生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 1183-1191.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.06.009
闫振宁1,2( ), 梅宝玲1,*(
), 梅宝玲1,*( ), 张桂萍3, 韩广轩2, 谢宝华2,*(
), 张桂萍3, 韩广轩2, 谢宝华2,*( ), 张树岩4, 周英锋4, 刘展航2,5
), 张树岩4, 周英锋4, 刘展航2,5
收稿日期:2021-01-02
出版日期:2021-06-18
发布日期:2021-09-10
通讯作者:
谢宝华,副研究员,研究方向为湿地生态学。E-mail: bhxie@yic.ac.cn作者简介:闫振宁(1994年生),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为湿地生态学。E-mail: 404052051@qq.com
基金资助:
YAN Zhenning1,2( ), MEI Baoling1,*(
), MEI Baoling1,*( ), ZHANG Guiping3, HAN Guangxuan2, XIE Baohua2,*(
), ZHANG Guiping3, HAN Guangxuan2, XIE Baohua2,*( ), ZHANG Shuyan4, ZHOU Yingfeng4, LIU Zhanhang2,5
), ZHANG Shuyan4, ZHOU Yingfeng4, LIU Zhanhang2,5
Received:2021-01-02
Online:2021-06-18
Published:2021-09-10
摘要:
外来物种互花米草(Spartina alterniflora)入侵中国后,对潮间带滨海湿地的生态环境危害巨大,对河口湿地生态、景观、经济等方面均有不同程度影响,研究其入侵机制对有效防治互花米草是不可或缺的。黄河三角洲是中国北方受互花米草侵害最严重的地区之一。该研究在黄河三角洲潮间带开展互花米草移栽试验,2019年6月,在由海向陆方向上,把互花米草实生苗(种子萌发苗)与克隆苗(根茎萌发苗)移栽至高程范围为65.5—114.7 cm的不同地点,定期调查移栽点互花米草生长状况,同时进行潮汐与土壤性质监测,揭示潮间带不同高程对互花米草幼苗生长与扩散的影响,确定互花米草存活的高程阈值。结果表明:(1)随着高程升高,黄河三角洲潮间带的潮汐淹水时长和淹水深度有显著差异;(2)在黄河三角洲,影响互花米草生长与繁殖的主要环境因素为高程和潮汐共同作用的平均淹水时间、平均淹水深度和土壤盐度;(3)总体而言,互花米草实生苗与克隆苗的生长状况随高程升高而变差,实生苗可在盐地碱蓬分布区存活,克隆苗可在高程更高的芦苇和柽柳分布区存活;(4)在由海向陆方向上,短期内互花米草可快速扩散至盐地碱蓬分布区,经过长期适应后,互花米草可能扩散至芦苇分布区甚至柽柳分布区。因此,中国北方互花米草防控刻不容缓,首先应有效控制互花米草种子的有性繁殖,限制或阻止其通过种子进行远距离扩散,其次,应加快互花米草控制步伐,否则,经过长期适应之后,互花米草很可能继续向陆地方向扩张,与本土植被芦苇和柽柳产生直接竞争,扩大其对潮间带生态系统的威胁。
中图分类号:
闫振宁, 梅宝玲, 张桂萍, 韩广轩, 谢宝华, 张树岩, 周英锋, 刘展航. 高程对盐沼湿地互花米草生长与扩散的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1183-1191.
YAN Zhenning, MEI Baoling, ZHANG Guiping, HAN Guangxuan, XIE Baohua, ZHANG Shuyan, ZHOU Yingfeng, LIU Zhanhang. Effects of Elevation on the Invasion and Expansion of Spartina alterniflora in A Salt Marsh[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(6): 1183-1191.
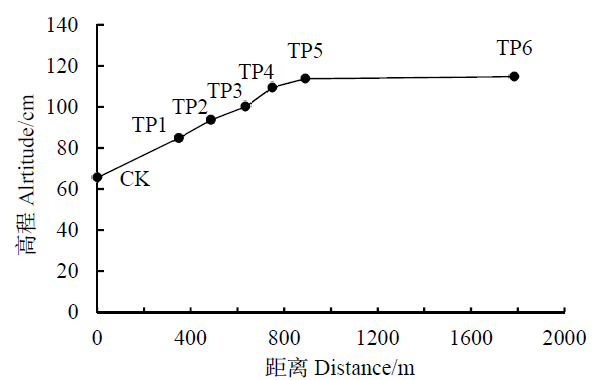
图2 各移栽点(TP1—TP6)的高程及移栽点与对照点(CK)之间的距离
Fig. 2 Elevation of each transplanting site (TP) and the distance between transplanting sites and control site (CK)
| 移栽点Transplanting site | 植被 Vegetation | 平均淹水深度 Average depth of flooding/(cm∙d-1) | 淹水频率 Foodding frequency/% | 淹水时长 Duration of flooding/h | 最大淹水深度 Maximum depth of flooding/cm | 电导率# Conductivity/ (ms∙cm-1) | 温度# Temperature/ ℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 互花米草 S. alterniflora | 14.56±0.001a | 100 | 270.53±15.8a | 132.83 | 10.03±0.4a | 25.27±1b |
| TP1 | 光滩 Bare flat | 7.80±0.001b | 94 | 160.08±12.2b | 112.43 | 10.00±0.4a | 24.85±1.1b |
| TP2 | 光滩+盐地碱蓬 Bare flat+S. salsa | 5.64±0.001c | 89 | 128.22±9.9c | 102.63 | 11.22±0.4a | 25.66±1.1b |
| TP3 | 盐地碱蓬 S. salsa | 4.27±0.001d | 85 | 107.92±8.2c | 95.13 | 10.82±0.4a | 26.68±1ab |
| TP4 | 盐地碱蓬+芦苇 S. salsa+P. australis | 2.78±0.001e | 78 | 81.00±6.1d | 84.83 | 11.29±0.4a | 26.54±1.1ab |
| TP5 | 芦苇P. australis | 1.78±0.001f | 67 | 59.81±4.3de | 75.63 | 10.32±0.5a | 28.06±1.1ab |
| TP6 | 柽柳 T. chinensis | 1.19±0.149g | 67 | 43.61±3.2e | 68.32 | 10.57±0.5a | 29.19±1.1a |
表1 不同移栽点的环境因子
Table 1 Environment factors at different transplanting site
| 移栽点Transplanting site | 植被 Vegetation | 平均淹水深度 Average depth of flooding/(cm∙d-1) | 淹水频率 Foodding frequency/% | 淹水时长 Duration of flooding/h | 最大淹水深度 Maximum depth of flooding/cm | 电导率# Conductivity/ (ms∙cm-1) | 温度# Temperature/ ℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 互花米草 S. alterniflora | 14.56±0.001a | 100 | 270.53±15.8a | 132.83 | 10.03±0.4a | 25.27±1b |
| TP1 | 光滩 Bare flat | 7.80±0.001b | 94 | 160.08±12.2b | 112.43 | 10.00±0.4a | 24.85±1.1b |
| TP2 | 光滩+盐地碱蓬 Bare flat+S. salsa | 5.64±0.001c | 89 | 128.22±9.9c | 102.63 | 11.22±0.4a | 25.66±1.1b |
| TP3 | 盐地碱蓬 S. salsa | 4.27±0.001d | 85 | 107.92±8.2c | 95.13 | 10.82±0.4a | 26.68±1ab |
| TP4 | 盐地碱蓬+芦苇 S. salsa+P. australis | 2.78±0.001e | 78 | 81.00±6.1d | 84.83 | 11.29±0.4a | 26.54±1.1ab |
| TP5 | 芦苇P. australis | 1.78±0.001f | 67 | 59.81±4.3de | 75.63 | 10.32±0.5a | 28.06±1.1ab |
| TP6 | 柽柳 T. chinensis | 1.19±0.149g | 67 | 43.61±3.2e | 68.32 | 10.57±0.5a | 29.19±1.1a |
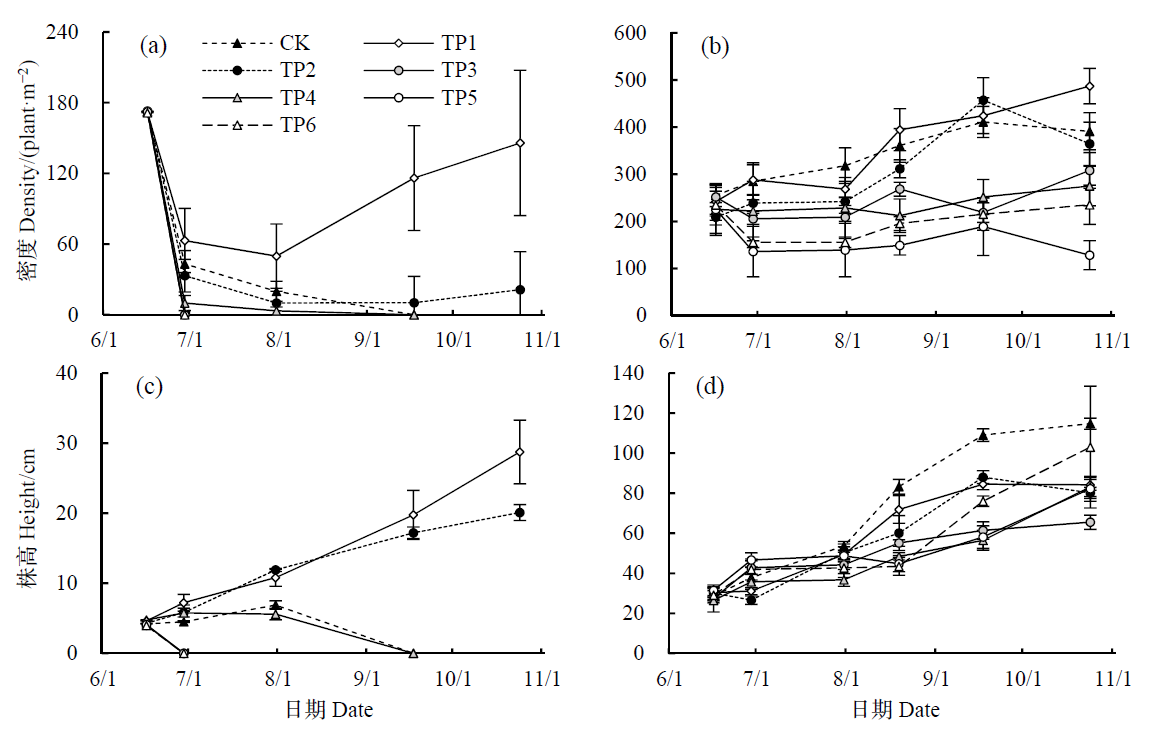
图3 不同高程处互花米草实生苗密度(a)与株高(c)、克隆苗密度(b)与株高(d)
Fig. 3 Density (a) and plant height (c) of seedlings, and density (b) and plant height (d) of clonal ramets of S. alterniflora at different elevations
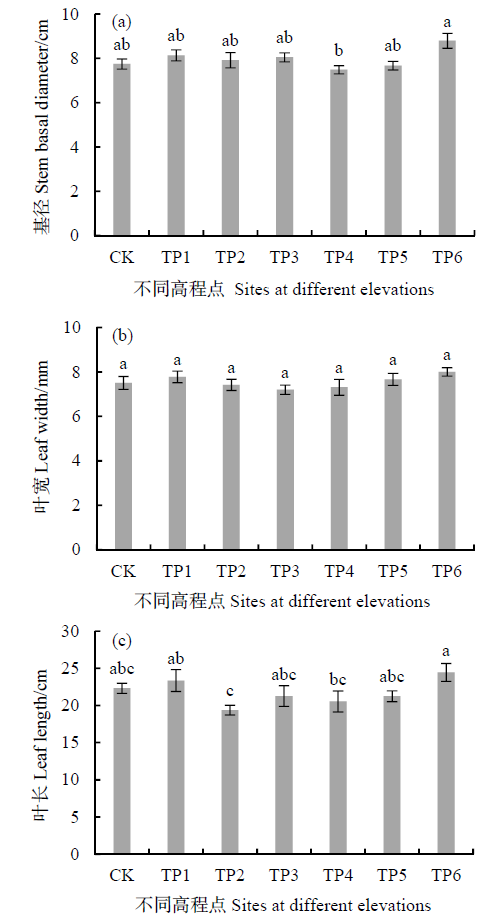
图4 生长季末期互花米草克隆分株的基径(a)、叶宽(b)和叶长(c)
Fig. 4 Stem basal diameter (a), leaf width (b) and leaf length (c) of clonal ramets of S. alterniflora at the end of growing season
| 环境因子 Environmental factors | 第Ⅰ轴 Axis Ⅰ | 第Ⅱ轴 Axis Ⅱ |
|---|---|---|
| 高程 Elevation | 0.720 | -0.276 |
| 平均淹水深度 Average depth of flooding | -0.678 | 0.088 |
| 最大淹水深度 Maximum depth of flooding | -0.410 | 0.089 |
| 淹水时长 Total duration of flooding | -0.699 | -0.209 |
| 淹水频率 The flood frequency | -0.649 | 0. 287 |
| 温度 Temperature | 0.559 | 0.457 |
| 电导率 Conductivity | -0.125 | -0.450 |
表2 环境因子与排序轴的相关关系
Table 2 Correlation of environmental factors with the axes
| 环境因子 Environmental factors | 第Ⅰ轴 Axis Ⅰ | 第Ⅱ轴 Axis Ⅱ |
|---|---|---|
| 高程 Elevation | 0.720 | -0.276 |
| 平均淹水深度 Average depth of flooding | -0.678 | 0.088 |
| 最大淹水深度 Maximum depth of flooding | -0.410 | 0.089 |
| 淹水时长 Total duration of flooding | -0.699 | -0.209 |
| 淹水频率 The flood frequency | -0.649 | 0. 287 |
| 温度 Temperature | 0.559 | 0.457 |
| 电导率 Conductivity | -0.125 | -0.450 |
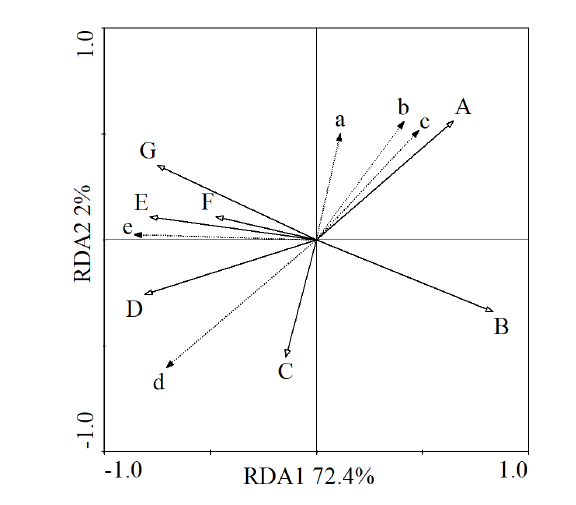
图8 互花米草克隆苗植物特征与环境因子关系的冗余分析排序图 A 温度 Temperature;B 高程 Elevation;C 电导率 Conductivity;D 淹水时长 Total duration of flooding;E 平均淹水深度 Average depth of flooding;F 最大淹水深度 Maximum depth of flooding;G 淹水频率 The flood frequency;a 叶长 Leaf length;b 叶宽 Leaf width;c 基径Stem basal diameter;d 株高 Height;e 密度 Density
Fig. 8 Biplot of the two axes of RDA(redundancy analysis) for environmental factor with growth characteristics of clonal ramets of S. alterniflora
| 环境因子 Environmental factors | 重要性排序 Importance rank | 环境因子所占 解释量 Variance explains of Environmental factors | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高程 Elevation | 1 | 50.4 | 33.593 | 0.002 |
| 淹水时长 Total duration of flooding | 2 | 47.5 | 29.893 | 0.002 |
| 平均淹水深度 Average depth of flooding | 3 | 44.6 | 26.555 | 0.002 |
| 淹水频率 The flood frequency | 4 | 41.0 | 22.950 | 0.002 |
| 温度 Temperature | 5 | 30.8 | 14.715 | 0.002 |
| 最大淹水深度 Maximum depth of flooding | 6 | 16.3 | 6.438 | 0.020 |
| 电导率 Conductivity | 7 | 2.10 | 0.696 | 0.412 |
表3 环境因子变量解释的重要性排序和显著性检验结果
Table 3 Importance and signification level of environmental factors
| 环境因子 Environmental factors | 重要性排序 Importance rank | 环境因子所占 解释量 Variance explains of Environmental factors | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高程 Elevation | 1 | 50.4 | 33.593 | 0.002 |
| 淹水时长 Total duration of flooding | 2 | 47.5 | 29.893 | 0.002 |
| 平均淹水深度 Average depth of flooding | 3 | 44.6 | 26.555 | 0.002 |
| 淹水频率 The flood frequency | 4 | 41.0 | 22.950 | 0.002 |
| 温度 Temperature | 5 | 30.8 | 14.715 | 0.002 |
| 最大淹水深度 Maximum depth of flooding | 6 | 16.3 | 6.438 | 0.020 |
| 电导率 Conductivity | 7 | 2.10 | 0.696 | 0.412 |
| [1] |
ALLEN J R L, 2000. Morphodynamics of Holocene salt marshes: a review sketch from the Atlantic and Southern North Sea coasts of Europe[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 19(12): 1155-1231.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
BERTNESS M D, 1991. Zonation of Spartina Patens and Spartina alterniflora in New England Salt Marsh[J]. Ecology, 72(1): 138-148.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
HU Z, VAN B J, VAN D W D, et al., 2015. Windows of opportunity for salt marsh vegetation establishment on bare tidal flats: The importance of temporal and spatial variability in hydrodynamic forcing[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research-Biogeosciences, 120(7): 1450-1469.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
HUGGETT A J, 2005. The concept and utility of 'ecological thresholds' in biodiversity conservation[J]. Biological Conservation, 124(3): 301-310.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
KUEFFER C, 2017. Plant invasions in the Anthropocene[J]. Science, 358(6364): 724-725.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
LARSEN S, ALP M, 2015. Ecological thresholds and riparian wetlands:an overview for environmental managers[J]. Limnology, 16(1): 1-9.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
LI R X, YU Q, WANG Y W, et al., 2018. The relationship between inundation duration and Spartina alterniflora growth along the Jiangsu coast, China[J]. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 213: 305-313.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
MORRIS J T, SUNDARESHWAR P V, NIETCH C T, et al., 2002. Responses of coastal wetlands to rising sea level[J]. Ecology, 83(10): 2869-2877.
DOI URL |
| [9] | ORMEROD S J, WATKINSON A R, 2000. Large-scale ecology and hydrology: an introductory perspective from the editors of the Journal of Applied Ecology[J]. Journal of Applied Ecology, 37(s1): 1-5. |
| [10] |
PERRINGS C, WALKER B, 1997. Biodiversity, resilience and the control of ecological-economic systems: The case of fire-driven rangelands[J]. Ecological Economics, 22(1): 73-83.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
PIMENTEL D, MCNAIR S, JANECKA J, et al., 2001. Economic and environmental threats of alien plant, animal, and microbe invasions[J]. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 84(1): 1-20.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
REN G B, WANG J J, WANG A D, et al., 2019. Monitoring the Invasion of Smooth Cordgrass Spartina alterniflora within the Modern Yellow River Delta Using Remote Sensing[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, DOI: 10.2112/SI90-017.1.
DOI |
| [13] |
VAN WESENBEECK B K, KOPPEL J V D, Peter M J, et al., 2008. Does scale-dependent feedback explain spatial complexity in salt-marsh ecosystems?[J]. Oikos, 117(1): 152-159.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
WIJTE A H B M, GALLAGHER J L, 1996. Effect of oxygen availability and salinity on early life history stages of salt marsh plants.1. Different germination strategies of Spartina alterniflora and Phragmites australis (Poaceaei)[J]. American Journal of Botany, 83(10): 1337-1342.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
XIE B H, HAN G X, QIAO P Y, et al., 2019. Effects of mechanical and chemical control on invasive Spartina alterniflora in the Yellow River Delta, China[J]. Peerj, 7(8): e7655.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
XUE L, LI X Z, ZHANG Q, et al., 2018. Elevated salinity and inundation will facilitate the spread of invasive Spartina alterniflora in the Yangtze River Estuary, China[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 506: 144-154.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
ZHANG R S, SHEN Y M, LU L Y, et al., 2004. Formation of Spartina alterniflora salt marshes on the coast of Jiangsu Province, China[J]. Ecological Engineering, 23(2): 95-105.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
陈权, 马克明, 2015. 红树林生物入侵研究概况与趋势[J]. 植物生态学报, 39(3): 283-299.
DOI |
|
CHEN Q, MA K M, 2015. Research overview and trend on biological invasion in mangrove forests[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 39(3): 283-299.
DOI URL |
|
| [19] |
陈中义, 李博, 陈家宽, 2004. 米草属植物入侵的生态后果及管理对策[J]. 生物多样性, 12(2): 280-289.
DOI |
| CHEN Z Y, LI B, CHEN J K, 2004. Ecological consequences and management of Spartina spp. Invasions in coastal ecosystems[J]. Biodiversity Science, 12(2): 280-289. | |
| [20] | 陈正勇, 王国祥, 刘金娥, 等, 2011. 淹水调控对互花米草生长的影响[J]. 环境科学研究, 24(9): 1003-1007. |
| CHEN Z Y, WANG G X, LIU J E, et al., 2011. Effects of Waterlogging Regulation on Growth of Spartina Alterniflora[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 24(9): 1003-1007. | |
| [21] | 冯建祥, 黄茜, 陈卉, 等, 2018. 互花米草入侵对盐沼和红树林滨海湿地底栖动物群落的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 37(3): 943-951. |
| FENG J X, HUANG Q, CHEN H, et al., 2018. Effects of Spartina alterniflora invasion on benthic faunal community in saltmarsh and mangrove wetland[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 37(3): 943-951. | |
| [22] | 李大林, 2014. 我国每年因外来生物入侵经济损失超两千亿元[J]. 广西质量监督导报 (11): 30. |
| LI D L, 2014. China loses more than 200 billion yuan due to alien biological invasion every year[J]. Guangxi Quality Supervision Guide Periodical (11): 30. | |
| [23] | 李伟, 袁琳, 张利权, 等, 2018. 海三棱藨草及互花米草对模拟盐胁迫的响应及其耐盐阈值[J]. 生态学杂志, 37(9): 2596-2602. |
| LI W, YUAN L, ZHANG L Q, et al., 2018. Responses of Scirpus mariqueter and Spartina alterniflora to simulated salt stress and salttolerance thresholds[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 37(9): 2596-2602. | |
| [24] | 刘会玉, 林振山, 齐相贞, 等, 2015. 基于个体的空间显性模型和遥感技术模拟入侵植物扩张机制[J]. 生态学报, 35(23): 7794-7802. |
| LIU H Y, LIN Z S, QI X Z, et al., 2015. The dispersal mechanism of invasive plants based on a spatially explicit individual-based model and Remote sensing technology: A case study of Spartina alterniflora[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35(23): 7794-7802. | |
| [25] | 刘潞, 余夏杨, 唐洪根, 等, 2019. 围垦对条子泥互花米草种群年季扩张特征的影响[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 36(3): 376-384. |
| LIU L, YU X Y, TANG H G, et al., 2019. Effect of reclamation on the annual and seasonal characteristics of Spartina alterniflora population in Tiaozini coastal wetland[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 36(3): 376-384. | |
| [26] | 孙书存, 蔡永立, 刘红, 2001. 长江口盐沼海三棱藨草在高程梯度上的生物量分配(英文)[J]. 植物学报, 43(2): 178-185. |
| SUN S C, CAI Y L, LIU H, 2001. Biomass Allocation of Scirpus mariqueter Along an Elevational Gradient in a Salt Marsh of the Yangtse River Estuary[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 43(2): 178-185. | |
| [27] |
唐海萍, 陈姣, 薛海丽, 2015. 生态阈值: 概念、方法与研究展望[J]. 植物生态学报, 39(9): 932-940.
DOI |
|
TANG H P, CHEN J, XUE H L, 2015. Ecological thresholds: Concept, methods and research outlooks[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 39(9): 932-940.
DOI URL |
|
| [28] | 徐国万, 卓荣宗, 曹豪, 等, 1989. 互花米草生物量年动态及其与滩涂生境的关系[J]. 植物生态学与地植物学学报, 13(3): 230-235. |
| XU G W, ZHUO R Z, CAO H, et al., 1989. Annual changes of biomass of Spartina alterniflora and the relationships between biomass and tidalland habits[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 13(3): 230-235. | |
| [29] | 袁连奇, 张利权, 2010. 调控淹水对互花米草生理影响的研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 41(2): 175-179. |
| YUAN L Q, ZHANG L Q, 2010. Effects of Waterlogging on the Physiology of Spartina Alterniflora[J]. Oceanologia ET Limnologia Sinica, 41(2): 175-179. | |
| [30] | 张华兵, 韩爽, 王娟, 等, 2020. 生态恢复视角下海滨湿地景观模拟——以江苏盐城湿地珍禽国家级自然保护区为例[J]. 水生态学杂志, 41(4): 41-47. |
| ZHANG B H, HAN S, WANG J, et al., 2020. Landscape Simulation of Coastal Wetlands to Support Ecological Restoration: A Case Study of the Jiangsu Yancheng Wetland Rare Birds National Nature Reserve[J]. Journal of Hydroecology, 41(4): 41-47. | |
| [31] | 赵相健, 赵彩云, 柳晓燕, 等, 2015. 不同纬度地区互花米草生长性状及适应性研究[J]. 生态科学, 34(1): 119-128. |
| ZHAO X J, ZHAO C Y, LIU X Y, et al., 2015. Growth characteristics and adaptability of Spartina alterniflora in different Iatitude areas along China coast[J]. Ecological Science, 34(1): 119-128. | |
| [32] | 赵志远, 袁琳, 李伟, 等, 2018. 生境异质性及源株密度对互花米草入侵力的影响[J]. 生态学报, 38(18): 6632-6641. |
| ZHAO Z Y, YUAN L, LI W, et al., 2018. Effects of habitat heterogeneity and ortet density on the invasiveness of Spartina alterniflora[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(18): 6632-6641. | |
| [33] | 朱晓泾, 袁琳, 赵志远, 等, 2019. 环境因子对互花米草定居潮滩的影响分析[J]. 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版) (6): 140-152. |
| ZHU X J, YUAN L, ZHAO Z Y, et al., 2019. The influence of environmental factors on the settlement of Spartina alterniflora on tidal flats[J]. Journal of East China Normal University (Natural Science) (6): 140-152. | |
| [34] | 祝振昌, 张利权, 肖德荣, 2011. 上海崇明东滩互花米草种子产量及其萌发对温度的响应[J]. 生态学报, 31(6): 1574-1581. |
| ZHU Z C, ZHANG L Q, XIAO D R, 2011. Seed production of Spartina alterniflora and its response of germination to temperature at Chongming Dongtan,Shanghai[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31(6): 1574-1581. |
| [1] | 王洁, 单燕, 马兰, 宋延静, 王向誉. 秸秆/生物质炭协同还田措施对黄河三角洲盐碱土壤的改良效果研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 90-98. |
| [2] | 刘展航, 张树岩, 侯玉平, 朱书玉, 王立冬, 施欣悦, 李培广, 韩广轩, 谢宝华. 互花米草入侵对黄河口湿地土壤碳氮磷及其生态化学计量特征的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1360-1369. |
| [3] | 刘志君, 崔丽娟, 李伟, 李晶, 雷茵茹, 朱怡诺, 王汝苗, 窦志国. 互花米草入侵对盐城滨海湿地nirS型反硝化细菌多样性及群落结构的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 704-714. |
| [4] | 张楷悦, 刘增辉, 王颜昊, 王敬宽, 崔德杰, 柳新伟. 黄河三角洲自然保护区土壤PAHs的风险评估和空间特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2198-2205. |
| [5] | 王瑞, 宋祥云, 柳新伟. 黄河三角洲不同植被类型土壤酶活性的季节变化[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 62-69. |
| [6] | 王浩, 陈永金, 刘加珍, 万波, 张丽. 黄河三角洲新生湿地3种柽柳灌丛对土壤有机碳空间分布的影响研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 9-16. |
| [7] | 王永志, 刘胜林. 黄河三角洲芦苇湿地生态系统碳通量动态特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(5): 949-956. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
