Ecology and Environment ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (1): 44-51.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.01.006
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Shulan1,2( ), HAN Yong1,2, YANG Pan1, YAN Yuying1, LIU Zhaoxue1, LI Zhuoyao1
), HAN Yong1,2, YANG Pan1, YAN Yuying1, LIU Zhaoxue1, LI Zhuoyao1
Received:2021-08-02
Online:2022-01-18
Published:2022-03-10
张淑兰1,2( ), 韩勇1,2, 杨盼1, 闫育盈1, 刘昭雪1, 李卓瑶1
), 韩勇1,2, 杨盼1, 闫育盈1, 刘昭雪1, 李卓瑶1
作者简介:张淑兰(1980年生),女,副教授,博士,研究方向为生态水文过程与模型应用研究。E-mail: zhangshulan1980@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
ZHANG Shulan, HAN Yong, YANG Pan, YAN Yuying, LIU Zhaoxue, LI Zhuoyao. Evaluation of Hydrological Function of Litter of Quercus Acuvarius at Different Ages in the Upper Reaches of Han River[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(1): 44-51.
张淑兰, 韩勇, 杨盼, 闫育盈, 刘昭雪, 李卓瑶. 汉江上游不同林龄麻栎林枯落物的水文功能评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 44-51.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.01.006
| 样地 Sample plot | 平均林龄 Average forest age/a | 海拔 Altitude/m | 坡向 Aspect | 林分起源 Stand origin | 平均胸径 Average diameter at breast height/cm | 平均树高 ATH/m | 郁闭度 Canopy density | 林分密度 Stand density/ (trees∙hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 15 | 575 | 阳坡 | 人工次生林 | 3.4±1.5 | 2.5±0.53 | 0.85 | 1.6×105 |
| B | 25 | 576 | 半阴半阳 | 人工次生林 | 15.5±3.4 | 11.8±1.2 | 0.75 | 7.8×104 |
| C | 33 | 658 | 阳坡 | 人工次生林 | 17.2±4.5 | 12.6±1.3 | 0.75 | 1.0×104 |
Table 1 General situation of Quercus acutum forest plot at different ages
| 样地 Sample plot | 平均林龄 Average forest age/a | 海拔 Altitude/m | 坡向 Aspect | 林分起源 Stand origin | 平均胸径 Average diameter at breast height/cm | 平均树高 ATH/m | 郁闭度 Canopy density | 林分密度 Stand density/ (trees∙hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 15 | 575 | 阳坡 | 人工次生林 | 3.4±1.5 | 2.5±0.53 | 0.85 | 1.6×105 |
| B | 25 | 576 | 半阴半阳 | 人工次生林 | 15.5±3.4 | 11.8±1.2 | 0.75 | 7.8×104 |
| C | 33 | 658 | 阳坡 | 人工次生林 | 17.2±4.5 | 12.6±1.3 | 0.75 | 1.0×104 |
| 样地 Sample plot | 平均林龄 Average forest age/a | 枯落物层厚度 Litter layer thickness/cm | 枯落物层 总厚度 Total thickness of litter layer/ cm | 蓄积量 Volume of litter/(t∙hm-2) | 总蓄积量 Total volume of litter/ (t∙hm-2) | 占蓄积量比例 Proportion of the volume/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 未分解层 Undecomposed layer | 半分解层 Semi-decomposed layer | 未分解层Undecomposed layer | 半分解层Semi-decomposed layer | 未分解层Undecomposed layer | 半分解层Semi-decomposed layer | ||||
| A | 15 | 1.20 | 1.80 | 3.00 | 3.63 | 10.20 | 13.83 | 26.25 | 73.75 |
| B | 25 | 2.40 | 1.40 | 3.80 | 6.04 | 7.72 | 13.76 | 43.90 | 56.10 |
| C | 33 | 3.60 | 1.20 | 4.80 | 9.94 | 4.45 | 14.39 | 69.08 | 30.92 |
Table 2 Litter volume and composition of Quercus acutum forest at different forest ages
| 样地 Sample plot | 平均林龄 Average forest age/a | 枯落物层厚度 Litter layer thickness/cm | 枯落物层 总厚度 Total thickness of litter layer/ cm | 蓄积量 Volume of litter/(t∙hm-2) | 总蓄积量 Total volume of litter/ (t∙hm-2) | 占蓄积量比例 Proportion of the volume/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 未分解层 Undecomposed layer | 半分解层 Semi-decomposed layer | 未分解层Undecomposed layer | 半分解层Semi-decomposed layer | 未分解层Undecomposed layer | 半分解层Semi-decomposed layer | ||||
| A | 15 | 1.20 | 1.80 | 3.00 | 3.63 | 10.20 | 13.83 | 26.25 | 73.75 |
| B | 25 | 2.40 | 1.40 | 3.80 | 6.04 | 7.72 | 13.76 | 43.90 | 56.10 |
| C | 33 | 3.60 | 1.20 | 4.80 | 9.94 | 4.45 | 14.39 | 69.08 | 30.92 |
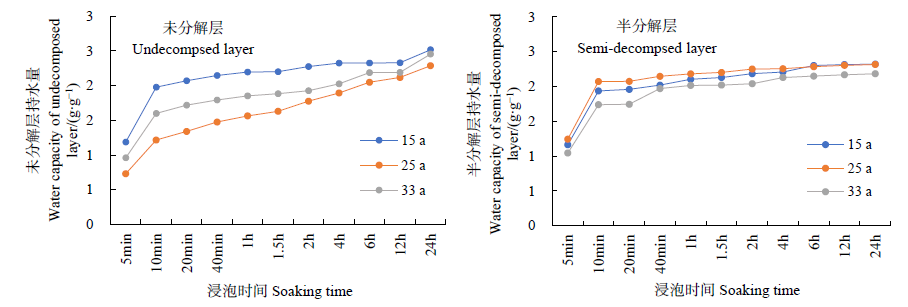
Figure 1 Change of water capacity of litter in undecomposed layer and semi-decomposed layer with soaking time in Quercus acutissima forest at different ages
| 林龄 Forest age/a | 未分解层 Undecomposed layer | 半分解层 Semi-decomposed layer | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 关系式 Relation | R2 | 关系式Relation | R2 | ||
| 15 | s=0.4317ln(t)+1.4537 | 0.8549 | s=0.3559ln(t)+1.5538 | 0.7646 | |
| 25 | s=0.4991ln(t)+1.0778 | 0.9204 | s=0.4085ln(t)+1.4072 | 0.8664 | |
| 33 | s=0.5925ln(t)+0.7004 | 0.9606 | s=0.4196ln(t)+1.2589 | 0.8922 | |
Table 3 Relation between water holding capacity and soaking time of litter of Quercus acutum forest at different ages
| 林龄 Forest age/a | 未分解层 Undecomposed layer | 半分解层 Semi-decomposed layer | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 关系式 Relation | R2 | 关系式Relation | R2 | ||
| 15 | s=0.4317ln(t)+1.4537 | 0.8549 | s=0.3559ln(t)+1.5538 | 0.7646 | |
| 25 | s=0.4991ln(t)+1.0778 | 0.9204 | s=0.4085ln(t)+1.4072 | 0.8664 | |
| 33 | s=0.5925ln(t)+0.7004 | 0.9606 | s=0.4196ln(t)+1.2589 | 0.8922 | |
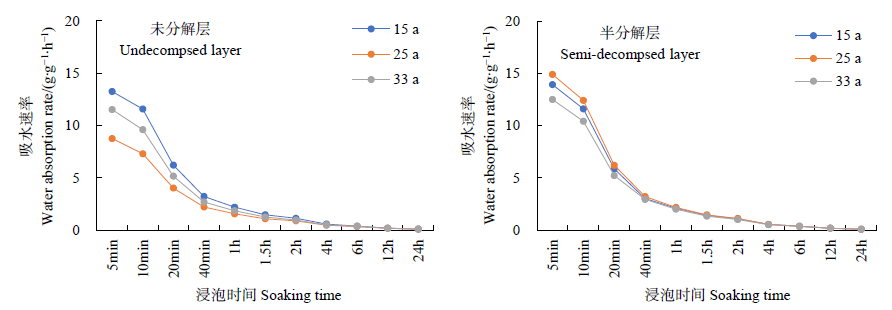
Figure 2 Change of water absorption rate of litter in undecomposed layer and semi-decomposed layer with soaking time in Quercus acutissima forest at different ages
| 林龄 Forest age/a | 未分解层 Undecomposed layer | 半分解层 Semi-decomposed layer | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 关系式 Relation | R2 | 关系式 Relation | R2 | ||
| 15 | v=2.0379t -0.912 | 0.9938 | v=1.9616t -0.914 | 0.9942 | |
| 25 | v=1.4775t -0.83 | 0.9941 | v=2.0388t -0.929 | 0.9941 | |
| 33 | v=1.7446t -0.878 | 0.9943 | v=1.8257t -0.905 | 0.9933 | |
Table 4 The relation between the water holding rate and the soaking time of litters of Quercus acutissima forest at different ages
| 林龄 Forest age/a | 未分解层 Undecomposed layer | 半分解层 Semi-decomposed layer | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 关系式 Relation | R2 | 关系式 Relation | R2 | ||
| 15 | v=2.0379t -0.912 | 0.9938 | v=1.9616t -0.914 | 0.9942 | |
| 25 | v=1.4775t -0.83 | 0.9941 | v=2.0388t -0.929 | 0.9941 | |
| 33 | v=1.7446t -0.878 | 0.9943 | v=1.8257t -0.905 | 0.9933 | |
| 林龄 Forest age/ a | 枯落物层 Litter layer | 自然持水率 Natural water holdup/ % | 自然持水量 Natural water capacity/ (t∙hm-2) | 最大持水率 Maximum water holdup/% | 最大持水量 Maximum water-holding capacity/(t∙hm-2) | 最大持水深度 Maximum water holding depth/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 未分解层 | 65.84 | 2.39 | 251.67 | 9.14 | 0.9 |
| 半分解层 | 90.19 | 9.20 | 232.12 | 23.68 | 2.4 | |
| 总枯落物层 | 78.02 | 11.59 | 241.89 | 32.81 | 3.3 | |
| 25 | 未分解层 | 46.92 | 2.83 | 260.04 | 15.71 | 1.6 |
| 半分解层 | 50.28 | 3.88 | 231.68 | 17.89 | 1.8 | |
| 总枯落物层 | 48.60 | 6.72 | 245.86 | 33.59 | 3.4 | |
| 33 | 未分解层 | 50.60 | 5.03 | 245.37 | 24.39 | 2.4 |
| 半分解层 | 68.48 | 3.05 | 218.31 | 9.71 | 1.0 | |
| 总枯落物层 | 59.54 | 8.08 | 231.84 | 34.10 | 3.4 |
Table 5 Natural water holding capacity and maximum water holding capacity of litter in Quercus acutum forest at different ages
| 林龄 Forest age/ a | 枯落物层 Litter layer | 自然持水率 Natural water holdup/ % | 自然持水量 Natural water capacity/ (t∙hm-2) | 最大持水率 Maximum water holdup/% | 最大持水量 Maximum water-holding capacity/(t∙hm-2) | 最大持水深度 Maximum water holding depth/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 未分解层 | 65.84 | 2.39 | 251.67 | 9.14 | 0.9 |
| 半分解层 | 90.19 | 9.20 | 232.12 | 23.68 | 2.4 | |
| 总枯落物层 | 78.02 | 11.59 | 241.89 | 32.81 | 3.3 | |
| 25 | 未分解层 | 46.92 | 2.83 | 260.04 | 15.71 | 1.6 |
| 半分解层 | 50.28 | 3.88 | 231.68 | 17.89 | 1.8 | |
| 总枯落物层 | 48.60 | 6.72 | 245.86 | 33.59 | 3.4 | |
| 33 | 未分解层 | 50.60 | 5.03 | 245.37 | 24.39 | 2.4 |
| 半分解层 | 68.48 | 3.05 | 218.31 | 9.71 | 1.0 | |
| 总枯落物层 | 59.54 | 8.08 | 231.84 | 34.10 | 3.4 |
| 林龄 Forest age/ a | 枯落物层 Litter layer | 最大拦蓄率 Maximum retention rate/% | 最大拦蓄量 Maximum storage capacity/(t∙hm-2) | 有效拦蓄率 Effective retention rate/% | 有效拦蓄量 Effective storage capacity/(t∙hm-2) | 有效拦蓄水深 Effective water depth retention/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 未分解层 | 185.83 | 6.75 | 157.95 | 3.34 | 0.3 |
| 半分解层 | 141.93 | 14.48 | 120.64 | 3.11 | 0.3 | |
| 总枯落物层 | 163.88 | 21.22 | 139.29 | 6.45 | 0.6 | |
| 25 | 未分解层 | 181.80 | 10.98 | 154.53 | 6.50 | 0.6 |
| 半分解层 | 181.40 | 14.00 | 154.19 | 8.02 | 0.8 | |
| 总枯落物层 | 181.60 | 24.98 | 154.36 | 14.52 | 1.5 | |
| 33 | 未分解层 | 194.77 | 19.36 | 165.55 | 11.43 | 1.1 |
| 半分解层 | 149.83 | 6.67 | 127.35 | 2.62 | 0.3 | |
| 总枯落物层 | 172.30 | 26.03 | 146.45 | 14.05 | 1.4 |
Table 6 The maximum and effective storage of litter in Quercus acuvarius stands at different ages
| 林龄 Forest age/ a | 枯落物层 Litter layer | 最大拦蓄率 Maximum retention rate/% | 最大拦蓄量 Maximum storage capacity/(t∙hm-2) | 有效拦蓄率 Effective retention rate/% | 有效拦蓄量 Effective storage capacity/(t∙hm-2) | 有效拦蓄水深 Effective water depth retention/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 未分解层 | 185.83 | 6.75 | 157.95 | 3.34 | 0.3 |
| 半分解层 | 141.93 | 14.48 | 120.64 | 3.11 | 0.3 | |
| 总枯落物层 | 163.88 | 21.22 | 139.29 | 6.45 | 0.6 | |
| 25 | 未分解层 | 181.80 | 10.98 | 154.53 | 6.50 | 0.6 |
| 半分解层 | 181.40 | 14.00 | 154.19 | 8.02 | 0.8 | |
| 总枯落物层 | 181.60 | 24.98 | 154.36 | 14.52 | 1.5 | |
| 33 | 未分解层 | 194.77 | 19.36 | 165.55 | 11.43 | 1.1 |
| 半分解层 | 149.83 | 6.67 | 127.35 | 2.62 | 0.3 | |
| 总枯落物层 | 172.30 | 26.03 | 146.45 | 14.05 | 1.4 |
| 林龄 Forest age/a | 枯落物厚度 Thickness of litter | 枯落物蓄积量 Volume of litter | 最大持水率 Maximum water holdup | 最大持水量 Maximum water holding capacity | 有效拦蓄率Effective retention rate | 有效拦蓄量 Effective storage capacity | 综合评价 Comprehensive assessment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 4.71 | 5.83 | 6.08 | 5.86 | 5.57 | 2.30 | 30.35 |
| 25 | 5.50 | 5.80 | 5.79 | 5.66 | 6.17 | 5.18 | 34.10 |
| 33 | 6.59 | 6.07 | 5.83 | 6.09 | 5.86 | 5.01 | 35.45 |
Table 7 Comprehensive evaluation scores of hydrological functions of litter in Quercus acutum forest at different ages
| 林龄 Forest age/a | 枯落物厚度 Thickness of litter | 枯落物蓄积量 Volume of litter | 最大持水率 Maximum water holdup | 最大持水量 Maximum water holding capacity | 有效拦蓄率Effective retention rate | 有效拦蓄量 Effective storage capacity | 综合评价 Comprehensive assessment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 4.71 | 5.83 | 6.08 | 5.86 | 5.57 | 2.30 | 30.35 |
| 25 | 5.50 | 5.80 | 5.79 | 5.66 | 6.17 | 5.18 | 34.10 |
| 33 | 6.59 | 6.07 | 5.83 | 6.09 | 5.86 | 5.01 | 35.45 |
| [1] |
RAO L Y, ZHU J Z, 2007. Hydrological effects of forest litter and soil in the Simianshan Mountains in Chonging, China[J]. Frontiers of Forestry in China, 2(2): 157-162.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
SUN J M, YU X X, WANG H N, et al., 2018. Effects of forest structure on hydrological processes in China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 561: 187-199.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
XIA L, SONG X Y, FU N, et al., 2019. Effects of forest litter cover on hydrological response of hillslopes in the Loess Plateau of China[J]. Catena, DOI: 10.1016/j.catena.2019.104076.
DOI |
| [4] | 陈进, 徐明, 邹晓, 等, 2018. 贵阳市不同林龄马尾松林凋落物储量及持水特性[J]. 水土保持研究, 25(6): 146-151. |
| CHEN J, XU M, ZOU X, et al., 2018 Litter layer reserve and water holding capacity of Pinus massoniana in different successional stages in Guiyang[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 25(6): 146-151. | |
| [5] | 高迪, 郭建斌, 王彦辉, 等, 2019. 宁夏六盘山不同林龄华北落叶松人工林枯落物水文效应[J]. 林业科学研究, 32(4): 26-32. |
| GAO D, GUO J B, WANG Y H, et al., 2019. Hydrological effects of forest litter of larix principis rupprechtii plantations with varying ages in Liupanshan of Ningxia, China[J]. Forest Research, 32(4): 26-32. | |
| [6] | 公博, 师忱, 何会宾, 等, 2019. 冀北山区6种人工林的林地水源涵养能力[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 11(3): 165-170. |
| GONG F, SHI C, HE H B, et al., 2019. The water conservation capacity of six kind of planted forests in northern mountain area of Hebei province[J]. Journal of arid land resources and environment, 11(3): 165-170. | |
| [7] | 郭建荣, 朱学灵, 刘晓静, 等, 2012. 宝天曼自然保护区不同林龄锐齿栎林枯落物层水文特性[J]. 河南农业大学学报, 46(3): 268-272. |
| GUO J R, ZHU X L, LIU X J, et al., 2012. Hydrological characteristics of litter layer of Quercus aliena var. acutus forest of different age in Baotianman Nature Reserve[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural University, 46(3): 268-272. | |
| [8] | 李阳, 万福绪, 2019. 黄浦江中游5种典型林分枯落物和土壤水源涵养能力研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 33(2): 264-271. |
| LI Y, WAN F X, 2019. Water conservation capacities of litters and soils in five typical stands in the middle reaches of Huangpu river[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 33(2): 264-271. | |
| [9] | 陕西省发展与改革委员会, 2018. 秦岭生态系统综合管理研究[M]. 北京: 中国发展出版社. |
| Development and Reform Commission of Shaanxi Province, 2018. Research on integrated ecosystem management in Qinling Mountains[M]. Beijing: China Development Press. | |
| [10] | 时忠杰, 王彦辉, 徐丽宏, 等, 2009. 六盘山主要森林类型枯落物的水文功能[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 31(1): 91-100. |
| SHI Z J, WANG Y H, XU L H, et al., 2009. Hydrological functions of litter layer of typical forest types in Liupan mountain of Ningxia, northwestern China[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 31(1): 91-100. | |
| [11] | 王美莲, 王飞, 姚晓娟, 等, 2015. 不同林龄兴安落叶松枯落物及土壤水文效应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 24(6): 925-931. |
| WANG M L, WANG F, YAO X J, et al., 2015. Hydrological effects of forest litters and soil in Xing’an Larch forest at different stand ages[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 24(6): 925-931. | |
| [12] | 袁秀锦, 王晓荣, 潘磊, 等, 2018. 三峡库区不同类型马尾松林枯落物层持水特性比较[J]. 水土保持学报, 32(3): 160-166. |
| YUAN X J, WANG X R, PAN L, et al., 2018. Comparison of water holding capacity of litter in different types of Pinus massoniana plantation in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 32(3): 160-166. | |
| [13] | 杨良辰, 张春茹, 2018. 沿坝地区3种典型林分类型枯落物层与土壤层水源涵养能力综合评价[J]. 水土保持研究, 25(6): 177-182. |
| YANG L C, ZHANG C R, 2018. Comprehensive evaluation of water conservation capacity in litter and soil layer of three typical forest types along the highland area[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 25(6): 177-182. | |
| [14] | 杨家慧, 谭伟, 卯光宪, 等, 2020. 黔中不同龄组柳杉人工林枯落物水源涵养能力综合评价[J]. 水土保持学报, 34(2): 296-301, 308. |
| YANG J H, TAN W, MAO G X, et al., 2020. Water conservation ability of litter of Cryptomeria fortunei plantation with different age groups in central Guizhou[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 34(2): 296-301, 308. | |
| [15] | 杨建红, 传燕, 汪红, 等, 2020. 祁连山天涝池流域不同植被群落枯落物持水能力及时间动态变化[J]. 兰州大学学报: 自然科学版, 56(6): 733-739. |
| YANG J H, ZHAO C Y, WANG H, et al., 2020. Study on the water-holding capacity of litter of different vegetation types in Tianluochi catchment of Qilian Mountains[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University: Natural Sciences, 56(6): 733-739. | |
| [16] | 张海涛, 宫渊波, 付万权, 等, 2016. 川南马尾松低效人工林不同改造模式后枯落物持水特性分析[J]. 水土保持学报, 30(4): 136-141. |
| ZHANG H T, GONG Y B, FU W Q, et al., 2016. Water holding characteristics of litter under different transformation patterns of low-efficiency Pinus massoniana Lamb. plantation in southern Sichuan province[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 30(4): 136-141. | |
| [17] | 张淑兰, 张海军, 张武, 等, 2015. 小兴安岭不同森林类型枯落物储量及其持水特性比较[J]. 水土保持通报, 35(4): 85-90. |
| ZHANG S L, ZHANG H J, ZHANG W, et al., 2015. Comparison of water-holding characteristics and biomass of litter under different forest types in Xiaoxingan mountains[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 35(4): 85-90. | |
| [18] | 张学龙, 金铭, 刘贤德, 等, 2015. 祁连山5种典型灌木林枯落物蓄积量及其持水特性[J]. 生态环境学报, 24(5): 735-740. |
| ZHANG X L, JIN M, LIU X D, et al., 2015. Litter storage and its water holding capacity characteristics of five typical shrubs in Qilian mountains[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 24(5): 735-740. | |
| [19] | 赵鹏, 马佳明, 李艳茹, 等, 2020. 太行山典型区域不同林分类型枯落物水文效应[J]. 水土保持学报, 34(5): 176-185. |
| ZHAO P, MA J M, LI Y R, et al., 2020. Hydrological effects of litter in different forest types in typical areas of Taihang Mountains[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 34(5): 176-185. | |
| [20] | 甄学渊, 郭敏, 胡晓静, 等, 2014. 秦巴山区陕南栎类生长特点及资源现状[J]. 西北植物学报, 34(10): 2101-2108. |
| ZHEN X Y, GUO M, HU X J, et al., 2014. Growth characteristics and resource status of Oak in Qin-Ba mountains[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 34(10): 2101-2108. |
| [1] | CHEN Keyi, LIN Tianmiao, WANG Jianjun, HE Youjun, ZHANG Liwen. Effects of Natural Forest Conservation Project on Forest Carbon Pool of Key State-Owned Forest Region of Daxing’anling, Heilongjiang Province in the Past 20 Years [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(6): 1016-1025. |
| [2] | CHEN Zhizhong, ZAN Mei, YANG Xuefeng, DONG Yu. Prediction of Forest Vegetation Carbon Storage in Xinjiang [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(2): 226-234. |
| [3] | CHEN Keyi, WANG Jianjun, HE Youjun, ZHANG Liwen. Estimations of Forest Carbon Storage and Carbon Sequestration Potential of Key State-Owned Forest Region in Daxing’anling, Heilongjiang Province [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(9): 1725-1734. |
| [4] | HAN Cui, KANG Yangmei, YU Hailong, Li Bing, HUANG Juying. Effects of Precipitation on Soil Enzyme Activities during Litter Decomposition in A Desert Steppe of Northwestern China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(9): 1802-1812. |
| [5] | LI Xun, CUI Ningjie, ZHANG Yan, QIN Yu, ZHANG Jian. Mixed Effects on Cellulose, Total phenols and Condensed Tannins Degradation in the Litter Leaves of Pinus massoniana and Native Broad-leaved Tree Species [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(9): 1813-1822. |
| [6] | LIANG Lei, MA Xiuzhi, HAN Xiaorong, LI Changsheng, ZHANG Zhijie. Effects of Litter on Soil Greenhouse Gas Flux of Pinus tabulaeformis Plantation in Daqing Mountain under Simulated Warming [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 478-486. |
| [7] | LIU Peiling, LIU Xiaodong, FENG Yingjie, SU Yuqiao, GAN Xianhua, ZHANG Weiqiang. Characteristics of Soil Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity of Water Conservation Forests in the Xinfengjiang Reservoir Area [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(10): 1993-2001. |
| [8] | WANG Xuan, XIONG Xin, ZHANG Huiling, ZHAO Mengdi, HU Minghui, CHU Guowei, MENG Ze, ZHANG Deqiang. Effects of Simulated Acid Rain on Litter Decomposition and Soil Respiration in A Low Subtropical Forest [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(9): 1805-1813. |
| [9] | SUN Xuejiao, LI Jimei, ZHANG Yutao, LI Xiang, LU Jianjiang, SHE Fei. Characteristics and Influence of Runoff and Sediment Yield in Mountain Forest on the North Slope of Tianshan Mountains [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(9): 1821-1830. |
| [10] | ZHAO Na, WANG Junbo, LI Shaoning, LU Shaowei, XU Xiaotian. Study on Water Holding Characteristics of Four Typical Forest Litter in Songshan, Beijing [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(6): 1139-1147. |
| [11] | ZHANG Naimu, SONG Yali, WANG Keqin, ZHANG Yujian, PAN Yu, ZHENG Xingrui. Nutrient Release Characteristics of Forest Litter under Simulated Nitrogen Deposition in the Subalpine of Central Yunnan, China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(5): 920-928. |
| [12] | ZHANG Yangyang, ZHOU Qinghui, XU Jiaoyang, WEI Ming, CHEN Jihao, HE Wei, WANG Pengcheng, YAN Zhaogui. Effects of Forest Ages on the Diversity of Understory Plants and Soil Seed Bank of Pinus massoniana Plantations [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(11): 2121-2129. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
