Ecology and Environment ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (1): 56-69.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.01.007
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
XIANG Xing1,2( ), MAN Baiying1,2,*(
), MAN Baiying1,2,*( ), ZHANG Junzhong3, LUO Yang1, MAO Xiaotao1, ZHANG Chao1, SUN Binghua2, WANG Xi2
), ZHANG Junzhong3, LUO Yang1, MAO Xiaotao1, ZHANG Chao1, SUN Binghua2, WANG Xi2
Received:2022-06-09
Online:2023-01-18
Published:2023-04-06
Contact:
MAN Baiying
向兴1,2( ), 满百膺1,2,*(
), 满百膺1,2,*( ), 张俊忠3, 罗洋1, 毛小涛1, 张超1, 孙丙华2, 王希2
), 张俊忠3, 罗洋1, 毛小涛1, 张超1, 孙丙华2, 王希2
通讯作者:
满百膺
作者简介:向兴(1989年生),男(苗族),讲师,博士,研究方向为微生物生态学。E-mail: xiangxing1989@126.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
XIANG Xing, MAN Baiying, ZHANG Junzhong, LUO Yang, MAO Xiaotao, ZHANG Chao, SUN Binghua, WANG Xi. Vertical Distribution of Bacterial Community and Functional Groups Mediating Nitrogen Cycling in Mount Huangshan, Anhui, China[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(1): 56-69.
向兴, 满百膺, 张俊忠, 罗洋, 毛小涛, 张超, 孙丙华, 王希. 黄山土壤细菌群落及氮循环功能群的垂向分布格局[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 56-69.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.01.007
| 海拔分组 | t/℃ | pH | w(AN)/(mg·kg-1) | w(AP)/(mg·kg-1) | w(AK)/(mg·kg-1) | w(TN)/(g·kg-1) | w(TP)/(g·kg-1) | w(TK)/(g·kg-1) | w(SOM)/(g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低海拔 (L, n=3) | 17.80±0.10a | 4.25±0.28 | 844.67±281.76a | 8.83±3.37ab | 162.33±32.15a | 8.94±1.79a | 0.67±0.06a | 25.53±3.33 | 233.67±70.89a |
| 中低海拔 (ML, n=6) | 15.72±0.78b | 4.89±0.63 | 444.67±150.14b | 2.10±0.91b | 96.67±18.98b | 5.07±1.05b | 0.45±0.08b | 30.75±5.15 | 124.67±12.06b |
| 中海拔 (M, n=6) | 15.25±0.43b | 5.18±0.80 | 539.33±164.18b | 12.42±8.07a | 100.83±40.47b | 5.82±1.27b | 0.69±0.17a | 29.27±3.42 | 148.40±49.35b |
| 高海拔 (H, n=9) | 12.22±0.63c | 4.38±0.42 | 624.11±156.81ab | 2.70±2.25b | 95.89±37.72b | 5.37±1.466b | 0.50±0.10b | 27.98±1.69 | 123.62±24.41b |
Table 1 Physicochemical properties of forest soil samples in Mount Huangshan, east China
| 海拔分组 | t/℃ | pH | w(AN)/(mg·kg-1) | w(AP)/(mg·kg-1) | w(AK)/(mg·kg-1) | w(TN)/(g·kg-1) | w(TP)/(g·kg-1) | w(TK)/(g·kg-1) | w(SOM)/(g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低海拔 (L, n=3) | 17.80±0.10a | 4.25±0.28 | 844.67±281.76a | 8.83±3.37ab | 162.33±32.15a | 8.94±1.79a | 0.67±0.06a | 25.53±3.33 | 233.67±70.89a |
| 中低海拔 (ML, n=6) | 15.72±0.78b | 4.89±0.63 | 444.67±150.14b | 2.10±0.91b | 96.67±18.98b | 5.07±1.05b | 0.45±0.08b | 30.75±5.15 | 124.67±12.06b |
| 中海拔 (M, n=6) | 15.25±0.43b | 5.18±0.80 | 539.33±164.18b | 12.42±8.07a | 100.83±40.47b | 5.82±1.27b | 0.69±0.17a | 29.27±3.42 | 148.40±49.35b |
| 高海拔 (H, n=9) | 12.22±0.63c | 4.38±0.42 | 624.11±156.81ab | 2.70±2.25b | 95.89±37.72b | 5.37±1.466b | 0.50±0.10b | 27.98±1.69 | 123.62±24.41b |
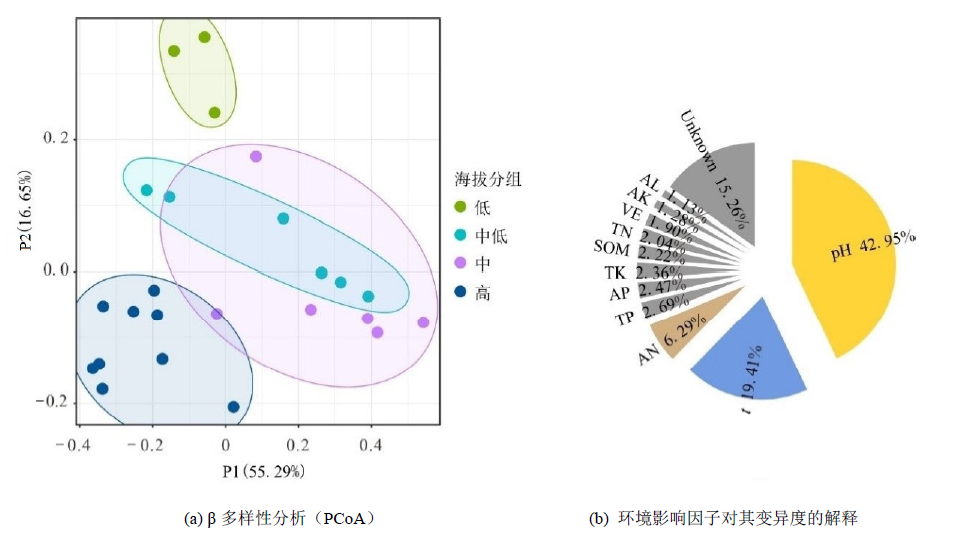
Figure 2 PCoA analysis of diversity for forest soil bacterial communities and variability of diversity explained by environment factors in Mount Huangshan, east China
| [1] |
BARNS S M, CAIN E C, SOMMERVILLE L, et al., 2007. Acidobacteria phylum sequences in uranium-contaminated subsurface sediments greatly expand the known diversity within the phylum[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 73(9): 3113-3116.
PMID |
| [2] |
BLUMENBERG M, KRÜGER M, NAUHAUS K, et al., 2006. Biosynthesis of hopanoids by sulfate-reducing bacteria (genus Desulfovibrio)[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 8(7): 1220-1227.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
BOLYEN E, RIDEOUT J R, DILLON M R, et al., 2019. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 37(8): 852-857.
DOI PMID |
| [4] | BRYANT J A, LAMANNA C, MORLON H, et al., 2008. Microbes on mountainsides: contrasting elevational patterns of bacterial and plant diversity[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105: 11505-11511. |
| [5] |
CALLAHAN B J, MCMURDIE P J, ROSEN M J, et al., 2016. DADA2: high-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data[J]. Nature Methods, 13(7): 581-583.
DOI PMID |
| [6] | CHEN W X, WANG E T, DAVID KUYKENDALL L, 2015. Mesorhizobium[C]//DEVOS P, DEDYSH S, HEDLUND B, et al., Bergey’s manual of systematics of archaea and bacteria. Wiley, in association with Bergey’s Manual Trust: 1-11. |
| [7] | COLIN Y, NICOLITCH O, TURPAULT M-P, et al., 2017. Mineral types and tree species determine the functional and taxonomic structures of forest soil bacterial communities[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 83(5): e02684-16. |
| [8] | DAHAL R H, CHAUDHARY D K, KIM D-U, et al., 2021. Cold-shock gene cspC in the genome of Massilia polaris sp. nov. revealed cold-adaptation[J]. Antonievan Leeuwenhoek, 114(8): 1275-1284. |
| [9] |
DAIMS H, WAGNER M, 2018. Nitrospira[J]. Trends in Microbiology, 26(5): 462-463.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
DEDYSH S N, YILMAZ P, 2018. Refining the taxonomic structure of the phylum Acidobacteria[J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 68(12): 3796-3806.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
FAITH D P, 1992. Conservation evaluation and phylogenetic diversity[J]. Biological Conservation, 61(1): 1-10.
DOI URL |
| [12] | GEORGE D, MALLERY P, 2011. SPSS for windows step by step: a simple study guide and reference, 18.0 update[M]. 11th Edition. Boston: Allyn & Bacon: 143-152. |
| [13] |
HAN D X, WANG N, SUN X, et al., 2018. Biogeographical distribution of bacterial communities in Changbai Mountain, Northeast China[J]. Microbiologyopen, 7(2): e00529.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
HILL T C, WALSH K A, HARRIS J A, et al., 2003. Using ecological diversity measures with bacterial communities[J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 43(1): 1-11.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
HUGHES J B, HELLMANN J J, RICKETTS T H, et al., 2001. Counting the uncountable: statistical approaches to estimating microbial diversity[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 67(10): 4399-4406.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
JANSSEN P H, 2006. Identifying the dominant soil bacterial taxa in libraries of 16S rRNA and 16S rRNA genes[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 72(3): 1719-1728.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
JIN H, YANG X Y, LIU R T, et al., 2018. Bacterial community structure associated with the rhizosphere soils and roots of Stellera chamaejasme L. along a Tibetan elevation gradient[J]. Annals of Microbiology, 68(5): 273-286.
DOI |
| [18] |
KEMBEL S W, 2009. Disentangling niche and neutral influences on community assembly: Assessing the performance of community phylogenetic structure tests[J]. Ecology Letters, 12(9): 949-960.
DOI PMID |
| [19] | KENNEDY C, 2016. Beijerinckia[C]//DEVOS P, DEDYSH S, HEDLUND B, et al., Bergey’s manual of systematics of archaea and bacteria. Hoboken NJ: Wiley: 1-15 |
| [20] |
LARANJO M, ALEXANDRE A, OLIVEIRA S, 2014. Legume growth-promoting rhizobia: an overview on the Mesorhizobium genus[J]. Microbiological Research, 169(1): 2-17.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
LAUBER C L, HAMADY M, KNIGHT R, et al., 2009. Pyrosequencing- based assessment of soil pH as a predictor of soil bacterial community structure at the continental scale[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 75(15): 5111-5120.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
LI G X, XU G R, SHEN C C, et al., 2016. Contrasting elevational diversity patterns for soil bacteria between two ecosystems divided by the treeline[J]. Science China Life Sciences, 59(11): 1177-1186.
PMID |
| [23] | LIN Y T, WHITMAN W B, COLEMAN D C, et al., 2015. Changes of soil bacterial communities in bamboo plantations at different elevations[J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 91(5): fiv033. |
| [24] |
LOUCA S, PARFREY L W, DOEBELI M, 2016. Decoupling function and taxonomy in the global ocean microbiome[J]. Science, 353(6305): 1272-1277.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
LOZUPONE C, HAMADY M, KNIGHT R, 2006. UniFrac-an online tool for comparing microbial community diversity in a phylogenetic context[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 7(1): 1-14.
DOI |
| [26] | MATTEOLI F P, OLIVARES F L, VENANCIO T M, et al., 2020. Herbaspirillum[C]//AMARESAN N, SENTHIL KUMAR M, ANNAPURNA K, et al., Beneficial microbes in agro-ecology. New York: Academic Press: 493-508. |
| [27] |
MCARDLE B H, ANDERSON M J, 2001. Fitting multivariate models to community data: a comment on distance-based redundancy analysis[J]. Ecology, 82(1): 290-297.
DOI URL |
| [28] | MEI W, YU G, LAI J, et al., 2018. The basicTrendline package[EB/OL]. [2021-12-18]. Rpackageversion2.0.3, https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/basicTrendline. |
| [29] | MIRETE S, MORGANTE V, GONZáLEZ-PASTOR J E, 2017. Acidophiles: Diversity and mechanisms of adaptation to acidic environments[C]//STAN-LOTTER H, FENDRIHAN S, Adaption of Microbial Life to Environmental Extremes. Cham: Springer: 27-251. |
| [30] | OKSANEN J, KINDT R, LEGENDRE P, et al., 2007. The vegan package[EB/OL]. [2021-12-18]. R package version 2.5-7, https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/vegan/. |
| [31] |
ORMEÑO-ORRILLO E, MARTÍNEZ-ROMERO E, 2019. A genomotaxonomy view of the Bradyrhizobium genus[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 10: 1334.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
OSBURN E D, MINIAT C F, ELLIOTT K J, et al., 2021. Effects of Rhododendron removal on soil bacterial and fungal communities in southern Appalachian forests[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 496:119398.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
RAHBEK C, 2005. The role of spatial scale and the perception of large-scale species-richness patterns[J]. Ecology letters, 8(2): 224-239.
DOI URL |
| [34] | RIZZATTI G, LOPETUSO L, GIBIINO G, et al., 2017. Proteobacteria: A common factor in human diseases[J]. Biomed Research International, 2017: 1-7. |
| [35] |
SAHM H, ROHMER M, BRINGER-MEYER S, et al., 1993. Biochemistry and physiology of hopanoids in bacteria[J]. Advances in Microbial Physiology, 35: 247-273.
PMID |
| [36] |
SHEN C C, NI Y Y, LIANG W J, et al., 2015. Distinct soil bacterial communities along a small-scale elevational gradient in alpine tundra[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 6: 582.
DOI PMID |
| [37] |
SHEN C C, XIONG J B, ZHANG H Y, et al., 2013. Soil pH drives the spatial distribution of bacterial communities along elevation on Changbai Mountain[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 57: 204-211.
DOI URL |
| [38] | SHEN C C, SHI Y, NI Y Y, et al., 2016. Dramatic increases of soil microbial functional gene diversity at the treeline ecotone of Changbai Mountain[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 7: 12. |
| [39] |
SINGAVARAPU B, BEUGNON R, BRUELHEIDE H, et al., 2022. Tree mycorrhizal type and tree diversity shape the forest soil microbiota[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 24(9): 4236-4255.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
SINGH D, LEE-CRUZ L, KIM W-S, et al., 2014. Strong elevational trends in soil bacterial community composition on Mt. Halla, South Korea[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 68:140-149.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
SINGH D, TAKAHASHI K, KIM M, et al., 2012. A hump-backed trend in bacterial diversity with elevation on Mount Fuji, Japan[J]. Microbial Ecology, 63(2): 429-437.
DOI PMID |
| [42] |
SOLIMAN M, ELDYASTI A, 2018. Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB): opportunities and applications: A review[J]. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/Technology, 17(2): 285-321.
DOI |
| [43] | TER BRAAK C J, SMILAUER P, 2012. Canoco reference manual and user's guide: software for ordination, version 5.0[M]. Ithaca: Microcomputer Power. |
| [44] | TRUJILLO M E, DEDYSH S, DEVOS P, et al., 2015. Massilia[C]// DEVOS P, DEDYSH S, HEDLUND B, et al., Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley: 1-2 |
| [45] | WALTER H, 2012. Vegetation of the earth and ecological systems of the geo-biosphere[M]. Berlin: Springer. |
| [46] |
WANG J, SOININEN J, HE J, et al., 2012. Phylogenetic clustering increases with elevation for microbes[J]. Environmental Microbiology Reports, 4(2): 217-226.
DOI PMID |
| [47] |
WEBB C O, ACKERLY D D, MCPEEK M A, et al., 2002. Phylogenies and community ecology[J]. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 33: 475-505.
DOI URL |
| [48] | WICKHAM H, 2016. The ggplot2 package[EB/OL]. [2021-12-25]. R package version 3.3.5, https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/ggplot2. |
| [49] |
WOOD D E, LU J, LANGMEAD B, 2019. Improved metagenomic analysis with Kraken 2[J]. Genome Biology, 20(1): 1-13.
DOI |
| [50] | XIANG X, WANG H, TIAN W, et al., 2020. Composition and function of bacterial communities of bryophytes and their underlying sediments in the Dajiuhu Peatland,central China[EB/OL]. [2020-12-23]. Journal of Earth Science, https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1788.P.20201222.1817.004.html. |
| [51] |
YANG Y F, GAO Y, WANG S P, et al., 2014. The microbial gene diversity along an elevation gradient of the Tibetan grassland[J]. ISME Journal, 8(2): 430-440.
DOI PMID |
| [52] |
YIN Y L, WANG Y Q, LI S X, et al., 2021. Soil microbial character response to plant community variation after grazing prohibition for 10 years in a Qinghai-Tibetan alpine meadow[J]. Plant and Soil, 458(2): 175-189.
DOI |
| [53] |
ZHANG Y G, CONG J, LU H, et al., 2014. Community structure and elevational diversity patterns of soil Acidobacteria[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 26(8): 1717-1724.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
ZHANG Y G, CONG J, LU H, et al., 2015. Soil bacterial diversity patterns and drivers along an elevational gradient on Shennongjia Mountain, China[J]. Microbial Biotechnology, 8(4): 739-746.
DOI PMID |
| [55] | 巩劼, 陆林, 晋秀龙, 等, 2009. 黄山风景区旅游干扰对植物群落及其土壤性质的影响[J]. 生态学报, 29(5): 2239-2251. |
| GONG J, LU L, JIN X L, et al., 2009. Impacts of tourist disturbance on plant communities and soil properties in Huangshan Mountain scenic area[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 29(5): 2239-2251. | |
| [56] | 国家林业局, 2015. 森林土壤氮的测定: LY/T 1228—2015[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社: 1-9. |
| State forestry administration, 2015. Nitrogen determination methods of forest soils: LY/T 1228—2015[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press: 1-9. | |
| [57] | 国家林业局, 1999. 森林土壤有效磷的测定: LY/T 1233—1999[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社: 92-94. |
| State forestry administration, 1999. Determination of available phosphorus in forest soil: LY/T 1233—1999[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press: 92-94. | |
| [58] | 国家林业局, 2015. 森林土壤钾的测定: LY/T 1234—2015[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社: 1-9. |
| State Forestry Administration, 2015. Potassium determination methods of forest soils: LY/T 1234—2015[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press: 1-9. | |
| [59] | 环境保护部, 2011. 土壤总磷的测定碱熔-钼锑抗分光光度法: HJ 632—2011[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社: 1-4. |
| Ministry of Environmental Protection, 2011. Soil determination of total phosphorus by alkali fusion-Mo-Sb anti spectrophotometric method: HJ 632—2011[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press: 1-4. | |
| [60] | 厉桂香, 马克明, 2018. 土壤微生物多样性海拔格局研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 38(5): 1521-1529. |
| LI G X, MA K M, 2018. Progress in the study of elevational patterns of soil microbial diversity[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(5): 1521-1529. | |
| [61] | 柳春林, 左伟英, 赵增阳, 等, 2012. 鼎湖山不同演替阶段森林土壤细菌多样性[J]. 微生物学报, 52(12): 1489-1496. |
| LIU C L, ZUO W Y, ZHAO Z Y, et al., 2012. Bacterial diversity of different successional stage forest soils in Dinghushan[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 52(12): 1489-1496. | |
| [62] | 马转转, 乔沙沙, 曹苗文, 等, 2018. 环境选择和扩散限制驱动温带森林土壤细菌群落的构建[J]. 应用生态学报, 29(4): 1179-1189. |
|
MA Z Z, QIAO S S, CAO M W, et al., 2018. Environmental selection and dispersal limitation drive the assemblage of bacterial community in temperate forest soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 29(4): 1179-1189.
DOI |
|
| [63] | 满百膺, 向兴, 罗洋, 等, 2021. 黄山典型植被类型土壤真菌群落特征及其影响因素[J]. 菌物学报, 40(10):2735-2751. |
| MAN B Y, XIANG X, LUO Y, et al., 2021. Characteristics and influencing factors of soil fungal community of typical vegetation types in Mount Huangshan, East China[J]. Mycosystema, 40(10): 2735-2751. | |
| [64] | 王振中, 张友梅, 李忠武, 2009. 黄山森林生态系统土壤动物群落结构特征及其多样性[J]. 林业科学, 45(10): 168-173. |
| WANG Z Z, ZHANG Y M, LI Z W, 2009. Structural characteristics and biodiversity of soil animal community in Huangshan forest systems[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 45(10): 168-173. | |
| [65] | 姚兰, 胡立煌, 张焕朝, 等, 2019. 黄山土壤细菌群落和酶活性海拔分布特征[J]. 环境科学, 40(2): 859-868. |
| YAO L, HU L H, ZHANG H C, et al., 2019. Elevational distribution characteristics of soil bacterial community and enzyme activities in Mount Huangshan[J]. Environmental Science, 40(2): 859-868. | |
| [66] | 张舒, 张招崇, 艾羽, 等, 2009. 安徽黄山花岗岩岩石学、矿物学及地球化学研究[J]. 岩石学报, 25(1): 25-38. |
| ZHANG S, ZHANG Z C, AI Y, et al., 2009. The petrology, mineralogy and geochemistry study of the Huangshan granite instrusion in Anhui province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(1): 25-38. | |
| [67] | 中华人民共和国农业部, 2006. 土壤检测第六部分:土壤有机质的测定: NY/T 1121.6—2006[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社: 1-3. |
| Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China, 2006. Soil testing part 6: method for determination of soil organic matter: NY/T 1121.6—2006[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press: 1-3. |
| [1] | FAN Huilin, ZHANG Jiamin, LI Huan, WANG Yanling. Study on the Profile Storage Pattern and Loss Risk of Phosphorus in Sloping Paddy Red Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(2): 283-291. |
| [2] | WANG Lixiao, LIU Jinxian, CHAI Baofeng. Response of Soil Bacterial Community and Nitrogen Cycle during the Natural Recovery of Abandoned Farmland in Subalpine of the North China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(8): 1537-1546. |
| [3] | WANG Lei, WEN Yuanguang, ZHOU Xiaoguo, ZHU Hongguang, SUN Dongjing. Effects of Mixing Eucalyptus urophylla×E. grandis with Castanopsis hystrix on Understory Vegetation and Soil Properties [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(7): 1340-1349. |
| [4] | CHEN Yao, LI Yunhong, SHAO Yingnan, LIU Yulong, LIU Yankun. Study on Species Diversity and Soil Physical and Chemical Characteristics of Broad-leaved Pinus koraiensis Forest [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(4): 679-687. |
| [5] | XIA Kai, DENG Pengfei, MA Ruihao, WANG Fei, WEN Zhengyu, XU Xiaoniu. Changes of Soil Bacterial Community Structure and Diversity from Conversion of Masson Pine Secondary Forest to Slash Pine and Chinese Fir Plantations [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 460-469. |
| [6] | HAN Xin, YUAN Chunyang, LI Jihong, HONG Zongwen, LIU Xuan, DU Ting, LI Han, YOU Chenming, TAN Bo, ZHU Peng, XU Zhenfeng. Effects of Tree Species and Soil Layers on Soil Extractable Nitrogen Content [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(11): 2143-2151. |
| [7] | LI Chunhuan, WANG Pan, HAN Cui, XU Yixin, HUANG Juying. Variation Characteristics of Soil Properties Around A Northwest Desert Coal-mining Region under Sulphur and Nitrogen Deposition [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(1): 170-180. |
| [8] | CHEN Shuangshuang, ZHU Ninghua, ZHOU Guangyi, YUAN Xingming, SHANG Hai, WANG Yixuan. Vegetation and Soil Physical Characteristics of Artificial Arbor Forests under Different Grades of Rocky Desertification [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(1): 52-61. |
| [9] | WANG Rui, SONG Xiangyun, LIU Xinwei. Seasonal Characteristics of Soil Enzymes in Different Vegetations in the Yellow River Delta [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(1): 62-69. |
| [10] | ZHENG Zhiheng, XIONG Kangning, RONG Li, CHI Yongkuan. Effects of Biological Crusts on Soil Properties in Karst Rocky Desertification Areas of Different Levels [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(6): 1202-1212. |
| [11] | LIN Li, DAI Lei, LIN Zebei, WU Jitong, YAN Wei, WANG Zhijie. Plant Diversity and Its Relationship with Soil Physicochemical Properties of Urban Forest Communities in Central Guizhou [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(11): 2130-2141. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
