生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (10): 2100-2108.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.10.017
• 研究论文 •
上一篇
武岩1( ), 靳拓2, 王跃飞1, 贺鹏程3, 罗军1, 刘宏金1,*(
), 靳拓2, 王跃飞1, 贺鹏程3, 罗军1, 刘宏金1,*( ), 张雷1,*(
), 张雷1,*( ), 郭晓宇1, 陈瑞英4
), 郭晓宇1, 陈瑞英4
收稿日期:2021-06-09
出版日期:2021-10-18
发布日期:2021-12-21
通讯作者:
张雷(1978年生),男,高级农艺师,主要从事农业生态保护方面的研究。E-mail: 13847176858@126.com作者简介:武岩(1991年生),男,农艺师,硕士研究生,主要从事农业面源污染防治方面的研究。E-mail: 824079115@qq.com
基金资助:
WU Yan1( ), JIN Tuo2, WANG Yuefei1, HE Pengcheng3, LUO Jun1, LIU Hongjin1,*(
), JIN Tuo2, WANG Yuefei1, HE Pengcheng3, LUO Jun1, LIU Hongjin1,*( ), ZHANG Lei1,*(
), ZHANG Lei1,*( ), GUO Xiaoyu1, CHEN Ruiying4
), GUO Xiaoyu1, CHEN Ruiying4
Received:2021-06-09
Online:2021-10-18
Published:2021-12-21
摘要:
内蒙古阴山北麓作为内蒙古的粮食主产区,普遍存在农田残膜污染的问题。应用全生物降解地膜是解决农田残膜污染的重要途径,研究聚己二酸对苯二甲酸丁二醇酯/聚乳酸(PBAT/PLA)全生物降解地膜增温保墒性能、降解性能及其产量经济效益对于解决农田残膜污染、保护生态环境、实现农业绿色高质量发展具有重要意义。本研究在马铃薯田开展了3种PBAT/PLA全生物降解地膜、1种普通PE地膜和裸地处理(分别标记为F1、F2、F3、CK和OF)的覆膜栽培试验和降解地膜填埋试验。结果表明,各覆膜处理5—6月土壤温度逐渐升高,7—8月中旬达到作物生育期峰值,随后降低至较低水平。与普通PE地膜相比,3种全生物降解地膜在马铃薯发芽、幼苗期(5—6月)平均土壤温度和土壤含水量未形成显著差异(P>0.05),能够满足马铃薯生育前期的生长需求。F1和F2处理在作物覆膜后42—56 d进入诱导期,当季作物收获前均能进入破碎期,降解率为34.21%—42.74%,填埋365 d后基本降解完全;F3处理覆膜后68—84 d进入诱导期,作物收获前降解率为15.47%—28.04%,填埋365—540 d基本降解完全。3种全生物降解地膜作物产量和经济效益分别为49.64—58.53 t∙hm-2和1.6×104—2.4×104 yuan∙hm-2,未与普通PE地膜形成显著差异(P>0.05)。F1和F2处理作物产量和经济效益显著高于裸地(P<0.05),其中作物产量分别提高36.85%和38.27%,经济效益分别增加1.43×104 yuan∙hm-2和1.5×104 yuan∙hm-2;与普通PE地膜相比,作物产量分别增加4.1%和5.18%。根据降解性能和作物产量综合评价,在内蒙古阴山北麓马铃薯种植条件下,F1和F2处理具有较好的降解性能,且在提高作物产量、保护耕地生态环境方面具有较好效果。
中图分类号:
武岩, 靳拓, 王跃飞, 贺鹏程, 罗军, 刘宏金, 张雷, 郭晓宇, 陈瑞英. 内蒙古阴山北麓马铃薯应用PBAT/PLA全生物降解地膜可行性分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(10): 2100-2108.
WU Yan, JIN Tuo, WANG Yuefei, HE Pengcheng, LUO Jun, LIU Hongjin, ZHANG Lei, GUO Xiaoyu, CHEN Ruiying. Feasibility Analysis of PBAT/PLA Biodegradable Plastic Film for Potatoes in the Northern Foot of Yinshan Mountain in Inner Mongolia[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(10): 2100-2108.
| 地膜种类 Types of mulching film | 原料 Raw material | 宽度 Width/ cm | 厚度 Thickness/μm | 颜色 Colour |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 上海弘睿全生物降解地膜 Shanghai hongrui biodegradable plastic film | PBAT/ PLA | 80 | 9.8 | 黑色Black |
| 巴斯夫全生物降解地膜 BASF biodegradable plastic film | PBAT/ PLA | 80 | 9.7 | 黑色Black |
| 兰州鑫银环全生物降解地膜 Lanzhou xinyinhuan biodegradable plastic film | PBAT/ PLA | 80 | 9.6 | 黑色Black |
| 普通PE地膜 Common polyethylene plastic (PE) mulch film | PE | 80 | 9.8 | 黑色Black |
表1 供试地膜基本情况
Table 1 The information of test mulch film
| 地膜种类 Types of mulching film | 原料 Raw material | 宽度 Width/ cm | 厚度 Thickness/μm | 颜色 Colour |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 上海弘睿全生物降解地膜 Shanghai hongrui biodegradable plastic film | PBAT/ PLA | 80 | 9.8 | 黑色Black |
| 巴斯夫全生物降解地膜 BASF biodegradable plastic film | PBAT/ PLA | 80 | 9.7 | 黑色Black |
| 兰州鑫银环全生物降解地膜 Lanzhou xinyinhuan biodegradable plastic film | PBAT/ PLA | 80 | 9.6 | 黑色Black |
| 普通PE地膜 Common polyethylene plastic (PE) mulch film | PE | 80 | 9.8 | 黑色Black |
| 降解阶段Degradation stage | 分级标准 Grading standards |
|---|---|
| 诱导期 Induction period | 覆膜到垄(畦)面地膜出现多处(每延长1 m 3处以上)≤2 cm自然裂缝或孔洞 There are many natural cracks or holes (more than 3 per extended meter) ≤2 cm from film mulching to ridge (border) surface |
| 开裂期 Cracking period | 垄(畦)面地膜出现≥2 cm、≤20 cm自然裂缝或孔洞 Natural cracks or holes ≥2 cm and ≤20 cm appear in the film on the ridge (border) surface |
| 大裂期 Rift stage | 垄(畦)面地膜出现≥20 cm自然裂缝 There are ≥20 cm natural cracks in the film on the ridge (border) surface |
| 破碎期Fragmentation period | 膜柔韧性尽失,垄(畦)面地膜出现碎裂,最大地膜残片面积≤16 cm2 The film flexibility is completely lost, the film on the ridge (border) surface is broken, and the maximum film fragment area is≤16 cm2 |
| 无膜期 No membrane period | 垄(畦)面地膜基本见不到地膜残片 There are basically no film fragments on the ridge (border) surface |
表2 降解地膜降解阶段分级标准
Table 2 Grading standard for degradation stage of biodegradable mulching film
| 降解阶段Degradation stage | 分级标准 Grading standards |
|---|---|
| 诱导期 Induction period | 覆膜到垄(畦)面地膜出现多处(每延长1 m 3处以上)≤2 cm自然裂缝或孔洞 There are many natural cracks or holes (more than 3 per extended meter) ≤2 cm from film mulching to ridge (border) surface |
| 开裂期 Cracking period | 垄(畦)面地膜出现≥2 cm、≤20 cm自然裂缝或孔洞 Natural cracks or holes ≥2 cm and ≤20 cm appear in the film on the ridge (border) surface |
| 大裂期 Rift stage | 垄(畦)面地膜出现≥20 cm自然裂缝 There are ≥20 cm natural cracks in the film on the ridge (border) surface |
| 破碎期Fragmentation period | 膜柔韧性尽失,垄(畦)面地膜出现碎裂,最大地膜残片面积≤16 cm2 The film flexibility is completely lost, the film on the ridge (border) surface is broken, and the maximum film fragment area is≤16 cm2 |
| 无膜期 No membrane period | 垄(畦)面地膜基本见不到地膜残片 There are basically no film fragments on the ridge (border) surface |
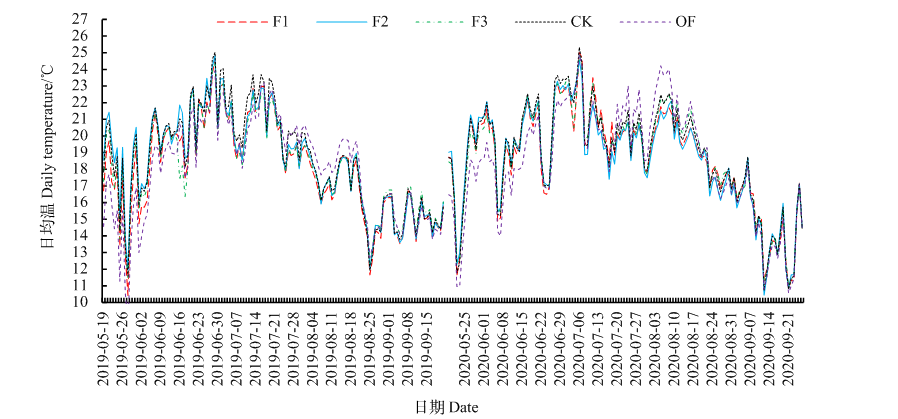
图1 不同地膜覆盖下土壤温度变化动态 F1,上海弘睿全生物降解地膜;F2,巴斯夫全生物降解地膜;F3,兰州鑫银环全生物降解地膜;CK,普通聚乙烯塑料(PE)地膜;OF,裸地不覆膜,下同
Fig. 1 Dynamic change of soil temperature under different mulching films F1, Shanghai Hongrui biodegradable plastic film; F2, BASF biodegradable plastic film; F3, Lanzhou Xinyinhuan biodegradable plastic film; CK, common polyethylene plastic (PE) mulch film; OF, bare ground without film, the same below
| 处理 Treatments | 2019年不同生育期平均土壤温度 Average soil temperature in different growth periods in 2019/℃ | 2020年不同生育期平均土壤温度 Average soil temperature in different growth periods in 2020/℃ | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GS | TE | SD | GS | TE | SD | ||
| F1 | 18.86±0.42bc | 19.06±0.37a | 14.77±0.30a | 19.15±0.60a | 20.68±0.32b | 15.98±0.11a | |
| F2 | 19.62±0.42a | 19.71±1.87a | 14.90±0.74a | 19.48±0.26a | 20.41±0.15b | 15.83±0.45a | |
| F3 | 18.85±0.31bc | 19.06±0.20a | 15.21±0.31a | 19.18±0.40a | 20.90±0.32ab | 16.11±0.11a | |
| CK | 19.40±0.26ab | 19.57±1.74a | 14.94±0.50a | 19.44±0.42a | 20.98±0.36a | 16.04±0.30a | |
| OF | 17.50±0.23d | 19.86±0.85a | 14.94±0.40a | 17.79±0.05b | 21.43±0.45a | 15.82±0.25a | |
表3 不同全生物降解地膜对马铃薯不同生育期平均土壤温度的影响
Table 3 Effects of different biodegradable plastic films on average soil temperature in different growth periods of potato
| 处理 Treatments | 2019年不同生育期平均土壤温度 Average soil temperature in different growth periods in 2019/℃ | 2020年不同生育期平均土壤温度 Average soil temperature in different growth periods in 2020/℃ | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GS | TE | SD | GS | TE | SD | ||
| F1 | 18.86±0.42bc | 19.06±0.37a | 14.77±0.30a | 19.15±0.60a | 20.68±0.32b | 15.98±0.11a | |
| F2 | 19.62±0.42a | 19.71±1.87a | 14.90±0.74a | 19.48±0.26a | 20.41±0.15b | 15.83±0.45a | |
| F3 | 18.85±0.31bc | 19.06±0.20a | 15.21±0.31a | 19.18±0.40a | 20.90±0.32ab | 16.11±0.11a | |
| CK | 19.40±0.26ab | 19.57±1.74a | 14.94±0.50a | 19.44±0.42a | 20.98±0.36a | 16.04±0.30a | |
| OF | 17.50±0.23d | 19.86±0.85a | 14.94±0.40a | 17.79±0.05b | 21.43±0.45a | 15.82±0.25a | |
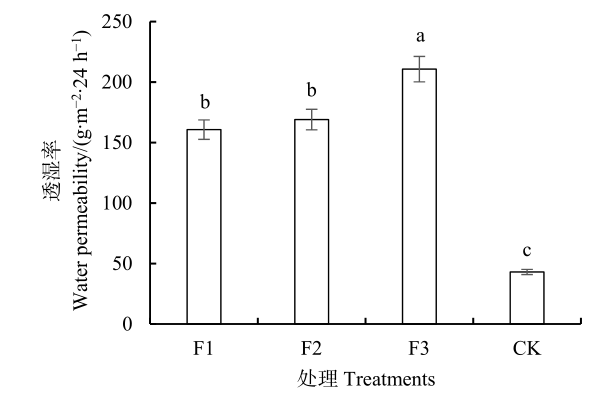
图2 各地膜处理透水性能 不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05),下同
Fig. 2 Characteristics of water permeability for different mulching film Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among treatments (P<0.05), the same below
| 年份Years | 处理Treatments | 降解率 Degradation rate/% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 作物覆膜栽培区 Crop film mulching cultivation area | 降解地膜填埋区 Degradable plastic film landfill | |||||||
| 覆膜后60 d | 覆膜后90 d | 覆膜后120 d | 填埋后180 d | 填埋后365 d | 填埋后540 d | |||
| 60 days after coating | 90 days after coating | 120 days after coating | 180 days after landfill | 365 days after landfill | 540 days after landfill | |||
| 2019 | F1 | 16.96±2.96a | 31.68±4.98a | 34.21±1.8a | 80.12±4.22a | 97.53±2.52a | 97.68±0.82a | |
| F2 | 19.66±4.43a | 36.51±7.23a | 40.14±7.47a | 75.32±14.02a | 96.88±2.94a | 97.54±2.50a | ||
| F3 | 8.78±2.23b | 13.54±4.21b | 15.47±3.19b | 53.61±11.04b | 85.43±9.37b | 98.54±1.01a | ||
| CK | 0.74±0.17c | 1.02±0.17c | 1.54±1.01c | 2.63±1.01c | 3.73±2.30c | 6.99±1.95b | ||
| 2020 | F1 | 22.29±5.18a | 30.54±7.4a | 42.74±5.92a | 85.06±5.82a | 97.44±1.81a | - | |
| F2 | 20.78±5.78a | 26.84±7.1a | 34.64±4.64a | 87.10±6.63a | 98.03±1.51a | - | ||
| F3 | 11.46±3.53b | 22.34±6.3a | 28.04±3.45c | 70.39±8.66b | 96.60±1.84a | - | ||
| CK | 0.96±0.59c | 1.11±0.5b | 1.3±0.63d | 2.30±0.57c | 3.47±1.11b | - | ||
表4 不同地膜处理降解率
Table 4 Degradation intensity of different plastic film treatments
| 年份Years | 处理Treatments | 降解率 Degradation rate/% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 作物覆膜栽培区 Crop film mulching cultivation area | 降解地膜填埋区 Degradable plastic film landfill | |||||||
| 覆膜后60 d | 覆膜后90 d | 覆膜后120 d | 填埋后180 d | 填埋后365 d | 填埋后540 d | |||
| 60 days after coating | 90 days after coating | 120 days after coating | 180 days after landfill | 365 days after landfill | 540 days after landfill | |||
| 2019 | F1 | 16.96±2.96a | 31.68±4.98a | 34.21±1.8a | 80.12±4.22a | 97.53±2.52a | 97.68±0.82a | |
| F2 | 19.66±4.43a | 36.51±7.23a | 40.14±7.47a | 75.32±14.02a | 96.88±2.94a | 97.54±2.50a | ||
| F3 | 8.78±2.23b | 13.54±4.21b | 15.47±3.19b | 53.61±11.04b | 85.43±9.37b | 98.54±1.01a | ||
| CK | 0.74±0.17c | 1.02±0.17c | 1.54±1.01c | 2.63±1.01c | 3.73±2.30c | 6.99±1.95b | ||
| 2020 | F1 | 22.29±5.18a | 30.54±7.4a | 42.74±5.92a | 85.06±5.82a | 97.44±1.81a | - | |
| F2 | 20.78±5.78a | 26.84±7.1a | 34.64±4.64a | 87.10±6.63a | 98.03±1.51a | - | ||
| F3 | 11.46±3.53b | 22.34±6.3a | 28.04±3.45c | 70.39±8.66b | 96.60±1.84a | - | ||
| CK | 0.96±0.59c | 1.11±0.5b | 1.3±0.63d | 2.30±0.57c | 3.47±1.11b | - | ||
| 处理Treatments | 投入 Input/(104 yuan∙hm-2) | 产出 Output | 纯利润 Net profit/ (104 yuan∙hm-2) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 农资投入 Agricultural input | 租地人工Rented labor | 地膜回收 Plastic film recycling | 合计 Total | 产量 Yield/(t∙hm-2) | 产值 Output value/(104 yuan∙hm-2) | |||
| F1 | 2.24 | 1.2 | 0 | 3.44 | 57.93±6.65a | 5.79 | 2.35±0.67ab | |
| F2 | 2.235 | 1.2 | 0 | 3.435 | 58.53±4.27a | 5.85 | 2.42±0.43a | |
| F3 | 2.205 | 1.2 | 0 | 3.405 | 49.64±2.79bc | 4.96 | 1.56±0.28bc | |
| CK | 2.09 | 1.2 | 0.045 | 3.335 | 55.65±3.46ab | 5.56 | 2.23±0.35ab | |
| OF | 2.01 | 1.3 | 0 | 3.31 | 42.33±3.08c | 4.23 | 0.92±0.31c | |
表5 不同地膜处理马铃薯作物产量及经济效益分析
Table 5 Analysis of potato crop yield and economic benefits treated with different plastic films
| 处理Treatments | 投入 Input/(104 yuan∙hm-2) | 产出 Output | 纯利润 Net profit/ (104 yuan∙hm-2) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 农资投入 Agricultural input | 租地人工Rented labor | 地膜回收 Plastic film recycling | 合计 Total | 产量 Yield/(t∙hm-2) | 产值 Output value/(104 yuan∙hm-2) | |||
| F1 | 2.24 | 1.2 | 0 | 3.44 | 57.93±6.65a | 5.79 | 2.35±0.67ab | |
| F2 | 2.235 | 1.2 | 0 | 3.435 | 58.53±4.27a | 5.85 | 2.42±0.43a | |
| F3 | 2.205 | 1.2 | 0 | 3.405 | 49.64±2.79bc | 4.96 | 1.56±0.28bc | |
| CK | 2.09 | 1.2 | 0.045 | 3.335 | 55.65±3.46ab | 5.56 | 2.23±0.35ab | |
| OF | 2.01 | 1.3 | 0 | 3.31 | 42.33±3.08c | 4.23 | 0.92±0.31c | |
| [1] | COZZOLINO E, GIORDANO M, FIORENTINO N, et al., 2020. Appraisal of biodegradable mulching films and vegetal-derived biostimulant application as eco-sustainable practices for enhancing lettuce crop performance and nutritive value[J]. Agronomy Journal, 10(3):427. |
| [2] |
GIL-CASTELL O, BADIA J D, KITTIKORN T, et al., 2016. Impact of hydrothermal ageing on the thermal stability, morphology and viscoelastic performance of PLA/sisal biocomposites[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 132:87-96.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
GAO H H, YAN C R, LIU Q, et al., 2019. Effects of plastic mulching and plastic residue on agricultural production: A meta-analysis[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 651(Part 1):484-492.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
GIORDANO M, AMOROSO C G, EL-NAKHEL C, et al., 2020. An appraisal of biodegradable mulch films with respect to strawberry crop performance and fruit quality[J]. Horticulturae, 6(3):48.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
MORRO A, CATALINA F, SANCHEZ L E, et al., 2019. Photodegradation and biodegradation under thermophile conditions of mulching films based on poly (butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) and its blend with poly (lactic acid)[J]. Journal of Polymers and the Environment, 27(2):352-363.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
PALSIKOWSKI P A, KUCHNIER C N, PINHEIRO I F, et al., 2017. Biodegradation in soil of PLA/PBAT blends compatibilized with chain extender[J]. Journal of Polymers and the Environment, 26(1):330-341.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
ROCHA D B, DE CARVALHO J S, DE OLIVEIRA S A, et al., 2018. A new approach for flexible PBAT/PLA/CaCO3 films into agriculture[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, DOI: 10.1002/app.46660.
DOI |
| [8] |
STEINMETZ Z, WOLLMANN C, SCHAEFER M, et al., 2016. Plastic mulching in agriculture. Trading short-term agronomic benefits for long-term soil degradation?[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 550:690-705.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
SOUZA P M S, MORALES A R, SANCHEZ E M S, et al., 2018. Study of PBAT photostabilization with ultraviolet absorber in combination with hindered amine light stabilizer and vitamin E, aiming mulching film application[J]. Journal of Polymers and the Environment, 26(8):3422-3436.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
SHANKAR S, RHIM J W, 2018. Preparation of antibacterial poly (lactide)/ poly (butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) composite films incorporated with grapefruit seed extract[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 120(Part A):846-852.
DOI URL |
| [11] | SHEN L X, ZHANG Y M, LAN Y C, et al., 2019. Effects of degradable films with different degradation cycles on soil temperature, moisture and maize yield[J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 12(3):36-44. |
| [12] |
WANG Z H, WU Q, FAN B H, et al., 2019a. Testing biodegradable films as alternatives to plastic films in enhancing cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) yield under mulched drip irrigation[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 192:196-205.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
WANG Z H, WU Q, FAN B H, et al., 2019b. Effects of mulching biodegradable films under drip irrigation on soil hydrothermal conditions and cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) yield[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 213:477-485.
DOI URL |
| [14] | 白云龙, 李晓龙, 张胜, 等, 2015. 内蒙古地膜残留污染现状及残膜回收利用对策研究[J]. 中国土壤与肥料 (6):139-145. |
| BAI Y L, LI X L, ZHANG S, et al., 2015. Study on the current situation of plastic film residue pollution and the countermeasures for the recovery and utilization of residual film in Inner Mongolia[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences (6):139-145. | |
| [15] | 段义忠, 张雄, 2018. 生物可降解地膜对土壤肥力及马铃薯产量的影响[J]. 作物研究, 32(1):23-27. |
| DUAN Y Z, ZHANG X, 2018. Influence of biodegradable membrane on soil fertility and potato yield[J]. Crop Research, 32(1):23-27. | |
| [16] | 国家统计局农村社会经济调查司, 2020. 中国农村统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社: 47-48. |
| Department of Rural Social and Economic Survey, 2020. National Bureau of statistics. China Rural Statistical Yearbook [M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press: 47-48. | |
| [17] | 邓方宁, 林涛, 何文清, 等, 2020. 生物降解地膜覆盖对棉田土壤水-热-盐及产量的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 39(6):1956-1965. |
| DENG F N, LIN T, HE W Q, et al., 2020. Effects of biodegradable plastic film mulching on soil moisture, temperature, salinity and yield of cotton field[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 39(6):1956-1965. | |
| [18] | 贺鹏程, 刘宏金, 魏静, 等, 2020. 全生物降解膜的降解及其对马铃薯产量性状的影响[J]. 北方农业学报, 48(1):30-34. |
| HE P C, LIU H J, WEI J, et al., 2020. Degradation of whole biodegradable membrane and its effect on potato yield trait[J]. Journal of Northern Agriculture, 48(1):30-34. | |
| [19] | 李海萍, 周杨全, 靳拓, 等, 2017. 不同类型地膜降解特征及其对马铃薯产量的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 33(24):36-40. |
| LI H P, ZHOU Y Q, JIN T, et al., 2017. Degradation characteristics of different mulch and the effect on potato yield[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 33(24):36-40. | |
| [20] |
马明生, 郭贤仕, 柳燕兰, 2020. 全生物降解地膜覆盖对旱地土壤水分状况及春小麦产量和水分利用效率的影响[J]. 作物学报, 46(12):1933-1944.
DOI |
| MA M S, GUO X S, LIU Y L, et al., 2020. Effects of full biodegradable film on soil water status and yield and water use efficiency of spring wheat in dryland[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 46(12):1933-1944. | |
| [21] | 曲萍, 郭宝华, 王海波, 等, 2017. PBAT全生物降解地膜在玉米田中的降解特性[J]. 农业工程学报, 33(17):194-199. |
| QU P, GUO B H, WANG H B, et al., 2017. Degaradation characteristics of PBAT mulch in maize field[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 33(17):194-199. | |
| [22] | 申丽霞, 王璞, 张丽丽, 2012. 可降解地膜的降解性能及对土壤温度、水分和玉米生长的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 28(4):111-116. |
| SHEN L X, WANG P, ZHANG L L, 2012. Degradation property of degradable film and its effect on soil temperature and moisture and maize growth[J]. Transactions of the CSAE, 28(4):111-116. | |
| [23] | 苏海英, 宝哲, 刘勤, 等, 2020. 新疆加工番茄应用PBAT全生物降解地膜可行性[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 37(4):615-622. |
| SUN H Y, BAO Z, LIU Q, et al., 2020. Degradation of biodegradable mulch film and its effect on tne yield of processing tomatoes in the Xinjiang region[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 37(4):615-622. | |
| [24] | 徐松, 王敬敬, 周婷婷, 等, 2018. 聚己二酸/对苯二甲酸丁二酯塑料地膜高效降解菌群筛选及其群落结构演替特征[J]. 微生物学通报, 45(11):38-49. |
| XU S, WANG J J, ZHOU T T, et al., 2018. Screening and community succession of high effective poly (butyleneadipate-co-terephthalate) plastic mulch degrading bacteria[J]. Microbiology China, 45(11):38-49. | |
| [25] | 夏文, 林涛, 邓方宁, 等, 2020. 生物降解地膜降解性能对南疆棉田籽棉产量形成的影响[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 37(6):951-959. |
| XIA W, LIN T, DENG F N, et al., 2020. Effects of degradation properties of different biodegradable films on cotton yield formation in southern Xinjiang[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 37(6):951-959. | |
| [26] | 杨惠娣, 唐赛珍, 1996. 降解塑料试验评价方法探讨[J]. 塑料 (2):16-22. |
| YANG H D, TANG S Z, 1996. Discussion on evaluation method of degradable plastics test[J]. Plastics (2):16-22. | |
| [27] | 严昌荣, 刘恩科, 舒帆, 等, 2014. 我国地膜覆盖和残留污染特点与防控技术[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 31(2):95-102. |
| YAN C R, LIU E K, SHU F, et al., 2014. Review of agricultural plastic mulching and its residual pollution and prevention measures in China[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 31(2):95-102. | |
| [28] | 严昌荣, 何文清, 薛颖昊, 等, 2016. 生物降解地膜应用与地膜残留污染防控[J]. 生物工程学报, 32(6):748-760. |
| YAN C R, HE W Q, XUE Y H, et al., 2016. Application of biodegradable plastic film to reduce plastic film residual pollution in Chinese agriculture[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 32(6):748-760. | |
| [29] | 张妮, 李琦, 侯振安, 等, 2016. 聚乳酸生物降解地膜对土壤温度及棉花产量的影响[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 33(2):114-119. |
| ZHANG N, LI Q, HOU Z A, et al., 2016. Effect of Polylactic acid-degradable film mulch on soil temperature and cotton yield[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 33(2):114-119. |
| [1] | 胡启瑞, 吉春容, 李迎春, 王雪姣, 杨明凤, 郭燕云. 膜下滴灌棉花蕾期干旱胁迫对光合特性及产量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1045-1052. |
| [2] | 王敬, 孟珂, 陈璇, 章家恩, 向慧敏, 钟嘉文, 石兆基. 酸雨对生菜和上海青的产量、品质及生理特性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1098-1107. |
| [3] | 姜超强, 李晨, 朱启法, 徐海清, 刘炎红, 沈嘉, 阎轶峰, 余飞, 祖朝龙. 皖南不同种植模式碳汇效应及经济效益评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1285-1292. |
| [4] | 刘江, 朱丽杰, 张开, 王晓明, 王立为, 高西宁. 不同生育期干旱胁迫/复水对大豆光合特性及产量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 286-296. |
| [5] | 黄巧义, 于俊红, 黄建凤, 黄旭, 李苹, 付弘婷, 唐拴虎, 刘一锋, 徐培智. 广东省主要农作物秸秆养分资源量及替代化肥潜力[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(2): 297-306. |
| [6] | 崔亮, 张钧瑞, 李思园. “双碳”背景下农村居民清洁取暖减排效益研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 2010-2018. |
| [7] | 张开, 王立为, 高西宁, 贺明慧. 基于DNDC模型不同降水年型下氮肥管理对马铃薯田N2O减排及增产潜力影响研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1672-1682. |
| [8] | 韩芳, 包媛媛, 刘项宇, 张新永, 韦灯会, 张浩然, 田清龙. 不同轮作方式对马铃薯根际土壤真菌群落结构的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(7): 1412-1419. |
| [9] | 党慧慧, 刘超, 伍翥嵘, 王圆媛, 胡正华, 李琪, 陈书涛. 不同播期粳稻稻田甲烷排放及综合效益研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(7): 1436-1446. |
| [10] | 朱勇勇, 宋秉羲, 杨王敏, 张宇鹏, 高志红, 陈晓远. 旱作条件下氮肥减施对水稻生长、产量与经济收益的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(11): 2150-2156. |
| [11] | 葛应兰, 孙廷. 马铃薯根际与非根际土壤微生物群落结构及多样性特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2020, 29(1): 141-148. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
