Ecology and Environment ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (9): 1802-1812.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.09.010
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
HAN Cui1,2( ), KANG Yangmei3, YU Hailong3, Li Bing2, HUANG Juying1,*(
), KANG Yangmei3, YU Hailong3, Li Bing2, HUANG Juying1,*( )
)
Received:2022-02-21
Online:2022-09-18
Published:2022-11-07
Contact:
HUANG Juying
韩翠1,2( ), 康扬眉3, 余海龙3, 李冰2, 黄菊莹1,*(
), 康扬眉3, 余海龙3, 李冰2, 黄菊莹1,*( )
)
通讯作者:
黄菊莹
作者简介:韩翠(1996年生),女,硕士研究生,主要从事降水量变化及氮添加下荒漠草原碳源汇特征研究。E-mail: 18838933825@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
HAN Cui, KANG Yangmei, YU Hailong, Li Bing, HUANG Juying. Effects of Precipitation on Soil Enzyme Activities during Litter Decomposition in A Desert Steppe of Northwestern China[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(9): 1802-1812.
韩翠, 康扬眉, 余海龙, 李冰, 黄菊莹. 荒漠草原凋落物分解过程中降水量对土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1802-1812.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.09.010
| 处理 Treatment | 降水状态 Status of precipitation | 降水量 Precipitation/mm | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | ||
| W1 | 减少 | 149.4 | 153.6 | 147.3 |
| 总接受 | 196.8 | 211.9 | 200.4 | |
| W2 | 减少 | 90.6 | 92.6 | 89.4 |
| 总接受 | 255.6 | 272.9 | 258.3 | |
| W3 (对照 Control) | 增加/减少 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 总接受 | 346.2 | 365.5 | 347.7 | |
| W4 | 增加 | 86.9 | 86.9 | 86.9 |
| 总接受 | 433.1 | 452.4 | 434.6 | |
| W5 | 增加 | 144.9 | 144.9 | 144.9 |
| 总接受 | 491.1 | 510.4 | 492.6 | |
Table 1 The actually altered precipitation and the received precipitation in each treatment during 2014-2016
| 处理 Treatment | 降水状态 Status of precipitation | 降水量 Precipitation/mm | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | ||
| W1 | 减少 | 149.4 | 153.6 | 147.3 |
| 总接受 | 196.8 | 211.9 | 200.4 | |
| W2 | 减少 | 90.6 | 92.6 | 89.4 |
| 总接受 | 255.6 | 272.9 | 258.3 | |
| W3 (对照 Control) | 增加/减少 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 总接受 | 346.2 | 365.5 | 347.7 | |
| W4 | 增加 | 86.9 | 86.9 | 86.9 |
| 总接受 | 433.1 | 452.4 | 434.6 | |
| W5 | 增加 | 144.9 | 144.9 | 144.9 |
| 总接受 | 491.1 | 510.4 | 492.6 | |
| 变异来源 Source of variation | 自由度 Degree of freedom | 过氧化氢酶活性 Catalase activity | 蔗糖酶活性 Sucrase activity | 脲酶活性 Urease activity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 降水量 Precipitation (α) | 4 | 2.499* | 7.373** | 11.195** |
| 分解时间 Decomposition time (β) | 5 | 93.920** | 35.552** | 20.134** |
| 降水量×分解时间 Interaction of α and β | 20 | 1.293 | 1.012 | 1.194 |
Table 2 Effect of precipitation, decomposition time and their interaction on soil enzyme activity
| 变异来源 Source of variation | 自由度 Degree of freedom | 过氧化氢酶活性 Catalase activity | 蔗糖酶活性 Sucrase activity | 脲酶活性 Urease activity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 降水量 Precipitation (α) | 4 | 2.499* | 7.373** | 11.195** |
| 分解时间 Decomposition time (β) | 5 | 93.920** | 35.552** | 20.134** |
| 降水量×分解时间 Interaction of α and β | 20 | 1.293 | 1.012 | 1.194 |
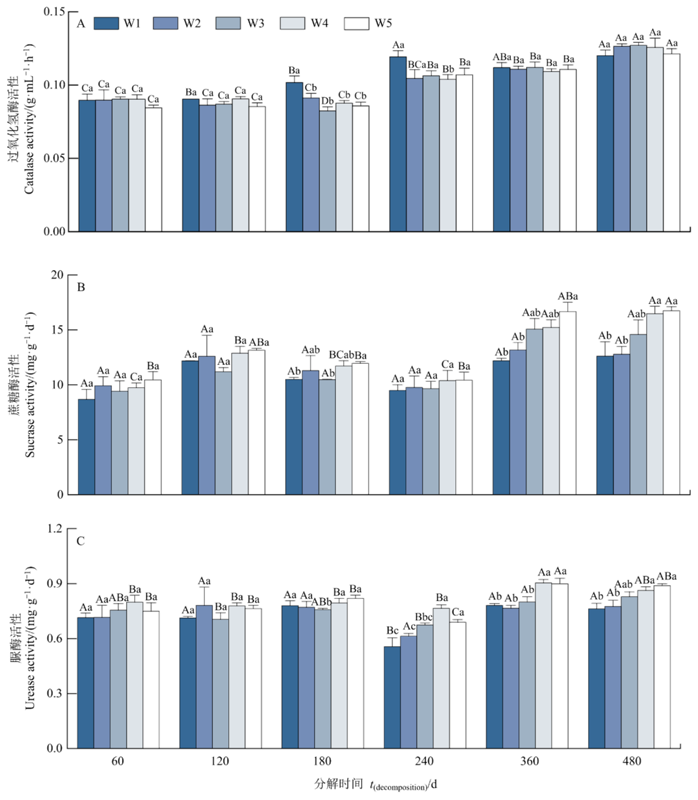
Figure 2 Effects of precipitation on soil enzyme activities Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences in soil enzyme activities between the precipitation treatments under the same decomposition time (P<0.05). Different capital letters indicate significant differences in soil enzyme activities between the decomposition times under the same precipitation treatment (P<0.05). n=5
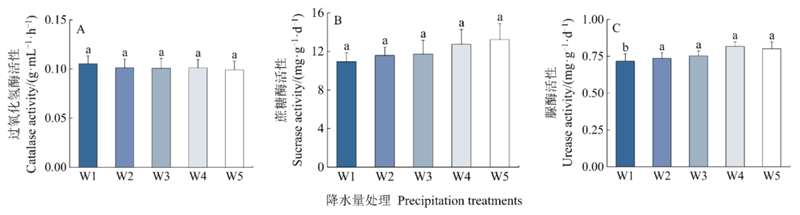
Figure 3 Effect of precipitation on soil enzyme activity Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences in soil enzyme activities between the precipitation treatments (P<0.05). n =30
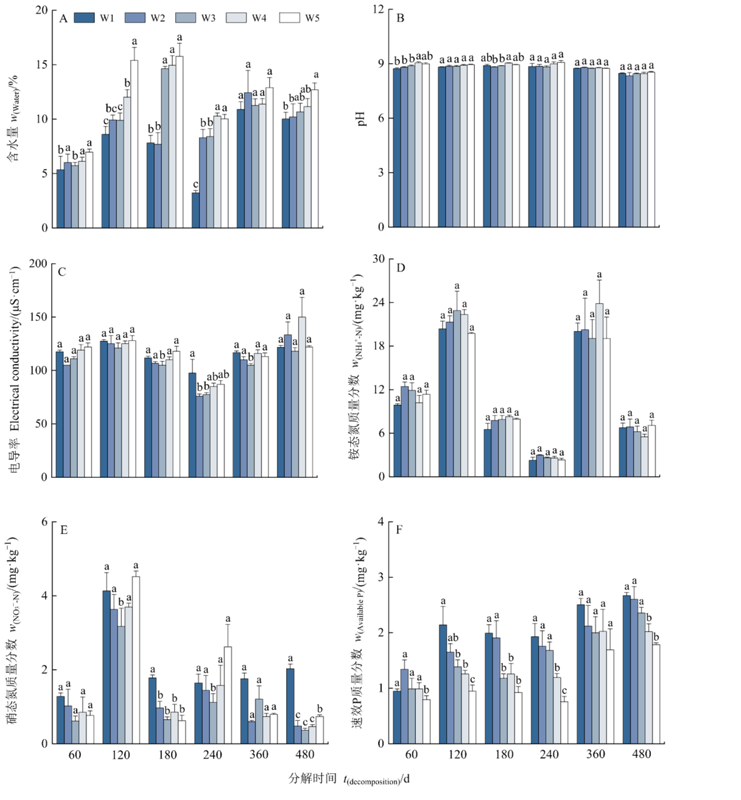
Figure 4 Effects of precipitation on soil physicochemical properties Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference in soil index between the precipitation treatments under the same decomposition time (P<0.05). n=5
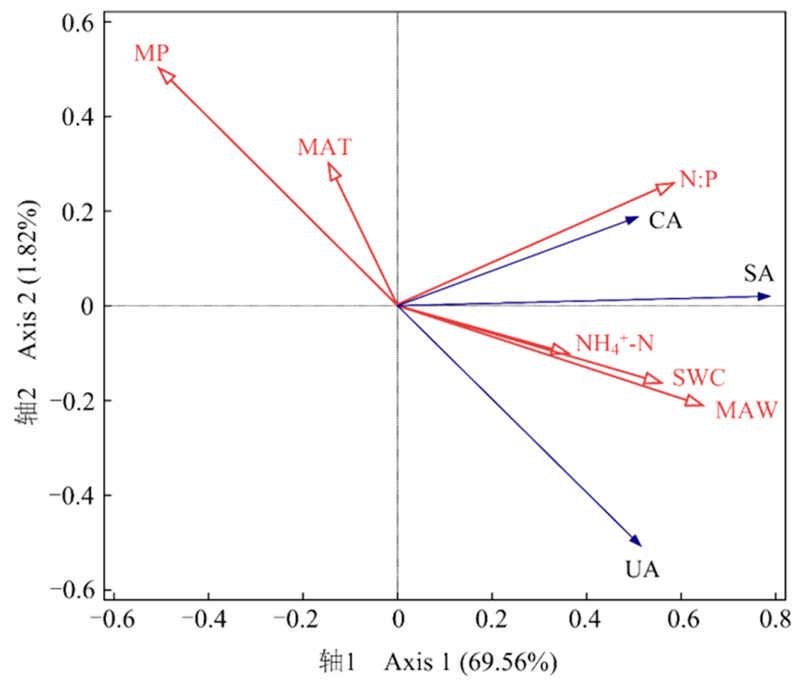
Figure 5 RDA of soil enzyme activities and environmental factors CA, SA and UA represent soil catalase activity, sucrase activity and urease activity, respectively. MP, MAT and MAW represent monthly precipitation, average atmospheric temperature and average wind speed, respectively. SWC, N:P and NH4+-N represent soil water content, N:P and NH4+-N, respectively. The environmental factors with P value less than 0.05 are not listed. n =150
| 因子 Factor | 贡献率 Contribution/% | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| 月平均风速 Monthly average wind speed | 40.7 | 41.4 | 0.002 |
| 土壤N:P Soil N:P | 36.8 | 53.3 | 0.002 |
| 月平均气温 Monthly average air temperature | 6.8 | 10.7 | 0.002 |
| 土壤含水量 Soil water content | 4.8 | 7.9 | 0.002 |
| 月降水量 Monthly precipitation | 3 | 5.2 | 0.020 |
| 土壤NH4+-N Soil NH4+-N | 3.2 | 5.7 | 0.010 |
| 土壤NO3--N Soil NO3--N | 1.5 | 2.7 | 0.098 |
| 土壤有机C Soil organic C | 0.9 | 1.6 | 0.200 |
| 土壤pH Soil pH | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.374 |
| 土壤C:P Soil C:P | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.506 |
| 土壤全P Soil total P | 1.1 | 2 | 0.168 |
| 土壤电导率 Soil electrical conductivity | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.524 |
| 土壤速效P Soil available P | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.692 |
| 土壤C:N Soil C:N | <0.1 | 0.1 | 0.774 |
| 土壤全N Soil total N | <0.1 | <0.1 | 0.884 |
Table 3 Statistics analysis in RDA of soil enzyme activities and environmental factors
| 因子 Factor | 贡献率 Contribution/% | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| 月平均风速 Monthly average wind speed | 40.7 | 41.4 | 0.002 |
| 土壤N:P Soil N:P | 36.8 | 53.3 | 0.002 |
| 月平均气温 Monthly average air temperature | 6.8 | 10.7 | 0.002 |
| 土壤含水量 Soil water content | 4.8 | 7.9 | 0.002 |
| 月降水量 Monthly precipitation | 3 | 5.2 | 0.020 |
| 土壤NH4+-N Soil NH4+-N | 3.2 | 5.7 | 0.010 |
| 土壤NO3--N Soil NO3--N | 1.5 | 2.7 | 0.098 |
| 土壤有机C Soil organic C | 0.9 | 1.6 | 0.200 |
| 土壤pH Soil pH | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.374 |
| 土壤C:P Soil C:P | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.506 |
| 土壤全P Soil total P | 1.1 | 2 | 0.168 |
| 土壤电导率 Soil electrical conductivity | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.524 |
| 土壤速效P Soil available P | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.692 |
| 土壤C:N Soil C:N | <0.1 | 0.1 | 0.774 |
| 土壤全N Soil total N | <0.1 | <0.1 | 0.884 |
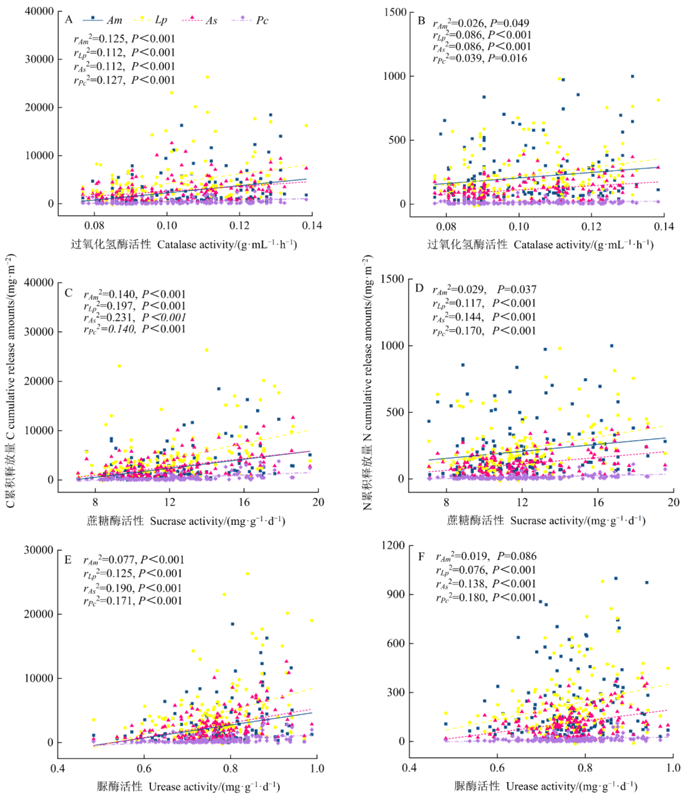
Figure 6 Linear fitting relationships between soil enzyme activities and elemental cumulative release amounts from plant species litters Am, Lp, As, and Pc represent Astragalus melilotoides, Lespedeza potaninii, Artemisia scoparia, and Pennisetum centrasiaticum, respectively. n=30
| [1] |
AKINYEMIA D S, ZHU Y K, ZHAO M Y, et al., 2020. Response of soil extracellular enzyme activity to experimental precipitation in a shrub-encroached grassland in Inner Mongolia[J]. Global Ecology and Conservation, DOI: 10.1016/j.gecco.2020.e01175.
DOI |
| [2] |
ALLISON S D, LU Y, WEIHE C, et al., 2013. Microbial abundance and composition influence litter decomposition response to environmental change[J]. Ecology, 94(3): 714-725.
PMID |
| [3] |
AVAZPOORL Z, MORADIL M, BASIRIL R, et al., 2019. Soil enzyme activity variations in riparian forests in relation to plant species and soil depth[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 12(23): 708.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
BURNS R G, DEFOREST G L, MARXSEN J, et al., 2013. Soil enzymes in a changing environment: Current knowledge and future directions[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 58: 216-234.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
ESCH, LIPSON D, CLELAND E E, 2017. Direct and indirect effects of shifting rainfall on soil microbial respiration and enzyme activity in a semi-arid system[J]. Plant and Soil, 411(1-2): 333-346.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
FENG Y, ZHAO X Y, 2015. Changes in spatiotemporal pattern of precipitation over China during 1980-2012[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 73: 1649-1662.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
GAO W L, REED S C, MUNSON S M, et al., 2021. Responses of soil extracellular enzyme activities and bacterial community composition to seasonal stages of drought in a semiarid grassland[J]. Geoderma, DOI: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2021.115327.
DOI |
| [8] |
GE X G, XIAO W F, ZENG L X, et al., 2017. Relationships between soil-litter interface enzyme activities and decomposition in Pinus massoniana plantations in China[J]. Journal of Soil and Sediments, 17(4): 996-1008.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
HEWINS D B, BROADBENT T, BORK E W, et al., 2016. Extracellular enzyme activity response to defoliation and water addition in two ecosites of the mixed grass prairie[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 230: 79-86.
DOI URL |
| [10] | IPCC, 2021. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis[R]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. |
| [11] |
JING X, WANG Y H, CHUNG H, et al., 2014. No temperature acclimation of soil extracellular enzymes to experimental warming in an alpine grassland ecosystem on the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Biogeochemistry, 117(1): 39-54.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
KIVLIN S N, TRESEDER K K, 2014. Soil extracellular enzyme activities correspond with abiotic factors more than fungal community composition[J]. Biogeochemistry, 117(1): 23-37.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
KOTROCZO Z, VERES Z, FEKETE I, et al., 2014. Soil enzyme activity in response to long-term organic matter manipulation[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 70: 237-224.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
KOURTEV P S, EHRENFELD J G, Huang W Z, 2002. Enzyme activities during litter decomposition of two exotic and two native plant species in hardwood forests of New Jersey[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 34(9): 1207-1218.
DOI URL |
| [15] | LADWIG L M, SINSABAUGH R L, COLLINS S L, et al., 2015. Soil enzyme responses to varying rainfall regimes in Chihuahuan Desert soils[J]. Ecosphere, 6(3): 1-10. |
| [16] |
MA W J, LI J, GAO Y, et al., 2020. Responses of soil extracellular enzyme activities and microbial community properties to interaction between nitrogen addition and increased precipitation in a semi-arid grassland ecosystem[J]. Science of the Total Environment, DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134691.
DOI |
| [17] |
NA X F, YU H L, WANG P, et al., 2019. Vegetation biomass and soil moisture coregulate bacterial community succession under altered precipitation regimes in a desert steppe in northwestern China[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, DOI: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2019.107520.
DOI |
| [18] |
NANNIPIERI P, GIAGNONI L, RENELLA G, et al., 2012. Soil enzymology: Classical and molecular approaches[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 48(7): 743-762.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
SHI A D, MARSCHNER P, 2014. Drying and rewetting frequency influences cumulative respiration and its distribution over time in two soils with contrasting management[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 72: 172-179.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
SUSEELA V, THARAYIL N, XING B S, et al., 2014. Warming alters potential enzyme activity but precipitation regulates chemical transformations in grass litter exposed to simulated climatic changes[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 75: 102-112.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
TAYLOR P G, CLEVELAND C C, WIEDER W R, et al., 2017. Temperature and rainfall interact to control carbon cycling in tropical forests[J]. Ecology Letters, 20(6): 779-788.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
WARING B G, 2013. Exploring relationships between enzyme activities and leaf litter decomposition in a wet tropical forest[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 64: 89-95.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
WU Y J, WU SVY, WEN J H, et al., 2016. Changing characteristics of precipitation in China during 1960-2012[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 36(3): 1387-1402.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
XU Z W, LI M H, ZIMMERMANN N E, et al., 2018. Plant functional diversity modulates global environmental change effects on grassland productivity[J]. Journal of Ecology, 106(5): 1941-1951.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
ZECHMEISTER-BOLTEBSTERN S, KEIBLINGER K M, MOOSHAMMER M, et al., 2015. The application of ecological stoichiometry to plant-microbial-soil organic matter transformations[J]. Ecological Monographs, 85(2): 133-155.
DOI URL |
| [26] | 白永飞, 赵玉金, 王扬, 等, 2020. 中国北方草地生态系统服务评估和功能区划助力生态安全屏障建设[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 35(6): 675-689. |
| BAI Y F, ZHAO Y J, WANG Y, et al., 2020. Assessment of ecosystem services and ecological regionalization of grasslands support establishment of ecological security barriers in Northern China[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 35(6): 675-689. | |
| [27] | 鲍士旦, 2000. 土壤农化分析[M]. 第3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社. |
| BAO S D, 2000. Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis[M]. Third Edition. Beijing: China Agriculture Press. | |
| [28] | 曹聪, 阮超越, 任寅榜, 等, 2020. 模拟增温对武夷山不同海拔森林表层土壤碳氮及酶活性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 40(15): 5347-5356. |
| CAO C, RUAN C Y, REN Y B, et al., 2020. Effects of stimulating warming on surface soil carbon, nitrogen and its enzyme activities across a subtropical elevation gradient in Wuyi Mountain, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(15): 5347-5356. | |
| [29] | 柴锦隆, 徐长林, 张德罡, 等, 2019. 模拟践踏和降水对高寒草甸土壤养分和酶活性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 39(1): 333-344. |
| CHAI J L, XU C L, ZHANG D G, et al., 2019. Effects of simulated trampling and rainfall on soil nutrients and enzyme activity in an alpine meadow[J]. Ecologica Sinica, 39(1): 333-344. | |
| [30] | 钞然, 张东, 陈雅丽, 等, 2018. 模拟增温增雨对典型草原土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 干旱区研究, 35(5): 1068-1074. |
| CHAO R, ZHANG D, CHEN Y L, et al., 2018. Effects of simulated temperature and precipitation increase on soil enzyme activity in typical steppe[J]. Arid Zone Research, 35(5): 1068-1074. | |
| [31] |
陈敏玲, 张兵伟, 任婷婷, 等, 2016. 内蒙古半干旱草原土壤水分对降水格局变化的响应[J]. 植物生态学报, 40(7): 658-668.
DOI |
|
CHEN M L, ZHANG B W, REN T T, et al., 2016. Responses of soil moisture to precipitation pattern change in semiarid grasslands in Nei Mongol, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 40(7): 658-668.
DOI URL |
|
| [32] | 陈晓丽, 王根绪, 杨燕, 等, 2015. 山地森林表层土壤酶活性对短期增温及凋落物分解的响应[J]. 生态学报, 35(21): 7071-7079. |
| CHEN X L, WANG G X, YANG Y, et al., 2015. Response of soil surface enzyme activities to short-term warming and litter decomposition in a mountain forest[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35(21): 7071-7079. | |
| [33] | 付琦, 邢亚娟, 闫国永, 等, 2019. 北方森林凋落物动态对长期氮沉降的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(7): 1341-1350. |
| FU Q, XING Y J, YAN G Y, et al., 2019. Response of litter dynamics of boreal forest to long-term nitrogen deposition[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 28(7): 1341-1350. | |
| [34] | 耿玉清, 王冬梅, 2012. 土壤水解酶活性测定方法的研究进展[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 20(4): 387-394. |
|
GENG Y Q, WANG D M, 2012. Research advances on the measurement methods for soil hydrolytic enzymes activities[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 20(4): 387-394.
DOI URL |
|
| [35] | 韩翠, 康扬眉, 余海龙, 等, 2022. 降水量对4种荒漠草原植物凋落物碳氮磷释放的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 41(6): 1090-1100. |
| HAN C, KANG Y M, YU H L, et al., 2022. Effects of precipitation on the release of carbon,nitrogen,and phosphorus from decomposing litter of four plant species in a desert steppe[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 41(6): 1090-1100. | |
| [36] | 黄菊莹, 余海龙, 刘吉利, 等, 2018. 控雨对荒漠草原植物、微生物和土壤C、N、P化学计量特征的影响[J]. 生态学报, 38(15): 5362-5373. |
| HUANG J Y, YU H L, LIU J L, et al., 2018. Effects of precipitation levels on the C:N:P stoichiometry in plants, microbes, and soils in a desert steppe in China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(15): 5362-5373. | |
| [37] | 黄小燕, 李耀辉, 冯建英, 等, 2015. 中国西北地区降水量及极端干旱气候变化特征[J]. 生态学报, 35(5): 1359-1370. |
| HUANG X Y, LI Y H, FENG J Y, et al., 2015. Climate characteristics of precipitation and extreme drought events in Northwest China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35(5): 1359-1370. | |
| [38] |
贾丙瑞, 2019. 凋落物分解及其影响机制[J]. 植物生态学报, 43(8): 648-657.
DOI |
|
JIA B R, 2019. Litter decomposition and its underlying mechanisms[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 43(8): 648-657.
DOI URL |
|
| [39] |
李明, 孙洪泉, 苏志诚, 2021. 中国西北气候干湿变化研究进展[J]. 地理研究, 40(4): 1180-1194.
DOI |
|
LI M, SUN H Q, SU Z C, 2021. Research progress in dry/wet climate variation in Northwest China[J]. Geographical Research, 40(4): 1180-1194.
DOI |
|
| [40] | 李吉玫, 张毓涛, 韩燕梁, 等, 2015. 降水变化对天山云杉细根分解及养分释放的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 24(9): 1453-1460. |
| LI J M, ZHANG Y T, HAN Y L, et al., 2015. Effects of variation of precipitation on the fine root decomposition and related nutrient release in Picea schrenkiana var. tianshanica[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 24(9): 1453-1460. | |
| [41] | 刘红梅, 周广帆, 李洁, 等, 2018. 氮沉降对贝加尔针茅草原土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 27(8): 1387-1394. |
| LIU H M, ZHOU G F, LI J, et al., 2018. Effects of nitrogen deposition on soil enzyme activities of Stipa baicalensis steppe[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 27(8): 1387-1394. | |
| [42] | 王理德, 王方琳, 郭春秀, 等, 2016. 土壤酶学硏究进展[J]. 土壤, 48(1): 12-21. |
| WANG L D, WANG F L, GUO C X, et al., 2016. Review: progress of soil enzymology[J]. Soil, 48(1): 12-21. | |
| [43] | 王涛, 马宇丹, 许亚东, 等, 2018. 退耕刺槐林土壤养分与酶活性关系[J]. 生态学杂志, 37(7): 2083-2091. |
| WANG T, MA Y D, XU Y D, et al., 2018. Relationship between soil nutrients and enzyme activity in Robinia pseudoacacia plantation[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 37(7): 2083-2091. | |
| [44] | 许华, 何明珠, 孙岩, 2018. 干旱荒漠区土壤酶活性对降水调控的响应[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 54(6): 790-797. |
| XU H, HE M Z, SUN Y, 2018. Response of soil enzyme activities to precipitation regulation in arid desert areas[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences), 54(6): 790-797. | |
| [45] | 闫钟清, 齐玉春, 彭琴, 等, 2017. 降水和氮沉降增加对草地土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 37(9): 3019-3027. |
| YAN Z Q, QI Y C, PENG Q, et al., 2017. Effects of increased precipitation and nitrogen deposition on soil enzyme activities[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37(9): 3019-3027. |
| [1] | DU Caiyan, YANG Peng, FENG Shuxian, MAO Yanting, TAO Qiong, CI Zhulamu, PENG Huiping, HE Jianmei, LI Weilin. Correlation between Quality and Ecological Factors of Weixi Glutinous Yam in Different Ecological Regions [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(6): 1053-1061. |
| [2] | ZHANG Shanwen, YANG Ran, HOU Wenxing, WANG Lili, LIU Shuang, SONG Hanyang, ZHAO Wenji, LI Lingjun. Analysis of Fractional Vegetation Cover Changes and Driving Forces on Both Banks of Yongding River Before and After Ecological Water Replenishment [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(2): 264-273. |
| [3] | SHENG Meijun, LI Shengjun, YANG Xinyue, WANG Rui, LI Jie, LI Gang, XIU Weiming. Changes of Soil Enzyme Activities in Cropland with Different Land Use Intensities in Fluvo-aquic Soil Area, North China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(2): 299-308. |
| [4] | FU Chuanbo, DAN Li, TONG Jinhe, CHEN Hong. Characteristics and Potential Source Analysis of Ozone pollution in Haikou City [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(2): 331-340. |
| [5] | HUANG Weijia, LIU Chun, LIU Yue, HUANG Bin, LI Dingqiang, YUAN Zaijian. Soil Ecological Stoichiometry and Its Influencing Factors at Different Elevations in Nanling Mountains [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(1): 80-89. |
| [6] | LI Xun, CUI Ningjie, ZHANG Yan, QIN Yu, ZHANG Jian. Mixed Effects on Cellulose, Total phenols and Condensed Tannins Degradation in the Litter Leaves of Pinus massoniana and Native Broad-leaved Tree Species [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(9): 1813-1822. |
| [7] | SUN Jianbo, CHANG Wenjun, LI Wenbin, ZHANG Shiqing, LI Chunqiang, PENG Ming. Dynamics of Soil Microbial Biomass and Enzyme Activities in Rhizosphere Soil at Different Growing Stages of Banana [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(6): 1169-1174. |
| [8] | FENG Yiqing, HAO Likai, GUO Yuan, XU Fei, XU Heng. Spatio-temporal Evolution Characteristics of Microbiome in Acid Mine Drainage and Microbial-mineral Interaction Mechanism [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(5): 1032-1046. |
| [9] | LIANG Lei, MA Xiuzhi, HAN Xiaorong, LI Changsheng, ZHANG Zhijie. Effects of Litter on Soil Greenhouse Gas Flux of Pinus tabulaeformis Plantation in Daqing Mountain under Simulated Warming [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 478-486. |
| [10] | HAO Yongpei, SONG Xiaowei, ZHAO Wenjun, XIANG Famin. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Air Pollution and Correlation Factors in Fenwei Plain [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 512-523. |
| [11] | ZHOU Chunfu, YU Rui, WANG Xiang, CHUANG Shaochuang, YANG Hongxing, XIE Yue. Effects of Antibiotics on Soil Enzyme Activities in Different Soils [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(11): 2234-2241. |
| [12] | CHEN Yang, ZHANG Jinpu, QIU Xiaonuan, JU Hong, HUANG Jun. Characteristic of Ozone Pollution and Meteorological Factors Analysis in Guangzhou in 2021 [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(10): 2028-2038. |
| [13] | DENG Yujiao, WANG Jiechun, XU Jie, WU Yongqi, CHEN Jingyang. Spatiotemporal Variation of Vegetation Carbon Sequestration and Its Meteorological Contribution in Guangdong Province [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(1): 1-8. |
| [14] | LI Chunhuan, WANG Pan, HAN Cui, XU Yixin, HUANG Juying. Variation Characteristics of Soil Properties Around A Northwest Desert Coal-mining Region under Sulphur and Nitrogen Deposition [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(1): 170-180. |
| [15] | ZHANG Shulan, HAN Yong, YANG Pan, YAN Yuying, LIU Zhaoxue, LI Zhuoyao. Evaluation of Hydrological Function of Litter of Quercus Acuvarius at Different Ages in the Upper Reaches of Han River [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(1): 44-51. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
