Ecology and Environment ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (7): 1063-1071.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.07.007
• Research Article [Ecology] • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Chengyang1,*( ), LIANG Zhihui1, LI Zhenming1, CAI Min1, XU Ruiyao1, CHEN Xiuyu1, DING Jiayin1, XU Qiuyun1, PENG Fei2
), LIANG Zhihui1, LI Zhenming1, CAI Min1, XU Ruiyao1, CHEN Xiuyu1, DING Jiayin1, XU Qiuyun1, PENG Fei2
Received:2024-01-18
Online:2024-07-18
Published:2024-09-04
Contact:
LI Chengyang
李成阳1,*( ), 梁志辉1, 李臻明1, 蔡敏1, 许瑞瑶1, 陈秀宇1, 丁佳音1, 许秋云1, 彭飞2
), 梁志辉1, 李臻明1, 蔡敏1, 许瑞瑶1, 陈秀宇1, 丁佳音1, 许秋云1, 彭飞2
通讯作者:
李成阳
作者简介:李成阳(1992年生),男,讲师,博士,研究方向为草地退化过程和机理。E-mail: lichengyang@lzb.ac.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
LI Chengyang, LIANG Zhihui, LI Zhenming, CAI Min, XU Ruiyao, CHEN Xiuyu, DING Jiayin, XU Qiuyun, PENG Fei. Plant Community Characteristics and Soil Characteristics of Degraded Alpine Meadows in the Beilu River Basin of the Yangtze River Source Area[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(7): 1063-1071.
李成阳, 梁志辉, 李臻明, 蔡敏, 许瑞瑶, 陈秀宇, 丁佳音, 许秋云, 彭飞. 长江源区北麓河流域退化高寒草甸植物群落特征和土壤特性[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(7): 1063-1071.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.07.007
| 变异来源 | BD | SM | pH | SOC | TN | NO3− | NH4+ | AN | TP | AP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LD | 46.6** 2) | 28.8** | 18.1** | 345.2** | 198.4** | 38.7** | 10.1** | 33.7** | 4.3* 1) | 0.7 |
| D | 7.2** | 0.1 | 13.3** | 58.7** | 73.6** | 6.9** | 19.3** | 25.5** | 1.9 | 0.8 |
| LD×D | 2.4 | 2.6 | 2.8 | 49.8** | 24.0** | 2.2 | 12.3** | 12.6** | 0.7 | 0.9 |
Table 1 Grassland degradation (LD), soil depth (D), and their interaction on various indicators based on Two-way ANOVA (F values)
| 变异来源 | BD | SM | pH | SOC | TN | NO3− | NH4+ | AN | TP | AP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LD | 46.6** 2) | 28.8** | 18.1** | 345.2** | 198.4** | 38.7** | 10.1** | 33.7** | 4.3* 1) | 0.7 |
| D | 7.2** | 0.1 | 13.3** | 58.7** | 73.6** | 6.9** | 19.3** | 25.5** | 1.9 | 0.8 |
| LD×D | 2.4 | 2.6 | 2.8 | 49.8** | 24.0** | 2.2 | 12.3** | 12.6** | 0.7 | 0.9 |
| 土壤深度/ cm | 退化 程度 | 土壤水分/ % | 土壤容重/ (g∙m−3) | pH | SOC 质量分数/ (g∙kg−1) | TN 质量分数/ (g∙kg−1) | TP 质量分数/ (g∙kg−1) | NO3− 质量分数/ (mg∙kg−1) | NH4+ 质量分数/ (mg∙kg−1) | AN 质量分数/ (mg∙kg−1) | AP 质量分数/ (mg∙kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0‒10 | CK | 27.01±2.02a | 1.00±0.05c | 7.97±0.02c | 21.18±0.91a | 1.37±0.06a | 0.08±0.02b | 16.91±1.77a | 28.61±6.07a | 45.52±6.16a | 2.05±0.33a |
| MD | 20.13±1.05b | 1.23±0.08b | 8.25±0.01b | 6.44±0.31b | 0.52±0.01b | 0.06±0.01b | 4.25±0.57b | 9.93±0.28b | 14.18±0.55b | 1.75±0.25a | |
| SD | 29.35±1.12a | 1.39±0.01a | 8.56±0.01a | 2.96±0.33b | 0.55±0.06b | 0.17±0.04a | 7.60±1.05b | 5.30±0.38b | 12.91±1.01b | 0.74±0.33a | |
| 10‒20 | CK | 32.36±2.14a | 1.17±0.07b | 8.24±0.03c | 10.68±0.68a | 0.76±0.04a | 0.06±0.01b | 9.83±2.09a | 5.85±1.28a | 15.68±3.29a | 1.92±0.36b |
| MD | 25.21±1.28b | 1.36±0.03a | 8.35±0.02b | 5.54±0.32b | 0.45±0.01b | 0.06±0.01b | 3.39±0.41b | 4.49±0.25a | 7.88±0.32b | 2.71±0.1a | |
| SD | 30.03±2.14a | 1.47±0.02a | 8.55±0.02a | 4.31±0.32b | 0.52±0.03b | 0.16±0.01a | 5.19±0.75b | 5.70±0.47a | 10.88±1.09ab | 1.85±0.17b | |
| 20‒30 | CK | 34.32±3.21a | 1.36±0.07b | 8.53±0.2a | 9.76±0.74a | 0.74±0.04a | 0.08±0.01b | 10.77±1.87a | 7.64±1.03a | 18.41±2.22a | 2.43±0.23a |
| MD | 26.10±0.06b | 1.43±0.04a | 8.47±0.01a | 4.62±0.11b | 0.4±0.01b | 0.06±0.01b | 4.29±0.67b | 3.71±0.25b | 8.0±0.76b | 1.91±0.33a | |
| SD | 28.17±1.08b | 1.49±0.02a | 8.66±0.05a | 3.23±0.33c | 0.25±0.03c | 0.14±0.01a | 4.29±0.74b | 0.06±0.01b | 2.43±0.67b | 2.19±0.43a |
Table 2 Physical and chemical characteristics of soil in alpine meadows with different degrees of degradation
| 土壤深度/ cm | 退化 程度 | 土壤水分/ % | 土壤容重/ (g∙m−3) | pH | SOC 质量分数/ (g∙kg−1) | TN 质量分数/ (g∙kg−1) | TP 质量分数/ (g∙kg−1) | NO3− 质量分数/ (mg∙kg−1) | NH4+ 质量分数/ (mg∙kg−1) | AN 质量分数/ (mg∙kg−1) | AP 质量分数/ (mg∙kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0‒10 | CK | 27.01±2.02a | 1.00±0.05c | 7.97±0.02c | 21.18±0.91a | 1.37±0.06a | 0.08±0.02b | 16.91±1.77a | 28.61±6.07a | 45.52±6.16a | 2.05±0.33a |
| MD | 20.13±1.05b | 1.23±0.08b | 8.25±0.01b | 6.44±0.31b | 0.52±0.01b | 0.06±0.01b | 4.25±0.57b | 9.93±0.28b | 14.18±0.55b | 1.75±0.25a | |
| SD | 29.35±1.12a | 1.39±0.01a | 8.56±0.01a | 2.96±0.33b | 0.55±0.06b | 0.17±0.04a | 7.60±1.05b | 5.30±0.38b | 12.91±1.01b | 0.74±0.33a | |
| 10‒20 | CK | 32.36±2.14a | 1.17±0.07b | 8.24±0.03c | 10.68±0.68a | 0.76±0.04a | 0.06±0.01b | 9.83±2.09a | 5.85±1.28a | 15.68±3.29a | 1.92±0.36b |
| MD | 25.21±1.28b | 1.36±0.03a | 8.35±0.02b | 5.54±0.32b | 0.45±0.01b | 0.06±0.01b | 3.39±0.41b | 4.49±0.25a | 7.88±0.32b | 2.71±0.1a | |
| SD | 30.03±2.14a | 1.47±0.02a | 8.55±0.02a | 4.31±0.32b | 0.52±0.03b | 0.16±0.01a | 5.19±0.75b | 5.70±0.47a | 10.88±1.09ab | 1.85±0.17b | |
| 20‒30 | CK | 34.32±3.21a | 1.36±0.07b | 8.53±0.2a | 9.76±0.74a | 0.74±0.04a | 0.08±0.01b | 10.77±1.87a | 7.64±1.03a | 18.41±2.22a | 2.43±0.23a |
| MD | 26.10±0.06b | 1.43±0.04a | 8.47±0.01a | 4.62±0.11b | 0.4±0.01b | 0.06±0.01b | 4.29±0.67b | 3.71±0.25b | 8.0±0.76b | 1.91±0.33a | |
| SD | 28.17±1.08b | 1.49±0.02a | 8.66±0.05a | 3.23±0.33c | 0.25±0.03c | 0.14±0.01a | 4.29±0.74b | 0.06±0.01b | 2.43±0.67b | 2.19±0.43a |
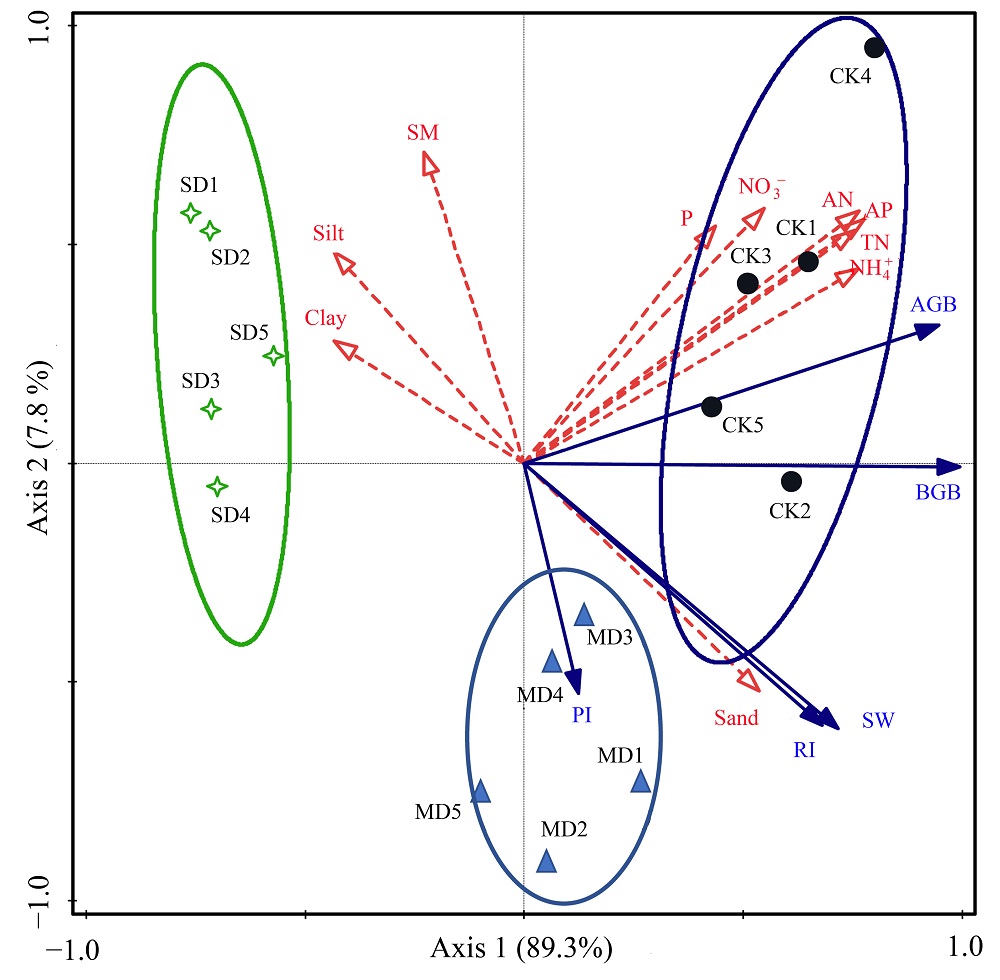
Figure 4 Relationship between plant properties (black solid line arrows) and soil properties (gray dashed line arrows) in degraded alpine meadow grassland
| 土壤因子 | 解释力度排序 | 土壤因子对植物变化的 解释量/% | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AN | 1 | 57.82 | 27.81 | <0.01** 1) |
| AP | 2 | 27.28 | 21.94 | <0.01** |
| SM | 3 | 9.91 | 21.32 | <0.01** |
| TN | 4 | 0.78 | 1.99 | 0.178 |
| NO3− | 5 | 0.61 | 1.41 | 0.154 |
| NH4+ | 6 | 0.43 | 0.83 | 0.454 |
| Silt | 7 | 0.28 | 0.61 | 0.472 |
| Sand | 8 | 0.19 | 0.54 | 0.494 |
| TP | 9 | <0.10 | <0.10 | 0.954 |
| Clay | 10 | <0.10 | <0.10 | 0.748 |
Table 3 Proportion of variance in plant properties that is explained by soil properties for degraded alpine meadow grassland
| 土壤因子 | 解释力度排序 | 土壤因子对植物变化的 解释量/% | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AN | 1 | 57.82 | 27.81 | <0.01** 1) |
| AP | 2 | 27.28 | 21.94 | <0.01** |
| SM | 3 | 9.91 | 21.32 | <0.01** |
| TN | 4 | 0.78 | 1.99 | 0.178 |
| NO3− | 5 | 0.61 | 1.41 | 0.154 |
| NH4+ | 6 | 0.43 | 0.83 | 0.454 |
| Silt | 7 | 0.28 | 0.61 | 0.472 |
| Sand | 8 | 0.19 | 0.54 | 0.494 |
| TP | 9 | <0.10 | <0.10 | 0.954 |
| Clay | 10 | <0.10 | <0.10 | 0.748 |
| [1] | CHE R X, WANG F, WANG W J, et al., 2017. Increase in ammonia-oxidizing microbe abundance during degradation of alpine meadows may lead to greater soil nitrogen loss[J]. Biogeochemistry, 136(3): 341-352. |
| [2] | CONG W, RUIJVEN J V, MOMMER L, et al., 2014. Plant species richness promotes soil carbon and nitrogen stocks in grasslands without legumes[J]. Journal of Ecology, 102(5): 1163-1170. |
| [3] | DAI L C, FU R Y, GUO X W, et al., 2021. Long-term grazing exclusion greatly improve carbon and nitrogen store in an alpine meadow on the northern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Catena, 197: 104955. |
| [4] | DONG Q M, ZHAO X Q, WU G L, et al., 2013. A review of formation mechanism and restoration measures of “black-soil-type” degraded grassland in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 70: 2359-2370. |
| [5] | DONG S K, WEN L, LI Y Y, et al., 2012. Soil quality effects of grassland degradation and restoration on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 76(6): 2256-2264. |
| [6] | HARRIS R B, 2010. Rangeland degradation on the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau: A review of the evidence of its magnitude and causes[J]. Journal of Arid Environments, 74(1): 1-12. |
| [7] | LAI C M, PENG F, SUN J B, et al., 2022. Niche differentiation and higher uptake of available nitrogen maintained the productivity of alpine meadow at early degradation[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 59(1): 35-49. |
| [8] | LI C Y, LAI C M, PENG F, et al., 2021. Dominant plant functional group determine the response of the temporal stability of plant community biomass to 9-year warming on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 12: 704138. |
| [9] | LI X L, PERRY G, BRIERLEY G, et al., 2014. Quantitative assessment of degradation classifications for degraded alpine meadows (Heitutan), Sanjiangyuan, western China[J]. Land Degradation Development, 25(5): 417-427. |
| [10] | MOU X M, YU Y W, ZHAO C Y, et al., 2022. Sedge replacement by grasses accelerates litter decomposition and decreases organic matter formation in alpine meadow soils[J]. Land Degradation & Development, 33(16): 3260-3270. |
| [11] | PENG F, XUE X, YOU Q G, et al., 2018. Changes of soil properties regulate the soil organic carbon loss with grassland degradation on the Qinghai-Tibet plateau[J]. Ecological Indictors, 93: 572-580. |
| [12] | WANG Y F, LÜ W W, XUE K, et al., 2022. Grassland changes and adaptive management on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 3(10): 668-683. |
| [13] | XUE X, GUO J, HAN B S, et al., 2009. The effect of climate warming and permafrost thaw on desertification in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Geomorphology, 108(3-4): 182-190. |
| [14] | YOU Q G, XUE X, PENG F, et al., 2014. Comparison of ecosystem characteristics between degraded and intact alpine meadow in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China[J]. Ecological Engineering, 71: 133-143. |
| [15] | ZHANG W J, XUE X, PENG F, et al., 2019. Meta-analysis of the effects of grassland degradation on plant and soil properties in the alpine meadows of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Global Ecology and Conservation, 20(10): e00774. |
| [16] | ZHOU J, LI X R, PENG F, et al., 2021. Mobilization of soil phosphate after 8 years of warming is linked to plant phosphorus-acquisition strategies in an alpine meadow on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Global Change Biology, 27(24): 6578-6591. |
| [17] |
安克俭, 魏霞, 赵恒策, 等, 2021. 长江源区高寒草原和高寒草甸土壤粒径分布特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 32(2): 433-440.
DOI |
| AN K J, WEI X, ZHAO H C, et al., 2021. Distribution characteristics of soil particle size in alpine steppe and alpine meadow in the source region of the Yangtze River, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 32(2): 433-440. | |
| [18] | 杜志勇, 丛楠, 2024. 植被与土壤特征对青藏高原不同程度退化草地的响应研究[J]. 生态学报, 44(6): 2504-2516. |
| DU Z Y, CONG N, 2024. Responses of vegetation and soil characterisitics to degraded grassland under different degrees on the Qinghai-Tibet plateau[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 44(6): 2504-2516. | |
| [19] | 高洋, 王根绪, 高永恒, 2015. 长江源区高寒草地土壤有机质和氮磷含量的分布特征[J]. 草业科学, 32(10): 1548-1554. |
| GAO Y, WANG G X, GAO Y H, 2015. Distribution characteristics of soil organic matter and nitrogen, phosphor content in alpine grassland ecosystem in upper Yangtze River[J]. Pratacultural Science, 32(10): 1548-1554. | |
| [20] | 根呷羊批, 周俗, 杨孔, 等, 2022. 若尔盖县不同退化程度草地植物群落特征及土壤理化性质[J]. 西南民族大学学报(自然科学版), 48(4): 369-378. |
| GEN GA Y P, ZHOU S, YANG K, et al., 2022. Community characteristics and soil physical and chemical properties under different degraded grassland in Zoige, Sichuan[J]. Journal of Southwest University for Nationalities (Natural Science Edition), 48(4): 369-378. | |
| [21] | 李成阳, 2022. 长江源区退化高寒草甸植物——土壤互馈及其机制研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学: 22-23. |
| LI C Y, 2022. Study on Plant-Soil feedbacks and its mechanism of degraded alpine meadow in the source area of the Yangtze River[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences: 22-23. | |
| [22] | 李成阳, 赖炽敏, 彭飞, 等, 2019. 青藏高原北麓河流域不同退化程度高寒草甸生产力和群落结构特征[J]. 草业科学, 36(4): 1044-1052. |
| LI C Y, LAI C M, PENG F, et al., 2019. Alpine meadows at different stages of degradation in the Beiluhe Basin of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: Productivity and community structure characteristics[J]. Pratacultural Science, 36(4): 1044-1052. | |
| [23] | 李成阳, 张文娟, 赖炽敏, 等, 2021. 黄河源区不同退化程度高寒草原群落生产力、物种多样性和土壤特性及其关系研究[J]. 生态学报, 41(11): 4541-4551. |
| LI C Y, ZHANG W J, LAI C M, et al., 2021. Plant productivity, species diversity, soil properties, and their relationships in an alpine steppe under different degradation degrees at the source of the Yellow River[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(11): 4541-4551. | |
| [24] |
刘洪来, 鲁为华, 陈超, 2011. 草地退化演替过程及诊断研究进展[J]. 草地学报, 19(5): 865-871.
DOI |
| LIU H L, LU W H, CHEN C, 2011. Research progress of grassland degraded succession and diagnosis[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 19(5): 865-871. | |
| [25] | 刘旻霞, 刘成, 杨春亮, 2024. 甘南高寒草甸退化对植物功能群物种多样性与物种多度分布的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 44(1): 142-153. |
| LIU M X, LIU C, YANG C L, 2024. Influences of alpine meadow degradation on species diversity and abundance distribution of plant functional groups in Gannan[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 44(1): 142-153. | |
| [26] |
罗亚勇, 孟庆涛, 张静辉, 等, 2014. 青藏高原东缘高寒草甸退化过程中植物群落物种多样性、生产力与土壤特性的关系[J]. 冰川冻土, 36(5): 1298-1305.
DOI |
|
LUO Y Y, MENG Q T, ZHANG J H, et al., 2014. Species diversity and biomass in relation to soil properties of alpine meadows in the eastern Tibetan Plateau in different degradation stages[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 36(5): 1298-1305.
DOI |
|
| [27] | 尤全刚, 2015. 高寒草甸水热过程及其对草地退化和气候变暖的响应与反馈[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学: 35-36. |
| YOU Q G, 2015. Impact of grassland degradation and climate warming on water-heat process of alpine meadow and its feedbacks[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences: 35-36. | |
| [28] | 周幼吾, 郭东信, 邱国庆, 等, 2000. 中国冻土[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 57-58. |
| ZHOU Y W, GUO D X, QIU G Q, et al., 2000. Permafrost in China[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 57-58. | |
| [29] |
赵帅, 杨文权, 蔺宝珺, 等, 2023. 祁连山国家公园不同退化高寒草甸植物与土壤特性研究[J]. 草地学报, 31(5): 1530-1538.
DOI |
|
ZHAO S, YANG W Q, LIN B J, et al., 2023. Plant and soil characteristics of different degraded alpine meadows in Qilian Mountain National Park[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 31(5): 1530-1538.
DOI |
| [1] | JIANG Yunfeng, YAN Ting, LIU Junnan, MA Bingzeng, WANG Haimeng, DOU Xiaomeng. Responses of Soil Mesofauna in Agricultural Fields to the Frequency of Corn Stover Mulching in Northeastern China’s Black Soil Region [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(5): 699-707. |
| [2] | LI Qing, ZHANG Mengyue, YU Mingqiao, LI Xiaoxuan, CHANG Ming, CHEN Libin, DING Sen. Community Structure and Influencing Factors of Macroinvertebrate in Urban Rivers of Dongguan [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(1): 101-110. |
| [3] | SONG Simeng, LIN Dongmei, ZHOU Hengyu, LUO Zongzhi, ZHANG Lili, YI Chao, LIN Hui, LIN Xingsheng, LIU Bin, SU Dewei, ZHENG Dan, YU Shikui, LIN Zhanxi. Effects of Planting Cenchrus fungigraminus on Plant Species Diversity and Soil Physicochemical Properties in the Ulan Buh Desert [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(9): 1595-1605. |
| [4] | LIANG Chuan, YANG Yanfang, YU Shanshan, ZHOU Li, ZHANG Jingwei, ZHANG Xiujuan. Differences of Microbial Biomass and Community Structure Characteristics in Sediments under Net-pen and Pond Fish Farming [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(8): 1487-1495. |
| [5] | HOU Hui, YAN Peixuan, XIE Qinmi, ZHAO Hongliang, PANG Danbo, CHEN Lin, LI Xuebin, HU Yang, LIANG Yongliang, NI Xilu. Characterization of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungal Community Diversity in the Rhizosphere Soils of Prunus mongolica Scrub of Helan Mountain [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 857-865. |
| [6] | JIANG Yongwei, DING Zhenjun, YUAN Junbin, ZHANG Zheng, LI Yang, WEN Qingchun, WANG Yeyao, JIN Xiaowei. Study on Benthic Macroinvertebrates Community Structure and Water Quality Evaluation in Main Rivers of Liaoning Province [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 969-979. |
| [7] | WANG Yun, ZHENG Xilai, CAO Min, LI Lei, SONG Xiaoran, LIN Xiaolei, GUO Kai. Study on Denitrification Performance and Control Factors in Brackish-Freshwater Transition Zone of Coastal Aquifer [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 980-988. |
| [8] | KOU Zhu, QING Chun, YUAN Changguo, LI Ping. Diversity and Distribution of Sulfur Oxidizing Bacteria in Hot Springs of Northeast Tibet, China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 989-1000. |
| [9] | HU Fang, LIU Jutao, WEN Chunyun, HAN Liu, WEN Hui. Phytoplankton Community Structure and Evaluation of Aquatic Ecological Conditions in Fu River Basin [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 744-755. |
| [10] | YU Fei, ZENG Hailong, FANG Huaiyang, FU Lingfang, LIN Shu, DONG Jiahao. Spatio-temporal Variation Characteristics of Phytoplankton Functional Groups and Water Quality Evaluation in the Typical Tidal River Network [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 756-765. |
| [11] | WU Weilong, CHEN Yijie, WEI Ting, YANG Guiqiong, YANG Changhong, ZHEN Zhen, LIN Zhong. Mechanisms of Earthworm-driven Biodegradation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Coastal Saline Agricultural Soils [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(11): 1996-2006. |
| [12] | ZHAO Yanchu, WANG Fei, WU Dan, HUANG Xin, CHEN Jialin, ZHOU Linpu, KONG Fanqing. Health Assessment of Haihe River Basin Based on Benthic Index of Biotic Integrity [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(10): 1785-1793. |
| [13] | LIANG Chuan, YANG Yanfang, YU Shanshan, ZHOU Li, ZHANG Jingwei, ZHANG Xiujuan. Differences of Microbial Biomass and Community Structure Characteristics in Sediments under Net-pen and Pond Fish Farming [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(10): 1802-1810. |
| [14] | LI Xuan, QIAN Xiuwen, HUANG Juan, WANG Mingyu, XIAO Jun. Responses of Operating Performance and Microbial Community in Constructed Wetlands to NiO NPs Exposure [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(10): 1833-1841. |
| [15] | WANG Lixiao, LIU Jinxian, CHAI Baofeng. Response of Soil Bacterial Community and Nitrogen Cycle during the Natural Recovery of Abandoned Farmland in Subalpine of the North China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(8): 1537-1546. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
