Ecology and Environment ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (9): 1574-1584.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.09.004
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
FANG Yuan1,3,4( ), LIANG Zhong5, ZHANG Yutao2,3,*(
), LIANG Zhong5, ZHANG Yutao2,3,*( ), SHI Qingdong1,4, SUN Xuejiao2,3, LI Jimei2,3, LI Xiang2,3, DONG Zhentao1,4
), SHI Qingdong1,4, SUN Xuejiao2,3, LI Jimei2,3, LI Xiang2,3, DONG Zhentao1,4
Received:2023-06-24
Online:2023-09-18
Published:2023-12-11
房园1,3,4( ), 梁中5, 张毓涛2,3,*(
), 梁中5, 张毓涛2,3,*( ), 师庆东1,4, 孙雪娇2,3, 李吉玫2,3, 李翔2,3, 董振涛1,4
), 师庆东1,4, 孙雪娇2,3, 李吉玫2,3, 李翔2,3, 董振涛1,4
通讯作者:
*张毓涛。E-mail: 作者简介:房园(1996年生),女,硕士研究生,主要从事森林生态、森林水文方面研究。E-mail: 2565542178@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
FANG Yuan, LIANG Zhong, ZHANG Yutao, SHI Qingdong, SUN Xuejiao, LI Jimei, LI Xiang, DONG Zhentao. Characteristics of Altitudinal Gradient Changes in Water Retention of Tianshan Spruce Forest Ecosystems[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(9): 1574-1584.
房园, 梁中, 张毓涛, 师庆东, 孙雪娇, 李吉玫, 李翔, 董振涛. 天山云杉森林生态系统的水源涵养能力海拔梯度变化特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(9): 1574-1584.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.09.004
| 海拔/m | 年均温度/℃ | 年降水量/mm | Kira 干湿度指数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1500 1700 2000 2200 2400 | 4.76 3.27 2.28 1.7 0.60 | 388 444 543 528 525 | 11.42 14.08 18.06 18.32 18.56 |
Table 1 Climatic factors changes along with the elevation
| 海拔/m | 年均温度/℃ | 年降水量/mm | Kira 干湿度指数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1500 1700 2000 2200 2400 | 4.76 3.27 2.28 1.7 0.60 | 388 444 543 528 525 | 11.42 14.08 18.06 18.32 18.56 |
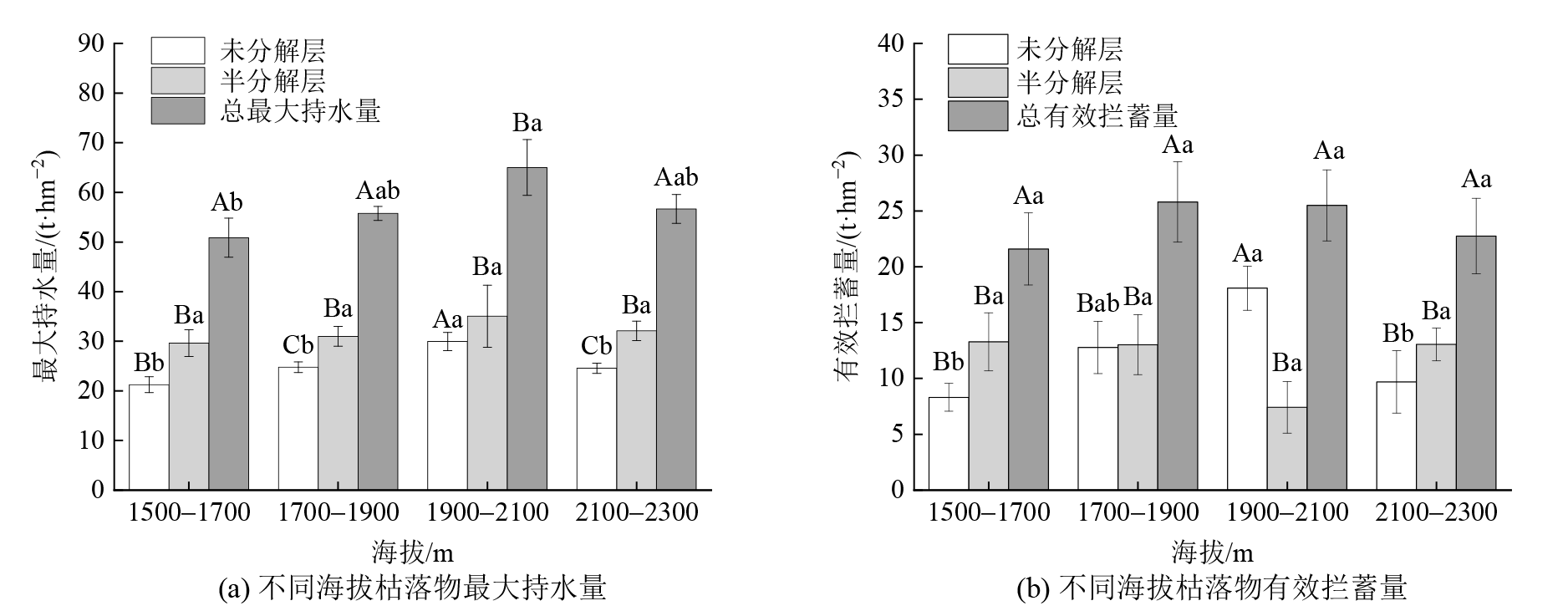
Figure 4 Characteristics of maximum water holding capacity (a) and effective retention capacity (b) of dead litter layer in Tianshan spruce forests at different elevations
| [1] |
BONELL M, 1993. Progress in the understanding of runoff generation dynamics in forests[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 150(2): 217-275.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
DAI L C, FU R Y, GUO X W, et al., 2023. Variations in and factors controlling soil hydrological Properties across different slope aspects in alPine meadows[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 616: 128756.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
DAVID DUNKERLEY, 2015. Percolation through leaf: What happens during rainfall events of varying intensity[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 525: 737-746.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
GEBRELIBANOS T, PASSEN M, 2014. Effects of slope aspect and vegetation types on selected soil Properties in a dryland Hirmi watershed and adjacent agro-ecosystem, northern highlands of Ethiopia[J]. African Journal Ecology, 52(3): 292-299.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
GEROY I, GRIBB M, MARSHALL, et al., 2011. Aspect influences on soil water retention and storage[J]. Hydrol Process, 25(25): 3836-3842.
DOI URL |
| [6] | LI X, NIU J Z, XIE B Y, 2014. The effect of leaf litter cover on surface runoff and soil erosion in Northern China[J]. PLoS One, 9(9): 107789. |
| [7] |
QIU D X, XU R R, WU C X, et al., 2022. Vegetation restoration improves soil hydrological properties by regulating soil physicochemical properties in the Loess Plateau, China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 609(2023): 127730.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
SUN Y, WANG Y B, YANG W J, et al., 2019. Variation in soil hydrological properties on shady and sunny slopes in the permafrost region, Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 78(3): 100. 1-100.11.
DOI |
| [9] | XIA L, SONG X Y, FU N, et al., 2019. Effects of forest litter cover on hydrological response of hillslopes in the Loess Plateau of China[J]. Catena, 181: 10407. |
| [10] |
ZHANG M F, LIU N, RICHARD HARPER, et al., 2017. Dingyuan Ning, Yiping Hou, Shirong Liu. A global review on hydrological responses to forest change across multiple spatial scales: Importance of scale, climate, forest type and hydrological regime[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 546: 44-59.
DOI URL |
| [11] | ZHENG X L, CHEN L H, 2019. Evaluation of the water conservation function of different forest types in northeastern China[J]. Sustainability Volume, 11(15): 4075-4075. |
| [12] | 蔡进军, 李维倩, 陈刚, 等, 2022. 宁夏黄土梁状丘陵区6种稀疏人工林的枯落物持水特征[J]. 林业科学, 58(11): 83-95. |
| CAI J J, LI W Q, CHEN G, et al., 2022. Water-holding characteristics of deadfall in six species of sparse plantation forests in the loess beam hills of Ningxia[J]. Forestry Science, 58(11): 83-95. | |
| [13] | 陈波, 孟成生, 赵耀新, 等, 2012. 冀北山地不同海拔华北落叶松人工林枯落物和土壤水文效应[J]. 水土保持学报, 26(3): 216-221. |
| CHEN B, MENG C S, ZHAO Y X, et al., 2012. Deadfall and soil hydrological effects of North China larch plantations at different elevations in the northern Hebei mountains[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 26(3): 216-221. | |
| [14] | 陈倩, 周志立, 史琛媛, 等, 2015. 河北太行山丘陵区不同林分类型枯落物与土壤持水效益[J]. 水土保持学报, 29(5): 206-211. |
| CHEN Q, ZHOU Z L, SHI C Y, et al., 2015. Deadfall and soil water-holding benefits of different forest types in the Taihang Mountains hilly area of Hebei[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 29(5): 206-211. | |
| [15] | 陈曦, 许文强, 罗格平, 等, 2008. 天山北坡不同环境条件下雪岭云杉 (Picea schrenkiana) 林限土壤属性[J]. 生态学报, 28(1): 53-61. |
| CHEN X, XU W Q, LUO G P, et al., 2008. Soil properties of snowy ridge spruce (Picea schrenkiana) forest limits under different environmental conditions on the northern slopes of Tianshan Mountains[J]. Journal of Ecology, 28(1): 53-61. | |
| [16] | 国家林业局, 1999. 森林土壤水分-物理性质的测定: LY/T 1215—1999 [S]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院. |
| State Forestry Administration, 1999. Determination of moisture- physical properties of forest soils: LY/T 1215—1999 [S]. Beijing: China Academy of Forestry Science. | |
| [17] | 胡仲豪, 常顺利, 张毓涛, 等, 2019. 天山林区不同类型群落土壤氮素对冻融过程的动态响应[J]. 生态学报, 39(2): 571-579. |
| HU Z H, CHANG S L, ZHANG Y T, et al., 2019. Dynamic response of soil nitrogen to freeze-thaw processes in different types of communities in the Tianshan Forest Region[J]. Journal of Ecology, 39(2): 571-579. | |
| [18] | 李娜, 赵传燕, 郝虎, 等, 2021. 海拔和郁闭度对祁连山青海云杉林叶凋落物分解的影响[J]. 生态学报, 41(11): 4493-4502. |
| LI N, ZHAO C Y, HAO H, et al., 2021. Effects of altitude and depression on leaf apoplastic decomposition in Qinghai spruce forests in Qilian Mountains[J]. Journal of Ecology, 41(11): 4493-4502. | |
| [19] | 李阳, 万福绪, 2019. 黄浦江中游5种典型林分枯落物和土壤水源涵养能力研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 33(2): 264-271. |
| LI Y, WAN F X, 2019. Study on the deadfall and soil water holding capacity of five typical forest stands in the middle reaches of Huangpu River[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 33(2): 264-271. | |
| [20] | 林立文, 邓羽松, 李佩琦, 等, 2020. 桂北地区不同密度杉木林枯落物与土壤水文效应[J]. 水土保持学报, 34(5): 200-207, 215. |
| LIN L W, DENG Y S, LI P Q, et al., 2020. Soil hydrological effects of deadfall in fir forests of different densities in northern Gui[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 34(5): 200-207, 215. | |
| [21] | 刘琳, 熊东红, 张宝军, 等, 2021. 拉萨河谷杨树人工林枯落物蓄积特征及持水性能[J]. 干旱区研究, 38(6): 1674-1682. |
| LIU L, XIONG D H, ZHANG B J, et al., 2021. Characteristics of deadfall accumulation and water-holding performance of poplar plantation forests in Lhasa Valley[J]. Arid Zone Research, 38(6): 1674-1682. | |
| [22] | 刘西刚, 王勇辉, 焦黎, 2019. 夏尔希里自然保护区典型植被土壤水源涵养功能探究[J]. 水土保持学报, 33(3): 121-128. |
| LIU X G, WANG Y F, JIAO L, 2019. Exploring the water-holding function of typical vegetation soil in Xarshiri Nature Reserve[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 33(3): 121-128. | |
| [23] | 刘忠玲, 吕跃东, 姚颖, 2020. 不同林分密度原始红松林枯落物和土壤的持水特性[J]. 森林工程, 36(5): 8-15. |
| LIU Z L, LÜ Y D, YAO Y, 2020. Water-holding characteristics of dead litter and soil in primary red pine forests with different stand densities[J]. Forest Engineering, 36(5): 8-15. | |
| [24] | 刘志, 2020. 草海流域不同土地利用类型土壤生态功能效应研究[D]. 贵州: 贵州大学. |
| LIU Z, 2020. Study on the effect of soil ecological function of different land use types in Caohai watershed[D]. Guizhou: Guizhou University. | |
| [25] | 陆恩富, 朱习爱, 曾欢欢, 等, 2021. 西双版纳典型林型凋落物及其水文特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 40(7): 2104-2112. |
| LU E F, ZHU X A, ZENG H H, et al., 2021. Apoplankton and its hydrological characteristics of typical forest types in Xishuangbanna[J]. Journal of Ecology, 40(7): 2104-2112. | |
| [26] | 鲁绍伟, 高琛, 李少宁, 等, 2014. 北京市松山不同海拔油松林枯落物及土壤水文效应[J]. 水土保持通报, 34(1): 1-6. |
| LU S W, GAO C, LI S N, et al., 2014. Deadfall and soil hydrological effects of oil pine forests at different elevations in Song Shan, Beijing[J]. Soil and Water Conservation Bulletin, 34(1): 1-6. | |
| [27] | 栾莉莉, 张光辉, 孙龙, 等, 2015. 黄土高原区典型植被枯落物蓄积量空间变化特征[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 13(6): 48-53. |
| LUAN L L, ZHANG G H, SUN L, et al., 2015. Spatial variation characteristics of typical vegetation deadfall accumulation in Loess Plateau area[J]. China Soil and Water Conservation Science, 13(6): 48-53. | |
| [28] | 吕宸, 龚伟, 车明轩, 等, 2020. 海拔和坡向对高寒灌丛草甸凋落物水源涵养功能的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 34(6): 219-225, 243. |
| LÜ C, GONG W, CHE M X, et al., 2020. Effects of elevation and slope orientation on the water-holding function of alpine scrub meadows with apophytosis[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 34(6): 219-225, 243. | |
| [29] | 孙雪娇, 常顺利, 张毓涛, 等, 2018. 天山森林植物功能性状与碳库沿海拔梯度的变化[J]. 生态学报, 38(14): 4994-5005. |
| SUN X J, CHANG S L, ZHANG Y T, et al., 2018. Changes in functional plant traits and carbon pools along an altitudinal gradient in Tianshan forests[J]. Journal of Ecology, 38(14): 4994-5005. | |
| [30] | 孙艳红, 张洪江, 杜士才, 等, 2009. 四面山不同林地类型土壤特性及其水源涵养功能[J]. 水土保持学报, 23(5): 109-112, 117. |
| SUN Y H, ZHANG H J, DU S C, et al., 2009. Soil characteristics of different woodland types and their water-holding functions in Sifangshan Mountain[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 23(5): 109-112, 117. | |
| [31] | 田超, 杨新兵, 李军, 等, 2011a. 冀北山地不同海拔蒙古栎林枯落物和土壤水文效应[J]. 水土保持学报, 25(4): 221-226. |
| TIAN C, YANG X B, LI J, et al., 2011. Effects of deadfall and soil hydrology in Mongolian oak forests at different elevations in the Hebei Mountains[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 25(4): 221-226. | |
| [32] | 田超, 杨新兵, 李军, 等, 2011b. 冀北山地阴坡枯落物层和土壤层水文效应研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 25(2): 97-103. |
| TIAN C, YANG X B, LI J, et al., 2011. Study on hydrological effects of deadfall layer and soil layer on shady slopes in the mountains of northern Hebei[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 25(2): 97-103. | |
| [33] | 汪建芳, 王兵, 王忠禹, 等, 2018. 黄土高原典型植被枯落物坡面分布及持水特征[J]. 水土保持学报, 32(4): 139-144. |
| WANG J F, WANG B, WANG Z Y, et al., 2018. Slope distribution and water-holding characteristics of typical vegetation deadfall on Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 32(4): 139-144. | |
| [34] |
王美莲, 王飞, 姚晓娟, 等, 2015. 不同林龄兴安落叶松枯落物及土壤水文效应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 24(6): 925-931.
DOI |
| WANG M L, WANG F, YAO X J, et al., 2015. Hydrological effects of forest litters and soil in Xing’an larch forest at different stand ages[J]. Journal of Ecology and Environment, 24(6): 925-931. | |
| [35] | 王盛琦, 傅文慧, 寇建村, 等, 2021. 黄土高原水蚀风蚀交错区沙地枯落物的水源涵养功能[J]. 水土保持通报, 41(5): 30-37. |
| WANG S Q, FU W H, KOU J C, et al., 2021. Water-holding function of sandy deadfall in the water and wind erosion zone of Loess Plateau[J]. Soil and Water Conservation Bulletin, 41(5): 30-37. | |
| [36] | 许小明, 邹亚东, 孙景梅, 等, 2021. 黄土高原北洛河流域林地枯落物特征及水分吸持效应[J]. 生态学报, 41(13): 5153-5165. |
| XU X M, ZOU Y D, SUN J M, et al., 2021. Characteristics and water uptake effects of dead litter in forested areas of the Beiluo River Basin on the Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Ecology, 41(13): 5153-5165. | |
| [37] | 杨建伟, 杨建英, 何会宾, 等, 2019. 冀北山区滦平县4种新造林地水源涵养能力研究[J]. 生态学报, 39(18): 6731-6737. |
| YANG J W, YANG J Y, HE H B, et al., 2019. Study on the water-holding capacity of four types of newly planted forest sites in Luanping County, North Hebei Mountainous Region[J]. Journal of Ecology, 39(18): 6731-6737. | |
| [38] | 杨晓霞, 赵锦梅, 张雪, 等, 2022. 祁连山东段山地典型灌丛枯落物及土壤水源涵养功能研究[J]. 干旱区地理, 45(1): 197-207. |
| YANG X X, ZHAO J M, ZHANG X, et al., 2022. Research on typical scrub dieback and soil water content function in the eastern part of Qilian Mountains[J]. Geography of Arid Regions, 45(1): 197-207. | |
| [39] | 杨霞, 陈丽华, 康影丽, 等, 2019. 辽东低山区5种典型水源涵养林枯落物持水特性[J]. 生态学杂志, 38(9): 2662-2670. |
| YANG X, CHEN L H, KANG Y L, et al., 2019. Water-holding characteristics of deadfall in five typical water-conserving forests in low mountainous areas of Liaodong[J]. Journal of Ecology, 38(9): 2662-2670. | |
| [40] | 章家恩, 2007. 生态学常用实验研究方法与技术[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社:20- 56. |
| ZHANG J E, 2007. Common experimental research methods and techniques in ecology[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press:20- 56. | |
| [41] | 张引, 黄永梅, 周长亮, 等, 2019. 冀北山地5个海拔梯度油松林枯落物与土壤水源涵养功能研究[J]. 水土保持研究, 26(2): 126-131. |
| ZHANG Y, HUANG Y M, ZHOU C L, et al., 2019. Study on deadfall and soil water content function of oleaginous pine forest in five elevation gradients in northern Hebei mountains[J]. Soil and Water Conservation Research, 26(2): 126-131. | |
| [42] | 张益, 林毅雁, 张杰铭, 等, 2023. 北京山区典型植被枯落物和土壤层水文功能[J]. 水土保持研究, 30(4): 160-168. |
| ZHANG Y, LIN Y Y, ZHANG J M, et al., 2023. Hydrological functions of typical vegetation dieback and soil layers in mountainous areas of Beijing[J]. Soil and Water Conservation Research, 30(4): 160-168. | |
| [43] | 张振明, 余新晓, 牛健植, 等, 2005. 不同林分枯落物层的水文生态功能[J]. 水土保持学报(3): 139-143. |
| ZHANG Z M, YU X X, NIU J Z, et al., 2005. Hydroecological functions of deadfall layers in different forest stands[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, (3): 139-143. | |
| [44] | 郑绍伟, 慕长龙, 陈祖铭, 等, 2010. 长江上游森林影响流域水文过程模拟分析[J]. 生态学报, 30(11): 3046-3056. |
| ZHENG S W, MU C L, CHEN Z M, et al., 2010. Simulation analysis of hydrological processes in forest-influenced watersheds of the upper Yangtze River[J]. Journal of Ecology, 30(11): 3046-3056. | |
| [45] | 周凌峰, 陈夙怡, 戴矜君, 等, 2022a. 7种木兰科观赏植物枯落物层及土壤层水文效应[J]. 中国水土保持科学(中英文), 20(6): 126-136. |
| ZHOU L F, CHEN S Y, DAI J J, et al., 2022. Hydrological effects of deadfall layer and soil layer of seven species of Magnoliaceae ornamental plants[J]. Soil and Water Conservation Science in China (in English and Chinese), 20(6): 126-136. | |
| [46] | 周凌峰, 戴矜君, 黄艳萍, 等, 2022b. 9种景观植物枯落物层及其土壤层水文效应[J]. 生态科学, 41(3): 90-97. |
| ZHOU L F, DAI J J, HUANG Y P, et al., 2022. Nine landscape plant deadfall layers and their soil layer hydrological effects[J]. Ecological Science, 41(3): 90-97. | |
| [47] | 朱志俊, 2019. 两种类型地被物覆盖下地被物层与土壤层水文动态过程研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学. |
| ZHU Z J, 2019. Study on the hydrological dynamic process of ground cover layer and soil layer under two types of ground cover[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University. |
| [1] | HUANG Weijia, LIU Chun, LIU Yue, HUANG Bin, LI Dingqiang, YUAN Zaijian. Soil Ecological Stoichiometry and Its Influencing Factors at Different Elevations in Nanling Mountains [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(1): 80-89. |
| [2] | WANG Xiaona, XU Danghui, WANG Xiejun, FANG Xiangwen. Changes of Shrub Community Structure with Altitudinal Gradient and Longitude in Qilian Mountains [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(2): 231-238. |
| [3] | HAN Xin, YUAN Chunyang, LI Jihong, HONG Zongwen, LIU Xuan, DU Ting, LI Han, YOU Chenming, TAN Bo, ZHU Peng, XU Zhenfeng. Effects of Tree Species and Soil Layers on Soil Extractable Nitrogen Content [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(11): 2143-2151. |
| [4] | WANG Rui, SONG Xiangyun, LIU Xinwei. Seasonal Characteristics of Soil Enzymes in Different Vegetations in the Yellow River Delta [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(1): 62-69. |
| [5] | ZHAO Na, WANG Junbo, LI Shaoning, LU Shaowei, XU Xiaotian. Study on Water Holding Characteristics of Four Typical Forest Litter in Songshan, Beijing [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(6): 1139-1147. |
| [6] | ZHANG Shasha, LI Aiqin, WANG Huirong, WANG Jingjing, XU Xiaoniu. Ecological Stoichiometry of Soil Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Cunninghamia lanceolata Plantation Across An Elevation Gradient [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2020, 29(1): 97-104. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
