopic tracing of mercury sources in estuarine-inner shelf sediments of the East China Sea[J]. Environmental Pollution, DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114356.
DOI |
| [30] |
WANG Y Z, ZHANG S L, CUI W Y, et al., 2018. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and organochlorine pesticides in surface water from the Yongding River basin, China: Seasonal distribution, source apportionment, and potential risk assessment[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 618: 419-429.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
WANG Y, LI X, LI B H, et al., 2012. Characterization, sources, and potential risk assessment of PAHs in surface sediments from nearshore and farther shore zones of the Yangtze estuary, China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 19(9): 4148-4158.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
WEI C, BANDOWE B A M, HAN Y M, et al., 2015. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and their derivatives (alkyl-PAHs, oxygenated-PAHs, nitrated-PAHs and azaarenes) in urban road dusts from Xi'an, Central China[J]. Chemosphere, 134: 512-520.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
YA M L, WU Y L, XU L, et al., 2021. Compound-specific radiocarbon reveals sources and land-sea transport of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in an urban estuary[J]. Water Research, DOI: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.117134.
DOI |
| [34] |
YAO P, ZHAO B, BIANCHI T S, et al., 2014. Remineralization of sedimentary organic carbon in mud deposits of the Changjiang Estuary and adjacent shelf: Implications for carbon preservation and authigenic mineral formation[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 91: 1-11.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
YIN R S, GUO Z G, HU L M, et al., 2018. Mercury inputs to Chinese marginal seas: impact of industrialization and development of China[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research-Oceans, 123(8): 5599-5611.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
ZAKARIA M P, TAKADA H, TSUTSUMI S, et al., 2002. Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in rivers and estuaries in Malaysia: A widespread input of petrogenic PAHs[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 36(9): 1907-1918.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
ZENG X, LIU Y, XU L, et al., 2021. Co-occurrence and potential ecological risk of parent and oxygenated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in coastal sediments of the Taiwan Strait[J]. Mar Pollut Bull, 173(Part B): 113093.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
ZHANG J, YANG L, MELLOUKI A, et al., 2018. Diurnal concentrations, sources, and cancer risk assessments of PM2.5-bound PAHs, NPAHs, and OPAHs in urban, marine and mountain environments[J]. Chemosphere, 209: 147-155.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
ZHAO J B, ZHANG Y J, WANG T, et al., 2019a. Characterization of PM2.5-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and their derivatives (nitro-and oxy-PAHs) emissions from two ship engines under different operating conditions[J]. Chemosphere, 225: 43-52.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
ZHAO T G, GUO Z G, YAO P, et al., 2019b. Deposition flux and mass inventory of polychlorinated biphenyls in sediments of the Yangtze River Estuary and inner shelf, East China Sea: Implications for contributions of large-river input and e-waste dismantling[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 647: 1222-1229.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
ZHENG B H, WANG L P, LEI K, et al., 2016. Distribution and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water, suspended particulate matter and sediment from Daliao River estuary and the adjacent area, China[J]. Chemosphere, 149: 91-100.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
ZHU T, RAO Z, GUO F, et al., 2018. Simultaneous Determination of 32 Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Derivatives and Parent PAHs Using Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry: Application in Groundwater Screening[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 101(5): 664-671.
DOI URL |
| [43] | 李慧娟, 2013. 短链氯化石蜡在东海近海环境中的分布及迁移转化研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学. |
| LI H J, 2013. The distribution and migration of short chain chlorinated paraffins in the offshore regions of East China Sea[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China. | |
| [44] | 栾晓琳, 2019. 我国典型潮间带沉积物中持久性毒害物的污染特征、风险评价和源汇分析[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学. |
| LUAN X L, 2019. Current pollution features, risk assessment and source analysis of persistent toxic substances in typical intertidal sediments of China[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences. | |
| [45] | 张佳雯, 2020. 基于被动采样的珠三角城市群大气持久性有机污染物的污染特征及暴露风险研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学. |
| ZHANG J W, 2020. A Study on pollution characteristics and exposure risks of airborne persistent organic pollutants in the Pearl River Delta Cities based on passive sampling[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences. | |
| [46] | 赵龙妹, 2018. 成晶节杆菌NT16降解多环芳烃和含氧多环芳烃的特性及机理研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学. |
| ZHAO L M, 2018. Study on the characteristics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and oxygen-containing polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons degradation by arthrobacter crystallopoietes NT16[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology. |
| [1] | ZHANG Guangyi, ZHANG Jiatao, WANG Xiaowei. Phosphorus Speciation Distribution and Release in Lake Sediment Microbial Fuel Cells [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 590-598. |
| [2] | YANG Qili, DOU Weili, LIU Zhiwen, GUO Jing, LÜ Gang. Analysis of Petroleum Hydrocarbon Pollution Characteristics and Influencing Factors Based on N-alkanes Tracing in the River Channel of Fuxin Xihe River [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 599-608. |
| [3] | YANG Nie, SUN Xiaoxun, KONG Tianle, SUN Weimin, CHEN Quanyuan, GAO Pin. Response of Microbial Communities to Changes in Antimony Pollution Concentrations in Fluvial Sediment [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 609-618. |
| [4] | TONG Yindong, HUANG Lanlan, YANG Ning, ZHANG Yiyan, LI Zipeng, SHAO Bo. Distribution Characteristics and Potential Environmental Risk Analysis of Microcystins in Global Water Bodies [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(1): 129-138. |
| [5] | LI Xiuhua, ZHAO Ling, TENG Ying, LUO Yongming, HUANG Biao, LIU Chong, LIU Benle, ZHAO Qiguo. Characteristics, Spatial Distribution and Risk Assessment of Combined Mercury and Cadmium Pollution in Farmland Soils Surrounding Mercury Mining Areas in Guizhou [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(8): 1629-1636. |
| [6] | KE Qihua, ZHANG Keli. Scale Effect on Water and Soil Loss in China: A Bibliometric Analysis [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(7): 1489-1498. |
| [7] | PENG Hongli, TAN Haixia, WANG Ying, WEI Jianmei, FENG Yang. The Discrepancy of Heavy Metals Morphological Distribution in Soil and Its Associated Ecological Risk Evaluation under Different Planting Patterns [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(6): 1235-1243. |
| [8] | ZHU Li'an, ZHANG Huihua, CHENG Jiong, LI Ting, LIN ZI, LI Junjie. Potential Ecological Risk Pattern Analysis of Heavy Metals in Soil of Forestry Land in The Pearl River Delta [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(6): 1253-1262. |
| [9] | SHI Jianfei, JIN Zhengzhong, ZHOU Zhibin, WANG Xin. Evaluation of Heavy Metal Pollution in the Soil Around A Typical Tailing Reservoir in Irtysh River Basin [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(5): 1015-1023. |
| [10] | REN Jun, PAN Jiaxuan, TAO Ling, TONG Yunlong, WANG Ruo’an, SUN Xinni. Stabilization Remediation of Soil Polluted by Cd Using Palygorskite Modified by NaOH [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(12): 2422-2430. |
| [11] | XIE Jiefen, ZHANG Jiaen, WEI Hui, LIU Ziqiang, CHEN Xuan. Microplastic-based Compound Pollution in Soil: An overview [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(12): 2431-2440. |
| [12] | XIE Shaowen, GUO Xiaosong, YANG Fen, HUANG Qiang, CHEN Manjia, WEI Xinghu, LIU Chengshuai. Accumulation Characteristics, Geochemical Fractions Distribution and Ecological Risk of Heavy Metals in Soils of Urban Parks in Guangzhou, China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(11): 2206-2215. |
| [13] | LIU Zhijian, DONG Yuanhua, ZHANG Xiu, QING Chengshi. Contamination and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in the Soil of Agricultural Land in Weining Plain, Northwest China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(11): 2216-2224. |
| [14] | WANG Fei, ZHAO Ying. Pollution Characteristics and Risk Assessment of PAHs in Agricultural Soil from Sewage Irrigation Area of Taiyuan City, Shanxi Province [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(1): 160-169. |
| [15] | SUN Xuejiao, LI Jimei, ZHANG Yutao, LI Xiang, LU Jianjiang, SHE Fei. Characteristics and Influence of Runoff and Sediment Yield in Mountain Forest on the North Slope of Tianshan Mountains [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(9): 1821-1830. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
