生态环境学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (5): 720-730.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2025.05.006
张丹丹1,2( ), 毋振海2, 吴渴2,3, 毕方2, 李云凤1, 安聪2, 韩翼昕2,4, 刘正阳2,4, 朱玲1,*(
), 毋振海2, 吴渴2,3, 毕方2, 李云凤1, 安聪2, 韩翼昕2,4, 刘正阳2,4, 朱玲1,*( ), 王学中2,*(
), 王学中2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-10-13
出版日期:2025-05-18
发布日期:2025-05-16
通讯作者:
*朱玲。E-mail: zhuling75@bipt.edu.cn;王学中。E-mail: wangxz@craes.org.cn作者简介:张丹丹(2000年生),女,硕士研究生,主要从事大气复合污染特征及成因分析。E-mail: zdd1841501728@126.com
基金资助:
ZHANG Dandan1,2( ), WU Zhenhai2, WU Ke2,3, BI Fang2, LI Yunfeng1, AN Cong2, HAN Yixin2,4, LIU Zhengyang2,4, ZHU Ling1,*(
), WU Zhenhai2, WU Ke2,3, BI Fang2, LI Yunfeng1, AN Cong2, HAN Yixin2,4, LIU Zhengyang2,4, ZHU Ling1,*( ), WANG Xuezhong2,*(
), WANG Xuezhong2,*( )
)
Received:2024-10-13
Online:2025-05-18
Published:2025-05-16
摘要: 为了解不同类型O3污染日关键O3前体物和气象因素差异及其影响,在研究2017-2022年中国重点区域不同类型O3污染日O3污染特征的基础上,以苏皖鲁豫交界地区典型城市亳州市为例,分析了不同类型O3污染日下O3前体物和气象因素变化特征及差异;同时,通过相关性分析、后向轨迹、随机森林等方法研究了O3污染气象条件、气团来源,及前体物与气象因素影响大小。结果表明,1)O3高值超标(O3质量浓度小时值和日最大8 h均值均超标)和O3低值超标(O3质量浓度小时值不超标,但日最大8 h均值超标)天数的占比与其前体物质量浓度的高低整体呈现一致的变化关系;NO2质量浓度日均值在30-40 μg·m−3区间时,O3高值超标日占比高达71.4%;CO质量浓度日均值<0.4 mg·m−3时,O3低值超标日占比为83.3%。2)O3污染状态与气象条件较为密切。当日均气温在35 ℃以下时,气温的升高有利于O3质量浓度的升高且高值超标天数出现频率占比呈增加趋势;当相对湿度在50%-60%区间时,更有利于O3高值超标天的出现;当相对湿度在60%-70%区间时,更有利于O3低值超标天的出现。3)O3高值超标日受西北和东南气团影响较大,低值超标日受南部和东北方向气团影响较大。4)随机森林分析结果表明,O3高值超标日相对湿度(40.9%)和气温(26.4%)影响较大;O3低值超标日相对湿度(30.4%)和NO2(26.0%)影响较大。
中图分类号:
张丹丹, 毋振海, 吴渴, 毕方, 李云凤, 安聪, 韩翼昕, 刘正阳, 朱玲, 王学中. 基于不同类型臭氧污染日的臭氧污染特征及影响因素分析:以亳州市为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2025, 34(5): 720-730.
ZHANG Dandan, WU Zhenhai, WU Ke, BI Fang, LI Yunfeng, AN Cong, HAN Yixin, LIU Zhengyang, ZHU Ling, WANG Xuezhong. Characterization of Ozone Pollution and Influencing Factors Based on Different Types of Ozone Pollution Days: A Case Study in Bozhou City[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2025, 34(5): 720-730.
| 区域 | 包含城市 |
|---|---|
| 京津冀及周边 (38个) | 北京、天津、石家庄、唐山、秦皇岛、邯郸、邢台、保定、沧州、廊坊、衡水、济南、淄博、枣庄、东营、潍坊、济宁、泰安、日照、临沂、德州、聊城、滨州、菏泽、郑州、开封、洛阳、平顶山、安阳、鹤壁、新乡、焦作、 濮阳、许昌、漯河、三门峡、商丘、周口 |
| 长三角 (31个) | 上海、南京、苏州、无锡、常州、镇江、南通、泰州、扬州、盐城、淮安、宿迁、徐州、连云港、杭州、宁波、 嘉兴、湖州、绍兴、舟山、合肥、芜湖、蚌埠、淮南、马鞍山、淮北、滁州、阜阳、宿州、六安、亳州 |
| 苏皖鲁豫交界地区 (22个) | 徐州、连云港、宿迁、淮北、阜阳、宿州、亳州、青岛、枣庄、东营、潍坊、泰安、日照、临沂、平顶山、许昌、漯河、南阳、商丘、信阳、周口、驻马店 |
表1 3个重点区域所包含的城市
Table 1 Cities lists of the three key regions
| 区域 | 包含城市 |
|---|---|
| 京津冀及周边 (38个) | 北京、天津、石家庄、唐山、秦皇岛、邯郸、邢台、保定、沧州、廊坊、衡水、济南、淄博、枣庄、东营、潍坊、济宁、泰安、日照、临沂、德州、聊城、滨州、菏泽、郑州、开封、洛阳、平顶山、安阳、鹤壁、新乡、焦作、 濮阳、许昌、漯河、三门峡、商丘、周口 |
| 长三角 (31个) | 上海、南京、苏州、无锡、常州、镇江、南通、泰州、扬州、盐城、淮安、宿迁、徐州、连云港、杭州、宁波、 嘉兴、湖州、绍兴、舟山、合肥、芜湖、蚌埠、淮南、马鞍山、淮北、滁州、阜阳、宿州、六安、亳州 |
| 苏皖鲁豫交界地区 (22个) | 徐州、连云港、宿迁、淮北、阜阳、宿州、亳州、青岛、枣庄、东营、潍坊、泰安、日照、临沂、平顶山、许昌、漯河、南阳、商丘、信阳、周口、驻马店 |
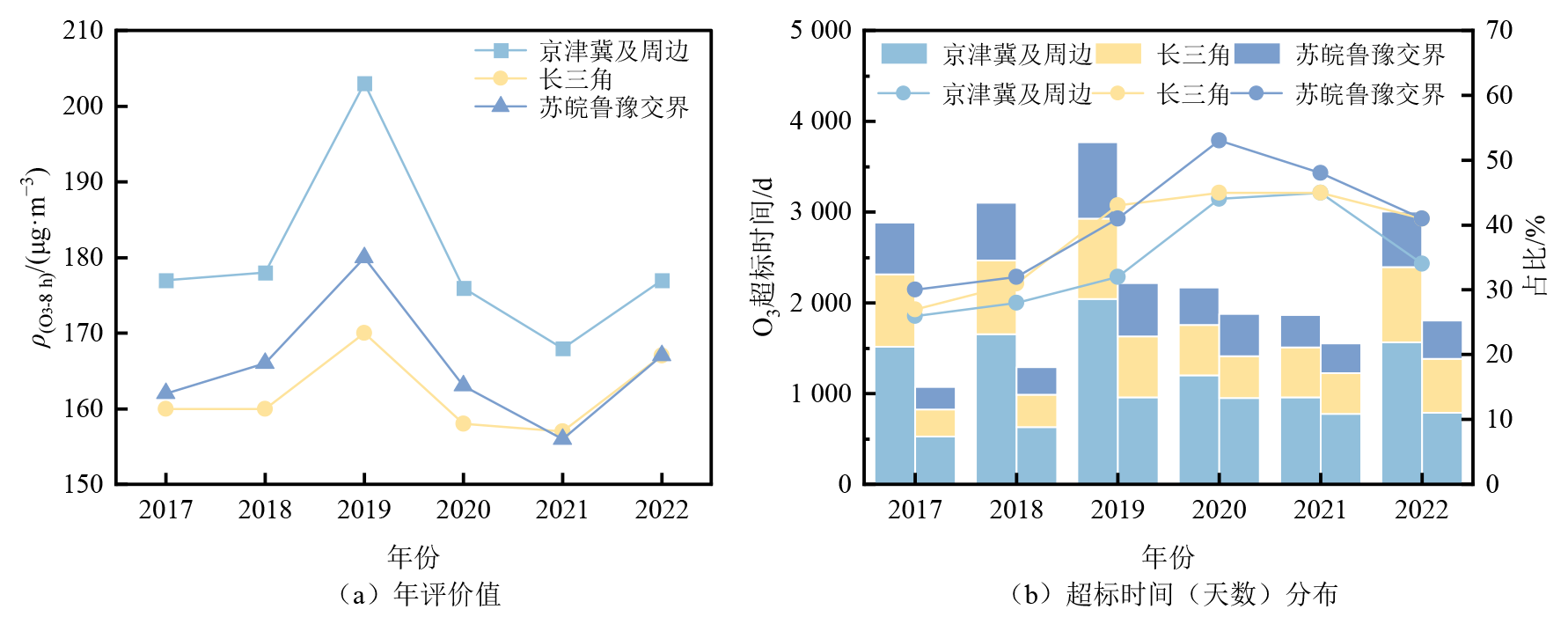
图1 2017-2022年重点区域O3年评价值变化趋势及超标时间(天数)分布 (b)中左侧柱代表O3高值超标天,右侧柱代表O3低值超标天,折线表示O3低值超标天占比
Figure 1 Trends of annual average concentration of O3 in key areas from 2017 to 2022 and the distribution of days exceeding the standard
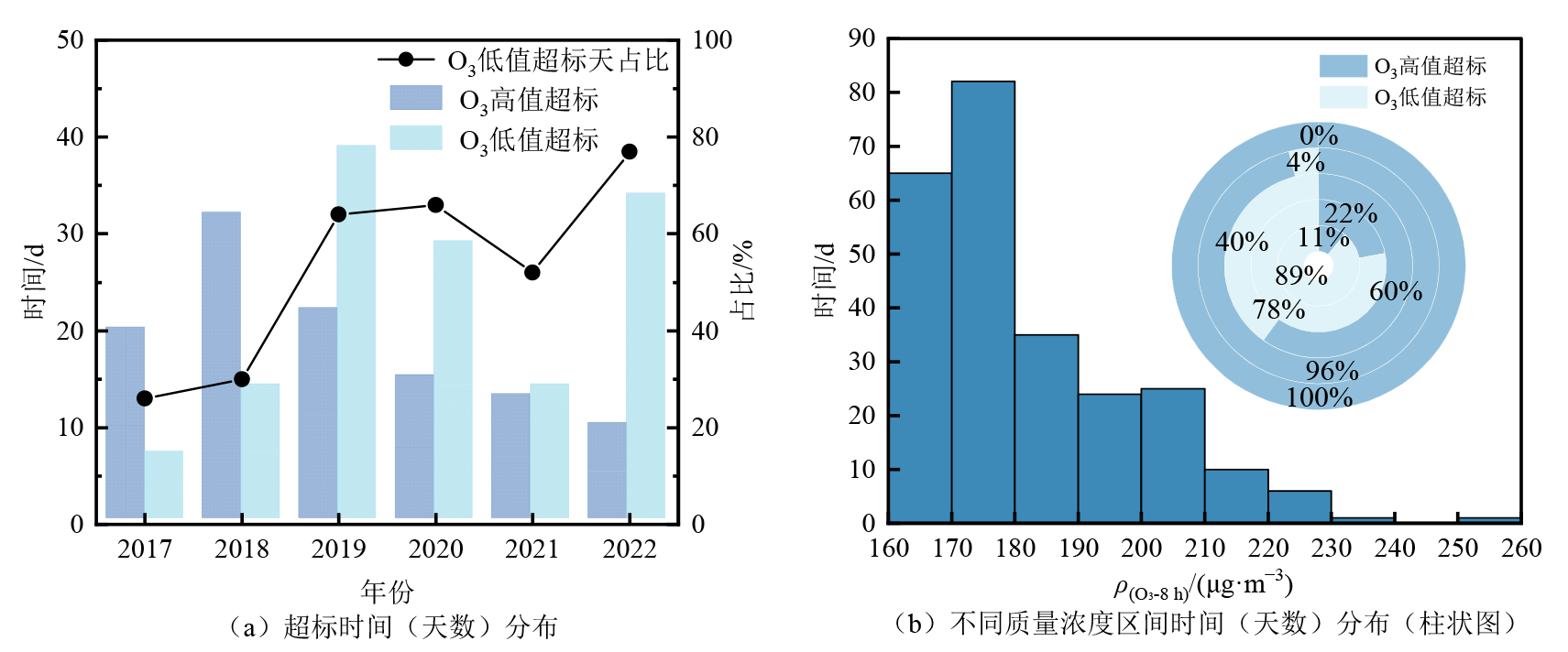
图3 2017-2022年亳州市O3两种超标日时间(天数)分布及日评价值分布 (b)中环从内到外依次为161-170、171-180、181-190、191-200、201-260 μg·m?3
Figure 3 Temporal distribution and daily assessment of two types of O3 exceedance days in Bozhou City from 2017 to 2022
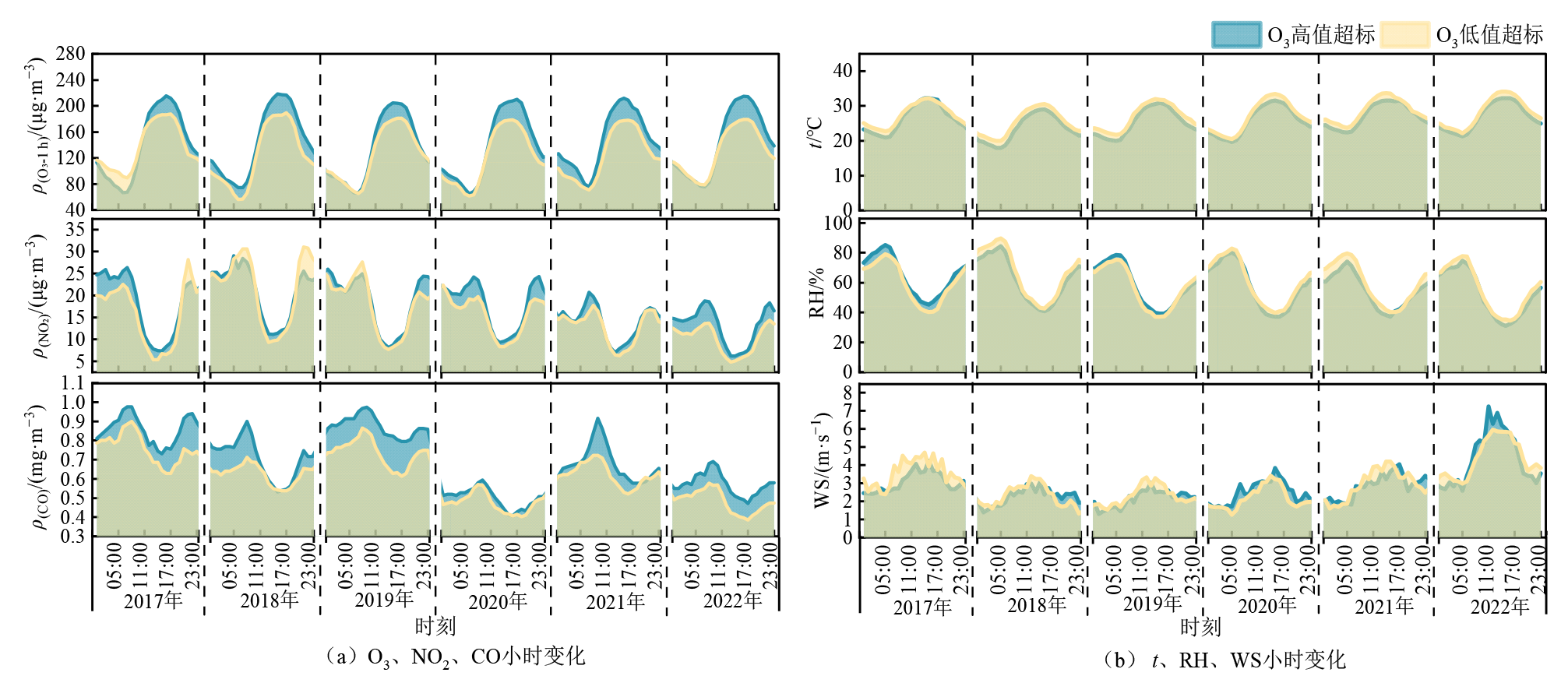
图4 2017-2022年亳州市O3两种超标日前体物和气象要素小时质量浓度变化
Figure 4 Hourly concentration changes of precursors and meteorological elements for two types of O3 exceedance days in Bozhou City from 2017 to 2022
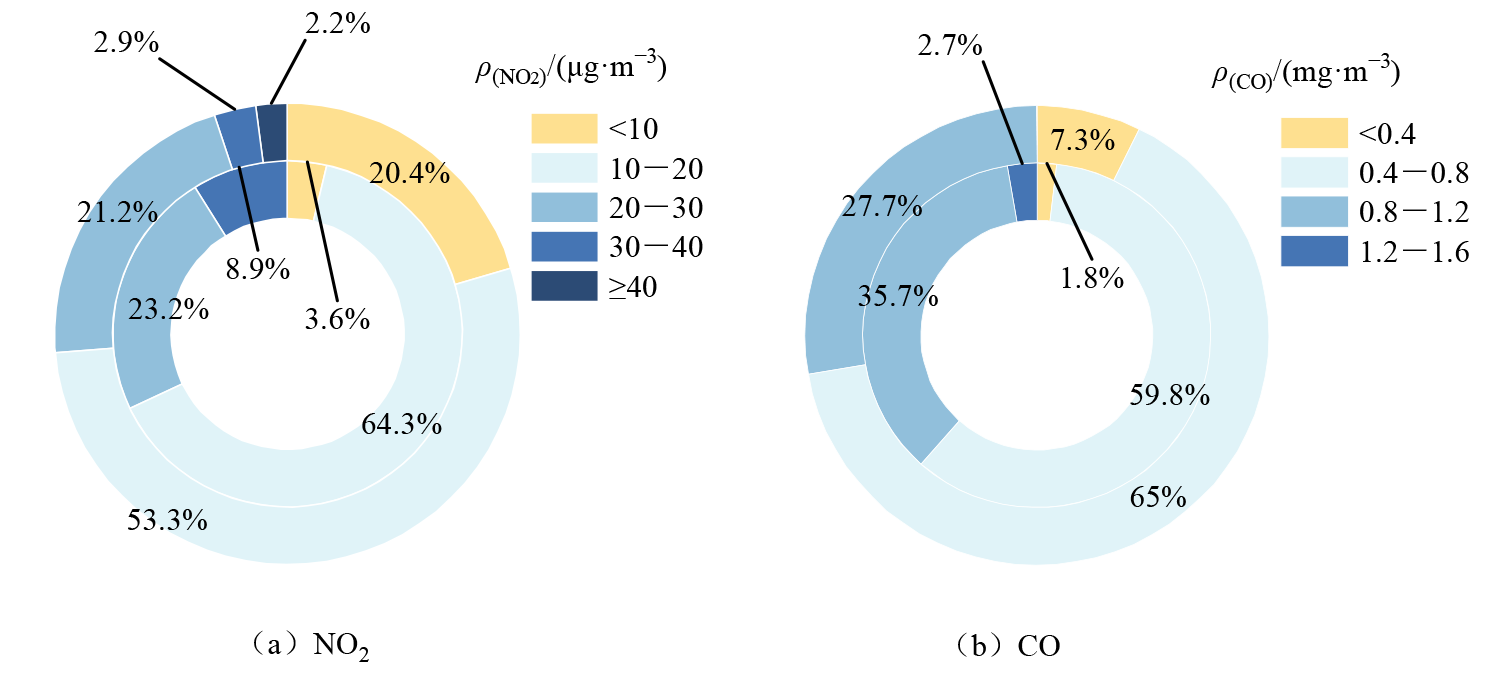
图5 2017-2022年亳州市O3两种超标日NO2、CO日均值质量浓度不同区间占比 内环为O3高值超标,外环为O3低值超标
Figure 5 Proportion of different ranges of daily average concentrations of NO2 and CO for two types of O3 exceedance days in Bozhou City from 2017 to 2022
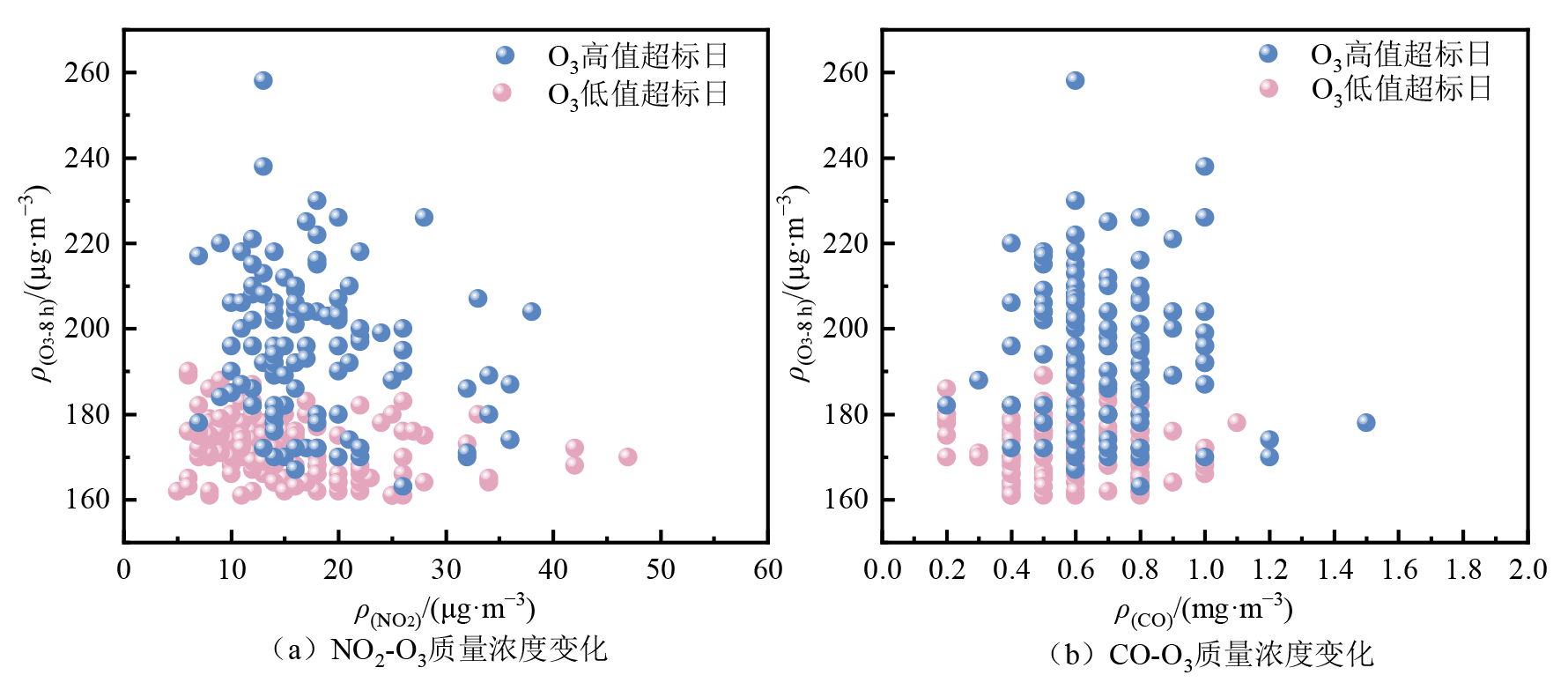
图6 2017-2022年亳州市O3两种超标日NO2、CO与O3质量浓度散点图
Figure 6 Scatter plot of NO2 and CO concentrations during two types of O3 exceedance days in Bozhou City from 2017 to 2022
| t区间 | 高值超标 日占比/% | 低值超标 日占比/% | RH区间 | 高值超标 日占比/% | 低值超标 日占比/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <15 | 0.7 | 30-40 | 2.7 | 3.6 | |
| 15-20 | 5.4 | 5.8 | 40-50 | 14.3 | 24.8 |
| 20-25 | 15.2 | 24.1 | 50-60 | 34.8 | 20.4 |
| 25-30 | 67.9 | 57.7 | 60-70 | 34.8 | 39.6 |
| 30-35 | 11.5 | 11.7 | 70-80 | 12.5 | 10.9 |
| 80-90 | 0.9 | 0.7 |
表2 2017-2022年亳州市不同t与RH区间下污染天数的占比分布
Table 2 Polluted days distribution by temperature and relative humidity thresholds in Bozhou City, 2017-2022
| t区间 | 高值超标 日占比/% | 低值超标 日占比/% | RH区间 | 高值超标 日占比/% | 低值超标 日占比/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <15 | 0.7 | 30-40 | 2.7 | 3.6 | |
| 15-20 | 5.4 | 5.8 | 40-50 | 14.3 | 24.8 |
| 20-25 | 15.2 | 24.1 | 50-60 | 34.8 | 20.4 |
| 25-30 | 67.9 | 57.7 | 60-70 | 34.8 | 39.6 |
| 30-35 | 11.5 | 11.7 | 70-80 | 12.5 | 10.9 |
| 80-90 | 0.9 | 0.7 |
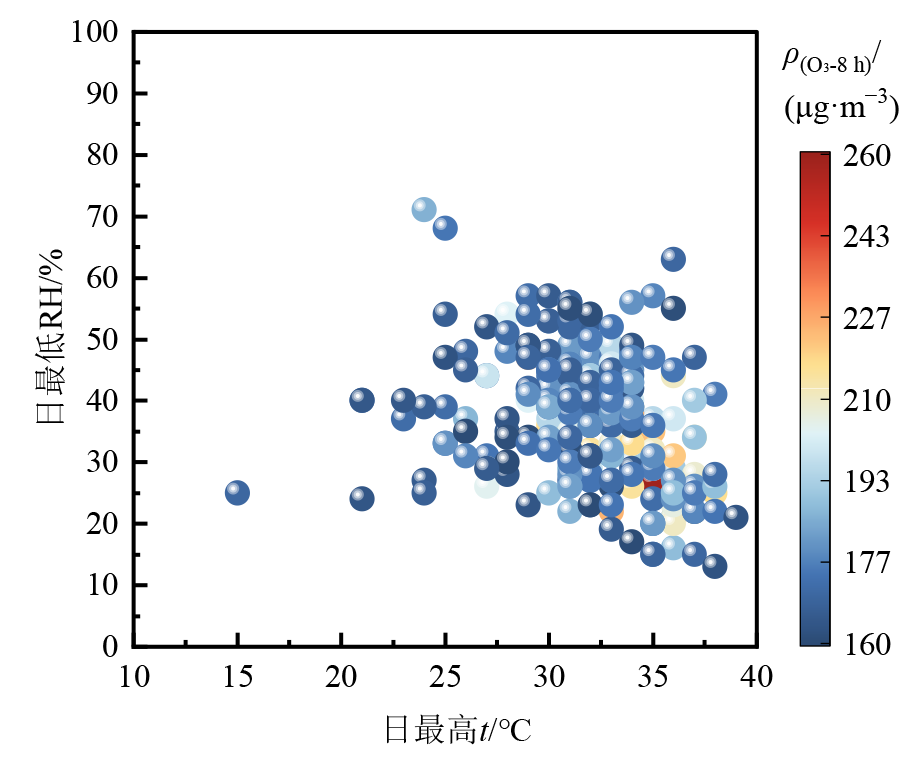
图7 2017-2022年O3-8 h质量浓度与日最高t、日最低RH变化关系
Figure 7 Relationship between O3-8 h concentration and daily maximum temperature, daily minimum relative humidity from 2017 to 2022
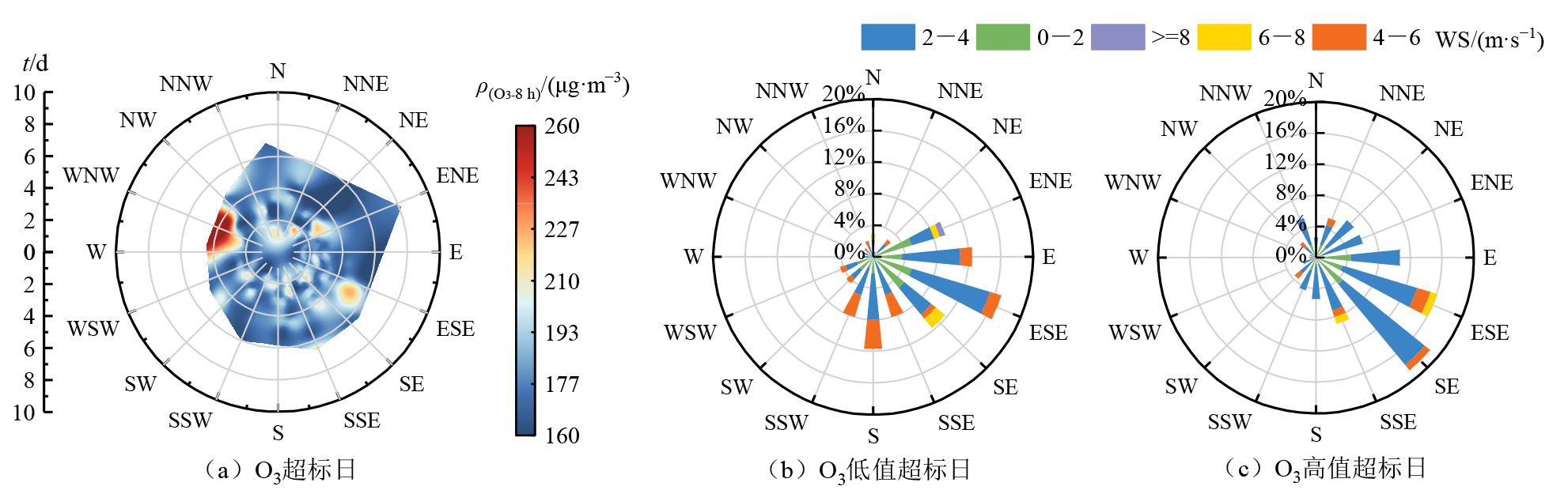
图8 2017-2022年亳州市O3污染日O3与风向、风速的关系
Figure 8 Relationship between O3 and wind direction and wind speed on O3 pollution days in Bozhou City from 2017 to 2022
| [1] | BENTÉJAC C, CSORGO A, MARTINEZ-MUNOZ G, 2021. A comparative analysis of gradient boosting algorithms[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review, 54(3): 1937-1967. |
| [2] | BREIMAN L, 2001. Random forests[J]. Machine Learning, 45(1): 5-32. |
| [3] | CHEN Y C, ZHANG L, CHEN J Y, et al., 2017. Characteristics of ambient ozone O3 pollution and health risks in Zhejiang Province[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(35): 27436-27444. |
| [4] | GAO A F, GAO B Y, LI S R, et al., 2024. Pollution characteristics, potential source areas, and transport pathways of PM2.5 and O3 in an inland city of Shijiazhuang, China[J]. Air Quality, Atmosphere & Health, 17(6): 1307-1323. |
| [5] | LAM K, CHENG W, SU Y T, et al., 2020. Use of random forest analysis to quantify the importance of the structural characteristics of beta-glucans for prebiotic development[J]. Food Hydrocolloids, 108: 106001. |
| [6] | LUPASCU A, BUTLER T, 2019. Source attribution of European surface O3 using a tagged O3 mechanism[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 19(23): 14535-14558. |
| [7] | MONKS P S, 2000. A review of the observations and origins of the spring ozone maximum[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 34(21): 3545-3561. |
| [8] | ROMERO-ALVAREZ J, LUPASCU A, LOWE D, et al., 2022. Sources of surface O3 in the UK: tagging O3 within WRF-Chem[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 22(20): 13797-13815. |
| [9] | WANG W J D. PARRISH D, WANG S W, et al., 2022. Long-term trend of ozone pollution in China during 2014-2020: Distinct seasonal and spatial characteristics and ozone sensitivity[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 22(13): 8935-8949. |
| [10] | WEI N N, ZHAO W X, YAO Y C, et al., 2023. Peroxy radical chemistry during ozone photochemical pollution season at a suburban site in the boundary of Jiangsu-Anhui-Shandong-Henan region, China[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 904: 166355. |
| [11] | XU J W, HUANG X, WANG N, et al., 2021. Understanding ozone pollution in the Yangtze River Delta of eastern China from the perspective of diurnal cycles[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 752: 141928. |
| [12] | YAO L Y, HAN Y, QI X, et al., 2024. Determination of major drive of ozone formation and improvement of O3 prediction in typical North China Plain based on interpretable random forest model[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 934: 173193. |
| [13] | ZHANG J, WANG C, QU K, et al., 2019. Characteristics of ozone pollution, regional distribution and causes during 2014-2018 in Shandong Province, East China[J]. Atmosphere, 10(9): 501. |
| [14] | 蔡敏, 谷欣, 赵正昱, 等, 2023. 2016-2021年运城市区臭氧浓度特征及其与气象因素的关系[J]. 环境科学学报, 43(9): 229-243. |
| CAI M, GU X, ZHAO Z Y, et al., 2023. Characteristics of ozone concentration and relationships with meteorological factors in Yuncheng City from 2016 to 2021[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 43(9): 229-243. | |
| [15] | 陈伟, 徐学哲, 刘文清, 2024. 2017-2021年苏皖鲁豫交界区域PM2.5和O3时空变化特征及影响因素[J]. 环境科学, 45(4): 1950-1962. |
| CHEN W, XU X Z, LIU W Q, 2024. Spatial-temporal Characteristics and influencing factors of PM2.5 and ozone in the border area of Jiangsu, Anhui, Shangdong, and Henan from 2017 to 2021[J]. Environmental Science, 45(4): 1950-1962. | |
| [16] | 陈煜升, 张宇静, 赵天良, 等, 2019. 近5年徐州市大气污染变化及相关气象作用[J]. 环境科学与技术, 42(S1): 152-158. |
| CHEN Y S, ZHANG Y J, ZHAO T L, et al., 2019. Changes in air pollution in Xuzhou City and related meteorological effects in the Past 5 Years[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 42(S1): 152-158. | |
| [17] | 董昊, 程龙, 王含月, 等, 2021. 安徽省臭氧污染特征及气象影响因素分析[J]. 中国环境监测, 37(1): 58-68. |
| DONG H, CHENG L, WANG H Y, et al., 2021. Analysis of ozone pollution characteristics and meteorological factors in Anhui Province[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 37(1): 58-68. | |
| [18] | 范瑜, 李昌龙, 2015. 徐州市空气质量预测预报中的气象因素影响分析[J]. 环境科技, 28(2): 54-56. |
| FAN Y, LI C L, 2015. Analysis of the impact of meteorological factors in air quality forecasting in Xuzhou City[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 28(2): 54-56. | |
| [19] | 胡娜, 李源清, 张晓东, 等, 2024. 郑州市高新区夏季臭氧及前体物污染特征和关键前体物溯源研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 44(9): 32-41. |
| HU N, LI Y Q, ZHANG X D, et al., 2024. Research on the characteristics of summer ozone and its precursor pollution and key precursor traceability in Zhengzhou High-tech Development Zone[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 44(9): 32-41. | |
| [20] | 黄继章, 高健, 余美芳, 等, 2024. 广州市2022年臭氧污染特征与成因分析[J]. 中国环境科学, 44(6): 3100-3110. |
| HUANG J Z, GAO J, YU M F, et al., 2024. Analysis of characteristics and cause of ozone pollution in Guangzhou in 2022[J]. China Environmental Science, 44(6): 3100-3110. | |
| [21] | 贾利祥, 2018. “十二五” 期间亳州市环境空气质量变化趋势及对策建议[J]. 绿色科技, (10): 133-134. |
| JIA L X, 2018. Trends in ambient air quality and countermeasure suggestions in Bozhou City during the 12th Five-Year Plan Period[J]. Green Science and Technology, (10): 133-134. | |
| [22] | 孔玉雪, 2022. 安徽省宿州市臭氧污染特征及成因分析[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学. |
| KONG Y X, 2022. Analyses of characteristics and causes of ozone pollution in Suzhou City, Anhui Province[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum. | |
| [23] | 刘娜, 余晔, 何建军, 等, 2015. 兰州冬季大气污染来源分析[J]. 环境科学研究, 28(4): 509-516. |
| LIU N, YU Y, HE J J, et al., 2015. Analysis of air pollutant transport in winter in Lanzhou[J]. Environmental Science Research, 28(4): 509-516. | |
| [24] | 刘玉, 蔡秋亮, 佟磊, 等, 2023. 海陆风对宁波东南滨海郊区大气臭氧变化特征及预测的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 43(4): 27-39. |
| LIU Y, CAI Q L, TONG L, et al., 2023. Influence of sea-land breeze on the variation characteristics and prediction of ozone in the suburban coastal atmosphere of southeast Ningbo[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 43(4): 27-39. | |
| [25] | 罗丽彤, 章炎麟, 林煜棋, 等, 2024. 南京夏季大气臭氧光化学特征与敏感性分析[J]. 环境科学, 45(3): 1382-1391. |
| LUO L T, ZHANG Y L, LIN Y Q, et al., 2024. Analysis of photochemical characteristics and sensitivity of atmospheric ozone in Nanjing in summer[J]. Environmental Science, 45(3): 1382-1391. | |
| [26] | 钱悦, 许彬, 夏玲君, 等, 2021. 2016-2019年江西省臭氧污染特征与气象因子影响分析[J]. 环境科学, 42(5): 2190-2201. |
| QIAN Y, XU B, XIA L J, et al., 2021. Characteristics of ozone pollution and relationships with meteorological factors in Jiangxi Province[J]. Environmental Science, 42(5): 2190-2201. | |
| [27] | 石春娥, 杨关盈, 张浩, 等, 2020. 安徽省臭氧污染特征及其气象成因[J]. 三峡生态环境监测, 5(3): 71-84. |
| SHI C E, YANG G Y, ZHANG H, et al., 2020. Characteristics and meteorological causes of ozone pollution in Anhui Province[J]. Sanxia Environmental Monitoring, 5(3): 71-84. | |
| [28] | 王磊, 刘端阳, 韩桂荣, 等, 2018. 南京地区近地面臭氧浓度与气象条件关系研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 38(4): 1285-1296. |
| WANG L, LIU D Y, HAN G R, et al., 2018. Study on the relationship between surface ozone concentrations and meteorological conditions in Nanjing, China[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 38(4): 1285-1296. | |
| [29] | 王中杰, 霍娟, 杜惠云, 等, 2021. 2015-2019年日照市PM2.5长期变化特征及其潜在源区分析[J]. 中国环境科学, 41(9): 3969-3980. |
| WANG Z J, HUO J, DU H Y, et al., 2021. Long term characteristics and potential sources of PM2.5 in Rizhao City from 2015 to 2019[J]. China Environmental Science, 41(9): 3969-3980. | |
| [30] | 严文莲, 刘端阳, 康志明, 等, 2019. 江苏臭氧污染特征及其与气象因子的关系[J]. 气象科学, 39(4): 477-487. |
| YAN W L, LIU D Y, KANG Z M, et al., 2019. The characteristics of ozone pollution and its relationship with meteorological factors in Jiangsu[J]. Journal of Meteorological Sciences, 39(4): 477-487. | |
| [31] | 杨镇江, 李柯, 廖宏, 等, 2023. 2022年夏季历史极端高温下我国近地表臭氧污染及气象成因分析[J/OL]. 大气科学, 1-12 [2024-11-28]. https://doi.org/10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2302.22211. |
| [32] | 杨镇江, 李柯, 廖宏, 等, 2025. 2022年夏季历史极端高温下我国近地表臭氧污染及气象成因分析[J]. 大气科学, 49(01): 1-12. |
| YANG Z J, LI K, LIAO H, et al., 2025. Analysis of surface ozone pollution in China amid the record summertime extreme heat of 2022[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 49(01): 1-12. | |
| [33] | 张咪, 张宇, 李坤鹏, 等, 2021. 赤壁市臭氧污染特征及气象影响因素分析[J]. 环境科学与技术, 44(11): 18-24. |
| ZHANG M, ZHANG Y, LI K P, et al., 2021. Distribution characteristics of ozone and associated meteorological factors in Chibi, Hubei[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 44(11): 18-24. | |
| [34] | 中华人民共和国环境保护部,国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 2012. 环境空气质量标准: GB 3095—2012 [S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China, General Administration of Quality Supervision,Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, 2012. Ambient air quality standards: GB 3095—2012 [S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. | |
| [35] | 中华人民共和国环境保护部, 2013. 环境空气质量评价技术规范(试行): HJ 663—2013 [S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China. 2013. Technical regulation on ambient air quality assessment (trial): HJ 663—2013 [S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. | |
| [36] | 中华人民共和国生态环境部, 2024. 2023中国生态环境状况公报[R]. 北京: 中国人民共和国生态环境部. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, 2024. China environmental condition bulletin 2023[R]. Beijing: Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. | |
| [37] | 周颖, 2023. 苏皖鲁豫交界区域空气质量状况及气象因子对其影响的研究[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学. |
| ZHOU Y, 2023. A study on the air quality status and the impact of meteorological factors in the border area of Jiangsu, Anhui, Shandong, and Henan[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology. |
| [1] | 李建付, 黄志霖, 和成忠, 姜昕, 宋琳, 刘佳鑫, 陈利顶. 滇东喀斯特断陷盆地土壤有机碳空间分布特征及其关键影响因子[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(9): 1339-1352. |
| [2] | 周玉祥, 赵玉, 聂仁东, 丁丁, 郭立华, 周佳峥. 下辽河平原土地沙漠化程度及预测研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1133-1139. |
| [3] | 温丽容, 江明, 黄渤, 袁鸾, 周炎, 陆炜梅, 张莹, 刘明, 张力昀. 珠三角典型区域臭氧成因分析与VOCs来源解析——以中山为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 500-513. |
| [4] | 王成武, 罗俊杰, 唐鸿湖. 基于InVEST模型的太行山沿线地区生态系统碳储量时空分异驱动力分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 215-225. |
| [5] | 张鐥文, 杨冉, 侯文星, 王丽丽, 刘爽, 宋汉扬, 赵文吉, 李令军. 生态补水前后永定河两岸植被覆盖度变化及驱动力分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 264-273. |
| [6] | 符传博, 丹利, 佟金鹤, 陈红. 海口市区臭氧污染变化特征及潜在源区分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 331-340. |
| [7] | 郑晓豪, 陈颖彪, 郑子豪, 郭城, 黄卓男, 周泳诗. 湖北省生态系统服务价值动态变化及其影响因素演变[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 195-206. |
| [8] | 闫胜文, 刘加珍, 陈永金, 马笑丹, 张亚茹, 朱海勇. 聊城大气降水氢氧同位素特征及水汽来源分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 546-555. |
| [9] | 郝永佩, 宋晓伟, 赵文珺, 向发敏. 汾渭平原大气污染时空分布及相关因子分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 512-523. |
| [10] | 廖彤, 熊鑫, 王在华, 杨夏捷, 黄映楠, 冯嘉颖. 世界三大湾区大气污染治理经验及对粤港澳大湾区的启示[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2242-2250. |
| [11] | 王雪梅, 玉米提∙买明, 毛东雷, 梁婷. 干旱区绿洲耕层土壤重金属铬含量的高光谱估测[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(10): 2076-2084. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
