生态环境学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (10): 1741-1749.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.10.003
收稿日期:2023-08-15
出版日期:2023-10-18
发布日期:2024-01-16
通讯作者:
*廖立国。E-mail: liaoliguo1996@163.com作者简介:王如(1989年生),女(黎族),林业工程师,主要从事珍稀濒危植物保育研究。E-mail: 510227185@qq.com
基金资助:
WANG Ru( ), NONG Shouqian, PENG Wencheng, WU Biao, YANG Jia, LIAO Liguo(
), NONG Shouqian, PENG Wencheng, WU Biao, YANG Jia, LIAO Liguo( )
)
Received:2023-08-15
Online:2023-10-18
Published:2024-01-16
摘要:
海南粗榧(Cephalotaxus hainanensis)野外分布稀少,自然更新能力弱,加之受到人类砍伐的严重威胁,种群数量急剧减少。为探明海南粗榧所在群落树种组成与种间关系,分析其种群濒危机制,创造海南粗榧种群恢复的适宜生境,制定针对性保护措施,通过在野外实地调查海南热带雨林国家公园海南粗榧群落样地的基础上,对群落伴生树种的物种多样性、区系组成进行分析,并采用方差比率法(Rv)、χ2检验、联结系数(AC)、共同出现百分率(PC)、Pearson相关系数(rp)和Spearman秩相关系数(rs)对海南粗榧群落16种常见树种的总体关联性、种间联结显著性及关联强度进行探讨分析。结果表明,在8个20 m×20 m样地中,共发现乔木树种44科78属105种;植物区系以热带性质为主,占总科数的65.9%;16种常见树种总体关联性表现为不显著的负关联(Rv =0.534,统计量W=4.27),物种的独立性较强;χ2检验结果表明负关联种对数(41对)多于正关联种对(33对),群落中无显著关联种对;AC>0.67的种对9对,PC>0.75的种对7对,大多数树种间联结性较弱,海南粗榧仅与短药蒲桃存在显著正关联(P=0.018);相关性检验rp与rs显示显著负关联种对多于显著正关联种对,海南粗榧与药用狗牙花呈显著负相关(P=0.027),绝大多数种对不显著相关。综上所述,海南粗榧群落整体结构较为松散,物种可能存在较为频繁更迭,群落尚处不稳定阶段,海南粗榧趋于独立存活。为缓解海南粗榧种群存在的衰退现象,应对其个体采取就地保护措施,适当改造群落生境,进行人工补植,扩大其种群数量。
中图分类号:
王如, 农寿千, 彭文成, 吴彪, 杨佳, 廖立国. 珍稀濒危植物海南粗榧群落树种组成与种间联结性[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(10): 1741-1749.
WANG Ru, NONG Shouqian, PENG Wencheng, WU Biao, YANG Jia, LIAO Liguo. Tree Species Composition and Interspecific Associations of Rare and Endangered Plant Cephalotaxus hainanensis Community[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(10): 1741-1749.
| 调查地点 | 编号 | 胸径/cm | 树龄/a | 经度 | 纬度 | 海拔/m | 坡度/(°) | 森林类型 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 霸王岭 | 峨贤岭 | C1 | 58 | 150 | 109°06′36.69″E | 19°00′48.27″N | 886 | 15 | 热带山地雨林 |
| 东二 | C2 | 95 | 400 | 109°10′44.52″E | 19°05′41.00″N | 1013 | 8 | 热带山地雨林 | |
| 东二 | C3 | 70 | 200 | 109°10′58.21″E | 19°05′23.90″N | 1093 | 16 | 热带山地雨林 | |
| 尖峰岭 | 茅草坡 | L1 | 49 | 120 | 108°59′29.73″E | 18°42′41.84″N | 668 | 27 | 热带低地雨林 |
| 茅草坡 | L2 | 71 | 200 | 108°59′28.20″E | 18°42′43.25″N | 673 | 14 | 热带低地雨林 | |
| 黎母山 | 林区 | Q1 | 144 | 600 | 109°42′28.32″E | 19°09′54.49″N | 956 | 70 | 热带山地雨林 |
| 五指山 | 主峰 | W1 | 43 | 100 | 109°41′14.36″E | 18°54′11.07″N | 906 | 6 | 热带山地雨林 |
| 主峰 | W2 | 47 | 120 | 109°41′17.17″E | 18°54′10.92″N | 937 | 10 | 热带山地雨林 | |
表1 海南粗榧样方地理位置及母树信息
Table 1 Geographic location and maternal plants information of Cephalotaxus hainanensis sample plot
| 调查地点 | 编号 | 胸径/cm | 树龄/a | 经度 | 纬度 | 海拔/m | 坡度/(°) | 森林类型 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 霸王岭 | 峨贤岭 | C1 | 58 | 150 | 109°06′36.69″E | 19°00′48.27″N | 886 | 15 | 热带山地雨林 |
| 东二 | C2 | 95 | 400 | 109°10′44.52″E | 19°05′41.00″N | 1013 | 8 | 热带山地雨林 | |
| 东二 | C3 | 70 | 200 | 109°10′58.21″E | 19°05′23.90″N | 1093 | 16 | 热带山地雨林 | |
| 尖峰岭 | 茅草坡 | L1 | 49 | 120 | 108°59′29.73″E | 18°42′41.84″N | 668 | 27 | 热带低地雨林 |
| 茅草坡 | L2 | 71 | 200 | 108°59′28.20″E | 18°42′43.25″N | 673 | 14 | 热带低地雨林 | |
| 黎母山 | 林区 | Q1 | 144 | 600 | 109°42′28.32″E | 19°09′54.49″N | 956 | 70 | 热带山地雨林 |
| 五指山 | 主峰 | W1 | 43 | 100 | 109°41′14.36″E | 18°54′11.07″N | 906 | 6 | 热带山地雨林 |
| 主峰 | W2 | 47 | 120 | 109°41′17.17″E | 18°54′10.92″N | 937 | 10 | 热带山地雨林 | |
| 科名 | 属数量 | 种数量 | 植物类型 | 科名 | 属数量 | 种数量 | 植物类型 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 三尖杉科 Cephalotaxaceae | 1 | 1 | 裸子 | 杜英科 Elaeocarpaceae | 2 | 4 | 双子叶 |
| 桃金娘科 Myrtaceae | 2 | 4 | 双子叶 | 山龙眼科 Proteaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 |
| 夹竹桃科 Apocynaceae | 4 | 5 | 双子叶 | 心翼果科 Cardiopteridaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 |
| 番荔枝科 Annonaceae | 3 | 4 | 双子叶 | 柿科 Ebenaceae | 1 | 2 | 双子叶 |
| 楝科 Meliaceae | 4 | 7 | 双子叶 | 紫葳科 Bignoniaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 |
| 无患子科 Sapindaceae | 4 | 4 | 双子叶 | 猕猴桃科 Actinidiaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 |
| 桑科 Moraceae | 4 | 10 | 双子叶 | 冬青科 Aquifoliaceae | 1 | 2 | 双子叶 |
| 杨柳科 Salicaceae | 2 | 3 | 双子叶 | 大戟科 Euphorbiaceae | 2 | 2 | 双子叶 |
| 樟科 Lauraceae | 5 | 10 | 双子叶 | 罗汉松科 Podocarpaceae | 1 | 1 | 裸子 |
| 荨麻科 Urticaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 | 胡桃科 Juglandaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 |
| 叶下珠科 Phyllanthaceae | 3 | 3 | 双子叶 | 榆科 Ulmaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 |
| 五加科 Araliaceae | 2 | 2 | 双子叶 | 大麻科 Cannabaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 |
| 大风子科 Flacourtiaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 | 唇形科 Lamiaceae | 2 | 2 | 双子叶 |
| 省沽油科 Staphyleaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 | 蔷薇科 Rosaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 |
| 山榄科 Sapotaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 | 木樨科 Oleaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 |
| 报春花科 Primulaceae | 2 | 2 | 双子叶 | 藤黄科 Clusiaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 |
| 清风藤科 Sabiaceae | 1 | 2 | 双子叶 | 安息香科 Styracaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 |
| 豆科 Fabaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 | 芸香科 Rutaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 |
| 茜草科 Rubiaceae | 5 | 6 | 双子叶 | 海桐科 Pittosporaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 |
| 锦葵科 Malvaceae | 4 | 5 | 双子叶 | 橄榄科 Burseraceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 |
| 山茱萸科 Cornaceae | 1 | 2 | 双子叶 | 漆树科 Anacardiaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 |
| 棕榈科 Arecaceae | 1 | 1 | 单子叶 | 木兰科 Magnoliaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 |
表2 海南粗榧伴生群落树种科属统计
Table 2 Family and genus statistics of tree species in Cephalotaxus hainanensis concomitant community
| 科名 | 属数量 | 种数量 | 植物类型 | 科名 | 属数量 | 种数量 | 植物类型 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 三尖杉科 Cephalotaxaceae | 1 | 1 | 裸子 | 杜英科 Elaeocarpaceae | 2 | 4 | 双子叶 |
| 桃金娘科 Myrtaceae | 2 | 4 | 双子叶 | 山龙眼科 Proteaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 |
| 夹竹桃科 Apocynaceae | 4 | 5 | 双子叶 | 心翼果科 Cardiopteridaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 |
| 番荔枝科 Annonaceae | 3 | 4 | 双子叶 | 柿科 Ebenaceae | 1 | 2 | 双子叶 |
| 楝科 Meliaceae | 4 | 7 | 双子叶 | 紫葳科 Bignoniaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 |
| 无患子科 Sapindaceae | 4 | 4 | 双子叶 | 猕猴桃科 Actinidiaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 |
| 桑科 Moraceae | 4 | 10 | 双子叶 | 冬青科 Aquifoliaceae | 1 | 2 | 双子叶 |
| 杨柳科 Salicaceae | 2 | 3 | 双子叶 | 大戟科 Euphorbiaceae | 2 | 2 | 双子叶 |
| 樟科 Lauraceae | 5 | 10 | 双子叶 | 罗汉松科 Podocarpaceae | 1 | 1 | 裸子 |
| 荨麻科 Urticaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 | 胡桃科 Juglandaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 |
| 叶下珠科 Phyllanthaceae | 3 | 3 | 双子叶 | 榆科 Ulmaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 |
| 五加科 Araliaceae | 2 | 2 | 双子叶 | 大麻科 Cannabaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 |
| 大风子科 Flacourtiaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 | 唇形科 Lamiaceae | 2 | 2 | 双子叶 |
| 省沽油科 Staphyleaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 | 蔷薇科 Rosaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 |
| 山榄科 Sapotaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 | 木樨科 Oleaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 |
| 报春花科 Primulaceae | 2 | 2 | 双子叶 | 藤黄科 Clusiaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 |
| 清风藤科 Sabiaceae | 1 | 2 | 双子叶 | 安息香科 Styracaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 |
| 豆科 Fabaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 | 芸香科 Rutaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 |
| 茜草科 Rubiaceae | 5 | 6 | 双子叶 | 海桐科 Pittosporaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 |
| 锦葵科 Malvaceae | 4 | 5 | 双子叶 | 橄榄科 Burseraceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 |
| 山茱萸科 Cornaceae | 1 | 2 | 双子叶 | 漆树科 Anacardiaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 |
| 棕榈科 Arecaceae | 1 | 1 | 单子叶 | 木兰科 Magnoliaceae | 1 | 1 | 双子叶 |
| 分布区类型 | 科数 | 比例/% |
|---|---|---|
| 1 世界分布 | 8 | 18.2 |
| 2 泛热带分布 | 21 | 47.7 |
| 3 东亚 (热带、亚热带) 及热带南美间断分布 | 5 | 11.4 |
| 4 旧世界热带 | 1 | 2.27 |
| 5 热带亚洲至热带大洋洲 | 1 | 2.27 |
| 6 热带亚洲分布 | 1 | 2.27 |
| 7 北温带 | 4 | 9.09 |
| 8 东亚及北美间断 | 1 | 2.27 |
| 9 东亚 | 2 | 4.55 |
表3 海南粗榧伴生群落树种科的分布区类型
Table 3 Distribution area types of tree species family in Cephalotaxus hainanensis concomitant community
| 分布区类型 | 科数 | 比例/% |
|---|---|---|
| 1 世界分布 | 8 | 18.2 |
| 2 泛热带分布 | 21 | 47.7 |
| 3 东亚 (热带、亚热带) 及热带南美间断分布 | 5 | 11.4 |
| 4 旧世界热带 | 1 | 2.27 |
| 5 热带亚洲至热带大洋洲 | 1 | 2.27 |
| 6 热带亚洲分布 | 1 | 2.27 |
| 7 北温带 | 4 | 9.09 |
| 8 东亚及北美间断 | 1 | 2.27 |
| 9 东亚 | 2 | 4.55 |
| 缩写 | 树种 | 缩写 | 树种 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ch | 海南粗榧 Cephalotaxus hainanensis | Fr | 大叶刺篱木 Flacourtia rukam |
| Sg | 短药蒲桃 Syzygium globiflorum | Lv | 黄椿木姜子 Litsea variabilis |
| Wl | 蓝树 Wrightia laevis | Or | 红紫麻 Oreocnide rubescens |
| Po | 沙煲暗罗 Polyalthia obliqua | Bj | 秋枫 Bischofia javanica |
| Dg | 红果樫木 Dysoxylum gotadhora | Hh | 鹅掌柴 Heptapleurum heptaphyllum |
| Lo | 赛木患 Lepisanthes oligophylla | Tb | 药用狗牙花 Tabernaemontana bovina |
| Pl | 海南暗罗 Polyalthia lauii | Ho | 红花天料木 Homalium hainanense |
| Ff | 水同木 Ficus fistulosa | Cm | 白背厚壳桂 Cryptocarya maclurei |
表4 海南粗榧群落常见树种种名及缩写
Table 4 Name and abbrevition of common species in Cephalotaxus hainanensis community
| 缩写 | 树种 | 缩写 | 树种 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ch | 海南粗榧 Cephalotaxus hainanensis | Fr | 大叶刺篱木 Flacourtia rukam |
| Sg | 短药蒲桃 Syzygium globiflorum | Lv | 黄椿木姜子 Litsea variabilis |
| Wl | 蓝树 Wrightia laevis | Or | 红紫麻 Oreocnide rubescens |
| Po | 沙煲暗罗 Polyalthia obliqua | Bj | 秋枫 Bischofia javanica |
| Dg | 红果樫木 Dysoxylum gotadhora | Hh | 鹅掌柴 Heptapleurum heptaphyllum |
| Lo | 赛木患 Lepisanthes oligophylla | Tb | 药用狗牙花 Tabernaemontana bovina |
| Pl | 海南暗罗 Polyalthia lauii | Ho | 红花天料木 Homalium hainanense |
| Ff | 水同木 Ficus fistulosa | Cm | 白背厚壳桂 Cryptocarya maclurei |
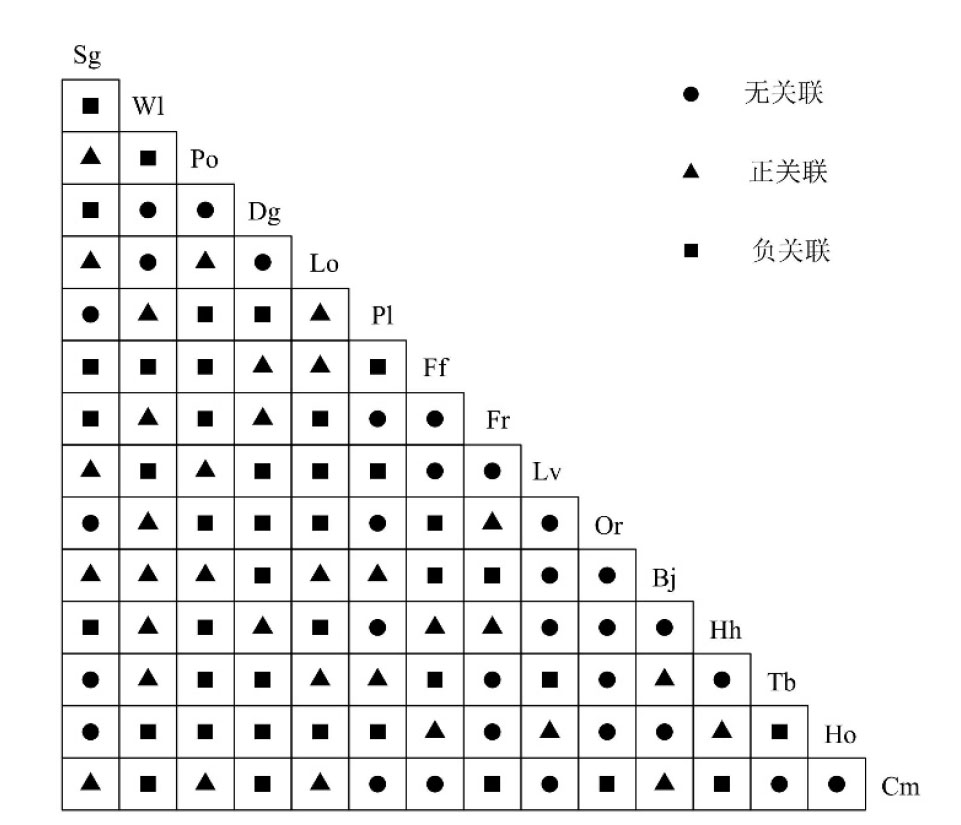
图1 海南粗榧群落常见树种种间关联χ2半矩阵图
Figure 1 Semi-matrix of interspecific correction χ2-test of association of common species in Cephalotaxus hainanensis community
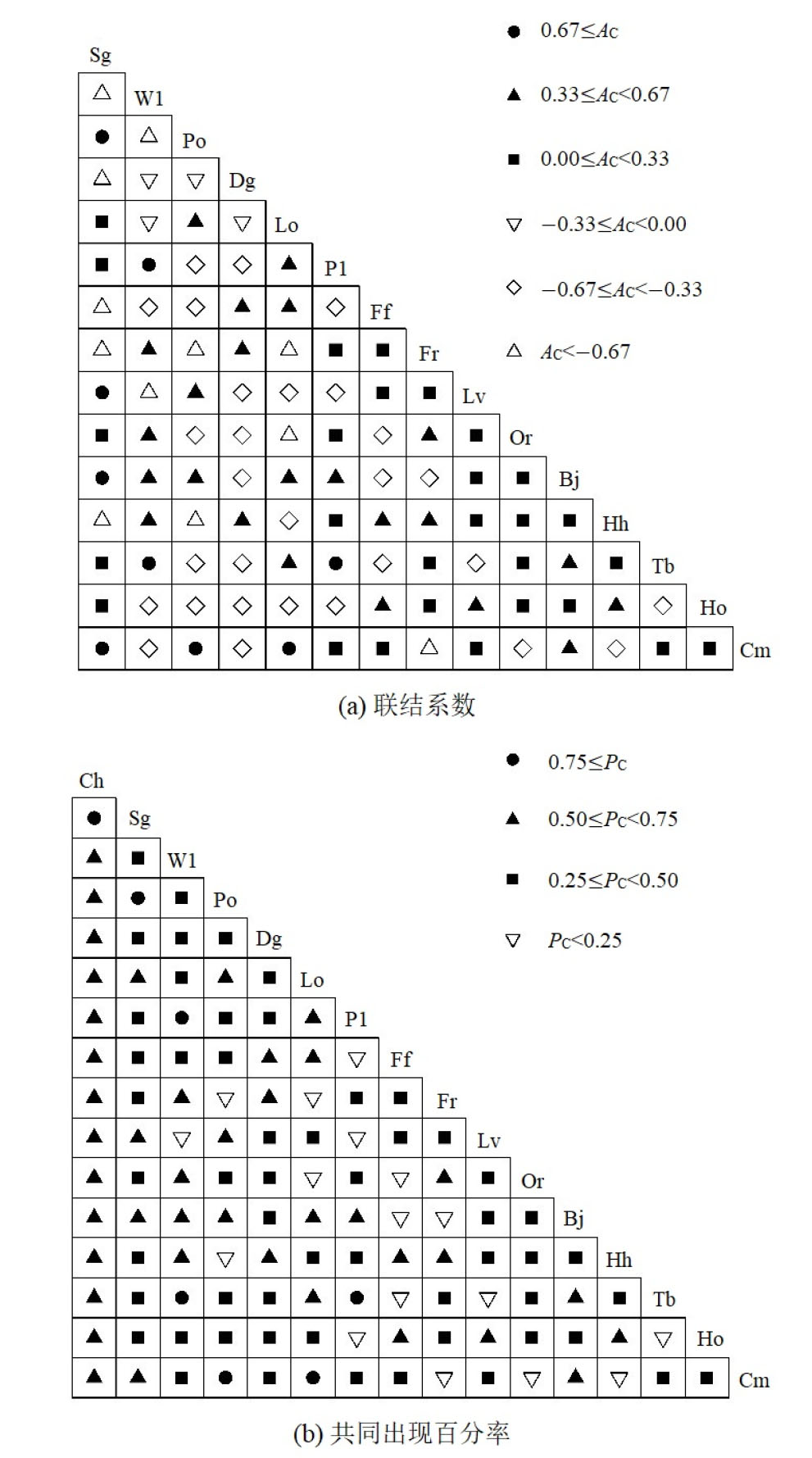
图2 海南粗榧群落常见树种种间关联AC值(a)和PC值(b)半矩阵图
Figure 2 Semi-matrix of interspecific correction AC value (a), PC value (b) of association of common species in Cephalotaxus hainanensis community
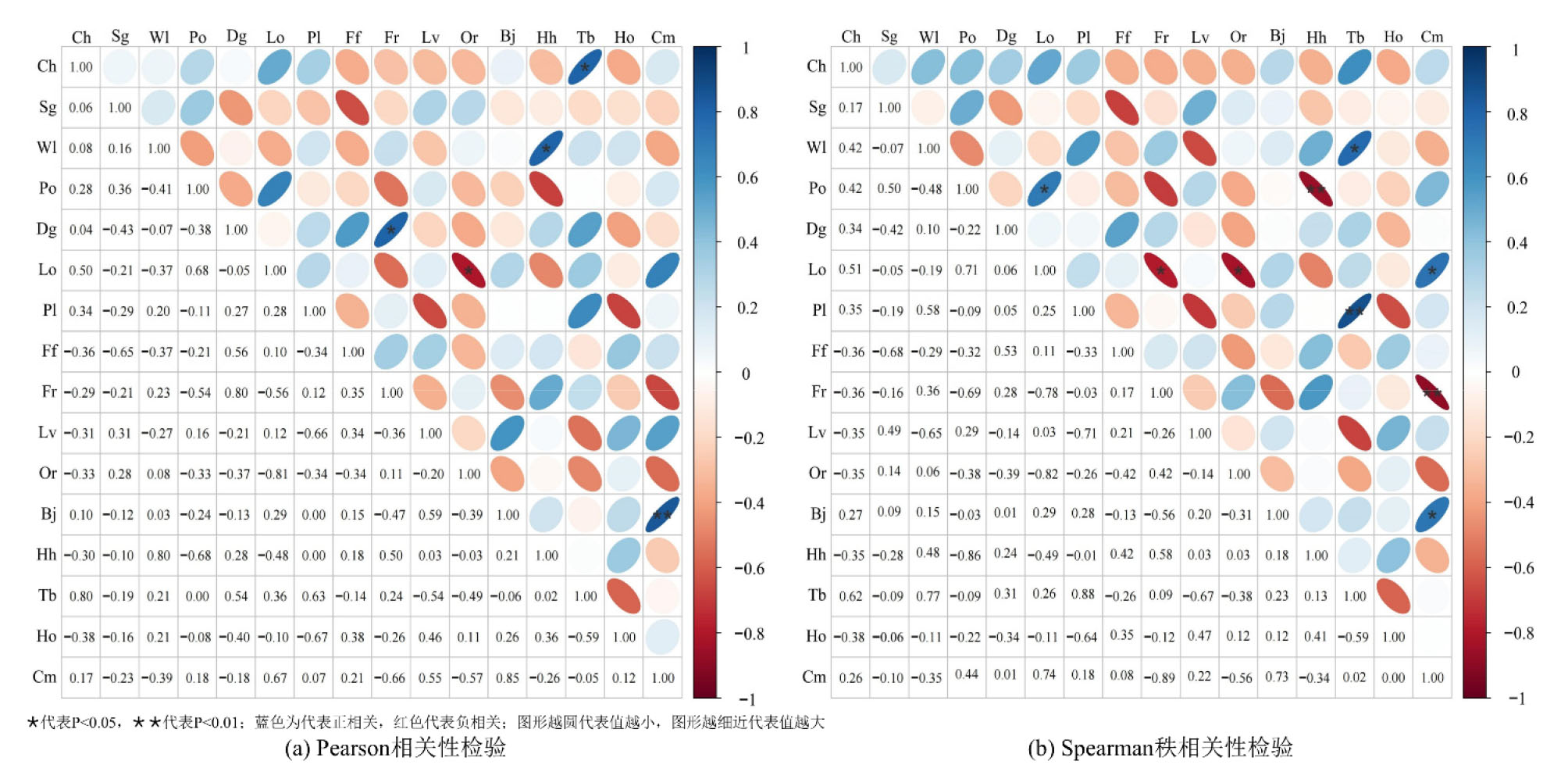
图3 海南粗榧群落常见树种Pearson相关性和Spearman秩相关性检验
Figure 3 Pearson correlation coefficien and Spearman rank correlation coefficient of common species in Cephalotaxus hainanensis community
| [1] |
AKATOV V V, AKATOVA T V, CHEFRANOV S G, 2018. Degree of dominance and species richness in plant communities with high and low intensity of interspecies competition[J]. Biology Bulletin Reviews, 8(5): 389-400.
DOI |
| [2] |
DE SEQUEIRA M M, JARDIM R, GOUVEIA M, et al., 2021. Population decline in the Critically Endangered Musschia isambertoi (Campanulaceae) endemic to Desertas Islands (Madeira Archipelago) calls for urgent conservation management[J]. Journal for Nature Conservation, 60: 125955.
DOI URL |
| [3] | DU D L, SU J, FU Y C, et al., 2002. Genetic Diversity of Cephalotaxus mannii, a Rare and Endangered Plant[J]. Acta Botanica Sinica, 44(2): 193-198. |
| [4] |
QIAO F, HE Y D, ZHANG Y H, et al., 2023. Elucidation of the 1-phenethylisoquinoline pathway from an endemic conifer Cephalotaxus hainanensis [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 120(1): e2209339120.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
SCHLUTER D, 1984. A variance test for detecting species associations, with some example applications[J]. Ecology, 65(3): 998-1005.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
TILMAN D, REICH P B, KNOPS J M H, 2006. Biodiversity and ecosystem stability in a decade-long grassland experiment[J]. Nature, 441(7093): 629-632.
DOI |
| [7] | 蔡鑫, 陈波, 陈锋, 等, 2019. 珍稀特有植物华顶杜鹃的种群结构和种间联结[J]. 浙江大学学报(理学版), 46(3): 354-363. |
| CAI X, CHEN B, CHEN F, et al., 2019. Population structure and interspecific association of Rhododendron huadingense, a rare and endemic species in China[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Science Edition), 46(3): 354-363. | |
| [8] | 陈玉凯, 杨小波, 李东海, 等, 2011. 海南霸王岭海南油杉群落优势种群的种间联结性研究[J]. 植物科学学报, 29(3): 278-287. |
| CHEN Y K, YANG X B, LI D H, et al., 2011. Interspecific associations among dominant plant populations in Keteleeria hainanensis communities in Bawangling, Hainan Island[J]. Plant Science Journal, 29(3): 278-287. | |
| [9] |
陈宗铸, 雷金睿, 吴庭天, 等, 2021. 国家公园生态系统生产总值核算——以海南热带雨林国家公园为例[J]. 应用生态学报, 32(11): 3883-3892.
DOI |
| CHEN Z Z, LEI J R, WU T T, et al., 2021. Gross ecosystem product accounting of national park: Taking Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park as an example[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 32(11): 3883-3892. | |
| [10] | 杜家贤, 刘闯, 殷崇敏, 等, 2020. 海南猕猴岭自然保护区海南锥+黄牛木群落特征研究[J]. 植物科学学报, 38(5): 609-617. |
| DU J X, LIU C, YIN C M, et al., 2020. Characteristics of the Castanopsis hainanensis+Cratoxylum cochinchinense community in Mt. Mihouling Nature Reserve, Hainan, China[J]. Plant Science Journal, 38(5): 609-617. | |
| [11] | 戴志聪, 祁珊珊, 邢旭煌, 等, 2010. 珍稀濒危植物海南粗榧幼苗天然更新与环境因子的灰色关联分析[J]. 林业资源管理 (2): 50-56. |
| DAI Z C, QI S S, XING X H, et al., 2010. Gray Relational Analysis on Natural Regeneration of Rare and Endangered Species Cephalotaxus mannii Hookfand Environment Factors[J]. Forest Resources Wanagement (2): 50-56. | |
| [12] | 符文英, 杜道林, 邢诒旺, 2003. 海南粗榧保护和开发利用的研究[J]. 分子植物育种, 1(5-6): 795-799. |
| FU W Y, DU D L, XING Y W, 2003. Study on the protection and exploita tion of Cephalotaxus mannii[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 1(5-6): 795-799. | |
| [13] | 黄祥童, 王绍先, 黄炳军, 等, 2015. 珍稀植物对开蕨与其伴生物种的联结性及群落稳定性[J]. 生态学报, 35(1): 80-90. |
| HUANG X T, WANG S X, HUANG B J, et al., 2015. Analyses of community stability and interspecific associations between the rare plant Phyllitis scolopendrium and its associated species[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35(1): 80-90. | |
| [14] |
姜超, 谭珂, 任明迅, 2017. 季风对亚洲热带植物分布格局的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 41(10): 1103-1112.
DOI |
|
JIANG C, TAN K, REN M X, 2017. Effects of monsoon on distribution patterns of tropical plants in Asia[J]. Chinese Journal Plant Ecology, 41(10): 1103-1112.
DOI URL |
|
| [15] | 罗金环, 洪文君, 何书奋, 等, 2018. 极小种群海南假韶子群落物种及种群结构研究[J]. 西南农业学报, 31(9): 1912-1918. |
| LUO J H, HONG W J, HE S F, et al., 2018. Study on community compositions and population structure of Paranephelium hainanensis of extremely small populations[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 31(9): 1913-1918. | |
| [16] | 罗敏贤, 林碧华, 陈绪辉, 等, 2022. 福建龟山伞花木所在群落乔灌层优势种的种间联结性[J]. 植物资源与环境学报, 31(6): 63-72. |
| LUO M X, LIN B H, CHEN X H, et al., 2022. Interspecific associations of dominant species in arbor and shrub layers of Eurycorymbus cavaleriei located community in Guishan Mountain of Fujian Province[J]. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment, 31(6): 63-72. | |
| [17] | 潘元琪, 杜彦君, 陈文德, 等, 2020. 植物物候是否能解释物种共存:以浙江古田山亚热带常绿阔叶林为例[J]. 中国科学: 生命科学, 50(4): 362-375. |
| PAN Y Q, DU Y J, CHEN W D, et al., 2020. Can plant phenology explain species coexistence: A case study in the subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest of Gutianshan, Zhejiang, China[J]. Science in China (Series C), 50(4): 362-372. | |
| [18] | 祁珊珊, 戴志聪, 司春灿, 等, 2010. 珍稀濒危抗癌植物海南粗榧种群结构和资源价值研究[J]. 林业资源管理 (1): 53-58. |
| QI S S, DAI Z C, SI C C, et al., 2010. Study on population structure and resource value of Cephalotaxus mannii Hook. f., A rare and endangered anti-cancer plant in Hainan[J]. Forest Resources Wanagement (1): 53-8. | |
| [19] | 祁珊珊, 戴志聪, 司春灿, 等, 2010. 珍稀濒危植物海南粗榧保育群落植被生物多样性研究[J]. 福建林业科技, 37(1): 6-11. |
| QI S S, DAI Z C, SI C C, et al., 2010. Investigation on the biodiversity of rare and en dangeredspecies Cephalotaxus mannii Hook. f. conservation communi-ty[J]. Journal of Fujian Forestry Science and Technology, 37(1): 6-11. | |
| [20] |
王博, 王亮, 王立龙, 等, 2017. 濒危植物裸果木 (Gymnocarpos przewalskii) 与其伴生种种间联结性及群落稳定性[J]. 中国沙漠, 37(1): 86-92.
DOI |
| WANG B, WANG L, WANG L L, et al., 2017. Interspecific association and community stability of endangered plant Gymnocarpos przewalskii with its associated species[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 37(1): 86-92. | |
| [21] | 王加国, 李晓芳, 安明态, 等, 2015. 雷公山濒危植物台湾杉群落主要乔木树种种间联结性研究[J]. 西北林学院学报, 30(4): 78-83. |
| WANG J G, LI X F, AN M T, et al., 2015. lnterspecific associations among main tree species in Taiwania cryptomerioides community in Leigong Mountain[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 30(4): 78-83. | |
| [22] | 王丽, 常锦利, 周守标, 等, 2019. 鹞落坪国家级自然保护区乔木物种多样性与种间联结[J]. 生态学报, 39(1): 309-319. |
| WANG L, CHANG J L, ZHOU S B, et al., 2019. Species diversity and interspecific association of trees in the Yaoluoping Nation Nature Reserve[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(1): 309-319. | |
| [23] |
王世彤, 吴浩, 刘梦婷, 等, 2018. 极小种群野生植物黄梅秤锤树群落结构与动态[J]. 生物多样性, 26(7): 749-759.
DOI |
|
WANG S T, WU H, LIU M T, et al., 2018. Community structure and dynamics of a remnant f orest dominated by a plant species with extremely small population(Sinojackia huangmeiensis)in central China[J]. Biodiversity Science, 26(7): 749-759.
DOI URL |
|
| [24] | 王献溥, 王有生, 1994. 海南粗榧濒危的原因和保护措施[J]. 广西植物, 14(4): 369-372. |
| WANG X P, WANG Y S, 1994. Factors caused endangerment of hainanplumyew (Cephalotaxus mannii) and its conservation means[J]. Guihaia, 14(4): 369-372. | |
| [25] | 魏亚情, 宋希强, 赵莹, 等, 2022. 吊罗山石碌含笑群落木本植物种间联结性研究[J]. 热带作物学报, 43(12): 2606-2613. |
| WEI Y Q, SONG X Q, ZHAO Y, et al., 2022. Interspecific association of woody plants in Michelia shiluensis community, Diaoluoshan Nature Reserve, Hainan Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 43(12): 2606-2613. | |
| [26] | 吴征镒, 周浙昆, 李德铢, 等, 2003. 世界种子植物科的分布区类型系统[J]. 云南植物研究, 25(3): 245-257. |
| WU Z Y, ZHOU Z K, LI D Z, et al., 2003. Distribution area type system of the seed plant families of the world[J]. Yunnan Botanical Research, 25(3): 245-257. | |
| [27] | 向志强, 刘玉成, 张欣桐, 2002. 海南粗榧 (Cephalotaxus mannii) 不同种群表型结构的数量分析[J]. 生态学杂志, 21(5): 18-21. |
| XIANG Z Q, LIU Y C, ZHANG X T, 2002. Numerical analysis on morphologic structure of different populations of Cephalotaxus mannii[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 21(5): 18-21. | |
| [28] | 徐满厚, 刘敏, 翟大彤, 等, 2016. 植物种间联结研究内容与方法评述[J]. 生态学报, 36(24): 8224-8233. |
| XU M H, LIU M, ZHAI D T, et al., 2016. A review of contents and methods used to analyze various aspects of plant interspecific associations[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36(24): 8224-8233. | |
| [29] | 薛卫星, 李春辉, 艾训儒, 等, 2023. 鹅掌楸天然林优势树种生态位与种间联结性[J]. 森林与环境学报, 43(1): 26-34. |
| XUE W X, LI C H, AI X R, et al., 2023. Niche and interspecific association of dominant tree species in Liriodendron chinense natural forest[J]. Journal of Forest and Environment, 43(1): 26-34. | |
| [30] | 杨阳, 马立辉, 王海洋, 2019. 濒危植物树枫杜鹃 (Rhododendron changii) 种群结构及伴生群落特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 38(5): 1352-1362. |
| YANG Y, MA L H, WANG H Y, 2019. Population structure and companion community characteristics of the endangered species, Rhododendron changii [J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 38(5): 1352-1362. | |
| [31] | 杨小波, 2015. 海南植物图志[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| YANG X B, 2015. Flora of Hainan Province[M]. Beijing: Science Press. | |
| [32] | 叶兴状, 王妙青, 程诺, 等, 2021. 福建天台山半枫荷天然群落的物种组成、生态位和种间关系[J]. 植物资源与环境学报, 30(6): 19-28. |
| YE X Z, WANG M Q, CHENG N, et al., 2021. Species composition, niche, and interspecific relationships of Semiliquidambar cathayensis natural community in Tiantai Mountain of Fujian Province[J]. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment, 30(6): 19-28. | |
| [33] | 曾祥全, 陈飞飞, 农寿千, 2016. 浅谈海南粗榧育苗技术及其发展前景[J]. 热带林业, 44(3): 11-14. |
| ZENG X Q, CHEN F F, NONG S Q, 2016. Preliminary discussion on seedling raising technology and development prospect of Cephalotaxus hainanensis[J]. Tropical Forestry, 44(3): 11-14. | |
| [34] | 张金屯, 2018. 数量生态学[M]. 第3版. 北京: 科学出版社: 147-162. |
| ZHANG J T, 2018. Quantitative Ecology[M]. Third Edition. Beijing: Science Press: 147-162. |
| [1] | 王哲, 田胜尼, 张永梅, 张和禹, 周忠泽. 巢湖派河口滩涂植物群落特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1823-1831. |
| [2] | 陈小南, 李琼雯, 余建平, 余顺海, 李双, 曹铭昌. 钱江源国家公园白颈长尾雉生境适宜性评价研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1832-1839. |
| [3] | 何斌, 李青, 陈群利, 李望军, 游萍. 黔西北黄杉群落物种多样性的海拔梯度格局[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1111-1120. |
| [4] | 姜倪皓, 张诗函. 楚雄市西郊云南松林下草本优势种种间联结及环境解释[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(11): 2109-2120. |
| [5] | 张晓龙, 周继华, 来利明, 郑元润. 黑河下游胡杨群落多样性沿河岸距离的变化特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(10): 1952-1960. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
