Ecology and Environmental Sciences ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (10): 1598-1608.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2025.10.010
• Research Article [Environmental Science] • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHEN Fan1( ), CHI Shanqing2, LIN Caiqiang2, YU Bolin2,*(
), CHI Shanqing2, LIN Caiqiang2, YU Bolin2,*( ), XIE Rongrong1,3,4, LI Jiabing1,3,4, HUANG Xiangfeng5, ZHANG Haiping5, LIU Jia5, WU Qiaofeng2,5
), XIE Rongrong1,3,4, LI Jiabing1,3,4, HUANG Xiangfeng5, ZHANG Haiping5, LIU Jia5, WU Qiaofeng2,5
Received:2025-03-04
Online:2025-10-18
Published:2025-09-26
陈凡1( ), 池善庆2, 林财强2, 俞伯林2,*(
), 池善庆2, 林财强2, 俞伯林2,*( ), 谢蓉蓉1,3,4, 李家兵1,3,4, 黄翔峰5, 张海平5, 刘佳5, 吴乔枫2,5
), 谢蓉蓉1,3,4, 李家兵1,3,4, 黄翔峰5, 张海平5, 刘佳5, 吴乔枫2,5
通讯作者:
E-mail: 作者简介:陈凡(2001年生),女,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为水域温室气体排放。E-mail: 1194881687@qq.com
CLC Number:
CHEN Fan, CHI Shanqing, LIN Caiqiang, YU Bolin, XIE Rongrong, LI Jiabing, HUANG Xiangfeng, ZHANG Haiping, LIU Jia, WU Qiaofeng. Surface Dissolved N2O Concentration and Emission Fluxes in an Urban River-canal-artificial Lake Linkage System[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2025, 34(10): 1598-1608.
陈凡, 池善庆, 林财强, 俞伯林, 谢蓉蓉, 李家兵, 黄翔峰, 张海平, 刘佳, 吴乔枫. 城市河渠-人工湖连通系统表层溶存N2O浓度及排放通量研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(10): 1598-1608.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2025.10.010
| 采样点 | 采样时间 | pH | ρ(DO)/(mg∙L−1) | tw/℃ | ρ(BOD5)/(mg∙L−1) | ρ(CODMn)/(mg∙L−1) | ρ(叶绿素a)/(μg∙L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 夏季 | 6.62±0.26C | 6.09±0.43cB | 28.7±0.33aB | 1.16±0.07cB | 2.86±0.19bC | 2.50±0.49bB |
| 秋季 | 7.06±0.52B | 5.92±0.23cA | 22.3±0.52b | 1.54±0.27cB | 2.60±0.19bB | 5.24±1.22bB | |
| 冬季 | 7.28±0.15C | 9.73±0.42a | 17.5±3.26c | 3.15±0.51b | 2.81±0.36bAB | 17.8±3.34aA | |
| 春季 | 6.52±0.71B | 7.07±0.06bB | 18.6±1.27c | 4.30±0.55aA | 3.37±0.08aB | 2.96±0.21bB | |
| R2 | 夏季 | 6.69±0.08cC | 3.60±0.13bB | 31.4±0.91aA | 4.33±0.91aA | 6.13±0.68aA | 3.49±1.25B |
| 秋季 | 7.69±0.20aAB | 7.27±0.41aA | 22.4±0.90b | 1.85±0.73bAB | 3.16±0.19bB | 1.74±0.54B | |
| 冬季 | 7.20±0.24bC | 8.26±0.63a | 19.8±2.77b | 3.10±1.37ab | 3.36±0.42bA | 3.67±1.78B | |
| 春季 | 7.08±0.28bAB | 7.63±0.84aAB | 20.0±2.34b | 1.56±0.96bB | 3.44±0.39bB | 3.77±2.24B | |
| R3 | 夏季 | 7.70±0.22B | 4.48±0.56cB | 28.1±1.88aB | 1.60±0.32bB | 3.32±0.27bcC | 3.37±0.67B |
| 秋季 | 7.69±0.30AB | 3.69±0.37cB | 21.9±1.29b | 3.30±0.90bA | 4.56±1.05abA | 2.29±0.64B | |
| 冬季 | 7.96±0.20B | 8.94±0.37a | 17.8±3.00b | 2.32±0.50b | 2.12±0.60cB | 3.65±1.02B | |
| 春季 | 8.15±0.22A | 7.85±0.42bAB | 18.3±0.70b | 5.50±1.78aA | 4.98±0.74aA | 4.33±2.17B | |
| LC | 夏季 | 9.11±0.16aA | 11.4±2.35A | 32.7±0.85aA | 3.81±0.45A | 4.73±0.22aB | 33.2±5.15aA |
| 秋季 | 7.80±0.06bA | 7.48±1.39A | 21.9±0.35b | 2.38±1.00AB | 3.58±0.34bAB | 14.9±7.40bA | |
| 冬季 | 8.80±0.09aA | 8.61±4.13 | 17.5±2.16c | 2.85±0.74 | 2.33±0.19cB | 14.2±5.46bA | |
| 春季 | 7.75±0.85bA | 8.98±1.41A | 19.2±0.78bc | 4.46±1.42A | 5.05±0.49aA | 33.2±10.1aA |
Table 1 Physico-chemical parameters of water bodies in the studied area
| 采样点 | 采样时间 | pH | ρ(DO)/(mg∙L−1) | tw/℃ | ρ(BOD5)/(mg∙L−1) | ρ(CODMn)/(mg∙L−1) | ρ(叶绿素a)/(μg∙L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 夏季 | 6.62±0.26C | 6.09±0.43cB | 28.7±0.33aB | 1.16±0.07cB | 2.86±0.19bC | 2.50±0.49bB |
| 秋季 | 7.06±0.52B | 5.92±0.23cA | 22.3±0.52b | 1.54±0.27cB | 2.60±0.19bB | 5.24±1.22bB | |
| 冬季 | 7.28±0.15C | 9.73±0.42a | 17.5±3.26c | 3.15±0.51b | 2.81±0.36bAB | 17.8±3.34aA | |
| 春季 | 6.52±0.71B | 7.07±0.06bB | 18.6±1.27c | 4.30±0.55aA | 3.37±0.08aB | 2.96±0.21bB | |
| R2 | 夏季 | 6.69±0.08cC | 3.60±0.13bB | 31.4±0.91aA | 4.33±0.91aA | 6.13±0.68aA | 3.49±1.25B |
| 秋季 | 7.69±0.20aAB | 7.27±0.41aA | 22.4±0.90b | 1.85±0.73bAB | 3.16±0.19bB | 1.74±0.54B | |
| 冬季 | 7.20±0.24bC | 8.26±0.63a | 19.8±2.77b | 3.10±1.37ab | 3.36±0.42bA | 3.67±1.78B | |
| 春季 | 7.08±0.28bAB | 7.63±0.84aAB | 20.0±2.34b | 1.56±0.96bB | 3.44±0.39bB | 3.77±2.24B | |
| R3 | 夏季 | 7.70±0.22B | 4.48±0.56cB | 28.1±1.88aB | 1.60±0.32bB | 3.32±0.27bcC | 3.37±0.67B |
| 秋季 | 7.69±0.30AB | 3.69±0.37cB | 21.9±1.29b | 3.30±0.90bA | 4.56±1.05abA | 2.29±0.64B | |
| 冬季 | 7.96±0.20B | 8.94±0.37a | 17.8±3.00b | 2.32±0.50b | 2.12±0.60cB | 3.65±1.02B | |
| 春季 | 8.15±0.22A | 7.85±0.42bAB | 18.3±0.70b | 5.50±1.78aA | 4.98±0.74aA | 4.33±2.17B | |
| LC | 夏季 | 9.11±0.16aA | 11.4±2.35A | 32.7±0.85aA | 3.81±0.45A | 4.73±0.22aB | 33.2±5.15aA |
| 秋季 | 7.80±0.06bA | 7.48±1.39A | 21.9±0.35b | 2.38±1.00AB | 3.58±0.34bAB | 14.9±7.40bA | |
| 冬季 | 8.80±0.09aA | 8.61±4.13 | 17.5±2.16c | 2.85±0.74 | 2.33±0.19cB | 14.2±5.46bA | |
| 春季 | 7.75±0.85bA | 8.98±1.41A | 19.2±0.78bc | 4.46±1.42A | 5.05±0.49aA | 33.2±10.1aA |
| 指标 | 时间差异(季节对比) | 空间差异(点位对比) |
|---|---|---|
| pH | R2:秋季>冬、春季>夏季;LC:夏、冬季>秋、春季 | LC>R1、R2、R3(夏、冬季) |
| DO | R1、R2、R3:冬季最高;LC:夏季最高 | 非冬季时,LC最高 |
| tw | 夏季>秋、冬、春季 | R2、LC>R1、R3(夏季) |
| BOD5 | R2:夏、冬季>秋、春季;其他点位:春季最高 | R2、LC>R1、R3(夏季);R1、R3、LC>R2(冬季) |
| CODMn | 除R2外,春季普遍偏高 | R2>LC>R1、R3(夏季);R3、LC>R1、R2(春季) |
| 叶绿素a | R1:冬季>夏、秋、春季;LC:夏、春季>秋、冬季 | LC>R1、R2、R3(夏、秋、春季) |
Table 2 Summary of differences in key water quality parameters in the studied area
| 指标 | 时间差异(季节对比) | 空间差异(点位对比) |
|---|---|---|
| pH | R2:秋季>冬、春季>夏季;LC:夏、冬季>秋、春季 | LC>R1、R2、R3(夏、冬季) |
| DO | R1、R2、R3:冬季最高;LC:夏季最高 | 非冬季时,LC最高 |
| tw | 夏季>秋、冬、春季 | R2、LC>R1、R3(夏季) |
| BOD5 | R2:夏、冬季>秋、春季;其他点位:春季最高 | R2、LC>R1、R3(夏季);R1、R3、LC>R2(冬季) |
| CODMn | 除R2外,春季普遍偏高 | R2>LC>R1、R3(夏季);R3、LC>R1、R2(春季) |
| 叶绿素a | R1:冬季>夏、秋、春季;LC:夏、春季>秋、冬季 | LC>R1、R2、R3(夏、秋、春季) |
| 点位 | 夏季 | 秋季 | 冬季 | 春季 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| z | p | z | p | z | p | z | p | ||||
| R1 | −4.32 | 0 | −3.62 | 0.002 | −2.35 | 0.114 | −3.63 | 0.002 | |||
| R3 | 4.21 | 0 | 1.95 | 0.310 | 4.18 | 0 | 2.57 | 0.061 | |||
| LC | 1.71 | 0.528 | 4.34 | 0 | 3.7 | 0.001 | 2.61 | 0.054 | |||
Table 3 Significantly different values of dissolved N2O at R2 site compared to other sites in different seasons
| 点位 | 夏季 | 秋季 | 冬季 | 春季 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| z | p | z | p | z | p | z | p | ||||
| R1 | −4.32 | 0 | −3.62 | 0.002 | −2.35 | 0.114 | −3.63 | 0.002 | |||
| R3 | 4.21 | 0 | 1.95 | 0.310 | 4.18 | 0 | 2.57 | 0.061 | |||
| LC | 1.71 | 0.528 | 4.34 | 0 | 3.7 | 0.001 | 2.61 | 0.054 | |||
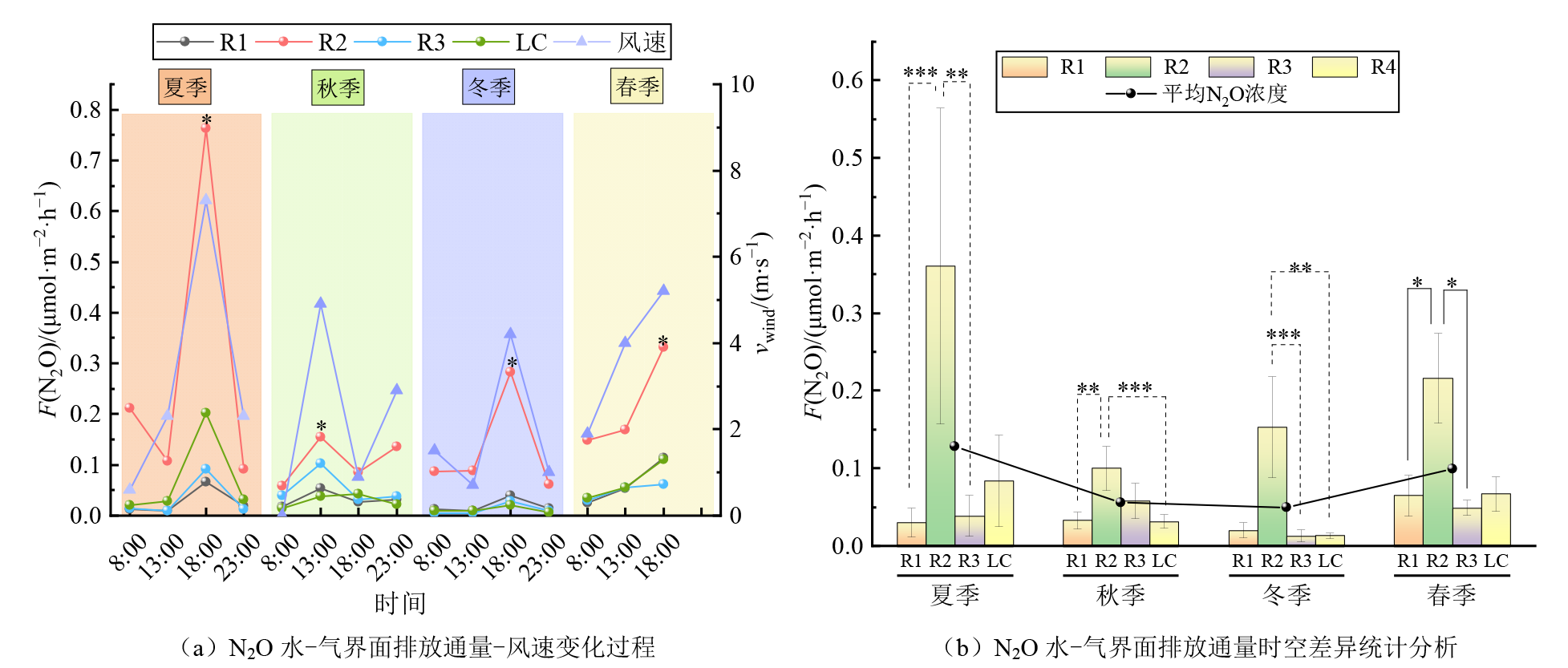
Figure 3 Statistical analysis of processes of N?O emission flux-wind speed variations across water-air interface and their spatiotemporal differences in the studied area
| 点位 | 夏季 | 秋季 | 冬季 | 春季 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| z | p | z | p | z | p | z | p | ||||
| R1 | −3.73 | 0.001 | −3.44 | 0.004 | −2.53 | 0.068 | −3.1 | 0.012 | |||
| R3 | 3.57 | 0.002 | 2 | 0.274 | 4.1 | 0 | 3.10 | 0.012 | |||
| LC | 1.87 | 0.373 | 3.73 | 0.001 | 3.6 | 0.002 | 2.61 | 0.054 | |||
Table 4 Significantly different values of N2O emission fluxes at R2 site and other sites in different seasons
| 点位 | 夏季 | 秋季 | 冬季 | 春季 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| z | p | z | p | z | p | z | p | ||||
| R1 | −3.73 | 0.001 | −3.44 | 0.004 | −2.53 | 0.068 | −3.1 | 0.012 | |||
| R3 | 3.57 | 0.002 | 2 | 0.274 | 4.1 | 0 | 3.10 | 0.012 | |||
| LC | 1.87 | 0.373 | 3.73 | 0.001 | 3.6 | 0.002 | 2.61 | 0.054 | |||
| 研究区域 | 河湖类型 | cw(N2O)/ (nmol·L−1) | F(N2O)/(nmol·m−2·h−1) | ρ(DO)/(mg·L−1) | ρ(NH3-N)/(mg·L−1) | ρ(TN)/(mg·L−1) | 文献来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 本研究 | 城市河湖连通系统 | 11-476, 平均:89 | 5-763, 平均:83 | 7.303±2.525 | 0.836±0.798 | 4.48±3.82 | |
| 中国东南部 鳝鱼滩湿地 | 天然河流 | 季节平均: 5.6-14.2 | 平均:322 | 冬季:8.4 春季:8.5 | 季节平均: 0.44-1.35 | 季节平均: 1.62-2.81 | Yang et al., |
| 闽江河口 | 天然河流 | 0.99-55.9 | −118-180 | 2.54-10.3 | 0.03-0.7 | - | 漆梦婷等, |
| 太湖北部梅梁湾和 东南部徐口湾湖滨区 | 天然湖泊 | 北部:15.1 东南部:14.5 | 北部:150 东南部:20 | 北部:4.79 东南部:5.61 | - | - | Yang et al., |
| 渤海湾典型闸 控入海河流 | 天然河流 | 0.4-185 | −300-670 | 9.4-13.1 | 最高:0.21 | 最高:1.38 | 李肖正等, |
| 武汉市:长江以南7个河流和11个湖泊 | 城市河流、 城市河湖 连通系统 | 城市河流:326 城市河湖系统:49.7 | 城市河流:1.95×104城市河湖系统:2.8×103 | 城市河流:5.93 城市河湖系统:9.2 | 城市河流:3.6 城市河湖系统:1.1 | 城市河流:10.4 城市河湖系统:2.1 | Wang et al., |
| 天津城市河流 | 城市河流 | 18.7-234 | 87.5 | 7.9±2.8 | 1.9±1.6 | 6.01±2.13 | Liu et al., |
| 中国东部巢湖 | 城市湖泊 | 11.7-5.96×103 平均:410 | 1.96×104 | 6.37±3.2 | 3.31±3.78 | 7.68±4.26 | Miao et al., |
Table 5 Comparison of dissolved N2O concentration and emission flux results between the studied area and other regions
| 研究区域 | 河湖类型 | cw(N2O)/ (nmol·L−1) | F(N2O)/(nmol·m−2·h−1) | ρ(DO)/(mg·L−1) | ρ(NH3-N)/(mg·L−1) | ρ(TN)/(mg·L−1) | 文献来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 本研究 | 城市河湖连通系统 | 11-476, 平均:89 | 5-763, 平均:83 | 7.303±2.525 | 0.836±0.798 | 4.48±3.82 | |
| 中国东南部 鳝鱼滩湿地 | 天然河流 | 季节平均: 5.6-14.2 | 平均:322 | 冬季:8.4 春季:8.5 | 季节平均: 0.44-1.35 | 季节平均: 1.62-2.81 | Yang et al., |
| 闽江河口 | 天然河流 | 0.99-55.9 | −118-180 | 2.54-10.3 | 0.03-0.7 | - | 漆梦婷等, |
| 太湖北部梅梁湾和 东南部徐口湾湖滨区 | 天然湖泊 | 北部:15.1 东南部:14.5 | 北部:150 东南部:20 | 北部:4.79 东南部:5.61 | - | - | Yang et al., |
| 渤海湾典型闸 控入海河流 | 天然河流 | 0.4-185 | −300-670 | 9.4-13.1 | 最高:0.21 | 最高:1.38 | 李肖正等, |
| 武汉市:长江以南7个河流和11个湖泊 | 城市河流、 城市河湖 连通系统 | 城市河流:326 城市河湖系统:49.7 | 城市河流:1.95×104城市河湖系统:2.8×103 | 城市河流:5.93 城市河湖系统:9.2 | 城市河流:3.6 城市河湖系统:1.1 | 城市河流:10.4 城市河湖系统:2.1 | Wang et al., |
| 天津城市河流 | 城市河流 | 18.7-234 | 87.5 | 7.9±2.8 | 1.9±1.6 | 6.01±2.13 | Liu et al., |
| 中国东部巢湖 | 城市湖泊 | 11.7-5.96×103 平均:410 | 1.96×104 | 6.37±3.2 | 3.31±3.78 | 7.68±4.26 | Miao et al., |
| 水体类型 | 采样点及时间 | pH | DO | tw | BOD5 | NH3-N | TN | CODMn | 叶绿素a | 风速 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 自然河流 | R1-秋-18:00 | - | 谷值 | 接近谷值 | - | 峰值 | - | 接近谷值 | - | - |
| R1-冬-18:00 | 接近峰值 | 接近峰值 | - | - | 峰值 | - | 峰值 | 接近谷值 | 峰值 | |
| R3-冬-18:00 | 峰值 | 峰值 | - | 谷值 | 谷值 | 峰值 | - | - | 峰值 | |
| 人工湖 | LC-秋-18:00 | 接近峰值 | - | 接近峰值 | - | 峰值 | 峰值 | 峰值 | 谷值 | - |
| 排污渠 | R2-夏-8:00 | 接近峰值 | 峰值 | 谷值 | - | - | - | 峰值 | 峰值 | 谷值 |
| R2-秋-23:00 | 谷值 | 接近谷值 | 谷值 | 峰值 | 谷值 | - | 谷值 | 接近谷值 | - | |
| R2-冬-18:00 | 峰值 | 接近峰值 | - | - | 谷值 | - | - | - | 峰值 | |
| R2-春-8:00 | 峰值 | 谷值 | - | 谷值 | 峰值 | 谷值 | 接近谷值 | 谷值 | 谷值 |
Table 6 Analysis of peak dissolved N2O concentration and extreme values of environmental factors in the studied area
| 水体类型 | 采样点及时间 | pH | DO | tw | BOD5 | NH3-N | TN | CODMn | 叶绿素a | 风速 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 自然河流 | R1-秋-18:00 | - | 谷值 | 接近谷值 | - | 峰值 | - | 接近谷值 | - | - |
| R1-冬-18:00 | 接近峰值 | 接近峰值 | - | - | 峰值 | - | 峰值 | 接近谷值 | 峰值 | |
| R3-冬-18:00 | 峰值 | 峰值 | - | 谷值 | 谷值 | 峰值 | - | - | 峰值 | |
| 人工湖 | LC-秋-18:00 | 接近峰值 | - | 接近峰值 | - | 峰值 | 峰值 | 峰值 | 谷值 | - |
| 排污渠 | R2-夏-8:00 | 接近峰值 | 峰值 | 谷值 | - | - | - | 峰值 | 峰值 | 谷值 |
| R2-秋-23:00 | 谷值 | 接近谷值 | 谷值 | 峰值 | 谷值 | - | 谷值 | 接近谷值 | - | |
| R2-冬-18:00 | 峰值 | 接近峰值 | - | - | 谷值 | - | - | - | 峰值 | |
| R2-春-8:00 | 峰值 | 谷值 | - | 谷值 | 峰值 | 谷值 | 接近谷值 | 谷值 | 谷值 |
| [1] | BEAULIEU J J, SHUSTER W D, REBHOLZ J A, 2010. Nitrous oxide emissions from a large, impounded river: The Ohio river[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 44(19): 7527-7533. |
| [2] | BEAULIEU J J, TANK J L, HAMILTON S K, 2011. Nitrous oxide emission from denitrification in stream and river networks[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 108(1): 214-219. |
| [3] | COLE J J, CARACO N F, 1998. Atmospheric exchange of carbon dioxide in a low‐wind oligotrophic lake measured by the addition of SF6[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 43(4): 647-656. |
| [4] | HAMPTON T B, ZARNETSKE J P, BRIGGS M A, et al., 2020. Experimental shifts of hydrologic residence time in a sandy urban stream sediment-water interface alter nitrate removal and nitrous oxide fluxes[J]. Biogeochemistry, 149: 195-219. |
| [5] | HE Y X, WANG X F, CHEN H, et al., 2017. Effect of watershed urbanization on N2O emissions from the Chongqing metropolitan river network, China[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 171: 70-81. |
| [6] | HERREID A M, WYMORE A S, VARNER R K, et al., 2021. Divergent controls on stream greenhouse gas concentrations across a land-use gradient[J]. Ecosystems, 24(6): 1299-1316. |
| [7] | HO L, JERVES-COBO R, BARTHEL M, et al., 2020. Effects of land use and water quality on greenhouse gas emissions from an urban river system[J]. Biogeosciences Discussions, 2020: 1-22. |
| [8] | HOUGHTON J T, DING Y, GRIGGS D J, et al., 2001. Climate change 2001: The scientific basis[M]. Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press: 1-881. |
| [9] | HU B B, WANG D Q, ZHOU J, et al., 2018. Greenhouse gases emission from the sewage draining rivers[J]. Science of Total Environment, 612: 1454-1462. |
| [10] |
KORTELAINEN P, LARMOLA T, RANTAKARI M, et al., 2020. Lakes as nitrous oxide sources in the boreal landscape[J]. Global Change Biology, 26(3): 1432-1445.
DOI PMID |
| [11] | LIANG X, WANG B, GAO D, et al., 2022. Nitrification regulates the spatiotemporal variability of N2O emissions in a eutrophic lake[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 56(23): 17430-17442. |
| [12] | LIU X L, BAI L, WANG Z L, et al., 2015. Nitrous oxide emissions from river network with variable nitrogen loading in Tianjin, China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 157: 153-161. |
| [13] |
MAAVARA T, LAUERWALD R, LARUELLE G G, et al., 2019. Nitrous oxide emissions from inland waters: Are IPCC estimates too high?[J]. Global Change Biology, 25(2): 473-488.
DOI PMID |
| [14] | MIAO Y Q, HUANG J, DUAN H T, et al., 2020. Spatial and seasonal variability of nitrous oxide in a large freshwater lake in the lower reaches of the Yangtze River, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 721: 137716. |
| [15] | OGILVIE B, NEDWELL D B, HARRISON R M, et al., 1997. High nitrate, muddy estuaries as nitrogen sinks: the nitrogen budget of the River Colne estuary (United Kingdom)[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 150(1-3): 217-228. |
| [16] | QUICK A M, REEDER W J, FARRELL T B, et al., 2019. Nitrous oxide from streams and rivers: A review of primary biogeochemical pathways and environmental variables[J]. Earth-science Reviews, 191: 224-262. |
| [17] |
RAVISHANKARA A R, DANIEL J S, PORTMANN R W, 2009. Nitrous oxide (N2O): The dominant ozone-depleting substance emitted in the 21st century[J]. Science, 326: 123-125.
DOI PMID |
| [18] | SMITH R L, BÖHLKE J K, 2019. Methane and nitrous oxide temporal and spatial variability in two midwestern USA streams containing high nitrate concentrations[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 685: 574-588. |
| [19] | TIAN H Q, XU R T, CANADELL J G, et al., 2020. A comprehensive quantification of global nitrous oxide sources and sinks[J]. Nature, 586: 248-256. |
| [20] | WANG C L, XV Y H, WU Z F, et al., 2024. Denitrification regulates spatiotemporal pattern of N2O emission in an interconnected urban river-lake network[J]. Water Research, 251: 121144. |
| [21] | WANG G Q, XIA X H, LIU S D, et al., 2021. Distinctive patterns and controls of nitrous oxide concentrations and fluxes from urban inland waters[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 55(12): 8422-8431. |
| [22] | WANG R, ZHANG H, ZHANG W, et al., 2020. An urban polluted river as a significant hotspot for water-atmosphere exchange of CH4 and N2O[J]. Environmental Pollution, 264: 114770. |
| [23] | WANG X F, YU L L, LIU T T, et al., 2022. Methane and nitrous oxide concentrations and fluxes from heavily polluted urban streams: Comprehensive influence of pollution and restoration[J]. Environmental Pollution, 313: 120098. |
| [24] | WANNINKHOF R, 1992. Relationship between wind speed and gas exchange over the ocean[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 97(C5): 7373-7382. |
| [25] | WUEBBLES D J, 2009. Nitrous oxide: No laughing matter[J]. Science, 326(5949): 56-57. |
| [26] | XIAO Q T, XU X F, ZHANG M, et al., 2019. Coregulation of nitrous oxide emissions by nitrogen and temperature in China’s third largest freshwater lake (Lake Taihu)[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 64(3): 1070-1086. |
| [27] | YANG F Y, ZHENG X L, WANG D Q, et al., 2024a. Significant diurnal variations in nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions from two contrasting habitats in a large eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China)[J]. Environmental Research, 261: 119691. |
| [28] | YANG P, LIN Y X, YANG H, et al., 2024b. Spatiotemporal distributions of dissolved N2O concentration, diffusive N2O flux and relevant functional genes along a coastal creek in southeastern China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 637: 131331. |
| [29] |
YU Z J, DENG H G, WANG D Q, et al., 2013. Nitrous oxide emissions in the Shanghai river network: Implications for the effects of urban sewage and IPCC methodology[J]. Global Change Biology, 19(10): 2999-3010.
DOI PMID |
| [30] | ZHANG G L, ZHANG J, LIU S M, et al., 2010. Nitrous oxide in the Changjiang (Yangtze River) Estuary and its adjacent marine area: Riverine input sediment release and atmospheric fluxes[J]. Biogeosciences, 7(11): 3505-3516. |
| [31] | ZHANG W S, LI H P, XIAO Q T, et al., 2020a. Surface nitrous oxide (N2O) concentrations and fluxes from different rivers draining contrasting landscapes: Spatio-temporal variability, controls, and implications based on IPCC emission factor[J]. Environmental Pollution, 263(Part A): 114457. |
| [32] | ZHANG W S, LI H P, XIAO Q T, et al., 2020b. Urban rivers are hotspots of riverine greenhouse gas (N2O, CH4, CO2) emissions in the mixed-landscape Chaohu Lake Basin[J]. Water Research, 189: 116624. |
| [33] | 陈姝, 2022. 不同时间尺度城市河流水体温室气体排放特征[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学: 1-238. |
| CHEN S, 2022. Characteristics of greenhouse gases emission from urban rivers at different time scales[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University: 1-238. | |
| [34] | 池善庆, 林财强, 吴礼贵, 等, 2024. 城市人工湖营养盐与抗生素的时空分布特征及生态风险评价[J]. 环境工程, 42(1): 29-36. |
| CHI S Q, LIN C Q, WU L G, et al., 2024. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of nutrients and antibiotics in urban artificial lakes[J]. Environmental Engineering, 42(1): 29-36. | |
| [35] | 金宝石, 2018. 福建主要河口湿地围垦养虾塘氧化亚氮产生、溶存与释放[D]. 福建: 福建师范大学: 1-200. |
| JIN B S, 2018. Production, dissolution and emissions of nitrous oxide from reclaimed shrimp ponds in the two main estuaries, Fujian[D]. Fujian: Fujian Normal University: 1-200. | |
| [36] | 李玲玲, 闫人华, 2024. 滨湖城市河网N2O溶存浓度、空间分布及对生态修复的响应[J]. 湖泊科学, 36(5): 1412-1424. |
| LI L L, YAN R H, 2024. Concentration, spatial distribution, and response to ecological restoration of N2O in urban river networks of lakeside city[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 36(5): 1412-1424. | |
| [37] | 李轩, 苑心, 门聪, 等, 2024. 城市河流CH4和N2O产生及排放研究进展[J]. 环境科学, 45(8): 4932-4945. |
| LI X, YUAN X, MEN C, et al., 2024. Research progress on production and emission of CH4 and N2O from urban rivers[J]. Environmental Science, 45(8): 4932-4945. | |
| [38] | 李肖正, 岳甫均, 周滨, 等, 2022. 渤海湾典型闸控入海河流水体N2O释放研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 42(1): 356-366. |
| LI X Z, YUE F J, ZHOU B, et al., 2022. Spatial and temporal variations and influencing factors of nitrous oxide emissions from surface water in Min River Estuary[J]. China Environmental Science, 42(1): 356-366. | |
| [39] | 刘朝荣, 朱俊羽, 李宇阳, 等, 2022. 太湖氧化亚氮 (N2O) 排放特征及潜在驱动因素[J]. 环境科学, 43(8): 4118-4126. |
| LIU C R, ZHU J Y, LI Y Y, et al., 2022. Emissiom of nitrous oxide (N2O) from LakeTaihu and corresponding potential driving factors[J]. Environmental Science, 43(8): 4118-4126. | |
| [40] | 漆梦婷, 罗柳, 洪晓静, 等, 2022. 闽江河口表层水体氧化亚氮释放时空变化特征及其影响因素[J]. 环境科学学报, 42(7): 489-500. |
| QI M T, LUO L, HONG X J, et al., 2022. Spatial and temporal variations and influencing factors of nitrous oxide emissions from surface water in Min River Estuary[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 42(7): 489-500. | |
| [41] | 王红岩, 周旭东, 孙国新, 等, 2022. 城市化地区典型水体的N2O排放通量特征——以南京市为例[J]. 生态学报, 42(23): 9577-9589. |
| WANG H Y, ZHOU X D, SUN G X, et al., 2022. N2O emission in typical urban waterbodies: Example of Nanjing[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42(23): 9577-9589. | |
| [42] | 中华人民共和国生态环境部, 国家市场监督管理总局, 2002. 地表水环境质量标准: GB 3838—2002[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社: 1-12. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation, 2002. Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water: GB 3838—2002[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press: 1-12. |
| [1] | GUO Jiawen, LIU Kai, LIU Gaoyuan, GAO Xinxin, YANG Kun, PAN Bo. Effects of Exogenous Cane Leaf Additives in Different Forms on Properties of Red Soil and Sugarcane Growth Yunnan [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2025, 34(7): 1100-1110. |
| [2] | REN Chenjian, HAO Ruixia, ZHANG Yang, HAN Lijuan, WEI Yuxing, CHAI Lu. The Release Characteristics of Ammonia Nitrogen from River Sediments Driven by Hydrodynamic Forces [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2025, 34(6): 931-940. |
| [3] | PAN Xuan, LUO Junxiao, TANG Bingran, GUO Xiangyu, HE Qiang, LI Hong. The Influence of Oxygen-carrying Zeolite and Tubificid Worm on Nitrogen Migration and Transformation in the Sediment-water Core [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2025, 34(5): 763-772. |
| [4] | HUANG Deng-lingyao, TANG Bingran, MA Yuanyuan, HE Qiang, LI Hong. The Effect of As on the Transformation of Nitrogen in Paddy Soil: A Case Study Towards Purple Soil [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2025, 34(5): 784-795. |
| [5] | MEI Yaoping, WU Benli, HUANG Long, WU Cangcang, CHEN Jing, CHEN Xiajun, HE Jixiang. Purification of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Aquaculture Wastewater Using Different Aquatic Plants [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2025, 34(3): 442-450. |
| [6] | SUN Yujia, LU Mei, ZHAO Xuyan, FENG Jun, LIU Guoqing, GUO Chuxiao, WANG Mingliu, HUANG Minchao, CHEN Zhiming. Response of Soil Bacterial Community Structure to Nitrogen Addition in Degraded Napahai Alpine Meadow [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2025, 34(2): 233-246. |
| [7] | ZHANG Yangyang, LIU Xuejun. Atmospheric Ammonia Concentrations, Source Apportionment, and Implications during Winter in the Urban Area of Beijing [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2025, 34(10): 1579-1587. |
| [8] | LI Li, ZHAO Qiuyue, HAN Junzan, LI Huipeng. Agricultural Ammonia Emission Inventory and Characteristics in Yancheng City from 2013 to 2021 [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2025, 34(1): 67-76. |
| [9] | LI Yanlin, CHEN Yangyang, YANG Shuangrong, LIU Jumei. Study on the Effects of Organic Acids in Plant Root Exudates on Soil Organic Carbon and Nitrogen Mineralization [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2024, 33(9): 1362-1371. |
| [10] | ZHU Leyang, ZHANG Xizhe, TAO Jiang, WANG Xiu, HAN Yanying, YE Yanhui. The Effect of Nitrogen Addition on Soil Respiration in the Abies Georgei var. Smithii Forest of Sygera Mountains [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2024, 33(9): 1384-1396. |
| [11] | WU Xinyu, KANG Jiahui, DU Xiaoyun, SHEN Qikun, FENG Sijie, MENG Fanlei, PAN Yuepeng, LIU Xuejun, XU Wen. Study on Characteristics of Cropland Ammonia Emissions and Its Near-source Deposition in Typical Small Watershed of Plateau Lake [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2024, 33(8): 1236-1244. |
| [12] | XIA Fan, HAN Yimeng, ZHOU Jianxing, XIE Danni. The Distribution Characteristics of Nitrogen and Sulfur in the Artificially Disturbed Tibetan Plateau Alpine Forests [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2024, 33(5): 689-698. |
| [13] | CHEN Xiaohui, HU Xisheng. Analysis of the Driving Forces of Ecological Environment Quality in Fuzhou City Coupled with ER and GWR [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2024, 33(5): 812-823. |
| [14] | LIU Chutian, GUO Dongdong, HOU Lei, LIANG Qibin, WANG Yanxia, SHI Yanting, QI Yane. Analysis of the Effect Model for Nutrient Regulation on Cadmium Accumulation in Populus yunnanensis Seedlings [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2024, 33(3): 460-468. |
| [15] | LI Xia, CHEN Yonghao, CHEN Zhe, ZHANG Guozhuang, TANG Mengya. Analysis of Spatio-temporal Changes and Driving Vegetation NDVI in Coastal Areas of China [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2024, 33(2): 180-191. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
