Ecology and Environment ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (8): 1732-1741.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.08.020
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Juan1,3( ), ZHANG Naiming2,3,*(
), ZHANG Naiming2,3,*( ), YUAN Qihui2,3
), YUAN Qihui2,3
Received:2020-12-14
Online:2021-08-18
Published:2021-11-03
Contact:
ZHANG Naiming
通讯作者:
张乃明
作者简介:刘娟(1990年生),女,博士研究生,研究方向为农用化学物质与环境。E-mail: 15587214232@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
LIU Juan, ZHANG Naiming, YUAN Qihui. Passivation Effect and Influencing Factors of Different Passivators on Lead-cadmium Compound Contaminated Soils[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(8): 1732-1741.
刘娟, 张乃明, 袁启慧. 不同钝化剂对铅镉复合污染土壤钝化效果及影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1732-1741.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.08.020
| 重金属 Heavy metal | 测定值 Measured value | 不同pH条件下重金属限值 Limit values of heavy metals under different PH conditions | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH≤5.50 | 5.50<pH≤6.50 | 6.50<pH≤7.50 | pH>7.50 | ||
| Cd | 筛选值 Screening values | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.60 |
| 管控值 Intervention values | 1.50 | 2.00 | 3.00 | 0.60 | |
| Pb | 筛选值 Screening values | 70.00 | 90.00 | 120.00 | 170.00 |
| 管控值 Intervention values | 400.00 | 500.00 | 700.00 | 1000.00 | |
Table 1 Risk value of heavy metal pollution in agricultural land soil mg∙kg-1
| 重金属 Heavy metal | 测定值 Measured value | 不同pH条件下重金属限值 Limit values of heavy metals under different PH conditions | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH≤5.50 | 5.50<pH≤6.50 | 6.50<pH≤7.50 | pH>7.50 | ||
| Cd | 筛选值 Screening values | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.60 |
| 管控值 Intervention values | 1.50 | 2.00 | 3.00 | 0.60 | |
| Pb | 筛选值 Screening values | 70.00 | 90.00 | 120.00 | 170.00 |
| 管控值 Intervention values | 400.00 | 500.00 | 700.00 | 1000.00 | |
| 钝化剂 Passivators | pH | 全镉 w(total cadmium)/ (mg∙kg-1) | 全铅 w(total lead)/ (mg∙kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 钝化剂 Passivator A | 7.88 | 0.19 | 13.17 |
| 钝化剂 Passivator B | 9.78 | 0.22 | 16.02 |
| 钝化剂 Passivator C | 9.88 | 0.11 | 19.31 |
| 钝化剂 Passivator D | 8.63 | 0.15 | 26.03 |
Table 2 Basic properties of passivators
| 钝化剂 Passivators | pH | 全镉 w(total cadmium)/ (mg∙kg-1) | 全铅 w(total lead)/ (mg∙kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 钝化剂 Passivator A | 7.88 | 0.19 | 13.17 |
| 钝化剂 Passivator B | 9.78 | 0.22 | 16.02 |
| 钝化剂 Passivator C | 9.88 | 0.11 | 19.31 |
| 钝化剂 Passivator D | 8.63 | 0.15 | 26.03 |
| 水平 Levels | 因素Facter | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| A施肥量 The amount of fertilizer/ (kg∙hm-2) | B土壤水分 Soil Moisture/ % | C土壤粒径 Soil particle size/ mm | |
| 1 | 225 | 40 | <1 |
| 2 | 450 | 60 | 1‒2 |
| 3 | 675 | 80 | >2 |
Table 3 The table of factor level
| 水平 Levels | 因素Facter | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| A施肥量 The amount of fertilizer/ (kg∙hm-2) | B土壤水分 Soil Moisture/ % | C土壤粒径 Soil particle size/ mm | |
| 1 | 225 | 40 | <1 |
| 2 | 450 | 60 | 1‒2 |
| 3 | 675 | 80 | >2 |
| 试验号 Test number | 因素 Facter | 试验组 Test Group | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | ||
| T1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | A1B1C1 |
| T2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | A1B2C3 |
| T3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | A1B3C2 |
| T4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | A2B1C2 |
| T5 | 2 | 2 | 1 | A2B2C1 |
| T6 | 2 | 3 | 3 | A2B3C3 |
| T7 | 3 | 1 | 3 | A3B1C3 |
| T8 | 3 | 2 | 2 | A3B2C2 |
| T9 | 3 | 3 | 1 | A3B3C1 |
Table 4 The design of orthogonal experimental
| 试验号 Test number | 因素 Facter | 试验组 Test Group | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | ||
| T1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | A1B1C1 |
| T2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | A1B2C3 |
| T3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | A1B3C2 |
| T4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | A2B1C2 |
| T5 | 2 | 2 | 1 | A2B2C1 |
| T6 | 2 | 3 | 3 | A2B3C3 |
| T7 | 3 | 1 | 3 | A3B1C3 |
| T8 | 3 | 2 | 2 | A3B2C2 |
| T9 | 3 | 3 | 1 | A3B3C1 |
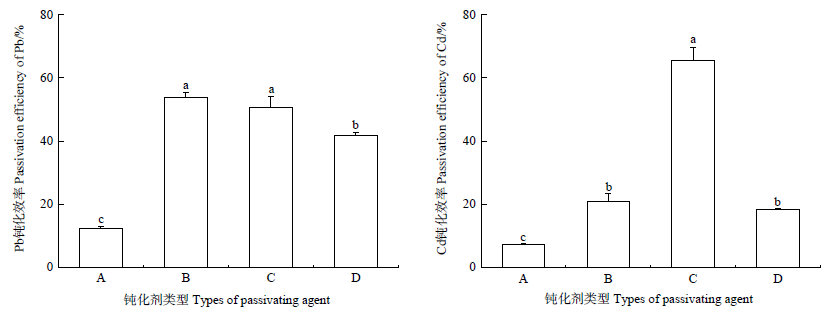
Fig. 1 Passivation effect of different passivators on soil available Pb and Cd Different lowercase letters showed significant difference in passivation efficiency between different passivator types of the same heavy metal (P<0.05, n=3) A: sulfur-containing soil conditioner; B: biochar passivating agent; C: mineral passivating agent; D: organic-inorganic passivating agent
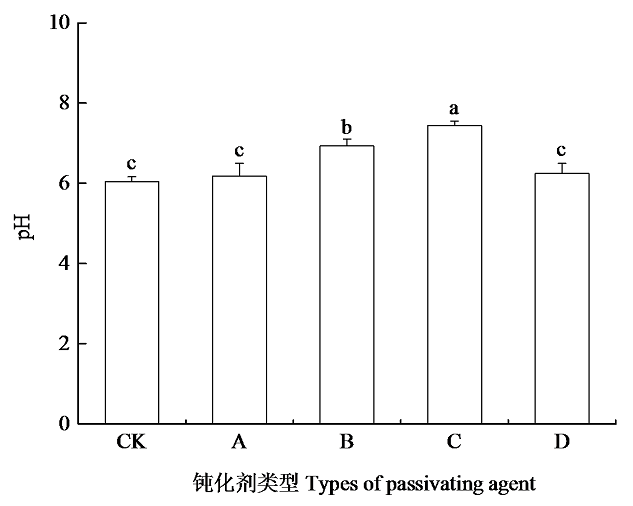
Fig. 2 Effects of different passivators on soil pH Different lowercase letters indicated significant Ph difference among different passivator types (P<0.05, n=3) A: sulfur-containing soil conditioner; B: biochar passivating agent; C: mineral passivating agent; D: organic-inorganic passivating agent
| 试验号 Test number | 因素 Facter | 钝化效果 Passivation effect/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | 铅 Lead | ||
| T1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 38.52 | |
| T2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 41.6 | |
| T3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 21.61 | |
| T4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 23.09 | |
| T5 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 39.53 | |
| T6 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 21.48 | |
| T7 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 47.79 | |
| T8 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 40.8 | |
| T9 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 23.72 | |
| | 33.91 | 36.47 | 33.92 | ||
| | 28.03 | 40.64 | 28.5 | ||
| | 37.44 | 30.29 | 36.96 | ||
| 极差R(3) | 9.41 | 10.35 | 8.46 | ||
| 分析较优水平 | A3 | B2 | C3 | ||
| 主次因素 | BAC | ||||
Table 5 Orthogonal test results of soil available lead
| 试验号 Test number | 因素 Facter | 钝化效果 Passivation effect/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | 铅 Lead | ||
| T1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 38.52 | |
| T2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 41.6 | |
| T3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 21.61 | |
| T4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 23.09 | |
| T5 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 39.53 | |
| T6 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 21.48 | |
| T7 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 47.79 | |
| T8 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 40.8 | |
| T9 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 23.72 | |
| | 33.91 | 36.47 | 33.92 | ||
| | 28.03 | 40.64 | 28.5 | ||
| | 37.44 | 30.29 | 36.96 | ||
| 极差R(3) | 9.41 | 10.35 | 8.46 | ||
| 分析较优水平 | A3 | B2 | C3 | ||
| 主次因素 | BAC | ||||
| 因素 Factor | 偏差平方和 Deviation sum of squares | 自由度 Degree of freedom | F | F0.05 (2, 2) | 显著性 Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 135.395 | 2 | 1.902 | 19 | 不显著 No significance |
| B | 556.569 | 2 | 7.818 | 19 | 不显著 No significance |
| C | 110.129 | 2 | 1.547 | 19 | 不显著 No significance |
| 误差 Error | 71.187 | 2 |
Table 6 Analysis of variance of available lead
| 因素 Factor | 偏差平方和 Deviation sum of squares | 自由度 Degree of freedom | F | F0.05 (2, 2) | 显著性 Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 135.395 | 2 | 1.902 | 19 | 不显著 No significance |
| B | 556.569 | 2 | 7.818 | 19 | 不显著 No significance |
| C | 110.129 | 2 | 1.547 | 19 | 不显著 No significance |
| 误差 Error | 71.187 | 2 |
| 试验号 Test number | 因素 Facter | 钝化效果Passivation effect/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | 镉 Cadmium | ||
| T1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 46.42 | |
| T2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 53.99 | |
| T3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 13.5 | |
| T4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 17.8 | |
| T5 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 48.33 | |
| T6 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 21.24 | |
| T7 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 56.3 | |
| T8 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 46.07 | |
| T9 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 12.13 | |
| | 37.97 | 40.17 | 35.63 | ||
| | 29.12 | 49.46 | 25.79 | ||
| | 38.17 | 15.62 | 43.84 | ||
| 极差R(3) | 9.05 | 33.84 | 18.05 | ||
| 分析较优水平 Analysis of superior level | A3 | B2 | C3 | ||
| 主次因素 Primary and secondary factor | BCA | ||||
Table 7 Orthogonal test results of available cadmium in soil
| 试验号 Test number | 因素 Facter | 钝化效果Passivation effect/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | 镉 Cadmium | ||
| T1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 46.42 | |
| T2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 53.99 | |
| T3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 13.5 | |
| T4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 17.8 | |
| T5 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 48.33 | |
| T6 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 21.24 | |
| T7 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 56.3 | |
| T8 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 46.07 | |
| T9 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 12.13 | |
| | 37.97 | 40.17 | 35.63 | ||
| | 29.12 | 49.46 | 25.79 | ||
| | 38.17 | 15.62 | 43.84 | ||
| 极差R(3) | 9.05 | 33.84 | 18.05 | ||
| 分析较优水平 Analysis of superior level | A3 | B2 | C3 | ||
| 主次因素 Primary and secondary factor | BCA | ||||
| 因素 Factor | 偏差平方和 Deviation sum of squares | 自由度 Degree of freedom | F | F0.05 (2, 2) | 显著性 Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 160.084 | 2 | 0.693 | 19 | 不显著 No significance |
| B | 1834.152 | 2 | 7.943 | 19 | 不显著 No significance |
| C | 490.196 | 2 | 2.122 | 19 | 不显著 No significance |
| 误差 Error | 230.924 | 2 |
Table 8 Analysis of variance of available cadmium
| 因素 Factor | 偏差平方和 Deviation sum of squares | 自由度 Degree of freedom | F | F0.05 (2, 2) | 显著性 Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 160.084 | 2 | 0.693 | 19 | 不显著 No significance |
| B | 1834.152 | 2 | 7.943 | 19 | 不显著 No significance |
| C | 490.196 | 2 | 2.122 | 19 | 不显著 No significance |
| 误差 Error | 230.924 | 2 |
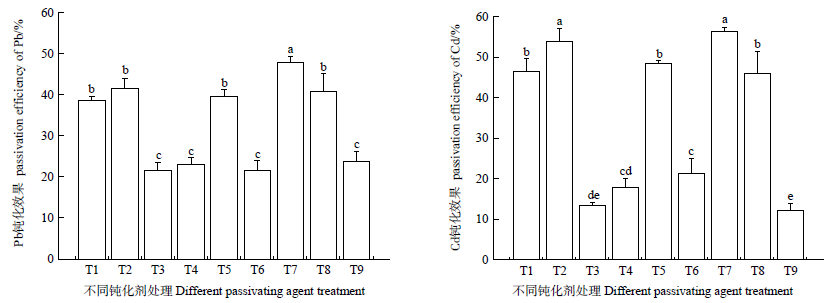
Fig. 3 Passivation efficiency of available lead and cadmium by different treatments Different lowercase letters represent significant differences between different treatments of the same heavy metal element (P<0.05, n=3)
| [1] |
YAN X L, LIN L, LIAO X Y, et al., 2012 Arsenic accumulation and resistance mechanism in Panax notoginseng: A traditional rare medicinal herb[J]. Chemosphere, 87(1): 31-36.
DOI URL |
| [2] | 陈盾, 王小兵, 汪晓丽, 等, 2020. 镉污染红壤的钝化剂筛选及钝化效果[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 36(1): 115-120. |
| CHEN D, WANG X B, WANG X L, et al., 2020. Screening of passivators for cadmium-contaminated red soil and their effects on soil remediation[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 36(1): 115-120. | |
| [3] | 崔岩山, 王鹏飞, 琚宜文, 2018. 纳米材料在土壤重金属污染修复中的应用[J]. 地球科学, 43(5): 379-387. |
| CUI Y S, WANG P F, JU Y W, 2018. Progress of applications of nanomaterials in soil heavy metal remediation[J]. Earth Science, 43(5): 379-387. | |
| [4] | 代豫杰, 郭建英, 董智, 等, 2017. 不同沙生灌木下土壤颗粒及重金属空间分布特征[J]. 环境科学, 38(11): 365-374. |
| DAI Y J, GUO J Y, DONG Z, et al., 2017. Spatial distribution of soil particles and heavy metals under different psammophilic shrubs in the Ulan Buh Desert[J]. Environmental Science, 38(11): 365-374. | |
| [5] | 邓林, 李柱, 吴龙华, 等, 2014. 水分及干燥过程对土壤重金属有效性的影响[J]. 土壤, 25(4): 939-944. |
| DENG L, LI Z, WU L H, et al., 2014. Influence of moisture and drying process on soil heavy metal availability[J]. Soils, 25(4): 939-944. | |
| [6] | 杜彩艳, 段宗颜, 曾民, 等, 2015. 田间条件下不同组配钝化剂对玉米 (Zea mays) 吸收Cd、As和Pb影响研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 24(10): 1731-1738. |
| DU C Y, DUAN Z Y, ZENG M, et al., 2015. Effects of different combined amendments on cadmium, arsenic and lead absorption of maize under field conditions[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 24(10): 1731-1738. | |
| [7] | 杜彩艳, 木霖, 王红华, 等, 2016. 不同钝化剂及其组合对玉米 (Zea mays) 生长和吸收Pb、Cd、As、Zn影响研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 35(8): 1515-1522. |
| DU C Y, MU L, WANG H H, et al., 2016. Effects of different amendments on growth and Pb, Cd, As, Zn uptake by Zea mays[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 35(8): 1515-1522. | |
| [8] | 樊霆, 叶文玲, 陈海燕, 等, 2013. 农田土壤重金属污染状况及修复技术研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 22(10): 1727-1736. |
| FAN T, YE W L, CHEN H Y, et al., 2013. Review on contamination and remediation technology of heavy metal in agricultural soil[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 22(10):1727-1736. | |
| [9] | 郭文娟, 梁学峰, 林大松, 等, 2013. 土壤重金属钝化修复剂生物炭对镉的吸附特性研究[J]. 环境科学, 34(9): 3716-3721. |
| GUO W J, LIANG X F, LIN D S, et al., 2013. Absorption of Cd2+ on biochar from aqueous solution[J]. Environmental Science, 34(9): 3716-3721. | |
| [10] | 胡洁, 周海燕, 刘成, 等, 2018. 无机有机钝化剂对土壤镉有效态及小白菜吸收镉的影响[J]. 工业安全与环保, 44(11): 91-95. |
| HU J, ZHOU H Y, LIU C, et al., 2018. Effects of inorganic organic amendments on soil cadmium availability and cadmium uptake in pakchoi[J]. Industrial Safety and Environmental Protection, 44(11): 91-95. | |
| [11] | 金睿, 刘可星, 艾绍英, 等, 2016. 生物炭复配调理剂对镉污染土壤性状和小白菜镉吸收及其生理特性的影响[J]. 南方农业学报, 47(9): 1480-1487. |
| JIN R, LIU K X, AI S Y, et al., 2016. Effects of biochar complex conditioner on properties of cadmium contaminated soil and cadmium absorption and physiological characterisitics of Brassica chinensis[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 47(9): 1480-1487. | |
| [12] | 焦鹏, 高建培, 王宏镔, 等, 2011. N、P、K肥对玉米幼苗吸收和积累重金属的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 30(6): 1094-1102. |
| JIAO P, GAO J P, WANG H B, et al., 2011. Effects of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer on heavy metal uptake and accumulation by maize seeding[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 30(6): 1094-1102. | |
| [13] | 李丁, 王济, 宣斌, 等, 2019. 不同钝化剂对外源铅在土壤中的钝化效果及粒径分布的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 13(12): 2934-2944. |
| LI D, WANG J, XUAN B, et al., 2019. Effects of different passivators on the immobilization effect and particle-size distribution of exogenous lead in soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 13(12): 2934-2944. | |
| [14] | 刘艺芸, 徐应明, 黄青青, 等, 2019. 水肥耦合对海泡石钝化修复镉污染土壤效率的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 38(9): 2086-2094. |
| LIU Y Y, XU Y M, HUANG Q Q, et al., 2019. Coupling effect of water management and fertilizers in remediation of Cd-contaminated soil using sepiolite[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 38(9): 2086-2094. | |
| [15] | 路轲, 宋正国, 2020. 喷施不同纳米材料对水稻幼苗磷含量的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 39(1): 28-36. |
| LU K, SONG Z G, 2020. Effects of different sprayed nanomaterials on the phosphorus content in rice seeding[J]. Journal of Agro- Environment Science, 39(1): 28-36. | |
| [16] | 鲁如坤, 2000. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社: 12-180. |
| LU R K, 2000. Soil agricultural chemical analysis method[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: 12-180. | |
| [17] | 沈章军, 侯万青, 徐德聪, 等, 2020. 不同钝化剂对重金属在土壤-油菜中迁移的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 39(12): 2779-2788. |
| SHEN Z J, HOU W Q, XU D C, et al., 2020. Effects of different immobilization materials on heavy metal migration in contaminated soil-rape[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 39(12): 2779-2788. | |
| [18] | 宋正国, 唐世荣, 丁永祯, 等, 2011. 田间条件下不同钝化材料对玉米吸收镉的影响研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 30(11): 2152-2159. |
| SONG Z G, TANG S R, DING Y Z, et al., 2011. Effects of different amendments on cadmium uptake by maize under field conditions[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 30(11): 2152-2159. | |
| [19] | 孙约兵, 王永昕, 李烨, 等, 2015. Cd-Pb复合污染土壤钝化修复效率与生物标记物识别[J]. 环境科学研究, 28(6): 951-958. |
| SUN Y B, WANG Y X, LI Y, et al., 2015. Effectiveness of immobilization remediation of Cd and Pb combined contaminated soil and biomarker identification[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 28(6): 951-958. | |
| [20] | 孙国红, 王鹏超, 徐应明, 等, 2019. 施用钾肥对稻田土镉污染钝化修复效应影响研究[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 38(5): 38-45. |
| SUN G H, WANG P C, XU Y M, et al., 2019. Potassium Fertilizer Enhances the Mobility of Cadmium in Paddy Soil Amended with Sepiolite[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 38(5): 38-45. | |
| [21] | 吴迪, 魏小娜, 彭湃, 等, 2019. 钝化剂对酸性高镉土壤钝化效果及水稻镉吸收的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 50(2): 482-488. |
| WU D, WEI X N, PENG P, et al., 2019. Effects of passivators on acid and cadmium farmland soils and cadmium absorption by rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 50(2): 482-488 | |
| [22] | 吴烈善, 曾东梅, 莫小荣, 等, 2015. 不同钝化剂对重金属污染土壤稳定化效应的研究[J]. 环境科学, 36(1): 309-313. |
| WU L S, ZENG D M, MO X R, et al., 2015. Immobilization impact of different fixatives on heavy metals contaminated soil[J]. Environmental Science, 36(1): 309-313. | |
| [23] | 徐磊, 蓝文翀, 张娜, 等, 2017. 水分调控对材料钝化重金属效果的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 33(35): 88-93. |
| XU L, LAN W C, ZHANG N, et al., 2017. Water Regulation: Influence on Passivation Effect of Heavy Metals[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 33(35): 88-93. | |
| [24] | 徐明岗, 刘平, 宋正国, 等, 2006. 施肥对污染土壤中重金属行为影响的研究进展[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 25(1): 328-333. |
| XU M G, LIU P, SONG Z G, et al., 2006. Progress in Fertilization on Behavior of Heavy Metals in Contaminated Soils[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 25(1): 328-333. | |
| [25] | 殷飞, 王海娟, 李燕燕, 等, 2015. 不同钝化剂对重金属复合污染土壤的修复效应研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 34(3): 438-448. |
| YIN F, WANG H J, LI Y Y, et al., 2015. Remediation of multiple heavy metal polluted soil using different immobilizing agents[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 34(3): 438-448. | |
| [26] | 袁兴超, 李博, 朱仁凤, 等, 2019. 不同钝化剂对铅锌矿区周边农田镉铅污染钝化修复研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 38(4): 807-817. |
| YUAN X C, LI B, ZHU R F, et al., 2019. Immobilization of Cd and Pb using different amendments of cultivated soils around lead-zinc mines[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 38(4): 807-817. | |
| [27] | 袁启慧, 包立, 张乃明, 2019. 钝化剂种类和粒径对复合污染土壤镉铅有效态的影响[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 36(2): 192-197. |
| YUAN Q H, BAO L, ZHANG N M, 2019. The effect of type and particle size of passivator on effective state of Cd and Pb in compound polluted soil[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 36(2): 192-197. | |
| [28] | 张迪, 丁爱芳, 2018. 组配钝化剂对镉铅复合污染土壤修复效果研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 37(12): 2718-2726. |
| ZHANG D, DING A F, 2018. Effects of combined passivating agents on remediation of Cd and Pb compound-contaminated soil[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 37(12): 2718-2726. | |
| [29] | 张乃明, 2013. 环境土壤学[M]. 北京: 中国农业大学出版社. |
| ZHANG N M, 2013. Environmental soil science[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural University Press. | |
| [30] | 张连科, 刘心宇, 王维大, 等, 2018. 两种油料作物秸秆生物炭对土壤中铅的钝化修复[J]. 生态环境学报, 27(1): 166-173. |
| ZHANG L K, LIU X Y, WANG W D, et al., 2018. Immobilization of lead in contaminated soil by biochar produced from two kinds of oil crops straw[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 27(1): 166-173. | |
| [31] | 郑顺安, 郑向群, 张铁亮, 等, 2011. 水分条件对紫色土中铅形态转化的影响[J]. 环境化学, 30(12): 2080-2084. |
| ZHENG S A, ZHENG X Q, ZHANG T L, et al., 2011. Effect of moisture regime on the fractionation of lead in purple soil[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 30 (12): 2080-2084. | |
| [32] | 周启星, 宋玉芳, 2004. 污染土壤修复原理与方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| ZHOU Q X, SONG Y F, 2004. Principles and methods of remediation of contaminated soil[M]. Beijing: Science Press. |
| [1] | DU Dandan, GAO Ruizhong, FANG Lijing, XIE Longmei. Spatial Variation of Soil Heavy Metals and Their Responses to Physicochemical Factors of Salt Lake Basin in Arid Area [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(6): 1123-1132. |
| [2] | FENG Shuna, LÜ Jialong, HE Hailong. Effect of KI Leaching on the Hg (Ⅱ) Removal of Loess Soil and the Physicochemical Properties of the Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 776-783. |
| [3] | CHEN Minyi, ZHU Hanghai, SHE Weiduo, YIN Guangcai, HUANG Zuzhao, YANG Qiaoling. Health Risk Assessment and Source Apportionment of Soil Heavy Metals at A Legacy Shipyard Site in Pearl River Delta [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 794-804. |
| [4] | XIAO Jieyun, ZHOU Wei, SHI Peiqi. Hyperspectral Inversion of Soil Heavy Metals [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(1): 175-182. |
| [5] | HAUNG Hong, ZHENG Xinyun, LI Yingdong, ZHAO Xu, YU Jinchen, WANG Zhenhua. A study on Enrichment of Heavy Metals in Sebastiscus marmoratus at Different Ages in Dachen Islands Sea Area [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(9): 1885-1891. |
| [6] | MA Chuang, WANG Yuyang, ZHOU Tong, WU Longhua. Enrichment Characteristics and Desorption Behavior of Cadmium and Zinc in Particulate Organic Matter of Polluted Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(9): 1892-1900. |
| [7] | TAO Ling, HUANG Lei, ZHOU Yilei, LI Zhongxing, REN Jun. Influences of Biochar Prepared by Co-pyrolysis with Sludge and Attapulgite on Bioavailability and Environmental Risk of Heavy Metals in Mining Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(8): 1637-1646. |
| [8] | LI Ying, ZHANG Zhou, YANG Gaoming, ZU Yanqun, LI Bo, CHEN Jianjun. The Relationship between the Radial Oxygen Loss and the Iron Plaque on Root Surfaces to Wetland Plants Absorb Heavy Metals [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(8): 1657-1666. |
| [9] | LUO Songying, LI Qiuxia, QIU Jinkun, DENG Suyan, LI Yifeng, CHEN Bishan. Speciation Characteristics, Migration and Transformation of Heavy Metals in Mangrove Soil-plant System in Nansan Island [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(7): 1409-1416. |
| [10] | DONG Leheng, WANG Xugang, CHEN Manjia, WANG Zihao, SUN Lirong, SHI Zhaoyong, Wu Qiqi. Interaction of Iron Redox and Cu Activities in Calcareous Paddy Soil under Light and Dark Condition [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(7): 1448-1455. |
| [11] | LEI Jun, ZHANG Jian, ZHAO Funian, QI Yue, ZHANG Xiuyun, LI Qiang, SHANG Junlin. Response of Photosynthetic Parameters for Spring Wheat at Flowering Stage to Soil Moisture and Temperature [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(6): 1151-1159. |
| [12] | PENG Hongli, TAN Haixia, WANG Ying, WEI Jianmei, FENG Yang. The Discrepancy of Heavy Metals Morphological Distribution in Soil and Its Associated Ecological Risk Evaluation under Different Planting Patterns [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(6): 1235-1243. |
| [13] | HUANG Min, ZHAO Xiaofeng, LIANG Rongxiang, WANG Pengzhong, DAI Anran, HE Xiaoman. Comparison of Three Chelating Agents to Remove the Cd and Cu in Contaminated Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(6): 1244-1252. |
| [14] | ZHU Li'an, ZHANG Huihua, CHENG Jiong, LI Ting, LIN ZI, LI Junjie. Potential Ecological Risk Pattern Analysis of Heavy Metals in Soil of Forestry Land in The Pearl River Delta [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(6): 1253-1262. |
| [15] | SHI Jianfei, JIN Zhengzhong, ZHOU Zhibin, WANG Xin. Evaluation of Heavy Metal Pollution in the Soil Around A Typical Tailing Reservoir in Irtysh River Basin [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(5): 1015-1023. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
