Ecology and Environment ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (3): 556-564.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.03.014
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
HE Xiaojia( ), FENG Shuhua, JIANG Ming, LI Mingrui, ZHAN Fangdong, LI Yuan, HE Yongmei*(
), FENG Shuhua, JIANG Ming, LI Mingrui, ZHAN Fangdong, LI Yuan, HE Yongmei*( )
)
Received:2021-03-22
Online:2022-03-18
Published:2022-05-25
Contact:
HE Yongmei
贺晓佳( ), 冯书华, 蒋明, 李明锐, 湛方栋, 李元, 何永美*(
), 冯书华, 蒋明, 李明锐, 湛方栋, 李元, 何永美*( )
)
通讯作者:
何永美
作者简介:贺晓佳(1997年生),女,硕士研究生,主要从事紫外辐射生态研究。E-mail: 1974507515@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
HE Xiaojia, FENG Shuhua, JIANG Ming, LI Mingrui, ZHAN Fangdong, LI Yuan, HE Yongmei. Effects of UV-B Radiation on Conversion of Active Organic Carbon and Methane Production Potential of Rice Rhizosphere Soil[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 556-564.
贺晓佳, 冯书华, 蒋明, 李明锐, 湛方栋, 李元, 何永美. UV-B辐射对水稻根际土壤活性有机碳转化和产甲烷潜力的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 556-564.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.03.014
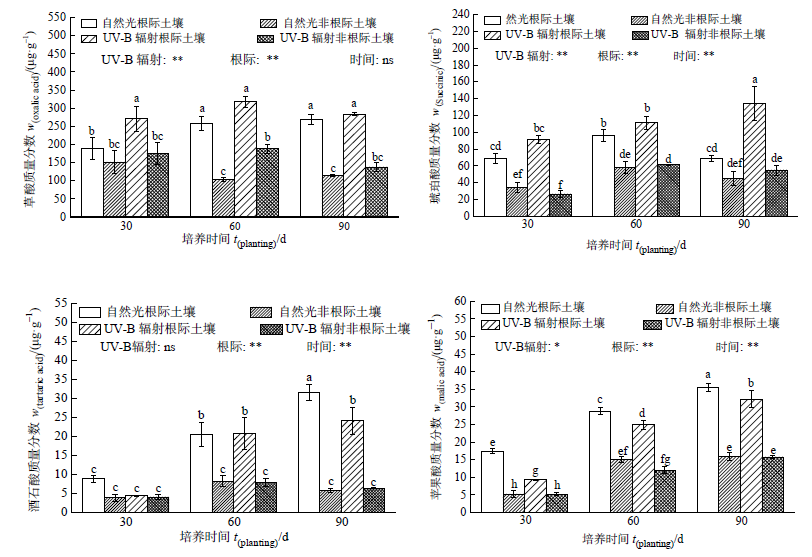
Figure 1 Effects of UV-B Radiation on the Content of Low Molecular Weight Organic Acids in rice Rhizosphere and non-Rhizosphere Soil Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments during the three period (P<0.05), * indicates significant effect (P<0.05), ** indicates extremely significant effect (P<0.01). ns indicate no effect, n=4. The same below
| 有机酸 Organic acid | 甲烷排放通量 Methane emission flux | 微生物量碳 Microbial biomass carbon | 可溶性有机碳 Dissolved organic carbon |
|---|---|---|---|
| 草酸 Oxalic acid | 0.585* | 0.249 | 0.403 |
| 苹果酸 Malic acid | 0.535* | 0.791** | 0.534* |
| 琥珀酸 Succinic acid | 0.387 | 0.487 | 0.685** |
| 酒石酸 Tartaric acid | 0.304 | 0.550* | 0.490 |
Table 1 Correlation between organic acid content and soil active organic carbon content and methane emission
| 有机酸 Organic acid | 甲烷排放通量 Methane emission flux | 微生物量碳 Microbial biomass carbon | 可溶性有机碳 Dissolved organic carbon |
|---|---|---|---|
| 草酸 Oxalic acid | 0.585* | 0.249 | 0.403 |
| 苹果酸 Malic acid | 0.535* | 0.791** | 0.534* |
| 琥珀酸 Succinic acid | 0.387 | 0.487 | 0.685** |
| 酒石酸 Tartaric acid | 0.304 | 0.550* | 0.490 |
| 指标 Target | 多酚氧化酶 Polyhenol oxidase activity | 蔗糖酶 Sucrose enzyme activity | 过氧化氢酶 Catalase activity | 微生物量碳 Microbial biomass carbon | 可溶性有机碳 Dissolved organic carbon | 易氧化有机碳 Labile organic carbon |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甲烷排放通量 Methane emission flux | -0.930** | 0.872* | 0.988** | -0.930** | -0.907* | -0.884* |
| 多酚氧化酶 Polyhenol oxidase activity | — | — | — | 0.778 | 0.718 | 0.803 |
| 蔗糖酶 Sucrose enzyme activity | — | — | — | -0.863 | -0.72 | -0.589 |
| 过氧化氢酶 Catalase activity | — | — | — | -0.922** | -0.860* | -0.827* |
Table 2 Correlation between methane emission and enzymatic active and soil active organic carbon content
| 指标 Target | 多酚氧化酶 Polyhenol oxidase activity | 蔗糖酶 Sucrose enzyme activity | 过氧化氢酶 Catalase activity | 微生物量碳 Microbial biomass carbon | 可溶性有机碳 Dissolved organic carbon | 易氧化有机碳 Labile organic carbon |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甲烷排放通量 Methane emission flux | -0.930** | 0.872* | 0.988** | -0.930** | -0.907* | -0.884* |
| 多酚氧化酶 Polyhenol oxidase activity | — | — | — | 0.778 | 0.718 | 0.803 |
| 蔗糖酶 Sucrose enzyme activity | — | — | — | -0.863 | -0.72 | -0.589 |
| 过氧化氢酶 Catalase activity | — | — | — | -0.922** | -0.860* | -0.827* |
| [1] |
ALVAREZ G, SHAHZAD T, ANDANSON L, et al., 2018. Catalytic power of enzymes decreases with temperature: New insights for understanding soil C cycling and microbial ecology under warming[J]. Global Change Biology, 24(9): 4238-4250.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
BURNS R G, DEFOREST J L, MARXSEN J, et al., 2013. Soil enzymes in a changing environment: current knowledge and future directions[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 58: 216-234.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
BUSSELL J S, GWYNN-JONES D, GRIFFITH G W, et al., 2012. Above and below-ground responses of Calamagrostis purpurea to UV-B radiation and elevated CO2 under phosphorus limitation[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 145(4): 619-628.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
CHOUDHARY K K, PANDEY D, AGRAWAL S B, 2013. Deterioration of rhizospheric soil health due to elevated ultraviolet-B[J]. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 59(10): 1419-1437.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
HE Y M, ZHAN F D, LI Y, et al., 2016. Effect of enhanced UV-B radiation on methane emission in a paddy field and rice root exudation of low-molecular-weight organic acids[J]. Photochemical and Photobiological Sciences, 15(6): 735-743.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
JIANG Y, WANG L L, YAN X J, et al., 2013. Super Rice Cropping Will Enhance Rice Yield and Reduce CH4 Emission: A Case Study in Nanjing, China[J]. Rice Science, 20(6): 427-433.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
KERDCHOECHUEN O, 2005. Methane emission in four rice varieties as related to sugars and organic acids of roots and root exudates and biomass yield[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 108(2): 155-163.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
KOFFI E N, BERGAMASCHI P, ALKAMA R, et al., 2020. An observation-constrained assessment of the climate sensitivity and future trajectories of wetland methane emissions[J]. Science Advances, DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aay4444.
DOI |
| [9] |
LEMANOWICZ J, 2019. Activity of selected enzymes as markers of ecotoxicity in technogenic salinization soils[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(3): 13014-13024.
DOI URL |
| [10] | LIANG Y, ZOU C H, LI JD, et al., 2019. Research Progress of Medicinal Secondary Metabolites and Gene Cloning of Dendrobium officinale[J]. Medicinal Plant, 10(3): 16-18, 23. |
| [11] |
LING K, CHU L M, 2018. Subtropical urban turfs: Carbon and nitrogen pools and the role of enzyme activity[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 65(3): 18-28.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
LOU Y S, GU X T, ZHOU W L, 2017. Effect of elevated UV-B radiation on microbial biomass C and soil respiration in different barley cultivars under field conditions[J]. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 228(3): 1-8.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
MONTIEL-ROZAS M M, MADEJON E, MADEJON P, 2016. Effect of heavy metals and organic matter on root exudates (low molecular weight organic acids) of herbaceous species: An assessment in sand and soil conditions under different levels of contamination[J]. Environmental Pollution, 216: 273-281.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
MRSKY S K, HAAPALA J K, RINNAN R, et al., 2012. Minor long-term effects of ultraviolet-B radiation on methane dynamics of a subarctic fen in Northern Finland[J]. Biogeochemistry, 108(1-3): 233-243.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
NAYAK D R, ADHYA T K, BABU Y J, et al., 2006. Methane emission from a flooded field of Eastern India as influenced by planting date and age of rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings[J]. Agriculture Ecosystems and Environment, 115(1): 79-87.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
RINNAN R, GEHRKE C, MICHELSEN A, 2006. Two mire species respond differently to enhanced ultraviolet-B radiation: Effects on biomass allocation and root exudation[J]. New Phytologist, 169(4): 809-818.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
SAMUEL A F, BONNETT, NICK O, 2006. Seasonal variations in decomposition processes in a valley bottom riparian peatland[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 370(2-3): 561-573.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
SINGH S, KUMARI R, AGRAWAL M, et al., 2012. Differential response of radish plants to supplemental ultraviolet-B radiation under varying NPK levels: Chlorophyll fluorescence, gas exchange and antioxidants[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 145(3): 474-484.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
STEPNIEWSKA Z, WOLINSKA A, ZIOMEK J, 2009. Response of soil catalase activity to chromium contamination[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 21(8): 1142-1147.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
SERRANOS N, SARRIA G Y, DENDOOVEN L, et al., 2014. Methanogenesis and methanotrophy in soil: A review[J]. Pedosphere, 24(3): 291-307.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
XIAO M, WU F C, 2014. A review of environmental characteristics and effects of low-molecular weight organic acids in the surface ecosystem[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 26(5): 935-954.
DOI URL |
| [22] | 蔡昆争, 骆世明, 段舜山, 2003. 水稻根系在根袋处理条件下对氮养分的反应[J]. 生态学报, 23(6): 1109-1116. |
| CAI K Z, LUO S M, DUAN S S, 2003. Response of rice root system to nitrogen under root bag treatment[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 23(6): 1109-1116. | |
| [23] | 戴凌燕, 唐呈瑞, 殷奎德, 等, 2015. 苏打盐碱胁迫对甜高粱植株有机酸含量的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 34(3): 681-687. |
| DAI L Y, TANG C R, YIN K D, et al., 2015. Effects of saline-alkali stress on organic acid content in sweet sorghum plants[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 34(3): 681-687. | |
| [24] | 耿玉清, 王冬梅, 2012. 土壤水解酶活性测定方法的研究进展[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 20(4): 387-394. |
| GENG Y Q, WANG D M, 2012. Research on the method of the study of soil hydrolytic enzyme activity[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecological Agriculture, 20(4): 387-394. | |
| [25] | 龚松贵, 王兴祥, 张桃林, 2009. 低分子量有机酸对红壤磷酸单酯酶活性的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 46(6): 1089-1095. |
| GONG S G, WANG X X, ZHANG T L, 2009. Effects of low molecular weight organic acids on phosphomonoesterase activity in red soil[J]. Journal of Soil, 46(6): 1089-1095. | |
| [26] | 关松荫, 1987. 土壤酶及其研究法[M]. 北京: 农业出版社: 123-339. |
| GUAN S Y, 1986. Soil enzyme and its research method[M]. Beijing: Agricultural Press: 123-339. | |
| [27] | 郭乾坤, 梁国庆, 周卫, 等, 2020. 长期有机培肥提高红壤性水稻土生物学特性及水稻产量的微生物学机制[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 26(3): 492-501. |
| GUO Q K, LIANG G Q, ZHOU W, et al., 2020. Microbiological mechanism of long-term organic fertilizer cultivation to improve the biological characteristics and rice yield of red paddy soil[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 26(3): 492-501. | |
| [28] | 何永美, 湛方栋, 吴炯, 等, 2016. UV-B辐射对元阳梯田水稻根系LMWOAs分泌量和根际微生物数量的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 35(4): 613-619. |
| HE Y M, ZHAN F D, WU J, et al., 2016. Effects of UV-B radiation on the secretion of LDWOAs in rice root system and the number of rhizosphere microorganisms in Yuanyang terraces[J]. Journal of Agriculture Environment Science, 35(4): 613-619. | |
| [29] | 胡正华, 凌慧, 陈书涛, 等, 2011. UV-B增强对稻田呼吸速率、CH4和N2O排放的影响[J]. 环境科学, 32(10): 3018-3022. |
| HU Z H, LING H, CHEN S T, et al., 2011. UV-B enhanced effects on respiration rate, CH4 and N2O emissions in rice fields[J]. Environmental Science, 32(10): 3018-3022. | |
| [30] | 蒋梦蝶, 王秋敏, 徐鹏, 等, 2017a. 不同水分梯度下UV-B辐射对2个稻田土壤碳氮转化的影响[J]. 环境科学, 38(11): 4819-4827. |
| JIANG M D, WANG Q M, XU P, et al., 2017a. Effects of UV-B radiation on carbon and nitrogen transformation in two paddy fields under different water gradients[J]. Environmental Science, 38(11): 4819-4827. | |
| [31] | 蒋梦蝶, 王秋敏, 徐鹏, 等, 2017b. UV-B辐射增强对土壤有机碳稳定性的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 31(2): 171-176. |
| JIANG M D, WANG Q M, XU P, et al., 2017b. Effects of UV-B radiation enhancement on soil organic carbon stability[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 31(2): 171-176. | |
| [32] | 李昌晓, 魏虹, 吕茜, 等, 2010. 水分胁迫对枫杨幼苗生长及根系草酸与酒石酸含量的影响[J]. 林业科学, 46(11): 81-88. |
| LI C X, WEI H, LÜ Q, et al., 2010. Effects of water stress on growth and root oxalic acid and tartaric acid content of Chinese poplar seedlings[J]. Science Forestry, 46(11):81-88. | |
| [33] | 李果梅, 王殳屹, 史奕, 等, 2008. O3浓度升高及温度对麦田土壤酶活性及酚酸类物质含量的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 27(1): 121-125. |
| LI G M, WANG D Y, SHI Y, et al., 2008. Effects of elevated O3 concentration and temperature on soil enzyme activity and phenolic acid content in wheat fields[J]. Journal of Agro-Environmental Science, 27(1): 121-125. | |
| [34] | 李小飞, 侯立军, 刘敏, 2019. 长江口沉积物甲烷产生潜力与产甲烷菌群落特征[J]. 环境科学学报, 39(5): 1682-1690. |
| LI X F, HOU L J, LIU M, 2019. Methane production potential and community characteristics of methanogens in sediments of the Yangtze estuary[J]. Journal of Environmental Science, 39(5): 1682-1690. | |
| [35] | 李新华, 郭洪海, 朱振林, 等, 2016. 不同秸秆还田模式对土壤有机碳及其活性组分的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 32(9): 130-135. |
| LI X H, GUO H H, ZHU Z L, et al., 2016. Effects of different straw mulching modes on soil organic carbon and its active components[J]. Journal of Agricultural Engineering, 32(9): 130-135. | |
| [36] | 林启美, 吴玉光, 刘焕龙, 1999. 熏蒸法测定土壤微生物量碳的改进[J]. 生态学杂志, 18(2): 63-66. |
| LIN Q M, WU Y G, LIU H L, 1999. Improvement of soil microbial biomass carbon determination by fumigation method[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 18(2): 63-66. | |
| [37] | 刘洪升, 宋秋华, 李凤民, 2002. 根分泌物对根际矿物营养及根际微生物的效应[J]. 西北植物学报, 22(3): 693-702. |
| LIU H S, SONG Q H, LI F M, 2002. Effects of root secretions on rhizosphere mineral nutrition and rhizosphere microorganisms[J]. Northwest Journal of Botany, 22(3): 693-702. | |
| [38] | 娄运生, 顾夏天, 周文鳞, 等, 2012. UV-B辐射增强对不同品种大麦田土壤微生物量碳和土壤呼吸的影响[J]. 中国农业气象, 33(4): 505-511. |
| LOU Y S, GU X T, ZHOU W L, et al., 2012. Effects of UV-B radiation enhancement on soil microbial biomass carbon and soil respiration in different barley varieties[J]. China Agricultural Meteorology, 33(4): 505-511. | |
| [39] | 娄运生, 周文鳞, 2012. UV-B辐射增强对抗除草剂转基因水稻CH4排放的影响[J]. 生态学报, 32(15): 4731-4736. |
|
LOU Y S, ZHOU W L, 2012. Effect of elevated ultraviolet-B (UV-B) radiation on CH4 emission in herbicide resistant transgenic rice from a paddy soil[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32(15): 4731-4736.
DOI URL |
|
| [40] | 吕志伟, 万国峰, 张朋, 等, 2012. CO2倍增和UV-B辐射增强对大豆根际氨氧化细菌数量及土壤酶活的影响[J]. 大豆科学, 31(1): 69-72. |
| LÜ Z W, WAN G F, ZHANG P, et al., 2012. Effects of CO2 doubling and UV-B radiation enhancement on the number of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and soil enzyme activity in soybean rhizosphere[J]. Soybean Science, 31(1): 69-72. | |
| [41] | 万忠梅, 宋长春, 2009. 土壤酶活性对生态环境的响应研究进展[J]. 土壤通报, 40(4): 951-956. |
| WAN Z M, SONG C C, 2009. Research progress of soil enzyme activity in response to ecological environment[J]. Soil Bulletin, 40(4): 951-956. | |
| [42] | 王灿, 李虹茹, 湛方栋, 等, 2018. UV-B辐射对元阳梯田稻田土壤活性有机碳含量与温室气体排放的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 37(2): 383-391. |
| WANG C, LI H R, ZHAN F D, et al., 2018. Effects of UV-B radiation on soil active organic carbon content and greenhouse gas emissions in rice paddies in Yuanyang terrace[J]. Chinese Journal of Agro- Environmental Science, 37(2): 383-391. | |
| [43] | 巫芯宇, 廖和平, 杨伟, 2013. 耕作方式对稻田土壤有机碳与易氧化有机碳的影响[J]. 农机化研究, 35(1): 184-188. |
| WU X Y, LIAO H P, YANG W, 2013. Effects of tillage on organic carbon and easily oxidized organic carbon in paddy soil[J]. Agricultural Mechanization Research, 35(1): 184-188. | |
| [44] | 吴家梅, 纪雄辉, 霍莲杰, 等, 2013. 稻田土壤氧化态有机碳组分变化及其与甲烷排放的关联性[J]. 生态学报, 33(15): 4599-4607. |
|
WU J M, JI X H, HUO L J, et al., 2013. Variation of organic carbon components in soil oxidation state in rice field and its correlation with methane emissions[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33(15): 4599-4607.
DOI URL |
|
| [45] | 徐渭渭, 何永美, 湛方栋, 等, 2015. UV-B辐射增强对元阳哈尼梯田稻田CH4排放规律的影响[J]. 生态学报, 35(5): 1329-1336. |
| XU W W, HE Y M, ZHAN F D, et al., 2015. Effects of UV-B radiation enhancement on CH4 emission in rice field of hani rice terrace in yuanyang[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35(5): 1329-1336. | |
| [46] | 许超, 林小方, 夏北成, 2010. 玉米幼苗根系分泌物对芘污染的响应[J]. 生态学报, 30(12): 3280-3288. |
| XU C, LIN X F, XIA B C, 2010. Response of maize seedling root exudates to pyrene pollution[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30(12): 3280-3288. | |
| [47] | 严昌荣, 刘恩科, 何文倩, 等, 2010. 耕作措施对土壤有机碳和活性有机碳的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料 (6): 58-63. |
| YAN C R, LIU N K, HE W Q, et al., 2010. Effects of tillage on soil organic carbon and active organic carbon[J]. Chinese Soil and Fertilizer (6): 58-63. | |
| [48] | 杨博涵, 欧阳亚南, 闵卓, 等, 2019. UV-B辐射对葡萄叶片中酚类物质含量及显微结构的影响[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 47(5): 59-66. |
| YANG B H, OUYANG Y N, MIN Z, et al., 2019. Effects of UV-B radiation on phenolic content and microstructure in grape leaves[J]. Journal of Northwest Agriculture and Forestry (Natural Science Edition), 47(5): 59-66. | |
| [49] | 张飞, 罗学刚, 王佳, 2015. U及伴生重金属Mn、Pb对土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 环境科学与技术, 38(3): 44-49. |
| ZHANG F, LUO X G, WANG J, 2015. Effects of U and associated heavy metals Mn and Pb on soil enzyme activities[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 38(3): 44-49. | |
| [50] | 张慧玲, 宋新章, 哀建国, 等, 2010. 增强紫外线-B辐射对凋落物分解的影响研究综述[J]. 浙江林学院学报, 27(1): 134-142. |
| ZHANG H L, SONG X Z, AI J G, et al., 2010. A review of the effects of enhanced UV-B radiation on litter decomposition[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Forestry College, 27(1): 134-142. | |
| [51] | 张令瑄, 谢婷婷, 王瑾, 等, 2016. 大田条件下UV-B辐射增强对大豆根际土壤相关指标的影响[J]. 江苏农业学报, 32(1): 118-122. |
| ZHANG L Z, XIE T T, WANG J, et al., 2016. Effect of enhanced UV-B radiation on soybean rhizosphere soil-related indexes under field conditions[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Journal, 32(1): 118-122. | |
| [52] | 张英英, 蔡立群, 武均, 等, 2017. 不同耕作措施下陇中黄土高原旱作农田土壤活性有机碳组分及其与酶活性间的关系[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 35(1): 1-7. |
| ZHANG Y Y, CAI L Q, WU J, et al., 2017. Soil active organic carbon components and their relationship with enzyme activities in dry farmland of the Longzhong Loess Plateau under different cultivation practices[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 35(1): 1-7. | |
| [53] | 赵鹏志, 陈祥伟, 杨小燕, 等, 2018. 低分子有机酸对东北黑土酶活性与养分关系的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 42(1): 105-112. |
| ZHAO P Z, CHEN X W, YANG X Y, et al., 2018. Effect of low molecular organic acids on the relationship between enzyme activities and nutrients in black soil of Northeast China[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 42(1): 105-112. | |
| [54] | 赵仁竹, 汤洁, 梁爽, 等, 2015. 吉林西部盐碱田土壤蔗糖酶活性和有机碳分布特征及其相关关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 24(2): 244-249. |
| ZHAO R Z, TANG J, LIANG S, et al., 2015. Distribution of soil organic carbon and invertase activity and its correlation in saline-alkali paddy field in west Jilin[J]. Journal of Ecology and Environment, 24(2): 244-249. | |
| [55] | 肇思迪, 娄运生, 张祎玮, 等, 2017. UV-B增强下施硅对稻田CH4和N2O排放及其增温潜势的影响[J]. 生态学报, 37(14): 4715-4724. |
| ZHAO S D, LOU Y S, ZHANG Y W, et al., 2017. Effects of silicon application on the emission of CH4and N2O from rice fields and their heating potential under UV-B enhancement[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37(14): 4715-4724. | |
| [56] | 周艳翔, 吕茂奎, 谢锦升, 等, 2013. 深层土壤有机碳的来源、特征与稳定性[J]. 亚热带资源与环境学报, 8(1): 48-55. |
| ZHOU Y X, LÜ M K, XIE J S, et al., 2013. Sources, characteristics and stability of organic carbon in deep soil[J]. Journal of Subtropical Resources and Environment, 8(1): 48-55. | |
| [57] | 张玉铭, 胡春胜, 张佳宝, 等, 2011. 农田土壤主要温室气体 (CO2、CH4、N2O) 的源/汇强度及其温室效应研究进展[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 19(4): 966-975. |
| ZHANG Y M, HU C S, ZHANG J B, et al., 2011. Research progress on source/sink intensity of major greenhouse gases (CO2, CH4, N2O) in farmland soil and their greenhouse effect[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology and Agriculture, 19(4): 966-975. | |
| [58] | 钟娟, 傅志强, 刘莉, 等, 2017. 水稻植株甲烷传输能力与根系特性的相关性分析[J]. 作物杂志 (4): 105-112. |
| ZHONG J, FU Z Q, LIU L, et al., 2017. Correlation analysis between methane transport capacity and root characteristics of rice plants[J]. Journal of Crops (4): 105-112. |
| [1] | DONG Leheng, WANG Xugang, CHEN Manjia, WANG Zihao, SUN Lirong, SHI Zhaoyong, Wu Qiqi. Interaction of Iron Redox and Cu Activities in Calcareous Paddy Soil under Light and Dark Condition [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(7): 1448-1455. |
| [2] | CHEN Si, WANG Can, LI Xiang, Li Mingrui, ZHAN Fangdong, LI Yuan, ZU Yanquan, HE Yongmei. Effects of Different UV-B Radiation Levels on Soil Enzyme Activities, Active Organic Carbon Content and Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Paddy Fields [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(6): 1260-1268. |
| [3] | HUANG Cheng, WU Yueying, JI Hengkuan, CHEN Liming, LI Beiying, FU Chuanliang, LI Jianhong, WU Weidong, WU Zhipeng. Response of Iron Reduction Characteristics to DOM Molecular Properties under Anaerobic Conditions in Typical Paddy Soils of Hainan Island [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(5): 957-967. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
