生态环境学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (2): 235-244.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.02.003
郎漫1,2( ), 许力文2, 朱恺文3, 吴泓瑾3, 张佳音3, 李平1,2,*(
), 许力文2, 朱恺文3, 吴泓瑾3, 张佳音3, 李平1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-12-16
出版日期:2023-02-18
发布日期:2023-05-11
通讯作者:
*李平(1982年生),男,副教授,博士,主要从事土壤氮循环及其生态环境效应、土壤环境化学过程与污染控制研究。E-mail: pli@nuist.edu.cn作者简介:郎漫(1982年生),女(满族),副教授,博士,主要从事土壤氮循环及其生态环境效应研究。E-mail: mlang@nuist.edu.cn
基金资助:
LANG Man1,2( ), XU Liwen2, ZHU Kaiwen3, WU Hongjin3, ZHANG Jiayin3, LI Ping1,2,*(
), XU Liwen2, ZHU Kaiwen3, WU Hongjin3, ZHANG Jiayin3, LI Ping1,2,*( )
)
Received:2022-12-16
Online:2023-02-18
Published:2023-05-11
摘要:
研究外源碳氮施加对土壤氮素转化和温室气体排放的影响可为土壤养分管理、温室气体减排提供科学依据。以东北农田黑土为对象,采用室内培养试验,在25 ℃和60% WHC水分条件下研究外源碳(葡萄糖和乙酸)、氮(硫酸铵)施加对土壤净氮转化速率和温室气体排放的影响。结果表明,对照处理土壤净氮矿化速率为0.03 mg·kg-1·d-1,单施氮肥抑制了土壤有机氮的矿化,净氮矿化速率降为-0.56 mg·kg-1·d-1,表现为对氮素的固定,而净硝化速率和N2O排放速率分别显著增加至对照处理的33.3倍和4.69倍,但对CO2排放速率没有显著影响。与单施氮肥处理相比,氮肥配施葡萄糖或乙酸处理显著降低了土壤中铵态氮和硝态氮含量,氮肥配施葡萄糖对铵态氮的影响程度大于氮肥配施乙酸处理。碳氮配施使得净氮矿化速率进一步降低,氮肥配施葡萄糖处理的净氮矿化速率为-5.97 mg·kg-1·d-1,显著低于氮肥配施乙酸处理(-5.00 mg·kg-1·d-1)。单施氮肥处理的净硝化速率为10.66 mg·kg-1·d-1,氮肥配施葡萄糖和氮肥配施乙酸处理的净硝化速率分别降低至7.28 mg·kg-1·d-1和8.27 mg·kg-1·d-1。碳氮配施显著促进了N2O和CO2的排放,氮肥配施葡萄糖(43.60 μg·kg-1·d-1)和氮肥配施乙酸处理(30.17 μg·kg-1·d-1)的N2O平均排放速率分别是单施氮肥处理(18.85 μg·kg-1·d-1)的2.31倍和1.60倍,CO2平均排放速率(75.25、108.87 mg·kg-1·d-1)分别是单施氮肥处理(20.69 mg·kg-1·d-1)的3.63倍和5.26倍。由此表明,碳氮配施能够显著降低土壤中的无机氮含量,促进氮素的固定,对硝化作用的抑制效应降低了反硝化作用发生和硝态氮淋溶的风险。但是,碳氮配施促进了土壤中温室气体的排放,施加活性碳源对农田生态效应的影响还需综合评估。
中图分类号:
郎漫, 许力文, 朱恺文, 吴泓瑾, 张佳音, 李平. 碳氮施加对农田黑土氮素转化和温室气体排放的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 235-244.
LANG Man, XU Liwen, ZHU Kaiwen, WU Hongjin, ZHANG Jiayin, LI Ping. Effects of Carbon and Nitrogen Addition on Nitrogen Transformations and Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Black Cropland Soil[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(2): 235-244.
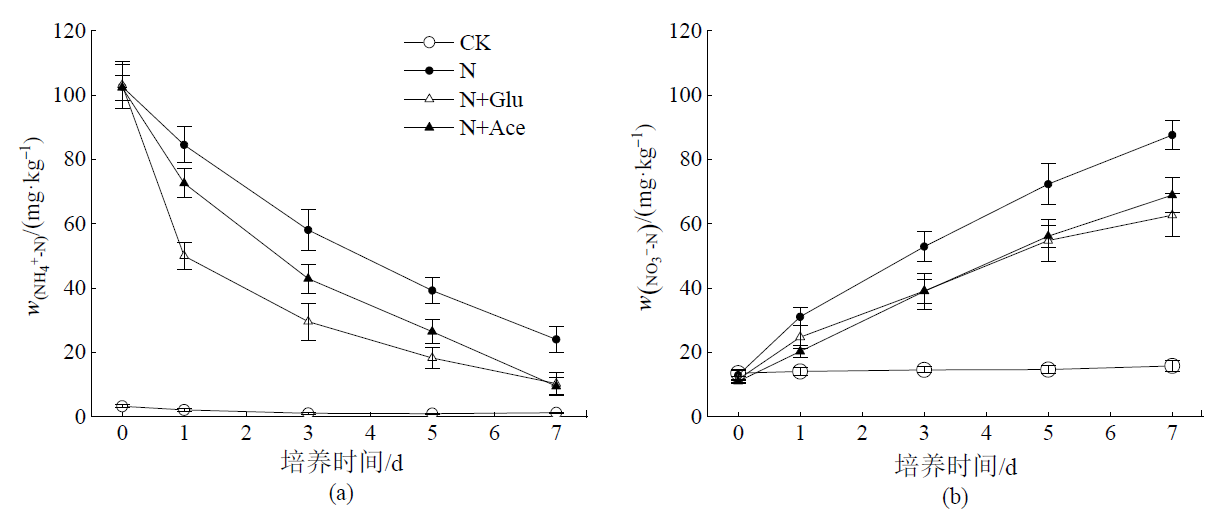
图1 碳氮施加后农田黑土中铵态氮(a)和硝态氮(b)含量的动态变化
Figure 1 The dynamic changes of ammonium (a) and nitrate (b) contents in black cropland soil after addition of C and N
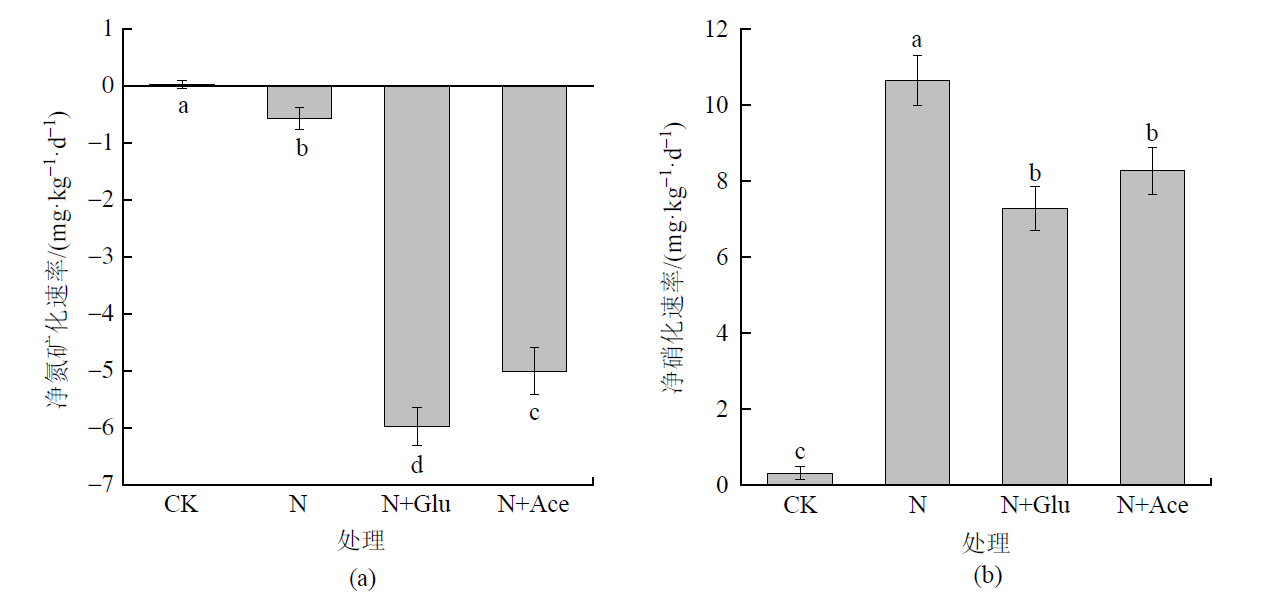
图2 碳氮施加后培养期间农田黑土的平均净氮矿化速率(a)和平均净硝化速率(b) 不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05)
Figure 2 The average net N mineralization (a) and nitrification (b) rates in black cropland soil after addition of C and N during incubation period
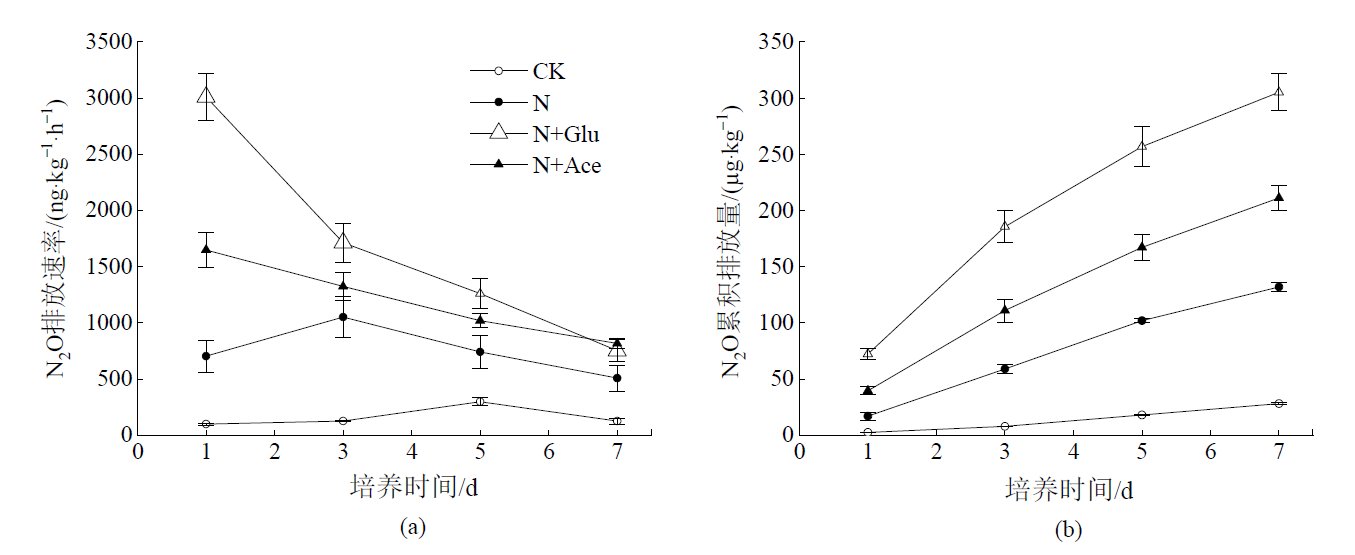
图3 碳氮施加后农田黑土中N2O排放速率(a)和累积排放量(b)的动态变化
Figure 3 The dynamic changes of N2O flux (a) and cumulative emissions (b) from black cropland soil after addition of C and N
| 回归公式 | r | |
|---|---|---|
| NH4+-N2O | y=20.35x+413.46 | 0.701** |
| NO3--N2O | y= -0.523x+1033.9 | 0.055 |
表1 培养期间土壤NH4+、NO3-含量与N2O排放量的相关性
Table 1 The correlations of NH4+, NO3- contents in soil and N2O emissions
| 回归公式 | r | |
|---|---|---|
| NH4+-N2O | y=20.35x+413.46 | 0.701** |
| NO3--N2O | y= -0.523x+1033.9 | 0.055 |
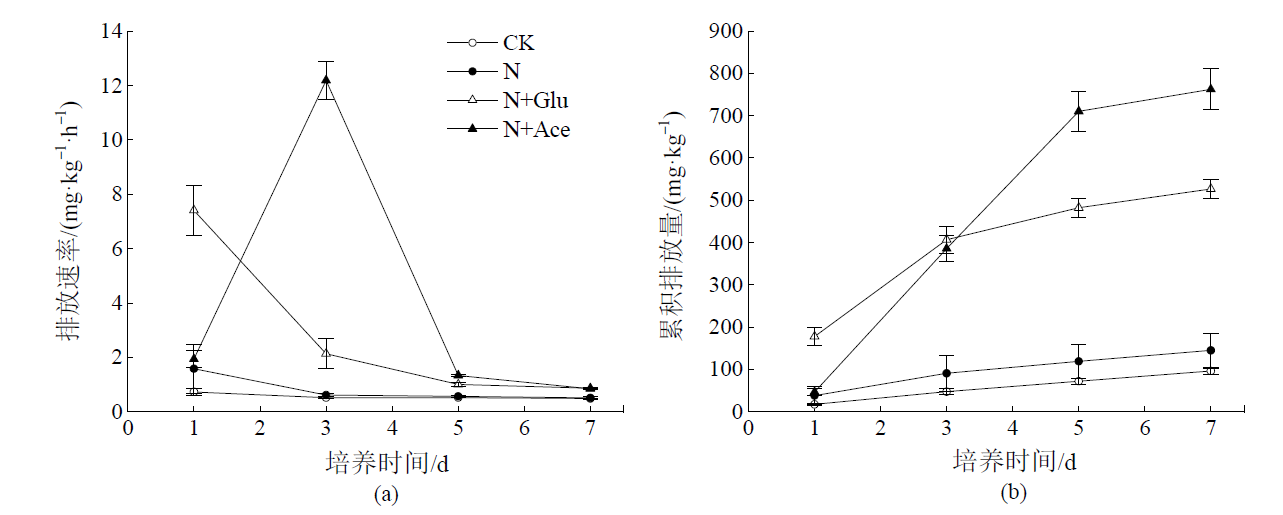
图5 碳氮施加后农田黑土中CO2排放速率(a)和累积排放量(b)的动态变化
Figure 5 The dynamic changes of CO2 flux (a) and cumulative emissions (b) from black cropland soil after addition of C and N
| [1] |
BAKKEN L R, BERGAUST L, LIU B B, et al., 2012. Regulation of denitrification at the cellular level: A clue to the understanding of N2O emissions from soils[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society Biological Sciences, 367(1593): 1226-1234.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
CHEN R R, SENBAYRAM M, BLAGODATSKY S, et al., 2014. Soil C and N availability determine the priming effect: Microbial N mining and stoichiometric decomposition theories[J]. Global Change Biology, 20(7): 2356-2367.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
CHEN Z X, TU X S, MENG H, et al., 2021. Microbial process-oriented understanding of stimulation of soil N2O emission following the input of organic materials[J]. Environmental Pollution, 284: 117176.
DOI URL |
| [4] | CHU G Y, YU D S, WANG X X, et al., 2021. Comparison of nitrite accumulation performance and microbial community structure in endogenous partial denitrification process with acetate and glucose served as carbon source[J]. Bioresource Technology, 320(Part B): 124405. |
| [5] |
DALY E J, HERNANDEZ-RAMIREZ G, 2020. Sources and priming of soil N2O and CO2 production: Nitrogen and simulated exudate additions[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 149(7): 107942.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
DUNHAM-CHEATHAM S M, ZHAO Q, OBRIST D, et al., 2020. Unexpected mechanism for glucose-primed soil organic carbon mineralization under an anaerobic-aerobic transition[J]. Geoderma, 376(15): 114535.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
ENWALL K, NYBERGA K, BERTILSSONB S, et al., 2007. Long-term impact of fertilization on activity and composition of bacterial communities and metabolic guilds in agricultural soil[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 39(1): 106-115.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
HUYGENS D, RÜTTING T, BOECKX P, et al., 2007. Soil nitrogen conservation mechanisms in a pristine south Chilean Nothofagus forest ecosystem[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 39(10): 2448-2458.
DOI URL |
| [9] | IPCC, 2007. Climate change 2007:Synthesis report. Fourth assessment report of the first, second and third report of the IPCC[R]. Geneva, Switzerland. |
| [10] | IPCC, 2014. Climate change 2014:Synthesis report. Contribution of working groups I, II and III to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change[R]. Geneva. Switzerland. |
| [11] |
KEILUWEIT M, BOUGOURE J J, 2015. Mineral protection of soil carbon counteracted by root exudates[J]. Nature Climate Change, 5(6): 588-595.
DOI |
| [12] |
KHALIL K, MARY B, RENAULT P, 2004. Nitrous oxide production by nitrification and denitrification in soil aggregates as affected by O2 concentration[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 36(4): 687-699.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
LAN T, HAN Y, ROELCKE M, et al., 2013. Processes leading to N2O and NO emissions from two different Chinese soils under different soil moisture contents[J]. Plant and Soil, 371(1-2): 611-627.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
LEPTIN A, WHITEHEAD D, ANDERSON C R, et al., 2021. Increased soil nitrogen supply enhances root-derived available soil carbon leading to reduced potential nitrification activity[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 159: 103842.
DOI URL |
| [15] | LIN D R, WU S R, LI Z Y, 2010. Impact assessment of climate change on forestry development in china[J]. Chinese Forestry Science and Technology, 9(3): 1-9. |
| [16] |
MAAG M, VINTHER F P, 1996. Nitrous oxide emission by nitrification and denitrification in different soil types and at different soil moisture contents and temperatures[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 4(1): 5-14.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
MASON-JONES K, SCHMÜCKER N, KUZYAKOV Y, 2018. Contrasting effects of organic and mineral nitrogen challenge the N-Mining Hypothesis for soil organic matter priming[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 124: 38-46.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
SCHLEUSNER P, LAMMIRATO C, TIERLING J, et al., 2018. Primed N2O emission from native soil nitrogen: A 15N-tracing laboratory experiment[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 181(4): 621-627.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
SONG X T, JU X T, TOPP C F E, et al., 2019. Oxygen regulates nitrous oxide production directly in agricultural soils[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 53(21): 12539-12547.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
YAMASAKI A, TATENO R, SHIBATA H, 2011. Effects of carbon and nitrogen amendment on soil carbon and nitrogen mineralization in volcanic immature soil in southern kyushu, Japan[J]. Journal of Forest Research, 16(5): 414-423.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
YANG L Q, ZHU G D, LIU R, 2020. How nitrification-related N2O is associated with soil ammonia oxidizers in two contrasting soils in China?[J] Science of the Total Environment, 770(9): 143212.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
ZHANG J J, PENG C H, ZHU Q, et al., 2016. Temperature sensitivity of soil carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide emissions in mountain forest and meadow ecosystems in China[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 142: 340-350.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
ZHU T B, ZHANG J B, CAI Z C, 2011. The contribution of nitrogen transformation processes to total N2O emissions from soils used for intensive vegetable cultivation[J]. Plant and Soil, 343(1-2): 313-327.
DOI URL |
| [24] | ZOU W X, LANG M, ZHANG L, et al., 2021. Ammonia-oxiding bacteria rather than ammonia-oxidizing archaea dominate nitrification in a nitrogen-fertilized calcareous soil[J]. Scicence of the Total Environment, 811: 151402. |
| [25] | 蔡祖聪, MOSI A R, 1999. 土壤水分状况对CH4氧化, N2O和CO2排放的影响[J]. 土壤, 31(6): 289-294. |
| CAI Z C, MOSI A R, 1999. Effect of soil moisture on CH4 oxidation, emissions of N2O and CO2[J]. Soils, 31(6): 289-294. | |
| [26] | 高涵, 肖礼, 牛丹, 等, 2019. 宁南山区退耕还林还草对土壤氮素组成及其转化酶活的影响[J]. 环境科学, 40(8): 3825-3832. |
| GAO H, XIAO L, NIU D, et al., 2019. Effects of converting farmland into forest and grassland on soil nitrogen component and conversion enzyme activity in the mountainous area of southern Ningxia[J]. Environmental Science, 40(8): 3825-3832. | |
| [27] | 高洁, 朱思佳, 高人, 等, 2016. 有机碳源对森林土壤真菌/细菌活性产生的N2O通量的影响[J]. 亚热带资源与环境学报, 11(4): 29-36. |
| GAO J, ZHU S J, GAO R, et al., 2016. Effects of exogenous organic carbons on N2O emissions attributable to forest soil fungal/bacterial activities[J]. Journal of Subtropical Resources and Environment, 11(4): 29-36. | |
| [28] | 高琳, 潘志华, 杨书运, 等, 2016. 碳源和巨大芽孢杆菌施加对土壤微生物环境及N2O、CH4排放的影响[J]. 中国农业气象, 37(6): 645-653. |
| GAO L, PAN Z H, YANG S Y, et al., 2016. Effects of carbon source and bacillus megaterium on soil microbial environment and N2O, CH4 emission[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 37(6): 645-653. | |
| [29] | 贾俊仙, 李忠佩, 车玉萍, 2011. 施加葡萄糖对不同肥力黑土氮素转化的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 48(1): 207-211. |
| JIA J X, LI Z P, CHE Y P, 2011. Effects of glucose addition on nitrogen transformation in black soils different in organic carbon content[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 48(1): 207-211. | |
| [30] |
焦亚鹏, 齐鹏, 王晓娇, 等, 2020. 施氮量对农田土壤有机氮组分及酶活性的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 53(12): 2423-2434.
DOI |
|
JIAO Y P, QI P, WANG X J, et al., 2020. Effects of different nitrogen application rates on soil organic nitrogen components and enzyme activities in farmland[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 53(12): 2423-2434.
DOI |
|
| [31] | 李海波, 韩晓增, 王风, 等, 2008. 不同土地利用下黑土密度分组中碳、氮的分配变化[J]. 土壤学报, 45(1): 113-119. |
| LI HB, HAN X Z, WANG F, et al., 2008. Distribution of soil organic carbon and nitrogen in density fractions on black soil as affected by land use[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 45(1): 113-119. | |
| [32] | 李平, 郎漫, 李煜姗, 等, 2015. 不同施肥处理对黑土硝化作用和矿化作用的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 34(7): 1326-1332. |
| LI P, LANG M, LI Y S, et al., 2015. Effects of different fertilization on nitrification and mineralization in black soil[J]. Journal of Aro-Environment Science, 34(7): 1326-1332. | |
| [33] | 李青山, 王德权, 杜传印, 等, 2020. 外源碳施加对植烟土壤氮素转化及N2O排放的影响[J]. 中国烟草科学, 41(4): 13-19. |
| LI Q S, WANG D Q, DU C Y, et al., 2020. Effects of exogenous carbon sources on nitrogen transformation and N2O emission in tobacco-planting soil[J]. Chinese Tobacco Science, 41(4): 13-19. | |
| [34] | 栗方亮, 李忠佩, 刘明, 等, 2012. 氮素浓度和水分对水稻土硝化作用和微生物特性的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 20(9): 1113-1118. |
|
LI F L, LI Z P, LIU M, et al., 2012. Effects of different concentrations of nitrogen and soil moistures on paddy soil nitrification and microbial characteristics[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 20(9): 1113-1118.
DOI URL |
|
| [35] | 吕玉, 周龙, 龙光强, 等, 2016. 不同氮水平下间作对玉米土壤硝化势和氨氧化微生物数量的影响[J]. 环境科学, 37(8): 3229-3236. |
| LÜ Y, ZHOU L, LONG G Q, et al., 2016. Effect of different nitrogen rates on the nitrification potential and abundance of ammonia-oxidizer in intercropping maize soils[J]. Environmental Science, 37(8): 3229-3236. | |
| [36] | 马启翔, 李伟, 潘开文, 等, 2013. 持续碳源施加对油松和连香树林地土壤氮转化的影响[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 19(3): 426-433. |
|
MA Q X, LI W, PAN K W, et al., 2013. Effect of continuous glucose addition on soil N transformation of the Pinus tabulaeformis and Cercidiphyllum japonicum plantations[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 19(3): 426-433.
DOI URL |
|
| [37] | 马舒坦, 颜晓元, 2019. 甲酸盐和葡萄糖对两种土壤N2O排放的刺激作用[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 38(1): 235-242. |
| MA S T, YAN X Y, 2019. Effect of formate and glucose organic carbon on N2O emission from two soils[J]. Journal of Aro-Environment Science, 38(1): 235-242. | |
| [38] | 钱琛, 2008. 亚热带红壤的硝化作用及其对NO3--N淋溶和土水酸化的影响[D]. 南京: 中国科学院南京土壤研究所. |
| QIAN C, 2008. Nitrification of subtropical red soil and its influences on nitrate leaching, soil and water acidification[D]. Nanjing: Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences. | |
| [39] | 田亚男, 张水清, 林杉, 等, 2015. 外加碳氮对不同有机碳土壤N2O和CO2排放的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 34(12): 2410-2417. |
| TIAN Y N, ZHANG S Q, LIN S, et al., 2015. Influence of soluble carbon and nitrogen additions on N2O and CO2 emissions from two soils with different organic carbon content[J]. Journal of Aro-Environment Science, 34(12): 2410-2417. | |
| [40] | 王风, 陈思, 杨厚花, 等, 2017. 葡萄糖施加对室温和冻结过程土壤N2O排放特征影响[J]. 生态科学, 36(3): 31-35. |
| WANG F, CHEN S, YANG H H, et al., 2017. Effect of glucose addition on N2O emission from three types of cultivated soils under ambient and freezing temperature[J]. Ecological Science, 36(3): 31-35. | |
| [41] | 王琳, 周晓丽, 马银丽, 等, 2016. 铵态氮源和碳源对土壤N2O, CO2释放的影响[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 33(1): 23-28. |
| WANG L, ZHOU X L, MA Y L, et al., 2016. Effect of ammonium nitrogen source and carbon source on the CO2 and N2O emissions of soil[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 33(1): 23-28. | |
| [42] | 王晓维, 徐健程, 龙昌智, 等, 2018. 施氮量和土壤含水量对黑麦草还田红壤氮素矿化的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 24(2): 365-374. |
| WANG X W, XU J C, LONG C Z, et al., 2018. Effect of nitrogen rates and soil water contents on soil nitrogen mineralization under ryegrass returning into red soil[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 24(2): 365-374. | |
| [43] | 徐鹏, 邬磊, 胡金丽, 等, 2017. 施加葡萄糖、乙酸、草酸对红壤旱地土壤氮素矿化及反硝化的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 37(12): 4740-4746. |
| XU P, WU L, HU J L, et al., 2017. Effects of glucose, acetic acid and oxalic acid additions on nitrogen mineralizaiton and denitrification in red upland soil[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 37(12): 4740-4746. | |
| [44] | 杨程, 刘秋香, 2016. 活性碳源对蔬菜地土壤硝态氮及氮氧化物气体的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 44(2): 378-381. |
| YANG C, LIU Q Z, 2016. Effects of activated carbon sources on nitrate and nitrogen oxides in vegetable soil[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 44(2): 378-381. | |
| [45] | 张乐, 何红波, 章建新, 等, 2008. 不同用量葡萄糖对土壤氮素转化的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 39(4): 775-778. |
| ZHANG L, HE H B, ZHANG J X, et al., 2008. Effect of glucose addition with different amount on extraneous nitrogen transformation in soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 39(4): 775-778. | |
| [46] | 张丽君, 陈锦亮, 李巍, 等, 2018. 添加葡萄糖对果园土壤微生物CO2释放量的影响[J]. 福建农业科技, 49(4): 52-54. |
| ZHANG L J, CHEN J L, LI W, et al., 2018. Effects of glucose addition on CO2 release from soil microbes in orchard[J]. Fujian Agricultural Science and Technology, 49(4): 52-54. | |
| [47] | 张丽敏, 徐明岗, 娄翼来, 等, 2015. 长期有机无机肥配施增强黄壤性水稻土有机氮的物理保护作用[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 21(6): 1481-1486. |
| ZHANG L M, XU M G, LOU Y L, et al., 2015. Combined application of chemical and organic fertilizers long-term increase physical protection of organic nitrogen in yellow paddy soil[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 21(6): 1481-1486. | |
| [48] | 周晓丽, 王琳, 张艺磊, 等, 2016. 硝态氮源及碳源有效性对土壤N2O和CO2排放的影响[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 33(2): 170-175. |
| ZHOU X L, WANG L, ZHANG Y L, et al., 2016. Effect of the availability of nitrate nitrogen and carbon source on N2O and CO2 emission from soil[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 33(2): 170-175. | |
| [49] |
朱春权, 韦翠珍, 曹小闯, 等, 2020. 外加碳源和氮源对酸化水稻土温室气体释放的影响[J]. 中国稻米, 26(6): 40-45.
DOI |
| ZHU C Q, WEI C Z, CAO X C, et al., 2020. Effects of carbon and nitrogen resources addition on greenhouse gas emission in acidified paddy soils[J]. China Rice, 26(6): 40-45. | |
| [50] | 朱霞, 韩晓增, 乔云发, 等, 2009. 外加可溶性碳,氮对不同热量带土壤N2O排放的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 28(12): 2637-2644. |
| ZHU X, HAN X Z, QIAO Y F, et al., 2009. Influence of soluble carbon and nitrogen on N2O emission from different thermal zones soil[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 28(12): 2637-2644. |
| [1] | 王云, 郑西来, 曹敏, 李磊, 宋晓冉, 林晓宇, 郭凯. 滨海含水层咸-淡水过渡带反硝化性能与控制因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 980-988. |
| [2] | 王馨雨, 高灯州, 刘博林, 王斌, 郑艳玲, 李小飞, 侯立军. 长江口水体化能自养固碳过程的潮周期变化特征及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 733-743. |
| [3] | 唐海明, 石丽红, 文丽, 程凯凯, 李超, 龙泽东, 肖志武, 李微艳, 郭勇. 长期施肥对双季稻田根际土壤氮素的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 492-499. |
| [4] | 龚玲玄, 王丽丽, 赵建宁, 刘红梅, 杨殿林, 张贵龙. 不同覆盖作物模式对茶园土壤理化性质及有机碳矿化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1141-1150. |
| [5] | 黄敏, 赵晓峰, 梁荣祥, 王鹏忠, 戴安然, 何晓曼. 3种螯合剂对Cd、Cu复合污染土壤淋洗修复的对比研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1244-1252. |
| [6] | 张涵, 唐常源, 禤映雪, 江涛, 黄品怡, 杨秋, 曹英杰. 珠江口红树林土壤甲烷和二氧化碳通量特征及其影响因素研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 939-948. |
| [7] | 李梦丽, 徐墨馨, 陈永山, 叶丽丽, 蒋金平. 石灰性土壤添加不同量碳酸钙对秸秆有机碳矿化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 2002-2009. |
| [8] | 邹晨怡, 丁洪, 王亚萨, 张玉树, 余居华, 郑祥洲. 秸秆对尿素氮在土壤中转化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1213-1219. |
| [9] | 丛超, 杨宁柯, 王海娟, 王宏镔. 吲哚乙酸和激动素配合施用提高蜈蚣草和龙葵对砷、镉富集的田间试验[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1299-1309. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
