Ecology and Environment ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (9): 1797-1804.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.09.003
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Tianlin1,2( ), CAI Zhanglin1,2, ZHAO Houben1,2,*(
), CAI Zhanglin1,2, ZHAO Houben1,2,*( ), WU Zhongmin1,2, ZHOU Guangyi1,2, QIU Zhijun1,2
), WU Zhongmin1,2, ZHOU Guangyi1,2, QIU Zhijun1,2
Received:2021-02-26
Online:2021-09-18
Published:2021-12-08
Contact:
ZHAO Houben
张天霖1,2( ), 蔡章林1,2, 赵厚本1,2,*(
), 蔡章林1,2, 赵厚本1,2,*( ), 吴仲民1,2, 周光益1,2, 邱治军1,2
), 吴仲民1,2, 周光益1,2, 邱治军1,2
通讯作者:
赵厚本
作者简介:张天霖(1996年生),男,硕士研究生,主要从事森林土壤养分循环等方面的研究。E-mail: zhangtianlineric@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
ZHANG Tianlin, CAI Zhanglin, ZHAO Houben, WU Zhongmin, ZHOU Guangyi, QIU Zhijun. Priming Effect on Soil Organic Carbon by Abnormal Litter Following 13C Pulse-labeling[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(9): 1797-1804.
张天霖, 蔡章林, 赵厚本, 吴仲民, 周光益, 邱治军. 13C脉冲标记法研究非正常凋落物对土壤有机碳的激发效应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(9): 1797-1804.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.09.003
| 树种 Species | w(有机碳OC)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(全氮TN)/ (g∙kg-1) | 碳氮比w(C)꞉w(N) | 13C丰度值 δ13C/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 马尾松 Pinus massoniana | 474.52±4.23 | 0.93±0.05 | 51.12 | 424.86±22.43 |
| 黧蒴锥 Castanopsis fissa | 467.98±13.10 | 1.13±0.05 | 41.47 | 645.50±83.28 |
| 浙江润楠 Machilus chekiangensis | 432.92±22.35 | 1.30±0.03 | 33.72 | 681.07±51.13 |
Table 1 Characteristics of the 13C-labeled plant leaves
| 树种 Species | w(有机碳OC)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(全氮TN)/ (g∙kg-1) | 碳氮比w(C)꞉w(N) | 13C丰度值 δ13C/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 马尾松 Pinus massoniana | 474.52±4.23 | 0.93±0.05 | 51.12 | 424.86±22.43 |
| 黧蒴锥 Castanopsis fissa | 467.98±13.10 | 1.13±0.05 | 41.47 | 645.50±83.28 |
| 浙江润楠 Machilus chekiangensis | 432.92±22.35 | 1.30±0.03 | 33.72 | 681.07±51.13 |
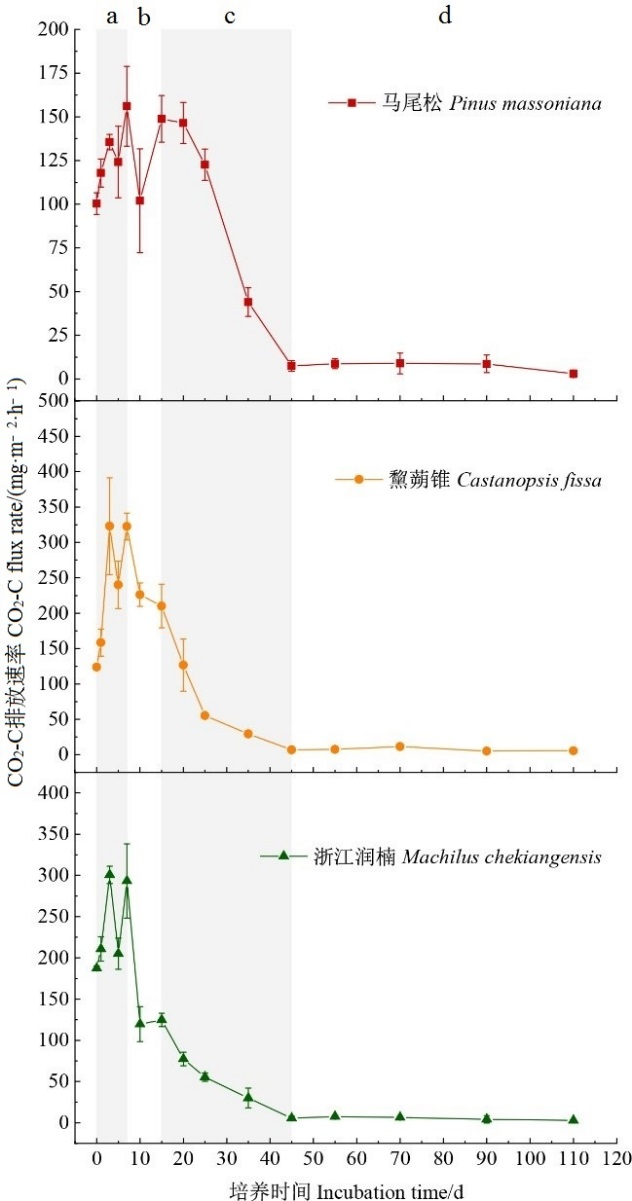
Fig. 1 The dynamics of total CO2 flux of different abnormal litters The data in the table is the mean ± standard error. The different lowercase letters at the top a, b, c and d indicates different stages. n=3
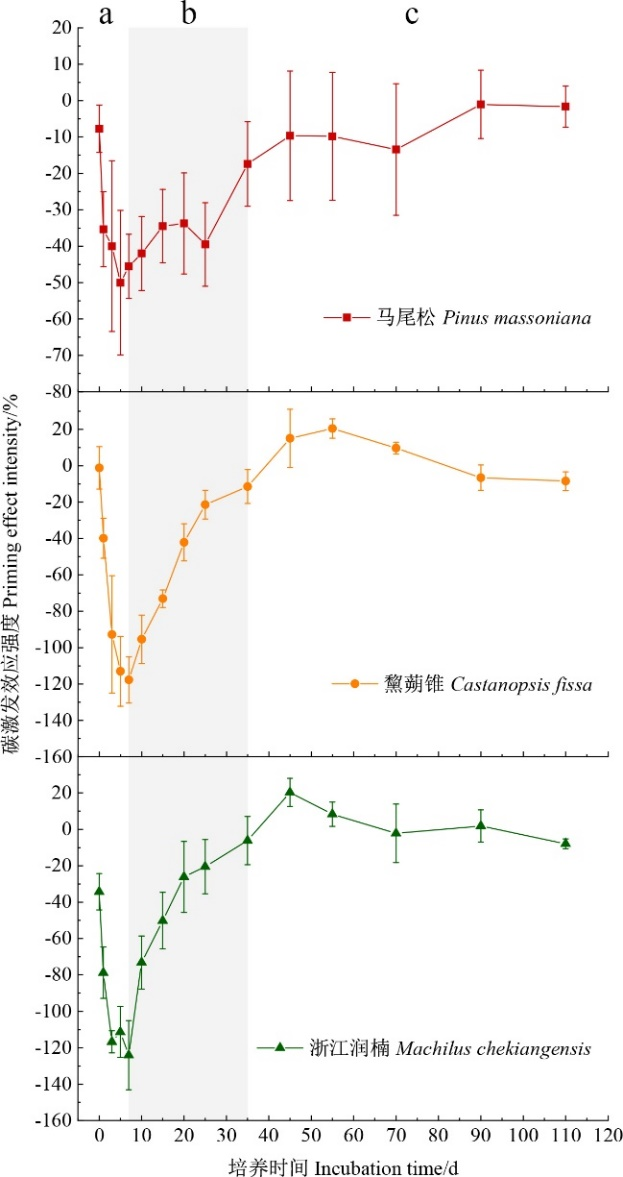
Fig. 2 The priming effects intensity of different abnormal litters The data in the table is the mean±standard error. The different lowercase letters at the top a, b, and c indicates different stages. n=3
| 处理组 Treatment | 土壤深度 Depth/cm | w(有机碳OC)/(g·kg-1) | w(全氮TN)/(g·kg-1) | w(有效氮AN)/(mg·kg-1) | 13C丰度值 δ13C/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 培养前 Before incubation | 0-5 | 120.36±2.94b | 3.71±0.27 | 328.00±11.23 | -28.23±0.26b |
| 5-10 | 89.27±1.86b | 2.32±0.15 | 231.77±11.97 | -27.13±0.66b | |
| 10-20 | 40.58±1.80a | 1.39±0.03 | 130.57±5.46 | -22.96±0.27a | |
| 对照组 Control group | 0-5 | 123.66±2.04b | 3.32±0.20 | 338.17±17.58 | -28.44±0.07b |
| 5-10 | 95.67±3.66ab | 2.59±0.05 | 265.49±8.00 | -27.62±0.18b | |
| 10-20 | 50.08±5.65a | 1.65±0.22 | 142.72±36.73 | -23.27±1.07a | |
| 马尾松 Pinus massoniana | 0-5 | 135.40±4.17a | 3.33±0.27 | 321.33±34.06 | -27.48±0.58ab |
| 5-10 | 102.05±2.37a | 2.73±0.14 | 298.28±19.73 | -26.37±0.41a | |
| 10-20 | 39.92±0.75a | 1.47±0.09 | 122.77±13.04 | -22.32±0.35a | |
| 黧蒴锥 Castanopsis fissa | 0-5 | 135.12±2.03a | 3.25±0.15 | 290.75±19.13 | -26.96±0.55a |
| 5-10 | 99.41±11.54a | 2.70±0.29 | 259.28±15.66 | -26.42±0.45a | |
| 10-20 | 44.33±4.04a | 1.65±0.32 | 128.44±10.17 | -23.35±1.75a | |
| 浙江润楠 Machilus chekiangensis | 0-5 | 122.50±6.09b | 3.63±0.31 | 284.10±19.12 | -27.52±0.48ab |
| 5-10 | 82.48±4.34b | 2.73±0.17 | 316.01±11.91 | -26.39±0.54a | |
| 10-20 | 47.07±11.50a | 1.88±0.31 | 148.92±46.97 | -22.88±1.96a | |
| F值 F value | |||||
| 土壤深度 Depth | 410.90** | 115.71** | 122.67** | 60.01** | |
| 处理组 Species | 2.92 | 1.48 | 1.33 | 1.69 | |
| 土壤深度*处理组 Depth*Species | 2.70* | 0.44 | 2.00 | 0.39 |
Table 2 Soil nutrient content before and after incubation in different treatments groups
| 处理组 Treatment | 土壤深度 Depth/cm | w(有机碳OC)/(g·kg-1) | w(全氮TN)/(g·kg-1) | w(有效氮AN)/(mg·kg-1) | 13C丰度值 δ13C/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 培养前 Before incubation | 0-5 | 120.36±2.94b | 3.71±0.27 | 328.00±11.23 | -28.23±0.26b |
| 5-10 | 89.27±1.86b | 2.32±0.15 | 231.77±11.97 | -27.13±0.66b | |
| 10-20 | 40.58±1.80a | 1.39±0.03 | 130.57±5.46 | -22.96±0.27a | |
| 对照组 Control group | 0-5 | 123.66±2.04b | 3.32±0.20 | 338.17±17.58 | -28.44±0.07b |
| 5-10 | 95.67±3.66ab | 2.59±0.05 | 265.49±8.00 | -27.62±0.18b | |
| 10-20 | 50.08±5.65a | 1.65±0.22 | 142.72±36.73 | -23.27±1.07a | |
| 马尾松 Pinus massoniana | 0-5 | 135.40±4.17a | 3.33±0.27 | 321.33±34.06 | -27.48±0.58ab |
| 5-10 | 102.05±2.37a | 2.73±0.14 | 298.28±19.73 | -26.37±0.41a | |
| 10-20 | 39.92±0.75a | 1.47±0.09 | 122.77±13.04 | -22.32±0.35a | |
| 黧蒴锥 Castanopsis fissa | 0-5 | 135.12±2.03a | 3.25±0.15 | 290.75±19.13 | -26.96±0.55a |
| 5-10 | 99.41±11.54a | 2.70±0.29 | 259.28±15.66 | -26.42±0.45a | |
| 10-20 | 44.33±4.04a | 1.65±0.32 | 128.44±10.17 | -23.35±1.75a | |
| 浙江润楠 Machilus chekiangensis | 0-5 | 122.50±6.09b | 3.63±0.31 | 284.10±19.12 | -27.52±0.48ab |
| 5-10 | 82.48±4.34b | 2.73±0.17 | 316.01±11.91 | -26.39±0.54a | |
| 10-20 | 47.07±11.50a | 1.88±0.31 | 148.92±46.97 | -22.88±1.96a | |
| F值 F value | |||||
| 土壤深度 Depth | 410.90** | 115.71** | 122.67** | 60.01** | |
| 处理组 Species | 2.92 | 1.48 | 1.33 | 1.69 | |
| 土壤深度*处理组 Depth*Species | 2.70* | 0.44 | 2.00 | 0.39 |
| [1] |
AERTS R, 1997. Climate, leaf litter chemistry and leaf litter decomposition in terrestrial ecosystems: a triangular relationship[J]. Oikos, 79(3): 439-449.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
BLAGODATSKAYA Е, KUZYAKOV Y. 2008. Mechanisms of real and apparent priming effects and their dependence on soil microbial biomass and community structure: Critical review[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 45(2): 115-131.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
BROMAND S, WHALEN J K, JANZEN H H, et al., 2001. A pulse-labelling method to generate 13C-enriched plant materials[J]. Plant and Soil, 235(2): 253-257.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
CHENG W X, 1999. Rhizosphere feedback in elevated CO2[J]. Tree physiology, 19(4-5): 313-320.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
CLEMMENSEN K E, BAHR A, OVASKAINEN O, et al., 2013. Roots and associated fungi drive long-term carbon sequestration in boreal forest[J]. Science, 339(6127): 1615-1618.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
FISCHER A P, 2019. Adapting and coping with climate change in temperate forests[J]. Global Environmental Change, 54: 160-171.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
FONTAINE S, BAROT S, BARRE P, et al., 2007. Stability of organic carbon in deep soil layers controlled by fresh carbon supply[J]. Nature, 450(7167): 277-280.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
GUENET B, CAMINO-SERRANO M, CIAIS P, et al., 2018. Impact of priming on global soil carbon stocks[J]. Global Change Biology, 24(11): 1873-1883.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
GUENET B, NEILL C, BARDOUX G, et al., 2010. Is there a linear relationship between priming effect intensity and the amount of organic matter input?[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 46(3): 436-442.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
JOBBAGY E G, JACKSON R B, 2000. The vertical distribution of soil organic carbon and its relation to climate and vegetation[J]. Ecological Applications, 10(2): 423-436.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
KUZYAKOV Y, FRIEDEL J K, STAHRA K, 2000. Review of mechanisms and quantification of priming effects[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 32(11-12): 1485-1498.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
LENKA S, TRIBEDI P, SINGH B, et al., 2019. Effect of crop residue addition on soil organic carbon priming as influenced by temperature and soil properties[J]. Geoderma, 347: 70-79.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
LI L J, ZHU X, YE R Z, et al., 2018. Soil microbial biomass size and soil carbon influence the priming effect from carbon inputs depending on nitrogen availability[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 119: 41-49.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
LODGE D J, SCATENA F N, ASBURY C E, et al., 1991. Fine litterfall and related nutrient inputs resulting from Hurricane Hugo in subtropical wet and lower montane rain forests of Puerto Rico[J]. Biotropica, 23(4): 336-342.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
LU Y, WATANABE A, KIMURA M, 2003. Carbon dynamics of rhizodeposits, root- and shoot-residues in a rice soil[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 35(9): 1223-1230.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
MOORHEAD D, SINSABAUGH R, 2006. A theoretical model of litter decay and microbial interaction[J]. Ecological Monographs, 76(2): 151-174.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
OKEY T A, ALIDINA H M, LO V, et al., 2014. Effects of climate change on Canada's Pacific marine ecosystems: A summary of scientific knowledge[J]. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries, 24(2): 519-559.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
SAYER E J, HEARD M S, GRANT H K, et al., 2011. Soil carbon release enhanced by increased tropical forest litterfall[J]. Nature Climate Change, 1(6): 304-307.
DOI URL |
| [19] | SCHOLZE M, KNORR W, ARNELL N, et al., 2009. A risk analysis for world ecosystems under future climate change[J]. IOP Conference Series, 6(30): 302033. |
| [20] | SMITH P, FANG C M, DAWSON J J C, et al., 2008. Impact of global warming on soil organic carbon[J]. Advances in Agronomy, 97: 1-43. |
| [21] |
TRESEDER K K, HOLDEN S R, 2013. Fungal carbon sequestration[J]. Science, 339(6127): 1528-1529.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
TRUMBORE S E, CZIMCZIK C I, 2008. An uncertain future for soil carbon[J]. Science, 321(5895): 1455-1456.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
WANG H, BOUTTON T W, XU W H, et al., 2015. Quality of fresh organic matter affects priming of soil organic matter and substrate utilization patterns of microbes[J]. Scientific Reports, DOI: 10.1038/srep10102.
DOI |
| [24] |
WANG Q K, WANG Y P, WANG S L, et al., 2014. Fresh carbon and nitrogen inputs alter organic carbon mineralization and microbial community in forest deep soil layers[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 72: 145-151.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
XU L, YU G R, HE N P, et al., 2018. Carbon storage in China's terrestrial ecosystems: A synthesis[J]. Scientific Reports, DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-20764-9.
DOI |
| [26] |
XU X N, 2006. Nutrient dynamics in decomposing needles of Pinus luchuensis after typhoon disturbance in a subtropical environment[J]. Annals of Forest Science, 63(7): 707-713.
DOI URL |
| [27] | YU G R, CHEN Z, PIAO S L, et al., 2014. High carbon dioxide uptake by subtropical forest ecosystems in the East Asian monsoon region[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 111(13): 4910-4915. |
| [28] |
YU G C, ZHAO H B, CHEN J, et al., 2020. Soil microbial community dynamics mediate the priming effects caused by in situ decomposition of fresh plant residues[J]. Science of The Total Environment, DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139708.
DOI |
| [29] |
ZHANG W D, WANG S L, 2012. Effects of NH4+ and NO3- on litter and soil organic carbon decomposition in a Chinese fir plantation forest in South China[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 47: 116-122.
DOI URL |
| [30] | 陈耀德, 叶青峯, 刘美娟, 等, 2006. 台湾山地雾林带的水分与养分循环研究[J]. 资源科学, 28(3): 174-180. |
| CHEN Y T, YE Q F, LIU M J, et al., 2006. The investigation of nutrients and hydrological cycling in the Yuanyang Lake montane cloud forest in Taiwan[J]. Resources Scinence, 28(3): 174-180. | |
| [31] | 郭培培, 江洪, 余树全, 等, 2009. 亚热带6种针叶和阔叶树种凋落叶分解比较[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 15(5): 655-659. |
| GOU P P, JIANG H, YU S Q, et al., 2009. Comparison of litter decomposition of six species of coniferous and broad-leaved trees in Subtropical China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 15(5): 655-659. | |
| [32] | 何敏毅, 孟凡乔, 史雅娟, 等, 2008. 用13C脉冲标记法研究玉米光合碳分配及其向地下的输入[J]. 环境科学, 29(2): 446-453. |
|
HE M Y, MENG F Q, SHI Y J, et al., 2008. Estimating Photosynthesized Carbon Distribution and Inputs into Belowground in a Maize Soil Following 13C Pulse-labeling[J]. Environmental Science, 29(2): 446-453.
DOI URL |
|
| [33] | 刘光崧, 1996. 土壤理化分析与剖面描述[M]. 北京: 中国标准出版社: 31-37. |
| LIU G S, 1996. Soil physical and chemical analysis and description of soil profiles[M]. Beijing: Standards Press of China: 31-37. | |
| [34] | 刘世荣, 王晖, 栾军伟, 2011. 中国森林土壤碳储量与土壤碳过程研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 31(19): 5437-5448. |
| LIU S R, WANG H, LUAN J W, 2011. A review of research progress and future prospective of forest soil carbon stock and soil carbon process in China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31(19): 5437-5448. | |
| [35] | 刘世荣, 温远光, 蔡道雄, 等, 2014. 气候变化对森林的影响与多尺度适应性管理研究进展[J]. 广西科学, 21(5): 419-435. |
| LIU S R, WEN Y G, CAI D X, et al., 2014. Impacts of climate change on forests and adaptive multi-scales management: A review[J]. Guangxi Sciences, 21(5): 419-435. | |
| [36] | 骆土寿, 张国平, 吴仲民, 等, 2008. 雨雪冰冻灾害对广东杨东山十二度水保护区常绿与落叶混交林凋落物的影响[J]. 林业科学, 44(11): 177-183. |
| LUO T S, ZHANG G P, WU Z M, et al., 2008. Effects of the frozen rain and snow disaster to the litterfall of evergreen and deciduous broadleaved mixed forest in Yangdongshan Shierdushui nature reserve of Guangdong[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 44(11): 177-183. | |
| [37] | 冉珊珊, 时宇, 黄黄, 等, 2019. 用13C 脉冲标记法研究互花米草光合碳的分配[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(2): 270-275. |
| RAN S S, SHI Y, HUANG H, et al., 2019. Researching photosynthesized carbon allocation of S. alterniflora following 13C pulse-labeling[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 28(2): 270-275. | |
| [38] | 王清奎, 2011. 碳输入方式对森林土壤碳库和碳循环的影响研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 22(4): 1075-1081. |
| WANG Q K, 2011. Responses of forest soil carbon pool and carbon cycle to the changes of carbon input[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 22(4): 1075-1081. | |
| [39] | 吴仲民, 李意德, 周光益, 等, 2008. “非正常凋落物”及其生态学意义[J]. 林业科学, 44(11): 28-31. |
| WU Z M, LI Y D, ZHOU G Y, et al., 2008. Abnormal litterfall and its ecological significance[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 44(11): 28-31. | |
| [40] | 吴仲民, 卢俊培, 杜志鹄, 1994. 海南岛尖峰岭热带山地雨林及其更新群落的凋落物量与贮量[J]. 植物生态学报, 18(4): 306-313. |
| WU Z M, LU J P, DU Z H, et al., 1994. Litter production and storage in the natural and regenerated tropical montane rain forests at Jianfenglin, Hainan island[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 18(4): 306-313. | |
| [41] | 肖以华, 刘世荣, 佟富春, 等, 2013. “非正常”凋落物对冰雪灾后南岭森林土壤有机碳的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 22(9): 1504-1513. |
| XIAO Y H, LIU S R, TONG F C, et al., 2013. Effects of abnormal litter input on forest soil organic carbon after ice-storm: A case of Nanling[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 22(9): 1504-1513. | |
| [42] | 许涵, 李意德, 骆土寿, 等, 2008. 达维台风对海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林群落的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 32(6): 116-127. |
| XU H, LI Y D, LUO T S, et al., 2008. Influence of typhoon Damrey on the tropical montane rain forest community in Jianfengling, Hainan Island, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 32(6): 116-127. | |
| [43] | 徐璇, 王维枫, 阮宏华, 2019. 土壤动物对森林凋落物分解的影响:机制和模拟[J]. 生态学杂志, 38(9): 2858-2865. |
| XU X, WANG W F, RUAN H H, 2019. Effects of soil fauna on the decomposition of forest litter: Mechanism and modeling[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 38(9): 2858-2865. |
| [1] | WANG Chao, YANG Qiannan, ZHANG Chi, LIU Tongxu, ZHANG Xialong, CHEN Jing, LIU Kexue. The Characteristics of Soil Phosphorus Fractions and Their Availability under Different Land Use Types in Danxia Mountain [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 889-897. |
| [2] | TANG Haiming, SHI Lihong, WEN Li, CHENG Kaikai, LI Chao, LONG Zedong, XIAO Zhiwu, LI Weiyan, GUO Yong. Effects of Different Long-term Fertilizer Managements on Rhizosphere Soil Nitrogen in the Double-cropping Rice Field [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 492-499. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
