Ecology and Environment ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (1): 89-99.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.01.011
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
FU Chuanbo1,3( ), DAN Li2,*(
), DAN Li2,*( ), LIU Lijun1,3, TONG Jinhe1,3
), LIU Lijun1,3, TONG Jinhe1,3
Received:2021-07-06
Online:2022-01-18
Published:2022-03-10
Contact:
DAN Li
符传博1,3( ), 丹利2,*(
), 丹利2,*( ), 刘丽君1,3, 佟金鹤1,3
), 刘丽君1,3, 佟金鹤1,3
通讯作者:
丹利
作者简介:符传博(1985年生),男,正高级工程师,主要从事大气环境与气候模拟的研究。E-mail: hnfuchuanbo@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
FU Chuanbo, DAN Li, LIU Lijun, TONG Jinhe. Characteristics of A Typical Ozone Pollution Event and Its Meteorological Reason in Sanya City in Autumn 2019[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(1): 89-99.
符传博, 丹利, 刘丽君, 佟金鹤. 2019年秋季三亚市一次典型臭氧污染个例气象成因解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 89-99.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.01.011
| 日期 Date | AQI | PM2.5/ (μg∙m-3) | PM10/ (μg∙m-3) | SO2/ (μg∙m-3) | NO2/ (μg∙m-3) | O3-8 h/ (μg∙m-3) | O3-1 h/ (μg∙m-3) | CO/ (mg∙m-3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 26 | 6 | 14 | 4 | 5 | 52 | 59 | 0.4 |
| 2 | 37 | 12 | 29 | 4 | 4 | 74 | 79 | 0.4 |
| 3 | 67 | 20 | 39 | 4 | 13 | 120 | 136 | 0.4 |
| 4 | 102 | 46 | 76 | 7 | 20 | 162 | 185 | 0.7 |
| 5 | 119 | 40 | 71 | 7 | 16 | 180 | 203 | 0.6 |
| 6 | 82 | 36 | 62 | 6 | 14 | 141 | 144 | 0.6 |
Table 1 Comparison of AQI and air pollutant concentration in Sanya City from November 1-6, 2019
| 日期 Date | AQI | PM2.5/ (μg∙m-3) | PM10/ (μg∙m-3) | SO2/ (μg∙m-3) | NO2/ (μg∙m-3) | O3-8 h/ (μg∙m-3) | O3-1 h/ (μg∙m-3) | CO/ (mg∙m-3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 26 | 6 | 14 | 4 | 5 | 52 | 59 | 0.4 |
| 2 | 37 | 12 | 29 | 4 | 4 | 74 | 79 | 0.4 |
| 3 | 67 | 20 | 39 | 4 | 13 | 120 | 136 | 0.4 |
| 4 | 102 | 46 | 76 | 7 | 20 | 162 | 185 | 0.7 |
| 5 | 119 | 40 | 71 | 7 | 16 | 180 | 203 | 0.6 |
| 6 | 82 | 36 | 62 | 6 | 14 | 141 | 144 | 0.6 |
| 日期 Date | 日降水量 Daily precipitation/ mm | 平均气温 Average temperature/ ℃ | 相对湿度 Relative humidity/ % | 平均风速 Average wind speed/ (m∙s-1) | 平均气压 Average pressure/ hPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 105.8 | 22.7 | 100 | 6.2 | 965.0 |
| 2 | 3.9 | 23.3 | 90 | 8.5 | 964.8 |
| 3 | 0.0 | 23.1 | 81 | 4.9 | 964.9 |
| 4 | 0.0 | 23.1 | 78 | 5.5 | 965.3 |
| 5 | 0.0 | 22.3 | 72 | 4.0 | 964.5 |
| 6 | 0.0 | 21.6 | 79 | 4.0 | 962.9 |
Table 2 Comparison of meteorological factors in Sanya City from November 1-6, 2019
| 日期 Date | 日降水量 Daily precipitation/ mm | 平均气温 Average temperature/ ℃ | 相对湿度 Relative humidity/ % | 平均风速 Average wind speed/ (m∙s-1) | 平均气压 Average pressure/ hPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 105.8 | 22.7 | 100 | 6.2 | 965.0 |
| 2 | 3.9 | 23.3 | 90 | 8.5 | 964.8 |
| 3 | 0.0 | 23.1 | 81 | 4.9 | 964.9 |
| 4 | 0.0 | 23.1 | 78 | 5.5 | 965.3 |
| 5 | 0.0 | 22.3 | 72 | 4.0 | 964.5 |
| 6 | 0.0 | 21.6 | 79 | 4.0 | 962.9 |
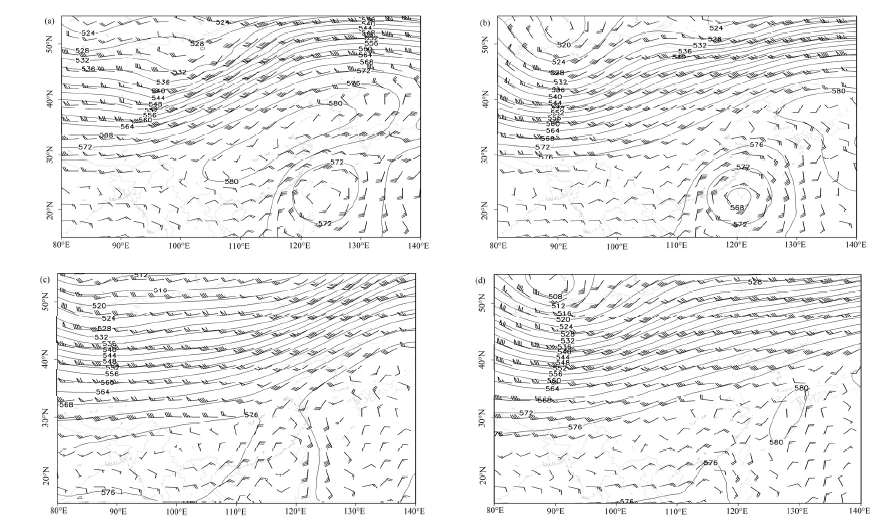
Figure 3 500 hPa geopotential height and wind fields in early November 2019 (a) Nov., 1, (b) Nov., 2, (c) Nov., 4, (d) Nov., 5 of geopotential height (black contours, 100 dagpm) and wind speed (m∙s-1)

Figure 6 Distribution of 950 hPa wind field, air temperature and vertical velocity fields in early November 2019 (a) Nov., 1 at 14:00, (b) Nov., 2 at 14:00, (c) Nov., 4 at 14:00, (d) Nov., 5 at 14:00 of wind field, air temperature and vertical speed. Positive numbers represent vertical downward movement, negative numbers represent vertical upward movement
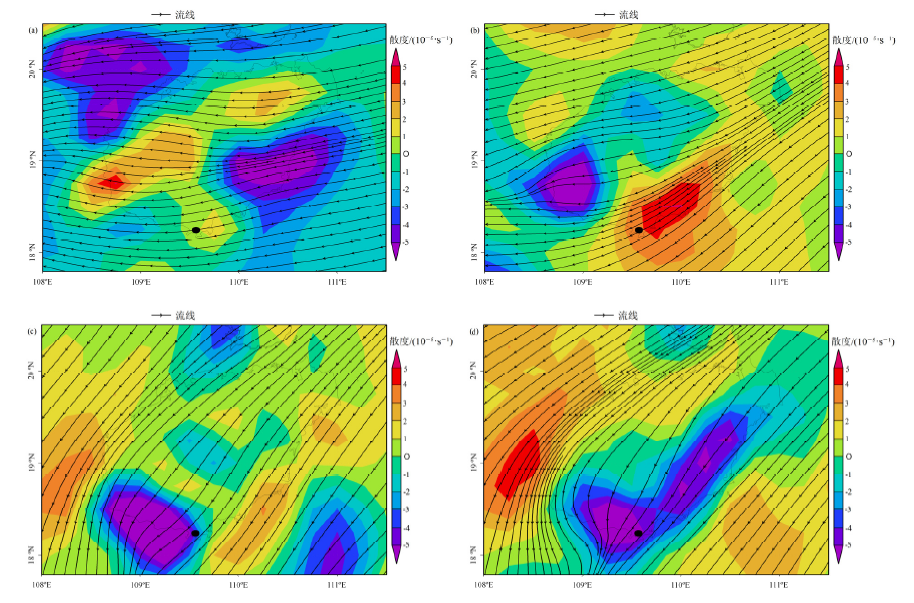
Figure 7 Distribution of 950 hPa divergence and flow fields in early November 2019 (a) Nov., 1 at 14:00, (b) Nov., 2 at 14:00, (c) Nov., 4 at 14:00, (d) Nov., 5 at 14:00 of divergence and streamline. Positive numbers represent horizontal divergence, negative numbers represent horizontal convergence
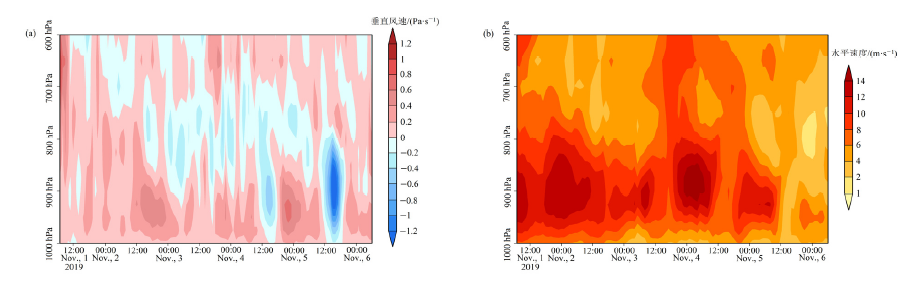
Figure 8 Distribution of vertical wind and horizontal velocity at different levels in Sanya in early November 2019 Positive numbers of vertical wind represent vertical downward movement, and negative numbers represent vertical upward movement
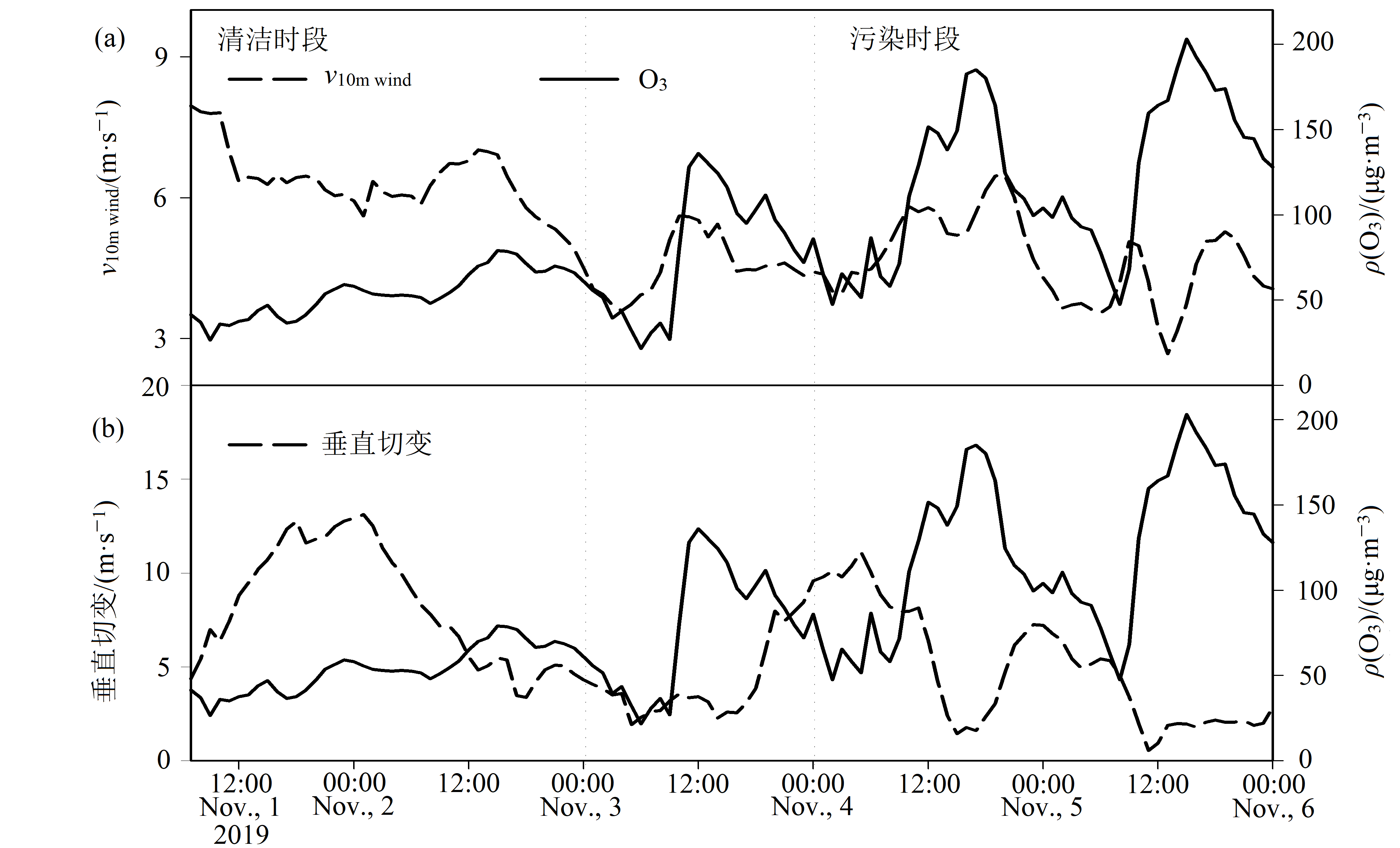
Figure 10 Hourly change of 10m wind speed and 500hPa and 850hPa horizontal wind vertical shear at different levels in Sanya in early November 2019 (a) wind speed, (b) horizontal wind vertical shear
| [1] |
ANENERG S C, HOROWITZ L W, TONG D Q, et al., 2010. An estimate of the global burden of anthropogenic ozone and fine particulate matter on premature human mortality using atmospheric modeling[J]. Environmental Health Perspectives, 118(9): 1189-1195.
DOI URL |
| [2] | CROZE M, ZIMMER L, LEE H, 2018. Ozone atmospheric pollution and alzheimer’s disease: from epidemiological facts to molecular mechanisms[J]. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 62(2): 503-522. |
| [3] |
FU Y, LIAO H, YANG Y, et al., 2019. Interannual and decadal changes in tropospheric ozone in China and the associated chemistry–climate interactions: A review[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 36(9): 975-993.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
FUHRER J, 2009. Ozone Risk for Crops and Pastures in Present and Future Climates[J]. Die Naturwissenschaften, 96(2): 173-94.
DOI URL |
| [5] | LI M, ZHANG Q, ZHENG B, et al., 2019. Persistent growth of anthropogenic non-Methane volatile organic compound (NMVOC) emissions in China during 1990-2017: Drivers, speciation and ozone formation potential[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 19(13): 8897-8913. |
| [6] |
LIU H, LIU S, XUE B R, et al., 2018. Ground-level ozone pollution and its health impacts in China[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 173: 223-230.
DOI URL |
| [7] | 程麟钧, 王帅, 宫正宇, 等, 2017. 中国臭氧浓度的时空变化特征及分区[J]. 中国环境科学, 37(11): 4003-4012. |
| CHENG L J, WANG S, GONG Z Y, et al., 2017. Spatial and seasonal variation and regionalization of ozone concentrations in China[J]. China Environmental Science, 37(11): 4003-4012. | |
| [8] | 程麟钧, 2018. 我国臭氧污染特征及分区管理方法研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学. |
| CHENG L J., 2018. A study on the evolution of ozone pollution in China and regional management methods[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences. | |
| [9] | 冯兆忠, 李品, 袁相洋, 等, 2018. 我国地表臭氧生态环境效应研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 38(5): 1530-1541. |
| FENG Z Z, LI P, YUAN X Y, et al., 2018. Progress in ecological and environmental effects of ground-level O3 in China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(5): 1530-1541. | |
| [10] | 符传博, 唐家翔, 丹利, 等, 2016. 2014年海口市大气污染物演变特征及典型污染个例分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 36(6): 2160-2169. |
| FU C B, TANG J X, DAN L, et al., 2016. Evolution of ambient air quality and case study of an air pollution event in 2014 over Haikou, China[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 36(6): 2160-2169. | |
| [11] | 符传博, 丹利, 徐文帅, 等, 2020a. 2014-2019年三亚市臭氧浓度变化特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(10): 2028-2033. |
| FU C B, DAN L, XU W S, et al., 2020a. Variation of O3 concentration in Sanya city from 2014 to 2019 [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 29(10): 2028-2033. | |
| [12] | 符传博, 丹利, 徐文帅, 等, 2020b. 基于轨迹模式分析海口市大气污染的输送及潜在源区[J]. 环境科学学报, 40(1): 36-42. |
| FU C B, DAN L, XU W S, et al., 2020b. Analysis of air polluted transportation and potential source in Haikou City based on trajectory model[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 40(1): 36-42. | |
| [13] | 符传博, 周航, 2021. 中国城市臭氧的形成机理及污染影响因素研究进展[J]. 中国环境监测, 37(2): 33-43. |
| FU C B, ZHOU H, 2021. Research progress on the formation mechanism and impact factors of urban ozone pollution in China[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 37(2): 33-43. | |
| [14] | 耿春梅, 王宗爽, 任丽红, 等, 2014. 大气臭氧浓度升高对农作物产量的影响[J]. 环境科学研究, 27(3): 239-245. |
| GENG C M, WANG Z S, REN L H, et al., 2014. Study on the impact of elevated atmospheric ozone on crop yield[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 27(3): 239-245. | |
| [15] | 姜允迪, 祁斌, 2000. 兰州城区臭氧浓度时空变化特征及其与气象条件的关系[J]. 兰州大学学报 (自然科学版), 36(5):118-125. |
| JIANG Y D, QI B, 2000. Temporal and spatial variations of ozone concentration and its relations with meteorological factors in Lanzhou proper[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Science), 36(5):118-125. | |
| [16] | 李莉莉, 王隆, 刘喜平, 等, 2020. 哈尔滨市臭氧时空分布特征及气象要素的关系[J]. 中国环境科学, 40(5): 1991-1999. |
| LI L L, WANG L, LIU X P, et al., 2020. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of ozone and its relationship with meteorological factors in Harbin[J]. China Environmental Science, 40(5): 1991-1999. | |
| [17] | 李全喜, 王金艳, 刘筱冉, 等, 2018. 兰州市区臭氧时空分布特征及气象和环境因子对臭氧的影响[J]. 环境保护科学, 44(2): 78-84. |
| LI Q X, WANG J Y, LIU X R, et al., 2018. Temporal and spatial distribution of ozone and effects of meteorological and environmental factors on ozone in the urban areas of Lanzhou City[J]. Environmental Protection Science, 44(2): 78-84. | |
| [18] | 李霄阳, 李思杰, 刘鹏飞, 等, 2018. 2016年中国城市臭氧浓度的时空变化规律[J]. 环境科学学报, 38(4): 1263-1274. |
| LI X Y, LI S J, LIU P F, et al., 2018. Spatial and temporal variations of ozone concentrations in China in 2016[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 38(4): 1263-1274. | |
| [19] | 李崇, 袁子鹏, 吴宇童, 等, 2017. 沈阳一次严重污染天气过程持续和增强气象条件分析[J]. 环境科学研究, 30(3): 349-358. |
| LI C, YUAN Z P, WU Y T, et al., 2017. Analysis of persistence and intensification mechanism of a heavy haze event in Shenyang[J]. Research of Environment Sciences, 30(3): 349-358. | |
| [20] | 梁从诫, 2006. 2005年: 中国的环境危局与突围[M]. 北京: 社会科学文献出版社: 1-20. |
| LIANG C J, 2006. Crisis and breakthrough of China’s environment (2005)[M]. Beijing: Social Sciences Literature Press: 1-20 | |
| [21] | 刘超, 张恒德, 张天航, 等, 2020. 青岛“上合峰会”期间夜间臭氧增长成因分析[J]. 中国环境科学, 40(8): 3332-3341. |
| LIU C, ZHANG H D, ZHANG T H, et al., 2020. The causes of ozone concentration growth in the night during the “Shanghai Coopetation Organization Summit” in Qingdao[J]. China Environmental Science, 40(8): 3332-3341. | |
| [22] | 陆倩, 王国辉, 冯一淳, 等, 2019. 气象条件对承德市臭氧重污染天气的影响[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 35(8): 992-999. |
| LU Q, WANG G H, FENG Y C, et al., 2019. The influence of Meteorological conditions on a heavy ozone pollution process in Chengde City[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 35(8): 992-999. | |
| [23] | 孟宪贵, 郭俊建, 韩永清, 2018. ERA5再分析数据适用性初步评估[J]. 海洋气象学报, 38(1): 91-99. |
| MENG X G, GUO J J, HAN Y Q, 2018. Preliminarily assessment of ERA5 reanalysis data[J]. Journal of Marine Meteorology, 38(1): 91-99. | |
| [24] | 沈劲, 何灵, 程鹏, 等, 2019. 珠三角北部背景站臭氧浓度变化特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(10): 2006-2011. |
| SHEN J, HE L, CHENG P, et al., 2019. Characteristics of ozone concentration variation in the northern background site of the Pearl River Delta[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 28(10): 2006-2011. | |
| [25] | 生态环境部, 2018. 环境空气质量标准: GB 3095-2012[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| MINISTRY OF ECOLOGY AND ENVIRONMENT, 2018. Ambient air quality standards: GB 3095-2012[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. | |
| [26] | 宋海清, 孙小龙, 李云鹏, 2020. 欧洲中期天气预报中心第五代全球再分析土壤湿度资料在内蒙古的适用性评估[J]. 科学技术与工程, 20(6): 2161-2168. |
| SONG H Q, SUN X L, LI Y P, 2020. Evaluation of ERA5 reanalysis soil moisture over inner Mongolia[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 20(6): 2161-2168. | |
| [27] | 王玫, 郑有飞, 柳艳菊, 等, 2019. 京津冀臭氧变化特征及与气象要素的关系[J]. 中国环境科学, 39(7): 2689-2698. |
| WANG M, ZHENG Y F, LIU Y J, et al., 2019. Characteristics of ozone and its relationship with meteorological factors in Beijing-Tianjin- Hebei region[J]. China Environmental Science, 39(7): 2689-2698. | |
| [28] | 吴锴, 康平, 王占山, 等, 2017. 成都市臭氧污染特征及气象成因研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 37(11): 4241-4252. |
| WU K, KANG P, WANG Z S, et al., 2017. Ozone temporal variation and its meteorological factors over Chengdu City[J]. Environmental Protection Science, 37(11): 4241-4252. | |
| [29] | 肖建能, 杜国明, 施益强, 等, 2016. 厦门市环境空气污染时空特征及其与气象因素相关分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 36(9): 3363-3371. |
| XIAO J N, DU G M, SHI Y Q, et al., 2016. Spatiotemporal distribution pattern of ambient air pollution and its correlation with meteorological factors in Xiamen City[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 36(9): 3363-3371. | |
| [30] | 徐锟, 刘志红, 何沐全, 等, 2018. 成都市夏季近地面臭氧污染气象特征[J]. 中国环境监测, 34(5): 36-45. |
| XU K, LIU Z H, HE M Q, et al., 2018. Meteorological characteristics of O3 pollution near the ground in summer of Chengdu[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 34(5): 36-45. | |
| [31] | 徐祥德, 王寅钧, 赵天良, 等, 2015. 中国大地形东侧霾空间分布“避风港”效应及其“气候调节”影响下的年代际变异[J]. 科学通报, 60(12): 1132-1143. |
| XU X D, WANG Y J, ZHAO T L, et al., 2015. “Harbor” effect of large topography on haze distribution in eastern China and its climate modulation on decadal variations in haze China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 60(12): 1132-1143. | |
| [32] | 颜敏, 黄晓波, 陈丹, 等, 2021. 深圳市臭氧污染特征及其与前体物关系分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(4): 763-770. |
| YAN M, HUANG X B, CHEN D, et al., 2021. Characteristics of ozone pollution and relationship between ozone and precursors in Shenzhen[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(4): 763-770. | |
| [33] | 张小曳, 孙俊英, 王亚强, 等, 2013. 我国雾-霾成因及其治理的思考[J]. 科学通报, 58(13): 1178-1187. |
| ZHANG X Y, SUN J Y, WANG Y Q, et al., 2013. Factors contributing to haze and fog in China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 58(13): 1178-1187. | |
| [34] | 中华人民共和国生态环境部, 2021. 2020年中国生态环境状况公报[R]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People's Republic of China, 2021. 2020 Bulletin on the State of China's Ecological Environment[R]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. | |
| [35] | 朱景, 袁慧珍, 2019. ERA再分析陆面温度资料在浙江省的适用性[J]. 气象科技, 47(2): 289-298. |
| ZHU J, YUAN H Z, 2019. Applicability of ERA reanalysis data of land surface temperature in Zhejiang Province[J]. Meteorological Science and Technology, 47(2): 289-298. |
| [1] | YAN Xuejun, HAO Saimei, ZHANG Rongrong, QIN Hua, GAO Sulian, WANG Feng, JIN Xianzhong, SUN Youmin, ZHANG Guiqin. Composition Spectrum and Emission Estimation of VOCs from Furniture Malls [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(6): 1070-1077. |
| [2] | XU Xiaoyun, RAO Zhihan, JIANG Hongbin, ZHANG Wei, CHEN Chao, YANG Yongan, HU Yanli, WEI Haichuan. Pollution Characteristics and Formation Potential for O3 and SOA of Ambient VOCs in Suining Industrial Zone in Summer [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 956-968. |
| [3] | WEN Lirong, JIANG Ming, HUANG Bo, YUAN Luan, ZHOU Yan, LU Weimei, ZHANG Ying, LIU Ming, ZHANG Liyun. Analysis of Ozone Pollution Causes and Source Analysis of VOCs in Typical Areas of Pearl River Delta: A Case Study of Zhongshan City [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 500-513. |
| [4] | FU Chuanbo, DAN Li, TONG Jinhe, CHEN Hong. Characteristics and Potential Source Analysis of Ozone pollution in Haikou City [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(2): 331-340. |
| [5] | LI Chengcheng, ZHANG Zirui, SONG Xiaoxuan, KONG Juanjuan, HAN Yang, RUAN Yanan. Effects of Ozone Stress on Antioxidant Metabolism and Reproductive Growth of Soybean [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(7): 1383-1392. |
| [6] | CHEN Xuequan, KONG Bin, LAN Qing, YU Zhiquan, XIE Yinsi, HUANG Junyi. Emission Characteristics and Ozone Formation Potential Assessment of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) from Adhesive Manufacturing Industry [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(4): 750-758. |
| [7] | LI Yinghui, GUO Qianjin, YAN Yulong, HU Dongmei, DENG Mengjie, PENG Lin. Variation Characteristics and Source Apportionment of Ambient BTEX in Jincheng City [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 504-511. |
| [8] | CHEN Yaoyao, LIAO Tong, WANG Yu, SHEN Jin, ZHAI Yuhong, YE Siqi, CHEN Duohong, CHEN Jingyang. Characteristics of Ozone Pollution in Guangdong Province from 2016 to 2020 [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(12): 2374-2381. |
| [9] | LIAO Tong, XIONG Xin, WANG Zaihua, YANG Xiajie, HUANG Yingnan, FENG Jiaying. The Experience of Prevention and Control of Air Pollution in International Advanced Bay Areas and Its Enlightenment to Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area in China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(11): 2242-2250. |
| [10] | CHEN Yang, ZHANG Jinpu, QIU Xiaonuan, JU Hong, HUANG Jun. Characteristic of Ozone Pollution and Meteorological Factors Analysis in Guangzhou in 2021 [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(10): 2028-2038. |
| [11] | DENG Huiying, CHEN Lixin, YU Yongjiang, WANG Hong. Characteristics of Ozone Pollution Distribution and Its Correlation Analysis with Meteorological Factors in Wuyishan [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(7): 1428-1435. |
| [12] | HONG Yingying, CHEN Chen, BAO Hongyan, SHEN Jin. Sources and Sensitivity Analysis of Ozone in Spring Over the Southwestern Part of Pearl River Delta Region [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(5): 984-994. |
| [13] | WAN Wuxing, ZHANG Shuai, LI Jie, SUN Xu, GUAN Zuguang, YU Xiaohong, YANG Yonghong, WANG Xiaoke. Regional Differences of Urban Ozone Pollution and Its Damage to Plants in Hebei Province [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(11): 2185-2194. |
| [14] | ZHOU Yingtong, WANG Yan, SUN Mingyu, SAN Yu, YAO Xingzhou, ZHAO Tianhong. Effect of Ozone Concentration Increasing Near the Ground on Antioxidant System of Parent and Offspring Soybean Leaves [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(11): 2195-2203. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
