Ecology and Environmental Sciences ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (6): 950-960.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2025.06.012
• Research Article [Environmental Science] • Previous Articles Next Articles
MENG Chang1,2( ), HONG Mei1,2,*(
), HONG Mei1,2,*( ), LI Fei1,2,*(
), LI Fei1,2,*( )
)
Received:2024-11-14
Online:2025-06-18
Published:2025-06-11
通讯作者:
* 李斐, E-mail: 作者简介:孟畅(1997年生),女,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为农业遥感。E-mail: 2021202040012@emails.imau.edu.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
MENG Chang, HONG Mei, LI Fei. Collaborative Enhancement of Soil Heavy Metal Prediction Accuracy Using Hyperspectral Sensitive Band Selection and Machine Learning[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2025, 34(6): 950-960.
孟畅, 红梅, 李斐. 高光谱敏感波段筛选与机器学习协同提升土壤重金属预测精度[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(6): 950-960.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2025.06.012
| 类别 | 名称 | 缩略词 | 参考 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 过滤法 | 相关分析 | CA | Liu et al., |
| 互信息系数 | MI | Zhou et al., | |
| 相关特征 | RELIEF | Li et al., | |
| 最大信息系数 | MIC | Liu et al., | |
| 最小冗余 | MRMR | Gu et al., | |
| 包裹法 | K选择 | SKB | Liu et al., |
| 可变迭代空间收缩法 | VISSA | Zhang et al., | |
| 连续投影算法 | SPA | Mei et al., | |
| 遗传算法 | GA | Rostami et al., | |
| 竞争性自适应重加权抽样 | CARS | Mei et al., | |
| 无信息变量消除 | UVE | Song et al., | |
| 嵌入法 | 随即森林重要度 | RFI | Yang et al., |
| 逐步多元线性回归 | SMLR | Liu et al., | |
| 偏最小二乘回归-VIP | PLSR-VIP | Yang et al., | |
| 岭回归 | RR | Malik et al., | |
| 套索回归 | LR | Tibshirani, |
Table 1 Band selection method
| 类别 | 名称 | 缩略词 | 参考 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 过滤法 | 相关分析 | CA | Liu et al., |
| 互信息系数 | MI | Zhou et al., | |
| 相关特征 | RELIEF | Li et al., | |
| 最大信息系数 | MIC | Liu et al., | |
| 最小冗余 | MRMR | Gu et al., | |
| 包裹法 | K选择 | SKB | Liu et al., |
| 可变迭代空间收缩法 | VISSA | Zhang et al., | |
| 连续投影算法 | SPA | Mei et al., | |
| 遗传算法 | GA | Rostami et al., | |
| 竞争性自适应重加权抽样 | CARS | Mei et al., | |
| 无信息变量消除 | UVE | Song et al., | |
| 嵌入法 | 随即森林重要度 | RFI | Yang et al., |
| 逐步多元线性回归 | SMLR | Liu et al., | |
| 偏最小二乘回归-VIP | PLSR-VIP | Yang et al., | |
| 岭回归 | RR | Malik et al., | |
| 套索回归 | LR | Tibshirani, |
| 区域与元素 | 变异系数/% | 重金属质量分数/(mg∙kg−1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最大值 | 最小值 | 平均值 | 偏斜率 | 内蒙古土壤背景值 | 中国土壤背景值 | |||
| 区域a | Cu | 1.39 | 1617.45 | 4.82 | 218.47 | 2.28 | 22.91 | 100.00 |
| Zn | 1.34 | 354.66 | 24.81 | 32.37 | 1.72 | 48.60 | 300.00 | |
| Cr | 1.29 | 193.08 | 12.61 | 19.97 | 1.20 | 68.20 | 350.00 | |
| Pb | 1.39 | 559.92 | 1.75 | 64.92 | 2.11 | 34.20 | 250.00 | |
| 区域b | Cu | 0.75 | 432.00 | 3.77 | 126.68 | 1.33 | - | - |
| Zn | 0.30 | 123.56 | 8.46 | 68.87 | 0.61 | - | - | |
| Cr | 0.14 | 87.92 | 36.43 | 66.48 | 0.76 | - | - | |
| Pb | 1.21 | 715.84 | 4.62 | 77.74 | 2.49 | - | - | |
Table 2 Descriptive statistics of heavy metal mass fraction in the studied area
| 区域与元素 | 变异系数/% | 重金属质量分数/(mg∙kg−1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最大值 | 最小值 | 平均值 | 偏斜率 | 内蒙古土壤背景值 | 中国土壤背景值 | |||
| 区域a | Cu | 1.39 | 1617.45 | 4.82 | 218.47 | 2.28 | 22.91 | 100.00 |
| Zn | 1.34 | 354.66 | 24.81 | 32.37 | 1.72 | 48.60 | 300.00 | |
| Cr | 1.29 | 193.08 | 12.61 | 19.97 | 1.20 | 68.20 | 350.00 | |
| Pb | 1.39 | 559.92 | 1.75 | 64.92 | 2.11 | 34.20 | 250.00 | |
| 区域b | Cu | 0.75 | 432.00 | 3.77 | 126.68 | 1.33 | - | - |
| Zn | 0.30 | 123.56 | 8.46 | 68.87 | 0.61 | - | - | |
| Cr | 0.14 | 87.92 | 36.43 | 66.48 | 0.76 | - | - | |
| Pb | 1.21 | 715.84 | 4.62 | 77.74 | 2.49 | - | - | |
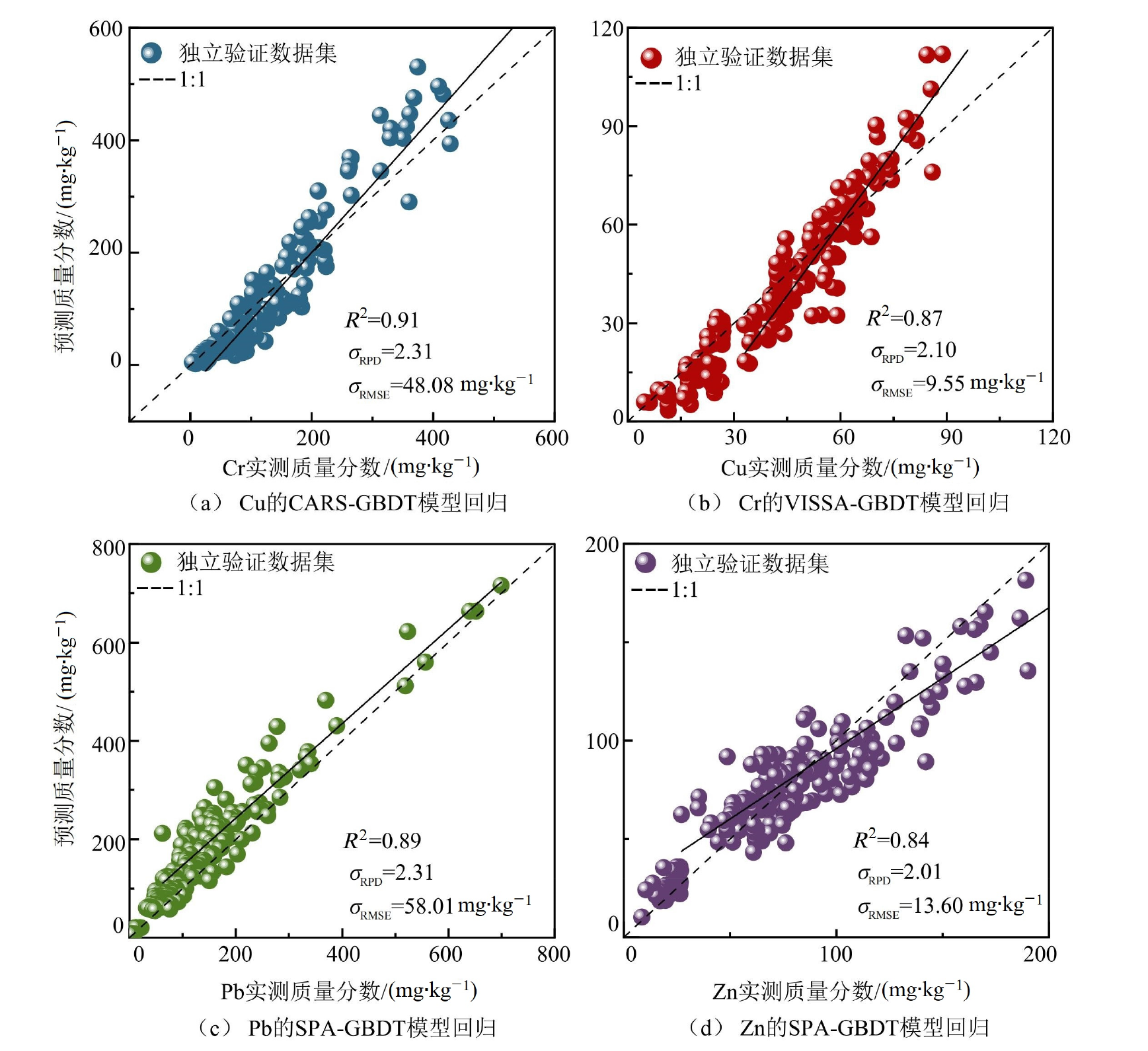
Figure 6 Independent verification results of the optimal sensitive band method combined with the GBDT model to estimate heavy metal concentration in soil
| [1] | BESSADOK A, BEN A S, 2019. Feature selection for hyperspectral data using mutual information and MRMR methods[J]. Remote Sensing, 11(8): 1932-1945. |
| [2] | CHEN Z L, YIN W Y, LIU H T, et al., 2017. Review of monitoring petroleum-hydrocarbon contaminated soils with visible and near-Infrared spectroscopy[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 37(6): 1723-1727. |
| [3] | GOMEZ C, LAGACHERIE P, COULOUM G, 2008. Continuum removal versus PLSR method for clay and calcium carbonate content estimation from laboratory and airborne hyperspectral measurements[J]. Geoderma, 148(2): 141-148. |
| [4] | GU X Y, GUO J C, XIAO L J, et al., 2022. Conditional mutual information-based feature selection algorithm for maximal relevance minimal redundancy[J]. Applied Intelligence, 52(2): 1436-1447. |
| [5] | HUANG Y, WANG L Y, WANG W J, et al., 2019. Current status of agricultural soil pollution by heavy metals in China: A meta-analysis[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 651(Part 2): 3034-3042. |
| [6] | JIN J M, 2021. A comparison of a gradient boosting decision tree, random forests, and artificial neural networks to model urban land use changes: The case of the seoul metropolitan area[J]. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 35(4): 1-19. |
| [7] | LI B, XU X M, ZHANG L, et al., 2020. Above-ground biomass estimation and yield prediction in potato by using UAV-based RGB and hyperspectral imaging[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 162: 161-172. |
| [8] | LIU H, YU L, 2005. Toward integrating feature selection algorithms for classification and clustering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 17(4): 491-502. |
| [9] | LIU Y, FENG H K, YUE J B, et al., 2022. Remote-sensing estimation of potato above-ground biomass based on spectral and spatial features extracted from high-definition digital camera images[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 198: 107089. |
| [10] | LU Q, WANG S J, BAI X Y, et al., 2019. Rapid inversion of heavy metal concentration in karst grain producing areas based on hyperspectral bands associated with soil components[J]. Microchemical Journal, 148: 404-411. |
| [11] | MALIK A, JAMEI M, ALI M, et al., 2022. Multi-step daily forecasting of reference evapotranspiration for different climates of India: A modern multivariate complementary technique reinforced with ridge regression feature selection[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 272: 107812. |
| [12] | MEI Y S, JIN Y Z, XIAO H Y, et al., 2023. A spectral decomposition method for estimating the leaf nitrogen status of maize by UAV-based hyperspectral imaging[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 212: 108100. |
| [13] | PARVEEN S, ALI K, VINOD K, 2019. Comparison of different approaches for modeling of heavy metal estimations[J]. SN Applied Sciences, 25(1): 780. |
| [14] | PENG Y P, WANG L, ZHAO L, et al., 2021. Estimation of soil nutrient content using hyperspectral data[J]. Agriculture, 11(11): 1129. |
| [15] | RIVERA J L, BONILLA C A, 2020. Predicting soil aggregate stability using readily available soil properties and machine learning techniques[J]. Catena, 187: 104408. |
| [16] | RONG G Z, ALU S, LI K W, et al., 2020. Rainfall lnduced landslide susceptibility mapping based on bayesian optimized random forest and gradient boosting decision tree models: A case study of Shuicheng county, China[J]. Water, 12(11): 3066. |
| [17] | ROSTAMI M, BERAHMAND K, FOROUZANDE S, 2021. A novel community detection based genetic algorithm for feature selection[J]. Journal of Big Data, 8: 2. |
| [18] | SHARMA P, GUPTA R, 2021. Soil heavy metal prediction using decision tree and its applications in environmental management[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 193(2): 51. |
| [19] | SONG X Z, HUANG Y, TIAN K D, 2020. Near infrared spectral variable optimization by final complexity adapted models combined with uninformative variables elimination-a validation study[J]. Optik, 203: 164019. |
| [20] | SUN W C, LIU S, ZHANG X, et al., 2022. Estimation of soil organic matter content using selected spectral subset of hyperspectral data[J]. Geoderma, 49: 115653. |
| [21] | SUN W C, ZHANG X, 2017. Estimating soil zinc concentrations using reflectance spectroscopy[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinfirmation, 58: 126-133. |
| [22] | SWIERENGA H, WULFERT F, DE N O E, et al., 2000. Development of robust calibration models in near infra-red spectrometric applications[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 411(1-2): 121-131. |
| [23] | TIBSHIRANI R, 1996. Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B: Statistical Methodology, 58(1): 267-288. |
| [24] | WANG Y, LI Y, ZHANG S, 2023. Soil high contribution band selection using random forest and ridge regression for improved prediction accuracy[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 195(7): 456. |
| [25] | WANG Z, DING J L, ZHANG Z P, 2022. Estimation of soil organic matter in arid zones with coupled environmental variables and spectral features[J]. Sensors, 22(3): 1194. |
| [26] | WEI J, LI X, CHEN Y et al., 2021a. Estimation of soil heavy metal concentrations using laboratory-based hyperspectral data: A comparison of models and preprocessing methods[J]. Remote Sensing, 13(2): 234. |
| [27] | WEI L, YANG X, YANG Z, 2019. Application of decision tree and random forest models for soil pollution monitoring[J]. Environmental Pollution, 246: 329-338. |
| [28] | WEI Z, HAN Y, LL J X, et al., 2021b. Hyperspectral inversion of soil heavy metals in three-river source region based on random forest model[J]. Catena, 202: 105222. |
| [29] | WU L J, JIANG Q F, ZHANG Y, et al., 2022. Peroxidase activity in tomato leaf cells under salt stress based on micro-hyperspectral imaging technique[J]. Horticultrae, 8(9): 813. |
| [30] | XIE X, LIU H, CHEN W, 2021. Feature selection with genetic algorithm and decision tree for hyperspectral data classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 59(9): 7864-7875. |
| [31] | YANG H B, LI F, WANG W, et al., 2021. Estimating above-ground biomass of potato using random forest and optimized hyperspectral indices[J]. Remote Sensing, 13(12): 2339. |
| [32] | YANG H B, YIN H, LI F, et al., 2023. Machine learning models fed with optimized spectral indices to advance crop nitrogen monitoring[J]. Field Crops Research, 293: 108844. |
| [33] | YANG H F, XU H, ZHONG H, 2022. Prediction of soil heavy metal concentrations in copper tailings area using hyperspectral reflectance[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 81(6): 183. |
| [34] | YANG H, ZHANG Q, 2020. Predicting soil properties and quality using GBDT based model and hyperspectral data[J]. Geoderma, 368: 114250. |
| [35] | YIN F, WU M M, LIU L, et al., 2021. Predicting the abundance of copper in soil using reflectance spectroscopy and GF5 hyperspectral imagery[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 102: 102420. |
| [36] | ZHANG C, PENG T, NAZIR M S, 2022. A novel hybrid approach based on variational heteroscedastic gaussian process regression for multi-step ahead wind speed forecasting[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 136: 107717. |
| [37] | ZHANG S W, SHEN Q, NIE C J, et al., 2019. Hyperspectral inversion of heavy metal content in reclaimed soil from a mining wasteland based on different spectral transformation and modeling methods[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 211: 393-400. |
| [38] | ZHAO B, ZHANG Q, 2020. Improved stepwise regression and sequential projection algorithm for feature selection in hyperspectral image classification[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 14(3): 335-348. |
| [39] | ZHAO M S, GAO Y F, LU Y Y, et al., 2022. Hyperspectral modeling of soil organic matter based on characteristic wavelength in east China[J]. Sustainability, 14(14): 8455. |
| [40] | ZHOU H F, WANG X Q, ZHU R R, 2022. Feature selection based on mutual information with correlation coefficient[J]. Applied Intelligence, 52: 5457-5474. |
| [41] | 梅雪, 刘鸿雁, 吴龙华, 等, 2023. 基于HDXRF和ICP-MS的黔西北土壤重金属空间分布及影响因素研究[J]. 土壤, 55(2): 399-408. |
| MEI X, LIU H Y, WU L H, et al., 2023. Spatial distribution of soil heavy metal contents and influencing factors in northwest of Guizhou based on HDXRF and ICP-MS[J]. Soils, 55(2): 399-408. | |
| [42] | 徐英杰, 张睿, 王丽, 2019. 中国土壤环境质量标准GB 1518—2018解析与应用[J]. 土壤学报, 56(2): 234-242. |
| XU Y J, ZHANG R, WANG L, 2019. Analysis and application of the China soil environmental quality standard GB 1518—2018[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 56(2): 234-242. | |
| [43] |
肖洁芸, 周伟, 石佩琪, 2023. 土壤重金属含量高光谱反演[J]. 生态环境学报, 32(1): 175-182.
DOI |
| XIAO J Y, ZHOU W, SHI P Q, 2023. Hyperspectral inversion of soil heavy metals[J]. Ecology and Environment, 32(1): 175-182. | |
| [44] |
赵玉玲, 杨楠楠, 张海霞, 等, 2020. 基于高光谱的邯郸市土壤重金属统计估算模型研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(4): 819-826.
DOI |
| ZHAO Y L, YANG N N, ZHANG H X, et al., 2020. Study on the statistical estimation model of soil heavy metals in Handan city based on hyper-spectral[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 29(4): 819-826. | |
| [45] | 魏复盛, 1990. 中国土壤元素背景值[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| WEI F S, 1990. Background values of soil elements in China[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Publishing. |
| [1] | LIU Honglin, ZHAO Fangkai, YANG Lei, SHEN Linjun, YANG Kaifeng, LI Min, CHEN Liding. Study on Heavy Metal Pollution in Urban Park Soil and Influencing Factors: A Case Study of Ningbo City [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2025, 34(5): 773-783. |
| [2] | LIU Dongyi, QU Yonghua, FENG Yaowei, QU Ran. Research on Chromium Ion Content Inversion of GF-5 Satellite Images Based on Grid Search Optimization CatBoost Model [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2024, 33(9): 1460-1470. |
| [3] | WU Wenwei, SHEN Cheng, SHA Chenyan, LIN Kuangfei, WU Jian, XIE Yuqing, ZHOU Xuan. Soil Heavy Metal Enrichment Characteristics, Risk Assessment, and Source Analysis in Redevelopment Areas during Urban Industrial Plots [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2024, 33(5): 791-801. |
| [4] | TANG Shuya, WANG Chunhui, SONG Jing, LI Gang. Characteristics and Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution in the Xiangshan Bay Area [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2024, 33(11): 1768-1781. |
| [5] | CHEN Minyi, ZHU Hanghai, SHE Weiduo, YIN Guangcai, HUANG Zuzhao, YANG Qiaoling. Health Risk Assessment and Source Apportionment of Soil Heavy Metals at A Legacy Shipyard Site in Pearl River Delta [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2023, 32(4): 794-804. |
| [6] | XIAO Jieyun, ZHOU Wei, SHI Peiqi. Hyperspectral Inversion of Soil Heavy Metals [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2023, 32(1): 175-182. |
| [7] | LIU Di, SU Chao, ZHANG Hong, QIN Guanyu. Pollution Characteristics and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution in A Typical Coal-based Industrial Cluster Zone [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2022, 31(2): 391-399. |
| [8] | TA Weiyuan, KANG Zhen, MENG Zhaojun, JIN Shenghua, YANG Xing, GUO Longfei, ZHAO Dongxu, ZHANG Xin. Research of Pollution Characteristics of Heavy Metals in Soil of Typical Closed Zinc Smelting Enterprises in Qinling Mountains [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2021, 30(7): 1513-1521. |
| [9] | CHA Lijuan, ZHOU Dandan, FENG Hongjuan, ZHAO Shuyuan, FENG Kaiping. Research on the Bioaccumulation Characteristics of Two Kinds of Wild Edible Fungi to Soil Heavy Metals [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2021, 30(10): 2093-2099. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
