Ecology and Environment ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (6): 1091-1100.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.06.003
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Bowen( ), QIN Juan*(
), QIN Juan*( ), REN Zhongming, CHEN Ziqi, YAO Shunjia, LIU Ye, SONG Yanyu
), REN Zhongming, CHEN Ziqi, YAO Shunjia, LIU Ye, SONG Yanyu
Received:2021-12-03
Online:2022-06-18
Published:2022-07-29
Contact:
QIN Juan
张博文( ), 秦娟*(
), 秦娟*( ), 任忠明, 陈子齐, 姚舜佳, 刘烨, 宋炎玉
), 任忠明, 陈子齐, 姚舜佳, 刘烨, 宋炎玉
通讯作者:
秦娟
作者简介:张博文(1998年生),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为植物生态学。E-mail: zzzborn63@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
ZHANG Bowen, QIN Juan, REN Zhongming, CHEN Ziqi, YAO Shunjia, LIU Ye, SONG Yanyu. Effects of Slope Aspect on Understory Plant Diversity of Pinus massoniana Pure Forest and Different Coniferous and Broad-leaved Mixed Forest Types in North Subtropical Region[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(6): 1091-1100.
张博文, 秦娟, 任忠明, 陈子齐, 姚舜佳, 刘烨, 宋炎玉. 坡向对北亚热带区马尾松纯林及不同针阔混交林型林下植物多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1091-1100.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.06.003
| 坡向 Slope aspect | 林分类型 Forest type | 林分密度 Density/ (plant∙hm-2) | 海拔 Altitude/ m | 坡度 Slope/ (°) | 平均树高 Mean tree height/ m | 平均胸径 Mean diameter of breast/ cm | 主要树种比例 Proportion of major tree species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 东南 South-east (SE) | PF | 1510 | 43 | 24 | 马尾松 14.4±2.76Ab | 马尾松 24.4±0.84Ba | — |
| PQM | 1120 (450) | 96 | 24 | 马尾松 8.5±1.21Aa 麻栎 15.4±1.30Ba | 马尾松 19.0±1.12Bc 麻栎 24.3±0.49Bb | 马尾松:麻栎=2:1 | |
| PLM | 1050 (515) | 109 | 24 | 马尾松 11.7±1.75Bb 枫香 10.9±4.61Ab | 马尾松 22.5±0.66Ab 枫香 23.8±1.02Ab | 马尾松:枫香=2:1 | |
| PPM | 1095 (360) | 51 | 27 | 马尾松 11.8±1.55Ab 化香 9.8±0.29Ab | 马尾松 24.7±0.97Aa 化香 25.3±1.60Aa | 马尾松:化香=3:1 | |
| 西北 North-west (NW) | PF | 1485 | 47 | 22 | 马尾松 15.2±0.78Ab | 马尾松 26.7±1.29Aa | — |
| PQM | 1260 (450) | 126 | 26 | 马尾松 19.7±0.36Aa 麻栎 18.1±0.52Aa | 马尾松 21.1±0.97Abc 麻栎 27.8±0.80Aa | 马尾松:麻栎=2:1 | |
| PLM | 1050 (515) | 126 | 28 | 马尾松 13.5±0.63Ac 枫香 11.2±0.61Ab | 马尾松 18.9±1.29Bc 枫香 16.9±1.39Bb | 马尾松:枫香=2:1 | |
| PPM | 1095 (360) | 199 | 30 | 马尾松 8.8±0.36Bd 化香 8.8±0.85Ac | 马尾松 23.2±1.15Bb 化香 18.1±0.66Bb | 马尾松:化香=3:1 |
Table1 General conditions of four forest types of P. massoniana sample plots
| 坡向 Slope aspect | 林分类型 Forest type | 林分密度 Density/ (plant∙hm-2) | 海拔 Altitude/ m | 坡度 Slope/ (°) | 平均树高 Mean tree height/ m | 平均胸径 Mean diameter of breast/ cm | 主要树种比例 Proportion of major tree species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 东南 South-east (SE) | PF | 1510 | 43 | 24 | 马尾松 14.4±2.76Ab | 马尾松 24.4±0.84Ba | — |
| PQM | 1120 (450) | 96 | 24 | 马尾松 8.5±1.21Aa 麻栎 15.4±1.30Ba | 马尾松 19.0±1.12Bc 麻栎 24.3±0.49Bb | 马尾松:麻栎=2:1 | |
| PLM | 1050 (515) | 109 | 24 | 马尾松 11.7±1.75Bb 枫香 10.9±4.61Ab | 马尾松 22.5±0.66Ab 枫香 23.8±1.02Ab | 马尾松:枫香=2:1 | |
| PPM | 1095 (360) | 51 | 27 | 马尾松 11.8±1.55Ab 化香 9.8±0.29Ab | 马尾松 24.7±0.97Aa 化香 25.3±1.60Aa | 马尾松:化香=3:1 | |
| 西北 North-west (NW) | PF | 1485 | 47 | 22 | 马尾松 15.2±0.78Ab | 马尾松 26.7±1.29Aa | — |
| PQM | 1260 (450) | 126 | 26 | 马尾松 19.7±0.36Aa 麻栎 18.1±0.52Aa | 马尾松 21.1±0.97Abc 麻栎 27.8±0.80Aa | 马尾松:麻栎=2:1 | |
| PLM | 1050 (515) | 126 | 28 | 马尾松 13.5±0.63Ac 枫香 11.2±0.61Ab | 马尾松 18.9±1.29Bc 枫香 16.9±1.39Bb | 马尾松:枫香=2:1 | |
| PPM | 1095 (360) | 199 | 30 | 马尾松 8.8±0.36Bd 化香 8.8±0.85Ac | 马尾松 23.2±1.15Bb 化香 18.1±0.66Bb | 马尾松:化香=3:1 |
| 坡向 Slope aspects | 林分类型 Forest type | 灌木层重要值/% | 草本层重要值/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 东南 South-east (SE) | PF | 檵木 Loropetalum (45.39±6.16a) 马尾松 P. massoniana (19.90±2.15b) 山矾 Symplocos sumuntia (13.17±2.56c) | 欧洲蕨 Pteridium aquilinum (48.66±10.77a) 淡竹叶 Lophatherum gracile (32.18±4.48b) |
| PQM | 麻栎Quercus acutissima (17.61±2.41a) 白蜡 Fraxinus chinensis (17.29±1.76a) 黄檀 Dalbergia hupeana (15.94±1.01ab) | 泽兰 Eupatorium japonicum (56.37±11.62a) 小蓬草 Conyza canadensis (7.89±4.05b) 兰香草 Caryopteris incana (5.01±4.01b) | |
| PLM | 麻栎 Quercus acutissima (28.26±4.63a) 黄檀 Dalbergia hupeana (24.28±6.52a) 黄连木 Pistacia chinensis (17.03±3.40ab) | 香港薹草 Carex ligata (36.15±6.20a) 淡竹叶 Lophatherum gracile (28.16±6.93ab) 紫苑 Aster tataricus (23.14±1.08b) | |
| PPM | 牡荆 Vitex negundo (29.22±4.04a) 白背叶 Mallotus apelta (22.72±5.96ab) 化香 Platycarya strobilacea (14.54±5.46bc) | 香港薹草 Carex ligata (68.29±4.34a) 铁线蕨 Adiantum capillus-veneris (8.66±6.72b) | |
| 西北 North-west (NW) | PF | 白背叶 Mallotus apelta (28.84±4.77 a) 杜鹃 Rhododendron simsii (23.93±2.76ab) 菝葜 Smilax china (17.64±2.28bc) | 芒 Miscanthus sinensis (46.47±20.83a ) 香港薹草 Carex ligata (18.22±10.47ab ) 泽兰 Eupatorium japonicum (7.63±4.77c) |
| PQM | 络石 Trachelospermum jasminoides (18.50±8.43a) 麻栎 Quercus acutissima (13.42±1.84ab) 白背叶 Mallotus apelta (13.40±3.27ab) | 泽兰 Eupatorium japonicum (64.63±5.93a) 紫苑 Aster tataricus (27.81±2.64b) | |
| PLM | 山莓 Rubus corchorifolius (29.37±5.71a) 刚竹 Phyllostachys sulphurea (25.97±5.85a) 白背叶 Mallotus apelta (6.89±3.27b) | 狗脊 Woodwardia japonica (53.29±2.98a) 小蓬草 Conyza canadensis (14.10±4.54b) 黑足鳞毛蕨 Dryopteris fuscipes (12.97±8.44b) | |
| PPM | 山莓 Rubus corchorifolius (37.83±1.47a) 白背叶 Mallotus apelta (16.95±10.17b) 紫藤 Wisteria sinensis (12.43±6.23b) | 黑足鳞毛蕨 Dryopteris fuscipes (32.94±7.25a) 香港薹草 Carex ligata (29.27±5.50a) 博落回 Macleaya cordata (15.89±2.67b) |
Table 2 Importance values of understory species in four forest types of P. massoniana under two slopes
| 坡向 Slope aspects | 林分类型 Forest type | 灌木层重要值/% | 草本层重要值/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 东南 South-east (SE) | PF | 檵木 Loropetalum (45.39±6.16a) 马尾松 P. massoniana (19.90±2.15b) 山矾 Symplocos sumuntia (13.17±2.56c) | 欧洲蕨 Pteridium aquilinum (48.66±10.77a) 淡竹叶 Lophatherum gracile (32.18±4.48b) |
| PQM | 麻栎Quercus acutissima (17.61±2.41a) 白蜡 Fraxinus chinensis (17.29±1.76a) 黄檀 Dalbergia hupeana (15.94±1.01ab) | 泽兰 Eupatorium japonicum (56.37±11.62a) 小蓬草 Conyza canadensis (7.89±4.05b) 兰香草 Caryopteris incana (5.01±4.01b) | |
| PLM | 麻栎 Quercus acutissima (28.26±4.63a) 黄檀 Dalbergia hupeana (24.28±6.52a) 黄连木 Pistacia chinensis (17.03±3.40ab) | 香港薹草 Carex ligata (36.15±6.20a) 淡竹叶 Lophatherum gracile (28.16±6.93ab) 紫苑 Aster tataricus (23.14±1.08b) | |
| PPM | 牡荆 Vitex negundo (29.22±4.04a) 白背叶 Mallotus apelta (22.72±5.96ab) 化香 Platycarya strobilacea (14.54±5.46bc) | 香港薹草 Carex ligata (68.29±4.34a) 铁线蕨 Adiantum capillus-veneris (8.66±6.72b) | |
| 西北 North-west (NW) | PF | 白背叶 Mallotus apelta (28.84±4.77 a) 杜鹃 Rhododendron simsii (23.93±2.76ab) 菝葜 Smilax china (17.64±2.28bc) | 芒 Miscanthus sinensis (46.47±20.83a ) 香港薹草 Carex ligata (18.22±10.47ab ) 泽兰 Eupatorium japonicum (7.63±4.77c) |
| PQM | 络石 Trachelospermum jasminoides (18.50±8.43a) 麻栎 Quercus acutissima (13.42±1.84ab) 白背叶 Mallotus apelta (13.40±3.27ab) | 泽兰 Eupatorium japonicum (64.63±5.93a) 紫苑 Aster tataricus (27.81±2.64b) | |
| PLM | 山莓 Rubus corchorifolius (29.37±5.71a) 刚竹 Phyllostachys sulphurea (25.97±5.85a) 白背叶 Mallotus apelta (6.89±3.27b) | 狗脊 Woodwardia japonica (53.29±2.98a) 小蓬草 Conyza canadensis (14.10±4.54b) 黑足鳞毛蕨 Dryopteris fuscipes (12.97±8.44b) | |
| PPM | 山莓 Rubus corchorifolius (37.83±1.47a) 白背叶 Mallotus apelta (16.95±10.17b) 紫藤 Wisteria sinensis (12.43±6.23b) | 黑足鳞毛蕨 Dryopteris fuscipes (32.94±7.25a) 香港薹草 Carex ligata (29.27±5.50a) 博落回 Macleaya cordata (15.89±2.67b) |
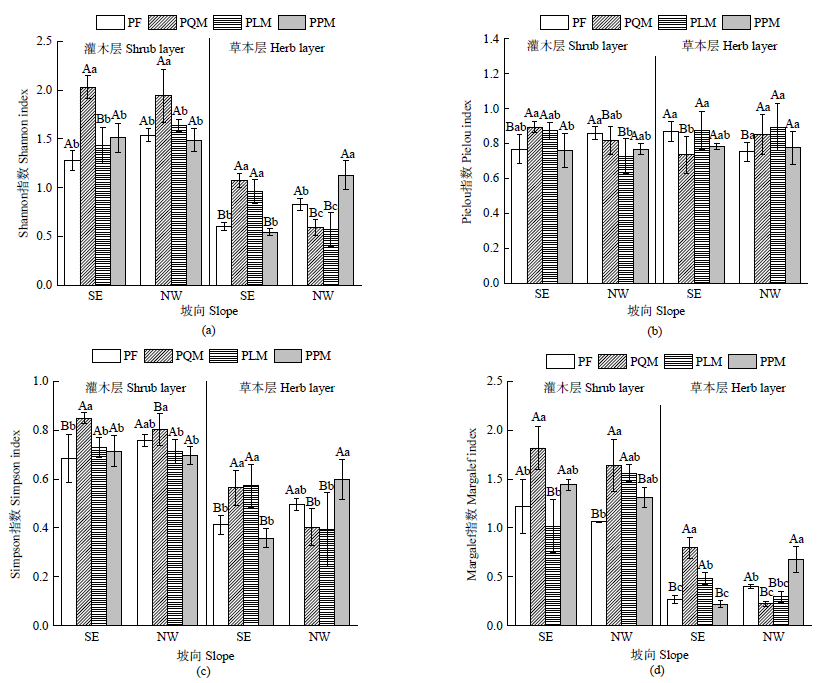
Figure 2 Shannon-wiener index (H), Pielou index (Jsw), Simpson index (D) and Margalef index (M) of four forest types of P. massoniana under different slope aspects SE: Southeast slope; NW: northwest slope Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different forest types in the same aspect (a=0.05), and different uppercase letters indicate significant differences between different aspects in the same forest type (A=0.05)
| [1] |
DENG C, ZHANG S G, LU Y C, et al., 2020. Thinning effects on forest evolution in Masson pine (Pinus massoniana Lamb.) conversion from pure plantations into mixed forests[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, DOI: 10.1016/j.foreco.2020.118503.
DOI URL |
| [2] | DUNCK B, ALGERTE V M, CIANCIARUSO M V, et al., 2016. Functional diversity and trait-environment relationship of periphytic algae in subtropical floodplain lakes[J]. Ecological Indicators, 67: 257-266. |
| [3] | GONG X, BRUECK H, GIESE K M, et al., 2008. Slope aspect has effects on productivity and species composition of hilly grassland in the Xilin River Basin, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Journal of Arid Environments, 72(4): 483-493. |
| [4] | HOLLAND P G, STEYN D G, 1975. Vegetational responses to latitudinal variations in slope angle and aspect[J]. Journal of Biogeography, 2(3): 179-183. |
| [5] | MAREN I E, KARKI S, PRAJAPATI C, et al., 2015. Facing north or south: Does slope aspect impact forest stand characteristics and soil properties in a semiarid trans-Himalayan valley?[J]. Journal of Arid Environments, 121: 112-123. |
| [6] | NEPALI BR, SKARTVEIT J, BANIVA C B, 2021. Impacts of slope aspects on altitudinal species richness and species composition of Narapani-Masina landscape, Arghakhanchi, West Nepal[J]. Journal of Asia-Pacific Biodiversity, 14(67): 415-424. |
| [7] | 方精云, 王襄平, 沈泽昊, 等, 2009. 植物群落清查的主要内容、方法和技术规范[J]. 生物多样性, 17(6): 533-548. |
| FANG J Y, WANG X P, SHEN Z H, et al., 2009. Methods and protocols for plant community inventory[J]. Biodiversity Science, 17(6): 533-548. | |
| [8] | 谷振军, 刘倩, 曾纪孟, 等, 2021. 马尾松人工林密度控制对林下植被多样性的影响[J]. 森林与环境学报, 41(5): 504-509. |
| GU Z J, LIU Q, ZENG J M, et al., 2021. Effects of density management on understory plant diversity in plantation forests of Pinus massoniana[J]. Journal of Forest and Environment, 41(5): 504-509. | |
| [9] | 郝建锋, 王德艺, 唐永彬, 等, 2014. 人为干扰对江油地区马尾松人工林群落结构和物种多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 23(5): 729-735. |
| HAO J F, WANG D Y, TANG Y B, et al., 2014. Effects of human disturbance on species diversity of Pinus massoniana plantation in Jiangyou district, Sichuan province[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 3(5): 729-735. | |
| [10] | 何斌, 李青, 陈群利, 等, 2021. 黔西北黄杉群落物种多样性的海拔梯度格局[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(6): 1111-1120. |
| HE B, LI Q, CHEN Q L, et al., 2021. Altitudinal pattern of species diversity of Pseudotsuga sinensis community in northwestern Guizhou, China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(6): 1111-1120. | |
| [11] | 黄鑫, 2021. 区域尺度马尾松生产力的空间分异、影响因素及模拟预测[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学. |
| HUANG X, 2021. Spatial differentiation, influencing factors and simulation prediction of Masson Pine productivity at regional scale[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University. | |
| [12] |
黄小荣, 2018. 广西马尾松林植物功能多样性与生产力的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 26(7): 690-700.
DOI |
| HUANG X R, 2018. Relationship between plant functional diversity and productivity of Pinus massoniana plantations in Guangxi[J]. Biodiversity Science, 26(7): 690-700. | |
| [13] | 吉文丽, 2007. 苔草属植物对异质环境生理生态响应研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学. |
| JI W L, 2007. Study on ecophysiological response of Sedges (Carex: Cyperaceae) to heterogeneous environment[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University. | |
| [14] | 刘旻霞, 南笑宁, 张国娟, 等, 2021. 高寒草甸不同坡向植物群落物种多样性与功能多样性的关系[J]. 生态学报, 41(13): 5398-5407. |
| LIU M X, NAN X N, ZHANG G J, et al., 2021. Relationship between species diversity and functional diversity of plant communities in different slopes in alpine meadow[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(13): 5398-5407. | |
| [15] | 柳小妮, 孙九林, 张德罡, 等, 2008. 东祁连山不同退化阶段高寒草甸群落结构与植物多样性特征研究[J]. 草业学报, 17(4): 1-11. |
| LIU X N, SUN J L, ZHANG D G, 2008. A study on the community structure and plant diversity of alpine meadow under different degrees of degradation in the Eastern Qilian Mountains[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 17(4): 1-11. | |
| [16] | 南笑宁, 2020. 甘南高寒草甸不同坡向植物群落功能多样性研究[D]. 兰州: 西北师范大学. |
| NAN S N, 2020. Study on the functional diversity of plant communities on different slopes in the alpine meadow of Gannan[D]. Lanzhou: Northwest Normal University. | |
| [17] | 聂莹莹, 李新娥, 王刚, 2010. 阳坡-阴坡生境梯度上植物群落α多样性与β多样性的变化模式及与环境因子的关系[J]. 兰州大学学报 (自然科学版), 46(3):73-79. |
| NIE Y Y, LI X E, WANG G, et al., 2010. Variation mode of α diversity and β diversity of plant community of different habitat gradients from south-facing slope to north-facing slope and its relation with different environmental factors[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences), 46(3): 73-79. | |
| [18] | 盘远方, 李娇凤, 黄昶吟, 等, 2019. 桂林岩溶石山不同坡向灌丛植物多样性与土壤环境因子的关系[J]. 广西植物, 39(8): 1115-1125. |
| PAN Y F, LI J F, HUANG C Y, et al., 2019. Relationship between plant diversity of shrubs and soil environmental factors along with slope aspects in karst hills of Guilin,Southwest China[J]. Guihaia, 39(8): 1115-1125. | |
| [19] | 盘远方, 李娇凤, 姚玉萍, 等, 2021. 桂林岩溶石山青冈群落植物功能多样性和环境因子与坡向的关联研究[J]. 生态学报, 41(11): 4484-4492. |
| PAN Y F, LI F J, YAO Y P, et al., 2021. Changes in plant functional diversity and environmental factors of cyclobalanopsis glauca community in response to slope gradient[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(11): 4484-4492. | |
| [20] | 秦娟, 孔海燕, 刘华, 2016. 马尾松不同林型土壤C、N、P、K的化学计量特征[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报 (自然科学版), 44(2): 68-76, 82. |
| QIN J, KONG H Y, LIU H, 2016. Stoichiometric characteristic of soil C, N, P and K in different Pinus massoniana forests[J]. Journal of Northwest Agricultural & Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 44(2): 68-76, 82. | |
| [21] | 沈泽昊, 张新时, 金义兴, 2000. 三峡大老岭森林物种多样性的空间格局分析及其地形解释[J]. 植物学报, 42(6): 620-627. |
| SHEN Z H, ZHANG X S, JIN Y X, 2000. Spatial pattern analysis and topographical interpretation of species diversity in the forests of Dalaoling in the region of the Three Gorges[J]. Acta Botanica Sinica, 42(6): 620-627. | |
| [22] | 汤雷吼, 2021. 不同林龄马尾松人工林生物生产力及养分特性研究[D]. 南宁: 广西大学. |
| TANG L H, 2021. Study on biological productivity and nutrient characteristics of Pinus massoniana plantation with different ages[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University. | |
| [23] | 王大伟, 孙帅, 刘金平, 等, 2017. 坡向对退化冷季型护坡草坪中植物种类及多样性的影响[J]. 草学 (1): 40-44, 48. |
| WANG D W, SUN S, LIU J P, et al., 2017. Effect of slope direction on species and diversity of plant in the degenerative cold season lawn[J]. Journal of Grassland and Forage Science (1): 40-44, 48. | |
| [24] | 王飞, 屠彩芸, 曹秀文, 等, 2018. 白龙江干旱河谷不同坡向主要灌丛群落随海拔梯度变化的物种多样性研究[J]. 植物研究, 38(1): 26-36. |
| WANG F, TU C Y, CAO X W, et al., 2018. The different altitude gradient change rules of the main shrub community in arid valleys of the Bailongjiang River with different slope[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 38(1): 26-36. | |
| [25] | 王永琪, 秦佳双, 马姜明, 等, 2020. 南亚热带马尾松人工林林下木本植物的物种多样性[J]. 广西师范大学学报 (自然科学版), 38(6): 131-139. |
| WANG Y Q, QIN J S, MA J M, et al., 2020b. Understory woody species diversity of Pinus massoniana plantations in south subtropical area[J]. Journal of Guangxi Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 38(6): 131-139. | |
| [26] | 吴强, PENG Yuanying, 马恒运, 等, 2019. 森林生态系统服务价值及其补偿校准--以马尾松林为例[J]. 生态学报, 39(1): 117-130. |
| WU Q, PENG Y Y, MA H Y, et al., 2019. Research on the value of forest ecosystem services and compensation in a Pinus massoniana forest[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(1): 117-130. | |
| [27] | 肖洋, 陈丽华, 余新晓, 2010. 北京密云麻栎人工混交林凋落物养分归还特征[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 38(7):13-15. |
| XIAO Y, CHENG L H, YU X X, 2010. Characteristics of nutrient return of litter fall in Quercus acutissima mixed forest in Miyun of Beijing[J]. Journal of northeast forestry University, 38(7): 13-15. | |
| [28] | 杨云礼, 徐明, 张姣, 等, 2022. 黔中地区不同马尾松群丛植物群落与土壤理化性质特征[J]. 水土保持研究, 29(1): 119-126. |
| YANG Y L, XU M, ZHANG J, et al., 2022. Characteristics of communities and soil physicochemical properties of different Pinus massoniana in central Guizhou[J]. Reserach of Soil and Water Conservation, 30(12): 2303-2308. | |
| [29] | 么旭阳, 胡耀升, 刘艳红, 2014. 长白山阔叶红松林典型森林群落功能多样性及其与地形因子的关系[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报 (自然科学版), 42(10): 95-102. |
| YAO X Y, HU Y S, LIU Y H, 2014. Functional diversity of typical broad-leaved Korean pine forest communities in Changbai Mountains and its relationship with topographical factors[J]. Journal of Northwest Agricultural&Forestry University, 42(10): 95-102. | |
| [30] | 张健, 徐明, 王阳, 等, 2021. 黔中地区不同马尾松群丛土壤球囊霉素分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(12): 2303-2308. |
| ZHANG J, XU M, WANG Y, et al., 2021. Distribution characteristics of the glomalin-related soil protein of different Pinus massoniana association in central Guizhou[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(12): 2303-2308. | |
| [31] |
张荣, 余飞燕, 周润惠, 等, 2020. 坡向和坡位对四川夹金山灌丛群落结构与物种多样性特征的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 31(8): 2507-2514.
DOI |
|
ZHANG R, YU F Y, ZHOU R H, et al., 2020. Effects of slope position and aspect on structure and species diversity of shrub community in the Jiajin Mountains, Sichuan Province, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 31(8): 2507-2514.
DOI |
|
| [32] | 张晓龙, 周继华, 蔡文涛, 等, 2017. 水分梯度下黑河流域荒漠植物群落多样性特征[J]. 生态学报, 37(14): 4627-4635. |
| ZHANG X L, ZHOU J H, CAI W T, et al., 2017. Diversity characteristics of plant communities in the arid desert of the Heihe basin under different moisture gradients[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37(14): 4627-4635. | |
| [33] | 朱云云, 王孝安, 王贤, 等, 2016. 坡向因子对黄土高原草地群落功能多样性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 36(21): 6823-6833. |
| ZHU Y Y, WANG X A, WANG X, et al., 2016. Effect of slope aspect on the functional diversity of grass communities in the Loess Plateau[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36(21): 6823-6833. | |
| [34] | 宗宁, 石培礼, 牛犇, 等, 2014. 氮磷配施对藏北退化高寒草甸群落结构和生产力的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 25(12): 3458-3468. |
| ZONG N, SHI P L, NIU B, et al., 2014. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorous fertilization on community structure and productivity of degraded alpine meadows in northern Tibet, China[J]. The Journal of Applied Ecology, 25(12): 3458-3468. | |
| [35] | 邹文涛, 姜艳, 尹光天, 等, 2014. 石门森林公园不同海拔或坡向林地物种多样性的比较[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 34(4): 77-81. |
| ZOU W T, JIANG Y, YI G T, et al., 2014. Biodiversity comparison of forestland with different altitude or aspect in Shimen National Forest Park[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 34(4): 77-81. |
| [1] | LI Yang, HOU Zhiyong, CHEN Wei, YU Xiaoying, XIE Yonghong, HUANG Xin, TAN Peiyang, LI Jicheng, LI Shanglin, YANG Hui. Plant Diversity and Systematic Composition of Alpine Wetlands in Dawei Mountain [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 643-650. |
| [2] | LI Xun, CUI Ningjie, ZHANG Yan, QIN Yu, ZHANG Jian. Mixed Effects on Cellulose, Total phenols and Condensed Tannins Degradation in the Litter Leaves of Pinus massoniana and Native Broad-leaved Tree Species [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(9): 1813-1822. |
| [3] | WANG Zhe, TIAN Shengni, ZHANG Yongmei, ZHANG Heyu, ZHOU Zhongze. Study on the Plant Community Characteristics of the Estuary of Pai River in Chaohu Lake [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(9): 1823-1831. |
| [4] | CHENG Chuanpeng, XU Mingjie, LIU Huifeng. Effects of Thinning on Carbon Dynamics and Economic Value of Carbon Fixation in Subtropical Pinus massoniana Plantation [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(8): 1499-1509. |
| [5] | WANG Lixiao, LIU Jinxian, CHAI Baofeng. Response of Soil Bacterial Community and Nitrogen Cycle during the Natural Recovery of Abandoned Farmland in Subalpine of the North China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(8): 1537-1546. |
| [6] | XUAN Jin, LI Zuchan, ZOU Cheng, QIN Zibo, WU Yahua, HUANG Liujing. Multi-scale Effects of Central Bar Landscape Class and Pattern on Plant Diversity in Minjiang River: The Case of Minjiang River Basin (Fuzhou Section) Planning [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(12): 2320-2330. |
| [7] | CHEN Shuangshuang, ZHU Ninghua, ZHOU Guangyi, YUAN Xingming, SHANG Hai, WANG Yixuan. Vegetation and Soil Physical Characteristics of Artificial Arbor Forests under Different Grades of Rocky Desertification [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(1): 52-61. |
| [8] | WANG Xuan, XIONG Xin, ZHANG Huiling, ZHAO Mengdi, HU Minghui, CHU Guowei, MENG Ze, ZHANG Deqiang. Effects of Simulated Acid Rain on Litter Decomposition and Soil Respiration in A Low Subtropical Forest [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(9): 1805-1813. |
| [9] | ZHAO Li, GUO Chunyan, ZHANG Wenjun, WANG Xiaojiang, LIU Pingsheng. Community Characteristics and Their Correlation Analysis of Typical Natural Forest in Zhalantun [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(7): 1353-1359. |
| [10] | HONG Wenjun, MO Luojian, ZHANG Hao. Effects of Different Thinning on the Structure of Acacia mangium Plantation in South China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(7): 1360-1367. |
| [11] | ZHANG Jian, XU Ming, WANG Yang, WEN Chunyu, YANG Yunli, ZHANG Jiao, NIE Kun. Distribution Characteristics of the Glomalin-Related Soil Protein of Different Pinus massoniana Association in Central Guizhou [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(12): 2303-2308. |
| [12] | ZHANG Yangyang, ZHOU Qinghui, XU Jiaoyang, WEI Ming, CHEN Jihao, HE Wei, WANG Pengcheng, YAN Zhaogui. Effects of Forest Ages on the Diversity of Understory Plants and Soil Seed Bank of Pinus massoniana Plantations [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(11): 2121-2129. |
| [13] | LIN Li, DAI Lei, LIN Zebei, WU Jitong, YAN Wei, WANG Zhijie. Plant Diversity and Its Relationship with Soil Physicochemical Properties of Urban Forest Communities in Central Guizhou [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(11): 2130-2141. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
