Ecology and Environment ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (4): 802-813.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.04.019
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
XU Meihua1( ), GU Minghua1, WANG Chengzhen1, LEI Jing2,*(
), GU Minghua1, WANG Chengzhen1, LEI Jing2,*( ), WEI Yanyan1, SHEN Fangke1
), WEI Yanyan1, SHEN Fangke1
Received:2021-11-08
Online:2022-04-18
Published:2022-06-22
Contact:
LEI Jing
徐梅华1( ), 顾明华1, 王骋臻1, 雷静2,*(
), 顾明华1, 王骋臻1, 雷静2,*( ), 韦燕燕1, 沈方科1
), 韦燕燕1, 沈方科1
通讯作者:
雷静
作者简介:徐梅华(1997年生),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为土壤学。E-mail: xu_meihua02@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
XU Meihua, GU Minghua, WANG Chengzhen, LEI Jing, WEI Yanyan, SHEN Fangke. Effect of Manganese on Arsenic Speciation in Soil and Arsenic Migration to Rice[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(4): 802-813.
徐梅华, 顾明华, 王骋臻, 雷静, 韦燕燕, 沈方科. 锰对土壤砷形态转化及水稻吸收砷的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 802-813.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.04.019
| 土壤类型 Soil types | 土壤基本性质 Basic properties of soils | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| w(总铁 Total Fe)/ % | w(总锰 Total Mn)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(总砷 Total As)/ (mg∙kg-1) | pH | w(有机质 Organic matter)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(总氮 Total nitrogen)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(有效磷 Effective phosphorus)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(有效钾 Effective potassium)/ (mg∙kg-1) | |
| 低锰土 Soil with low Mn mass fraction | 6.56 | 582.67 | 57.54 | 6 | 24 | 1.82 | 0.55 | 410.25 |
| 高锰土 Soil with high Mn mass fraction | 6.85 | 4232.66 | 69.75 | 6.6 | 26.4 | 2.03 | 1.14 | 398.47 |
Table 1 Related properties of tested soils
| 土壤类型 Soil types | 土壤基本性质 Basic properties of soils | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| w(总铁 Total Fe)/ % | w(总锰 Total Mn)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(总砷 Total As)/ (mg∙kg-1) | pH | w(有机质 Organic matter)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(总氮 Total nitrogen)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(有效磷 Effective phosphorus)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(有效钾 Effective potassium)/ (mg∙kg-1) | |
| 低锰土 Soil with low Mn mass fraction | 6.56 | 582.67 | 57.54 | 6 | 24 | 1.82 | 0.55 | 410.25 |
| 高锰土 Soil with high Mn mass fraction | 6.85 | 4232.66 | 69.75 | 6.6 | 26.4 | 2.03 | 1.14 | 398.47 |
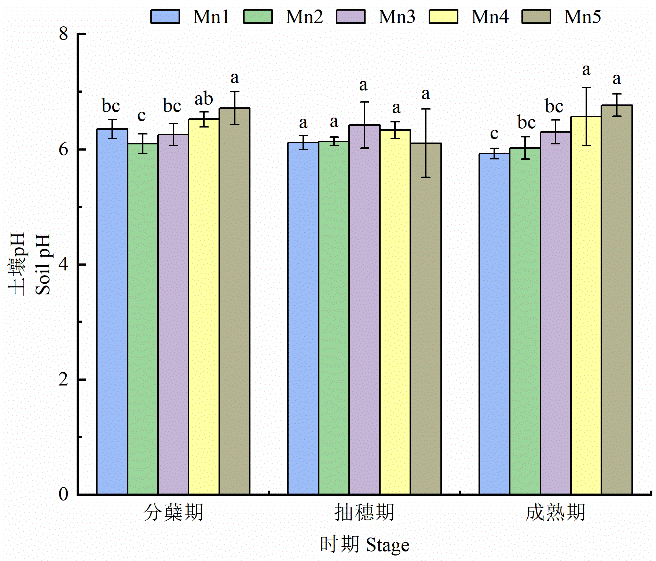
Figure 1 Effects of different treatments on soil pH Different letters indicate significant differences between treatments during the same period (P<0.05), n=4, the same as below
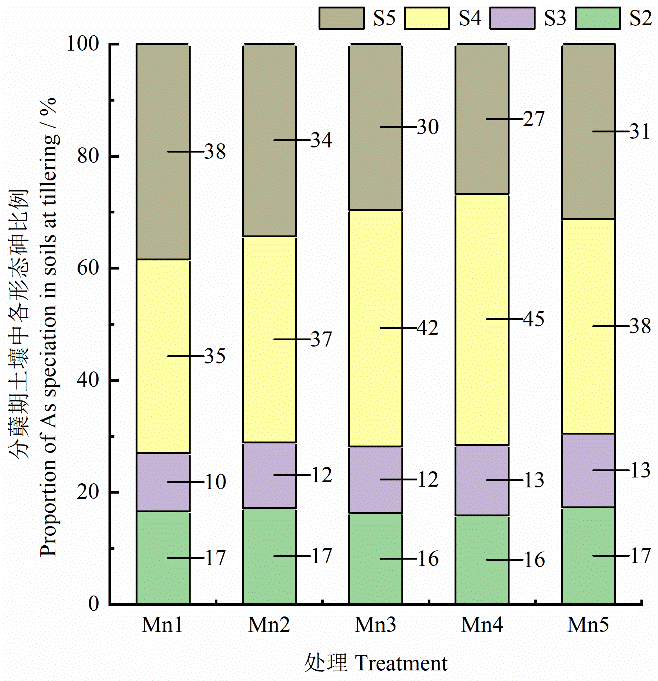
Figure 5 Effects of different treatments on mass fractions of As speciation in soils at tillering stage S2, S3, S4, S5 denote obligate adsorbed As, amorphous Fe oxides bound As, crystalline Fes oxide bound As and residual As, respectively, n=4, The same as below
| 处理 Treatment | 非专性吸附态砷质量分数的比例 Proportion of non-obligate adsorbed As mass fraction in soils/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 分蘖期 Tillering | 抽穗期 Heading | 成熟期 Maturity | |
| Mn1 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.13 |
| Mn2 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.09 |
| Mn3 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.08 |
| Mn4 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.06 |
| Mn5 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.06 |
Table 2 Effects of different treatments on the mass fraction ratio of non-obligate adsorbed As to total As in soils
| 处理 Treatment | 非专性吸附态砷质量分数的比例 Proportion of non-obligate adsorbed As mass fraction in soils/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 分蘖期 Tillering | 抽穗期 Heading | 成熟期 Maturity | |
| Mn1 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.13 |
| Mn2 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.09 |
| Mn3 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.08 |
| Mn4 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.06 |
| Mn5 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.06 |
| 土壤砷形态 Speciation of As in soil | 土壤铁锰氧化物形态 Speciation of Fe oxides and Mn oxides in soils | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 无定形铁 氧化物 Amorphous Fe oxides | 无定形锰 氧化物 Amorphous Mn oxides | 游离铁 氧化物 Free Fe oxides | 游离锰 氧化物 Free Mn oxides | |
| S1 | 0.035 | -0.409** | -0.071 | -0.438** |
| S2 | -0.137 | 0.114 | 0.429** | 0.182 |
| S3 | 0.278* | 0.652** | -0.258* | 0.747** |
| S4 | 0.370** | 0.365** | -0.282* | 0.387** |
| S5 | 0.238 | 0.302* | -0.0816 | 0.272* |
Table 3 Correlation analysis between As speciation and Fe/Mn oxides in soils
| 土壤砷形态 Speciation of As in soil | 土壤铁锰氧化物形态 Speciation of Fe oxides and Mn oxides in soils | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 无定形铁 氧化物 Amorphous Fe oxides | 无定形锰 氧化物 Amorphous Mn oxides | 游离铁 氧化物 Free Fe oxides | 游离锰 氧化物 Free Mn oxides | |
| S1 | 0.035 | -0.409** | -0.071 | -0.438** |
| S2 | -0.137 | 0.114 | 0.429** | 0.182 |
| S3 | 0.278* | 0.652** | -0.258* | 0.747** |
| S4 | 0.370** | 0.365** | -0.282* | 0.387** |
| S5 | 0.238 | 0.302* | -0.0816 | 0.272* |
| 孔隙水离子 Ion in pore water | 土壤铁、锰、砷形态和Eh Speciation of Fe, Mn, As in soils and soil Eh | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | 无定形铁 Amorphous Fe | 无定形锰 Amorphous Mn | 游离铁 Free Fe | 游离锰 Free Mn | Eh | |
| As(III) | 0.052 | 0.331** | -0.245 | -0.522** | 0.252 | -0.476** | -0.48** | 0.097 | -0.447** | -0.759** |
Table 4 Correlation analysis between As (III) concentration in soil pore water and As speciation of in soils, Fe/Mn oxides mass fraction, Eh value
| 孔隙水离子 Ion in pore water | 土壤铁、锰、砷形态和Eh Speciation of Fe, Mn, As in soils and soil Eh | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | 无定形铁 Amorphous Fe | 无定形锰 Amorphous Mn | 游离铁 Free Fe | 游离锰 Free Mn | Eh | |
| As(III) | 0.052 | 0.331** | -0.245 | -0.522** | 0.252 | -0.476** | -0.48** | 0.097 | -0.447** | -0.759** |
| 砷形态 As speciation | 水稻各部位的总砷质量分数 Total As mass fraction in different parts of rice | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 茎 Stems | 根 Roots | 上部叶 Upper leaves | 下部叶 Lower leaves | 籽粒 Grains | |
| S1 | 0.582** | 0.574** | 0.809** | 0.798** | 0.745** |
| S2 | -0.237 | -0.243 | -0.299* | -0.329* | -0.032 |
| S3 | -0.413** | -0.616** | -0.597** | -0.721** | -0.519* |
| S4 | 0.182 | -0.117 | 0.151 | -0.076 | 0.191 |
| S5 | -0.174 | -0.137 | -0.241 | -0.069 | -0.683** |
Table 5 Correlation analysis between As mass fraction in different parts of rice and As mass fraction in soils
| 砷形态 As speciation | 水稻各部位的总砷质量分数 Total As mass fraction in different parts of rice | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 茎 Stems | 根 Roots | 上部叶 Upper leaves | 下部叶 Lower leaves | 籽粒 Grains | |
| S1 | 0.582** | 0.574** | 0.809** | 0.798** | 0.745** |
| S2 | -0.237 | -0.243 | -0.299* | -0.329* | -0.032 |
| S3 | -0.413** | -0.616** | -0.597** | -0.721** | -0.519* |
| S4 | 0.182 | -0.117 | 0.151 | -0.076 | 0.191 |
| S5 | -0.174 | -0.137 | -0.241 | -0.069 | -0.683** |
| [1] |
ABBASI S, LAMB D T, KADER M, et al., 2021. The influence of long-term ageing on arsenic ecotoxicity in soil[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124819.
DOI |
| [2] |
CAO Z Z, PAN J Y, YANG Y J, et al., 2020. Water management affects arsenic uptake and translocation by regulating arsenic bioavailability, transporter expression and thiol metabolism in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, DOI: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020. 111208.
DOI |
| [3] |
CHEN H, LEI J, TONG H, et al., 2019. Effects of Mn (II) on the oxidation of Fe in soils and the uptake of cadmium by rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 230(8): 1-13.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
CHIU V Q, HERING J G, 2000. Arsenic adsorption and oxidation at manganite surfaces. 1. method for simultaneous determination of adsorbed and dissolved arsenic species[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 34(10): 2029-2034.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
DIXIT S, HERING J G, 2003. Comparison of arsenic(V) and arsenic(III) sorption onto iron oxide minerals: implications for arsenic mobility[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 37(18): 4182-4189.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
DONG G W, HAN R W, PAN Y J, et al., 2021. Role of MnO2 in controlling iron and arsenic mobilization from illuminated flooded arsenic-enriched soils[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020. 123362.
DOI |
| [7] |
GEBEL T, 2000. Confounding variables in the environmental toxicology of arsenic[J]. Toxicology, 144(1-3): 155-162.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
HIMENO S, SUMI D, FUJISHIRO H, 2019. Toxicometallomics of cadmium, manganese and arsenic with special reference to the roles of metal transporters[J]. Toxicological Research, 35(4): 311-317.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
HOU J T, LUO J L, SONG S X, et al., 2017. The remarkable effect of the coexisting arsenite and arsenate species ratios on arsenic removal by manganese oxide[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 315: 159-166.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
KEIMOWITZ A R, MAILLOUX B J, WOVKULICH K, et al., 2017. Manganese redox buffering limits arsenic release from contaminated sediments, Union Lake, New Jersey[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 77: 24-30.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
LI J H, DONG F, LU Y, et al., 2014. Mechanisms controlling arsenic uptake in rice grown in mining impacted regions in south China[J]. PloS One, 9(9): e108300.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
LIN L N, SONG Z G, LIU X W, et al., 2019. Arsenic volatilization in flooded paddy soil by the addition of Fe-Mn-modified biochar composites[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 674: 327-335.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
LIU H J, ZHANG J L, CHRISTIE P, et al., 2008. Influence of iron plaque on uptake and accumulation of Cd by rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings grown in soil[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 394(2-3): 361-368.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
MA L, CAI D M, TU S X, 2020. Arsenite simultaneous sorption and oxidation by natural ferruginous manganese ores with various ratios of Mn/Fe[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123040.
DOI |
| [15] |
MAGUFFIN S C, ABU-ALI L, TAPPERO R V, et al., 2020. Influence of manganese abundances on iron and arsenic solubility in rice paddy soils[J]. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 276: 50-69.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
MATSUMOTO S, KASUGA J, MAKINO T, et al., 2016. Evaluation of the effects of application of iron materials on the accumulation and speciation of arsenic in rice grain grown on uncontaminated soil with relatively high levels of arsenic[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 125: 42-51.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
NIAZI N K, SINGH B, SHAH P. 2011. Arsenic Speciation and Phytoavailability in Contaminated Soils Using a Sequential Extraction Procedure and XANES Spectroscopy[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 45(17): 7135-7142.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
QIAN Z Y, XUE S G, CUI M Q, et al., 2021. Arsenic availability and transportation in soil-rice system affected by iron-modified biochar[J]. Journal of Central South University, 28(6): 1901-1918.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
RAHMAN M S, CLARK M W, YEE L H, et al., 2017. Arsenic solid-phase speciation and reversible binding in long-term contaminated soils[J]. Chemosphere, 168: 1324-1336.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
SARWAR T, KHAN S, MUHAMMAD S, et al., 2021. Arsenic speciation, mechanisms, and factors affecting rice uptake and potential human health risk: A systematic review[J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation, DOI: 10.1016/j.eti.2021.101392.
DOI |
| [21] |
ULTRA V U J E, NAKAYAMA A, TANAKA S, et al., 2009. Potential for the alleviation of arsenic toxicity in paddy rice using amorphous iron-(hydr)oxide amendments[J]. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition (Tokyo), 55(1): 160-169.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
WANG J, WANG P M, GU Y, et al., 2019. Iron-Manganese (Oxyhydro) oxides, rather than oxidation of sulfides, determine mobilization of Cd during soil drainage in paddy soil systems[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 53(5): 2500-2508.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
WENZEL W W, KIRCHBAUMER N, PROHASKA T, et al., 2001. Arsenic fractionation in soils using an improved sequential extraction procedure[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 436(2): 309-323.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
XU X W, CHEN C, WANG P, et al., 2017. Control of arsenic mobilization in paddy soils by manganese and iron oxides[J]. Environmental Pollution, 231(Part 1): 37-47.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
YANG H, HAN M X, JIANG P P, 2021. Research Progress on the treatment of arsenic pollution by manganese oxide[J]. E3S Web of Conferences, DOI: 10.1051/e3sconf/202126104032.
DOI |
| [26] |
ZANG X Y, ZHOU Z G, ZHANG T L, et al., 2021. Aging of exogenous arsenic in flooded paddy soils: Characteristics and predictive models[J]. Environmental Pollution, DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116561.
DOI |
| [27] |
ZHANG G S, LIU F D, LIU H J, et al., 2014. Respective role of Fe and Mn oxide contents for arsenic sorption in iron and manganese binary oxide: An X-ray absorption spectroscopy investigation[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 48(17): 10316-10322.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
ZHANG L Y, XIAO J, JI J F, et al., 2021. Arsenate Adsorption on Different Fractions of Iron Oxides in the Paddy Soil from the Karst Region of China[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 106(1): 126-133.
DOI URL |
| [29] | 鲍士旦, 2013. 土壤农化分析[M]. 第3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社: 100-115. |
| BAO S D, 2013. Soil agrochemical analysis[M]. Third Edition. Beijing: China Agricultural Publishing House: 100-115. | |
| [30] | 陈家坊, 何群, 邵宗臣, 1983. 土壤中氧化铁的活化过程的探讨[J]. 土壤学报, 20(4): 387-393. |
| CHEN J F, HE Q, SHAO Z C, 1983. Discussion on the activation process of iron oxide in soil[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 20(4): 387-393. | |
| [31] | 陈耀祖, 汪宜敏, 李明, 等, 2019. 老化对Cd-As污染土壤上金属形态及其生物效应的影响[J]. 环境科技, 32(6): 35-40. |
| CHEN Y Z, WANG Y M, LI M, et al., 2019. Effect of Aging on Metal Morphology and Biological Effects of Cd-As Contaminated Soil[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 32(6): 35-40. | |
| [32] | 杜艳艳, 王欣, 谢伟城, 等, 2017. 负载铁生物炭对土壤-水稻系统As溶出特性与生物有效性的影响与机理解析[J]. 环境科学学报, 37(8): 3158-3168. |
| DU Y Y, WANG X, XIE W C, et al., 2017. Effects and mechanisms of Fe-impregnated biochar on arsenic solubility and bioavailability in soil-rice system[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 37(8): 3158-3168. | |
| [33] | 顾明华, 李志明, 陈宏, 等, 2020. 施锰对土壤锰氧化物形成及镉固定的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(2): 360-368. |
| GU M H, LI Z M, CHEN H, et al., 2020. Effects of manganese application on the formation of manganese oxides and cadmium fixation in soil[J]. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 29(2): 360-368. | |
| [34] | 何群, 陈家坊, 许祖诒, 1981. 土壤中氧化铁的转化及其对土壤结构的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 18(4): 326-334. |
| HE Q, CHEN J F, XU Z Y, 1981. Transformation of iron oxide in soil and its effect on soil structure[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 18(4): 326-334. | |
| [35] | 黄永东, 杜应琼, 陈永坚, 等, 2020. 水淹条件下锰改性生物炭对水稻砷吸收及形态分布的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(11): 2288-2295. |
| HUANG Y D, DU Y Q, CHEN Y J, et al., 2020. Effects of manganese-modified biochar on arsenic uptake and its species distribution in rice under flooding[J]. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 29(11): 2288-2295. | |
| [36] | 李志明, 丁氏祝, 奇奇格, 等, 2020. 施用铁锰对土壤砷形态及水稻吸收砷的影响[J]. 西南农业学报, 33(8): 1722-1728. |
| LI Z M, DING S Z, QI Q G, et al., 2020. Effects of Fe and Mn application on arsenic speciation in soil and arsenic uptake by rice[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 33(8): 1722-1728. | |
| [37] | 鲁如坤, 1999. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社: 20-347. |
| LU R K, 1999. Soil agrochemical analysis method[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: 20-347. | |
| [38] | 律兆, 松徐琪, 1995. 中国白浆土研究Ⅱ白浆土机械组成特点及元素地球化学分异特征[J]. 土壤学报, 32(1): 274-288. |
| LU Z, SONG X Q, 1995. Study on Chinese Albic Soil Ⅱ Characteristics of mechanical composition and element geochemical differentiation of albic soil[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 32(1): 274-288. | |
| [39] | 毛凌晨, 叶华, 2018. 氧化还原电位对土壤中重金属环境行为的影响研究进展[J]. 环境科学研究, 31(10): 1669-1676. |
| MAO L C, YE H, 2018. Research progress on the effect of redox potential on the environmental behavior of heavy metals in soil[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 31(10): 1669-1676. | |
| [40] | 王欣, 钟松雄, 陈志良, 等, 2018. 厌氧条件水稻土铁对砷释放的影响[J]. 环境科学, 39(6): 2912-2918. |
|
WANG X, ZHONG C X, CHEN Z L, et al., 2018. Effects of anaerobic conditions on arsenic release from paddy soil iron[J]. Environmental Science, 39(6): 2912-2918.
DOI URL |
|
| [41] | 薛培英, 刘文菊, 刘会玲, 等, 2010. 中轻度砷污染土壤-水稻体系中砷迁移行为研究[J]. 土壤学报, 47(5): 872-879. |
| XUE P Y, LIU W J, LIU H L, et al., 2010. Study on arsenic migration behavior in soil rice system with moderate and mild arsenic pollution[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 47(5): 872-879. | |
| [42] | 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 2015. 食品中总砷及无机砷的测定: GB 5009.11—2014 [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China, 2015. Determination of total arsenic and abio-arsenic in foods: GB 5009.11—2014 [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China. | |
| [43] | 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 2008. 土壤中总砷的测定: GB/T 22105.2—2008[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, 2008. Analysis of total arsenic contents in soils: GB/T 22105.2—2008[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China. |
| [1] | HUANG Yingmei, ZHONG Songxiong, ZHU Yiwen, WANG Xiangqin, LI Fangbai. Effects and Mechanism of Element Sulfur Inhibiting Methylmercury Accumulation in Rice Plants [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(6): 1115-1122. |
| [2] | DU Dandan, GAO Ruizhong, FANG Lijing, XIE Longmei. Spatial Variation of Soil Heavy Metals and Their Responses to Physicochemical Factors of Salt Lake Basin in Arid Area [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(6): 1123-1132. |
| [3] | LI Chuanfu, ZHU Taochuan, MING Yufei, YANG Yuxuan, GAO Shu, DONG Zhi, LI Yongqiang, JIAO Shuying. Effect of Organic Fertilizer and Desulphurized Gypsum on Soil Aggregates and Organic Carbon and Its Fractions Contents in the Saline-alkali Soil of the Yellow River Delta [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 878-888. |
| [4] | CHEN Junfang, WU Xian, LIU Xiaolin, LIU Juan, YANG Jiarong, LIU Yu. Shaping Characteristics of Elemental Stoichiometry on Microbial Diversity under Different Soil Water Contents [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 898-909. |
| [5] | DONG Zhijin, ZHANG Chengchun, ZHAN Xiuli, ZHANG Weifu. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Soil Nutrients of Biological Soil Crusts and Their Underlying Soil of Sandy Land in the East of Yellow River in Ningxia [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 910-919. |
| [6] | YANG Kai, YANG Jingrui, CAO Peipei, LÜ Chunhua, SUN Wenjuan, YU Lingfei, DENG Xi. Dynamic Response of Rice Plant Height, Tillering and SPAD under Elevated CO2 Concentration and Their Simulation [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 933-942. |
| [7] | ZHOU Qinyuan, DONG Quanmin, Wang Fangcao, LIU Yuzhen, FENG Bin, YANG Xiaoxia, YU Yang, ZHANG Chunping, CAO Quan, LIU Wenting. Effects of Mixed Grazing on Aggregates and Organic Carbon in Rhizosphere Soil of Stellera chamaejasme in Alpine Grassland [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 660-667. |
| [8] | PAN Yuling, QU Xiangning, LI Qing, WANG Lei, WANG Xiaoping, TAN Peng, CUI Geng, AN Yu, TONG Shouzheng. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Soil Physicochemical Factors and Their Response to Microtopography in a Typical Beach Wetland of the Yellow River in Ningxia [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 668-677. |
| [9] | ZHAO Weibin, TANG Li, WANG Song, LIU Lingling, WANG Shufeng, XIAO Jiang, CHEN Guangcai. Improvement Effect of Two Biochars on Coastal Saline-Alkaline Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 678-686. |
| [10] | FENG Shuna, LÜ Jialong, HE Hailong. Effect of KI Leaching on the Hg (Ⅱ) Removal of Loess Soil and the Physicochemical Properties of the Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 776-783. |
| [11] | CHEN Minyi, ZHU Hanghai, SHE Weiduo, YIN Guangcai, HUANG Zuzhao, YANG Qiaoling. Health Risk Assessment and Source Apportionment of Soil Heavy Metals at A Legacy Shipyard Site in Pearl River Delta [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 794-804. |
| [12] | ZHANG Lin, QI Shi, ZHOU Piao, WU Bingchen, ZHANG Dai, ZHANG Yan. Study on Influencing Factors of Soil Organic Carbon Content in Mixed Broad-leaved and Coniferous Forests Land in Beijing Mountainous Areas [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 450-458. |
| [13] | QIN Hao, LI Mengai, GAO Jin, CHEN Kailong, ZHANG Yinbo, ZHANG Feng. Composition and Diversity of Soil Bacterial Communities in Shrub at Different Altitudes in Luya Mountain [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 459-468. |
| [14] | TANG Haiming, SHI Lihong, WEN Li, CHENG Kaikai, LI Chao, LONG Zedong, XIAO Zhiwu, LI Weiyan, GUO Yong. Effects of Different Long-term Fertilizer Managements on Rhizosphere Soil Nitrogen in the Double-cropping Rice Field [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 492-499. |
| [15] | YANG Yu, DENG Renjian, LONG Pei, HUANG Zhongjie, Ren Bozhi, WANG Zhenghua. Isolation and Identification of Arsenic-oxidizing Bacterium Pseudomonas sp. AO-1 and Its Oxidation Properties for As(Ⅲ) [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 619-626. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
