Ecology and Environment ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (10): 1600-1611.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.10.012
• Research Article [Environmental Science] • Previous Articles Next Articles
HU Yunfei1( ), TAO Liang2,*(
), TAO Liang2,*( ), LUO Yiwen1
), LUO Yiwen1
Received:2024-07-12
Online:2024-10-18
Published:2024-11-15
Contact:
TAO Liang
通讯作者:
陶亮
作者简介:胡韵菲(1990年生),女,助理研究员,博士,研究方向为农业区域发展。E-mail: huyunfei2015@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
HU Yunfei, TAO Liang, LUO Yiwen. The Influencing Factors and Spatial Pattern Evolution of the Potential for Green Agricultural Development in Guangdong Province[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(10): 1600-1611.
胡韵菲, 陶亮, 罗旖文. 广东省农业绿色发展潜力影响因素及空间格局演变[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(10): 1600-1611.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.10.012
| 目标层 | 准则层- 代码 | 指标层 | 权重 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 农业生产水平 | 农业物质装备水平-fac_l (0.28) | 耕种收综合机械化率/% | 0.04 |
| 农机总动力/(10000 kW∙h) | 0.05 | ||
| 有效灌溉指数 1) | 0.04 | ||
| 节水灌溉指数 2) | 0.03 | ||
| 人均农林牧渔业固定资产投资/万元 | 0.06 | ||
| 每公顷农作物播种固定资产投资/万元 | 0.06 | ||
| 农业生产效率- prod_e (0.38) | 农村居民人均农林牧渔业产值/万元 | 0.10 | |
| 每公顷农地产值指数/万元3) | 0.08 | ||
| 粮食单产/(kg∙hm−2) | 0.04 | ||
| 农民人均农业经营收入贡献指数 4) | 0.08 | ||
| 第一产业从业人员占常住人口比重/% | 0.02 | ||
| 农民人均纯收入/元 | 0.06 | ||
| 农产品供给能力- supl_c (0.34) | 人均粮食产量/kg | 0.08 | |
| 人均猪牛羊肉产量/t | 0.06 | ||
| 人均牛奶产量/kg | 0.05 | ||
| 人均蔬菜产量/kg | 0.07 | ||
| 人均水产产量/kg | 0.05 | ||
| 人均油料产量/kg | 0.03 | ||
| 农业资源环境保障度 | 农业资源 保障度- resc_g (0.31) | 耕地保有率 5) | 0.09 |
| 人均水资源/m3 | 0.05 | ||
| 农业用水保障度/(105 m3∙hm−2) | 0.06 | ||
| 人均耕地面积/(1000 m2) | 0.07 | ||
| 农业减灾指数 6) | 0.04 | ||
| 农业资源使用效率- reuti_e (0.38) | 化肥使用经济效率/(104 yuan ∙t−1) 7) | 0.09 | |
| 农业用水经济效率/(yuan∙m−3) 8) | 0.08 | ||
| 农业加工指数 9) | 0.08 | ||
| 人均经营面积/(667 m2) | 0.08 | ||
| 农村用电经济效率/(yuan∙kW∙h−1) 10) | 0.05 | ||
| 农业生态环境-eco_e (0.31) | 总氮减排指数/(hm2∙t−1) 11) | 0.06 | |
| 总磷减排指数/(hm2∙t−1) | 0.06 | ||
| 复合肥减施指数/(hm2∙t−1) | 0.07 | ||
| 农药控制指数/(hm2∙t−1) | 0.07 | ||
| 农膜污染减排指数/(hm2∙t−1) | 0.05 |
Table 1 Evaluation indicators of agricultural production level and agricultural resource and environmental protection degree in Guangdong Province
| 目标层 | 准则层- 代码 | 指标层 | 权重 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 农业生产水平 | 农业物质装备水平-fac_l (0.28) | 耕种收综合机械化率/% | 0.04 |
| 农机总动力/(10000 kW∙h) | 0.05 | ||
| 有效灌溉指数 1) | 0.04 | ||
| 节水灌溉指数 2) | 0.03 | ||
| 人均农林牧渔业固定资产投资/万元 | 0.06 | ||
| 每公顷农作物播种固定资产投资/万元 | 0.06 | ||
| 农业生产效率- prod_e (0.38) | 农村居民人均农林牧渔业产值/万元 | 0.10 | |
| 每公顷农地产值指数/万元3) | 0.08 | ||
| 粮食单产/(kg∙hm−2) | 0.04 | ||
| 农民人均农业经营收入贡献指数 4) | 0.08 | ||
| 第一产业从业人员占常住人口比重/% | 0.02 | ||
| 农民人均纯收入/元 | 0.06 | ||
| 农产品供给能力- supl_c (0.34) | 人均粮食产量/kg | 0.08 | |
| 人均猪牛羊肉产量/t | 0.06 | ||
| 人均牛奶产量/kg | 0.05 | ||
| 人均蔬菜产量/kg | 0.07 | ||
| 人均水产产量/kg | 0.05 | ||
| 人均油料产量/kg | 0.03 | ||
| 农业资源环境保障度 | 农业资源 保障度- resc_g (0.31) | 耕地保有率 5) | 0.09 |
| 人均水资源/m3 | 0.05 | ||
| 农业用水保障度/(105 m3∙hm−2) | 0.06 | ||
| 人均耕地面积/(1000 m2) | 0.07 | ||
| 农业减灾指数 6) | 0.04 | ||
| 农业资源使用效率- reuti_e (0.38) | 化肥使用经济效率/(104 yuan ∙t−1) 7) | 0.09 | |
| 农业用水经济效率/(yuan∙m−3) 8) | 0.08 | ||
| 农业加工指数 9) | 0.08 | ||
| 人均经营面积/(667 m2) | 0.08 | ||
| 农村用电经济效率/(yuan∙kW∙h−1) 10) | 0.05 | ||
| 农业生态环境-eco_e (0.31) | 总氮减排指数/(hm2∙t−1) 11) | 0.06 | |
| 总磷减排指数/(hm2∙t−1) | 0.06 | ||
| 复合肥减施指数/(hm2∙t−1) | 0.07 | ||
| 农药控制指数/(hm2∙t−1) | 0.07 | ||
| 农膜污染减排指数/(hm2∙t−1) | 0.05 |
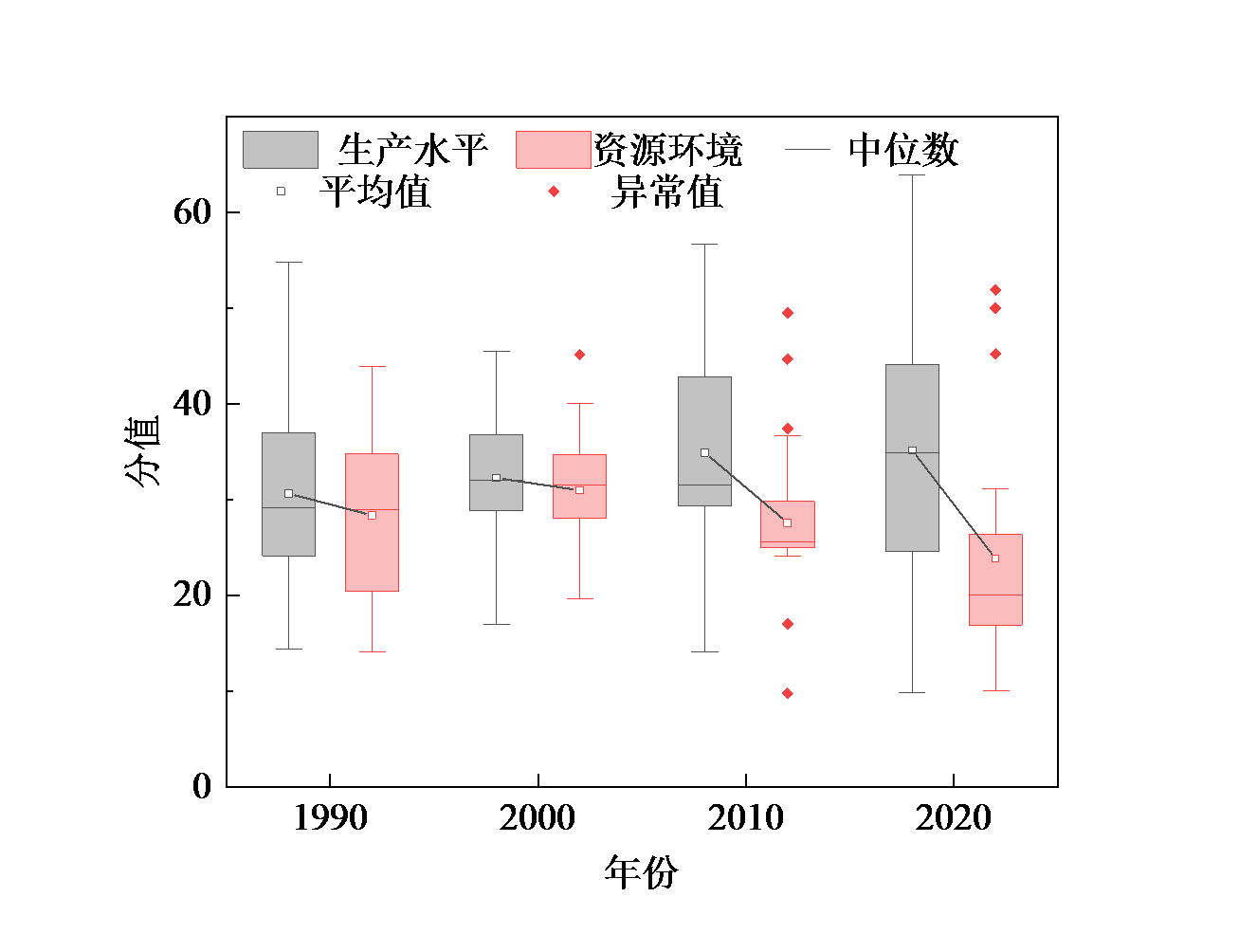
Figure 2 Box plot of agricultural production level and agricultural resource and environmental protection degree grouping in Guangdong Province in different years
| 变量 | facl_l | prod_e | supl_c | resc_g | ru_e | eco_e | P_gda |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| faci_l | 1 | ||||||
| prod_e | 0.21*3) | 1 | |||||
| supl_c | 0.174 | 0.655 | 1 | ||||
| resc_g | −0.088 | 0.1 | 0.355***1) | 1 | |||
| ru_e | −0.102 | −0.03 | −0.31*** | 0.006 | 1 | ||
| eco_e | −0.204* | −0.154 | 0.246** 2) | 0.364*** | 0.131 | 1 | |
| P_gda | −0.411*** | −0.497*** | −0.485*** | 0.185* | 0.586*** | 0.463*** | 1 |
Table 2 Correlation coefficient analysis
| 变量 | facl_l | prod_e | supl_c | resc_g | ru_e | eco_e | P_gda |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| faci_l | 1 | ||||||
| prod_e | 0.21*3) | 1 | |||||
| supl_c | 0.174 | 0.655 | 1 | ||||
| resc_g | −0.088 | 0.1 | 0.355***1) | 1 | |||
| ru_e | −0.102 | −0.03 | −0.31*** | 0.006 | 1 | ||
| eco_e | −0.204* | −0.154 | 0.246** 2) | 0.364*** | 0.131 | 1 | |
| P_gda | −0.411*** | −0.497*** | −0.485*** | 0.185* | 0.586*** | 0.463*** | 1 |
| 变量 | VIF | 1/VIF |
|---|---|---|
| faci_l | 1.115 | 0.897 |
| prod_e | 2.547 | 0.393 |
| supl_c | 3.305 | 0.303 |
| resc_g | 1.291 | 0.775 |
| ru_e | 1.380 | 0.725 |
| eco_e | 1.644 | 0.608 |
| Mean | 1.880 | 0.617 |
Table 3 Multicollinearity test
| 变量 | VIF | 1/VIF |
|---|---|---|
| faci_l | 1.115 | 0.897 |
| prod_e | 2.547 | 0.393 |
| supl_c | 3.305 | 0.303 |
| resc_g | 1.291 | 0.775 |
| ru_e | 1.380 | 0.725 |
| eco_e | 1.644 | 0.608 |
| Mean | 1.880 | 0.617 |
| 变量 | POOL模型 | FE模型 | RE模型 | 时间固定效应 | 双向固定效应 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| faci_l | −0.036* 3) (−1.991) | −0.046 (−1.287) | −0.036* (−1.991) | −0.043** (−2.524) | −0.054** (−2.040) |
| prod_e | −0.023** (−2.008) | −0.033** (−2.452) | −0.023** 2) (−2.008) | −0.032** (−2.582) | −0.085*** (−2.712) |
| supl_c | −0.047*** 1) (−4.041) | −0.042*** (−2.748) | −0.047*** (−4.041) | −0.039*** (−3.827) | −0.004 (−0.167) |
| resc_g | 0.037*** (6.379) | 0.036*** (4.849) | 0.037*** (6.379) | 0.039*** (3.970) | 0.059*** (3.893) |
| ru_e | 0.053*** (5.506) | 0.036*** (2.741) | 0.053*** (5.506) | 0.061*** (4.317) | 0.044*** (3.673) |
| eco_e | 0.050*** (4.629) | 0.056*** (4.203) | 0.050*** (4.629) | 0.049*** (5.325) | 0.068*** (5.203) |
| r2 | 0.779 | 0.752 | 0.779 | 0.772 | 0.540 |
| r2 (within) | 0.704 | 0.718 | 0.704 | 0.701 | 0.628 |
| N | 83 | 83 | 83 | 83 | 83 |
| 检验 | F(6, 76)=30.610, p=0.000 | F(6, 56)=12.777, p=0.000 | χ2(6)=183.658, p=0.000 | F(6, 73)=40.104, p=0.000 | F(6, 53)=16.609, p=0.000 |
Table 4 Regression analysis results of five explanatory models for panel models
| 变量 | POOL模型 | FE模型 | RE模型 | 时间固定效应 | 双向固定效应 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| faci_l | −0.036* 3) (−1.991) | −0.046 (−1.287) | −0.036* (−1.991) | −0.043** (−2.524) | −0.054** (−2.040) |
| prod_e | −0.023** (−2.008) | −0.033** (−2.452) | −0.023** 2) (−2.008) | −0.032** (−2.582) | −0.085*** (−2.712) |
| supl_c | −0.047*** 1) (−4.041) | −0.042*** (−2.748) | −0.047*** (−4.041) | −0.039*** (−3.827) | −0.004 (−0.167) |
| resc_g | 0.037*** (6.379) | 0.036*** (4.849) | 0.037*** (6.379) | 0.039*** (3.970) | 0.059*** (3.893) |
| ru_e | 0.053*** (5.506) | 0.036*** (2.741) | 0.053*** (5.506) | 0.061*** (4.317) | 0.044*** (3.673) |
| eco_e | 0.050*** (4.629) | 0.056*** (4.203) | 0.050*** (4.629) | 0.049*** (5.325) | 0.068*** (5.203) |
| r2 | 0.779 | 0.752 | 0.779 | 0.772 | 0.540 |
| r2 (within) | 0.704 | 0.718 | 0.704 | 0.701 | 0.628 |
| N | 83 | 83 | 83 | 83 | 83 |
| 检验 | F(6, 76)=30.610, p=0.000 | F(6, 56)=12.777, p=0.000 | χ2(6)=183.658, p=0.000 | F(6, 73)=40.104, p=0.000 | F(6, 53)=16.609, p=0.000 |
| 检验类型 | 检验目的 | 检验值 | 检验结论 |
|---|---|---|---|
| F检验 | FE模型和POOL 模型比较选择 | F (20, 56)=0.917, p=0.569 | POOL 模型 |
| BP检验 | RE模型和POOL 模型比较选择 | χ2(1)=0.371, p=0.271 | POOL 模型 |
| Hausman 检验 | FE模型和RE 模型比较选择 | χ2(5)=2.344, p=0.800 | RE模型 |
Table 5 Comparison of panel model test results
| 检验类型 | 检验目的 | 检验值 | 检验结论 |
|---|---|---|---|
| F检验 | FE模型和POOL 模型比较选择 | F (20, 56)=0.917, p=0.569 | POOL 模型 |
| BP检验 | RE模型和POOL 模型比较选择 | χ2(1)=0.371, p=0.271 | POOL 模型 |
| Hausman 检验 | FE模型和RE 模型比较选择 | χ2(5)=2.344, p=0.800 | RE模型 |
| 变量 | 基准模型 (POOL模型) | OLS回归模型 | Robust回归模型 |
|---|---|---|---|
| faci_l | −0.036* (−1.991) | −0.036*** (−3.113) | −0.026*** (−6.497) |
| prod_e | −0.023** (−2.008) | −0.023 (−1.714) | −0.036*** (−7.464) |
| supl_c | −0.047*** (−4.041) | −0.047*** (−4.044) | −0.024*** (−5.906) |
| resc_g | 0.037*** (6.379) | 0.037*** (2.992) | 0.030*** (6.867) |
| ru_e | 0.053*** (5.506) | 0.053*** (6.133) | 0.042*** (13.851) |
| eco_e | 0.050*** (4.629) | 0.050*** (5.545) | 0.030*** (9.343) |
| r2 | 0.779 | 0.779 | 0.715 |
| r2 (within) | 0.704 | 0.761 | 0.692 |
| N | 83 | 83 | 83 |
| 检验 | F(6, 76)=30.610, p=0.000 | F(6, 76)=44.535, p=0.000 | F(6, 76)=31.770, p=0.000 |
Table 6 Robustness test
| 变量 | 基准模型 (POOL模型) | OLS回归模型 | Robust回归模型 |
|---|---|---|---|
| faci_l | −0.036* (−1.991) | −0.036*** (−3.113) | −0.026*** (−6.497) |
| prod_e | −0.023** (−2.008) | −0.023 (−1.714) | −0.036*** (−7.464) |
| supl_c | −0.047*** (−4.041) | −0.047*** (−4.044) | −0.024*** (−5.906) |
| resc_g | 0.037*** (6.379) | 0.037*** (2.992) | 0.030*** (6.867) |
| ru_e | 0.053*** (5.506) | 0.053*** (6.133) | 0.042*** (13.851) |
| eco_e | 0.050*** (4.629) | 0.050*** (5.545) | 0.030*** (9.343) |
| r2 | 0.779 | 0.779 | 0.715 |
| r2 (within) | 0.704 | 0.761 | 0.692 |
| N | 83 | 83 | 83 |
| 检验 | F(6, 76)=30.610, p=0.000 | F(6, 76)=44.535, p=0.000 | F(6, 76)=31.770, p=0.000 |
| 变量 | 广东 | 珠三角 | 粤东 | 粤西 | 粤北 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| faci_l | −0.036* (−1.991) | −0.048 (−1.855) | −0.026** (−2.539) | −0.019* (−2.213) | −0.025 (−0.954) |
| prod_e | −0.023** (−2.008) | −0.027 (−0.911) | −0.031** (−2.496) | −0.006 (−0.579) | −0.036 (−0.870) |
| supl_c | −0.047*** (−4.041) | −0.036 (−1.550) | −0.042** (−2.347) | −0.040** (−3.317) | −0.055 (−1.693) |
| resc_g | 0.037*** (6.379) | 0.045* (2.020) | 0.044** (3.033) | 0.038*** (3.878) | 0.040 (0.978) |
| ru_e | 0.053*** (5.506) | 0.062*** (3.928) | 0.030 (1.709) | 0.017* (2.249) | 0.020 (0.607) |
| eco_e | 0.050*** (4.629) | 0.059*** (2.877) | 0.044*** (4.155) | 0.021*** (4.139) | 0.048*** (3.293) |
| r2 | 0.779 | 0.766 | 0.955 | 0.976 | 0.887 |
| r2 (within) | 0.704 | 0.718 | 0.925 | 0.957 | 0.812 |
| N | 83 | 36 | 16 | 15 | 16 |
| 检验 | F(6, 76)=30.610, p=0.000 | F(6, 29)=15.831, p=0.000 | F(6, 9)=31.786, p=0.000 | F(6, 8)=53.171, p=0.000 | F(6, 9)=11.787, p=0.001 |
Table 7 Heterogeneity test
| 变量 | 广东 | 珠三角 | 粤东 | 粤西 | 粤北 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| faci_l | −0.036* (−1.991) | −0.048 (−1.855) | −0.026** (−2.539) | −0.019* (−2.213) | −0.025 (−0.954) |
| prod_e | −0.023** (−2.008) | −0.027 (−0.911) | −0.031** (−2.496) | −0.006 (−0.579) | −0.036 (−0.870) |
| supl_c | −0.047*** (−4.041) | −0.036 (−1.550) | −0.042** (−2.347) | −0.040** (−3.317) | −0.055 (−1.693) |
| resc_g | 0.037*** (6.379) | 0.045* (2.020) | 0.044** (3.033) | 0.038*** (3.878) | 0.040 (0.978) |
| ru_e | 0.053*** (5.506) | 0.062*** (3.928) | 0.030 (1.709) | 0.017* (2.249) | 0.020 (0.607) |
| eco_e | 0.050*** (4.629) | 0.059*** (2.877) | 0.044*** (4.155) | 0.021*** (4.139) | 0.048*** (3.293) |
| r2 | 0.779 | 0.766 | 0.955 | 0.976 | 0.887 |
| r2 (within) | 0.704 | 0.718 | 0.925 | 0.957 | 0.812 |
| N | 83 | 36 | 16 | 15 | 16 |
| 检验 | F(6, 76)=30.610, p=0.000 | F(6, 29)=15.831, p=0.000 | F(6, 9)=31.786, p=0.000 | F(6, 8)=53.171, p=0.000 | F(6, 9)=11.787, p=0.001 |
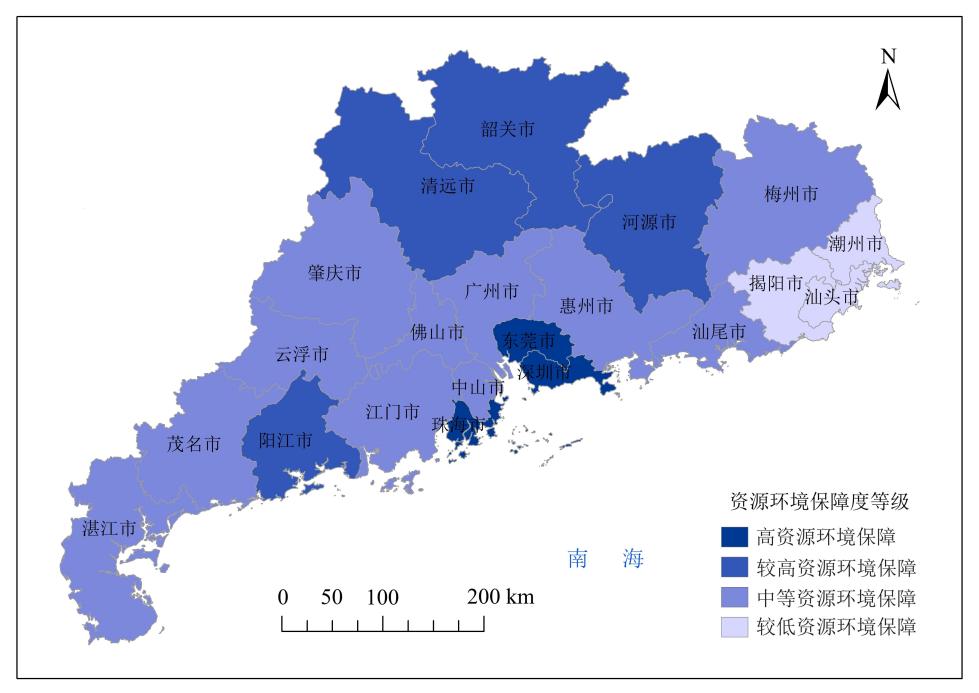
Figure5 Spatiotemporal clustering pattern of agricultural resource and environmental protection degree in prefecture level cities in Guangdong Province from 1990 to 2020
| [1] | VERGAMINI D, OLIVIERI M, ANDREOLI M, et al., 2024. Simulating policy mixes to reduce soil erosion and land abandonment in marginal areas: A case study from the Liguria Region (Italy)[J]. Land Use Policy, 143: 107188. |
| [2] | HAZRANA J, MISHRA A K, 2024. Effect of input subsidies and extension services: Evidence from rice productivity in Bangladesh[J]. Food Policy, 125: 102628. |
| [3] | KARNER K, MITTER H, SINABELL F, et al., 2024. Participatory development of Shared Socioeconomic Pathways for Austria’s agriculture and food systems[J]. Land Use Policy, 142: 107183. |
| [4] | PETTIGREW S, BOOTH L, FARRAR V, et al., 2024. An emerging food policy domain: The effects of autonomous transport technologies on food access and consumption[J]. Food Policy, 125: 102647. |
| [5] |
常谕, 孙业红, 杨海龙, 等, 2023. 农户视角下农业文化遗产地生态产品的旅游价值实现路径——以广东潮州单丛茶文化系统为例[J]. 资源科学, 45(2): 428-440.
DOI |
|
CHANG Y, SUN H Y, YANG H L, et al., 2023. Value realization paths of ecological products through tourism in agricultural heritage sites from the perspective of farmers: An example of the Dancong tea culture system in Chaozhou City[J]. Resources Science, 45(2): 428-440.
DOI |
|
| [6] | 陈婕, 2021. 农业机械化对广东潮州市农业发展的促进作用[J]. 农业工程技术, 41(5): 48-49. |
| CHEN J, 2021. The Promoting Effect of Agricultural Mechanization on Agricultural Development in Chaozhou City, Guangdong Province[J]. Agricultural Engineering Technology, 41(5): 48-49. | |
| [7] | 崔晓菁, 白蕾, 杨潇, 2022. 海岸线 “占补平衡” 实践工作的思考[J]. 自然资源情报 (6): 8-12. |
| CUI X J, BAI L, YANG X, 2022. Thoughts on the practice of coastline “Requisition-Compensation Balance”[J]. Natural Resources Information (6): 8-12. | |
| [8] | 付晶园, 王苍平, 金亚亚, 等, 2023. 甘肃省碳排放影响因素分析[J]. 中国资源综合利用, 41(12): 235-238. |
| FU J Y, WANG C P, JIN Y Y, et al., 2023. Analysis of factors influencing carbon emissions in Gansu Province[J]. China Resources Comprehensive Utilization, 41(12): 235-238. | |
| [9] | 顾晟景, 周宏, 2022. 生产性服务业对农业全要素生产率的影响研究——基于中介效应的影响路径分析[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 43(3): 106-116. |
| GU C J, ZHOU H, 2023. Study on the influence of producer services on agricultural total factor productivity: Analysis of the influence path based on mediating effect[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 43(3): 106-116. | |
| [10] | 管宁宁, 柳凌韵, 黄惠春, 2024. 农业产业链发展提高农业生产效率了吗?——基于服务视角的再考察[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 38(7): 13-21. |
| GUAN N N, LIU L Y, HUANG H C, 2024. Does the development of agricultural industry chain in improve agricultural production efficiency?: A perspective from production service[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 38(7): 13-21. | |
| [11] | 广东统计年鉴, 2023. 自然地理|气候[EB/OL]. 广东省情网, 2024-03-04. https://dfz.gd.gov.cn/sqyl/jbsq/content/post_4384863.html. |
| Guangdong Statistical Yearbook, 2023. Natural Geography|Climate[EB/OL]. Guangdong Province, Situation in Guangdong Province (dfz.gd.gov.cn), 2024-03-04. https://dfz.gd.gov.cn/sqyl/jbsq/content/post_4384863.html. | |
| [12] | 黄文庆, 2023. 广东省农业碳排放效率时空差异及驱动机制研究[D]. 长沙: 中南林业科技大学: 28-31. |
| HUANG W Q, 2023. A study of agricultural carbon emission efficiency and its determinants in Guangdong Province[D]. Changsha: Central South University of Forest and Technology: 28-31. | |
| [13] | 黎颂雯, 陈泽凯, 张晓露, 等, 2024. 农村人口老龄化对农业发展影响的实证分析——以广东省为例[J]. 中国市场 (11): 16-20. |
| LI S W, CHEN Z K, ZHANG X L, et al., 2024. Empirical analysis of the impact of rural population aging on agricultural development: A case study of Guangdong Province[J]. China Market (11): 16-20. | |
| [14] | 李靖, 张正尧, 毛翔飞, 等, 2016. 我国农业生产力布局评价及优化建议——基于资源环境承载力的分析[J]. 农业经济问题, 37(3): 26-33, 110. |
| LI J, ZHANG Z R, MAO X F, et al., 2016. Evaluation and optimization suggestions for the layout of agricultural productivity in China: Analysis based on resource and environmental carrying capacity[J]. Issues in Agricultural Economy, 37(3): 26-33, 110. | |
| [15] | 李姣, 李朗, 李科, 2022. 隐含水污染视角下的中国省际农业生态补偿标准研究[J]. 农业经济问题 (6): 106-121. |
| LI J, LI L, LI K, 2022. Inter-provincial agricultural ecological compensation standards in China from the perspective of embodied water pollution[J]. Issues in Agricultural Economy (6): 106-121. | |
| [16] | 李垚, 赵林, 宋小语, 等, 2024. 降碳减污视角下山东省农业绿色发展效率的时空格局与影响因素分析[J]. 地理与地理信息科学, 40(3): 104-112. |
| LI Y, ZHAO L, SONG X Y, et al., 2024. Spatio-temporal pattern and influencing factors of agricultural green development efficiency in Shandong Province under the perspective of reduction of pollution and carbon emissions[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 40(3): 104-112. | |
| [17] | 刘黎霞, 2023. 全国生态日从工业巨人到绿美样板, 广东的生态文明跨越发展之路[EB/OL]. [2024-06-05]. https://www.21jingji.com/article/20230815/herald/849a96029043e18ea02d60260e5a3d7a.html. |
| LIU L X, 2023. National ecological day: From an industrial giant to a green and beautiful model, Guangdong's ecological civilization leaps across the development road[EB/OL]. [2024-06-05]. https://www.21jingji.com/article/20230815/herald/849a96029043e18ea02d60260e5a3d7a.html. | |
| [18] | 刘姗, 赵胜, 栾雁宁, 等, 2022. 基于 “五感体验” 的生态农业型主题游乐空间创意实践——以深圳欢乐田园追光农场乐园为例[J]. 西部旅游 (21): 44-47. |
| LIU S, ZHAO S, LUAN Y N, et al., 2022. Creative practice of ecological agriculture themed amusement space based on “five senses experience”: Taking Shenzhen Happy Countryside Chasing Light Farm park as an example[J]. Western Travel (21): 44-47. | |
| [19] | 罗坤莉, 2023. 广东省水污染防治发展状况分析[J]. 中国资源综合利用, 41(12): 258-260. |
| LUO K L, 2023. Analysis on the development status of water pollution prevention and control in Guangdong Province[J]. China Resources Comprehensive Utilization, 41(12): 258-260. | |
| [20] | 漆雁斌, 韩绍䶮, 邓鑫, 2020. 中国绿色农业发展: 生产水平测度、空间差异及收敛性分析[J]. 农业技术经济 (4): 51-65. |
| QI Y B, HAN S Y, DENG X, 2020. Measurement, regional spatial difference and convergence analysis measurement, regional spatial difference and convergence analysis[J]. Journal of Agrotechnical Economics (4): 51-65. | |
| [21] | 佘晓芫, 2024. 广东农垦农业现代化路径探究[J]. 中国农垦 (1): 47-51. |
| SHE X Y, 2024. Exploration of the modernization path of Guangdong agricultural reclamation[J]. China State Farm (1): 47-51. | |
| [22] | 孙大元, 胡学应, 朱明鲲, 等, 2023. 智力支撑广东农业面源污染治理: 模式创建、实践成效与展望[J]. 农业研究与应用, 36(5): 88-95. |
| SUN D Y, HU X Y, ZHU M K, et al., 2023. Intellectual support model in Guangdong agricultural non-point source pollution control: model creation, practical results and prospects[J]. Agricultural Research and Application, 36(5): 88-95. | |
| [23] | 孙进, 刘启强, 2020. 以科技赋能农业聚产业振兴乡村——专访广州艾米生态人工智能农业有限公司[J]. 广东科技, 29(10): 32-35. |
| SUN J, LIU Q Q, 2020. Empowering agriculture, gathering industries, and revitalizing rural areas with technology: Interview with Guangzhou Amy Ecological Artificial Intelligence Agriculture Co., Ltd[J]. Guangdong Science & Technology, 29(10): 32-35. | |
| [24] | 孙眉, 赵博文, 2024. 跨“粤”向新再升级[N]. 农民日报, 2024-05-21(001). |
| SUN M, ZHAO B W, 2024. Cross Guangdong to new and further upgrade[N]. Farmers Daily, 2024-05-21(001). | |
| [25] | 唐柳雯, 陈颖, 黎华联, 等, 2023. 一江春水向岭南千帆竞发海天阔——全国性金融机构为广东高质量发展谱写共赢新篇章[N]. 南方日报, 2023-04-26(T02). |
| TANG L W, CHEN Y, LI H L, et al., 2023. A river of spring water flows towards Lingnan, with thousands of sails competing on the vast sea and sky: National financial institutions compose a win win new chapter for Guangdong’s high quality development[N]. Nan Fang Daily, 2023-04-26(T02). | |
| [26] | 王华, 陈慧华, 唐力生, 等, 2018. 气候变暖背景下广东冬种生产季气候资源和气象灾害的时空变化[J]. 应用生态学报, 29(1): 93-102. |
| WANG H, CHEN H H, TANG L S, et al., 2018. Temporal and spatial change of climate resources and meteorological disasters under climate change during winter crop growing season in Guangdong Province, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 29(1): 93-102. | |
| [27] | 习近平, 2024. 发展新质生产力是推动高质量发展的内在要求和重要着力点[J]. 创造, 32(6): 1-3. |
| XI J P, 2024. Developing new quality productive forces is an inherent requirement and important focus for promoting high-quality development[J]. Creation, 32(6): 1-3. | |
| [28] | 夏苒若, 2023. 民族地区气候资源价值评估探究——以广东连南瑶族自治县为例[J]. 环境与发展, 35(1): 33-43. |
| XIA R R, 2023. Study on the valuation of climate resources in ethnic regions: A case study of Liannan Yao Autonomous County in Guangdong Province[J]. Environment and Development, 35(1): 33-43. | |
| [29] | 幸红, 林鹏程, 2018. 刍议广东政府土壤污染修复治理现状与对策[J]. 江西理工大学学报, 39(4): 24-32. |
| XING H, LIN P C, 2018. On the current situation and countermeasures of soil pollution remediation and management by the Guangdong government[J]. Journal of Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, 39(4): 24-32. | |
| [30] | 闫丽君, 2016. 基于熵值法的广东农业可持续发展评价研究[J]. 农村经济与科技, 27(15): 150-151, 164. |
| YAN L J, 2016. Research on the evaluation of Guangdong agricultural sustainable development based on entropy method[J]. Rural Economy and Science-Technology, 27(15): 150-151, 164. | |
| [31] |
姚小英, 王劲松, 王莺, 等, 2015. 广东近40年气候变化特征及对农业的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 31(26): 222-228.
DOI |
|
YAO X Y, WANG J S, WANG Y, et al., 2015. Climate changing feature in recent 40 years in Guangdong and its impact on agriculture[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 31(26): 222-228.
DOI |
|
| [32] | 尤飞, 王秀芬, 2013. 中国区域农业现代化综合评价报告[M]. 北京: 中国农业科学出版社: 47-50. |
| YOU F, WANG X F, 2013. Comprehensive evaluation report on regional agricultural modernization in China[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science Press: 47-50. | |
| [33] | 张保亮, 2022. 广州乡村地区农业生态景观评价与指引研究[J]. 智能城市, 8(5): 72-74. |
| ZHANG B L, 2022. Research on evaluation and guidance of agricultural ecological landscape in rural areas of Guangzhou[J]. Intelligent City, 8(5): 72-74. | |
| [34] | 张清津, 2024. 农业服务业发展: 路径与趋势[J]. 中国农村经济 (5): 62-80. |
| ZHANG Q J, 2024. Development of agricultural service industry: Paths and trends[J]. Chinese Rural Economy (5): 62-80. | |
| [35] | 赵文珺, 刘丽红, 2023. 山西省农业生态经济系统协调发展及障碍因子分析[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 44(10): 179-190. |
| ZHAO W J, LIU L H, 2023. Analysis on the coordinated development and obstacle factors of agricultural eco-economic system in Shanxi Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 44(10): 179-190. | |
| [36] | 衷海燕, 林资龙, 黄耿, 等, 2020. 珠江三角洲传统农业景观变迁及其空间转移[J]. 农业考古 (6): 207-214. |
| ZHONG H Y, LIN Z L, HUANG G, et al., 2020. Changes and spatial transfer of traditional agricultural landscape in the Pearl River Delta[J]. Agricultural Archaeology (6): 207-214. | |
| [37] | 周展, 2024. “嵌入式干预”: 县域特色农业发展中的政府行为研究——基于山西省X县西瓜产业的案例分析[J/OL]. 农业经济问题, 1-14 [2024-05-30]. https://doi.org/10.13246/j.cnki.iae.20240515.001. |
| ZHOU Z, 2024. Embedded intervention: research in the development of county: Level characteristic agriculture based on the case analysis of watermelon industry in X county of Shanxi Province[J/OL]. Issues in Agricultural Economy, 1-14 [2024-05-30]. https://doi.org/10.13246/j.cnki.iae.20240515.001. |
| [1] | ZHANG Weichen, WANG Xingqi, WANG Bojie. Spatiotemporal Pattern and Influencing Factors of the Ecosystem Services in the Tabu River Basin [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(7): 1142-1152. |
| [2] | YAO Fulong, HUANG Jian, YAN Junjie, LIU Haijun, TANG Guoqian. The Assemblages of Surface Pollen and Their Ecological Significance from Major Meadow Communities Along the North Slope of Tianshan [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(7): 1350-1359. |
| [3] | XIANG Hengxing, ZHANG Jian, WANG Zongming, MAO Dehua. Relationships between Supply and Demand of Ecosystem Services in the Songnen Plain [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(8): 1769-1776. |
| [4] | YUAN Jie, ZHAO Yanqiang. Trends in Research on Wetland Restoration based on Web of Science Database [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(7): 1541-1548. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
