生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (7): 1350-1359.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.07.007
收稿日期:2022-02-08
出版日期:2022-07-18
发布日期:2022-08-31
作者简介:姚付龙(1982年生),男,副教授,博士,主要从事全新世环境演变研究。E-mail: njuwolf@foxmail.com
基金资助:
YAO Fulong( ), HUANG Jian, YAN Junjie, LIU Haijun, TANG Guoqian
), HUANG Jian, YAN Junjie, LIU Haijun, TANG Guoqian
Received:2022-02-08
Online:2022-07-18
Published:2022-08-31
摘要:
厘清天山草甸表土花粉与现代植被的关系,对用地层花粉解译该区第四纪环境演变具有重要意义。选取西天山北坡3类草甸(中山草甸、亚高山草甸、高山草甸)为研究对象,以9个植物群落的54个表土花粉样品为研究材料,依据花粉鉴定结果,对比野外样方调查数据,探讨了西天山北坡草甸表土花粉与现代植被的关系,基于除趋势对应分析方法揭示了花粉、植被的生态环境指示意义。研究表明,(1)云杉属(Picea)、藜科(Chenopodiaceae)、蒿属(Artemisia)在表土样品中含量高,分别为20.7%、18.2%、17.1%,影响了表土花粉组合与现代植被关系判别。禾本科(Poaceae)、莎草科(Cyperaceae)、蔷薇科(Rosaceae)、菊科(Compositae)花粉在以各自为建群种或优势种的群落中有较高含量,分别为12.1%、9.6%、7.8%、4.9%。(2)各植被带均存在特有的表土花粉组合,中山草甸以云杉属-禾本科-藜科-蒿属为特征,亚高山草甸演变为云杉属-蒿属-藜科-蔷薇科-禾本科组合,高山草甸由藜科-莎草科-蒿属-云杉属-禾本科花粉组成。(3)禾本科/(蒿属+藜科)、莎草科/(蒿属+藜科) 比值可用于区分中山草甸、亚高山草甸、高山草甸,还可分别指示湿度大小和温度高低。(4)除趋势对应分析、聚类分析能将表土花粉样品划分至各自群落。温度、湿度为西天山北坡重要的生态因子,温度促使植被带形成和分布,湿度使其进一步分化形成了不同群落。
中图分类号:
姚付龙, 黄健, 闫俊杰, 刘海军, 唐国乾. 西天山北坡草甸群落表土花粉组合及其生态指示意义[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1350-1359.
YAO Fulong, HUANG Jian, YAN Junjie, LIU Haijun, TANG Guoqian. The Assemblages of Surface Pollen and Their Ecological Significance from Major Meadow Communities Along the North Slope of Tianshan[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(7): 1350-1359.
| 植物群落 Plant community | 盖度 Coverage/% | 主要物种 Main plant composition |
|---|---|---|
| 早熟禾群落 Poa nemoralis community | 80-90 | 早熟禾 (Poa nemoralis)、车轴草 (Trifolium spp.)、天山羽衣草 (Alchemilla tianschanica)、无芒雀麦(Bromus inermis)、鸭茅 (Dactylis glomerata)、假梯牧草 (Phleum phleoides)、酸模 (Rumex acetosa)、草原老鹳草 (Geranium pratense)、新疆党参 (Codonopsis clematidea)、唐松草 (Thalictrum spp.)、蒲公英 (Taraxacum spp.) 等 |
| 短芒短柄草群落 Brachypodium pinnatum community | 70-90 | 短芒短柄草 (Brachypodium pinnatum)、鸭茅 (Dactylis glomerata)、早熟禾 (Poa nemoralis)、广布野豌豆 (Vicia cracca)、牛至 (Origanum vulgare)、唐松草 (Thalictrum spp.)、穗花婆婆纳 (Veronica spicata)、草原老鹳草 (Geranium pratense)、大叶橐吾 (Ligularia macrophylla)、白花蓼 (Polygonum coriarium) 等 |
| 高草杂类草草甸 Varii herbae meadow | 60-90 | 大叶橐吾 (Ligularia macrophylla)、西伯利亚羽衣草 (Alchemilla sibirica)、块根糙苏 (Phlomis tuberosa)、草原老鹳草 (Geranium pratense)、兴安独活 (Heracleum dissectum)、羊角芹 (Aegopodium spp.)、天山大黄 (Rheum wittrockii)、高山地榆 (Sanguisorba alpina)、蒲公英 (Taraxacum spp.) 等 |
| 大叶橐吾群落 Ligularia macrophylla community | 60-80 | 大叶橐吾 (Ligularia macrophylla)、蓍 (Achillea millefoliun)、火绒草 (Leontopodium spp.)、珠芽蓼 (Polygonum viviparum)、天山羽衣草 (Alchemilla tianschanica)、委陵菜 (Potentilla spp.)、紫苞鸢尾 (Iris ruthenica)、早熟禾 (Poa spp.)、高山梯牧草 (Phleum alpinum)、薹草 (Carex spp.)、蓝花老鹳草 (Geraniumpseudo sibiricum)、高山龙胆 (Gentiana algida)、金露梅 (Potentilla fruticosa)、鬼箭锦鸡儿 (Caragana jubata) 等 |
| 羽衣草群落 Alchemilla spp. community | 70-90 | 天山羽衣草 (Alchemilla tianschanica)、无芒雀麦 (Bromus inermis)、亚欧唐松草 (Thalictrum minus)、侧花种阜草 (Moehringia lateriflora)、无心菜 (Arenaria serpyllifolia)、大苞石竹 (Dianthus hoeltzeri)、毛茛 (Ranunculus spp.)、黑花薹草 (Carex melanantha) 等 |
| 杂类草草甸 Varii herbae meadow | 80-90 | 天山羽衣草 (Alchemilla tianschanica)、细叶早熟禾 (Poa angustifolia)、高山早熟禾 (Poa alpina)、珠芽蓼(Polygonum viviparum)、山地乌头 (Aconitum monticola)、老鸛草 (Geranium spp.)、天山风毛菊 (Saussurea larionowii)、高山紫菀 (Aster alpinus)、高山龙胆 (Gentiana algida)、高山唐松草 (Thalictrum alpinum)、准噶尔蓼 (Polygonum songoricum) 等 |
| 嵩草及杂类草草甸 Kobresia spp. & varii herbae meadow | 60-80 | 嵩草 (Kobresia spp.)、细柄茅 (Ptilagrostis mongholica)、唐松草 (Thalictrum spp.)、短筒獐牙菜 (Swertia connata)、白花老鹳草 (Geranium albiflorum)、匍匐委陵菜 (Potentilla reptans)、葶苈 (Draba nemorosa)、高山黄芪 (Astragalus alpinus)、棘豆 (Oxytropis spp.)、厚叶美花草 (Callianthemum alatavicum)、天山银莲花 (Anemone narcissiflora var. turkestanica)、天山点地梅 (Androsace ovczinnikovii) 等 |
| 薹草及杂类草草甸 Carex spp. & varii herbae meadow | 50-80 | 薹草 (Carex spp)、西伯利亚三毛草 (Trisetum sibiricum)、珠芽蓼 (Polygonum viviparum)、勿忘草 (Myosotis alpestris)、高山龙胆 (Gentiana algida)、匍枝毛茛 (Ranunculus repens)、天山卷耳 (Cerastium tianschanicum)、白花老鹳草 (Geranium albiflorum)、蒲公英 (Taraxacum spp.) 等 |
| 高山杂类草草甸 Varii herbae meadow | 40-60 | 珠芽蓼 (Polygonum viviparum)、嵩草 (Kobresia spp.)、穗状寒生羊茅 (Festuca ovina subsp. sphagnicola)、高山龙胆 (Gentiana algida)、岩生老鹳草 (Geranium saxatile)、大花毛建草 (Dracocephalum grandiflorum)、高山紫菀 (Aster alpinus) 等 |
表1 西天山北坡草甸主要物种组成
Table 1 Main plant species of the different vegetation types along the north slope of Tianshan
| 植物群落 Plant community | 盖度 Coverage/% | 主要物种 Main plant composition |
|---|---|---|
| 早熟禾群落 Poa nemoralis community | 80-90 | 早熟禾 (Poa nemoralis)、车轴草 (Trifolium spp.)、天山羽衣草 (Alchemilla tianschanica)、无芒雀麦(Bromus inermis)、鸭茅 (Dactylis glomerata)、假梯牧草 (Phleum phleoides)、酸模 (Rumex acetosa)、草原老鹳草 (Geranium pratense)、新疆党参 (Codonopsis clematidea)、唐松草 (Thalictrum spp.)、蒲公英 (Taraxacum spp.) 等 |
| 短芒短柄草群落 Brachypodium pinnatum community | 70-90 | 短芒短柄草 (Brachypodium pinnatum)、鸭茅 (Dactylis glomerata)、早熟禾 (Poa nemoralis)、广布野豌豆 (Vicia cracca)、牛至 (Origanum vulgare)、唐松草 (Thalictrum spp.)、穗花婆婆纳 (Veronica spicata)、草原老鹳草 (Geranium pratense)、大叶橐吾 (Ligularia macrophylla)、白花蓼 (Polygonum coriarium) 等 |
| 高草杂类草草甸 Varii herbae meadow | 60-90 | 大叶橐吾 (Ligularia macrophylla)、西伯利亚羽衣草 (Alchemilla sibirica)、块根糙苏 (Phlomis tuberosa)、草原老鹳草 (Geranium pratense)、兴安独活 (Heracleum dissectum)、羊角芹 (Aegopodium spp.)、天山大黄 (Rheum wittrockii)、高山地榆 (Sanguisorba alpina)、蒲公英 (Taraxacum spp.) 等 |
| 大叶橐吾群落 Ligularia macrophylla community | 60-80 | 大叶橐吾 (Ligularia macrophylla)、蓍 (Achillea millefoliun)、火绒草 (Leontopodium spp.)、珠芽蓼 (Polygonum viviparum)、天山羽衣草 (Alchemilla tianschanica)、委陵菜 (Potentilla spp.)、紫苞鸢尾 (Iris ruthenica)、早熟禾 (Poa spp.)、高山梯牧草 (Phleum alpinum)、薹草 (Carex spp.)、蓝花老鹳草 (Geraniumpseudo sibiricum)、高山龙胆 (Gentiana algida)、金露梅 (Potentilla fruticosa)、鬼箭锦鸡儿 (Caragana jubata) 等 |
| 羽衣草群落 Alchemilla spp. community | 70-90 | 天山羽衣草 (Alchemilla tianschanica)、无芒雀麦 (Bromus inermis)、亚欧唐松草 (Thalictrum minus)、侧花种阜草 (Moehringia lateriflora)、无心菜 (Arenaria serpyllifolia)、大苞石竹 (Dianthus hoeltzeri)、毛茛 (Ranunculus spp.)、黑花薹草 (Carex melanantha) 等 |
| 杂类草草甸 Varii herbae meadow | 80-90 | 天山羽衣草 (Alchemilla tianschanica)、细叶早熟禾 (Poa angustifolia)、高山早熟禾 (Poa alpina)、珠芽蓼(Polygonum viviparum)、山地乌头 (Aconitum monticola)、老鸛草 (Geranium spp.)、天山风毛菊 (Saussurea larionowii)、高山紫菀 (Aster alpinus)、高山龙胆 (Gentiana algida)、高山唐松草 (Thalictrum alpinum)、准噶尔蓼 (Polygonum songoricum) 等 |
| 嵩草及杂类草草甸 Kobresia spp. & varii herbae meadow | 60-80 | 嵩草 (Kobresia spp.)、细柄茅 (Ptilagrostis mongholica)、唐松草 (Thalictrum spp.)、短筒獐牙菜 (Swertia connata)、白花老鹳草 (Geranium albiflorum)、匍匐委陵菜 (Potentilla reptans)、葶苈 (Draba nemorosa)、高山黄芪 (Astragalus alpinus)、棘豆 (Oxytropis spp.)、厚叶美花草 (Callianthemum alatavicum)、天山银莲花 (Anemone narcissiflora var. turkestanica)、天山点地梅 (Androsace ovczinnikovii) 等 |
| 薹草及杂类草草甸 Carex spp. & varii herbae meadow | 50-80 | 薹草 (Carex spp)、西伯利亚三毛草 (Trisetum sibiricum)、珠芽蓼 (Polygonum viviparum)、勿忘草 (Myosotis alpestris)、高山龙胆 (Gentiana algida)、匍枝毛茛 (Ranunculus repens)、天山卷耳 (Cerastium tianschanicum)、白花老鹳草 (Geranium albiflorum)、蒲公英 (Taraxacum spp.) 等 |
| 高山杂类草草甸 Varii herbae meadow | 40-60 | 珠芽蓼 (Polygonum viviparum)、嵩草 (Kobresia spp.)、穗状寒生羊茅 (Festuca ovina subsp. sphagnicola)、高山龙胆 (Gentiana algida)、岩生老鹳草 (Geranium saxatile)、大花毛建草 (Dracocephalum grandiflorum)、高山紫菀 (Aster alpinus) 等 |
| 样号 No. | 地理位置 Location | 海拔 Elevation/m | 植物群落 Plant community | 样号 No. | 地理位置 Location | 海拔 Elevation/m | 植物群落 Plant community |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 43°20′56″N, 83°37′19″E | 2147 | I-1 | 28 | 42°53′16″N, 82°07′02″E | 2748 | II-2 |
| 2 | 43°20′56″N, 83°37′29″E | 2039 | I-1 | 29 | 43°04′51″N, 82°16′15″E | 2531 | II-2 |
| 3 | 43°20′51″N, 83°37′59″E | 2148 | I-1 | 30 | 43°01′10″N, 82°22′41″E | 2599 | II-2 |
| 4 | 43°20′33″N, 83°36′20″E | 2050 | I-1 | 31 | 43°07′53″N, 83°07′28″E | 2405 | II-3 |
| 5 | 43°20′28″N, 83°31′04″E | 2253 | I-1 | 32 | 43°05′30″N, 83°15′08″E | 2518 | II-3 |
| 6 | 43°20′34″N, 83°32′49″E | 2227 | I-1 | 33 | 43°05′20″N, 83°16′17″E | 2624 | II-3 |
| 7 | 43°20′23″N, 83°34′13″E | 2241 | I-2 | 34 | 43°05′40″N, 83°18′41″E | 2424 | II-3 |
| 8 | 43°20′19″N, 83°34′30″E | 2401 | I-2 | 35 | 43°08′50″N, 83°26′30″E | 2665 | II-3 |
| 9 | 43°20′34″N, 83°36′34″E | 2168 | I-2 | 36 | 43°13′57″N, 83°26′40″E | 2651 | II-3 |
| 10 | 43°20′41″N, 83°36′54″E | 2332 | I-2 | 37 | 43°03′21″N, 83°10′01″E | 2858 | III-1 |
| 11 | 43°20′49″N, 83°37′26″E | 2115 | I-2 | 38 | 43°03′19″N, 83°14′23″E | 3107 | III-1 |
| 12 | 43°20′48″N, 83°37′41″E | 2080 | I-2 | 39 | 43°04′16″N, 83°20′04″E | 3083 | III-1 |
| 13 | 43°20′55″N, 83°38′39″E | 2168 | I-3 | 40 | 43°08′40″N, 83°31′46″E | 3091 | III-1 |
| 14 | 43°20′31″N, 83°38′50″E | 2357 | I-3 | 41 | 43°10′14″N, 83°55′13″E | 2893 | III-1 |
| 15 | 43°20′38″N, 83°37′55″E | 2244 | I-3 | 42 | 43°09′47″N, 84°03′47″E | 2999 | III-1 |
| 16 | 43°20′48″N, 83°37′23″E | 2152 | I-3 | 43 | 43°47′09″N, 84°04′22″E | 2897 | III-2 |
| 17 | 43°20′32″N, 83°36′17″E | 2138 | I-3 | 44 | 43°50′59″N, 84°01′17″E | 2805 | III-2 |
| 18 | 43°20′21″N, 83°35′51″E | 2210 | I-3 | 45 | 43°51′31″N, 83°53′34″E | 2933 | III-2 |
| 19 | 42°20′13″N, 80°43′39″E | 2797 | II-1 | 46 | 43°51′58″N, 83°48′57″E | 2826 | III-2 |
| 20 | 42°40′24″N, 80°49′54″E | 2671 | II-1 | 47 | 43°52′03″N, 83°42′51″E | 2939 | III-2 |
| 21 | 42°40′44″N, 80°54′11″E | 2630 | II-1 | 48 | 43°53′10″N, 83°38′17″E | 2993 | III-2 |
| 22 | 42°41′54″N, 80°01′17″E | 2514 | II-1 | 49 | 43°55′28″N, 83°30′40″E | 2839 | III-3 |
| 23 | 42°42′33″N, 81°09′11″E | 2472 | II-1 | 50 | 43°56′28″N, 83°29′40″E | 2845 | III-3 |
| 24 | 42°45′31″N, 81°21′13″E | 2588 | II-1 | 51 | 43°57′32″N, 83°25′28″E | 3169 | III-3 |
| 25 | 42°50′38″N, 81°46′06″E | 2242 | II-2 | 52 | 43°57′02″N, 83°22′45″E | 3236 | III-3 |
| 26 | 42°52′17″N, 81°56′09″E | 2033 | II-2 | 53 | 43°55′43″N, 83°13′04″E | 3158 | III-3 |
| 27 | 42°53′06″N, 82°02′15″E | 2424 | II-2 | 54 | 43°56′38″N, 83°15′01″E | 3187 | III-3 |
表2 西天山北坡草甸表土花粉样点位置
Table 2 Location of surface pollen along the north slope of Tianshan
| 样号 No. | 地理位置 Location | 海拔 Elevation/m | 植物群落 Plant community | 样号 No. | 地理位置 Location | 海拔 Elevation/m | 植物群落 Plant community |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 43°20′56″N, 83°37′19″E | 2147 | I-1 | 28 | 42°53′16″N, 82°07′02″E | 2748 | II-2 |
| 2 | 43°20′56″N, 83°37′29″E | 2039 | I-1 | 29 | 43°04′51″N, 82°16′15″E | 2531 | II-2 |
| 3 | 43°20′51″N, 83°37′59″E | 2148 | I-1 | 30 | 43°01′10″N, 82°22′41″E | 2599 | II-2 |
| 4 | 43°20′33″N, 83°36′20″E | 2050 | I-1 | 31 | 43°07′53″N, 83°07′28″E | 2405 | II-3 |
| 5 | 43°20′28″N, 83°31′04″E | 2253 | I-1 | 32 | 43°05′30″N, 83°15′08″E | 2518 | II-3 |
| 6 | 43°20′34″N, 83°32′49″E | 2227 | I-1 | 33 | 43°05′20″N, 83°16′17″E | 2624 | II-3 |
| 7 | 43°20′23″N, 83°34′13″E | 2241 | I-2 | 34 | 43°05′40″N, 83°18′41″E | 2424 | II-3 |
| 8 | 43°20′19″N, 83°34′30″E | 2401 | I-2 | 35 | 43°08′50″N, 83°26′30″E | 2665 | II-3 |
| 9 | 43°20′34″N, 83°36′34″E | 2168 | I-2 | 36 | 43°13′57″N, 83°26′40″E | 2651 | II-3 |
| 10 | 43°20′41″N, 83°36′54″E | 2332 | I-2 | 37 | 43°03′21″N, 83°10′01″E | 2858 | III-1 |
| 11 | 43°20′49″N, 83°37′26″E | 2115 | I-2 | 38 | 43°03′19″N, 83°14′23″E | 3107 | III-1 |
| 12 | 43°20′48″N, 83°37′41″E | 2080 | I-2 | 39 | 43°04′16″N, 83°20′04″E | 3083 | III-1 |
| 13 | 43°20′55″N, 83°38′39″E | 2168 | I-3 | 40 | 43°08′40″N, 83°31′46″E | 3091 | III-1 |
| 14 | 43°20′31″N, 83°38′50″E | 2357 | I-3 | 41 | 43°10′14″N, 83°55′13″E | 2893 | III-1 |
| 15 | 43°20′38″N, 83°37′55″E | 2244 | I-3 | 42 | 43°09′47″N, 84°03′47″E | 2999 | III-1 |
| 16 | 43°20′48″N, 83°37′23″E | 2152 | I-3 | 43 | 43°47′09″N, 84°04′22″E | 2897 | III-2 |
| 17 | 43°20′32″N, 83°36′17″E | 2138 | I-3 | 44 | 43°50′59″N, 84°01′17″E | 2805 | III-2 |
| 18 | 43°20′21″N, 83°35′51″E | 2210 | I-3 | 45 | 43°51′31″N, 83°53′34″E | 2933 | III-2 |
| 19 | 42°20′13″N, 80°43′39″E | 2797 | II-1 | 46 | 43°51′58″N, 83°48′57″E | 2826 | III-2 |
| 20 | 42°40′24″N, 80°49′54″E | 2671 | II-1 | 47 | 43°52′03″N, 83°42′51″E | 2939 | III-2 |
| 21 | 42°40′44″N, 80°54′11″E | 2630 | II-1 | 48 | 43°53′10″N, 83°38′17″E | 2993 | III-2 |
| 22 | 42°41′54″N, 80°01′17″E | 2514 | II-1 | 49 | 43°55′28″N, 83°30′40″E | 2839 | III-3 |
| 23 | 42°42′33″N, 81°09′11″E | 2472 | II-1 | 50 | 43°56′28″N, 83°29′40″E | 2845 | III-3 |
| 24 | 42°45′31″N, 81°21′13″E | 2588 | II-1 | 51 | 43°57′32″N, 83°25′28″E | 3169 | III-3 |
| 25 | 42°50′38″N, 81°46′06″E | 2242 | II-2 | 52 | 43°57′02″N, 83°22′45″E | 3236 | III-3 |
| 26 | 42°52′17″N, 81°56′09″E | 2033 | II-2 | 53 | 43°55′43″N, 83°13′04″E | 3158 | III-3 |
| 27 | 42°53′06″N, 82°02′15″E | 2424 | II-2 | 54 | 43°56′38″N, 83°15′01″E | 3187 | III-3 |
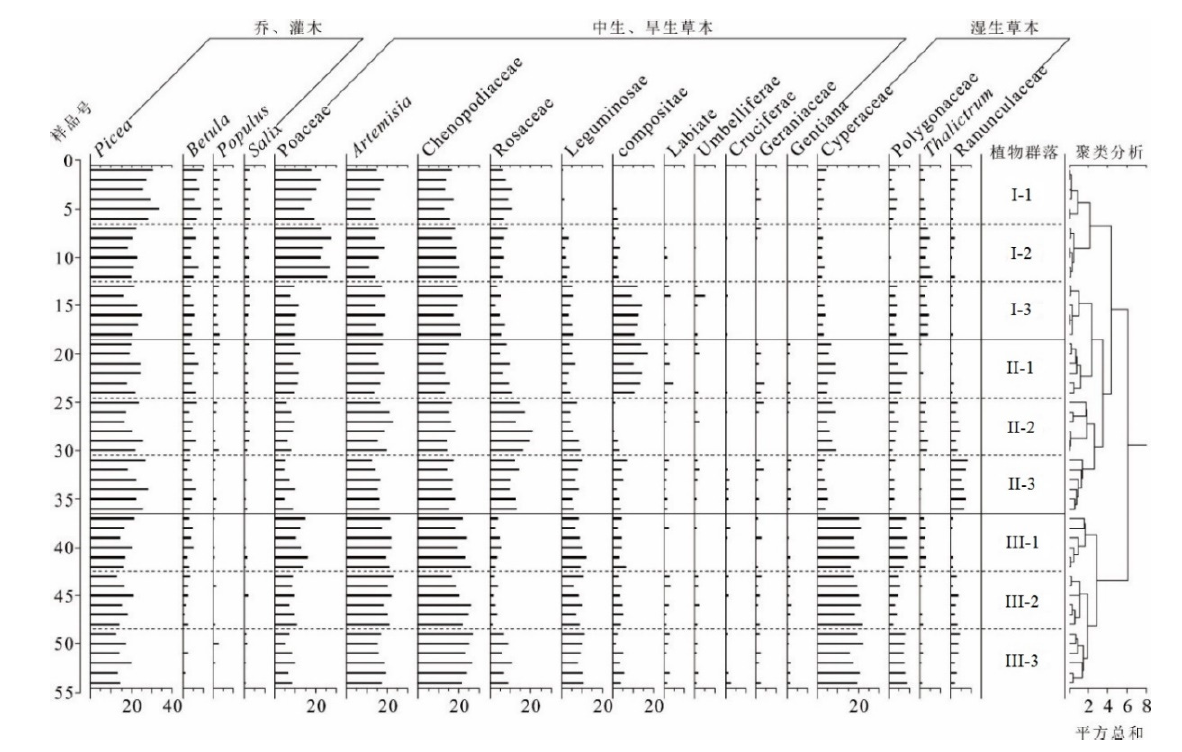
图3 西天山北坡表土花粉含量比例及聚类分析结果示意图
Figure 3 Percentage diagram and the results of cluster analysis of surface pollen along the north slope of Tianshan I-1:早熟禾群落 Poa nemoralis community;I-2:短芒短柄草群落 Brachypodium pinnatum community;I-3:高草杂类草草甸 Varii herbae meadow;II-1:大叶橐吾群落 Ligularia macrophylla community;II-2:羽衣草群落 Alchemilla spp. community;II-3:杂类草草甸 Varii herbae meadow;III-1:嵩草及杂类草草甸 Kobresia spp. & varii herbae meadow;III-2:薹草及杂类草草甸 Carex spp. & varii herbae meadow;III-3:高山杂类草草甸 Varii herbae meadow
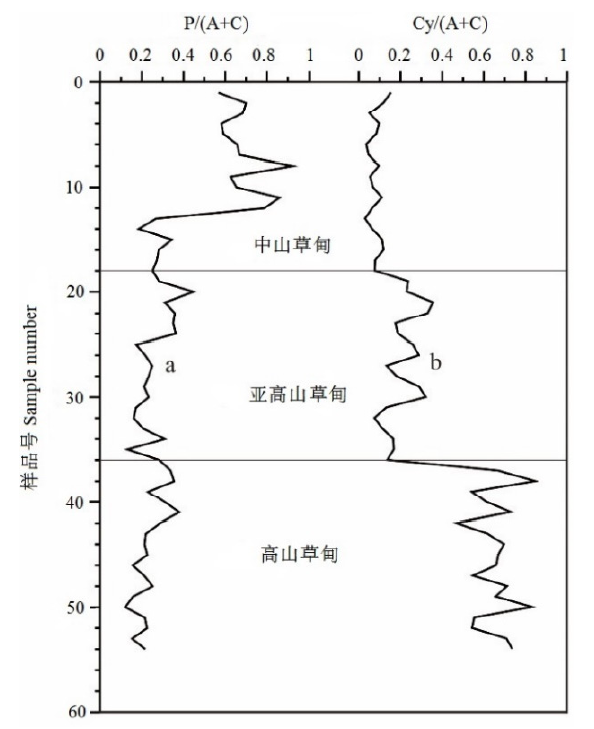
图5 西天山北坡表土花粉禾本科/(蒿属+藜科)、莎草科/(蒿属+藜科)值
Figure 5 Ratio of Poaceae/(Artemisia+Chenopodiaceae) and Cyperaceae/(Artemisia+Chenopodiaceae) along the north slope of Tianshan, Xinjiang, China
| [1] |
CHEN F H, CHEN J H, HUANG W, et al., 2019. Westerlies Asia and monsoonal Asia: Spatiotemporal differences in climate change and possible mechanisms on decadal to sub-orbital timescales[J]. Earth- Science Reviews, 192: 337-354.
DOI URL |
| [2] | FAEGRI K, KALAND P E, KRZYWINSKI K, 1989. Text Book of Pollen Analysis[M]. London: John Wiley & Sons Inc: 1-328. |
| [3] | HUANG X Z, ZHOU G, MA Y L, et al., 2009. Pollen distribution in large freshwater lake of arid region: a case study on the surface sediments from Bosten Lake, Xinjiang, China[J]. Frontiers of Earth Science, 4(2): 174-180. |
| [4] |
HUANG X Z, PENG W, RUDAYA N, et al., 2018. Holocene vegetation and climate dynamics in the Altai Mountains and surrounding areas[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 45(13): 6628-6636.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
LI F R, ZHAO Y, GAILLARD M J, et al., 2017. Modern pollen-climate relationships in north Xinjiang, northwestern China: Implications for pollen-based reconstruction of Holocene climate[J]. The Holocene, 27(7): 951-966.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
LI X L, WEI M J, ZHANG S R, et al., 2021. Surface pollen assemblages from different sedimentary environments in the Yinchuan Basin, North China, and their significance for stratigraphic pollen records[J]. Quaternary International, 583: 103-109.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
MA Q F, ZHU L P, WANG J B, et al., 2017. Artemisia/Chenopodiaceae ratio from surface lake sediments on the central and western Tibetan Plateau and its application[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 479: 138-145.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
ROY I, RANHOTRA P S, SHEKHAR M, et al., 2021. Modern Pollen-vegetation Relationships along the Vegetation Gradient in the Bhagirathi Valley, Western Himalaya, India[J]. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 97: 571-578.
DOI URL |
| [9] | WEI H C, ZHAO Y, 2016. Surface pollen and its relationships with modern vegetation and climate in the Tianshan Mountains, northwestern China[J]. Vegetation History & Archaeobotany, 25(1): 19-27. |
| [10] |
ZHAO K L, LI X Q, 2013. Modern pollen and vegetation relationships in the Yili Basin, Xinjiang, NW China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 58: 4133-4142.
DOI URL |
| [11] | 蔡遥, 王燕, 蒋复初, 等, 2010. 川北若尔盖高原表土孢粉的特征及其与现代植被的关系[J]. 地质通报, 29(5): 707-712. |
| CAI Y, WANG Y, JIANG F C, et al., 2010. Relationship between the surface pollen and modern vegetation in Zoigê Plateau, northern Sichuan, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 29(5): 707-712. | |
| [12] | 陈春珠, 黄小忠, 彭卫, 等, 2012. 天山南坡小尤尔都斯盆地表土花粉初步研究[J]. 冰川冻土, 34(6): 1526-1534. |
| CHEN C Z, HUANG X Z, PENG W, et al., 2012. Study of the Surface Sporo-pollen in the Small Yourdusi Basin on the Southern Slopes of the Tianshan Mountains[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 34(6): 1526-1534. | |
| [13] | 陈曦, 2010. 中国干旱区自然地理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 602-604. |
| [ CHEN X, 2010, Physical Geography of Arid Land in China [M]. Beijing: Science Press: 602-604. | |
| [14] | 程波, 陈发虎, 2010. 西北干旱区石羊河流域表土花粉分析[J]. 中国沙漠, 30(2): 350-356. |
| CHENG B, CHEN F H, 2010. Pollen Analysis of Topsoil Samples from Shiyang River Drainage, Northwest China[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 30(2): 350-356. | |
| [15] | 慈晖, 张强, 2016. 遥感手段及气象干旱指数在新疆干旱监测过程中的应用[J]. 生态环境学报, 25(10): 1653-1662. |
| CI H, ZHANG Q, 2016. Comparison of the vegetation condition index and meteorological drought indices in drought monitoring of Xinjiang, China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 25(10): 1653-1662. | |
| [16] | 丁之勇, 马龙, 吉力力·阿布都外力, 等, 2017. 新疆博尔塔拉河湖流域土壤元素空间变异性及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 26(6): 939-948. |
| DING Z Y, MA L, ABUDUWAILI J L L, et al., 2017. Spatial variations and influence factor analysis of heavy metals in topsoil of Bortala River Basin, Northwest China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 26(6): 939-948. | |
| [17] | 孔昭宸, 张芸, 王力, 等, 2018. 中国孢粉学的过去、现在及未来-侧重第四纪孢粉学[J]. 科学通报, 63(2): 164-171. |
| KONG Z C, ZHANG Y, WANG L, et al., 2018. The past, present and future of palynology in China-Concentrate on Quaternary palynology[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 63(2): 164-171. | |
| [18] | 郎青, 姚付龙, 杨海军, 2020. 新疆中天山山间盆地表土花粉谱特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 39(8): 2518-2527. |
| LANG Q, YAO F L, YANG H J, 2020. Surface pollen spectrum in intermountain basin of Middle Tianshan, Xinjiang, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 39(8): 2518-2527. | |
| [19] | 李怡雯, 许清海, 张生瑞, 等, 2019. 青藏高原高寒灌丛草甸花粉组合的植被指示性[J]. 科学通报, 64(20): 2141-2150. |
| LI Y W, XU Q H, ZHANG S R, et al., 2019. Significance of pollen assemblages for the vegetation composition of alpine shrub meadow in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 64(20): 2141-2150. | |
| [20] | 李月从, 许清海, 阳小兰, 等, 2005. 中国草原区主要群落类型花粉组合特征[J]. 生态学报, 25(3): 555-564. |
| LI Y C, XU Q H, YANG X L, et al., 2005. Pollen assemblages of major steppe communities in China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 25(3): 555-564. | |
| [21] | 吕新苗, 陈辉, 李双成, 等, 2004. 东祁连山表土花粉组合及其数量特征[J]. 山地学报, 22(2): 199-206. |
| LÜ X M, CHEN H, LI S C, et al., 2004. Surface Pollen Assemblages and Quantitative Characteristics in Eastern Qilian Mountains[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 22(2): 199-206. | |
| [22] | 庞有智, 李春海, 于革, 等, 2012. 青藏高原中部兹格塘错流域表土花粉的初步研究[J]. 微体古生物学报, 29(2): 145-151. |
| PANG Y Z, LI C H, YU G, et al., 2012. Pollen analysis of surface soil samples from the Zigetang Co area central Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica, 29(2): 145-151. | |
| [23] | 秦锋, 2021. 青藏高原草原带和荒漠带湖泊表层沉积物现代花粉研究[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 51(3): 437-452. |
| QIN F, 2021. Modern pollen assemblages of the surface lake sediments from the steppe and desert zones of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 51(3): 437-452. | |
| [24] | 邱筱兰, 2016. 青藏高原东北缘表土花粉初步分析[J]. 微体古生物学报, 33(1): 65-74. |
| QIU X L, 2016. A preliminary study of surface pollen from the northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China[J]. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinaca, 33(1): 65-74. | |
| [25] | 尚雪, 李小强, 安芷生, 等, 2009. 青海湖流域表土花粉分析[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 39(9): 1288-1296. |
| SHANG X, LI X Q, AN Z S, et al., 2009. Modern pollen rain in the Lake Qinghai basin, China[J]. Scientia Sinica Terrae, 39(9): 1288-1296. | |
| [26] | 孙湘君, 杜乃秋, 翁成郁, 等, 1994. 新疆玛纳斯湖盆周围近14000年以来的古植被古环境[J]. 第四纪研究, 14(3): 239-248. |
| SUN X J, DU N Q, WENG C Y, et al., 1994. Paleovegetation and paleoenvironmental of Manasi Lake, Xinjiang, N. W. China during the last 14000 years[J]. Quaternary Science, 14(3): 239-248. | |
| [27] | 唐领余, 毛礼米, 舒军武, 等, 2016. 中国第四纪孢粉图鉴[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 1-580. |
| TANG L Y, MAO L M, SHU J W, et al., 2016. An Illustrated Handbook of Quaternary pollen and Spores in China[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 1-580. | |
| [28] | 王伏雄, 钱南芬, 张玉龙, 等, 1995. 中国植物花粉形态[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 1-446. |
| WANG F X, QIAN N F, ZHANG Y L, et al., 1995. Pollen Flora of China[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 1-446. | |
| [29] | 熊嘉武, 2017. 新疆天山西部山地综合科学考察[M]. 北京: 中国林业出版社: 1-595. |
| XIONG J W, 2017. Comprehensive Scientific Investigation of the Western Tianshan Mountains in Xinjiang[M]. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House, 1-595. | |
| [30] | 许清海, 李曼玥, 张生瑞, 等, 2015. 中国第四纪花粉现代过程; 进展与问题[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 45(11): 1661-1682. |
|
XU Q H, LI M Y, ZHANG S R, et al., 2015. Modern pollen processes of China: Progress and Problems[J]. Scientia Sinica Terrae, 45(11): 1661-1682.
DOI URL |
|
| [31] | 杨庆华, 杨振京, 张芸, 等, 2019. 新疆夏尔希里自然保护区表土孢粉与植被的关系[J]. 干旱区地理, 42(5): 986-997. |
| YANG Q H, YANG Z J, ZHANG Y, et al., 2019. Relationship between surface sporepollen and modern vegetation in Xarxili Nature Reserve of Xinjiang[J]. Arid land Geography, 42(5): 986-997. | |
| [32] | 姚付龙, 马春梅, 敬一丹, 等, 2018. 新疆赛里木湖流域表土花粉组合与现代植被关系研究[J]. 微体古生物学报, 35(4): 423-435. |
| YAO F L, MA C M, JING Y D, et al., 2018. Relationship between surface pollen assemblage and the vegetation in the Sayram lake region, northern Xinjiang, China[J]. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinaca, 35(4): 423-435. | |
| [33] | 姚付龙, 马春梅, 朱诚, 等, 2021a. 中国西天山北坡表土花粉与区域植被关系[J]. 古生物学报, 60(3): 471-482. |
| YAO F L, MA C M, ZHU C, et al., 2021. Relationship between surface pollen and vegetation on the northern slope of west Tianshan Mountains, China[J]. Acta Palaeontologica Sinica, 60(3): 471-482. | |
| [34] | 姚付龙, 张静, 杨海军, 等, 2021b. 新疆博格达山北坡表土花粉散布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(3): 466-474. |
| YAO F L, ZHANG J, YANG H J, et al., 2021. Surface pollen distribution on the north slope of Bogda Mountain, Xinjiang, China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(3): 466-474. | |
| [35] | 姚付龙, 朱诚, 夏倩倩, 等, 2020. 高分辨率泥炭孢粉记录的天山北坡2400 cal yr B.P.以来植被演替及其对气候变化的响应[J]. 地层学杂志, 44(1): 104-112. |
| YAO F L, ZHU C, XIA Q Q, et al., 2020. Vegetation succession and its response to climate changes since 2400 cal yr B.P. by pollen record from a high resolution peat profile in the northern slope of Tianshan, China[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 44(1): 104-112. | |
| [36] | 张德怀, 韩晓丽, 代然然, 等, 2013. 尼洋河流域表土孢粉组合与年均降水量关系研究[J]. 地理与地理信息科学, 29(1): 80-85. |
| ZHANG D H, HAN X L, DAI R R, et al., 2013. Relationship between the Surface Pollen and Mean Annual Precipitation in the Niyang River Basin[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 29(1): 80-85. | |
| [37] | 张卉, 张芸, 杨振京, 等, 2013. 新疆石河子南山地区表土花粉研究[J]. 生态学报, 33(20): 6478-6487. |
|
ZHANG H, ZHANG Y, YANG Z J, et al., 2013. Surface pollen research of Nanshan region, Shihezi City in Xinjiang[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33(20): 6478-6487.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 杨春亮, 刘旻霞, 王千月, 苗乐乐, 肖音迪, 王敏. 单户与联户放牧经营下草玉梅与嵩草种群空间格局及其关联性[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 651-659. |
| [2] | 周选博, 王晓丽, 马玉寿, 王彦龙, 罗少辉, 谢乐乐. 返青期休牧措施下高寒草甸主要植物种群的生态位变化特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1547-1555. |
| [3] | 段文军, 李达, 李冲. 5种不同林龄尾巨桉人工林林下植物多样性及其影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 857-864. |
| [4] | 王英成, 姚世庭, 金鑫, 俞文政, 芦光新, 王军邦. 三江源区高寒退化草甸土壤细菌多样性的对比研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 695-703. |
| [5] | 魏建兵, 郑泓, 程雨露, 王阳. 基于CiteSpace的生态安全格局研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 835-844. |
| [6] | 相恒星, 张健, 王宗明, 毛德华. 松嫩平原生态系统服务供需研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1769-1776. |
| [7] | 姚世庭, 芦光新, 邓晔, 党宁, 王英成, 张海娟, 颜珲璘. 模拟增温对土壤真菌群落组成及多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(7): 1404-1411. |
| [8] | 袁洁, 赵晏强. 基于Web of Science数据库的湿地修复研究发展态势分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(7): 1541-1548. |
| [9] | 徐文印, 张宇鹏, 段成伟, 柴瑜, 宋娴, 李希来. 黄河源不同区域退化高寒草甸土壤养分空间变异研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(10): 1968-1975. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
