Ecology and Environment ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (8): 1499-1509.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.08.001
• Research Articles • Next Articles
CHENG Chuanpeng1,2( ), XU Mingjie2,3, LIU Huifeng1,*(
), XU Mingjie2,3, LIU Huifeng1,*( )
)
Received:2022-03-15
Online:2022-08-18
Published:2022-10-10
Contact:
LIU Huifeng
通讯作者:
刘慧峰
作者简介:程传鹏(1988年生),男,讲师,博士,主要从事森林生态学和生态经济学方面研究。E-mail: chengpeng4@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
CHENG Chuanpeng, XU Mingjie, LIU Huifeng. Effects of Thinning on Carbon Dynamics and Economic Value of Carbon Fixation in Subtropical Pinus massoniana Plantation[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(8): 1499-1509.
程传鹏, 徐明洁, 刘慧峰. 间伐对亚热带马尾松人工林碳动态及碳固定经济价值的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1499-1509.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.08.001
| 项目 Item | 2015 | 2016 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照Unthinned | T2014 | 对照Unthinned | T2014 | ||
| 生态系统碳吸收Ecosystem carbon uptake(by C)/(g∙m-2∙a-1) | -2313.87±77.91a | -1843.98±6.91b | -3061.80±70.50a | -2274.42±42.00b | |
| 生态系统碳排放Ecosystem carbon emissions(by C)/(g∙m-2∙a-1) | 1621.84±78.42a | 1658.36±7.27a | 2420.00±20.38b | 1604.47±39.40a | |
| 生态系统碳动态Ecosystem carbon dynamics(by C)/(g∙m-2∙a-1) | -455.21±30.90a | 182.06±6.08b | -409.96±16.79a | -274.65±7.63b | |
Table 1 Effects of thinning on ecosystem carbon dynamics in subtropical Pinus massoniana plantation
| 项目 Item | 2015 | 2016 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照Unthinned | T2014 | 对照Unthinned | T2014 | ||
| 生态系统碳吸收Ecosystem carbon uptake(by C)/(g∙m-2∙a-1) | -2313.87±77.91a | -1843.98±6.91b | -3061.80±70.50a | -2274.42±42.00b | |
| 生态系统碳排放Ecosystem carbon emissions(by C)/(g∙m-2∙a-1) | 1621.84±78.42a | 1658.36±7.27a | 2420.00±20.38b | 1604.47±39.40a | |
| 生态系统碳动态Ecosystem carbon dynamics(by C)/(g∙m-2∙a-1) | -455.21±30.90a | 182.06±6.08b | -409.96±16.79a | -274.65±7.63b | |
| 项目 Item | 2015 | 2016 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照 Unthinned | T2014 | 对照 Unthinned | T2014 | ||
| 乔木层碳吸收 Carbon fixation of tree layer/kg | -7450.67±298.62a | -5750.90±24.75b | -9635.55±268.07a | -7159.25±155.84b | |
| 林下植被碳吸收 Carbon fixation of understory community/kg | -930.17±12.85a | -909.33±14.41a | -1431.96±10.33a | -1062.26±2.80b | |
| 林下植被碳排放 Carbon emissions of understory community/kg | 870.90±5.14a | 1213.36±10.41b | 963.04±5.07a | 1304.49±9.24b | |
| 乔木层碳排放 Carbon emissions of tree layer/kg | 3079.64±120.32b | 2429.88±31.37a | 5894.92±92.92b | 2445.47±162.44a | |
Table 2 Effects of thinning on components of ecosystem carbon dynamics in subtropical Pinus massoniana plantation
| 项目 Item | 2015 | 2016 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照 Unthinned | T2014 | 对照 Unthinned | T2014 | ||
| 乔木层碳吸收 Carbon fixation of tree layer/kg | -7450.67±298.62a | -5750.90±24.75b | -9635.55±268.07a | -7159.25±155.84b | |
| 林下植被碳吸收 Carbon fixation of understory community/kg | -930.17±12.85a | -909.33±14.41a | -1431.96±10.33a | -1062.26±2.80b | |
| 林下植被碳排放 Carbon emissions of understory community/kg | 870.90±5.14a | 1213.36±10.41b | 963.04±5.07a | 1304.49±9.24b | |
| 乔木层碳排放 Carbon emissions of tree layer/kg | 3079.64±120.32b | 2429.88±31.37a | 5894.92±92.92b | 2445.47±162.44a | |
| 项目 Item | 对照 Unthinned | T2014 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 土层层次Soil layer/cm | 土壤性质Soil property | ||
| 0-10 | pH | 4.22±0.02a | 4.23±0.03a |
| w(NH4+-N)/(mg∙kg-1) | 8.15±0.34b | 5.66±0.22a | |
| w(NO3--N)/(mg∙kg-1) | 2.90±0.12b | 1.53±0.08a | |
| w(inorganic N)/(mg∙kg-1) | 11.05±0.22b | 7.60±0.33a | |
| 10-20 | pH | 4.23±0.01a | 4.21±0.02a |
| w(NH4+-N)/(mg∙kg-1) | 3.17±0.07a | 3.38±0.21a | |
| w(NO3--N)/(mg∙kg-1) | 1.28±0.12a | 1.09±0.02a | |
| w(inorganic N)/(mg∙kg-1) | 4.45±0.15a | 4.46±0.18a | |
| 5 cm土壤湿度 Soil water content at 5 cm/(cm3∙cm-3) | 12.98±0.29a | 13.90±0.22b | |
| 地表温度Surface temperature/℃ | 17.97±0.29a | 18.58±0.29a | |
| 5 cm 土壤温度Soil temperature at 5 cm/℃ | 16.5±0.08a | 17.21±0.33a | |
| LAI Leaf area index | 3.15±0.05b | 2.56±0.15a | |
| 冠层开度Canopy openness/% | 37.57±1.42a | 44.45±1.80b | |
| 总太阳辐射透过率 Total solar radiation transmittance (Ttot)/% | 37.94±1.10a | 55.15±1.53b | |
| 直接太阳辐射透过率 Direct solar radiation transmittance (Tdir)/% | 35.43±0.83a | 55.20±1.09b | |
| 散射太阳辐射透过率 Diffuse solar radiation transmittance (Tdif)/% | 35.43±1.37a | 55.10±1.97b | |
Table 3 Effects of thinning on soil physical and chemical properties, canopy structure and light transmittance in subtropical Pinus massoniana plantation
| 项目 Item | 对照 Unthinned | T2014 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 土层层次Soil layer/cm | 土壤性质Soil property | ||
| 0-10 | pH | 4.22±0.02a | 4.23±0.03a |
| w(NH4+-N)/(mg∙kg-1) | 8.15±0.34b | 5.66±0.22a | |
| w(NO3--N)/(mg∙kg-1) | 2.90±0.12b | 1.53±0.08a | |
| w(inorganic N)/(mg∙kg-1) | 11.05±0.22b | 7.60±0.33a | |
| 10-20 | pH | 4.23±0.01a | 4.21±0.02a |
| w(NH4+-N)/(mg∙kg-1) | 3.17±0.07a | 3.38±0.21a | |
| w(NO3--N)/(mg∙kg-1) | 1.28±0.12a | 1.09±0.02a | |
| w(inorganic N)/(mg∙kg-1) | 4.45±0.15a | 4.46±0.18a | |
| 5 cm土壤湿度 Soil water content at 5 cm/(cm3∙cm-3) | 12.98±0.29a | 13.90±0.22b | |
| 地表温度Surface temperature/℃ | 17.97±0.29a | 18.58±0.29a | |
| 5 cm 土壤温度Soil temperature at 5 cm/℃ | 16.5±0.08a | 17.21±0.33a | |
| LAI Leaf area index | 3.15±0.05b | 2.56±0.15a | |
| 冠层开度Canopy openness/% | 37.57±1.42a | 44.45±1.80b | |
| 总太阳辐射透过率 Total solar radiation transmittance (Ttot)/% | 37.94±1.10a | 55.15±1.53b | |
| 直接太阳辐射透过率 Direct solar radiation transmittance (Tdir)/% | 35.43±0.83a | 55.20±1.09b | |
| 散射太阳辐射透过率 Diffuse solar radiation transmittance (Tdif)/% | 35.43±1.37a | 55.10±1.97b | |
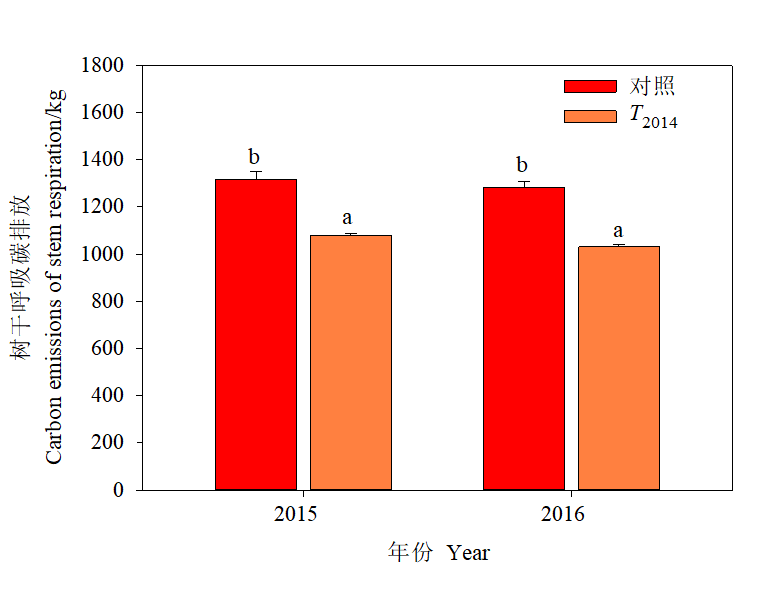
Figure 1 Effects of thinning on carbon emissions of stem respiration in subtropical Pinus massoniana plantation The data in the figure are the average values±standard deviation, n=3;Different letters after data indicate significant difference between different treatments (P<0.05). The same below
| 生态系统碳固定经济价值 Economic value of ecosystem carbon sequestration/(yuan∙hm-2) | 2015 | 2016 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照 Unthinned | T2014 | 对照 Unthinned | T2014 | |||
| 含间伐木材经济价值 Including the economic value of thinning wood | 碳价格1200元 The carbon price is 1200 yuan | 5462.54±370.74a | 17419.35±72.97b | 4919.55±201.46b | 3295.80±91.57a | |
| 碳价格150美元 The carbon price is 150 US dollars | 4192.50±284.54a | 17927.30±56.00b | 3775.76±154.61b | 2529.53±70.28a | ||
| 碳价格34.38元 The carbon price is 34.38 yuan | 156.50±10.62a | 19541.49±631.35b | 140.95±5.77b | 94.42±2.62a | ||
| 不含间伐木材经济价值 Excluding the economic value of thinning wood | 碳价格1200元 The carbon price is 1200 yuan | 5462.54±370.74b | -2184.73±30.87a | 4919.55±201.46b | 3295.80±91.57a | |
| 碳价格150美元 The carbon price is 150 US dollars | 4192.50±284.54b | -1676.78±27.23a | 3775.76±154.61b | 2529.53±70.28a | ||
| 碳价格34.38元 The carbon price is 34.38 yuan | 156.50±10.62b | -62.59±2.09a | 140.95±5.77b | 94.42±2.62a | ||
Table 4 Effects of thinning on the economic value of ecosystem carbon sequestration in subtropical Pinus massoniana plantation
| 生态系统碳固定经济价值 Economic value of ecosystem carbon sequestration/(yuan∙hm-2) | 2015 | 2016 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照 Unthinned | T2014 | 对照 Unthinned | T2014 | |||
| 含间伐木材经济价值 Including the economic value of thinning wood | 碳价格1200元 The carbon price is 1200 yuan | 5462.54±370.74a | 17419.35±72.97b | 4919.55±201.46b | 3295.80±91.57a | |
| 碳价格150美元 The carbon price is 150 US dollars | 4192.50±284.54a | 17927.30±56.00b | 3775.76±154.61b | 2529.53±70.28a | ||
| 碳价格34.38元 The carbon price is 34.38 yuan | 156.50±10.62a | 19541.49±631.35b | 140.95±5.77b | 94.42±2.62a | ||
| 不含间伐木材经济价值 Excluding the economic value of thinning wood | 碳价格1200元 The carbon price is 1200 yuan | 5462.54±370.74b | -2184.73±30.87a | 4919.55±201.46b | 3295.80±91.57a | |
| 碳价格150美元 The carbon price is 150 US dollars | 4192.50±284.54b | -1676.78±27.23a | 3775.76±154.61b | 2529.53±70.28a | ||
| 碳价格34.38元 The carbon price is 34.38 yuan | 156.50±10.62b | -62.59±2.09a | 140.95±5.77b | 94.42±2.62a | ||
| [1] |
ACUNA M, NAVARRO-CERRILLO R M, RUIZ-GÓMEZ F, et al., 2021. How does carbon pricing impact optimal thinning schedules and net present value in Mediterranean pine plantations?[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 482: 118847.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
AUN K, KUKMÄGI M, VARIK M, et al., 2021a. Short-term effect of thinning on the carbon budget of young and middle-aged silver birch (Betula pendula Roth) stands[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 480: 118660.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
AUN K, KUKMÄGI M, VARIK M, et al., 2021b. Short-term effect of thinning on the carbon budget of young and middle-aged Scots pine (Pinussylvestris L.) stands[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 492: 119241.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
AUSTIN K G, BAKER J S, SOHNGEN B L, et al., 2020. The economic costs of planting, preserving, and managing the world’s forests to mitigate climate change[J]. Nature communications, 11(1): 5946.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
BAUTISTA I, LIDÓM A, LULLl C, et al., 2021. Thinning decreased soil respiration differently intwo dryland Mediterranean forests with contrasted soil temperature andhumidity regimes[J]. European Journal of Forest Research, 140(6): 1469-1485.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
CHEN S, SHAHI C, CHEN H Y H, et al., 2017. Economic analysis of forest management alternatives: Compositional objectives, rotation ages, and harvest methods in boreal forests[J]. Forest Policy and Economics, 85(Part 1):124-134.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
CHENG C P, WANG Y D, FU X L, et al., 2017. Thinning effect on understory community and photosynthetic characteristics in a subtropical Pinus massoniana plantation[J]. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 47(8): 1104-1115.
DOI URL |
| [8] | CHENG X Q, HAN H R, ZHU J, et al., 2021. Forest thinning and organic matter manipulation drives changes in soil respiration in a Larix principis-rupprechtii plantation in China[J]. Soil & Tillage Research, 211: 104996. |
| [9] |
CHIANG J M, BROWN K J, 2010. The effects of thinning and burning treatments on within-canopy variation of leaf traits in hardwood forests of southern Ohio[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 260(6): 1065-1075.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
EGGERS J, RÄTY M, ÖHMAN K, et al., 2020. How well do stakeholder-defined forest management scenarios balance economic and ecological forest values?[J]. Forests, DOI: 10.3390/f11010086.
DOI |
| [11] |
ENRÍQUEZ-DE-SALAMANCA Á, 2021. Carbon versus timber economy in Mediterranean forests[J]. Atmosphere, 12(6): 746.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
FÖRSTER AGNES, CULMSEE H, LEYSCHNER C, 2021. Thinned northern German Scots pine forests have a low carbon storage and uptake potential in comparison to naturally developing beech forests[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 479: 118575.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
GONG C, TAN Q Y, LIU G B, et al., 2021. Forest thinning increases soil carbon stocks in China[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 482: 118812.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
LINDGREN P M F, SULLIVAN T P, 2013. Long-term response of tree and stand growth of young lodgepole pine to pre-commercial thinning and repeated fertilization[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 307: 155-164.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
LINDROTH A, HOLST J, HELIASZ M, et al., 2018. Effects of low thinning on carbon dioxide fluxes in a mixed hemiboreal forest[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 262: 59-70.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
LULL C, BAUTISTA I, LIDON A, et al., 2020. Temporal effects of thinning on soil organic carbon pools, basal respiration and enzyme activities in a Mediterranean Holm oak forest[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, DOI: 10.1016/j.foreco.2020.118088.
DOI |
| [17] |
PIAO S L, FANG J Y, CIAIS P, et al., 2009. The carbon balance of terrestrial ecosystems in China[J]. Nature, 458: 1009-1013.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
TAYE F A, FOLKERSEN M V, FLEMING C M, et al., 2021. The economic values of global forest ecosystem services: A meta-analysis[J]. Ecological Economics, 189: 107145.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
VICCARO M, COZZI M, FANELLI L, et al., 2019. Spatial modelling approach to evaluate the economic impacts of climate change on forests at a local scale[J]. Ecological Indicators, 106: 105523.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
WANG J L, WANG H M, FU X L, et al., 2016. Effects of site preparation treatments before afforestation on soil carbon release[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 361: 277-285.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
WANG W W, PAGE-DUMROESE D, JURGENSEN M, et al., 2018. Effect of forest thinning and wood quality on the short-term wood decomposition rate in a Pinus tabuliformis plantation[J]. Journal of Plant Research, 131(6): 897-905.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
XU M J, HU J, ZHANG T, et al., 2021. Specific responses of canopy conductance to environmental factors in a coniferous plantation in subtropical China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 131: 108168.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
XU M J, WEN X F, WANG H M, et al., 2014. Effects of Climatic Factors and Ecosystem Responses on the Inter-Annual Variability of Evapotranspiration in a Coniferous Plantation in Subtropical China[J]. PLOS ONE, 9(1): e85593.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
ZANCHI G, BRADY M V, 2019. Evaluating the contribution of forest ecosystem services to societal welfare through linking dynamic ecosystem modelling with economic valuation[J]. Ecosystem Services, 39: 101011.
DOI URL |
| [25] | 国家林业和草原局, 2019. 中国森林资源报告(2014- 2018)[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社: 2-9. |
| National Forestry and Grassland Administration, 2019. CHINA FOREST RESOURCES REPORT (2014-2018)[M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House: 2-9. | |
| [26] | 国家林业局, 2008. 森林生态系统服务功能评估规范:LY/T 1721-2008[M]. 北京: 中国标准出版社: 1-4. |
| National Forestry Administration, 2008. Specifications for assessment of forest ecosystem services in China:LY/T 1721-2008[M]. Beijing: Standards Press of China: 1-4. | |
| [27] | 胡原, 曾维忠, 2020. 碳汇造林项目促进了当地经济发展吗?--基于四川县域面板数据的PSM-DID实证研究[J]. 中国人口∙资源与环境, 30(2): 89-98. |
| HU Y, ZENG W Z, 2020. Does the carbon sink afforestation project promote local economic development?[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 30(2): 89-98. | |
| [28] | 李瑞霞, 马洪靖, 闵建刚, 等, 2012. 间伐对马尾松人工林林下植物多样性的短期和长期影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 21(5): 807-812. |
| LI R X, MA H J, MIN J G, et al., 2012. Short-term and long-term effects of thinning on the undergrowth diversity in the Pinusmassoniana plantation[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 21(5): 807-812. | |
| [29] | 李轩然, 刘琪璟, 蔡哲, 等, 2007. 千烟洲针叶林的比叶面积及叶面积指数[J]. 植物生态学报, 31(1): 93-101. |
| LI X R, LIU Q J, CAI Z, et al., 2007. Specific leaf area and leaf area index of conifer plantations in Qianyanzhou station of subtropical China[J]. Journal of Plant Ecology, 31(1): 93-101. | |
| [30] | 马浩然, 赵天忠, 2021. 森林生态效益补偿研究进展与展望[J]. 北京林业大学学报(社会科学版), 20(4): 90-99. |
| MA H Z, ZHAO T Z, 2021. Research of forest ecological benefit compensation: Progress and prospect[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University (Social Sciences), 20(4): 90-99. | |
| [31] | 马泽清, 王辉民, 杨风亭, 等, 2020. 基于长期观测研究支撑亚热带红壤丘陵区森林生态系统恢复与可持续发展[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 35(12): 1525-1536. |
| MA Z Q, WANG H M, YANG F T, et al., 2020. Ecological restoration and sustainable development of forest ecosystem in subtropical red soil hilly region based on long-term observation and research[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 35(12): 1525-1536. | |
| [32] | 梅梦媛, 雷一东, 2019. 我国人工林新时代发展形势分析[J]. 世界林业研究, 32(3): 73-77. |
| MEI M Y, LEI Y D, 2019. Analysis on development trend of china’s plantation in new era[J]. World Forestry Research, 32(3): 73-77. | |
| [33] | 王小玲, 沈月琴, 朱臻, 2013. 考虑碳汇收益的林地期望值最大化及其敏感性分析--以杉木和马尾松为例[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 37(4): 143-148. |
| WANG X L, SHEN Y Q, ZHU Z, 2013. The maximization of land expectation value (LEV) considering carbon benefits and its sensitivity analysis: Take Chinese fir and Masson pine for example[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 37(4): 143-148. | |
| [34] | 谢聪, 徐晋涛, 2020. 森林社会经济效益问题探讨[J]. 世界林业研究, 33(3): 101-106. |
| XIE C, XU J T, 2020. A discussion on forest socioeconomic benefit[J]. World Forestry Research, 33(3): 101-106. | |
| [35] | 薛蓓蓓, 田国双, 2021. 基于碳汇木材复合经营目标的综合效益及影响因素分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 45(2): 205-212. |
| XUE B B, TIAN G S, 2021. Analysis of comprehensive benefits and influencing factors based on the combined economic value of carbon sequestration and timber benefits[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 45(2): 205-212. | |
| [36] | 杨博文, 2021. 习近平新发展理念下碳达峰、碳中和目标战略实现的系统思维、经济理路与科学路径[J]. 经济学家(9): 5-12. |
| YANG B W, 2021. The systematic thinking, economic logic and scientific path for the realization of carbon summit and carbon neutral target strategy under Xi Jinping’s new development concept[J]. Economist, (9): 5-12. | |
| [37] | 杨尚东, 吴俊, 谭宏伟, 等, 2014. 南方红壤区西南桦和马尾松人工林土壤微生物活性及细菌多样性比较[J]. 生态环境学报, 23(3): 415-422. |
| YANG S D, WU J, TAN H W, et al., 2014. Comparison on soil microbial activities and bacterial diversity between Betula alnoides and Pinus massoniana plantations in red soil region, China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 23(3): 415-422. | |
| [38] | 张春华, 居为民, 王登杰, 等, 2018. 2004-2013年山东省森林碳储量及其碳汇经济价值[J]. 生态学报, 38(5): 1739-1749. |
| ZHANG C H, JU W M, WANG D J, et al., 2018. Biomass carbon stocks and economic value dynamics of forests in Shandong Province from 2004 to 2013 [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(5): 1739-1749. | |
| [39] | 张峰, 彭祚登, 2021. 北京市森林碳储量和碳汇经济价值研究[J]. 林业资源管理, (6): 52-58. |
| ZHANG F, PENG Z D, 2021. Biomass carbon stocks and carbon stock economic value of forests in Beijing[J]. Forest Resources Management, (6): 52-58. | |
| [40] | 张娟, 陈钦, 2021. 森林碳汇经济价值评估研究--以福建省为例[J]. 西南大学学报(自然科学版), 43(5): 121-128. |
| ZHANG J, CHEN Q, 2021. Study on economic value assessment of forest carbon sequestration[J]. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition), 43(5): 121-128. | |
| [41] | 朱梅钰, 龙飞, 祁慧博, 等, 2021. 基于行业减排的森林碳汇需求空间测度与分类[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 38(2): 377-386. |
| ZHU M Y, LONG F, QI H B, 2021. Spatial measurement and classification of forest carbon sink demand based on industry emission reduction[J]. Journal of Zhejiang A & F University, 38(2): 377-386. |
| [1] | LI Xun, CUI Ningjie, ZHANG Yan, QIN Yu, ZHANG Jian. Mixed Effects on Cellulose, Total phenols and Condensed Tannins Degradation in the Litter Leaves of Pinus massoniana and Native Broad-leaved Tree Species [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(9): 1813-1822. |
| [2] | ZHANG Bowen, QIN Juan, REN Zhongming, CHEN Ziqi, YAO Shunjia, LIU Ye, SONG Yanyu. Effects of Slope Aspect on Understory Plant Diversity of Pinus massoniana Pure Forest and Different Coniferous and Broad-leaved Mixed Forest Types in North Subtropical Region [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(6): 1091-1100. |
| [3] | CHEN Lijuan, ZHOU Wenjun, YI Yanyun, SONG Qinghai, ZHANG Yiping, LIANG Naishen, LU Zhiyun, WEN Handong, MOHD Zeeshan, SHA Liqing. Characteristics of Soil CH4 Flux in the Subtropical Evergreen Broad-leaved Forest in Ailao Mountain, Yunnan, Southwest China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(5): 949-960. |
| [4] | WEN Zhifeng, WEI Shiguang, LI Lin, YE Wanhui, LIAN Juyu. Spatial Distribution Patterns and Spatial Associations of Evergreen Broad-leaved Forest Plants in Tropical South Asia at Different Taxonomic Levels [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 440-450. |
| [5] | YANG Shifu, MA Lingling, CHEN Yunzhi, TANG Xuli. Characteristics of Soil Bacteria Community in Forests Along Monsoon Evergreen Broadleaved Forest Successional Sequence in Dinghushan National Nature Reserve [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(12): 2275-2282. |
| [6] | ZHANG Tianlin, CAI Zhanglin, ZHAO Houben, WU Zhongmin, ZHOU Guangyi, QIU Zhijun. Priming Effect on Soil Organic Carbon by Abnormal Litter Following 13C Pulse-labeling [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(9): 1797-1804. |
| [7] | HONG Wenjun, MO Luojian, ZHANG Hao. Effects of Different Thinning on the Structure of Acacia mangium Plantation in South China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(7): 1360-1367. |
| [8] | ZHOU Dixuan, LIN Yongbiao, WANG Yanjia, LIU Zhanfeng, ZHOU Lixia. Assessment of Main Ecosystem Services in Subtropical Plantations [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(5): 907-919. |
| [9] | ZHANG Jian, XU Ming, WANG Yang, WEN Chunyu, YANG Yunli, ZHANG Jiao, NIE Kun. Distribution Characteristics of the Glomalin-Related Soil Protein of Different Pinus massoniana Association in Central Guizhou [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(12): 2303-2308. |
| [10] | ZHANG Yangyang, ZHOU Qinghui, XU Jiaoyang, WEI Ming, CHEN Jihao, HE Wei, WANG Pengcheng, YAN Zhaogui. Effects of Forest Ages on the Diversity of Understory Plants and Soil Seed Bank of Pinus massoniana Plantations [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(11): 2121-2129. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
