Ecology and Environment ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (5): 957-967.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.05.008
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
HUANG Cheng1( ), WU Yueying1, JI Hengkuan1, CHEN Liming1, LI Beiying2, FU Chuanliang3, LI Jianhong4, WU Weidong1, WU Zhipeng1,*(
), WU Yueying1, JI Hengkuan1, CHEN Liming1, LI Beiying2, FU Chuanliang3, LI Jianhong4, WU Weidong1, WU Zhipeng1,*( )
)
Received:2020-12-07
Online:2021-05-18
Published:2021-08-06
Contact:
WU Zhipeng
黄成1( ), 吴月颖1, 吉恒宽1, 陈丽铭1, 李倍莹2, 符传良3, 李建宏4, 吴蔚东1, 吴治澎1,*(
), 吴月颖1, 吉恒宽1, 陈丽铭1, 李倍莹2, 符传良3, 李建宏4, 吴蔚东1, 吴治澎1,*( )
)
通讯作者:
吴治澎
作者简介:黄成(1997年生),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为土壤质量退化与调控研究。E-mail:15155549693@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
HUANG Cheng, WU Yueying, JI Hengkuan, CHEN Liming, LI Beiying, FU Chuanliang, LI Jianhong, WU Weidong, WU Zhipeng. Response of Iron Reduction Characteristics to DOM Molecular Properties under Anaerobic Conditions in Typical Paddy Soils of Hainan Island[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(5): 957-967.
黄成, 吴月颖, 吉恒宽, 陈丽铭, 李倍莹, 符传良, 李建宏, 吴蔚东, 吴治澎. 海南典型水稻土厌氧铁还原特征对DOM分子特性的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(5): 957-967.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.05.008
| 母质 Parent material | 有效硅 质量分数 ω(Effective Si)/ (mg∙kg-1) | 全硅质量分数 ω(Total Si)/ (mg∙kg-1) | pH | SOM 质量分数 ω(SOM)/ (g∙kg-1) | 速效氮 质量分数 ω(Available N)/ (mg∙kg-1) | 速效磷 质量分数 ω(Available P)/ (mg∙kg-1) | 速效钾 质量分数 ω(Available K)/ (mg∙kg-1) | 游离Fe2O3 质量分数 ω(Free Fe2O3)/ (g∙kg-1) | 非晶体氧化铁质量分数 ω(Amorphous Fe)/ (g∙kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 玄武岩 XW | 56.78±3.45a | 298.54±23.15c | 4.31±0.05d | 17.24±1.03b | 61.48±2.11d | 4.70±0.11d | 100.05±8.09a | 24.92±1.08a | 10.78±0.11a |
| 花岗岩 HG | 54.3±4.73a | 386.32±16.21a | 5.43±0.09c | 19.72±1.41b | 88.12±6.01a | 5.46±0.22c | 100.36±8.11a | 12.71±0.19bc | 7.73±0.30b |
| 砂页岩 SY | 53.43±6.48a | 302.34±15.15c | 5.43±0.08c | 17.29±1.98b | 75.15±4.61c | 6.23±0.28a | 81.45±6.08b | 14.01±0.41b | 7.69±0.14b |
| 海相沉积物HXCJ | 54.67±2.51a | 356.66±13.90b | 7.42±0.01a | 24.26±2.21a | 80.28±3.11b | 5.86±0.12b | 64.35±5.06d | 9.11±0.89c | 5.39±0.13c |
| 河流冲积物HLCJ | 53.42±2.49a | 342.11±4.85b | 6.42±0.03b | 22.47±2.51a | 91.89±3.51a | 5.44±0.15c | 73.62±0.46c | 9.98±0.99c | 5.59±0.21c |
Table 1 Basic physical and chemical properties of paddy soils developed from five different parent materials
| 母质 Parent material | 有效硅 质量分数 ω(Effective Si)/ (mg∙kg-1) | 全硅质量分数 ω(Total Si)/ (mg∙kg-1) | pH | SOM 质量分数 ω(SOM)/ (g∙kg-1) | 速效氮 质量分数 ω(Available N)/ (mg∙kg-1) | 速效磷 质量分数 ω(Available P)/ (mg∙kg-1) | 速效钾 质量分数 ω(Available K)/ (mg∙kg-1) | 游离Fe2O3 质量分数 ω(Free Fe2O3)/ (g∙kg-1) | 非晶体氧化铁质量分数 ω(Amorphous Fe)/ (g∙kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 玄武岩 XW | 56.78±3.45a | 298.54±23.15c | 4.31±0.05d | 17.24±1.03b | 61.48±2.11d | 4.70±0.11d | 100.05±8.09a | 24.92±1.08a | 10.78±0.11a |
| 花岗岩 HG | 54.3±4.73a | 386.32±16.21a | 5.43±0.09c | 19.72±1.41b | 88.12±6.01a | 5.46±0.22c | 100.36±8.11a | 12.71±0.19bc | 7.73±0.30b |
| 砂页岩 SY | 53.43±6.48a | 302.34±15.15c | 5.43±0.08c | 17.29±1.98b | 75.15±4.61c | 6.23±0.28a | 81.45±6.08b | 14.01±0.41b | 7.69±0.14b |
| 海相沉积物HXCJ | 54.67±2.51a | 356.66±13.90b | 7.42±0.01a | 24.26±2.21a | 80.28±3.11b | 5.86±0.12b | 64.35±5.06d | 9.11±0.89c | 5.39±0.13c |
| 河流冲积物HLCJ | 53.42±2.49a | 342.11±4.85b | 6.42±0.03b | 22.47±2.51a | 91.89±3.51a | 5.44±0.15c | 73.62±0.46c | 9.98±0.99c | 5.59±0.21c |
| Logistic 方程参数 Logistic model parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 母质 Parent material | a/ (mg∙g-1) | vmax/ [mg∙(g∙d)-1] | tvmax/ d | r2 |
| 玄武岩 XW | 7.93±0.12 | 1.28±0.15 | 1.02±0.09 | 0.975 |
| 花岗岩 HG | 7.50±0.09 | 0.68±0.06 | 5.25±0.38 | 0.956 |
| 砂页岩 SY | 6.33±0.04 | 0.99±0.12 | 2.97±0.23 | 0.922 |
| 海相沉积物 HXCJ | 3.91±0.15 | 0.47±0.00 | 4.46±0.09 | 0.943 |
| 河流冲积物 HLCJ | 4.55±0.02 | 0.86±0.05 | 2.24±0.13 | 0.966 |
Table 2 The Logistic kinetics parameters of microbial Fe (Ⅲ) reduction during anaerobic incubation of paddy soils
| Logistic 方程参数 Logistic model parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 母质 Parent material | a/ (mg∙g-1) | vmax/ [mg∙(g∙d)-1] | tvmax/ d | r2 |
| 玄武岩 XW | 7.93±0.12 | 1.28±0.15 | 1.02±0.09 | 0.975 |
| 花岗岩 HG | 7.50±0.09 | 0.68±0.06 | 5.25±0.38 | 0.956 |
| 砂页岩 SY | 6.33±0.04 | 0.99±0.12 | 2.97±0.23 | 0.922 |
| 海相沉积物 HXCJ | 3.91±0.15 | 0.47±0.00 | 4.46±0.09 | 0.943 |
| 河流冲积物 HLCJ | 4.55±0.02 | 0.86±0.05 | 2.24±0.13 | 0.966 |
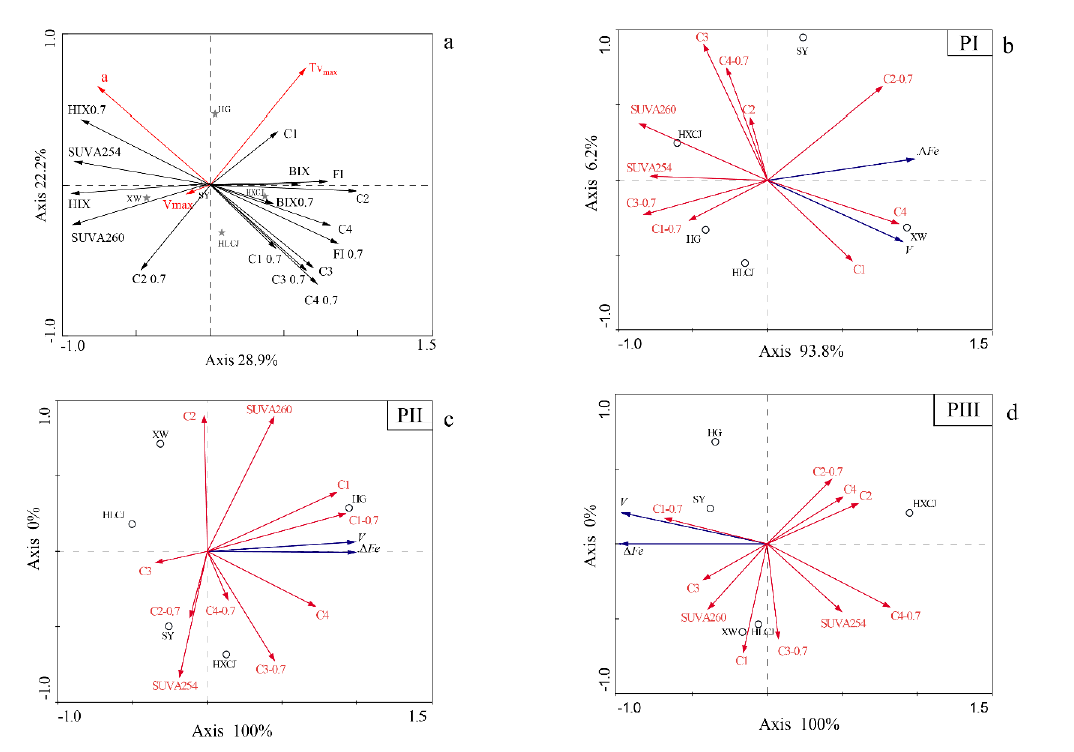
Fig. 11 RDA diagrams of soil environmental factors and Fe (III) reduction characteristics of developing parent materials at different stagesInitial-a, PⅠ-b, PⅡ-c, PⅢ-d
| [1] | AMON R M W, BENNER R, 1996. Bacterial utilization of different size classes of dissolved organic matter[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 41(1): 41-51. |
| [2] | BI R, LU Q, YU W M, et al., 2013. Electron transfer capacity of soil dissolved organic matter and its potential impact on soil respiration[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 13(9): 1553-1560. |
| [3] | BIRDWELL J E, VALSARAJ K T, 2010. Characterization of dissolved organic matter in fogwater by excitation-emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopy[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 44(27): 3246-3253. |
| [4] | BURGOS W D, FANG Y, ROYER R A, et al., 2003. Reaction-based modeling of quinone-mediated bacterial iron(III) reduction[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 67(15): 2735-2748. |
| [5] | DILLING J, KAISER K, 2003. Erratum to “Estimation of the hydrophobic fraction of dissolved organic matter in water samples using UV photometry”[J]. Water Research, 37(9): 2257. |
| [6] | GRYBOS M, DAVRANCHE M, GRUAU G, et al., 2009. Increasing pH drives organic matter solubilization from wetland soils under reducing conditions[J]. Geoderma, 154(1): 13-19. |
| [7] | HUANG Y, SUN W J, 2006. Changes in topsoil organic carbon of croplands in mainland China over the last two decades[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 51(15): 1785-1803. |
| [8] | HUGUET A, VACHER L, RELEXANS S, et al., 2009. Properties of fluorescent dissolved organic matter in the Gironde Estuary[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 40(6): 706-719. |
| [9] | JOHNSTON S J, BURTON E D, AASO T, et al., 2014. Sulfur, iron and carbon cycling following hydrological restoration of acidic freshwater wetlands[J]. Chemical Geology, 371: 9-26. |
| [10] | KÖGEL-KNABNER I, AMELUNG W, CAO Z H, et al., 2010. Biogeochemistry of paddy soils[J]. Geoderma, 157(1): 1-14. |
| [11] | LI H Y, WANG H, WANG H T, et al., 2018. The chemodiversity of paddy soil dissolved organic matter correlates with microbial community at continental scales[J]. Microbiome, 6(1): 187. |
| [12] | MCKNIGHT D M, BOYER E W, WESTERHOFF P K, et al., 2001. Spectrofluorometric characterization of dissolved organic matter for indication of precursor organic material and aromaticity[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 46(1): 38-48. |
| [13] | PAN W N, KAN J J, INAMDAR S, et al., 2016. Dissimilatory microbial iron reduction release DOC (dissolved organic carbon) from carbon-ferrihydrite association[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 103: 232-240. |
| [14] | RASILO T, OJALA A, HUOTARI J, et al., 2015. Concentrations and quality of DOC along the terrestrial-aquatic continuum in a boreal forested catchment[J]. Freshwater Science, 34(2): 440-455. |
| [15] | SAHRAWAT K L, 2003. Organic matter accumulation in submerged soils[J]. Advances in Agronomy, 81: 169-201. |
| [16] | SALVE P R, LOHKARE H, GOBRE T, et al., 2012. Characterization of chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in rainwater using fluorescence spectrophotometry[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 88(2): 215-218. |
| [17] | SCOTT D T, MCKNIGHT D M, BLUNT-HARRIS E L, et al., 1998. Quinone moieties act as electron acceptors in the reduction of humic substances by humics-reducing microorganisms[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 32(19): 372-372. |
| [18] | WU J, 2011. Carbon accumulation in paddy ecosystems in subtropical China: Evidence from landscape studies[J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 62(1): 29-34. |
| [19] | 鲍士旦, 2002. 土壤农化分析[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社:22-162. |
| BAO S D, 2000. Soil Agrochemical Analysis[M]. ThirdEdition. Beijing: China Agriculture Press:22-162. | |
| [20] | 陈志诚, 赵文君, 龚子同, 2003. 海南岛土壤发生分类类型在系统分类中的归属[J]. 土壤学报, 40(2): 170-177. |
| CHEN Z C, ZHAO W J, GONG Z T, 2003. Correlation of soil taxa of Hainan Island between chinese soil genetic classification and Chinese soil taxonomy[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 40(2): 170-177. | |
| [21] | 何伟, 白泽琳, 李一龙, 等, 2016. 溶解性有机质特性分析与来源解析的研究进展[J]. 环境科学学报, 36(2): 359-372. |
| HE W, BAI Z L, LI Y L, et al., 2016. Advances in the characteristics analysis and source identification of the dissolved organic matter[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 36(2): 359-372. | |
| [22] | 贾蓉, 2017. 水稻土中微生物发酵过程对氧化铁还原的贡献[D]. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学. |
| JIA R, 2017. Contribution of microbial fermentation to iron(III) Reduction in submerged paddy soils[D]. Xianyang: Northwest A&F University. | |
| [23] | 姜杰, 杨浈, 任谦, 等, 2015. 土壤腐殖质氧化还原电位及其相应电子转移能力分布[J]. 环境化学, 34(2): 219-224. |
| JIANG J, YANG Z, REN Q, et al., 2015. Distribution of soil humic acids redox potentials and corresponding electron transfer amounts[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 34(2): 219-224. | |
| [24] | 李红岩, 高峰, 杨敏, 2011. 微生物异化Fe(Ⅲ)还原及其作用机制研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 34(10): 100-105. |
| LI H Y, GAO F, YANG M, 2011. Review on microbial dissimilatory reduction of Fe(Ⅲ) and its mechanism[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 34(10): 100-105. | |
| [25] | 李睿, 屈明, 2004. 土壤溶解性有机质的生态环境效应[J]. 生态环境, 13(2): 271-275. |
| LI R, QU M, 2004. Effects of dissolved organic matter on environment[J]. Ecology and Environment, 13(2): 271-275. | |
| [26] | 李雅妮, 徐华成, 江和龙, 2020. 鄱阳湖水体溶解有机质分子量分布、荧光特征及对重金属分布的影响[J]. 湖泊科学, 32(4): 1029-1040. |
| LI Y N, XU H C, JIANG H L, 2020. Molecular weight distribution, fluorescence characteristics of dissolved organic matter and their effect on the distribution of heavy metals of Lake Poyang[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 32(4): 1029-1040. | |
| [27] | 梁俭, 江韬, 卢松, 等, 2016. 淹水条件下三峡库区典型消落带土壤释放DOM的光谱特征: 紫外-可见吸收光谱[J]. 环境科学, 37(7): 2496-2505. |
| LIANG J, JIANG T, LU S, et al., 2016. Spectral characteristics of dissolved organic matter (DOM) releases from soils of typical water-level fluctuation zones of Three Gorges Reservoir Areas: Fluorescence spectra[J]. Environmental Science, 37(7): 2496-2505. | |
| [28] | 刘娜娜, 李斌, 刘瑞霞, 等, 2014. 浑太水系水体中不同粒径有机胶体荧光光谱特性[J]. 环境科学, 35(11): 4103-4110. |
| LIU N N, LI B, LIU R X, 2014. Fluorescence characteristics of fractionated colloidal organic matter in freshwater from Hunhe and Taizihe Watersheds[J]. Environmental Science, 35(11): 4103-4110. | |
| [29] | 刘沛, 周卫军, 谭洁, 等, 2018. 水稻土有机碳及腐殖质结构特征的研究进展[J]. 南方农业, 12(33): 183-185. |
| LIU P, ZHOU W J, TAN J, et al., 2018. Progress in the Characterization of Paddy Soil Organic Carbon and Humus Structures[J]. South China Agriculture, 12(33): 183-185. | |
| [30] | 吕烈武, 王朝弼, 吴蔚东, 等, 2020. 海南岛典型水稻土硅形态空间分布特征及其有效性的影响因素[J]. 广东农业科学, 47(3): 81-89. |
| LV L W, WANG C B, WU W D, et al., 2020. Spatial distribution characteristics of silicon fractions and factors influencing their availability in typical paddy soils in Hainan Island[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 47(3): 81-89. | |
| [31] | 马琦琦, 李刚, 魏永, 2020. 城郊关键带土壤中溶解性有机质的光谱特性及其时空变异[J]. 环境化学, 39(2): 455-466. |
| MA Q Q, LI G, WEI Y, 2020. Spectral characteristics and spatiotemporal variation of DOM in peri-urban critical zone[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 39(2): 455-466. | |
| [32] | 曲植, 李丽娜, 贾蓉, 2018. 水稻土中水溶性有机碳对铁还原过程的贡献[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 24(2): 346-356. |
| QU Z, LI L N, JIA R, 2018. Contribution of water dissolved organic carbon to iron (Ⅲ) reduction in paddy soils[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 24(2): 346-356. | |
| [33] | 阮梦豫, 2019. 九龙江河水中溶解有机物的光学特征及其粒径分布[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学. |
| RUAN M Y, 2019. Optical characterization and size distribution of dissolved organic matter in the Jiulong River[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University. | |
| [34] | 孙正, 2019. 水稻土中铁的还原过程对于有机碳的分解的影响[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学. |
| SUN Z, 2019. The effect of iron reduction in paddy soil on decomposition of organic carbon[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University. | |
| [35] | 索慧慧, 2019. 生物炭和有机物料对水稻土DOM及厌氧铁还原过程的影响[D]. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学. |
| SUO H H, 2019. Effect of biochar and organic materials on DOM and anaerobic iron reduction in paddy soils[D]. Xianyang: Northwest A&F University. | |
| [36] | 王季斐, 2020. 不同磷含量水稻土微界面有机质转化的微观过程研究[D]. 赣州: 江西理工大学. |
| WANG J F, 2020. The microscopic process of organic matter transformation on microsurface in paddy soil with different phosphorus contents[D]. Ganzhou: Jiangxi University of Science and Technology. | |
| [37] | 王齐磊, 江韬, 赵铮, 等, 2015. 三峡库区典型农业小流域土壤溶解性有机质的紫外-可见及荧光特征[J]. 环境科学, 36(3): 879-887. |
| WANG Q L, JIANG T, ZHAO Z, et al., 2015. Ultraviolet-visible (uv-vis) and fluorescence spectral characteristics of soil dissolved organic matter (DOM) in typical agricultural watershed of Three Gorges Reservoir Region[J]. Environmental Science, 36(3): 879-887. | |
| [38] | 吴金水, 葛体达, 胡亚军, 2015. 稻田土壤关键元素的生物地球化学耦合过程及其微生物调控机制[J]. 生态学报, 35(20): 6626-6634. |
| WU J S, GE T D, HU Y J, 2015. A review on the coupling of bio-geochemical process for key elements and microbial regulation mechanisms in paddy rice Ecosystems[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35(20): 6626-6634. | |
| [39] | 吴月颖, 吉恒宽, 吴蔚东, 等, 2020. 海南北部滨海区不同土地利用模式下土壤DOM粒径分布与光谱特性[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 37(5): 654-665. |
| WU Y Y, JI H K, WU W D, et al., 2020. Size fractionation and optical properties of DOM under different land use types in the coastal area of northern Hainan Island[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 37(5): 654-665. | |
| [40] | 许金鑫, 王初, 姚东京, 等, 2020. 崇明东滩湿地土壤溶解性有机质的光谱特征研究[J/OL]. 环境工程:1-10[2020-12-05]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2097.X.20200609.1459.028.html. |
| XU J X, WANG C, YAO D J, et al., 2020. Spectral characteristics of soil dissolved organic matter in Chongming Dongtan Wetland[J/OL]. Environmental Engineering:1-10 [2020-12-05]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2097.X.20200609.1459.028.htm. | |
| [41] | 许伟, 2009. 水溶性有机物的电子转移能力及其对微生物异化铁还原影响的研究[D]. 成都: 四川师范大学. |
| XU W, 2009. Electron transfer capability of dissolved organic matter and its effects on microbial dissimilatory Fe(III) reduction[D]. Chengdu: Sichuan Normal University. | |
| [42] | 许志诚, 罗微, 洪义国, 等, 2006. 腐殖质在环境污染物生物降解中的作用研究进展[J]. 微生物学通报, 33(6): 122-127. |
| XU Z C, LUO W, HONG Y G, et al., 2006. Recent development in effects of the humic substances on the biodergradation of priority pollutants in environment[J]. Microbiology China, 33(6): 122-127. | |
| [43] | 易维洁, 曲东, 黄婉玉, 等, 2010. 淹水培养时间对水稻土中Fe(III)还原能力的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 29(9): 1723-1729. |
| YI W J, QU D, HUANG W Y, et al., 2010. Effect of Flooding Time on Dissimilatory Iron (III) Reduction in Paddy Soil[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 29(9): 1723-1729. | |
| [44] | 周江敏, 陈华林, 代静玉, 2011. 溶解性有机质在土壤固碳中的意义[J]. 土壤通报, 42(6): 1508-1514. |
| ZHOU J M, CHEN H L, DAI J Y, 2011. Significance of dissolved organic matter on carbon sequestration in soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 42(6): 1508-1514. |
| [1] | DU Dandan, GAO Ruizhong, FANG Lijing, XIE Longmei. Spatial Variation of Soil Heavy Metals and Their Responses to Physicochemical Factors of Salt Lake Basin in Arid Area [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(6): 1123-1132. |
| [2] | LI Shanjia, WANG Xingmin, LIU Haifeng, SUN Mengge, LEI Yuxin. Diversity of Desert Plants in Hexi Corridor and Its Response to Environmental Factors [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 429-438. |
| [3] | DONG Leheng, WANG Xugang, CHEN Manjia, WANG Zihao, SUN Lirong, SHI Zhaoyong, Wu Qiqi. Interaction of Iron Redox and Cu Activities in Calcareous Paddy Soil under Light and Dark Condition [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(7): 1448-1455. |
| [4] | MA Huiying, LI Xinzhu, MA Xinyu, GONG Lu. Characteristics and Driving Factors of Soil Organic Carbon Fractions under Different Vegetation Types of the mid-Northern Piedmont of the Tianshan Mountains, Xinjiang [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(6): 1124-1131. |
| [5] | CHEN Yao, LI Yunhong, SHAO Yingnan, LIU Yulong, LIU Yankun. Study on Species Diversity and Soil Physical and Chemical Characteristics of Broad-leaved Pinus koraiensis Forest [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(4): 679-687. |
| [6] | HE Xiaojia, FENG Shuhua, JIANG Ming, LI Mingrui, ZHAN Fangdong, LI Yuan, HE Yongmei. Effects of UV-B Radiation on Conversion of Active Organic Carbon and Methane Production Potential of Rice Rhizosphere Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 556-564. |
| [7] | HAN Xin, YUAN Chunyang, LI Jihong, HONG Zongwen, LIU Xuan, DU Ting, LI Han, YOU Chenming, TAN Bo, ZHU Peng, XU Zhenfeng. Effects of Tree Species and Soil Layers on Soil Extractable Nitrogen Content [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(11): 2143-2151. |
| [8] | SHI Hanzhi, LIU Fan, HUANG Yongdong, WU Zhichao, LI Furong, XU Shoujun, DENG Tenghaobo, WEN Dian, WANG Xu, WANG Fuhua, JIANG Qi, DU Ruiying. Effects of Dynamic Change of Dissolved Organic Matter in Soil on Water-Soluble Copper [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(9): 1896-1902. |
| [9] | GAO Feng, CHEN Xiaoling, YANG Wenfu, SHI Lijiang, WANG Wenwen. Study on the Absorption Characteristics of Different Types of Water Particles and CDOM in Summer in Taiyuan [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(7): 1455-1469. |
| [10] | HOU Suxia, LEI Xuyang, ZHANG Hui, DING Shujie, CUI Guangyu. Analysis of the Effect of Temperature on Vermicomposting of Municipal Sludge Based on EEM and PCR-DGGE [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(5): 1060-1068. |
| [11] | MA Feiyang, FAN Tuantuan, SUN Xiaoping, MING Junde, WANG Shitong, ZHANG Yinghao, YAO Xin. DOM Fluorescence Characteristics and Sources in Different Regions of Dongting Lake [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(12): 2370-2379. |
| [12] | JIANG Nihao, ZHANG Shihan. Interspecific Association and Environmental Interpretation of Dominant Herbaceous Species in Pinus yunnanensis Forest in the Western Suburbs of Chuxiong City [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(11): 2109-2120. |
| [13] | LIN Li, DAI Lei, LIN Zebei, WU Jitong, YAN Wei, WANG Zhijie. Plant Diversity and Its Relationship with Soil Physicochemical Properties of Urban Forest Communities in Central Guizhou [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(11): 2130-2141. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
