生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 1299-1309.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.06.022
收稿日期:2020-12-17
出版日期:2021-06-18
发布日期:2021-09-10
通讯作者:
* E-mail: whb1974@126.com作者简介:丛超(1994年生),男,硕士,研究方向为污染土壤的生物修复。E-mail: 1013344180@qq.com
基金资助:
CONG Chao( ), YANG Ningke, WANG Haijuan, WANG Hongbin*(
), YANG Ningke, WANG Haijuan, WANG Hongbin*( )
)
Received:2020-12-17
Online:2021-06-18
Published:2021-09-10
摘要:
植物激素可打破重金属超富集植物的种子休眠、促进发芽和快速生长,从而提高其富集重金属的效率。虽然人工合成的植物生长调节剂在促进超富集植物生长和提高重金属富集方面已取得很多成果,但大多是盆栽试验,大田试验甚少。文章在课题组前期室内盆栽试验筛选出的吲哚乙酸(IAA)和激动素(KT)提高砷(As)超富集植物蜈蚣草(Pteris vittata L.)砷提取效率的最佳配比(IAA?KT=25 mg∙L-1?20 mg∙L-1)基础上,在云南省个旧市大屯镇重金属污染农田分45个小区、喷施2次激素开展IAA和KT配合施用对As超富集植物蜈蚣草和镉(Cd)超富集植物龙葵(Solanum nigrum L.)超富集As和Cd的影响和机理研究。结果表明,大田条件下IAA和KT配合施用能够促进2种超富集植物快速生长,在含Cd为3.12 mg∙kg-1、含砷As 98.7 mg∙kg-1的农田土壤上,与未施用植物激素的对照相比,25 mg∙L-1 IAA和20 mg∙L-1 KT配合施用后,龙葵和蜈蚣草的株高、鲜物质量、地上部和地下部Cd/As含量、Cd/As转运系数和富集系数均显著增加,且龙葵对Cd、蜈蚣草对As的提取效率最高可分别达7.52%和6.06%。第2次喷施激素后,单加KT和激素配合施用条件下,龙葵和蜈蚣草间作时两种植物叶片过氧化物酶(POD)活性均显著增加。逐步回归分析结果表明,龙葵对As、蜈蚣草对Cd的提取效率均与叶片POD活性成显著正相关。因此,叶片保持较高的POD活性对两种超富集植物对Cd和As的提取具有重要意义。
中图分类号:
丛超, 杨宁柯, 王海娟, 王宏镔. 吲哚乙酸和激动素配合施用提高蜈蚣草和龙葵对砷、镉富集的田间试验[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1299-1309.
CONG Chao, YANG Ningke, WANG Haijuan, WANG Hongbin. Enhancing Arsenic and Cadmium Accumulation in Pteris vittata and Solanum nigrum by Combined Application of Indoleacetic Acid and Kinetin: A Field Experiment[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(6): 1299-1309.
| 项目 Items | pH值 pH value | ω(Total N)/ (g∙kg-1) | ω(Total P)/ (g∙kg-1) | ω(Total K)/ (g∙kg-1) | 重金属含量 Heavy metal concentrations/(mg·kg-1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总Cd Total cadmium | 总As Total arsenic | 总Pb Total lead | 有效Cd Bioavailable cadmium | 有效As Bioavailable arsenic | 有效Pb Bioavailable lead | |||||
| 最小值 Minimum | 5.68 | 0.43 | 0.86 | 14.5 | 2.76 | 79.8 | 298.5 | 0.76 | 2.8 | 153.4 |
| 最大值 Maximum | 6.21 | 0.51 | 0.89 | 14.9 | 3.59 | 118.9 | 390.7 | 1.31 | 6.1 | 185.6 |
| 平均值 Average | 5.87 | 0.47 | 0.88 | 14.5 | 3.12 | 98.7 | 342.7 | 1.03 | 4.02 | 167.7 |
| 标准差 Standard deviation | 0.14 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.9 | 0.25 | 5.8 | 18.6 | 0.17 | 0.94 | 13.1 |
| 《土壤环境质量 农用地土壤污染风险管控标准》 (GB 15618—2018),5.5<pH≤6.5 Soil environmental quality: Risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land (GB 15618—2018), 5.5<pH≤6.5 | 筛选值 Screening values | 0.3 | 40 | 90 | ||||||
| 管制值 Intervention values | 2.0 | 150 | 500 | |||||||
表1 大田试验土壤的基本理化性质和重金属含量
Table 1 The basic physico-chemical properties and heavy metal concentrations in the field soil
| 项目 Items | pH值 pH value | ω(Total N)/ (g∙kg-1) | ω(Total P)/ (g∙kg-1) | ω(Total K)/ (g∙kg-1) | 重金属含量 Heavy metal concentrations/(mg·kg-1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总Cd Total cadmium | 总As Total arsenic | 总Pb Total lead | 有效Cd Bioavailable cadmium | 有效As Bioavailable arsenic | 有效Pb Bioavailable lead | |||||
| 最小值 Minimum | 5.68 | 0.43 | 0.86 | 14.5 | 2.76 | 79.8 | 298.5 | 0.76 | 2.8 | 153.4 |
| 最大值 Maximum | 6.21 | 0.51 | 0.89 | 14.9 | 3.59 | 118.9 | 390.7 | 1.31 | 6.1 | 185.6 |
| 平均值 Average | 5.87 | 0.47 | 0.88 | 14.5 | 3.12 | 98.7 | 342.7 | 1.03 | 4.02 | 167.7 |
| 标准差 Standard deviation | 0.14 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.9 | 0.25 | 5.8 | 18.6 | 0.17 | 0.94 | 13.1 |
| 《土壤环境质量 农用地土壤污染风险管控标准》 (GB 15618—2018),5.5<pH≤6.5 Soil environmental quality: Risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land (GB 15618—2018), 5.5<pH≤6.5 | 筛选值 Screening values | 0.3 | 40 | 90 | ||||||
| 管制值 Intervention values | 2.0 | 150 | 500 | |||||||
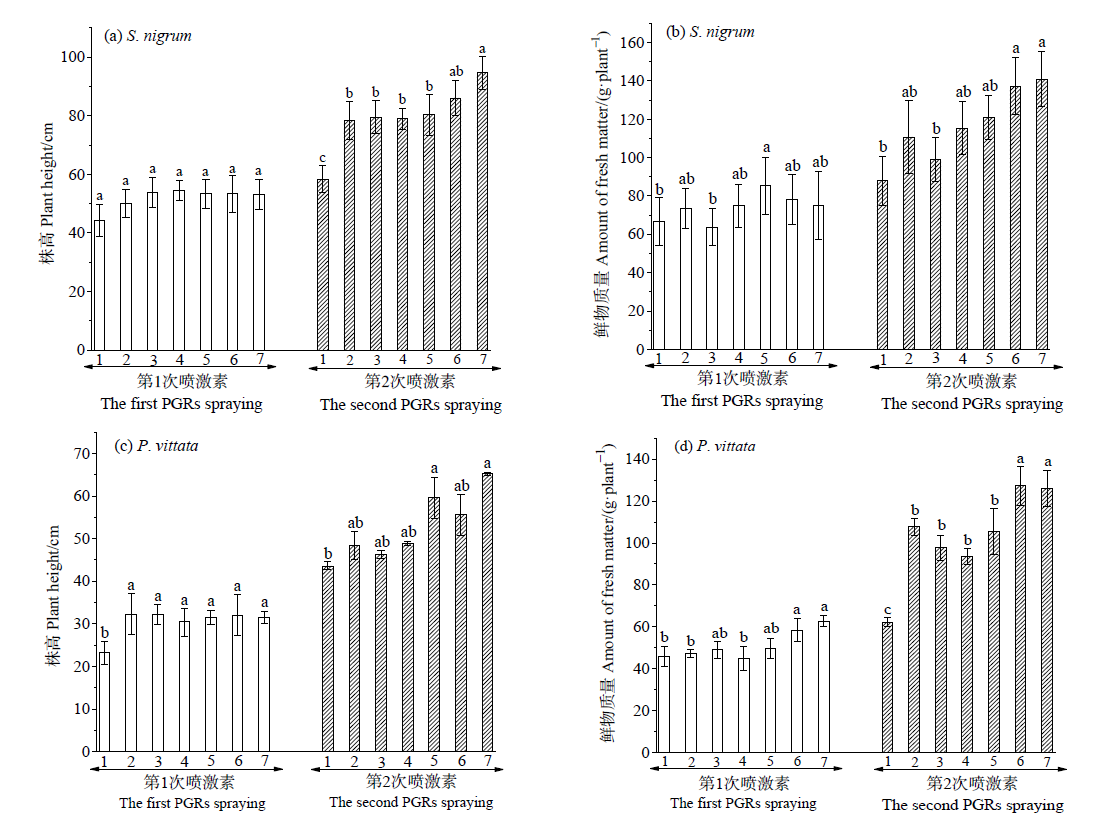
图2 IAA和KT配合施用对龙葵和蜈蚣草株高和鲜物质量的影响 1号代表不加激素的对照;2号代表单加IAA单作;3号代表单加KT单作;4号代表激素配合施用单作;5号代表单加IAA间作;6号代表单加KT间作;7号代表激素配合施用间作。小写字母表示对于同一次激素喷施,7个不同处理之间的差异程度,字母不同表示差异显著(P<0.05),字母相同则表示差异不显著(P>0.05),n=3,下同
Fig. 2 Effects of IAA and KT with combined application on plant height and fresh matter of Solanum nigrum and Pteris vittata No.1: the control without plant growth regulators (PGRs); No.2: Monoculture with indole acetic acid (IAA) alone; No. 3: Monoculture with kinetin (KT) alone; No. 4: Monoculture with combined PGRs; No.5: Intercropping with IAA alone; No.6: Intercropping with KT alone; No. 7: Intercropping with combined PGRs. Lowercase letters indicate the difference among 7 treatments for the same PGRs spraying. Different letters indicate a significant difference (P<0.05), while the same letters indicate no significant difference (P>0.05), n=3. The same below
| 处理 Treatments | 第1次喷施激素 The first PGRs spraying | 第2次喷施激素 The second PGRs spraying | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 富集系数 Bioconcentration factor | 转运系数 Translocation factor | 富集系数 Bioconcentration factor | 转运系数 Translocation factor | ||
| 对照组 Control | 2.22±0.29c | 0.69±0.08c | 2.73±0.06c | 0.93±0.09abc | |
| +IAA单作 Monoculture with IAA alone | 2.82±0.22bc | 1.2±0.15ab | 4.58±0.15bc | 1.42±0.12a | |
| +KT单作 Monoculture with KT alone | 3.06±0.35b | 1.41±0.14a | 4.84±0.28bc | 1.02±0.26b | |
| 激素配合施用单作 Monoculture with combined PGRs | 2.98±0.27bc | 1.06±0.25b | 5.4±0.34bc | 1.01±0.08abc | |
| +IAA间作 Intercropping with IAA alone | 4.15±0.27ab | 1.58±0.16a | 6.46±0.18b | 1.3±0.14ab | |
| +KT间作 Intercropping with KT alone | 3.64±0.34b | 1.45±005a | 6.34±0.44b | 1.07±0.16b | |
| 激素配合施用间作 Intercropping with combined PGRs | 4.51±0.13a | 1.3±0.14ab | 10.72±0.32a | 1.03±0.11b | |
表2 龙葵对Cd的富集系数和转运系数
Table 2 The bioconcentration factor and translocation factor of Cd by S. nigrum
| 处理 Treatments | 第1次喷施激素 The first PGRs spraying | 第2次喷施激素 The second PGRs spraying | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 富集系数 Bioconcentration factor | 转运系数 Translocation factor | 富集系数 Bioconcentration factor | 转运系数 Translocation factor | ||
| 对照组 Control | 2.22±0.29c | 0.69±0.08c | 2.73±0.06c | 0.93±0.09abc | |
| +IAA单作 Monoculture with IAA alone | 2.82±0.22bc | 1.2±0.15ab | 4.58±0.15bc | 1.42±0.12a | |
| +KT单作 Monoculture with KT alone | 3.06±0.35b | 1.41±0.14a | 4.84±0.28bc | 1.02±0.26b | |
| 激素配合施用单作 Monoculture with combined PGRs | 2.98±0.27bc | 1.06±0.25b | 5.4±0.34bc | 1.01±0.08abc | |
| +IAA间作 Intercropping with IAA alone | 4.15±0.27ab | 1.58±0.16a | 6.46±0.18b | 1.3±0.14ab | |
| +KT间作 Intercropping with KT alone | 3.64±0.34b | 1.45±005a | 6.34±0.44b | 1.07±0.16b | |
| 激素配合施用间作 Intercropping with combined PGRs | 4.51±0.13a | 1.3±0.14ab | 10.72±0.32a | 1.03±0.11b | |
| 处理 Treatments | 第1次喷施激素 The first PGRs spraying | 第2次喷施激素 The second PGRs spraying | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 富集系数 Bioconcentration factor | 转运系数 Translocation factor | 富集系数 Bioconcentration factor | 转运系数 Translocation factor | ||
| 对照组 Control | 4.19±0.24c | 1.25±0.21b | 8.32±0.16c | 1.27±0.07bc | |
| +IAA单作 Monoculture with IAA alone | 4.93±0.19abc | 1.22±0.13b | 10.82±0.11bc | 1.34±0.15b | |
| +KT单作 Monoculture with KT alone | 5.37±0.15b | 1.25±0.15b | 11.47±0.34bc | 1.37±0.22b | |
| 激素配合施用单作 Monoculture with combined PGRs | 6.94±0.17ab | 1.28±0.16b | 13.33±0.29b | 1.45±0.17b | |
| +IAA间作 Intercropping with IAA alone | 5.52±0.29b | 1.33±0.08ab | 10.74±0.31bc | 1.49±0.09ab | |
| +KT间作 Intercropping with KT alone | 6.28±0.24ab | 1.38±0.11a | 12.8±0.24b | 1.52±0.23ab | |
| 激素配合施用间作 Intercropping with combined PGRs | 7.50±0.17a | 1.45±0.18a | 20.53±0.22a | 1.75±0.19a | |
表3 蜈蚣草As富集系数和转运系数
Table 3 The bioconcentration factor and translocation factor of As by P. vittata
| 处理 Treatments | 第1次喷施激素 The first PGRs spraying | 第2次喷施激素 The second PGRs spraying | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 富集系数 Bioconcentration factor | 转运系数 Translocation factor | 富集系数 Bioconcentration factor | 转运系数 Translocation factor | ||
| 对照组 Control | 4.19±0.24c | 1.25±0.21b | 8.32±0.16c | 1.27±0.07bc | |
| +IAA单作 Monoculture with IAA alone | 4.93±0.19abc | 1.22±0.13b | 10.82±0.11bc | 1.34±0.15b | |
| +KT单作 Monoculture with KT alone | 5.37±0.15b | 1.25±0.15b | 11.47±0.34bc | 1.37±0.22b | |
| 激素配合施用单作 Monoculture with combined PGRs | 6.94±0.17ab | 1.28±0.16b | 13.33±0.29b | 1.45±0.17b | |
| +IAA间作 Intercropping with IAA alone | 5.52±0.29b | 1.33±0.08ab | 10.74±0.31bc | 1.49±0.09ab | |
| +KT间作 Intercropping with KT alone | 6.28±0.24ab | 1.38±0.11a | 12.8±0.24b | 1.52±0.23ab | |
| 激素配合施用间作 Intercropping with combined PGRs | 7.50±0.17a | 1.45±0.18a | 20.53±0.22a | 1.75±0.19a | |
| 试验处理 Treatments | 种植方式 Planting pattern | 砷 Arsenic | 铅 Lead | 镉 Cadmium |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照 Control | 龙葵 S. nigrum | 0.08±0.03b | 0.09±0.02b | 5.1±0.25c |
| +IAA | 龙葵单作 Monoculture of S. nigrum | 0.11±0.02ab | 0.12±0.01ab | 5.92±0.31abc |
| 龙葵与蜈蚣草间作 Intercropping of S. nigrum and P. vittata | 0.12±0.01ab | 0.11±0.02ab | 5.86±0.28b | |
| +KT | 龙葵单作 Monoculture of S. nigrum | 0.12±0.01ab | 0.12±0.03ab | 6.14±0.35b |
| 龙葵与蜈蚣草间作 Intercropping of S. nigrum and P. vittata | 0.13±0.02ab | 0.13±0.05ab | 6.32±0.41b | |
| +IAA/KT | 龙葵单作 Monoculture of S. nigrum | 0.16±0.03a | 0.14±0.02a | 7.14±0.26ab |
| 龙葵与蜈蚣草间作 S. nigrum Intercropping of S. nigrum and P. vittata | 0.17±0.03a | 0.16±0.02a | 7.52±0.42a | |
| 对照 Control | 蜈蚣草 P. vittata | 3.47±0.25c | 0.14±0.02b | 0.17±0.02b |
| +IAA | 蜈蚣草单作 Monoculture of P. vittata | 3.86±0.17c | 0.18±0.06b | 0.23±0.08b |
| 蜈蚣草与龙葵间作P. vittata Intercropping of P. vittata and S. nigrum | 4.02±0.25abc | 0.19±0.03ab | 0.24±0.06b | |
| +KT | 蜈蚣草单作 Monoculture of P. vittata | 4.05±0.22abc | 0.17±0.04b | 0.24±0.05b |
| 蜈蚣草与龙葵间作 Intercropping of P. vittata and S. nigrum | 4.13±0.18abc | 0.21±0.02ab | 0.26±0.04ab | |
| +IAA/KT | 蜈蚣草单作 Monoculture of P. vittata | 5.61±0.16b | 0.22±0.03a | 0.27±0.10ab |
| 蜈蚣草与龙葵间作 Intercropping of P. vittata and S. nigrum | 6.06±0.19a | 0.25±0.05a | 0.29±0.09a |
表4 两种植物重金属提取效率
Table 4 Heavy metal extraction rate of two plants %
| 试验处理 Treatments | 种植方式 Planting pattern | 砷 Arsenic | 铅 Lead | 镉 Cadmium |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照 Control | 龙葵 S. nigrum | 0.08±0.03b | 0.09±0.02b | 5.1±0.25c |
| +IAA | 龙葵单作 Monoculture of S. nigrum | 0.11±0.02ab | 0.12±0.01ab | 5.92±0.31abc |
| 龙葵与蜈蚣草间作 Intercropping of S. nigrum and P. vittata | 0.12±0.01ab | 0.11±0.02ab | 5.86±0.28b | |
| +KT | 龙葵单作 Monoculture of S. nigrum | 0.12±0.01ab | 0.12±0.03ab | 6.14±0.35b |
| 龙葵与蜈蚣草间作 Intercropping of S. nigrum and P. vittata | 0.13±0.02ab | 0.13±0.05ab | 6.32±0.41b | |
| +IAA/KT | 龙葵单作 Monoculture of S. nigrum | 0.16±0.03a | 0.14±0.02a | 7.14±0.26ab |
| 龙葵与蜈蚣草间作 S. nigrum Intercropping of S. nigrum and P. vittata | 0.17±0.03a | 0.16±0.02a | 7.52±0.42a | |
| 对照 Control | 蜈蚣草 P. vittata | 3.47±0.25c | 0.14±0.02b | 0.17±0.02b |
| +IAA | 蜈蚣草单作 Monoculture of P. vittata | 3.86±0.17c | 0.18±0.06b | 0.23±0.08b |
| 蜈蚣草与龙葵间作P. vittata Intercropping of P. vittata and S. nigrum | 4.02±0.25abc | 0.19±0.03ab | 0.24±0.06b | |
| +KT | 蜈蚣草单作 Monoculture of P. vittata | 4.05±0.22abc | 0.17±0.04b | 0.24±0.05b |
| 蜈蚣草与龙葵间作 Intercropping of P. vittata and S. nigrum | 4.13±0.18abc | 0.21±0.02ab | 0.26±0.04ab | |
| +IAA/KT | 蜈蚣草单作 Monoculture of P. vittata | 5.61±0.16b | 0.22±0.03a | 0.27±0.10ab |
| 蜈蚣草与龙葵间作 Intercropping of P. vittata and S. nigrum | 6.06±0.19a | 0.25±0.05a | 0.29±0.09a |
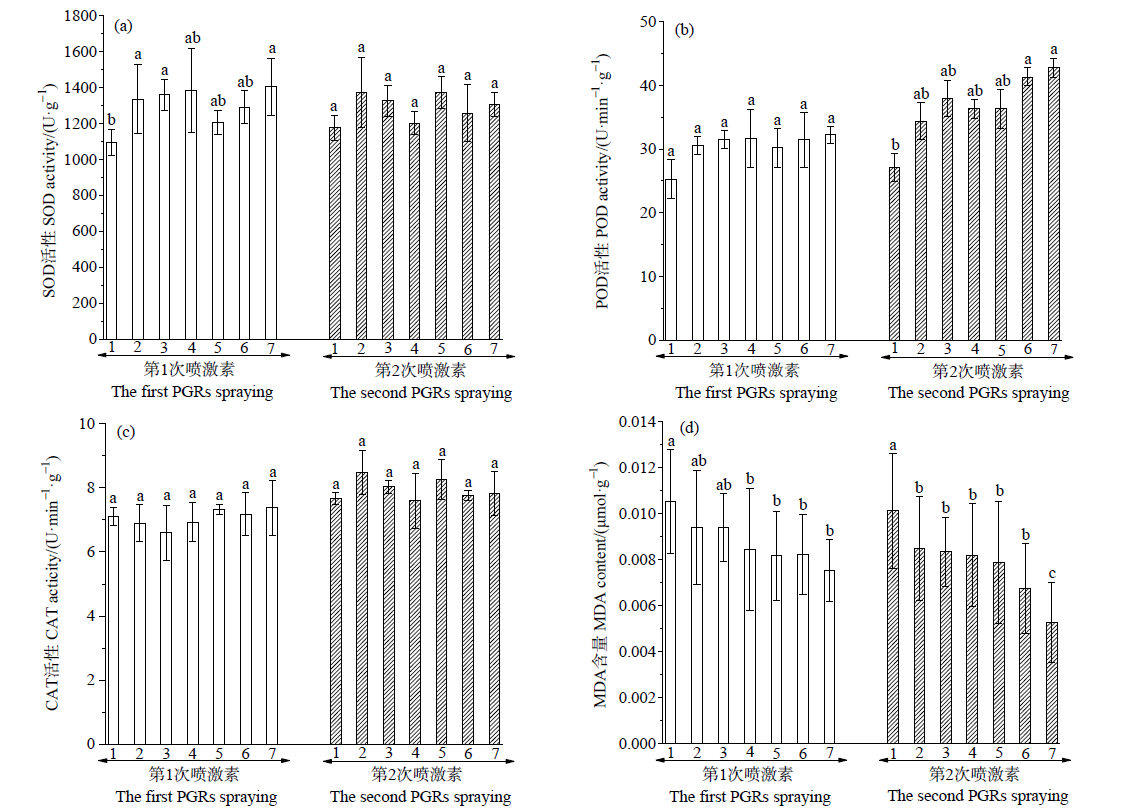
图6 IAA和KT配合施用对龙葵抗氧化酶活性和MDA含量的影响
Fig. 6 Effects of IAA and KT with combined application on activities of antioxidant enzymes and malondialdehyde content in S. nigrum
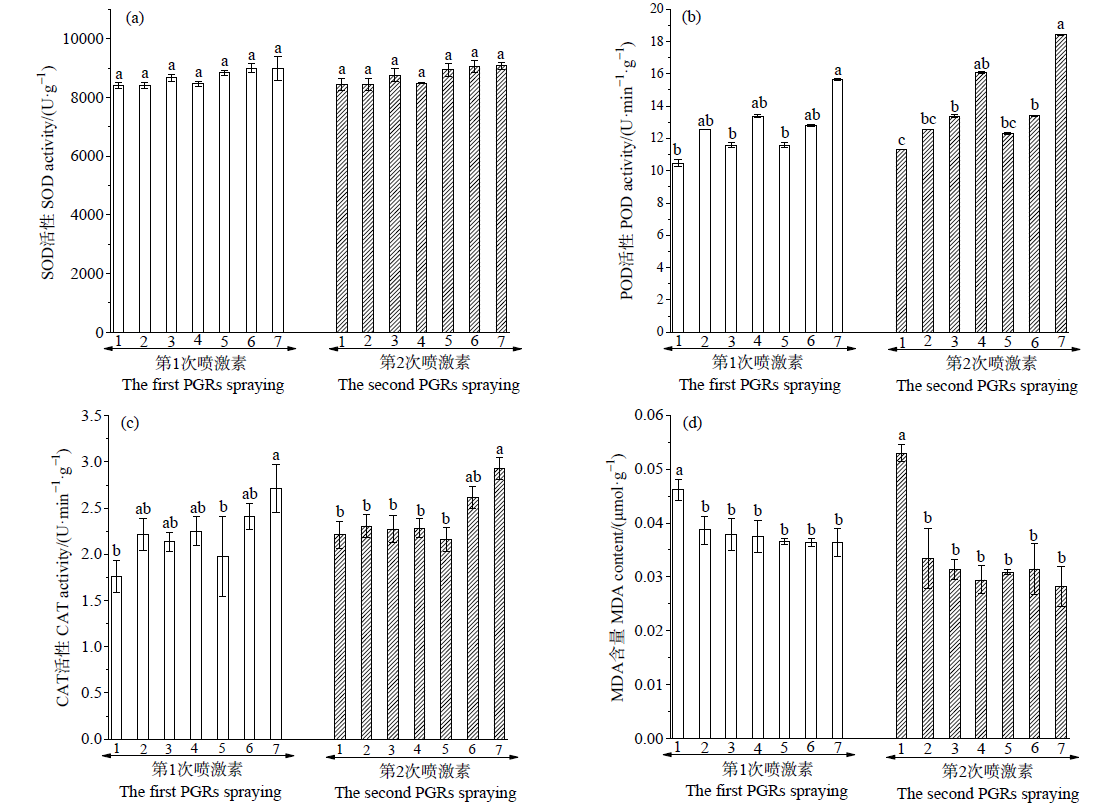
图7 IAA和KT配合施用对蜈蚣草抗氧化酶活性和MDA含量的影响
Fig. 7 Effects of IAA and KT with combined application on activities of antioxidant enzymes and malondialdehyde content in P. vittata
| [1] | ADRIANO D C, WENZEL W W, BLUM W E H, 1997. Role of phytoremediation in the establishment of a global soil remediation network[C]. In: Proceedings of International Seminar on Use Plants for Environmental Remediation, Kosaikaikan, Tokyo, Japan, 3-25. |
| [2] |
AGAMI R A, MOHAMED G F, 2013. Exogenous treatment with indole-3-acetic acid and salicylic acid alleviates cadmium toxicity in wheat seedlings[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 94: 164-171.
DOI URL |
| [3] | CABELLO-CONEJO M I, PRIETO-FERNÁNDEZ Á, KIDD P S, 2014. Exogenous treatments with phytohormones can improve growth and nickel yield of hyperaccumulating plants[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 494-495: 1-8. |
| [4] |
CHEN T B, WEI C Y, HUANG Z C, et al., 2002. Pteris vittata L.: An arsenic hyperaccumulator and its character in accumulating arsenic[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 47(3): 207-210.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
HA S, VANKOVA R, YAMAGUCHI-SHINOZAKI K, et al., 2012. Cytokinins: Metabolism and function in plant adaptation to environmental stresses[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 17(3): 172-179.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
HARE P D, CRESS W A, STADEN J V, 1997. The involvement of cytokinins in plant responses to environmental stress[J]. Plant Growth Regulation, 23(1-2): 79-103.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
ISRAR M, SAHI S V, 2008. Promising role of plant hormones in translocation of lead in Sesbania drummondii shoots[J]. Environmental Pollution, 153(1): 29-36.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
LI Q C, WANG H B, WANG H J, et al., 2018a. Effects of kinetin on plant growth and chloroplast ultrastructure of two Pteris species under arsenate stress[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 158: 37-43.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
LI S W, ZENG X Y, LENG YAN, et al., 2018b. Indole-3-butyric acid mediates antioxidative defense systems to promote adventitious rooting in mung bean seedlings under cadmium and drought stresses[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 161: 332-341.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
LIU D, LI T, YANG X, et al., 2007. Enhancement of lead by hyperaccumulator plant species Sedum alfredii Hance using EDTA and IAA[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 78: 280-283.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
MA L Q, KOMAR K M, TU C, et al., 2001. A fern that hyperaccumulates arsenic[J]. Nature, 409(6820): 579.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
PARK J E, PARK J Y, KIM Y S, et al., 2007. GH3-mediated auxin homeostasis links growth regulation with stress adaptation response in Arabidopsis [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 282(13): 10036-10046.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
REEVES R D, BAKER A J M, JAFFRÉ T, et al., 2017. A global database for plants that hyperaccumulate metal and metalloid trace elements[J]. New Phytologist, 218(2): 407-411.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
SUN S, ZHOU X F, CUI X Y, et al., 2020. Exogenous plant growth regulators improved phytoextraction efficiency by Amaranths hypochondriacus L. in cadmium contaminated soil[J]. Plant Growth Regulation, 90: 29-40.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
WANG H H, SHAN X Q, WEN B, et al., 2007. Effect of indole-3-acetic acid on lead accumulation in maize (Zea mays L.) seedlings and the relevant antioxidant response[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 61(3): 246-253.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
ZENG P, GUO Z H, XIAO X Y, et al., 2019. Dynamic response of enzymatic activity and microbial community structure in metal (loid)-contaminated soil with tree-herb intercropping[J]. Geoderma, 345: 5-16.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
ZHANG C Y, HE QUN, WANG H M, et al., 2020. Exogenous indole acetic acid alleviates Cd toxicity in tea (Camellia sinensis)[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 190: 110090.
DOI URL |
| [18] | 安玲瑶, 2012. 作物间作对重金属吸收的影响及其机制的研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学. |
| AN L Y, 2012. The effect and mechanism of crop intercropping on heavy metal absorption[J]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University. | |
| [19] | 鲍士旦, 2000. 土壤农化分析[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社. |
| BAO S D, 2000. Analysis of Soil and Agrochemicals[M]. 3rd edition. Beijing: China Agriculture Press. | |
| [20] | 和淑娟, 王宏镔, 王海娟, 等, 2016. 砷胁迫下3-吲哚乙酸对不同砷富集能力植物根系形态和生理的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 35(5): 878-885. |
| HE S J, WANG H B, WANG H J, et al., 2016. Effects of indole-3-acetic acid on morphologic and physiological characteristics of root systems of plants with different arsenic-accumulating abilities under As stress[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 35(5): 878-885. | |
| [21] | 李小方, 张志良, 2016. 植物生理学实验指导[M]. 第5版. 北京: 高等教育出版社: 30. |
| LI X F, ZHANG Z L, 2016. Experimental Guidance of Plant Physiology[M]. 5th edition. Beijing: Higher Education Press: 30. | |
| [22] | 刘祖祺, 张石城, 1994. 植物抗性生理学[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社: 371-372. |
| LIU Z Q, ZHANG S C, 1994. Plant Tolerance Physiology[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Press: 371-372. | |
| [23] | 秦欢, 何忠俊, 熊俊芬, 等, 2012. 间作对不同品种玉米和大叶井口边草吸收积累重金属的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 31(7): 1281-1288. |
| QIN H, HE Z J, XIONG J F, et al., 2012. Effects of intercropping on the contents and accumulation of heavy metals in maize varieties and Pteris cretica L.[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 31(7): 1281-1288. | |
| [24] | 生态环境部,国家市场监督管理总局, 2018. 土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准(GB 15618—2018). |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People's Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation, 2018. Soil environmental quality: Risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land in China (GB15618—2018). | |
| [25] | 孙约兵, 周启星, 郭观林, 2007. 植物修复重金属污染土壤的强化措施[J]. 环境工程学报, 1(3): 103-110. |
| SUN Y B, ZHOU Q X, GUO G L, 2007. Phytoremediation and strenthening measures for soil contaminated by heavy metals[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 1(3): 103-110. | |
| [26] | 王学奎, 2006. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M]. 第2版. 北京: 高等教育出版社: 170-171. |
| WANG X K, 2006. Principles and Techniques of Plant Physiological Biochemical Experiment[M]. 2nd edition. Beijing: Higher Education Press: 170-171. | |
| [27] | 魏树和, 周启星, 王新, 等, 2004. 一种新发现的镉超积累植物龙葵(Solanum nigrum L.)[J]. 科学通报, 49(24): 2568-2573. |
| WEI S H, ZHOU Q X, WANG X, et al., 2004. A newly-discovered Cd-hyperaccumulator Solanum nigrum L.[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49(24): 2568-2573. | |
| [28] | 吴东墨, 王宏镔, 王海娟, 等, 2018. 吲哚乙酸和激动素配合施用对蜈蚣草土壤砷提取效率的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 37(8): 1705-1715. |
| WU D M, WANG H B, WANG H J, et al., 2018. Effects of the combined application of indole acetic acid and kinetin on the arsenic extraction efficiency of soil after planting Pteris vittata[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 37(8): 1705-1715. | |
| [29] | 赵书晗, 王海娟, 王宏镔, 2017. 砷胁迫下吲哚乙酸对不同砷富集能力植物光合作用的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 36(6): 1093-1101. |
| ZHAO S H, WANG H J, WANG H B, 2017. Effects of indoleacetic acid on photosynthesis of arsenic-stressed plants with different arsenic-accumulating ability[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 36(6): 1093-1101. |
| [1] | 赵良侠, 高坤, 黄婷婷, 高也, 琚唐丹, 蒋秋阳, 金珩, 熊蕾, 汤在琳, 高灿红. 玉米籽粒高/低镉积累自交系不同生育期的镉累积特性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 766-775. |
| [2] | 杨耀东, 陈玉梅, 涂鹏飞, 曾清如. 经济作物轮作模式下镉污染农田修复潜力[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 627-634. |
| [3] | 刘抗旱, 郑刘根, 张理群, 丁丹, 单士锋. 复合型植物源活化剂强化蜈蚣草修复砷污染土壤的效应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 635-642. |
| [4] | 房献宝, 张智钧, 赖阳晴, 叶脉, 刁增辉. 新型污泥生物炭对土壤重金属Cr和Cd的修复研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1647-1656. |
| [5] | 高鹏, 高品, 孙蔚旻, 孔天乐, 黄端仪, 刘华清, 孙晓旭. 蜈蚣草根际及内生微生物群落对砷污染胁迫的响应机制研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1225-1234. |
| [6] | 秦秦, 段海芹, 宋科, 孙丽娟, 孙雅菲, 周斌, 薛永. 常规施肥对土壤水稳性团聚体镉吸附解吸特性及化学形态的影响研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2403-2413. |
| [7] | 伍德, 彭鸥, 刘玉玲, 张朴心, 尹雪斐, 黄薪铭, 铁柏清. 螯合剂及组配对伴矿景天修复两种镉污染土壤的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2414-2421. |
| [8] | 俞龙生, 李卫, 许铭宇, 林泽帆. 赤霉素浸种对2种矿区修复先锋植物种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2225-2233. |
| [9] | 李富荣, 王琳清, 李文英, 吴志超, 王旭. 水芹对重金属的吸收累积及其应用研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(12): 2423-2430. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
