Ecology and Environment ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (12): 1953-1963.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.12.013
• Research Article [Environmental Science] • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Pujun1,2( ), TANG Li1, ZHAO Bo2, DI Dongliu2, CHEN Yan2, XIAO Jiang2,*(
), TANG Li1, ZHAO Bo2, DI Dongliu2, CHEN Yan2, XIAO Jiang2,*( ), CHEN Guangcai2
), CHEN Guangcai2
Received:2024-08-16
Online:2024-12-18
Published:2024-12-31
Contact:
XIAO Jiang
李璞君1,2( ), 唐丽1, 赵博2, 邸东柳2, 陈岩2, 肖江2,*(
), 唐丽1, 赵博2, 邸东柳2, 陈岩2, 肖江2,*( ), 陈光才2
), 陈光才2
通讯作者:
肖江
作者简介:李璞君(1998年生),女,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为土壤重金属改良和植被恢复。E-mail: 3478094921@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
LI Pujun, TANG Li, ZHAO Bo, DI Dongliu, CHEN Yan, XIAO Jiang, CHEN Guangcai. The Amelioration of Biochar Soil Amendment on Antimony Mining Soil and Growth of Betula luminifera[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(12): 1953-1963.
李璞君, 唐丽, 赵博, 邸东柳, 陈岩, 肖江, 陈光才. 生物炭基土壤改良剂对锑矿区土壤质量及亮叶桦生长的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(12): 1953-1963.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.12.013
| 处理 | w(土壤水分)/% | 土壤容重/(g∙cm−3) | 土壤孔隙度/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK T1 T2 T3 | 0.19±0.02b 0.13±0.01a 0.16±0.01ab 0.16±0.02ab | 3.19±0.18a 2.81±0.09a 3.12±0.1a 2.86±0.16a | 0.42±0.05b 0.28±0.02a 0.37±0.02ab 0.34±0.05ab |
Table 1 Effects of BBOF on the soil physical properties
| 处理 | w(土壤水分)/% | 土壤容重/(g∙cm−3) | 土壤孔隙度/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK T1 T2 T3 | 0.19±0.02b 0.13±0.01a 0.16±0.01ab 0.16±0.02ab | 3.19±0.18a 2.81±0.09a 3.12±0.1a 2.86±0.16a | 0.42±0.05b 0.28±0.02a 0.37±0.02ab 0.34±0.05ab |
| 处理 | 脲酶活性/ (μmol·g−1·d−1) | 酸性磷酸酶活性/ (μmol·g−1·d−1) | β-葡萄糖苷酶活性/ (μmol·g−1·d−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK T1 T2 T3 | 0.48±0.015d 0.13±0.006a 0.19±0.006b 0.25±0.015c | 0.45±0.044b 0.31±0.002a 0.46±0.042b 0.43±0.068ab | 35.06±2.695b 24.65±0.888a 27.81±1.719a 34.96±2.445b |
Table 2 Effects of BBOF on the soil enzyme activity
| 处理 | 脲酶活性/ (μmol·g−1·d−1) | 酸性磷酸酶活性/ (μmol·g−1·d−1) | β-葡萄糖苷酶活性/ (μmol·g−1·d−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK T1 T2 T3 | 0.48±0.015d 0.13±0.006a 0.19±0.006b 0.25±0.015c | 0.45±0.044b 0.31±0.002a 0.46±0.042b 0.43±0.068ab | 35.06±2.695b 24.65±0.888a 27.81±1.719a 34.96±2.445b |
| 处理 | SOD (by FW)/ (U·g−1·min−1) | CAT (by FW)/ (U·g−1·min−1) | MDA (by FW)/ (μmol·g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK T1 T2 T3 | 2.63±0.08a 5.67±0.06d 3.57±0.11b 3.88±0.08c | 1.26±0.2a 1.52±0.11a 1.12±0.08a 1.13±0.22a | 1.56±0.02a 1.76±0.02b 1.68±0.01b 1.58±0.01a |
Table 3 Effects of BBOF on antioxidant system of Betula luminifera
| 处理 | SOD (by FW)/ (U·g−1·min−1) | CAT (by FW)/ (U·g−1·min−1) | MDA (by FW)/ (μmol·g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK T1 T2 T3 | 2.63±0.08a 5.67±0.06d 3.57±0.11b 3.88±0.08c | 1.26±0.2a 1.52±0.11a 1.12±0.08a 1.13±0.22a | 1.56±0.02a 1.76±0.02b 1.68±0.01b 1.58±0.01a |
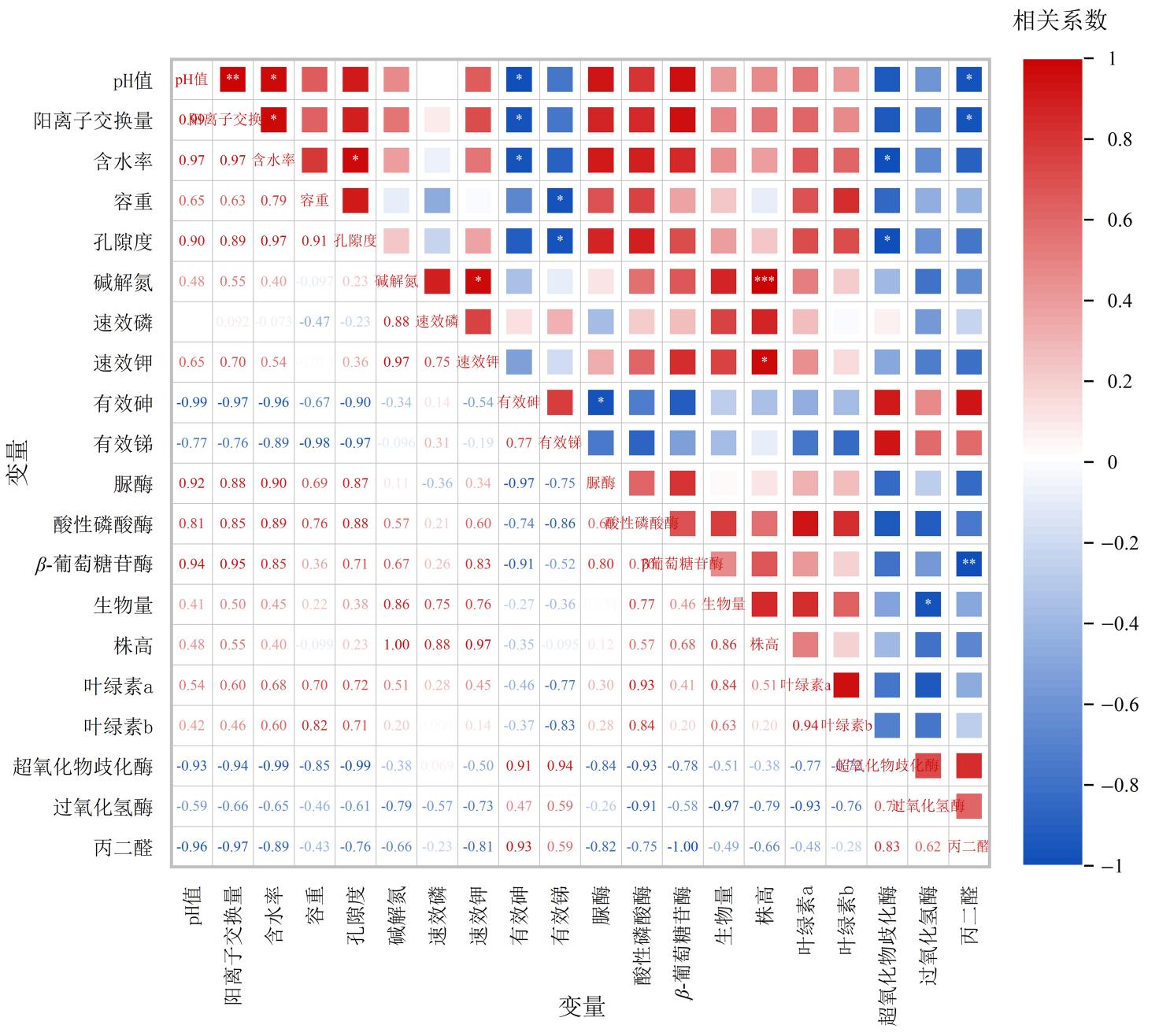
Figure 5 Correlation analysis of soil improvement in antimony mine area with growth physiology and heavy metal accumulation in Betula luminifera under BBOF treatment
| [1] | AHMAD M, LEE S S, LEE S E, et al., 2017. Biochar-induced changes in soil properties affected immobilization/mobilization of metals/metal loids in contaminated soils[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 17: 717-730. |
| [2] |
AHMAD M, LEE S S, LIM J E, et al., 2014. Speciation and phytoavailability of lead and antimony in a small arms range soil amended with mussel shell, cow bone and biochar: EXAFS spectroscopy and chemical extractions[J]. Chemosphere, 95: 433-441.
DOI PMID |
| [3] | AN Y J, KIM M, 2009. Effect of antimony on the microbial growth and the activities of soil enzymes[J]. Chemosphere, 74(5): 654-659. |
| [4] | BEESLEY L, MORENO-JIMÉNEZ E, Gomez-Eyles J L, et al., 2011. A review of biochars’ potential role in the remediation, revegetation and restoration of contaminated soils[J]. Environmental Pollution, 159(12): 3269-3282. |
| [5] | BOLAN N, KUNHIKRISHNAN A, GIBBS J, 2013. Rhizoreduction of arsenate and chromate in Australian native grass, shrub and tree vegetation[J]. Plant and Soil, 367: 615-625. |
| [6] | BOLAN N, KUNHIKRISHNAN A, THANGARAJAN R, et al., 2014. Remediation of heavy metal (loid) s contaminated soils-to mobilize or to immobilize?[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 266: 141-166. |
| [7] | CHEW J K, ZHU L L, NIELSEN S, et al., 2020. Biochar-based fertilizer: supercharging root membrane potential and biomass yield of rice[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 713: 136431. |
| [8] | DUPONT D, ARNOUT S, JONES P T, et al., 2016. Antimony recovery from end-of-life products and industrial process residues: A critical review[J]. Journal of Sustainable Metallurgy, 2(1): 79-103. |
| [9] | FENG R W, WEI C Y, TU S X, et al., 2009. Antimony accumulation and antioxidative responses in four fern plants[J]. Plant and Soil, 317: 93-101. |
| [10] | FENG R W, WEI C Y, TU S X, et al., 2013. The uptake and detoxification of antimony by plants: A review[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 96: 28-34. |
| [11] | GREGORY S J, ANDERSON C W N, ARBRSTAIN M C, et al., 2014. Response of plant and soil microbes to biochar amendment of an arsenic-contaminated soil[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 191: 133-141. |
| [12] | HALE B, EVANS L, LAMBERT R, 2012. Effects of cement or lime on Cd, Co, Cu, Ni, Pb, Sb and Zn mobility in field-contaminated and aged soils[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 199(15): 119-127. |
| [13] | HONG Y, LI D, XIE C, et al., 2022. Combined apatite, biochar, and organic fertilizer application for heavy metal co-contaminated soil remediation reduces heavy metal transport and alters soil microbial community structure[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 851(Part 1): 158033. |
| [14] | HU X Y, HE M C, LI S S, et al., 2017. The leaching characteristics and changes in the leached layer of antimony-bearing ores from China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 176: 76-84. |
| [15] | JIANG L, SHI G, DING Y, et al., 2013. Differential responses of two bamboo species (Phyllostachys auresulcata ‘Spectabilis’ and Pleioblastus Chino `Hisauchii') to excess copper[J]. BioEnergy Research, 6: 1223-1229. |
| [16] |
KUPPUSAMY S, THAVAMANI P, MEGHARAJ M, et al., 2016. Agronomic and remedial benefits and risks of applying biochar to soil: Current knowledge and future research directions[J]. Environment International, 87: 1-12.
DOI PMID |
| [17] | KUZYAKOV Y, SUBBOTINA I, CHEN H, et al., 2009. Black carbon decomposition and incorporation into soil microbial biomass estimated by 14C labeling[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 41(2): 210-219. |
| [18] | LEHMANN J, RILLIGM C, THIES J, et al., 2011. Biochar effects on soil biota: A review[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 43(9): 1812-1836. |
| [19] |
LI J N, WEI Y, ZHAO L, et al., 2014. Bioaccessibility of antimony and arsenic in highly polluted soils of the mine area and health risk assessment associated with oral ingestion exposure[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 110: 308-315.
DOI PMID |
| [20] | LI Y, DEMISIE W, ZHANG M K, 2015. Digestion tests to measure heavy metal bioavailability in soils[J]. CO2 Sequestration, Biofuels and Depollution, 275-305. |
| [21] | MA C L, HE M C, ZHONG Q Y, et al., 2019. Uptake, translocation and phytotoxicity of antimonite in wheat (Triticum aestivum)[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 669: 421-430. |
| [22] | OKKENHAUG G, AMSTÄTTER K, LASSEN BUE H, et al., 2013. Antimony (Sb) contaminated shooting range soil: Sb mobility and immobilization by soil amendments[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 47(12): 6431-6439. |
| [23] | PRAPAGDEE S, TAWINTEUNG N, 2017. Effects of biochar on enhanced nutrient use efficiency of green bean, Vigna radiata L[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(10): 9460-9467. |
| [24] | QIAN L B, CHEN B L, 2013. Dual role of biochars as adsorbents for aluminum: The effects of oxygen-containing organic components and the scattering of silicate particles[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 47(15): 8759-8768. |
| [25] | ROUT G R, SAMANTARAY S, DAS P, 1999. Differential cadmium tolerance of mung bean and rice genotypes in hydroponic culture[J]. Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica, Section B-Plant Soil Science, 49(4): 234-241. |
| [26] | RUIZ-CHANCHO M J, LÓPEZ-SÁNCHEZ J F, SCHMEISSER E, et al., 2008. Arsenic speciation in plants growing in arsenic-contaminated sites[J]. Chemosphere, 71(8): 1522-1530. |
| [27] | SCHULZ H, DUNST G, GLASER B, 2013. Positive effects of composted biochar on plant growth and soil fertility[J]. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 33: 817-827. |
| [28] | YAN B J, ZHANG Y P, WANG Y Z, et al., 2023. Biochar amendments combined with organic fertilizer improve maize productivity and mitigate nutrient loss by regulating the C-N-P stoichiometry of soil, microbiome, and enzymes[J]. Chemosphere, 324: 138293. |
| [29] | YANG W H, LI C J, WANG S S, et al., 2021. Influence of biochar and biochar-based fertilizer on yield, quality of tea and microbial community in an acid tea orchard soil[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 166: 104005. |
| [30] |
YE J, ZHANG R, NIELSEN S, et al., 2016. A combination of biochar-mineral complexes and compost improves soil bacterial processes, soil quality, and plant properties[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 7: 372.
DOI PMID |
| [31] |
ZHANG J N, ZHOU S, SUN H F, et al., 2019. Three-year rice grain yield responses to coastal mudflat soil properties amended with straw biochar[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 239: 23-29.
DOI PMID |
| [32] | ZHANG Q, ZHOU W, LIANG G Q, et al., 2015. Distribution of soil nutrients, extracellular enzyme activities and microbial communities across particle-size fractions in a long-term fertilizer experiment[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 94: 59-71. |
| [33] | ZHANG Z, JIA C X, GAN Y D, et al., 2022. Impact of biochars on the iron plaque formation and the antimony accumulation in rice seedings[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 109(6): 1088-1094. |
| [34] | ZHOU C, HEAL K, TIGABU M, et al., 2020. Biochar addition to forest plantation soil enhances phosphorus availability and soil bacterial community diversity[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 455: 117635. |
| [35] | ZHU P F, ZHU J R, PANG J Y, et al., 2020. Biochar improves the growth performance of maize seedling in response to antimony stress[J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 231(4): 1-12. |
| [36] | 鲍士旦, 2000. 土壤农化分析[M]. 第3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社. |
| BAO S D, 2000. Soil agricultural chemistry analysis[M]. Third edition. Beijing: China Agriculture Press. | |
| [37] | 杜忠毓, 邢文黎, 薛亮, 等, 2023. 喀斯特石漠化锑矿区植物群落主要物种生态位特征及其种间联结[J]. 生态学报, 43(7): 2865-2880. |
| DU Z Y, XING W L, XUE L, et al., 2023. Niche characteristics and interspecific association of main plant species in antimony mining sites of karst rocky desertification area Guizhou China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 43(7): 2865-2880. | |
| [38] | 关松荫, 1986. 土壤酶及其研究法[M]. 北京: 农业出版社. |
| GUAN S Y, 1986. Soil enzymes and their research methods[M]. Beijing: Agriculture Press. | |
| [39] | 李合生, 2000. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社. |
| LI H S, 2000. Principles and techniques of plant physiological biochemical experiment[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press. | |
| [40] | 柳骁桐, 纪立东, 孙权, 等, 2021. 炭基肥连续两年施用对土壤质量的影响[J]. 北方园艺 (7): 96-103. |
| LIU X T, JI L D, SUN Q, et al., 2021. Effects of continuous application of carbon-based fertilizer on soil quality for two years[J]. Northern Horticulture (7): 96-103. | |
| [41] | 刘振刚, 夏宇, 孟芋含, 等, 2021. 生物质炭材料修复重金属污染土壤的研究进展: 修复机理及研究热点分析[J]. 环境工程学报, 15(4): 1140-1148. |
| LIU Z G, XIA Y, MENG Y H, et al., 2021. Research advances in biomass-based carbon materials for remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil: Immobilization mechanism and analysis of related studies[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 15(4): 1140-1148. | |
| [42] | 环境保护部, 2017. 土壤阳离子交换量的测定三氯化六氨合钴浸提-分光光度法: HJ 889—2017 [S]. 北京: 中国环境出版社. |
| Ministry of Environmental Protection. 2017. Soil quality determination of cation exchange capacity (CEC) hexamminecobalt trichloride solution-spectrophotometric method: HJ 889—2017 [S]. Beijing: China Environment Press. | |
| [43] | 马兴, 2022. 锑污染对土壤酶的作用机理及生态效应研究[D]. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学. |
| MA X, 2022. The mechanism and ecological effect of antimony pollution on soil enzymes[D]. Xianyang: Northwest A & F University. | |
| [44] | 王友保, 2018. 土壤污染生态修复实验技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| WANG Y B, 2018. Experimental technology for ecological remediation of soil pollution[M]. Beijing: Science Press. | |
| [45] | 沈阳农业大学, 2016. 生物炭基肥料: NY 3041—2016 [S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社. |
| Shengyang Agricultural University, 2016. Biochar-based fertilizer: NY 3041—2016 [S]. Beijing: China Agricultural Press. | |
| [46] | 施海涛, 2016. 植物逆境生理学实验指导[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| SHI H T, 2016. Experimental guidance of plant stress physiology[M]. Beijing: Science Press. | |
| [47] | 宋刚练, 2018. 重金属锑污染土壤固化-稳定化修复技术研究及应用[J]. 环境与可持续发展, 43(2): 61-64. |
| SONG G L, 2018. Study and application of solidification-stabilization technology for heavy metal contaminated soil of antimony[J]. Environment and Sustainable Development, 43(2): 61-64. | |
| [48] | 张欢, 花莉, 罗婷, 2019. 锑胁迫下生物炭对番茄锑积累及生化特性的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 38(4): 983-994. |
| ZHANG H, HUA L, LUO T, 2019. Effects of biochar on Sb accumulation and biochemical characteristics of Lycopersicum esculentum in Sb-contaminated soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 38(4): 983-994. | |
| [49] | 张菊梅, 刘灵飞, 龙健, 等, 2019. 土壤锑污染及其修复技术研究进展[J]. 环境科学与技术, 42(4): 61-70. |
| ZHANG J M, LIU L F, LONG J, et al., 2019. Research progress on soil antimony pollution and its remediation technology[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 42(4): 61-70. | |
| [50] | 张继宁, 周胜, 孙会峰, 等, 2018. 生物质炭在我国蔬菜地应用的研究现状与展望[J]. 农业现代化研究, 39(4): 543-550. |
| ZHANG J N, ZHOU S, SUN H F, et al., 2018. Research progress and prospects on the biochar’s application in Chinese vegetable field[J]. Research of Agricultural Modernization, 39(4): 543-550. | |
| [51] | 赵晓鹏, 杨博一, 李超, 等, 2024. 贵州晴隆锑矿区土壤中锑的形态分布和地球化学模型[J]. 环境化学, 43(3): 911-919. |
| ZHAO X P, YANG B Y, LI C, et al., 2024. Species distribution and geochemical modeling of antimony in the Qinlong antimony mining area[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 43(3): 911-919. | |
| [52] | 赵泽州, 王晓玲, 李鸿博, 等, 2021. 生物质炭基肥缓释性能及对土壤改良的研究进展[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 27(5): 886-897. |
| ZHAO Z Z, WANG X L, LI H B, et al., 2021. Slow-release property and soil remediation mechanism of biochar-based fertilizers[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 27(5): 886-897. |
| [1] | CONG Xin, ZHANG Huaidi, ZHANG Rong, ZHAO Cen, CHEN Kun, LIU Hanbing. Pollution Characteristics and Risk Analysis of Heavy Metal in Farmland Soils of China in Recent 10 Years Based on Meta Analysis [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(9): 1451-1459. |
| [2] | LIU Dongyi, QU Yonghua, FENG Yaowei, QU Ran. Research on Chromium Ion Content Inversion of GF-5 Satellite Images Based on Grid Search Optimization CatBoost Model [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(9): 1460-1470. |
| [3] | OUYANG Meifeng, YIN Yuying, ZHANG Jinchen, LIU Qinglin, XIE Yinan, FANG Ping. Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Source Analysis of Heavy Metals in Typical Water Areas of Dongting Lake [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(8): 1269-1278. |
| [4] | WU Wenwei, SHEN Cheng, SHA Chenyan, LIN Kuangfei, WU Jian, XIE Yuqing, ZHOU Xuan. Soil Heavy Metal Enrichment Characteristics, Risk Assessment, and Source Analysis in Redevelopment Areas during Urban Industrial Plots [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(5): 791-801. |
| [5] | XIAO Jiang, LI Xiaogang, ZHAO Bo, CHEN Yan, CHEN Guangcai. Effect of Micro/nano Scale Phosphorus-enriched Biochar on Cu and Pb Stabilization in Soil-Salix jiangsuensis ‘172’ System [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(3): 439-449. |
| [6] | LIU Chutian, GUO Dongdong, HOU Lei, LIANG Qibin, WANG Yanxia, SHI Yanting, QI Yane. Analysis of the Effect Model for Nutrient Regulation on Cadmium Accumulation in Populus yunnanensis Seedlings [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(3): 460-468. |
| [7] | JIANG Runhai, WEN Shaofu, ZHU Chengqiang, ZHANG Mei, YANG Runling, WANG Chunxue, HOU Xiuli. Research on the Promotion of Maize Growth and Immobilization of Pb in the Rhizosphere by Pb-tolerant Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria in Pb-contaminated Mining Areas [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(2): 291-300. |
| [8] | LI Jiahui, TONG Hui, CHEN Manjia, LIU Chengshuai, JIANG Qi, YI Xiu. Formation of Fe(Ⅲ) Minerals by Microaerophilic Fe(Ⅱ)-oxidizing Bacteria and Its Effect on Immobilization of Heavy Metals: A Review [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(2): 310-320. |
| [9] | MA Zhiwei, ZHANG Congzhi, ZHAO Zhanhui, WU Qicong, ZHAO Jinhua, CHEN Zhuo, LI Jingwang, ZHANG Nan, XUE Ya, WANG Yaru, LU Yunxuan, ZHANG Jiabao. Research Progress on Soil Health Cultivation Based on Woody Peat [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(12): 1964-1977. |
| [10] | TANG Shuya, WANG Chunhui, SONG Jing, LI Gang. Characteristics and Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution in the Xiangshan Bay Area [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(11): 1768-1781. |
| [11] | YANG Zhengqiao, ZOU Qi, WEI Hang, ZHOU Kai, CHEN Zhiliang. Research Progress on the Adaptation and Regulation Mechanism of Micro-organisms in Metal Tailings [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(1): 156-166. |
| [12] | WANG Ning, LIU Xiaodong, GAN Xianhua, SU Yuqiao, WU Guozhang, HUANG Fangfang, ZHANG Weiqiang. Water Quality Effect in Precipitation by Typical Forests in Subtropical Region of China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(8): 1365-1375. |
| [13] | LIU Bingyu, WANG Yipei, YAO Zuofang, YANG Gairen, XU Xiaonan, DENG Yusong, HUANG Yuhan. Risk Assessment and Safe Consumption Analysis of Heavy Metals under Different Planting Patterns of Biogas Slurry [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(8): 1507-1515. |
| [14] | LI Zhenguo, HAO Xingyu, HE Tianlian, JING Rui, RONG Cheng, GU Chengzhen, ZHENG Xinyu. Study on the Alleviating Effect of Bamboo Vinegar on Cadmium Toxicity of Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt. [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(7): 1313-1324. |
| [15] | DU Dandan, GAO Ruizhong, FANG Lijing, XIE Longmei. Spatial Variation of Soil Heavy Metals and Their Responses to Physicochemical Factors of Salt Lake Basin in Arid Area [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(6): 1123-1132. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
