生态环境学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (8): 1496-1506.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.08.015
张睿含1( ), 智燕彩1, 贾明昊1, 李晓娜1,2,*(
), 智燕彩1, 贾明昊1, 李晓娜1,2,*( ), 王震宇1,2
), 王震宇1,2
收稿日期:2023-05-04
出版日期:2023-08-18
发布日期:2023-11-08
通讯作者:
*李晓娜。E-mail: xiaonali@jiangnan.edu.cn作者简介:张睿含(2002年生),女,研究方向为可再生资源利用。E-mail: 1103200214@stu.jiangnan.edu.cn
基金资助:
ZHANG Ruihan1( ), ZHI Yancai1, JIA Minghao1, LI Xiaona1,2,*(
), ZHI Yancai1, JIA Minghao1, LI Xiaona1,2,*( ), WANG Zhenyu1,2
), WANG Zhenyu1,2
Received:2023-05-04
Online:2023-08-18
Published:2023-11-08
摘要:
腐殖酸是土壤有机质中最活跃的部分,能改善土壤理化性质、提高土壤保肥性,是土壤的重要组成,也是植物营养的主要来源之一。为提高土壤中腐殖酸的含量,解决天然腐殖酸形成困难且周期长的问题,水热合成人工腐殖酸技术逐渐被关注。然而,水热条件和原料对人工腐殖酸性质的影响还鲜有报道。以乔木树枝——香樟树(Cinnamomum camphora)、灌木树枝——黄杨树(Buxus sinica)和香樟树叶为原料,在水热溶液pH分别为2、5、9和12的条件下制备人工腐殖酸并对其性质表征。结果表明,1)在水热过程中,纤维素相对含量高的树叶,其降解率随溶液pH升高而降低,在pH为2时,降解率为59.3%,而在pH为12时,降解率仅为41.0%,所得人工腐殖酸具有较好的导电性、营养价值和荧光特性;而木质素相对含量较高的乔木,其降解率随溶液pH升高而升高,在pH为12时,降解率可达到59.0%,所得人工腐殖酸具有较丰富的含氧官能团。2)强酸强碱条件下制备的人工腐殖酸具有较强导电性和较高的营养元素总量。强酸条件(pH=2)下提高人工腐殖酸中钠、钙和硫等元素的含量,强碱条件(pH=12)下提高人工腐殖酸中钠、硫和钾的含量。3)强碱条件(pH=12)更有利于人工腐殖酸的制备,所得人工腐殖酸自中和程度最佳,有机碳产量最高,导电性最强,营养价值和表面官能团能等性能方面均最佳;其中,由树叶生物质制备的人工腐殖酸,总有机碳含量最高且导电性最强,分别为2.60 g?L-1和3.10 mS?cm-1。研究结果为改良人工腐殖酸的制备工艺、指导人工腐殖酸的农业和环境应用提供了数据支撑,对环境的可持续发展具有积极意义。
中图分类号:
张睿含, 智燕彩, 贾明昊, 李晓娜, 王震宇. 生物质废弃物类型和水热pH对人工腐殖酸性能影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(8): 1496-1506.
ZHANG Ruihan, ZHI Yancai, JIA Minghao, LI Xiaona, WANG Zhenyu. Effects of Feedstock Types and Hydrothermal Solution pH on the Properties of Artificial Humic Acids[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(8): 1496-1506.
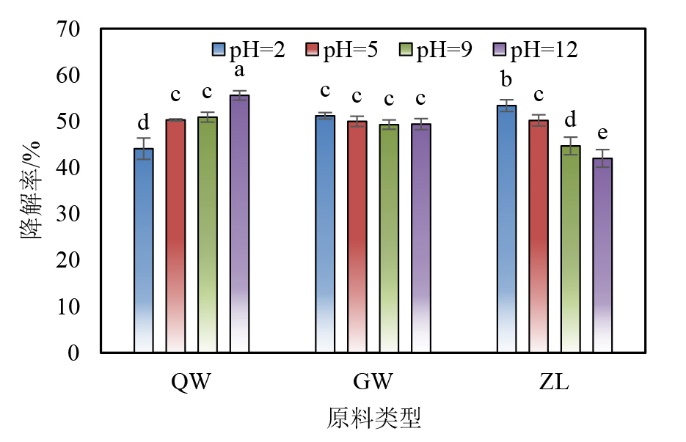
图1 水热合成人工腐殖酸过程中不同原料在不同溶液pH下的降解率 3种原料分别为:乔木—QW、灌木—GW、树叶—ZL。下同; 柱状图中柱高代表降解率的平均值大小,误差棒为降解率在同一处理的标准偏差,n=3,柱子上不同的英文字母代表处理间的显著差异
Figure 1 Degradation rate of different raw materials in solution with different pH during the hydrothermal synthesis of artificial humic acids
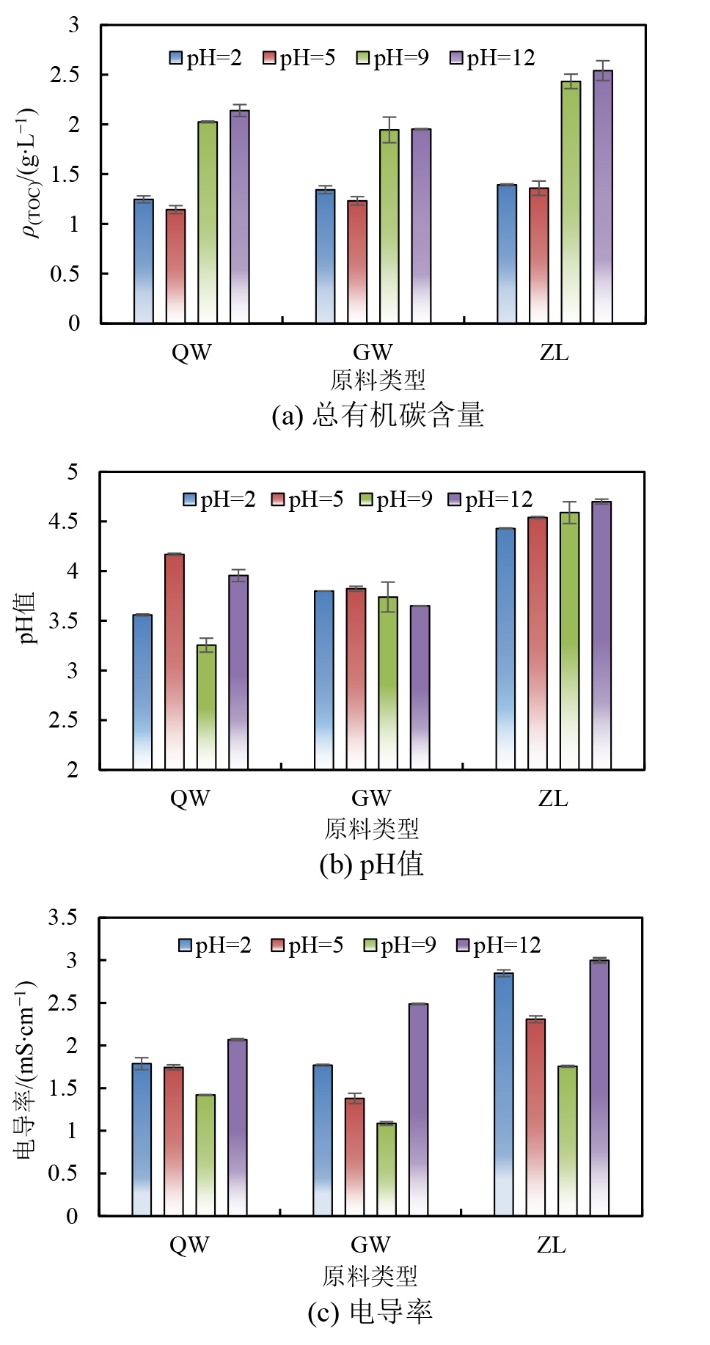
图2 不同原料及pH条件下制备人工腐殖酸的总有机碳含量,pH值和电导率 柱状图中柱高代表某指标的平均值大小,误差棒为某指标在同一处理的标准偏差,n=3
Figure 2 Total organic carbon content, pH and electrical conductivity of artificial humic acids prepared under different raw material and pH conditions
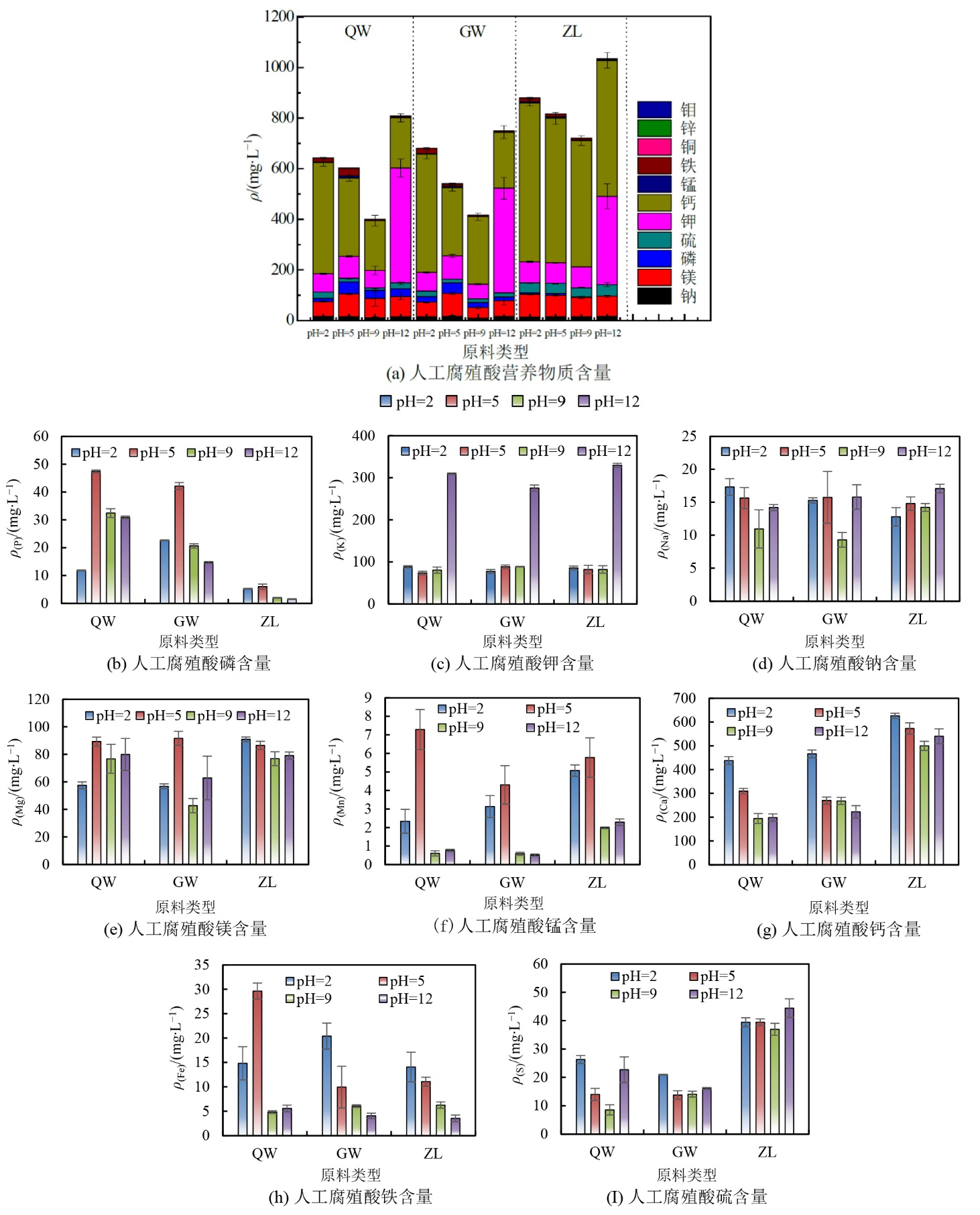
图3 不同原料及pH条件下制备人工腐殖酸的营养元素含量 堆积图中不同颜色矩形的大小代表对应营养元素的浓度大小,柱状图中柱高代表对应营养元素浓度的平均值大小,误差棒为对应营养元素浓度在同一处理的标准偏差,n=3;碱性水热过程以氢氧化钾作为反应溶液,图中钾离子浓度已去除溶液本底值
Figure 3 Nutrient content of artificial humic acid prepared under different raw material and pH conditions
| [1] |
ADANI F, RICCA G, 2004. The contribution of alkali soluble (humic acid-like) and unhydrolyzed-alkali soluble (core-humic acid-like) fractions extracted from maize plant to the formation of soil humic acid[J]. Chemoshere, 56(1): 13-22.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
ALONSO-SIMON A, KRISTENSEN J B, OBRO J, et al., 2010. High-throughput microarray profiling of cell wall polymers during hydrothermal pre-treatment of wheat straw[J]. Biotechnol Bioeng, 105(3): 509-514.
DOI URL |
| [3] | AKIN D E, 2008. Plant cell wall aromatics: influence on degradation of biomass[J]. Biofuels Bioproducts & Biorefining, 2(4): 288-303. |
| [4] |
CHEN J, GU B H, ROYER R A, et al., 2003. The roles of natural organic matter in chemical and microbial reduction of ferric iron[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 307(1-3): 167-178.
PMID |
| [5] |
CHUN I J, KIM H S, 2014. Influence of starch characteristics on the pasting properties of potato flours prepared from yellow-fleshed potatoes[J]. Food Engineering Progress, 18(4): 398-405.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
CRESPILHO F N, ZUCOLOTTO V, SIQUEIRA J R, et al., 2005. Immobilization of humic acid in nanostructured layer-by-layer films for sensing applications[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 39(14): 5385-5389.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
DARGIE G C, LEWIS S L, LAWSON I T, et al., 2017. Age, extent and carbon storage of the central Congo Basin peatland complex[J]. Nature, 542(7639): 86-90.
DOI |
| [8] |
DICK D P, MANGRICH A S, MENEZES S M C, et al., 2002. Chemical and spectroscopical characterization of humic acids from two south Brazilian coals of different ranks[J]. Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society, 13(2): 177-182.
DOI URL |
| [9] | DONG B, LIU G F, ZHOU J T, et al., 2020. Transformation of silver ions to silver nanoparticles mediated by humic acid under dark conditions at ambient temperature[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 383: 121190.1-121190.9. |
| [10] |
DU Q, LI G X, ZHANG S S, et al., 2020. High-dispersion zero-valent iron particles stabilized by artificial humic acid for lead ion removal[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 383: 121170.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
ERHAYEM M, SOHN M, 2014. Effect of humic acid source on humic acid adsorption onto titanium dioxide nanoparticles[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 470-471: 92-98.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
GERKE J, 2021. Review Article: The effect of humic substances on phosphate and iron acquisition by higher plants: Qualitative and quantitative aspects[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 184(3): 329-338.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
GIRISUTA B, JANSSEN L P B M, HEERES H J, 2006. A kinetic study on the decomposition of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural into levulinic acid[J]. Green Chemistry, 8(8): 701-709.
DOI URL |
| [14] | GOMES DE MELO B A, MOTTA F L, ANDRADE SANTANA M H, 2016. Humic acids:Structural properties and multiple functionalities for novel technological developments[J]. Materials Science & Engineering C-Materials for Biological Applications, 62: 967-974. |
| [15] |
GU Y L, YIN M X, ZHANG H M, et al., 2015. Study on the binding interaction of chromium(VI) with humic acid using UV-vis, fluorescence spectroscopy and molecular modeling[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 136: 1702-1709.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
JINDO K, MARTIM S A, NAVARRO E C, et al., 2012. Root growth promotion by humic acids from composted and non-composted urban organic wastes[J]. Plant and Soil, 353(1-2): 209-220.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
KHALED H, FAWY H A, 2011. Effect of different levels of humic acids on the nutrient content, plant growth, and soil properties under conditions of salinity[J]. Soil and Water Research, 6(1): 21-29.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
KSIEZOPOLSKA A, 2005. Electrolytic conductivity of synthetic organomineral complexes[J]. Scientia Agricola, 62(2): 133-137.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
LI M X, HE X S, TANG J, et al., 2021. Influence of moisture content on chicken manure stabilization during microbial agent-enhanced composting[J]. Chemosphere, 264(Part2): 128549.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
MAGGIONI A, VARANINI Z, NARDI S, et al., 1987. Action of soil humic matter on plant roots: Stimulationof ion uptake and effects on (Mg2++K+) ATPase activity[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 62: 355-363.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
MONDA H, MCKENNA A M, FOUNTAIN R, et al., 2021. Bioactivity of humic acids extracted from shale ore: molecular characterization and structure-activity relationship with tomato plant yield under nutritional stress[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 12: 660224.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
MOUSAVI S R, GALAVI M, AHMADVAND G, 2007. Effect of Zinc and Manganese foliar application on yield, quality and enrichment on potato (Solanum tuberosum L.)[J]. Asian Journal of Plant Sciences, 6(8): 1256-1260.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
OLAETXEA M, DE HITA D, ANDRES GARCIA C, et al., 2018. Hypothetical framework integrating the main mechanisms involved in the promoting action of rhizospheric humic substances on plant root- and shoot-growth[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 123: 521-537.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
PAGE S E, RIELEY J O, BANKSS C J, 2011. Global and regional importance of the tropical peatland carbon pool[J]. Global Change Biology, 17(2): 798-818.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
PENG X X, GAI S, CHENG K, et al., 2022. Roles of humic substances redox activity on environmental remediation[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 435: 129070.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
PICCOLO A, SPACCINI R, DE MARTINO A, et al., 2019. Soil washing with solutions of humic substances from manure compost removes heavy metal contaminants as a function of humic molecular composition[J]. Chemosphere, 225: 150-156.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
PRAMANIK P, SAFIQUE S, JAHAN A, 2019. Humic substrates extracted by recycling factory tea waste improved soil properties and tea productivity:an innovative approach[J]. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 16(7): 3761-3770.
DOI |
| [28] |
RODRIGUEZ F J, SCHLENGER P, GARCIA-VALVERDE M, 2014. A comprehensive structural evaluation of humic substances using several fluorescence techniques before and after ozonation. Part II: Evaluation of structural changes following ozonation[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 476-477: 731-742.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
SACHS S, REICH T, BERNHARD G, 2010. Study of the role of sulfur functionalities in humic acids for uranium(VI) complexation[J]. Radiochimica Acta, 98(8): 467-477.
DOI URL |
| [30] | SARDESSAI S, 1999. Amino acids in the sedimentary humic and fulvic acids[J]. Indian Journal of Marine Sciences, 28(4): 394-399. |
| [31] |
SCHMEIDE K, SACHS S, BERNHARD G, 2012. Np(V) reduction by humic acid: Contribution of reduced sulfur functionalities to the redox behavior of humic acid[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 419: 116-123.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
SPACCINI R, PICCOLO A, 2009. Molecular characteristics of humic acids extracted from compost at increasing maturity stages[J]. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 41(6): 1164-1172.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
TANG W W, ZENG G M, GONG J L, et al., 2014. Impact of humic/fulvic acid on the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions using nanomaterials: A review[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 468-469: 1014-1027.
DOI URL |
| [34] | VISSER S A, 1962. Production of humic substances in decomposing peat and compost samples[J]. Nature, 196: 1211-1212. |
| [35] |
VOTOLIN K S, ZHEREBTSOV S I, SHPAKODRAEV K M, et al., 2022. Composition of humic and fulvic acids from lignite[J]. Coke and Chemistry, 65(5): 191-200.
DOI |
| [36] |
WANG X, PENG B, TAN C Y, et al., 2015. Recent advances in arsenic bioavailability, transport[J]. Environment Science and Pollution Research, 22: 5742-5750.
DOI URL |
| [37] | WEI S X, LI Z C, SUN Y, et al., 2022. A comprehensive review on biomass humification: Recent advances in pathways, challenges, new applications,and perspectives[J]. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 170: 112984. |
| [38] |
WU F C, EVANS R D, DILLON P J, 2003a. Separation and characterization of NOM by high-performance liquid chromatography and on-line three-dimensional excitation emission matrix fluorescence detection[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 37(16): 3687-3693.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
WU F C, TANOUE E, 2001. Isolation and partial characterization of dissolved copper-complexing ligands in streamwaters[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 35(18): 3646-3652.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
WU F C, TANOUE E, LIU C Q, 2003b. Fluorescence and amino acid characteristics of molecular size fractions of DOM in the waters of Lake Biwa[J]. Biogeochemistry, 65(2): 245-257.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
WU J, WANG G Y, VIJVER M G, et al., 2020. Foliar versus root exposure of AgNPs to lettuce: Phytotoxic=ity, antioxidant responses and internal translocation[J]. Environmental Pollution, 261: 114117.
DOI URL |
| [42] | WÜNSCH U J, MURPHY K, 2021. A simple method to isolate fluorescence spectra from small dissolved organic matter datasets[J]. Water Research, 190: 116730.1-116730.9. |
| [43] |
XIAO K K, ABBT-BRAUN G, HORN H, 2020. Changes in the characteristics of dissolved organic matter during sludge treatment: A critical review[J]. Water Research, 187: 116441.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
XU B L, LIAN Z H, LIU F, et al., 2019. Sorption of pentachlorophenol and phenanthrene by humic acid coated hematite nanoparticles[J]. Environmental Pollution, 248: 929-937.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
XU J, DAI Y C, SHI Y F, et al., 2020. Mechanism of Cr(VI) reduction by humin: Role of environmentally persistent free radicals and reactive oxygen species[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 725: 138413.
DOI URL |
| [46] | YANG F, ZHANG S S, CHENG K, 2019. A hydrothermal process to turn waste biomass into artificial fulvic and humic acids for soil remediation[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 686: 1140-1151. |
| [47] |
YANG F, ANTONIETTI M, 2020. The sleeping giant: A polymer View on humic matter in synthesis and applications[J]. Progress in Polymer Science, 100: 101182.
DOI URL |
| [48] | ZARA M, AHMAD Z, AKHTARET J, et al., 2017. Extraction and characterization of humic acid from Pakistani lignite coals[J]. Energy Sources Part a-Recovery Utilization and Environmental Effects, 39(11): 1159-1166. |
| [49] |
ZHANG S S, DU Q, CHENG K, et al., 2020. Efficient phosphorus recycling and heavy metal removal from wastewater sludge by a novel hydrothermal humification-technique[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 394: 124832.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
ZHI Y C, LI X N, LIAN F, et al., 2022. Nanoscale Iron trioxide catalyzes the synthesis of auxins analogs in artificial humic acids to enhance rice growth[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 848: 157536-157536.
DOI URL |
| [51] | 程瑶, 2021. 不同磷用量对马铃薯产量和品质的影响[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学. |
| [52] | CHENG Y, 2021. Effects of different phosphorus applicationrate on yield and quality of potato[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University. |
| [53] | 杜贺贺, 贾建波, 黄光许, 等, 2018. 年老褐煤水解制备腐植酸及特性分析[J]. 煤炭转化, 41(2): 67-72. |
| [54] | DU H H, JIA J B, HUANG G X, et al., 2018. Preparation and characterization analysis of humic acids by hydrolysis of aged lignite[J]. Coal Conversion, 41(2): 67-72. |
| [55] | 傅平青, 吴丰昌, 刘丛强, 等, 2007. 高原湖泊溶解有机质的三维荧光光谱特性初步研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 38(6): 512-520. |
| [56] | FU P Q, WU F C, LIU C Q, et al., 2007. Three-dimensional excitation emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopy of dissolved organic matter from Chinese highland lakes[J]. Oceanologia ET Limnologia Sinica, 38(6): 512-520. |
| [57] | 贾陈忠, 王焰新, 张彩香, 2012. 光催化氧化处理过程中渗滤液溶解性有机物组分的三维荧光光谱变化特征[J]. 分析化学, 40(11): 1740-1746. |
| [58] | JIA C Z, WANG Y X, ZHANG C X, 2012. Variation characteristics of 3D-Excition Emission Matrix fluorescence spectra of dissolved organic matter from landfill leachate during photocatalytic degradation[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 40(11): 1740-1746. |
| [59] | 姜杰, 李黎, 孙国新, 2012. 基于三维荧光光谱特征研究土壤腐殖质氧化还原特性[J]. 环境化学, 31(12): 2002-2007. |
| [60] | JIANG J, LI L, SUN G X, 2012. Investigation of redox activities of soil humic acids using 3D excitation emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopy[J]. Environment Chemistry, 31(12): 2002-2007. |
| [61] | 吉喆, 2016. 稀酸碱预处理过程中植物细胞壁解构研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学. |
| [62] | JI Z, 2016. Deconstruction of plant cell wall during dilute acid and alkali pretreatment[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University. |
| [63] | 梁成华, 罗磊, 杜立宇, 等, 2005. 腐殖酸对耕地棕壤固钾与释钾作用的影响研究[J]. 土壤学报, 42(3): 468-472. |
| [64] | LIANG C H, LUO L, DU L Y, et al., 2005. Effect of humic acids on fixation and release of potassium in cultivated brown soil[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 42(3): 468-472. |
| [65] | 李金朝, 吴勇, 朱友君, 等, 2015. 宁波城市园林发展现状、问题与对策[J]. 浙江万里学报, 28(1):78-83. |
| [66] | LI J Z, WU Y, ZHU Y J, et al., 2015. The current situation, existing problems and countermeas of Ningbo city garden[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Wanli University, 28(1): 78-83. |
| [67] | 钱晓华, 杨平, 周学军, 等, 2018. 安徽省土壤有效硫现状及时空分布[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 24(5): 1357-1364. |
| [68] | QIAN X H, YANG P, ZHOU X J, et al., 2018. Current situation and spatial-temporal distribution of soil available sulfur in Anhui Province[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertitizer, 24(5): 1357-1364. |
| [69] | 宋凡浩, 2018. 土壤富里酸光谱表征及质子键合行为研究[D]. 北京: 中国环境科学研究院. |
| [70] | SONG F H, 2018. Spectral characterization and proton binding behavior of soil fulvic acid[D]. Beijing: Chinese Research Academy of Environmental Sciences. |
| [71] | 孙丽娟, 段德超, 彭程, 等, 2014. 硫对土壤重金属形态转化及植物有效性的影响研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 25(7): 2141-2148. |
| [72] | SUN L J, DUAN D C, PENG C, et al., 2014. Influence of sulfur on the speciation transformation and phyto-availability of heavy metals in soil: A review[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 25(7): 2141-2148. |
| [73] | 王波, 刘德军, 姚军, 等, 2009. 泥炭土中腐殖酸的提纯和表征研究[J]. 辐射防护, 29(3): 172-180. |
| [74] | WANG B, LIU D J, YAO J, et al., 2009. Isolation and characterization of humic acids from peat soil[J]. Radiation Protection, 29(3): 172-180. |
| [75] | 王彦宏, 2010. 硫酸镁对马铃薯生长发育及淀粉合成积累作用效应的研究[D]. 大庆: 黑龙江八一农垦大学. |
| [76] | WANG Y H, 2010. The research of the effect of Magnesium sulfate foliar spraying on potato growth and development and starch accumulation[D]. Daqing: Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University. |
| [77] | 王艺乔, 2022. 咸水灌溉配施有机肥对土壤理化性质及夏玉米产量的影响[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学. |
| [78] | WANG Y Q, 2022. Effects of saline water irrigation combined with organicmanure on soil physicochemical properties and maize yield[D]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University. |
| [79] | 徐栋, 冯科, 吴峰, 等, 2003. 天然水体底质中腐植酸的光谱表征[J]. 分析科学学报, 19(6): 499-502. |
| [80] |
XU D, FENG K, WU F, et al., 2003. Spectroscopy characterization of humic acids from the sediments in natural waters[J]. Journal of Analytical Science, 19(6): 499-502.
DOI URL |
| [81] | 祝鹏, 华祖林, 张润宇, 等, 2010. 太湖溶解有机质光谱和氮磷污染的区域分布差异特征[J]. 环境科学研究, 23(2): 129-136. |
| [82] | ZHU P, HUA Z L, ZHANG R Y, et al., 2010. Characteristics of spatial distribution differences of spectrum of dissolvedorganic matter and nitrogen/phosphorus pollution in Taihu Lake[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 23(2): 129-136. |
| [83] | 邹丽娜, 戴玉霞, 邱伟迪, 等, 2018. 硫素对土壤砷生物有效性与水稻吸收的影响研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 37(7): 1435-1447. |
| [84] | ZOU L N, DAI Y X, QIU W D, et al., 2018. Effect of sulfur on the bioavailability of arsenic in soil and its accumulation in rice plant (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 37(7): 1435-1447. |
| [1] | 王宁, 刘效东, 甘先华, 苏宇乔, 吴国章, 黄芳芳, 张卫强. 亚热带典型林分降水过程中的水质效应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(8): 1365-1375. |
| [2] | 向兴, 满百膺, 张俊忠, 罗洋, 毛小涛, 张超, 孙丙华, 王希. 黄山土壤细菌群落及氮循环功能群的垂向分布格局[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 56-69. |
| [3] | 魏岚, 黄连喜, 李翔, 王泽煌, 陈伟盛, 黄庆, 黄玉芬, 刘忠珍. 生物炭基质可显著地促进香蕉幼苗生长[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 732-739. |
| [4] | 张亚平, 陈慧敏, 吴志宇, 汤佳, 谢章彰, 刘芳华. 低量水铁矿促进稻田梭菌Clostridium sp. BY-1产氢效率[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2341-2349. |
| [5] | 李春环, 王攀, 韩翠, 许艺馨, 黄菊莹. 硫氮沉降下西北荒漠煤矿区周边土壤性质的变化特点[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(1): 170-180. |
| [6] | 阎洁, 余雪巍, 李鉴博, 顾海萍, 郭二辉. 一株菲降解细菌产生生物表面活性剂特性的研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1683-1694. |
| [7] | 路旭平, 李芳兰, 石亚飞, 张娟伟, 杨文伟, 罗成科, 田蕾, 李培富. 不同水稻品种幼苗响应碱胁迫的生理差异及胁迫等级构建[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1757-1768. |
| [8] | 宋玥言, 袁再健, 黄斌, 谢真越, 刘永杰. 生物炭对红壤团聚体吸附Cd的影响研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(12): 2402-2410. |
| [9] | 郝丽虹, 刘桂青, 张世晨, 苗宇萍. 城市加油站场地典型有机污染物空间分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(11): 2175-2184. |
| [10] | 韩秀娜, 董颖, 耿玉清, 李娜, 张超英. 覆盖煤矸石对矿区土壤养分及盐分特征的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(11): 2251-2256. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
