生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (7): 1360-1369.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.07.008
刘展航1,2,3( ), 张树岩4, 侯玉平1, 朱书玉4, 王立冬4, 施欣悦2,5, 李培广2,3, 韩广轩2,3, 谢宝华2,3,*(
), 张树岩4, 侯玉平1, 朱书玉4, 王立冬4, 施欣悦2,5, 李培广2,3, 韩广轩2,3, 谢宝华2,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-03-29
出版日期:2022-07-18
发布日期:2022-08-31
通讯作者:
*谢宝华,副研究员,研究方向为湿地生态学。E-mail: bhxie@yic.ac.cn作者简介:刘展航(1997年生),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为入侵生态学。E-mail: 756642237@qq.com
基金资助:
LIU Zhanhang1,2,3( ), ZHANG Shuyan4, HOU Yuping1, ZHU Shuyu4, WANG Lidong4, SHI Xinyue2,5, LI Peiguang2,3, HAN Guangxuan2,3, XIE Baohua2,3,*(
), ZHANG Shuyan4, HOU Yuping1, ZHU Shuyu4, WANG Lidong4, SHI Xinyue2,5, LI Peiguang2,3, HAN Guangxuan2,3, XIE Baohua2,3,*( )
)
Received:2022-03-29
Online:2022-07-18
Published:2022-08-31
摘要:
互花米草入侵(Spartina alterniflora)严重威胁滨海湿地生态系统的生态平衡。为了探究不同入侵年限互花米草对土壤碳氮磷及其生态化学计量特征在不同土层间的差异,选择黄河口盐沼互花米草湿地为研究对象,采用空间替代时间的方法,采集不同入侵年限互花米草湿地(SA3,2016年入侵;SA8,2011年入侵;SA13,2006年入侵)及邻近未入侵的光滩(SA0)的0—100 cm土壤,测定其总碳(TC)、总氮(TN)、总磷(TP)含量,分析互花米草入侵对土壤碳氮磷生态化学计量比的影响。研究结果表明:(1)互花米草入侵显著提升了0—10 cm土壤TC和0—20 cm土壤TN含量,但对土壤TP含量影响很小;(2)SA3、SA8和SA13的0—10 cm土层TC含量分别比光滩高18.9%、27.6%和57.6%,TN含量分别比光滩高1.39、2.37和3.66倍;(3)互花米草入侵对土壤w(C)/w(N)的影响很小且没有明显规律,使浅层土壤的w(C)/w(P)和w(N)/w(P)增加,但降低了深层土壤的w(C)/w(P)和w(N)/w(P),在0—10 cm土层,土壤w(C)/w(P)和w(N)/w(P)由大到小排序均依次为SA13>SA8>SA3>SA0,而在0—100 cm土层,土壤w(C)/w(N)由大到小排序依次为SA0>SA8>SA13>SA3,w(C)/w(P)依次为SA13>SA8>SA0>SA3,w(N)/w(P)依次为SA13>SA0>SA3>SA8。在0—100 cm土壤中,pH、电导率、容重、含水量是影响碳氮磷含量的重要环境因子,w(C)/w(N)与土壤环境因子没有显著相关性,而w(C)/w(P)和w(N)/w(P)受环境因子影响显著。综上,互花米草入侵改变了黄河口盐沼湿地土壤碳、氮含量,进而影响土壤养分资源配比的平衡状态。
中图分类号:
刘展航, 张树岩, 侯玉平, 朱书玉, 王立冬, 施欣悦, 李培广, 韩广轩, 谢宝华. 互花米草入侵对黄河口湿地土壤碳氮磷及其生态化学计量特征的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1360-1369.
LIU Zhanhang, ZHANG Shuyan, HOU Yuping, ZHU Shuyu, WANG Lidong, SHI Xinyue, LI Peiguang, HAN Guangxuan, XIE Baohua. Effects of Spartina alterniflora Invasion on Soil Carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Their Ecostoichiometric Characteristics in the Yellow River Estuary Wetlands[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(7): 1360-1369.
| 样点 Site | 高程 Elevation/m | 土壤pH值 Soil pH | 容重 Bulk density/(g∙cm-3) | 电导率 Conductivity γ/(ms∙cm-1) | 含水量 Soil moisture/% | 土壤温度 Soil temperature/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SA0 | 0.28 | 8.69±0.01a | 1.56±0.01a | 2.12±0.06b | 23.30±0.12b | 11.10±0.16b |
| SA3 | 0.45 | 8.50±0.01ab | 1.45±0.01b | 2.18±0.03b | 24.01±0.15b | 11.20±0.25b |
| SA8 | 0.17 | 8.27±0.01ab | 1.26±0.01c | 2.70±0.05ab | 30.72±0.57a | 12.25±0.74ab |
| SA13 | 0.06 | 8.28±0.02b | 1.23±0.02c | 3.01±0.09a | 31.87±0.75a | 14.95±0.72a |
表1 光滩和不同入侵年限互花米草湿地土壤理化性质
Table 1 Soil physical and chemical properties of bare flat and Spartina alterniflora wetland with different invasion years
| 样点 Site | 高程 Elevation/m | 土壤pH值 Soil pH | 容重 Bulk density/(g∙cm-3) | 电导率 Conductivity γ/(ms∙cm-1) | 含水量 Soil moisture/% | 土壤温度 Soil temperature/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SA0 | 0.28 | 8.69±0.01a | 1.56±0.01a | 2.12±0.06b | 23.30±0.12b | 11.10±0.16b |
| SA3 | 0.45 | 8.50±0.01ab | 1.45±0.01b | 2.18±0.03b | 24.01±0.15b | 11.20±0.25b |
| SA8 | 0.17 | 8.27±0.01ab | 1.26±0.01c | 2.70±0.05ab | 30.72±0.57a | 12.25±0.74ab |
| SA13 | 0.06 | 8.28±0.02b | 1.23±0.02c | 3.01±0.09a | 31.87±0.75a | 14.95±0.72a |
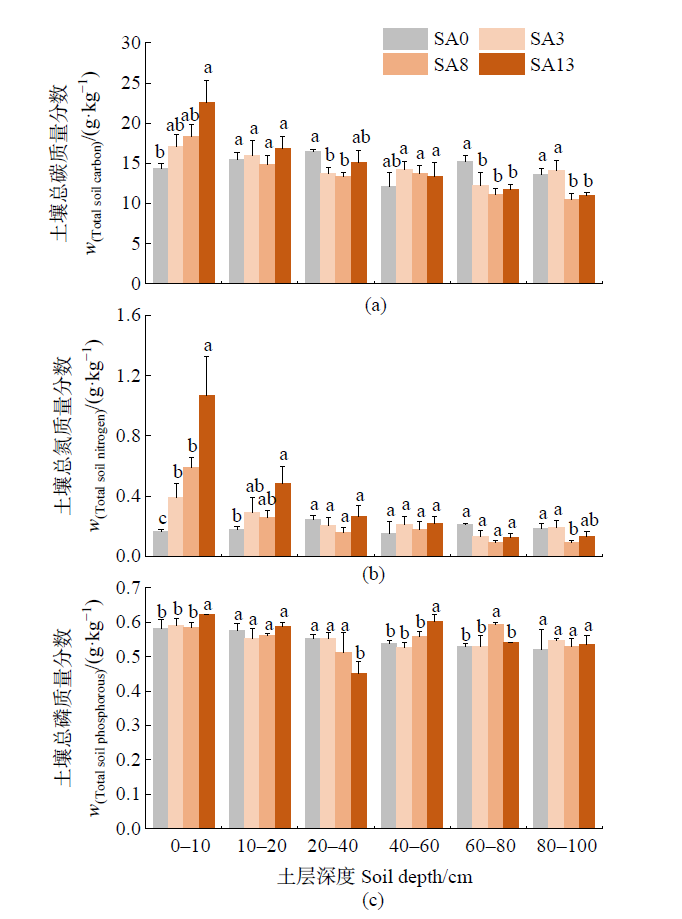
图2 光滩和互花米草湿地不同深度土层的碳、氮、磷含量 平均值±标准误,n=3。同一土层的不同小写字母表示不同点位间有显著差异(P<0.05)。下同
Figure 2 Soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus contents at different depths in bare falt and Spartina alterniflora wetlands Means±SE, n=3. Different small letters the same soil layer indicated significant differences among different site (P<0.05). The same below
| 储量 Storage | 土层深度 Soil depth/cm | SA0 | SA3 | SA8 | SA13 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤总碳储量 Total soil carbon storage/ (kg∙m-2) | 0-10 | 2.19±0.14b | 2.72±0.07a | 2.13±0.20b | 1.67±0.11c |
| 10-20 | 5.18±0.06a | 4.79±0.32b | 4.04±0.37c | 5.13±0.18a | |
| 20-40 | 5.02±0.08a | 4.74±0.22b | 3.97±0.20c | 4.29±0.38c | |
| 40-60 | 4.21±0.22a | 4.28±0.08a | 3.96±0.08b | 3.98±0.22b | |
| 60-80 | 4.58±0.24a | 4.09±0.23b | 3.76±0.10c | 3.87±0.25c | |
| 80-100 | 4.20±0.17b | 4.70±0.33a | 3.81±0.10c | 3.95±0.01c | |
| 0-100 | 25.37±0.40a | 25.31±1.76a | 21.67±1.23b | 22.89±1.48b | |
| 土壤总氮储量 Total soil nitrogen storage/(kg∙m-2) | 0-10 | 0.02±0.00c | 0.06±0.01b | 0.07±0.01a | 0.08±0.00a |
| 10-20 | 0.06±0.00b | 0.09±0.03b | 0.07±0.01b | 0.15±0.02a | |
| 20-40 | 0.08±0.01a | 0.07±0.00a | 0.04±0.00b | 0.08±0.01a | |
| 40-60 | 0.06±0.01a | 0.05±0.01a | 0.05±0.01a | 0.07±0.01a | |
| 60-80 | 0.06±0.00a | 0.04±0.01b | 0.03±0.00b | 0.04±0.01b | |
| 80-100 | 0.06±0.01a | 0.06±0.01a | 0.03±0.00b | 0.05±0.01a | |
| 0-100 | 0.34±0.01b | 0.38±0.08b | 0.30±0.03c | 0.45±0.08a | |
| 土壤总磷储量 Total soil phosphorus storage/(kg∙m-2) | 0-10 | 0.09±0.00a | 0.09±0.00a | 0.07±0.01b | 0.05±0.00c |
| 10-20 | 0.19±0.01a | 0.17±0.00a | 0.15±0.01b | 0.18±0.01a | |
| 20-40 | 0.17±0.01a | 0.19±0.01a | 0.15±0.01b | 0.13±0.01b | |
| 40-60 | 0.16±0.01b | 0.19±0.00a | 0.16±0.00b | 0.18±0.01a | |
| 60-80 | 0.16±0.01b | 0.18±0.01a | 0.20±0.00a | 0.18±0.01a | |
| 80-100 | 0.16±0.01b | 0.18±0.01a | 0.19±0.00a | 0.19±0.00a | |
| 0-100 | 0.93±0.05b | 1.00±0.02a | 0.93±0.05b | 0.90±0.02c |
表2 光滩和不同入侵年限互花米草湿地土壤不同土层间土壤总碳、总氮和总磷储量对比
Table 2 Comparison of soil total carbon, total nitrogen and total phosphorus storage between soil layers of bare flat and Spartina alterniflora wetland with different invasion years
| 储量 Storage | 土层深度 Soil depth/cm | SA0 | SA3 | SA8 | SA13 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤总碳储量 Total soil carbon storage/ (kg∙m-2) | 0-10 | 2.19±0.14b | 2.72±0.07a | 2.13±0.20b | 1.67±0.11c |
| 10-20 | 5.18±0.06a | 4.79±0.32b | 4.04±0.37c | 5.13±0.18a | |
| 20-40 | 5.02±0.08a | 4.74±0.22b | 3.97±0.20c | 4.29±0.38c | |
| 40-60 | 4.21±0.22a | 4.28±0.08a | 3.96±0.08b | 3.98±0.22b | |
| 60-80 | 4.58±0.24a | 4.09±0.23b | 3.76±0.10c | 3.87±0.25c | |
| 80-100 | 4.20±0.17b | 4.70±0.33a | 3.81±0.10c | 3.95±0.01c | |
| 0-100 | 25.37±0.40a | 25.31±1.76a | 21.67±1.23b | 22.89±1.48b | |
| 土壤总氮储量 Total soil nitrogen storage/(kg∙m-2) | 0-10 | 0.02±0.00c | 0.06±0.01b | 0.07±0.01a | 0.08±0.00a |
| 10-20 | 0.06±0.00b | 0.09±0.03b | 0.07±0.01b | 0.15±0.02a | |
| 20-40 | 0.08±0.01a | 0.07±0.00a | 0.04±0.00b | 0.08±0.01a | |
| 40-60 | 0.06±0.01a | 0.05±0.01a | 0.05±0.01a | 0.07±0.01a | |
| 60-80 | 0.06±0.00a | 0.04±0.01b | 0.03±0.00b | 0.04±0.01b | |
| 80-100 | 0.06±0.01a | 0.06±0.01a | 0.03±0.00b | 0.05±0.01a | |
| 0-100 | 0.34±0.01b | 0.38±0.08b | 0.30±0.03c | 0.45±0.08a | |
| 土壤总磷储量 Total soil phosphorus storage/(kg∙m-2) | 0-10 | 0.09±0.00a | 0.09±0.00a | 0.07±0.01b | 0.05±0.00c |
| 10-20 | 0.19±0.01a | 0.17±0.00a | 0.15±0.01b | 0.18±0.01a | |
| 20-40 | 0.17±0.01a | 0.19±0.01a | 0.15±0.01b | 0.13±0.01b | |
| 40-60 | 0.16±0.01b | 0.19±0.00a | 0.16±0.00b | 0.18±0.01a | |
| 60-80 | 0.16±0.01b | 0.18±0.01a | 0.20±0.00a | 0.18±0.01a | |
| 80-100 | 0.16±0.01b | 0.18±0.01a | 0.19±0.00a | 0.19±0.00a | |
| 0-100 | 0.93±0.05b | 1.00±0.02a | 0.93±0.05b | 0.90±0.02c |
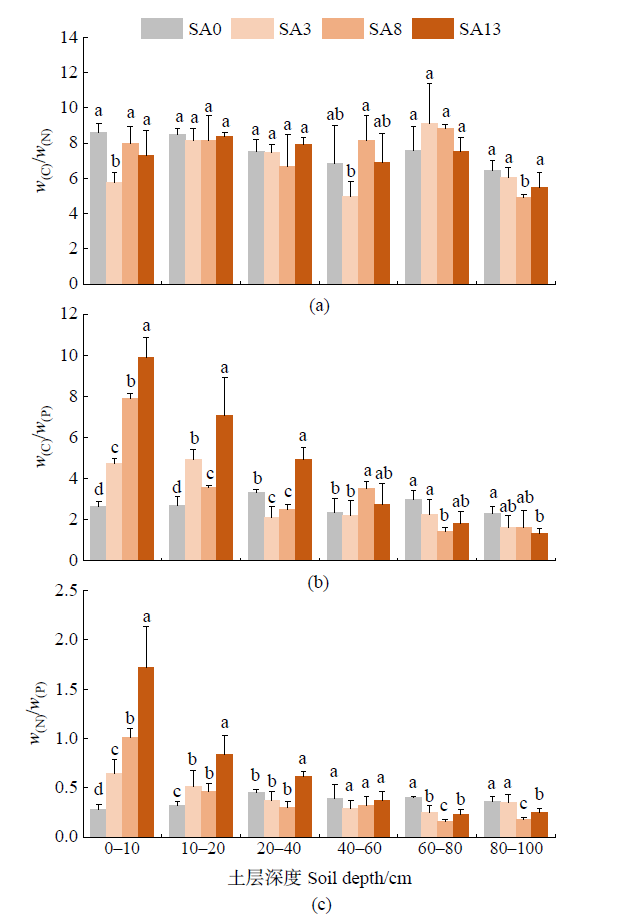
图3 光滩和互花米草湿地不同深度土层的w(C)/w(N)、w(C)/w(P)和w(N)/w(P)
Figure 3 Soil w(C)/w(N), w(C)/w(P) and w(N)/w(P) at different depths in bare falt and Spartina alterniflora wetlands
| 影响因素 Influence factor | df | 土壤总碳 Total soil carbon content | 土壤总氮 Total soil nitrogencontent | 土壤总磷 Total soil phosphorus content | 土壤w(C)/w(N) Soil w(C)/w(N) | 土壤w(C)/w(P) Soil w(C)/w(P) | 土壤w(N)/w(P) Soil w(N)/w(P) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 入侵年限 Invasion duration (Y) | 3 | 17.72** | 8.34** | 2.23 | 0.59 | 6.03** | 8.01** |
| 土壤深度 Soil depth (D) | 5 | 4.23** | 2.27 | 1.44 | 1.03 | 0.21 | 2.04 |
| 入侵年限×土壤深度 Y×D | 15 | 1.07 | 0.70 | 0.83 | 0.78 | 0.85 | 0.67 |
表3 土壤碳、氮、磷含量及生态化学计量指标的双因素方差分析
Table 3 Two-away AVOVA analysis of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus content and ecological stoichiometry indexes (F value)
| 影响因素 Influence factor | df | 土壤总碳 Total soil carbon content | 土壤总氮 Total soil nitrogencontent | 土壤总磷 Total soil phosphorus content | 土壤w(C)/w(N) Soil w(C)/w(N) | 土壤w(C)/w(P) Soil w(C)/w(P) | 土壤w(N)/w(P) Soil w(N)/w(P) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 入侵年限 Invasion duration (Y) | 3 | 17.72** | 8.34** | 2.23 | 0.59 | 6.03** | 8.01** |
| 土壤深度 Soil depth (D) | 5 | 4.23** | 2.27 | 1.44 | 1.03 | 0.21 | 2.04 |
| 入侵年限×土壤深度 Y×D | 15 | 1.07 | 0.70 | 0.83 | 0.78 | 0.85 | 0.67 |
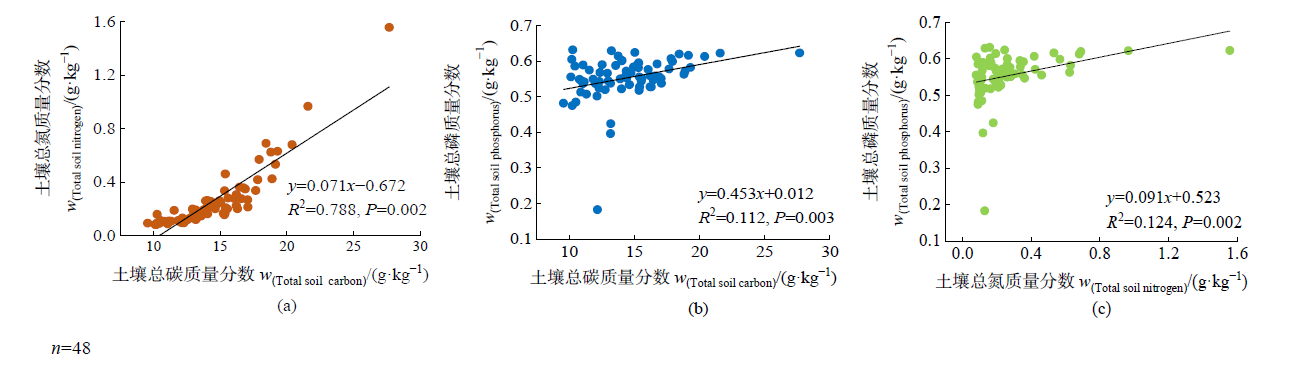
图4 光滩和互花米草湿地土壤碳、氮、磷含量的回归分析
Figure 4 Regression analysis of soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus concentration in bare falt and Spartina alterniflora wetlands
| 指标 Index | 土壤总碳 Total soil carbon | 土壤总氮 Total soil nitrogen | 土壤总磷 Total soil phosphorus | 土壤w(C)/w(N) Soil w(C)/w(N) | 土壤w(C)/w(P) Soil w(C)/w(P) | 土壤w(N)/w(P) Soil w(N)/w(P) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤w(C)/w(N) Soil w(C)/w(N) | 0.183 | -0.096 | 0.037 | |||
| 土壤w(C)/w(P) Soil w(C)/w(P) | 0.441** | 0.340** | -0.006 | 0.205 | ||
| 土壤w(N)/w(P) Soil w(N)/w(P) | 0.882** | 0.987** | 0.211 | 0.113 | 0.388** | |
| 土壤pH值 Soil pH | -0.154 | -0.398** | -0.173 | 0.115 | -0.145 | -0.378** |
| 电导率 Conductivity | 0.703** | 0.695** | 0.168 | 0.169 | 0.289* | 0.696** |
| 容重 Bulk density | -0.665** | -0.721** | -0.202 | -0.221 | -0.339** | -0.729** |
| 含水量 Soil moisture | 0.593** | 0.742** | 0.238* | 0.139 | 0.279* | 0.739** |
| 高程 Elevation | -0.053 | -0.221 | -0.044 | -0.196 | -0.120 | -0.234* |
表4 土壤碳氮磷含量及其生态化学计量特征与土壤理化性质的相关系数
Table 4 Correlation coefficients between soil C, N, P and its ecological stoichiometry and soil physical and chemical properties
| 指标 Index | 土壤总碳 Total soil carbon | 土壤总氮 Total soil nitrogen | 土壤总磷 Total soil phosphorus | 土壤w(C)/w(N) Soil w(C)/w(N) | 土壤w(C)/w(P) Soil w(C)/w(P) | 土壤w(N)/w(P) Soil w(N)/w(P) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤w(C)/w(N) Soil w(C)/w(N) | 0.183 | -0.096 | 0.037 | |||
| 土壤w(C)/w(P) Soil w(C)/w(P) | 0.441** | 0.340** | -0.006 | 0.205 | ||
| 土壤w(N)/w(P) Soil w(N)/w(P) | 0.882** | 0.987** | 0.211 | 0.113 | 0.388** | |
| 土壤pH值 Soil pH | -0.154 | -0.398** | -0.173 | 0.115 | -0.145 | -0.378** |
| 电导率 Conductivity | 0.703** | 0.695** | 0.168 | 0.169 | 0.289* | 0.696** |
| 容重 Bulk density | -0.665** | -0.721** | -0.202 | -0.221 | -0.339** | -0.729** |
| 含水量 Soil moisture | 0.593** | 0.742** | 0.238* | 0.139 | 0.279* | 0.739** |
| 高程 Elevation | -0.053 | -0.221 | -0.044 | -0.196 | -0.120 | -0.234* |
| 研究地点 Location | 调查时间 Survey times | 植被类型 Vegetation type | 土壤w(C)/w(N) Soil w(C)/w(N) | 土壤w(C)/w(P) Soil w(C)/w(P) | 土壤w(N)/w(P) Soil w(N)/w(P) | 土壤剖面 Soil profile/cm | 文献出处 References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 山东黄河口 Yellow River Estuary, Shandong Province | 2019 | SA0 | 7.39 | 2.72 | 0.38 | 0-100 | This study |
| SA3 | 6.90 | 2.61 | 0.37 | ||||
| SA8 | 7.33 | 2.95 | 0.34 | ||||
| SA13 | 7.13 | 3.85 | 0.55 | ||||
| 山东黄河口 Yellow River Estuary, Shandong Province | 2017 | SS | 10.06 | 0-100 | Zhang et al., | ||
| SA2 | 9.68 | ||||||
| SA5 | 11.09 | ||||||
| SA10 | 13.32 | ||||||
| 山东胶州湾 Jiaozhou Bay, Shandong Province* | 2015 | SA0 | 21.89 | 19.92 | 0.91 | 0-60 | 苗萍等, |
| SA | 23.20 | 21.93 | 0.95 | ||||
| 江苏盐城 Yancheng, Jiangsu Province | 2014 | SA0 | 9.61 | 2.28 | 0.24 | 0-20 | 高建华等, |
| SS | 11.50 | 6.30 | 0.55 | ||||
| PC | 10.89 | 7.37 | 0.68 | ||||
| SA | 12.66 | 9.21 | 0.73 | ||||
| 上海长江口 Yangtze River Estuary, Shanghai | 2004 | SM | 13.37 | 0-100 | Cheng et al., | ||
| SA7 | 12.16 | ||||||
| 浙江杭州湾 Hangzhou Bay, Zhejiang Province | 2020 | SA0 | 3.56 | 4.98 | 1.37 | 0-40 | 项琦, |
| SM | 3.99 | 7.20 | 1.71 | ||||
| PC | 12.53 | 13.04 | 0.95 | ||||
| SA2 | 1.69 | 7.80 | 4.62 | ||||
| SA7 | 3.24 | 10.39 | 3.25 | ||||
| 福建闽江口 Minjiang Estuary, Fujian Province* | 2014 | CM | 10.69 | 23.94 | 2.24 | 0-50 | 金宝石等, |
| SA0-4 | 11.07 | 25.37 | 2.29 | ||||
| SA4-8 | 11.25 | 27.11 | 2.40 | ||||
| SA8-12 | 11.49 | 26.54 | 2.31 | ||||
| 广东湛江; 广西北海 Zhanjiang, Guangdong Province; Beihai, Guangxi Province | 2015 | Ma | 11.2 | 24.6 | 2.30 | 0-40 | Wang et al., |
| SA | 10.7 | 21.2 | 2.06 |
表5 不同地点互花米草入侵湿地及本土湿地的土壤碳氮磷生态化学计量比
Table 5 Ecological stoichiometric ratio of soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus of Spartina alterniflora invaded wetlands and native wetlands in different places
| 研究地点 Location | 调查时间 Survey times | 植被类型 Vegetation type | 土壤w(C)/w(N) Soil w(C)/w(N) | 土壤w(C)/w(P) Soil w(C)/w(P) | 土壤w(N)/w(P) Soil w(N)/w(P) | 土壤剖面 Soil profile/cm | 文献出处 References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 山东黄河口 Yellow River Estuary, Shandong Province | 2019 | SA0 | 7.39 | 2.72 | 0.38 | 0-100 | This study |
| SA3 | 6.90 | 2.61 | 0.37 | ||||
| SA8 | 7.33 | 2.95 | 0.34 | ||||
| SA13 | 7.13 | 3.85 | 0.55 | ||||
| 山东黄河口 Yellow River Estuary, Shandong Province | 2017 | SS | 10.06 | 0-100 | Zhang et al., | ||
| SA2 | 9.68 | ||||||
| SA5 | 11.09 | ||||||
| SA10 | 13.32 | ||||||
| 山东胶州湾 Jiaozhou Bay, Shandong Province* | 2015 | SA0 | 21.89 | 19.92 | 0.91 | 0-60 | 苗萍等, |
| SA | 23.20 | 21.93 | 0.95 | ||||
| 江苏盐城 Yancheng, Jiangsu Province | 2014 | SA0 | 9.61 | 2.28 | 0.24 | 0-20 | 高建华等, |
| SS | 11.50 | 6.30 | 0.55 | ||||
| PC | 10.89 | 7.37 | 0.68 | ||||
| SA | 12.66 | 9.21 | 0.73 | ||||
| 上海长江口 Yangtze River Estuary, Shanghai | 2004 | SM | 13.37 | 0-100 | Cheng et al., | ||
| SA7 | 12.16 | ||||||
| 浙江杭州湾 Hangzhou Bay, Zhejiang Province | 2020 | SA0 | 3.56 | 4.98 | 1.37 | 0-40 | 项琦, |
| SM | 3.99 | 7.20 | 1.71 | ||||
| PC | 12.53 | 13.04 | 0.95 | ||||
| SA2 | 1.69 | 7.80 | 4.62 | ||||
| SA7 | 3.24 | 10.39 | 3.25 | ||||
| 福建闽江口 Minjiang Estuary, Fujian Province* | 2014 | CM | 10.69 | 23.94 | 2.24 | 0-50 | 金宝石等, |
| SA0-4 | 11.07 | 25.37 | 2.29 | ||||
| SA4-8 | 11.25 | 27.11 | 2.40 | ||||
| SA8-12 | 11.49 | 26.54 | 2.31 | ||||
| 广东湛江; 广西北海 Zhanjiang, Guangdong Province; Beihai, Guangxi Province | 2015 | Ma | 11.2 | 24.6 | 2.30 | 0-40 | Wang et al., |
| SA | 10.7 | 21.2 | 2.06 |
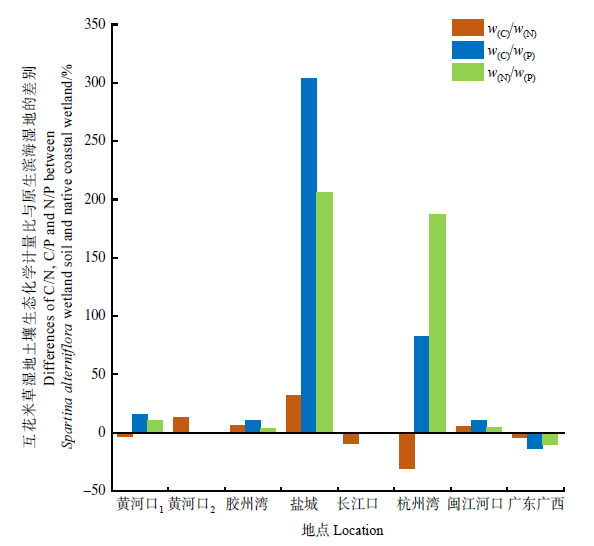
图5 互花米草湿地土壤生态化学计量比与原生滨海湿地的差别
Figure 5 Differences of w(C)/w(N), w(C)/w(P) and w(N)/w(P) between Spartina alterniflora wetland soil and native coastal wetland
| [1] |
CHENG X L, LUO Y Q, CHEN J Q, et al., 2006. Short-term C4 plant Spartina alterniflora invasions change the soil carbon in C3 plant-dominated tidal wetlands on a growing estuarine Island[J]. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 38(12): 3380-3386.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
FANG H L, LIU G H, KEARNEY M, 2005. Georelational analysis of soil type, soil salt content, landform, and land use in the Yellow River Delta, China[J]. Environmental Management, 35(1): 72-83.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
HU Y F, SHU X Y, HE J, et al., 2018. Storage of C, N, and P affected by afforestation with Salix cupularis in an alpine semiarid desert ecosystem[J]. Land Degradation & Development, 29(1):188-198.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
LI J B, LAI Y T, XIE R R, et al., 2018. Sediment phosphorus speciation and retention process affected by invasion time of Spartina alterniflora in a subtropical coastal wetland of China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(35): 35365-35375.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
LIU R S, WANG D M, 2021. C꞉N꞉P stoichiometric characteristics and seasonal dynamics of leaf-root-litter-soil in plantations on the loess plateau[J]. Ecological Indicators, DOI: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107772.
DOI |
| [6] |
REICH P B, TJOELKER M G, MACHADO J L, et al., 2006. Universal scaling of respiratory metabolism, size and nitrogen in plants[J]. Nature, 439(7075): 457-461.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
REN G B, WANG J J, WANG A D, et al., 2019. Monitoring the invasion of smooth cordgrass Spartina alterniflora within the modern Yellow River Delta using remote sensing[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 90(sp1): 135-145.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
WANG W Q, SARDANS J, WANG C, et al., 2019. The response of stocks of C, N, and P to plant invasion in the coastal wetlands of China[J]. Global Change Biology, 25(2): 733-743.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
WINDHAM L, EHRENFELD J G, 2003. Net impact of a plant invasion on nitrogen-cycling processes withina[J]. Ecological Applications, 13(4): 883-897.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
XIA S P, WANG W Q, SONG Z L, et al., 2021. Spartina alterniflora invasion controls organic carbon stocks in coastal marsh and mangrove soils across tropics and subtropics[J]. Global Change Biology, 27(8): 1627-1644.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
XIAO D R, LEI D, KIM DONG-GILL, et al., 2019. Carbon budgets of wetland ecosystems in China[J]. Global Change Biology, 25(6): 2061-2076.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
XIE B H, HAN G X, QIAO P Y, et al., 2019. Effects of mechanical and chemical control on invasive Spartina alterniflora in the Yellow River Delta, China[J]. PeerJ, DOI: 10.7717/peerj.7655.
DOI |
| [13] |
ZHANG G L, BAI J H, ZHAO Q Q, et al., 2020. Bacterial succession in salt marsh soils along a short-term invasion chronosequence of Spartina alterniflora in the Yellow River Estuary, China[J]. Microbial Ecology, 79(3): 644-661.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
ZHANG G L, BAI J H, ZHAO Q Q, et al., 2021. Soil carbon storage and carbon sources under different Spartina alterniflora invasion periods in a salt marsh ecosystem[J]. Catena, DOI: 10.1016/j.catena.2020.104831.
DOI |
| [15] |
ZHOU C F, ZHAO H, SUN Z Y, et al., 2015. The Invasion of Spartina alterniflora alters carbon dynamics in China’s Yancheng Natural Reserve[J]. Clean-Soil Air Water, 43(2): 159-165.
DOI URL |
| [16] | 高建华, 杨桂山, 欧维新, 2007. 互花米草引种对苏北潮滩湿地TOC、TN和TP分布的影响[J]. 地理研究, 26(4): 799-808. |
| GAO J H, YANG G S, OU W X, 2007. The influence after introduction of Spartina alterniflora on the distribution of TOC, TN and TP in the national Yancheng rare birds nature reserve, Jiangsu Province, China[J]. Geographical Research, 26(4): 799-808. | |
| [17] |
韩广轩, 李隽永, 屈文笛, 2021. 氮输入对滨海盐沼湿地碳循环关键过程的影响及机制[J]. 植物生态学报, 45(4): 321-333.
DOI |
|
HAN G X, LI J Y, QU W D, 2021. Effects of nitrogen input on carbon cycle and carbon budget in a coastal salt marsh[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 45(4): 321-333.
DOI URL |
|
| [18] | 胡敏杰, 任洪昌, 邹芳芳, 等, 2016. 闽江河口淡水、半咸水沼泽土壤碳氮磷分布及计量学特征[J]. 中国环境科学, 36(3): 917-926. |
| HU M J, REN H C, ZOU F F, et al., 2016. Spatiotemporal distribution and stoichiometry characteristics of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in surface soils of freshwater and brackish marshes in the Min River estuary[J]. Chinese Environmental Science, 36(3): 917-926. | |
| [19] |
姜少玉, 陈琳琳, 闫朗, 等, 2021. 互花米草入侵对黄河三角洲秋季底栖食物网的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 32(12): 4499-4507.
DOI |
| JIANG S Y, CHEN L L, YAN L, et al., 2021. Impacts of Spartina alterniflora invasion on the benthic food web in the Yellow River Delta during autumn[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 32(12): 4499-4507. | |
| [20] |
金宝石, 闫鸿远, 王维奇, 等, 2017. 互花米草入侵下湿地土壤碳氮磷变化及化学计量学特征[J]. 应用生态学报, 28(5): 1541-1549.
DOI |
| JIN B S, YAN H Y, WANG W Q, et al., 2017. Changes of soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus and stoichiometry characteristics in marsh invaded by Spartina alterniflora[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 28(5): 1541-1549. | |
| [21] | 李从娟, 雷加强, 徐新文, 等, 2013. 塔克拉玛干沙漠腹地人工植被及土壤CNP的化学计量特征[J]. 生态学报, 33(18): 5760-5767. |
|
LI C J, LEI J Q, XU X W, et al., 2013. The stoichiometric characteristics of C, N, P for artificial plants and soil in the hinterland of Taklimakan Desert[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33(18): 5760-5767.
DOI URL |
|
| [22] | 李家兵, 张秋婷, 张丽烟, 等, 2016. 闽江河口春季互花米草入侵过程对短叶茳芏沼泽土壤碳氮分布特征的影响[J]. 生态学报, 36(12): 3628-3638. |
| LI J B, ZHANG Q T, ZHANG L Y, et al., 2016. Effect of Spartina alterniflora invasion sequence on soil carbon and nitrogen distribution in a Cyperus malaccensis marsh of the Min River estuary in spring[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36(12): 3628-3638. | |
| [23] | 刘文龙, 谢文霞, 赵全升, 等, 2014. 胶州湾芦苇潮滩土壤碳、氮和磷分布及生态化学计量学特征[J]. 湿地科学, 12(3): 362-368. |
| LIU W L, XIE W X, ZHAO Q S, et al., 2014. Spatial distribution and ecological stoichiometry characteristics of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in soil in Phragmites australis tidal flat of Jiaozhou Bay[J]. Wetland Science, 12(3): 362-368. | |
| [24] | 马旭, 王安东, 付守强, 等, 2020. 黄河口互花米草对日本鳗草Zostera japonica的入侵生态效应[J]. 环境生态学, 2(4): 65-71. |
| MA X, WANG A D, FU S Q, et al., 2020. Ecological effects of invasive species Spartina alterniflora on Zostera japonica in the Yellow River Delta[J]. Environmental Ecology, 2(4): 65-71. | |
| [25] |
苗萍, 谢文霞, 于德爽, 等, 2017. 胶州湾互花米草湿地氮、磷元素的垂直分布及季节变化[J]. 应用生态学报, 28(5): 1533-1540.
DOI |
|
MIAO P, XIE W X, YU D S, et al., 2017. Vertical distribution and seasonal variation of nitrogen, phosphorus elements in Spartina alterniflora wetland of Jiaozhou Bay, Shandong, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 28(5): 1533-1540.
DOI |
|
| [26] | 乔沛阳, 王安东, 谢宝华, 等, 2019. 除草剂对黄河三角洲入侵植物互花米草的影响[J]. 生态学报, 39(15): 5627-5634. |
| QIAO P Y, WANG A D, XIE B H, et al., 2019. Effects of herbicides on invasive Spartina alterniflora in the Yellow River Delta[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(15): 5627-5634. | |
| [27] | 田家怡, 于祥, 申保忠, 等, 2008. 黄河三角洲外来入侵物种米草对滩涂鸟类的影响[J]. 中国环境管理干部学院学报, 18(3): 87-90. |
| TIAN J Y, YU X, SHEN B Z, et al., 2008. Effect of an alien invasive species Spartina anglicaon birds in shoal in Yellow River Delta[J]. Journal of Environmental Management College of China, 18(3): 87-90. | |
| [28] | 王绍强, 于贵瑞, 2008. 生态系统碳氮磷元素的生态化学计量学特征[J]. 生态学报, 28(8): 3937-3947. |
| WANG S Q, YU G R, 2008. Ecological stoichiometry characteristics of ecosystem carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus elements[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 28(8): 3937-3947. | |
| [29] | 汪宗飞, 郑粉莉, 2018. 黄土高原子午岭地区人工油松林碳氮磷生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态学报, 38(19): 6870-6880. |
| WANG Z F, ZHENG F L, 2018. C, N, and P stoichiometric characteristics of Pinus tabulaeformis plantation in the Ziwuling Region of the Loess Plateau[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(19): 6870-6880. | |
| [30] | 项琦, 2021. 互花米草入侵对杭州湾潮滩湿地土壤及植物碳、氮、磷生态化学计量特征的影响[D]. 金华: 浙江师范大学: 20-28. |
| XIANG Q, 2021. Effects of Spartina alterniflora invasion on ecological stoichiometry characteristics of soil and plant carbon, nitrogen and phpsphorus in Tidal Flat Wetlands, Hangzhou Bay[D]. Jinhua: Zhejiang Normal University: 20-28. | |
| [31] |
肖烨, 商丽娜, 黄志刚, 等, 2014. 吉林东部山地沼泽湿地土壤碳、氮、磷含量及其生态化学计量学特征[J]. 地理科学, 34(8): 994-1001.
DOI |
|
XIAO Y, SHANG L N, HUANG Z G, et al., 2014. Ecological stoichiometry characteristics of soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in mountain swamps of Eastern Jilin Province[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 34(8): 994-1001.
DOI |
|
| [32] |
谢宝华, 韩广轩, 2018. 外来入侵种互花米草防治研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 29(10): 3464-3476.
DOI |
| XIE B H, HAN G X, 2018. Control of invasive Spartina alterniflora: A review[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 29(10): 3464-3476. | |
| [33] | 解雪峰, 孙晓敏, 吴涛, 等, 2020. 互花米草入侵对滨海湿地生态系统的影响研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 31(6): 2119-2128. |
| XIE X F, SUN X M, WU T, et al., 2020. Impacts of Spartina alterniflora invasion on coastal wetland ecosystem: Advances and prospects[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 31(6): 2119-2128. | |
| [34] | 杨霞, 陈丽华, 郑学良, 2021. 不同林龄油松人工林土壤碳、氮和磷生态化学计量特征[J]. 中国水土保持科学(中英文), 19(2): 108-116. |
| YANG X, CHEN L H, ZHENG X L, 2021. Ecological stoichiometry characterization of soil carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus of Pinus tabuliformis plantations at different stand ages[J]. Science of Soil and Water Conservation, 19(2): 108-116. | |
| [35] | 杨永兴, 刘长娥, 杨杨, 2011. 长江河口九段沙中沙互花米草湿地植物-土壤间营养元素含量灰色关联分析[J]. 环境科学研究, 24(1): 66-72. |
| YANG Y X, LIU C E, YANG Y, 2011. Gray correlation analysis on nutrient element contents between plants and soils in Spartina alterniflora wetlands in the middle shoal of Jiuduansha, Yangtze River Estuary[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 24(1): 66-72. | |
| [36] | 姚润珏, 陈宗英, 王兆峰, 2011. 河西内陆河不同流域盐碱土壤碳、氮、氢分布特征[J]. 甘肃农业科技 (1): 27-30. |
| YAO R Y, CHEN Z Y, WANG Z F, 2011. The Distribution Characteristics of Carbon,Nitrogen and Hydrogen of Saline-alkali Soil in Different Inland River Basin of Hexi Areas[J]. Gansu Agricultural Science and Technology (1): 27-30. | |
| [37] | 张文敏, 吴明, 王蒙, 等, 2014. 杭州湾湿地不同植被类型下土壤有机碳及其组分分布特征[J]. 土壤学报, 51(6): 1351-1360. |
| ZHANG W M, WU M, WANG M, et al., 2014. Distribution characteristics of organic carbon and its components in soils under different types of vegetation in wetland of Hangzhou Bay[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 51(6): 1351-1360. |
| [1] | 王钊, 张曼胤, 胡宇坤, 刘魏魏, 张苗苗. 盐度对典型滨海湿地沉积物汞甲基化的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1876-1884. |
| [2] | 柯丽娜, 徐佳慧, 王楠, 侯俊轩, 韩旭, 阴曙升. 基于遥感生态指数的滨海湿地生态质量变化评价——以辽东湾北部区为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1417-1424. |
| [3] | 刘志君, 崔丽娟, 李伟, 李晶, 雷茵茹, 朱怡诺, 王汝苗, 窦志国. 互花米草入侵对盐城滨海湿地nirS型反硝化细菌多样性及群落结构的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 704-714. |
| [4] | 闫振宁, 梅宝玲, 张桂萍, 韩广轩, 谢宝华, 张树岩, 周英锋, 刘展航. 高程对盐沼湿地互花米草生长与扩散的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1183-1191. |
| [5] | 蔡杨, 李伟, 左雪燕, 崔丽娟, 雷茵茹, 赵欣胜, 翟夏杰, 李晶, 潘旭. 盐城滨海湿地土壤多环芳烃分布特征及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1249-1259. |
| [6] | 张乃木, 宋娅丽, 王克勤, 张雨鉴, 潘禹, 郑兴蕊. 模拟氮沉降下滇中亚高山森林凋落物养分元素释放特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(5): 920-928. |
| [7] | 张莎莎, 李爱琴, 王会荣, 王晶晶, 徐小牛. 不同海拔杉木人工林土壤碳氮磷生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2020, 29(1): 97-104. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
