Ecology and Environment ›› 2020, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (1): 97-104.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2020.01.011
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Shasha( ), LI Aiqin, WANG Huirong, WANG Jingjing, XU Xiaoniu*(
), LI Aiqin, WANG Huirong, WANG Jingjing, XU Xiaoniu*( )
)
Received:2019-05-20
Online:2020-01-18
Published:2020-03-09
Contact:
XU Xiaoniu
通讯作者:
徐小牛
作者简介:张莎莎(1994年生),女,硕士,主要从事森林生态学研究。E-mail: 247499746@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
ZHANG Shasha, LI Aiqin, WANG Huirong, WANG Jingjing, XU Xiaoniu. Ecological Stoichiometry of Soil Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Cunninghamia lanceolata Plantation Across An Elevation Gradient[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2020, 29(1): 97-104.
张莎莎, 李爱琴, 王会荣, 王晶晶, 徐小牛. 不同海拔杉木人工林土壤碳氮磷生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2020, 29(1): 97-104.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2020.01.011
| 林龄 Age of stand (26‒35 a) | 土层 Soil layer (0‒30 cm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 海拔梯度 Elevation gradient/ m | 林分密度 Stand Density/ (DBH≥5 cm, stem∙hm-2) | 平均胸径 Average DBH/ cm | 平均树高 Average height/ m | 土壤 pH Soil pH | 含水量 Soil moisture/ % | 土壤容重(体积质量) Soil bulk density/ (g∙cm-3) | |
| 750 | 1129±49 | 20.0±1.58 | 13.5±1.02 | 4.64±0.02 | 35.95±0.61 | 0.76±0.05 | |
| 850 | 2216±145 | 17.6±0.63 | 12.5±0.87 | 5.07±0.06 | 17.28±2.63 | 0.92±0.12 | |
| 1000 | 1584±129 | 17.5±0.94 | 12.1±0.24 | 4.80±0.04 | 32.16±1.06 | 0.91±0.09 | |
| 1150 | 2150±58 | 17.7±2.03 | 11.6±0.66 | 4.70±0.03 | 42.45±4.03 | 0.88±0.05 | |
Table 1 Basic situation of sample plots
| 林龄 Age of stand (26‒35 a) | 土层 Soil layer (0‒30 cm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 海拔梯度 Elevation gradient/ m | 林分密度 Stand Density/ (DBH≥5 cm, stem∙hm-2) | 平均胸径 Average DBH/ cm | 平均树高 Average height/ m | 土壤 pH Soil pH | 含水量 Soil moisture/ % | 土壤容重(体积质量) Soil bulk density/ (g∙cm-3) | |
| 750 | 1129±49 | 20.0±1.58 | 13.5±1.02 | 4.64±0.02 | 35.95±0.61 | 0.76±0.05 | |
| 850 | 2216±145 | 17.6±0.63 | 12.5±0.87 | 5.07±0.06 | 17.28±2.63 | 0.92±0.12 | |
| 1000 | 1584±129 | 17.5±0.94 | 12.1±0.24 | 4.80±0.04 | 32.16±1.06 | 0.91±0.09 | |
| 1150 | 2150±58 | 17.7±2.03 | 11.6±0.66 | 4.70±0.03 | 42.45±4.03 | 0.88±0.05 | |
| 海拔梯度 Elevation gradient/m | ω(SOC)/(g·kg-1) | ω(TN)/(g·kg-1) | ω(TP)/(g·kg-1) | ω(C)/ω(N | ω(C)/ω(P) | ω(N)/ω(P) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 750 | 35.44±2.81 | 2.23±0.16 | 0.55±0.03 | 15.79±0.21 | 67.19±5.41 | 4.23±0.31 |
| 850 | 21.28±2.60 | 1.17±0.17 | 1.32±0.06 | 19.26±0.53 | 16.53±2.08 | 0.91±0.13 |
| 1000 | 28.96±2.14 | 1.73±0.14 | 0.96±0.34 | 16.99±0.34 | 31.95±3.02 | 1.90±0.18 |
| 1150 | 32.36±3.00 | 1.92±0.17 | 0.61±0.05 | 16.73±0.15 | 58.69±5.45 | 3.48±0.31 |
| 平均值 | 30.26 | 1.82 | 0.82 | 17.01 | 46.05 | 2.79 |
Table 2 Soil C, N, P content and their stoichiometry in Cunninghamia lanceolata plantations
| 海拔梯度 Elevation gradient/m | ω(SOC)/(g·kg-1) | ω(TN)/(g·kg-1) | ω(TP)/(g·kg-1) | ω(C)/ω(N | ω(C)/ω(P) | ω(N)/ω(P) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 750 | 35.44±2.81 | 2.23±0.16 | 0.55±0.03 | 15.79±0.21 | 67.19±5.41 | 4.23±0.31 |
| 850 | 21.28±2.60 | 1.17±0.17 | 1.32±0.06 | 19.26±0.53 | 16.53±2.08 | 0.91±0.13 |
| 1000 | 28.96±2.14 | 1.73±0.14 | 0.96±0.34 | 16.99±0.34 | 31.95±3.02 | 1.90±0.18 |
| 1150 | 32.36±3.00 | 1.92±0.17 | 0.61±0.05 | 16.73±0.15 | 58.69±5.45 | 3.48±0.31 |
| 平均值 | 30.26 | 1.82 | 0.82 | 17.01 | 46.05 | 2.79 |
| 因素 Factor | F (and P) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ω(SOC) | ω(TN) | ω(TP) | ω(C)/ω(N) | ω(C)/ω(P) | ω(N)/ω(P) | |
| 土层 Soil depth | 42.20(<0.01) | 42.87(<0.01) | 2.23(0.12) | 2.99(<0.01) | 9.28(<0.01) | 8.93(<0.01) |
| 海拔 Elevation gradient | 7.91(<0.01) | 12.34(<0.01) | 53.54(<0.01) | 23.79(0.55) | 27.85(<0.01) | 33.42(<0.01) |
| 土层×海拔 Soil depth×Elevation gradient | 0.39(0.89) | 0.60(0.733) | 0.035(1.00) | 5.06(<0.01) | 0.47(0.83) | 0.55(0.77) |
Table 3 ANOVA results for the effects of elevational gradient and soil depth on soil C, N, P content and their ecological stoichiometric ratios
| 因素 Factor | F (and P) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ω(SOC) | ω(TN) | ω(TP) | ω(C)/ω(N) | ω(C)/ω(P) | ω(N)/ω(P) | |
| 土层 Soil depth | 42.20(<0.01) | 42.87(<0.01) | 2.23(0.12) | 2.99(<0.01) | 9.28(<0.01) | 8.93(<0.01) |
| 海拔 Elevation gradient | 7.91(<0.01) | 12.34(<0.01) | 53.54(<0.01) | 23.79(0.55) | 27.85(<0.01) | 33.42(<0.01) |
| 土层×海拔 Soil depth×Elevation gradient | 0.39(0.89) | 0.60(0.733) | 0.035(1.00) | 5.06(<0.01) | 0.47(0.83) | 0.55(0.77) |
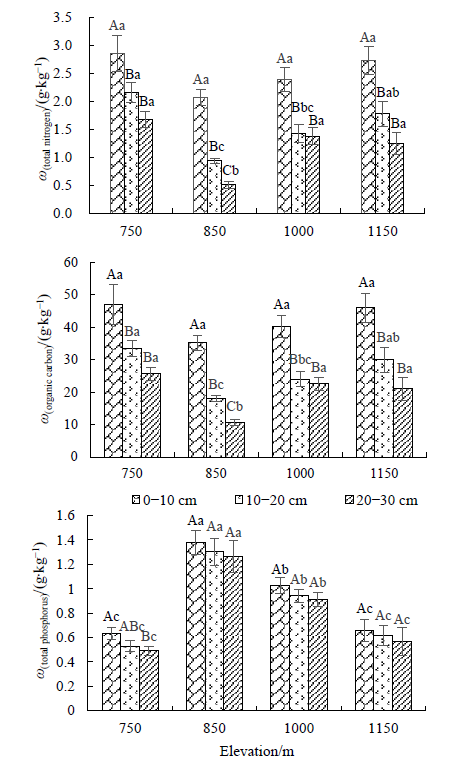
Fig. 1 Content of organic carbon, total nitrogen and total phosphorus in soil with different elevation gradient Different capital letters indicate significant differences between different soil layers at the same elevation (P<0.05), and different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between the different soil layers at different altitudes (P<0.05), the same below
| [1] | CHAPIN F S I, MATSON P A I, MOONEY H A, 2011. Principles of Terrestrial Ecosystem Ecology[M]. Berlin: Springer Verlag: 69-397. |
| [2] |
CHEN X W, LI B L. 2003. Change in soil carbon and nutrient storage after human disturbance of a primary koreanpine forest in northeast china[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 186(1-3): 197-206.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
CORYC C, DANIEL L, 2007. C꞉N꞉P stoichiometry in soil: is there a “Redfield ratio” for the microbial biomass[J]. Biogeochemistry, 85(3): 235-252.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
DON A, SCHUMACHER J, SCHERER-LORENZEN M, 2007. Spatial and vertical variation of soil carbon at two grassland sites-implications for measuring soil carbon stocks[J]. Geoderma, 141(3-4): 272-282.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
FAMIGLIETT J S, RUDNICKI J W, RODELL M, 1998. Variability in surface moisture content along a hillslope transect: Rattlesnake Hill, Texas[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 210(1-4): 259-281.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
GÜSEWELL S, KOERSELMAN W, VERHOEVEN J T A, 2003. Biomass N꞉P ratios as indicators of nutrient limitation for plant populations in wetlands[J]. Ecological Applications, 13(2): 372-384.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
HOBBIE S E, GOUGH L, 2016. Foliar and soil nutrients in tundra on glacial landscapes of contrasting ages in northern Alaska[J]. Oecologia, 131(3): 453-462.
DOI URL |
| [8] | LIU M, LI Z, ZHANG T, 2016. Changes of soil ecological stoichiometric ratios under different land uses in a small catchment of subtropical China[J]. Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica, 66(1): 67-74. |
| [9] |
TESSIER J T, RAYNAL D J, 2003. Use of nitrogen to phosphorus ratios in plant tissue as an indicator of nutrient limitation and nitrogen saturation[J]. Journal of Applied Ecology, 40(3): 523-534.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
TIAN H, CHEN G, ZHANG C, et al., 2010. Pattern and variation of C:N:P ratios in China’s soils: a synthesis of observational data[J]. Biogeochemistry, 98(1-3): 139-151.
DOI URL |
| [11] | YIN X R, LIANG C Z, WANG L X, et al., 2010. Ecological stoichiometry of plant nutrients at different restoration succession stages in typical steppe of Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 34(1): 39-47. |
| [12] | 白小芳, 徐福利, 王渭玲, 等, 2015. 华北落叶松人工林土壤碳氮磷生态化学计量特征[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 13(6): 68-75. |
| BAI X F, XU F L, WANG W L, et al., 2015. Ecological stoichiometry of soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in a Larix principis-rupprechtii plantation[J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 13(6): 68-75. | |
| [13] | 曹娟, 闫文德, 项文化, 等, 2015. 湖南会同3个林龄杉木人工林土壤碳、氮、磷化学计量特征[J]. 林业科学, 51(7): 1-8. |
| CAO J, YAN W D, XIANG W H, et al., 2015. Stoichiometry Characterization of Soil C, N, and P of Chinese Fir Plantations at Three Different Ages in Huitong, Hunan Province, China[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 51(7): 1-8. | |
| [14] | 陈安娜, 王光军, 陈婵, 等, 2018. 亚热带不同林龄杉木林叶-根-土氮磷化学计量特征[J]. 生态学报, 38(11): 4031-4036. |
| CHEN A N, WANG G J, CHEN J, et al., 2018. Variation in the N and P stoichiometry of leaf-root-soil during stand development in a Cunninghamia lanceolata plantation in subtropical China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(11): 4031-4036. | |
| [15] | 陈晓萍, 郭炳桥, 钟全林, 等, 2018. 武夷山不同海拔黄山松细根碳、氮、磷化学计量特征对土壤养分的适应[J]. 生态学报, 38(1): 273-281. |
| CHEN X P, GUO B Q, ZHONG Q L, et al., 2018. Response of fine root carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus stoichiometry to soil nutrients in Pinus taiwanensis along an elevation gradient in the Wuyi mountains[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(11): 4031-4036. | |
| [16] | 胡耀升, 么旭阳, 刘艳红, 2014. 长白山森林不同演替阶段植物与土壤氮磷的化学计量特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 25(3): 632-638. |
| HU Y S, ME X Y, LI Y H, 2014. N and P stoichiometric traits of plant and soil in different forest succession stages in Chang bai Mountains[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 25(3): 632-638. | |
| [17] | 纪文婧, 程小琴, 韩海荣, 等, 2016. 山西太岳山好地方典型植被类型土壤理化特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 35(1): 141-148. |
| JI W J, CHENG X Q, HAN H R, et al., 2016. Soil physicochemical properties of typical vegetation types in Haodifang, Taiyue Mountain of Shanxi[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 38(11): 4031-4036. | |
| [18] | 贾国梅, 何立, 程虎, 等, 2016. 三峡库区不同植被土壤微生物量碳氮磷生态化学计量特征[J]. 水土保持研究, 23(4): 23-27. |
| JIA G M, HE L, CHENG H, et al., 2016. Ecological Stoichiometry Characteristics of Soil Microbial Biomass Carbon,Nitrogen and Phosphorus Under Different Vegetation Covers in Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 38(11): 4031-4036. | |
| [19] | 李丹维, 王紫泉, 田海霞, 等, 2017. 太白山不同海拔土壤碳、氮、磷含量及生态化学计量特征[J]. 土壤学报, 54(1): 160-170. |
| LI D W, WANG Z Q, TIAN H X, et al., 2017. Carbon,Nitrogen and Phosphorus Contents in Soils on Taibai Mountain and Their Ecological Stoichiometry relative to Elevation[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 54(1): 160-170. | |
| [20] | 李红林, 贡璐, 朱美玲, 等, 2015. 塔里木盆地北缘绿洲土壤化学计量特征[J]. 土壤学报, 52(6): 1345-1355. |
| LI H L, GONG L, ZHU M L, et al., 2015. Stoihiometric characteristics of soil in an oasis on northern edge of tarim basin, Chian[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 52(6): 13 45- 1355. | |
| [21] | 李玮, 郑子成, 李廷轩, 2015. 不同植茶年限土壤团聚体碳氮磷生态化学计量学特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 26(1): 9-16. |
| LI W, ZHENG Z C, LI Y X, 2015. Ecological stoichiometry of soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus within soil aggregates in tea plantations with different ages[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 26(1): 9-16. | |
| [22] | 吕世丽, 李新平, 李文斌, 等, 2013. 牛背梁自然保护区不同海拔高度森林土壤养分特征分析[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报:自然科学版, 41(4): 161-168. |
| LV S L, LI X P, LI W B, et al., 2013. Forest soil nutrient characteristics at different altitudes in Niubeiliang National Natural Reserve[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 41(4): 161-168. | |
| [23] | 牛瑞龙, 高星, 徐福利, 等, 2016. 秦岭中幼林龄华北落叶松针叶与土壤的碳氮磷生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态学报, 36(22): 7384-7392. |
| NIU R L, GAO X, XU F L, et al., 2016. Carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus stoichiometric characteristics of soil and leaves from young and middle aged Larix principis-rupprechtii growing in a Qinling Mountain plantation[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36(22): 7384-7392. | |
| [24] | 欧阳林梅, 曾冬萍, 闵庆文, 等, 2014. 鼓山茶园土壤碳氮磷生态化学计量学特征[J]. 水土保持学报, 28(2): 297-301. |
| OUYANG L M, ZENG D P, MIN Q W, et al., 2014. Ecological Stoichiometry Characteristics of Soil Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus in the Tea Garden of Drum Mountain[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 28(2): 297-301. | |
| [25] | 任璐璐, 张炳学, 韩凤朋, 等, 2017. 黄土高原不同年限刺槐土壤化学计量特征分析[J]. 水土保持学报, 31(2): 339-344. |
| REN L L, ZHANG B X, HAN F P, et al., 2017. Ecological Stoichiometric Characteristics of Soils in Robinia pseudoacacia Forests of Different Ages on the Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 31(2): 339-344. | |
| [26] | 王绍强, 于贵瑞, 2008. 生态系统碳氮磷元素的生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态学报, 28(8): 3937-3947. |
| WANG S Q, YU G R, 2008. Ecological stoichiometry characteristics of ecosystem carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus elements[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 28(8): 3937-3947. | |
| [27] | 王维奇, 曾从盛, 钟春棋, 等, 2010. 人类干扰对闽江河口湿地土壤碳、氮、磷生态化学计量学特征的影响[J]. 环境科学, 31(10): 2411-2416. |
| WANG W Q, ZENG C S, ZHONG C Q, et al., 2010. Effect of Human Disturbance on Ecological Stoichiometry Characteristics of Soil Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Minjiang River Estuarine Wetland[J]. Chinese Journal of environmental science, 31(10): 2411-2416. | |
| [28] |
王雪梅, 闫帮国, 赵广, 等, 2017. 云南元谋不同海拔土壤微生物对车桑子碳、氮、磷化学计量特征及土壤特性的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 41(3): 311-324.
DOI |
|
WANG X M, MIN B G, ZHAO G, et al., 2017. Effects of microorganism on carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus of Dodonaea viscosa and the soils from different elevations in Yuanmou, Yunnan, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 41(3): 311-324.
DOI URL |
|
| [29] | 肖烨, 黄志刚, 武海涛, 等, 2014. 三江平原4种典型湿地土壤碳氮分布差异和微生物特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 25(10): 2847-2854. |
| XIAO Y, HUANG Z G, WU H T, et al., 2014. Carbon and nitrogen distributions and microbial characteristics in the soils of four types of wetlands in Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 25(10): 2847-2854. | |
| [30] | 谢锦, 常顺利, 张毓涛, 等, 2016. 天山北坡植物土壤生态化学计量特征的垂直地带性[J]. 生态学报, 36(14): 4363-4372. |
| XIE J, CHANG S L, ZHANG M T, et al., 2016. Plant and soil ecological stoichiometry with vertical zonality on the northern slope of the middle Tianshan Mountains[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36(14): 4363-4372. | |
| [31] | 徐沙, 龚吉蕊, 张梓榆, 等, 2014. 不同利用方式下草地优势植物的生态化学计量特征[J]. 草业学报, 23(6): 45-53. |
| XU S, GONG J R, ZHANG Z Y, et al., 2014. The ecological stoichiometry of dominant species in different land uses type of grassland[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 23(6): 45-53. | |
| [32] |
曾德慧, 陈广生, 2005. 生态化学计量学:复杂生命系统奥秘的探索[J]. 植物生态学报, 29(6): 1007-1019.
DOI |
| ZENG D H, CHEN G S, 2005. Ecological stoichiometay: A science to explore the complexity of living systems[J]. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 29(6): 1007-1019. | |
| [33] | 曾全超, 李鑫, 董扬红, 等, 2015. 陕北黄土高原土壤性质及其生态化学计量的纬度变化特征[J]. 自然资源学报, 30(5): 870-879. |
| ZENG Q C, LI X, DONG Y H, et al., 2015. Ecological Stoichiometry Characteristics and Physical-chemical Properties of Soils at Different Latitudes on the Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 29(6): 1007-1019. | |
| [34] | 张广帅, 邓浩俊, 杜锟, 等, 2016. 泥石流频发区山地不同海拔土壤化学计量特征--以云南省小江流域为例[J]. 生态学报, 36(3): 675-687. |
| ZHANG G S, DENG H J, DU K, et al., 2016. Soil stoichiometry characteristics at different elevation gradients of a mountain in an area with high frequency debris flow: a case study in Xiaojiang Watershed, Yunnan[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36(3): 675-687. | |
| [35] | 赵维俊, 刘贤德, 金铭, 等, 2016. 祁连山青海云杉林叶片-枯落物-土壤的碳氮磷生态化学计量特征[J]. 土壤学报, 53(2): 477-489. |
| ZHAO W J, LI X D, JIN M, et al., 2016. Ecological Stoichiometric Characteristics of Carbon,Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Leaf-Litter-Soil System of Picea Crassifolia Forest in the Qilian Mountains[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 53(2): 477-489. | |
| [36] | 朱秋莲, 邢肖毅, 张宏, 等, 2013. 黄土丘陵沟壑区不同植被区土壤生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态学报, 33(15): 4674-4682. |
|
ZHU Q L, XING X Y, ZHANG H, et al., 2013. Soil ecological stoichiometry under different vegetation area on loess hilly gully region[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33(15): 4674-4682.
DOI URL |
| [1] | DONG Zhijin, ZHANG Chengchun, ZHAN Xiuli, ZHANG Weifu. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Soil Nutrients of Biological Soil Crusts and Their Underlying Soil of Sandy Land in the East of Yellow River in Ningxia [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 910-919. |
| [2] | PAN Yuling, QU Xiangning, LI Qing, WANG Lei, WANG Xiaoping, TAN Peng, CUI Geng, AN Yu, TONG Shouzheng. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Soil Physicochemical Factors and Their Response to Microtopography in a Typical Beach Wetland of the Yellow River in Ningxia [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 668-677. |
| [3] | ZHANG Beier, WU Jianqiang, WANG Min, XIONG Lijun, TAN Juan, SHEN Cheng, HUANG Botao, HUANG Shenfa. Evaluation of Soil Health in Different Arable Land Ecological Conservation Projects [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(2): 388-396. |
| [4] | HUANG Weijia, LIU Chun, LIU Yue, HUANG Bin, LI Dingqiang, YUAN Zaijian. Soil Ecological Stoichiometry and Its Influencing Factors at Different Elevations in Nanling Mountains [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(1): 80-89. |
| [5] | XIA Enlong, NONG Junqing, WEI Songpo, LIU Xizhen, LIU Guanglu. Changes in Soil Nutrient Characteristics in Moso Bamboo Forest Expanding into Broadleaved Forest [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(6): 1110-1117. |
| [6] | WANG Xiaona, XU Danghui, WANG Xiejun, FANG Xiangwen. Changes of Shrub Community Structure with Altitudinal Gradient and Longitude in Qilian Mountains [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(2): 231-238. |
| [7] | LONG Jing, HUANG Yao, LIU Zhanfeng, JIAN Shuguang, WEI Liping, WANG Jun. Leaf Traits and Nutrient Resorption of Two Woody Species on A Tropical Coral Island [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(2): 248-256. |
| [8] | YU Fei, YE Caihong, XU Tiaozi, ZHANG Zhongrui, ZHU Hangyong, ZHANG Geng, HUA Lei, DENG Jianfeng, DING Xiaogang. Evaluation of Heavy Metal Pollution in Woodland Soil of Granite Area in Shaoguan City [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(2): 354-362. |
| [9] | SONG Ruipeng, YANG Qifan, ZHENG Zhiheng, XI Dan. Effects of Three Understory Vegetation Types on Soil Organic Carbon and Its Components in Cunninghamia lanceolata Plantation [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(12): 2283-2291. |
| [10] | SHENG Jifeng, LI Yao, YU MeiJia, HAN Yanying, YE Yanhui. Effects of Nitrogen and Phosphorus An Addition on Soil Nutrients and Activity of Related Enzymes in Alpine Grassland [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(12): 2302-2309. |
| [11] | ZHANG Xiaoli, WANG Guoli, CHANG Fangdi, ZHANG Hongyuan, PANG Huancheng, ZHANG Jianli, WANG Jing, JI Hongjie, LI Yuyi. Effects of Microbial Agents on Physicochemical Properties and Microbial Flora of Rhizosphere Saline-alkali Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(10): 1984-1992. |
| [12] | SONG Xianchong, CAI Xuemei, CHEN Tao, PAN Wen, SHI Yuanyuan, TANG Jian, CAO Jizhao. Variation Characteristics of Rhizosphere and Non-rhizosphere Soil Nutrient in Successive Eucalyptus Plantation [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(9): 1814-1820. |
| [13] | LIAO Yingchun, DUAN Honglang, SHI Xingxing, MENG Qingyin, LIU Wenfei, SHEN Fangfang, FAN Houbao, ZHU Tao. The Relationship between the Stand Growth and Root Biomass of Cunninghamia lanceolate Plantations [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(6): 1121-1128. |
| [14] | XU Wenyin, ZHANG Yupeng, DUAN Chengwei, CHAI Yu, SONG Xian, LI Xilai. Spatial Variability of Soil Nutrients in Degraded Alpine Meadows in Different Regions of the Yellow River [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(10): 1968-1975. |
| [15] | SUI Yanghui, GAO Jiping, WANG Yanbo, XIAO Wanxin, LIU Jing, SHI Lei, ZHAO Haiyan, ZHANG Yang. Biochar and Nitrogen Fertilizer Effects on Soil Nutrient and Root Distribution in Dryland Maize [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(10): 2026-2032. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
