Ecology and Environment ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 1139-1147.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.06.004
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHAO Na1,2( ), WANG Junbo2, LI Shaoning1,2, LU Shaowei1,2,*(
), WANG Junbo2, LI Shaoning1,2, LU Shaowei1,2,*( ), XU Xiaotian1,2
), XU Xiaotian1,2
Received:2021-01-13
Online:2021-06-18
Published:2021-09-10
Contact:
LU Shaowei
Supported by:
赵娜1,2( ), 王俊博2, 李少宁1,2, 鲁绍伟1,2,*(
), 王俊博2, 李少宁1,2, 鲁绍伟1,2,*( ), 徐晓天1,2
), 徐晓天1,2
通讯作者:
鲁绍伟
作者简介:赵娜(1985年生),女,助理研究员,主要从事森林生态系统水碳过程研究。E-mail: zhaona1019@126.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
ZHAO Na, WANG Junbo, LI Shaoning, LU Shaowei, XU Xiaotian. Study on Water Holding Characteristics of Four Typical Forest Litter in Songshan, Beijing[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(6): 1139-1147.
赵娜, 王俊博, 李少宁, 鲁绍伟, 徐晓天. 北京松山4种典型林分枯落物持水特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1139-1147.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.06.004
| 样地编号 Sample number | 林分类型 Stand type | 海拔 Altitude/m | 坡向 Aspect | 坡度 Slope/(°) | 坡位 Slope position | 叶面积指数 Leaf area index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 蒙古栎纯林 Quercus mongolica pure forest | 717 | 东北 Northeast | 40 | 坡中Middle | 3.38 |
| 2 | 油松纯林 Pinus tabuliformis pure forest | 790 | 西南 Southwest | 50 | 坡中Middle | 2.81 |
| 3 | 针阔混交林,优势树种主要为毛白杨和油松Coniferous-broadleaved mixed forest, dominant species are Populus tomentosa and Pinus tabuliformis | 810 | 西南 Southwest | 60 | 坡下Lower | 3.51 |
| 4 | 山杨纯林 Populus davidiana pure forest | 880 | 西北 Northwest | 59 | 坡上Upper | 2.94 |
Table 1 Basic situation of standard sample plots
| 样地编号 Sample number | 林分类型 Stand type | 海拔 Altitude/m | 坡向 Aspect | 坡度 Slope/(°) | 坡位 Slope position | 叶面积指数 Leaf area index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 蒙古栎纯林 Quercus mongolica pure forest | 717 | 东北 Northeast | 40 | 坡中Middle | 3.38 |
| 2 | 油松纯林 Pinus tabuliformis pure forest | 790 | 西南 Southwest | 50 | 坡中Middle | 2.81 |
| 3 | 针阔混交林,优势树种主要为毛白杨和油松Coniferous-broadleaved mixed forest, dominant species are Populus tomentosa and Pinus tabuliformis | 810 | 西南 Southwest | 60 | 坡下Lower | 3.51 |
| 4 | 山杨纯林 Populus davidiana pure forest | 880 | 西北 Northwest | 59 | 坡上Upper | 2.94 |
| 林分类型 Stand type | 未分解层 Non-decomposed layer of litter | 半分解层 Semi-decomposed layer of litter | 枯落物 总蓄积量 Total Accumulation volume of litter/(t∙hm-2) | 枯落物 总厚度 Total thickness of litter/cm | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 厚度 Thickness/ cm | 蓄积量 Accumulation volume/ (t∙hm-2) | 占总蓄积量 百分比 Percentage of total accumulation volume/% | 厚度 Thickness/ cm | 蓄积量Accumulation volume/ (t∙hm-2) | 占总蓄积量 百分比 Percentage of total accumulation volume/% | ||||
| 蒙古栎 Quercus mongolica | 6.00±0.82 | 9.64±2.64a | 40.53 | 2.75±0.20 | 14.14±1.92a | 59.47 | 23.78±0.72a | 8.75±0.61 | |
| 油松 Pinus tabuliformis | 2.65±1.10 | 7.97±0.82a | 50.25 | 2.30±0.73 | 7.88±0.82b | 49.75 | 15.85±1.63b | 4.95±1.84 | |
| 针阔混交林Coniferous-broadleaved mixed forest | 2.20±0.41 | 2.70±0.02b | 33.56 | 2.35±0.29 | 5.35±1.29ba | 66.44 | 8.05±1.31c | 4.55±0.12 | |
| 山杨 Populus davidiana | 5.00±1.63 | 7.52±0.71a | 35.37 | 3.50±0.41 | 13.74±2.10a | 64.63 | 21.26±2.80a | 8.50±1.22 | |
Table 2 Thickness and accumulation volume of four typical forest stands of litter layer in Songshan Mountain, Beijing
| 林分类型 Stand type | 未分解层 Non-decomposed layer of litter | 半分解层 Semi-decomposed layer of litter | 枯落物 总蓄积量 Total Accumulation volume of litter/(t∙hm-2) | 枯落物 总厚度 Total thickness of litter/cm | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 厚度 Thickness/ cm | 蓄积量 Accumulation volume/ (t∙hm-2) | 占总蓄积量 百分比 Percentage of total accumulation volume/% | 厚度 Thickness/ cm | 蓄积量Accumulation volume/ (t∙hm-2) | 占总蓄积量 百分比 Percentage of total accumulation volume/% | ||||
| 蒙古栎 Quercus mongolica | 6.00±0.82 | 9.64±2.64a | 40.53 | 2.75±0.20 | 14.14±1.92a | 59.47 | 23.78±0.72a | 8.75±0.61 | |
| 油松 Pinus tabuliformis | 2.65±1.10 | 7.97±0.82a | 50.25 | 2.30±0.73 | 7.88±0.82b | 49.75 | 15.85±1.63b | 4.95±1.84 | |
| 针阔混交林Coniferous-broadleaved mixed forest | 2.20±0.41 | 2.70±0.02b | 33.56 | 2.35±0.29 | 5.35±1.29ba | 66.44 | 8.05±1.31c | 4.55±0.12 | |
| 山杨 Populus davidiana | 5.00±1.63 | 7.52±0.71a | 35.37 | 3.50±0.41 | 13.74±2.10a | 64.63 | 21.26±2.80a | 8.50±1.22 | |
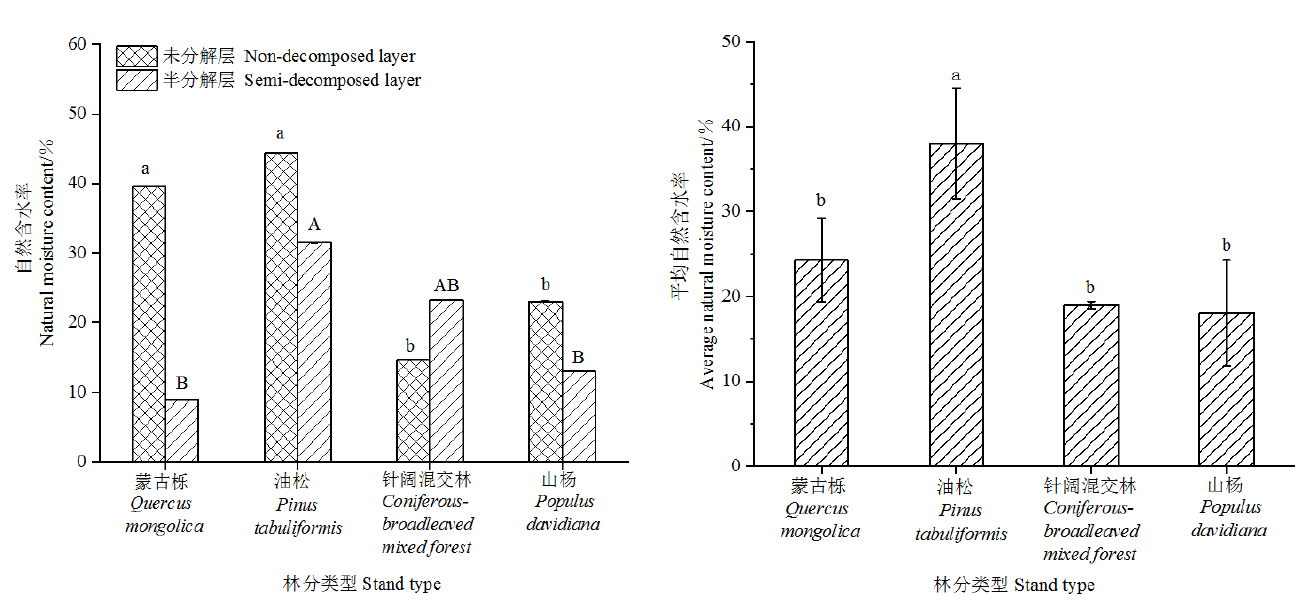
Fig. 1 Natural water content of undecomposed and semi-decomposed litter layers and average natural water content of litter layers in different stand types The different lowercase letters above the column on the left indicate that the difference between the undecomposed layer and the litter layer of different forest types is significant (P<0.05); the difference between the semi-decomposed layers of different forest types with different capital letters is significant (P<0.05)
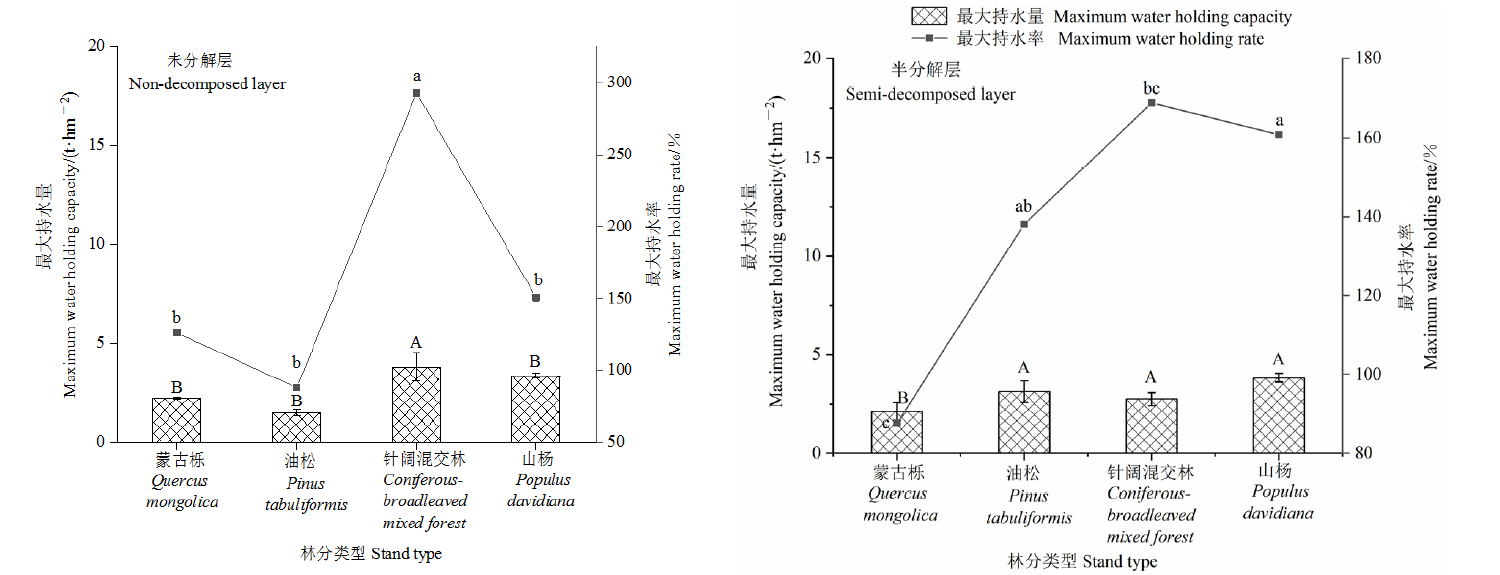
Fig. 2 Maximum water holding capacity and maximum water holding rate of undecomposed and semi-decomposed litter in different stand types There were significant differences in the maximum water holding capacity of litter among different forest types (P<0.05). There were significant differences in the maximum water holding capacity of litter among different capital letters and different stand types (P<0.05)
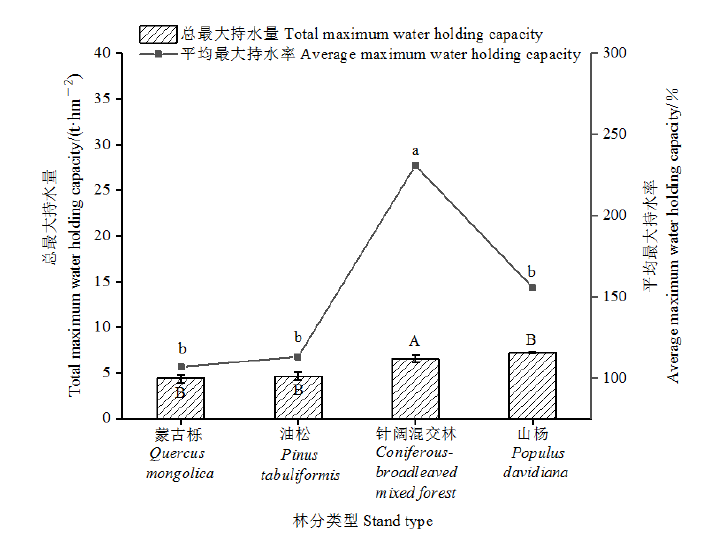
Fig. 3 Total maximum water holding capacity and water holding rate of litter in different stand types There were significant differences in the total maximum water holding capacity of litter among different forest types (P<0.05). There were significant differences in the average water holding rate of litter in different capital letters and different forest types (P<0.05)
| 分解层次 Litter layer | 林分类型 Stand type | 拟合方程 Fitting equation | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 未分解层 Non-decomposed layer | 蒙古栎 Quercus mongolica | Q=193.01lnx+899.42 | 0.9633 |
| 油松 Pinus tabuliformis | Q=252.57lnt+428.2 | 0.9642 | |
| 针阔混交林Coniferous-broadleaved mixed forest | Q=588.01lnt+1798.8 | 0.9823 | |
| 山杨 Populus davidiana | Q=156.13lnt+1252.1 | 0.9302 | |
| 半分解层 Semi-decomposed layer | 蒙古栎 Quercus mongolica | Q=172.09lnt+568.19 | 0.9589 |
| 油松 Pinus tabuliformis | Q=255.96lnt+880.3 | 0.9789 | |
| 针阔混交林 Coniferous-broadleaved mixed forest | Q=403.39lnt+990.29 | 0.9274 | |
| 山杨 Populus davidiana | Q=189.83lnt+1162 | 0.7508 |
Table 3 Relationship between litter water holding capacity and soaking time in different stands
| 分解层次 Litter layer | 林分类型 Stand type | 拟合方程 Fitting equation | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 未分解层 Non-decomposed layer | 蒙古栎 Quercus mongolica | Q=193.01lnx+899.42 | 0.9633 |
| 油松 Pinus tabuliformis | Q=252.57lnt+428.2 | 0.9642 | |
| 针阔混交林Coniferous-broadleaved mixed forest | Q=588.01lnt+1798.8 | 0.9823 | |
| 山杨 Populus davidiana | Q=156.13lnt+1252.1 | 0.9302 | |
| 半分解层 Semi-decomposed layer | 蒙古栎 Quercus mongolica | Q=172.09lnt+568.19 | 0.9589 |
| 油松 Pinus tabuliformis | Q=255.96lnt+880.3 | 0.9789 | |
| 针阔混交林 Coniferous-broadleaved mixed forest | Q=403.39lnt+990.29 | 0.9274 | |
| 山杨 Populus davidiana | Q=189.83lnt+1162 | 0.7508 |
| 分解层次 Litter layer | 林分类型 Stand type | 拟合方程 Fitting equation | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 未分解层 Non- decomposed layer | 蒙古栎 Quercus mongolica | V=1194.9t -1.507 | 0.9198 |
| 油松 Pinus tabuliformis | V=587.55t -1.307 | 0.8956 | |
| 针阔混交林Coniferous-broadleaved mixed forest | V=2401.5t -1.444 | 0.9211 | |
| 山杨 Populus davidiana | V=1644.8t -1.583 | 0.9225 | |
| 半分解层 Semi- decomposed layer | 蒙古栎 Quercus mongolica | V=757.49t -1.459 | 0.9225 |
| 油松 Pinus tabuliformis | V=1172.6t -1.467 | 0.9247 | |
| 针阔混交林Coniferous-broadleaved mixed forest | V=1323.7t -1.393 | 0.9081 | |
| 山杨 Populus davidiana | V=1540.1t -1.56 | 0.9479 |
Table 4 Relationship between water holding rate and soaking time of litter in different stands
| 分解层次 Litter layer | 林分类型 Stand type | 拟合方程 Fitting equation | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 未分解层 Non- decomposed layer | 蒙古栎 Quercus mongolica | V=1194.9t -1.507 | 0.9198 |
| 油松 Pinus tabuliformis | V=587.55t -1.307 | 0.8956 | |
| 针阔混交林Coniferous-broadleaved mixed forest | V=2401.5t -1.444 | 0.9211 | |
| 山杨 Populus davidiana | V=1644.8t -1.583 | 0.9225 | |
| 半分解层 Semi- decomposed layer | 蒙古栎 Quercus mongolica | V=757.49t -1.459 | 0.9225 |
| 油松 Pinus tabuliformis | V=1172.6t -1.467 | 0.9247 | |
| 针阔混交林Coniferous-broadleaved mixed forest | V=1323.7t -1.393 | 0.9081 | |
| 山杨 Populus davidiana | V=1540.1t -1.56 | 0.9479 |
| 林分类型 Stand type | 未分解层 Non-decomposed layer | 半分解层 Semi-decomposed layer | 总有效拦蓄量 Total effective storage capacity/ (t∙hm-2) | 平均有效拦蓄率 Average effective retention rate/ % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 有效拦蓄量 Modified interception/ (t∙hm-2) | 有效拦蓄率 Effective retention rate/% | 有效拦蓄量 Modified interception/ (t∙hm-2) | 有效拦蓄率 Effective retention rate/% | ||||
| 蒙古栎 Quercus mongolica | 4.17±2.27b | 67.58 | 8.40±2.84a | 65.46 | 12.56±0.65b | 66.52 | |
| 油松 Pinus tabuliformis | 1.22±0.10b | 30.32 | 3.24±1.65b | 85.91 | 4.46±1.75b | 58.11 | |
| 针阔混交林Coniferous-broadleaved mixed forest | 5.40±2.45a | 234.31 | 4.91±1.42ab | 120.25 | 10.31±1.08a | 177.28 | |
| 山杨 Populus davidiana | 6.21±1.53a | 104.93 | 7.46±2.24ab | 123.67 | 13.67±3.77a | 114.30 | |
Table 5 Retaining capacity of litter in different stands
| 林分类型 Stand type | 未分解层 Non-decomposed layer | 半分解层 Semi-decomposed layer | 总有效拦蓄量 Total effective storage capacity/ (t∙hm-2) | 平均有效拦蓄率 Average effective retention rate/ % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 有效拦蓄量 Modified interception/ (t∙hm-2) | 有效拦蓄率 Effective retention rate/% | 有效拦蓄量 Modified interception/ (t∙hm-2) | 有效拦蓄率 Effective retention rate/% | ||||
| 蒙古栎 Quercus mongolica | 4.17±2.27b | 67.58 | 8.40±2.84a | 65.46 | 12.56±0.65b | 66.52 | |
| 油松 Pinus tabuliformis | 1.22±0.10b | 30.32 | 3.24±1.65b | 85.91 | 4.46±1.75b | 58.11 | |
| 针阔混交林Coniferous-broadleaved mixed forest | 5.40±2.45a | 234.31 | 4.91±1.42ab | 120.25 | 10.31±1.08a | 177.28 | |
| 山杨 Populus davidiana | 6.21±1.53a | 104.93 | 7.46±2.24ab | 123.67 | 13.67±3.77a | 114.30 | |
| [1] | ADOLFO C C, LOURDES C H, SANDRA R O, 2017. Mass, nutrient pool, and mineralization of litter and fine roots in a tropical mountain cloud forest[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 575: 879-886. |
| [2] |
BONELL M, 1993. Progress in the understanding of runoff generation dynamics in forests[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 150(2-4): 217-275.
DOI URL |
| [3] | CAI D, YANG X H, WANG S Z, et al., 2017. Effects of dissolved organic matter derived from forest leaf litter on biodegradation of phenanthrene in aqueous phase[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 324(Part B): 516-525. |
| [4] |
ECAROL A, WILLIAMJ P, STEVENJ D G, et al., 2008. Simple three-pool model accurately describes patterns of long-term litter decomposition in diverse climates[J]. Global Change Biology, 14(11): 2636-2660.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
KULMALA L, PUMPANEN J, HARI P, et al., 2011. Photosynthesis of ground vegetation in different aged pine forests: Effect of environmental factors predicted with a process-based model[J]. Journal of Vegetation Science, 22(1): 96-110.
DOI URL |
| [6] | 陈继东, 周长亮, 李惠丽, 2017. 接坝地区9种典型林分类型枯落物层和土壤层水文效应[J]. 水土保持研究, 24(6): 216-221, 226. |
| CHEN J D, ZHOU C L, LI H L, 2017. Hydrological effects of litter layer and soil layer of nine typical forest types in Jieba area[J]. Soil and Water Conservation Research, 24(6): 216-221, 226. | |
| [7] | 陈琦, 刘苑秋, 刘士余, 等, 2019. 杉木取代阔叶林后林下水源涵养功能差异评价[J]. 水土保持学报, 33(2): 244-250. |
| CHEN Q, LIU Y Q, LIU S Y, et al., 2019. Evaluation of differences in understory water conservation function after Chinese fir replaces broad-leaved forest[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 33(2): 244-250. | |
| [8] | 董治宝, 李振山, 1998. 风成沙粒度特征对其风蚀可蚀性的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 4(4): 1-5. |
| DONG Z B, LI Z S, 1998. Influence of aeolian sand grain size characteristics on its wind erosion erodibility[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 4(4): 1-5. | |
| [9] | 胡淑萍, 余新晓, 岳永杰, 2008. 北京百花山森林枯落物层和土壤层水文效应研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 22(1): 146-150. |
| HU S P, YU X X, YUE Y J, 2008. Research on the Hydrological Effects of Forest Litter Layer and Soil Layer of Baihua Mountain in Beijing[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 22(1): 146-150. | |
| [10] | 季冬, 关文彬, 谢春华, 2007. 贡嘎山暗针叶林生态系统枯落物截留特征研究[J]. 林业调查规划, 32(1): 111-116. |
| JI D, GUAN W B, XIE C H, 2007. Study on the characteristics of litter interception in the dark coniferous forest ecosystem of Gongga Mountain[J]. Forestry Inventory and Planning, 32(1): 111-116. | |
| [11] | 金雅琴, 李冬林, 孙丽娟, 等, 2018. 南京近郊人工林地表枯落物的累积量及持水性[J]. 中国水土保持科学, 16(5): 95-104. |
| JIN Y Q, LI D L, SUN L J, et al., 2018. Accumulation and water holding capacity of surface litter in artificial forests in the suburbs of Nanjing[J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 16(5): 95-104. | |
| [12] | 李黎立, 蒋万杰, 吴记贵, 等, 2008. 北京松山自然保护区生物多样性现状与保护对策[J]. 林业调查规划, 33(5): 51-54. |
| LI L L, JIANG W J, WU J G, et al., 2008. Biodiversity status and protection countermeasures of Beijing Songshan Nature Reserve[J]. Forest Inventory and Planning, 33(5): 51-54. | |
| [13] | 李阳, 万福绪, 2019. 黄浦江中游5种典型林分枯落物和土壤水源涵养能力研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 33(2): 264-271. |
| LI Y, WAN F X, 2019. Research on litter and soil water conservation capacity of five typical forests in the middle reaches of huangpu river[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 33(2): 264-271. | |
| [14] | 梁文俊, 魏曦, 赵伟文, 等, 2021. 关帝山不同林分结构华北落叶松林枯落物水文效应[J]. 水土保持学报, 35(2): 324-329, 337. |
| LIANG W J, WEI X, ZHAO W W, et al., 2021. Hydrological effects of litter in Larix principis-rupprechtii forests with different stand structures in Guandi Mountain[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 35(2): 324-329, 337. | |
| [15] | 梁晓娇, 王树力, 2017. 阿什河源头不同类型红松人工林枯落物及其土壤水文特性[J]. 水土保持学报, 31(1): 140-145. |
| LIANG X J, WANG S L, 2017. Different types of Pinus koraiensis plantation litter and soil hydrological characteristics at the source of Ash River[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 31(1): 140-145. | |
| [16] | 林立文, 邓羽松, 李佩琦, 等, 2020. 桂北地区不同密度杉木林枯落物与土壤水文效应[J]. 水土保持学报, 34(5): 200-207, 215. |
| LIN L W, DENG Y S, LI P Q, et al., 2020. The litter and soil hydrological effects of Chinese fir plantations with different densities in northern Guangxi[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 34(5): 200-207, 215. | |
| [17] | 刘斌, 鲁绍伟, 李少宁, 等, 2015. 北京西山6种天然纯林枯落物及土壤水文效应[J]. 水土保持学报, 29(4): 73-78, 137. |
| LIU B, LU S W, LI S N, et al., 2015. The litter and soil hydrological effects of six natural pure forests in Xishan, Beijing[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 29(4): 73-78, 137. | |
| [18] | 卢振启, 黄秋娴, 杨新兵, 2014. 河北雾灵山不同海拔油松人工林枯落物及土壤水文效应研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 28(1): 112-116. |
| LU Z Q, HUANG Q X, YANG X B, 2014. Research on litter and soil hydrological effects of Pinus tabulaeformis plantations at different altitudes in Wuling Mountain, Hebei[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 28(1): 112-116. | |
| [19] | 鲁绍伟, 陈波, 潘青华, 等, 2013. 北京山地不同海拔人工油松林枯落物及其土壤水文效应[J]. 水土保持研究, 20(6): 54-58, 70. |
| LU S W, CHEN B, PAN Q H, et al., 2013. The litter and its soil hydrological effects of artificial Pinus tabulaeformis at different altitudes in Beijing mountainous areas[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 20(6): 54-58, 70. | |
| [20] | 鲁绍伟, 李少宁, 陈波, 等, 2015. 北京西山6种天然纯林枯落物及土壤水文效应[J]. 水土保持学报, 29(4): 73-78, 137. |
| LU S W, LI S N, CHEN B, et al., 2015. The litter and soil hydrological effects of six natural pure forests in Xishan, Beijing[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 29(4): 73-78, 137. | |
| [21] | 吕刚, 曹小平, 卢慧, 等, 2010. 辽西海棠山森林枯落物持水与土壤贮水能力研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 24(3): 203-208. |
| LV G, CAO X P, LU H, et al., 2010. Research on water holding capacity and soil water holding capacity of forest litter in Haitang Mountain in western Liaoning[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 24(3): 203-208. | |
| [22] | 庞梦丽, 朱辰光, 翟博超, 等, 2017. 河北省太行山区3种人工水土保持林枯落物及土壤水文效应[J]. 水土保持通报, 37(1): 51-56. |
| PANG M L, ZHU C H, ZHAI B C, et al., 2017. The litter and soil hydrological effects of three artificial soil and water conservation forests in the Taihang Mountains of Hebei province[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 37(1): 51-56. | |
| [23] | 涂志华, 范志平, 孙学凯, 等, 2019. 大伙房水库流域不同植被类型枯落物层和土壤层水文效应[J]. 水土保持学报, 33(1): 129-135. |
| TU Z H, FAN Z P, SUN X K, et al., 2019. Hydrological effects of litter layer and soil layer of different vegetation types in the Dahuofang Reservoir Basin[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 33(1): 129-135. | |
| [24] | 王玲, 赵广亮, 周红娟, 等, 2019. 八达岭林场不同密度油松人工林枯落物水文效应[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(9): 1767-1775. |
| WANG L, ZHAO G L, ZHOU H J, et al., 2019. Hydrological characteristics of litter in a Pinus tabulaeformis plantation with different densities in Badaling Forest Farm[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 28(9): 1767-1775. | |
| [25] | 王美莲, 王飞, 姚晓娟, 等, 2015. 不同林龄兴安落叶松枯落物及土壤水文效应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 24(6): 925-931. |
| WANG M L, WANG F, YAO X J, et al., 2015. Hydrological Effects of Forest Litters and Soil in Xing'an Larch Forest at Different Stand Ages[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 24(6): 925-931. | |
| [26] | 宣立辉, 佟彦国, 张军, 等, 2019. 冀北山区油松人工林林分密度对枯落物层和土壤层水文特征的影响[J]. 林业与生态科学, 34(1): 15-23. |
| XUAN L H, TONG Y G, ZHANG J, et al., 2019. Influence of stand density of Pinus tabulaeformis plantation on hydrological characteristics of litter layer and soil layer in mountainous area of northern Hebei[J]. Forestry and Ecological Sciences, 34(1): 15-23. | |
| [27] | 殷沙, 赵芳, 欧阳勋志, 2015. 马尾松木荷不同比例针阔混交林枯落物和土壤持水性能比较分析[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 37(3): 454-460. |
| YIN S, ZHAO F, OUYANG X Z, 2015. Comparative analysis of litter and soil water holding capacity of different proportions of coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forests of Pinus massoniana and Schima superba[J]. Journal of Jiangxi Agricultural University, 37(3): 454-460. | |
| [28] | 张更权, 2018. 大同县退耕还白桦林枯枝落物和土壤持水效应[J]. 安徽农业大学, 46(31): 107-110. |
| ZHANG G Q, 2018. The litter and soil water retention effect of returning farmland to Betula platyphylla forest in Datong County[J]. Anhui Agricultural University, 46(31): 107-110. | |
| [29] | 赵阳, 余新晓, 吴海龙, 等, 2011. 华北土石山区典型森林枯落物层和土壤层水文效应[J]. 水土保持学报, 25(6): 148-152. |
| ZHAO Y, YU X X, WU H L, et al., 2011. Hydrological effects of typical forest litter layer and soil layer in the rocky mountainous area of North China[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 25(6): 148-152. | |
| [30] | 赵雨森, 韩春华, 张宏光, 等, 2012. 阿什河上游小流域主要林分类型土壤水文功能研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 26(2): 203-208. |
| ZHAO Y S, HAN C H, ZHANG H G, et al., 2012. Study on soil hydrological function of main forest types in the small watershed of the upper Ashi River[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 26(2): 203-208. |
| [1] | LI Tingting, HOU Mengdan, DENG Xinyan, ZHOU Xuping, WANG Shunli, HUANG Dan, ZENG Zhiruo, PENG Tao. Diversity of Epiphytic Bryophytes for Four Vegetation Types in Guizhou Xishui National Nature Reserve [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(8): 1556-1565. |
| [2] | WANG Chaoyue, GUO Xianhua, GUO Li, BAI Lifang, XIA Lilin, WANG Chunbo, LI Tingzhen. Land Use Change and Its Impact on Carbon Storage in Northwest China Based on FLUS-Invest: A Case Study of Hu-Bao-Er-Yu Urban Agglomeration [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(8): 1667-1679. |
| [3] | ZHOU Xuping, TANG Luyan, HE Zhuoji, WANG Shunli, HUANG Dan, LI Dahua, DENG Xinyan, HOU Mengdan, YANG Shulin, PENG Tao. Deviation in the Composition of Bryophytes Geographic Elements in Relation to Environmental and Spatial Factors among 27 National Nature Reserves in China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(10): 1959-1970. |
| [4] | LI Cong, LÜ Jinghua, LU Mei, YANG Zhidong, LIU Pan, REN Yulian, DU Fan. Responses of Soil Bacterial Communities to Vertical Vegetarian Zone Changes in the Subtropical Forests, Southeastern Yunnan [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(10): 1971-1983. |
| [5] | DONG Xin, LANG Jiayu, CHUYUAN Mengran, ZHAO Shanshan, ZHANG Jindong, BAI Wenke. The Seasonal Characteristics of Home Range and Habitat Utilization of Sichuan Golden Monkeys (Rhinopithecus roxellana) [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(7): 1342-1352. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
