Ecology and Environment ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (8): 1236-1244.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.08.008
• Research Article [Environmental Science] • Previous Articles Next Articles
WU Xinyu1( ), KANG Jiahui1, DU Xiaoyun1, SHEN Qikun1, FENG Sijie1, MENG Fanlei1, PAN Yuepeng2, LIU Xuejun1, XU Wen1,*(
), KANG Jiahui1, DU Xiaoyun1, SHEN Qikun1, FENG Sijie1, MENG Fanlei1, PAN Yuepeng2, LIU Xuejun1, XU Wen1,*( )
)
Received:2024-07-10
Online:2024-08-18
Published:2024-09-25
吴馨俣1( ), 康嘉慧1, 杜晓芸1, 申其昆1, 冯思捷1, 孟凡磊1, 潘月鹏2, 刘学军1, 许稳1,*(
), 康嘉慧1, 杜晓芸1, 申其昆1, 冯思捷1, 孟凡磊1, 潘月鹏2, 刘学军1, 许稳1,*( )
)
通讯作者:
许稳。E-mail: 作者简介:吴馨俣(2001年生),女,硕士研究生,主要从事大气氨沉降与环境效应。E-mail: wuxinyu@cau.edu.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
WU Xinyu, KANG Jiahui, DU Xiaoyun, SHEN Qikun, FENG Sijie, MENG Fanlei, PAN Yuepeng, LIU Xuejun, XU Wen. Study on Characteristics of Cropland Ammonia Emissions and Its Near-source Deposition in Typical Small Watershed of Plateau Lake[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(8): 1236-1244.
吴馨俣, 康嘉慧, 杜晓芸, 申其昆, 冯思捷, 孟凡磊, 潘月鹏, 刘学军, 许稳. 高原湖泊典型小流域农田氨挥发与近源沉降特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(8): 1236-1244.
| 作物类型 | 基肥 | 追肥 | 总氮投入/ (kg·hm−2) | 施肥时期 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 肥料类型 | 肥料用量 (以N计)/(kg·hm−2) | 肥料类型 | 肥料用量 (以N计)/(kg·hm−2) | 基肥 | 追肥 | |||
| 玉米 | 复合肥 | 112.5 | 尿素 | 276 | 388.5 | 7月 | 8月 | |
| 烤烟 | 顺丰有机肥 | 7.5 | 含腐殖酸水溶肥料 | 108 | 322.5 | 5月 | 6月 | |
| 尿素 | 207 | |||||||
| 水稻 | 水溶有机肥 | 138 | 水溶肥 | 34.5 | 214.3 | 5月 | 6月 | |
| 菌肥 | 41.8 | |||||||
Table 1 Information on fertilization in Gusheng area during the growth season of major crops
| 作物类型 | 基肥 | 追肥 | 总氮投入/ (kg·hm−2) | 施肥时期 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 肥料类型 | 肥料用量 (以N计)/(kg·hm−2) | 肥料类型 | 肥料用量 (以N计)/(kg·hm−2) | 基肥 | 追肥 | |||
| 玉米 | 复合肥 | 112.5 | 尿素 | 276 | 388.5 | 7月 | 8月 | |
| 烤烟 | 顺丰有机肥 | 7.5 | 含腐殖酸水溶肥料 | 108 | 322.5 | 5月 | 6月 | |
| 尿素 | 207 | |||||||
| 水稻 | 水溶有机肥 | 138 | 水溶肥 | 34.5 | 214.3 | 5月 | 6月 | |
| 菌肥 | 41.8 | |||||||
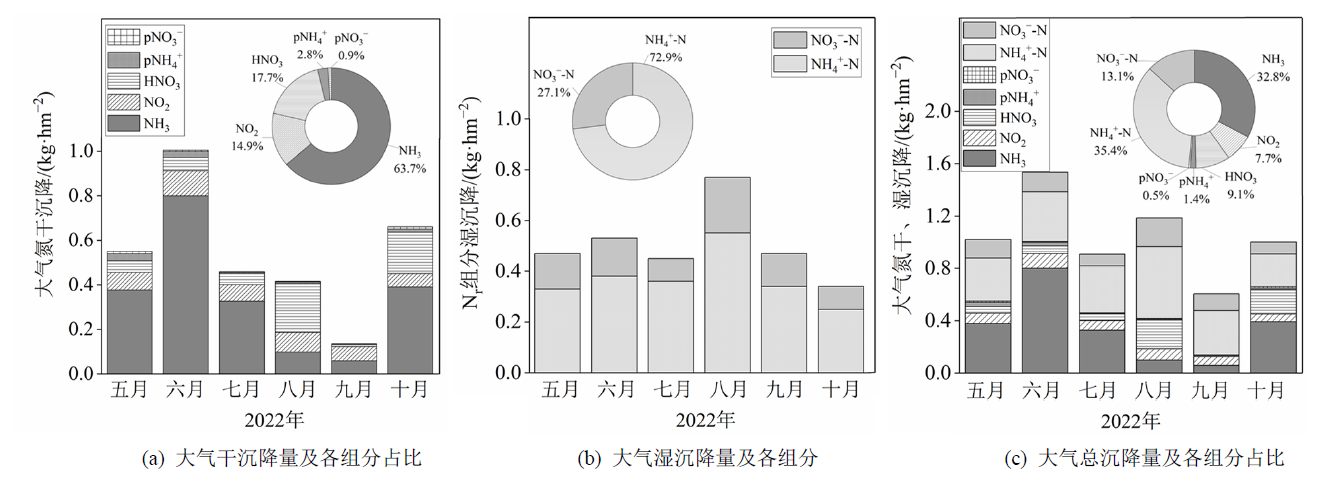
Figure 6 Monthly variations in dry and wet deposition of major reactive nitrogen species and the average proportions during the growing season of main crops in Gusheng area in 2022
| [1] |
DENG J M, NIE W, HUANG X, et al., 2023. Atmospheric reactive nitrogen deposition from 2010 to 2021 in Lake Taihu and the effects on phytoplankton[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 57(21): 8075-8084.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | FENG L, LIAO W J, 2016. Legislation, plans, and policies for prevention and control of air pollution in China: Achievements, challenges, and improvements[J]. Journal Cleaner Production, 112(Part 2): 1549-1558. |
| [3] | FOWLER D, STEADMAN C, STEVENSON D, et al., 2015. Effects of global change during the 21st century on the nitrogen cycle[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry Physics, 15(24): 13849-13893. |
| [4] | GALLOWAY J, DENTENER F J, CAPONE D G, et al., 2004. Nitrogen cycles: Past, present, and future[J]. Biogeochemistry, 70(2): 153-226. |
| [5] | GU B J, ZHANG L, VAN D R, et al., 2021. Abating ammonia is more cost-effective than nitrogen oxides for mitigating PM2.5 air pollution[J]. Science, 374(6568): 758-762. |
| [6] | GAO Y, ZHOU F, CIAIS P, et al., 2019. Human activities aggravate nitrogen-deposition pollution to inland water over China[J]. National Science Review, 7(2): 430-440. |
| [7] | GRELL G A, PECKHAM S E, SCHMITZ R, et al., 2005. Fully coupled “online” chemistry within the WRF model[J]. Atmospheric Environment 39(37): 6957-6975. |
| [8] | HEALD C L, COLLETT J, LEE T, et al., 2012. Atmospheric ammonia and particulate inorganic nitrogen over the United States[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 12(288): 10295-10312. |
| [9] | HOU K F, HO S S H, HUANG R J, 2016. Chemical composition and bioreactivity of PM2.5 during 2013 Haze events in China[J]. Atmospheric Environmental, 126: 162-170. |
| [10] | KANG J H, WANG J X, HEAL M R, et al., 2023. Ammonia mitigation campaign with smallholder farmers improves air quality while ensuring high cereal production[J]. Nature Food, 4(9): 751-761. |
| [11] | LIU X J, XU W, DU E Z, et al. 2020. Environmental impacts of nitrogen emissions in China and the role of policies in emission reduction[J]. Philosophical Transactions of The Royal Society A-mathematical Physical and Engi Science and Technology, 378(2183): 20190324-20190324. |
| [12] |
LIU X J, DUAN L, MO J M, et al., 2011. Nitrogen deposition and its ecological impact in China: An overview[J]. Environmental Pollution, 159(10): 2251-2264.
DOI PMID |
| [13] | LIU L, XU W, LU X K, et al., 2021. Exploring global changes in agricultural ammonia emissions and their contribution to nitrogen deposition since 1980[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 119(14): e2121998119. |
| [14] | LI Y, TAMMY M. THOMPSON, MARTIN V D, et al., 2017. Temporal and spatial variability of ammonia in urban and agricultural regions of northern Colorado, United States[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 17(10): 6197-6213. |
| [15] | MENG Z Y, XU X B, LIN W L, et al., 2018. Role of ambient ammonia in particulate ammonium formation at a rural site in the North China Plain[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 18(1): 167-184. |
| [16] | MENG F L, WANG M R, STROKAL M, et al., 2022. Nitrogen losses from food production in the North China plain: A case study for Quzhou[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 816: 151557. |
| [17] |
PAN Y P, TIAN S L, ZHAO Y H, et al., 2018. Identifying Ammonia Hotspots in China Using a National Observation Network[J]. Environmental science and technology, 52(7): 3926-3934.
DOI PMID |
| [18] | SUTTON M A, BURKHARD J K, GUERIN D, et al., 1998. Development of resistance models to describe measurements of bi-directional ammonia surface-atmosphere exchange[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 32(3): 473-480. |
| [19] | TANG Y S, BRABAN C F, DRAGOSITS U, et al., 2018. Drivers for spatial, temporal and long-term trends in atmospheric ammonia and ammonium in the UK[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 18(2): 705-733. |
| [20] | VAN D M, CLARISSE L, WHITBURN S, et al., 2018. Industrial and agricultural ammonia point sources exposed[J]. Nature, 564(7734): 99-103. |
| [21] | WEI W, HA Y W, WU H Q, et al., 2021. Application of the Source-sink Landscape Method in the Evaluation of Agricultural Non-point Source Pollution: First Estimation of an Orchard-dominated Area in China[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 252: 106910. |
| [22] | XU H, LIU S, DING J, et al., 2023. Mapping crop-specific emission factors highlights hotspots of ammonia mitigation in China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 908: 168157. |
| [23] | XU X R, OUYANG X, GU Y N, et al., 2021. Climate change may interact with nitrogen fertilizer management leading to different ammonia loss in China’s croplands[J]. Global Change Biology, 27(24): 6525-6535. |
| [24] | XI C, DEREK D, BRET S, et al., 2024. Seasonal ambient ammonia and ammonium concentrations in a pilot IMPROVE NHx monitoring network in the western United States[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 91: 118-126. |
| [25] |
XU W, SHANG B, XU Y S, et al., 2018. Effects of elevated ozone concentration and nitrogen addition on ammonia stomatal compensation point in a poplar clone[J]. Environmental Pollution, 238: 760-770.
DOI PMID |
| [26] | XU W, LUO X S, PAN Y P, et al., 2015. Quantifying atmospheric nitrogen deposition through a nationwide monitoring network across China[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry Physics, 15: 12345-12360. |
| [27] | YANG F, TAN J, ZHAO Q, 2011. Characteristics of PM2.5 speciation in representative megacities and across China[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 11(11): 5207-5219. |
| [28] | YI W Y, SHEN J L, LIU G P, et al., 2021. High NH3 deposition in the environs of a commercial fattening pig farm in central south China[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 16(12): 125007. |
| [29] | YI Y C, SHEN J L, YANG C D, et al., 2020. Dry Deposition of Ammonia around Paddy Fields in the Subtropical Hilly Area in Southern China[J]. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 13(3): 216-223. |
| [30] |
ZHANG Y, LIU C M, LIU X J, et al., 2019. Atmospheric nitrogen deposition around the Dongting Lake, China[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 207: 197-204.
DOI |
| [31] | ZHANG Y Y, AOHAN T, DANDAN W, et al., 2018. The vertical variability of ammonia in urban Beijing, China[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 18(22): 16385-16398. |
| [32] | ZOU T T, MENG F L, ZHOU J C, et al., 2023. Quantifying nitrogen and phosphorus losses from crop and livestock production and mitigation potentials in Erhai Lake Basin, China[J]. Agricultural Systems, 211: 103745. |
| [33] | ZHAN X Y, BO Y, ZHOU F, et al., 2017. Evidence for the Importance of Atmospheric Nitrogen Deposition to Eutrophic Lake Dianchi, China[J]. Environmental Science & Technology 51(12): 6699-6708. |
| [34] | ZHANG X Y, FANG Q C, ZHANG T, et al., 2019. Benefits and trade-offs of replacing synthetic fertilizers by animal manures in crop production in China: A meta-analysis[J]. Global Change Biology, 26(2): 888-900. |
| [35] | 陈小华, 钱晓雍, 李小平, 等, 2018. 洱海富营养化时间演变特征 (1988-2013年) 及社会经济驱动分析[J]. 湖泊科学, 30(1): 70-78. |
| CHEN X H, QIAN X Y, LI X P, et al., 2018. Time evolution characteristics of eutrophication in Erhai Lake (1988-2013) and socio-economic driving analysis[J]. Lake Science, 30(1): 70-78. | |
| [36] | 郝家璇, 2024. 洱海西部典型片区食物系统氮磷流动特征及减排潜力[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学. |
| HAO J X, 2024. Nitrogen and phosphorus flow characteristics and emission reduction of food system in western typical areas of Erhai Basin[D]. Beijing: China Agriculture University. | |
| [37] | 黄明雨, 2023. 洱海大气氮磷干沉降特征及其影响因素[J]. 环境科学与技术, 46(1): 33-38. |
| HUANG M Y, 2023. Characteristics and influencing factors of atmospheric nitrogen and phosphorus dry deposition in Erhai Lake[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 46(1): 33-38. | |
| [38] | 黄明雨, 吕兴菊, 董琼蕃, 等, 2022. 洱海大气氮磷湿沉降特征及入湖负荷估算[J]. 人民长江, 53(6): 68-73. |
| HUANG M Y, LÜ X J, DONG Q F, et al., 2022. Characteristics of atmospheric nitrogen and phosphorus deposition and load estimation in Erhai Lake[J]. People’s Yangtze River, 53(6): 68-73. | |
| [39] | 贾钩彦, 张颖, 蔡晓布, 等, 2009. 藏东南大气氮湿沉降动态变化——以林芝观测点为例[J]. 生态学报, 29(4): 1907-1913. |
| JIA J Y, ZHANG Y, CAI X B, et al., 2009. Dynamic change of atmospheric nitrogen precipitation in southeast Tibet: A case study of Nyingchi observation point[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 29(4): 1907-1913. | |
| [40] | 刘伯顺, 黄立华, 黄金鑫, 等, 2022. 我国农田氨挥发研究进展与减排对策[J]. 中国生态农业学报 (中英文), 30(6): 875-888 |
| LIU B S, HUANG L H, HUANG J X, et al., 2022. Research progress of ammonia volatilization and emission reduction strategies in farmland in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 30(6): 875-888. | |
| [41] | 韦莲芳, 段菁春, 谭吉华, 等, 2015. 北京春季大气中氨的气粒相转化及颗粒态铵采样偏差研究[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 45(2): 216-226. |
| WEI L F, DUAN J C, TAN J H, et al., 2015. Gast particle conversion of atmospheric ammonia and sampling artifacts of ammonium in spring of Beijing[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 58(3): 345-355. | |
| [42] |
尹兴, 张丽娟, 刘学军, 等, 2017. 河北平原城市近郊农田大气氮沉降特征[J]. 中国农业科学, 50(4): 698-710.
DOI |
| YIN X, ZHANG L J, LIU X J, et al., 2017. Characteristics of atmospheric nitrogen deposition in farmland near cities in Hebei Plain[J]. Scientia Agricultologica Sinica, 50(4): 698-710. | |
| [43] | 张天鹏, 2022. 洱海流域氮磷污染物入湖负荷估算模型研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院. |
| ZHANG T P, 2022. Study on load estimation model of nitrogen and phosphorus pollutants entering lake in Erhai Basin[D]. Beijing: China Academy of Agricultural Sciences. |
| [1] | ZHANG Xiaojin, DAI Zhengwei, DAI Yu, DAI Guofei, YANG Ping, FANG Yuanyuan, PENG Ningyan. Research Progress on the Methods of Simultaneous Algae Control and Microcystin Removal [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(7): 1549-1554. |
| [2] | LI Furong, WANG Linqing, LI Wenying, WU Zhichao, WANG Xu. Research and Application Progress on Heavy Metal Absorption and Accumulation of Oenanthe javanica [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(12): 2423-2430. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 72
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 124
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
