生态环境学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (11): 2180-2188.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.11.009
收稿日期:2022-06-27
出版日期:2022-11-18
发布日期:2022-12-22
通讯作者:
*孙蔚旻(1979年生),男,博士,研究员,研究方向为为类金属砷/锑与MTBE等的微生物转化机制研究。作者简介:郭丽芳(1995年生),硕士研究生,研究方向为尾矿固氮菌的分离筛选及其促生效应研究。E-mail: 572480672@qq.com
基金资助:
GUO Lifang1,2( ), YANG Rui2, SUN Weimin2,*
), YANG Rui2, SUN Weimin2,*
Received:2022-06-27
Online:2022-11-18
Published:2022-12-22
摘要:
尾矿是一种寡营养环境,含有大量重金属元素,然而营养元素的缺乏,尤其是氮素的缺乏严重阻碍了尾矿生物修复策略的发展。固氮菌可为植物提供可利用性氮,促进尾矿生态修复。然而,目前关于栖息在尾矿中固氮菌的分离研究较少。采用无氮培养基和稀释涂布平板分离法,从湖南怀化溆浦县黄家尾矿分离出7株具有固氮功能的菌株,结果表明,PC-3的固氮酶活性最高(7133.71 μmol·h-1·mL-1)。IAA、金属抗性和铁载体定性测定结果表明,G6、L31和PC-3同时具备有IAA特性、铁载体和金属抗性的能力。同时研究了菌株的最适生长pH,结果表明大部分菌株在pH偏中性下生长较好,但G6、L2+2在pH=9的条件下生长趋势最好。16S rRNA测序结果表明,上述7株菌分别为Brevundimonas(G15、G18),Xanthobacter(L31),Sphingobium(L2+2),Pseudomonas(PC-3),Mycobacterium(G6),Rhodococcus(L45)。为了进一步探究尾矿固氮菌的植物促生潜力,进行了盆栽试验。与对照组相比,接种L2+2、L31菌株显著提高了植物根长和茎长,其中L31菌株使植物根长和茎长分别增长了130%、93%;接种菌株也显著提高了植物根和茎的干质量,其中接种L2+2处理植物的根、茎的干质量分别增长了260%、188%;接种G6、L31处理植物根和茎的氮含量显著增加,效果最显著的是G6,增长量分别达到406%、131%。结果表明,L2+2、L31和G6具有较大的植物促生潜力,在获取营养物质和促进尾矿的生态演替方面发挥重要作用,可作为生物肥料的良好候选菌株,以促进尾矿生态环境的修复。
中图分类号:
郭丽芳, 杨瑞, 孙蔚旻. 尾矿固氮菌的分离筛选及其植物促生效应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2180-2188.
GUO Lifang, YANG Rui, SUN Weimin. Nitrogen-Fixing Bacteria Isolation from Mine Tailings and Their Plant Growth Promoting Properties[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(11): 2180-2188.
| 成分 Composition | 培养基 Medium | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 固体培养基 Jensen’s Medium | 液体培养基 Jensen’s Broth | 固体培养基 Luria-Bertani | 液体培养基 Luria-Bertani | |
| 蔗糖 Sucrose | 20 | 20 | - | - |
| 磷酸氢二钾 Dipotassium phosphate | 1 | 1 | - | - |
| 硫酸镁 Magnesium sulfate | 0.5 | 0.5 | - | - |
| 氯化钠 Sodium chloride | 0.5 | 0.5 | 10 | 10 |
| 硫酸亚铁 Ferrous sulfate | 0.1 | 0.1 | - | - |
| 钼酸钠 Sodium molybdate | 0.005 | 0.005 | - | - |
| 碳酸钠 Sodium carbonate | 2.0 | 2.0 | - | - |
| 胰蛋白胨Tryptone | - | - | 10 | 10 |
| 酵母粉 Yeast powder | - | - | 5 | 5 |
| 琼脂 Agar | 15 | - | 15 | - |
表1 培养基成分
Table 1 Media composition g·L-1
| 成分 Composition | 培养基 Medium | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 固体培养基 Jensen’s Medium | 液体培养基 Jensen’s Broth | 固体培养基 Luria-Bertani | 液体培养基 Luria-Bertani | |
| 蔗糖 Sucrose | 20 | 20 | - | - |
| 磷酸氢二钾 Dipotassium phosphate | 1 | 1 | - | - |
| 硫酸镁 Magnesium sulfate | 0.5 | 0.5 | - | - |
| 氯化钠 Sodium chloride | 0.5 | 0.5 | 10 | 10 |
| 硫酸亚铁 Ferrous sulfate | 0.1 | 0.1 | - | - |
| 钼酸钠 Sodium molybdate | 0.005 | 0.005 | - | - |
| 碳酸钠 Sodium carbonate | 2.0 | 2.0 | - | - |
| 胰蛋白胨Tryptone | - | - | 10 | 10 |
| 酵母粉 Yeast powder | - | - | 5 | 5 |
| 琼脂 Agar | 15 | - | 15 | - |
| 菌名 Name of the fungus | 菌株表观形状 Apparent shape of the strain |
|---|---|
| L45 | 黄色不透明,圆形,中间隆起、 边缘较整齐,表面光滑湿润 |
| G6 | 黄色不透明,菌落较小,圆形,边缘整齐 |
| G18 | 淡黄色,菌落形状不规则,透明边缘较整齐 |
| L2+2 | 黄色不透明,边缘较整齐,菌落平坦 |
| L31 | 菌落黄色不透明,圆形,光滑,边缘整齐 |
| G15 | 淡黄色透明,圆形 |
| PC-3 | 黄色不透明,圆形,中间凸起,光滑 |
表2 不同菌株的菌落特征
Table 2 Colony characteristics of the different strains
| 菌名 Name of the fungus | 菌株表观形状 Apparent shape of the strain |
|---|---|
| L45 | 黄色不透明,圆形,中间隆起、 边缘较整齐,表面光滑湿润 |
| G6 | 黄色不透明,菌落较小,圆形,边缘整齐 |
| G18 | 淡黄色,菌落形状不规则,透明边缘较整齐 |
| L2+2 | 黄色不透明,边缘较整齐,菌落平坦 |
| L31 | 菌落黄色不透明,圆形,光滑,边缘整齐 |
| G15 | 淡黄色透明,圆形 |
| PC-3 | 黄色不透明,圆形,中间凸起,光滑 |
| 菌名 Name of the fungus | IAA定性分析 IAA qualitative analysis | 铁载体定性分析 Characterisation of iron-containing carriers | 金属抗性(As) 定性分析 Qualitative analysis of metal resistance (As) |
|---|---|---|---|
| L45 | - | - | + |
| G6 | + | + | + |
| G18 | - | + | - |
| L2+2 | + | - | + |
| L31 | + | - | + |
| G15 | - | + | + |
| PC-3 | + | + | + |
表3 不同菌株的生理生化特性
Table 3 Physiological and biochemical properties of the different strains
| 菌名 Name of the fungus | IAA定性分析 IAA qualitative analysis | 铁载体定性分析 Characterisation of iron-containing carriers | 金属抗性(As) 定性分析 Qualitative analysis of metal resistance (As) |
|---|---|---|---|
| L45 | - | - | + |
| G6 | + | + | + |
| G18 | - | + | - |
| L2+2 | + | - | + |
| L31 | + | - | + |
| G15 | - | + | + |
| PC-3 | + | + | + |
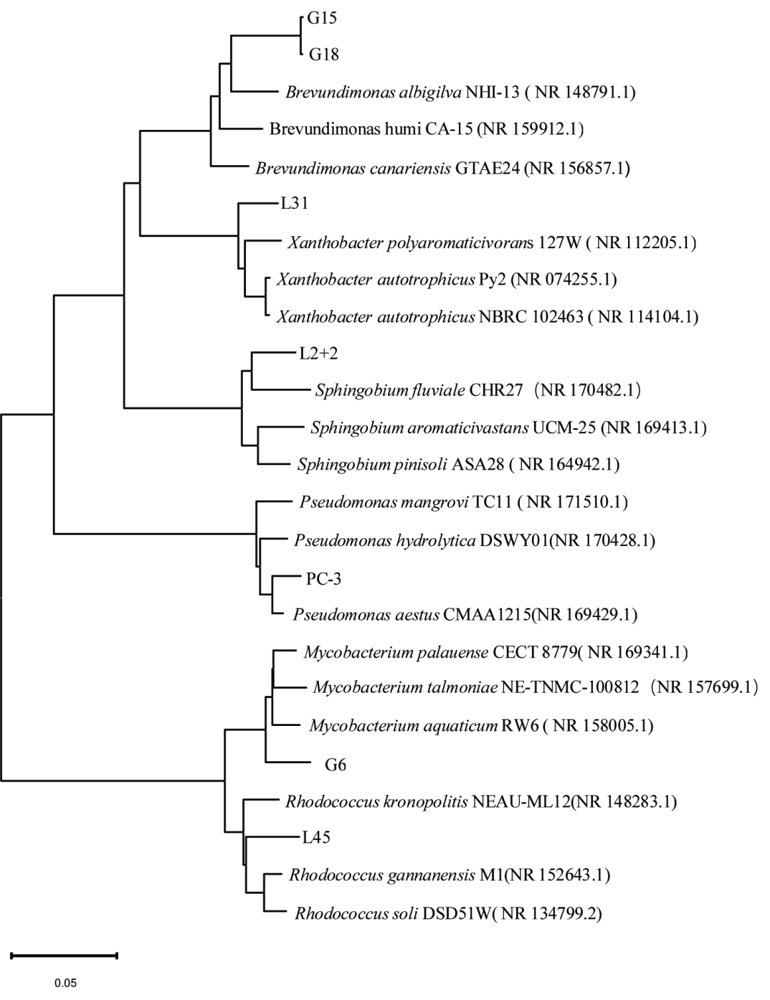
图3 根据16S rRNA序列分析构建的系统发育树 根据16S rRNA序列结果与NCBI数据库的参考基因组,利用MEGA 3.0软件绘制系统发育树,本实验的菌株用粗实线标注
Figure 3 Phylogenetic tree constructed from 16S rDNA sequence analysis Phylogenetic trees were drawn using CLUSTAL and MEGA 3.0 software based on 16S rRNA sequence results with the reference genome from the NCBI database, and strains for this experiment are marked with thick solid lines
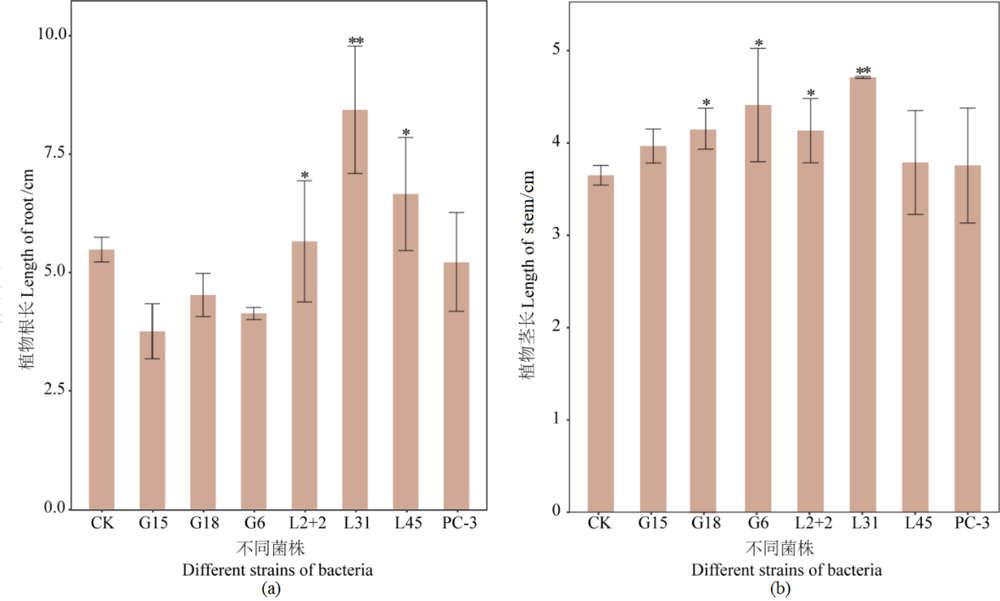
图4 接种不同菌株对植物根长和茎长的影响 *P<0.05;**P<0.01;表示处理组与对照组间对植物的根长和茎长促生效率具有显著差异
Figure 4 Effect of inoculation with different strains on plant root length and stem length *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; indicates a significant difference in root and stem length promotion efficiency of plants between the treatment and control groups
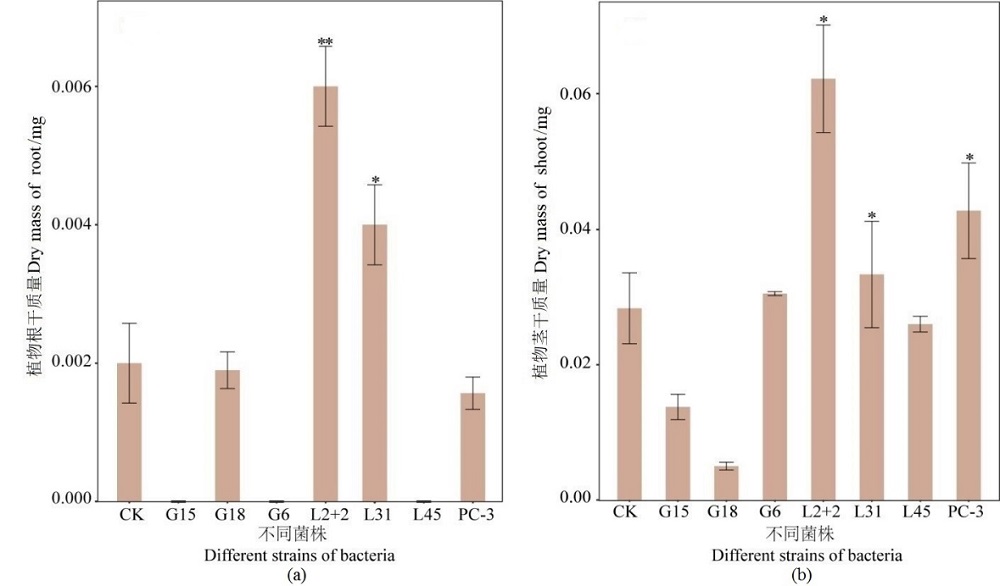
图5 接种不同菌株对植物根和茎干质量的影响 *,P<0.05;表示处理组与对照组间对植物根和茎的干质量促生效率具有显著差异
Figure 5 Effect of inoculation with different strains of bacteria on the dry mass of plant roots and stems *, P<0.05; indicates a significant difference in dry weight promotion efficiency of plant roots and stems between the treatment and control groups
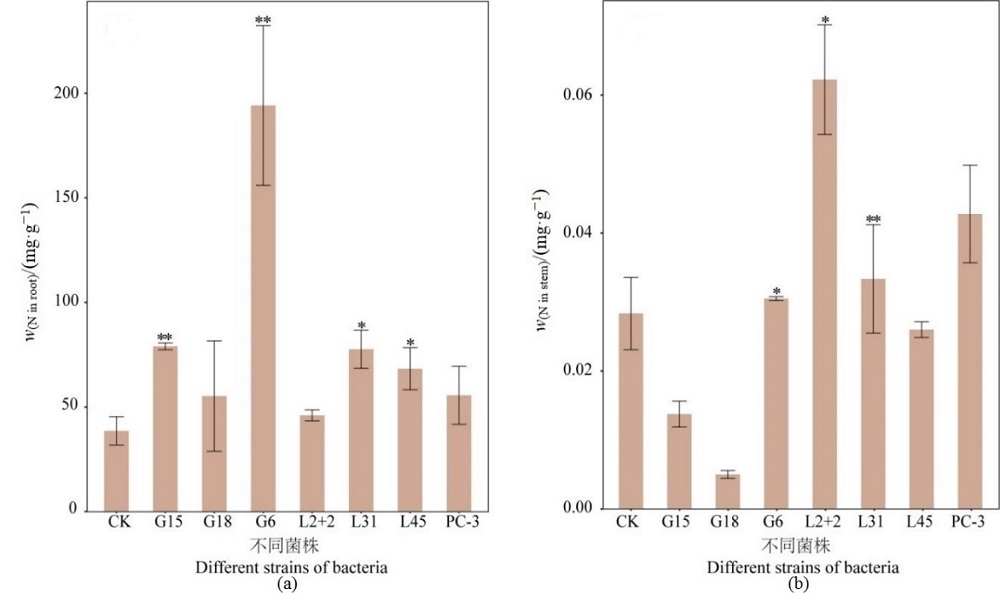
图6 接种不同菌株对植物根和茎氮含量的影响 *,P<0.05;**,P<0.01;表示处理组与对照组间对植物根和茎中氮含量具有显著差异
Figure 6 Effect of inoculation with different strains on the nitrogen concent of plant roots and stems *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; indicates significant differences between treatment and control groups for nitrogen content in plant roots and stems
| [1] |
HILLER E, LALINSKA B, CHOVAN M, et al., 2012. Arsenic and antimony contamination of waters, stream sediments and soils in the vicinity of abandoned antimony mines in the Western Carpathians, Slovakia[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 27(3): 598-614.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
HUANG L N, TANG F Z, SONG Y S, et al., 2011. Biodiversity, abundance, and activity of nitrogen-fixing bacteria during primary succession on a copper mine tailings[J]. Fems Microbiology Ecology, 78(3): 439-450.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
JANA U, CHASSANY V, BERTRAND G, et al., 2012. Analysis of arsenic and antimony distribution within plants growing at an old mine site in Ouche (Cantal, France) and identification of species suitable for site revegetation[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 110: 188-193.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
LI X F, BOND P L, VAN NOSTRAND J D, et al., 2015. From lithotroph- to organotroph-dominant: Directional shift of microbial community in sulphidic tailings during phytostabilization[J]. Scientific Reports, 5: 12978.
DOI PMID |
| [5] | LI X F, YOU F, BOND P L, et al., 2015. Establishing microbial diversity and functions in weathered and neutral Cu-Pb-Zn tailings with native soil addition[J]. Geoderma, 247: 108-116. |
| [6] |
LIN Y C, CHEN J C, C MAN S N, et al., 2012. Modulation of innate immunity and gene expressions in white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei following long-term starvation and re-feeding[J]. Results in immunology, 2: 148-156.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
LIU R F, ZHANG Y, CHEN P, et al., 2017. Genomic and phenotypic analyses of Pseudomonas psychrotolerans PRS08-11306 reveal a turnerbactin biosynthesis gene cluster that contributes to nitrogen fixation[J]. Journal of Biotechnology, 253: 10-13.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
MARASSI F M, 2011. Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rv0899 defines a family of membrane proteins widespread in nitrogen-fixing bacteria[J]. Proteins: Structure, Function, and Bioinformatics, 79(10): 2946-2955.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
MENDEZ M O, NEILSON J W, MAIER R M, 2008. Characterization of a bacterial community in an abandoned semiarid lead-zinc mine tailing site[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 74(12): 3899-3907.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
MOYNAHAN O S, ZABINSKI C A, GANNON J E, 2002. Microbial community structure and carbon-utilization diversity in a mine tailings revegetation study[J]. Restoration Ecology, 10(1): 77-87.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
NAQQASH T, IMRAN A, HAMEED S, et al., 2020. First report of diazotrophic Brevundimonas spp. as growth enhancer and root colonizer of potato[J]. Scientific Reports, 10: 12893.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
NAVARRO-NOYA Y E, HERNANDEZ-MENDOZA E, MORALES-JIMENEZ J, et al., 2012. Isolation and characterization of nitrogen fixing heterotrophic bacteria from the rhizosphere of pioneer plants growing on mine tailings[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 62: 52-60.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
OJUEDERIE O B, BABALOLA O O, 2017. Microbial and plant-assisted bioremediation of heavy metal polluted environments: A review[J]. International journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14(12): 1504.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
PASCUAN C, FOX A R, SOTO G, et al., 2015. Exploring the ancestral mechanisms of regulation of horizontally acquired nitrogenases[J]. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 81(3-4):84-89.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
SULTANA M, VOGLER S, ZARGAR K, et al., 2012. New clusters of arseniate oxidase and unusual bacterial groups in enrichments from arsenic-contaminated soil[J]. Archives of Microbiology, 194: 623-635.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
SUN W M, SUN X X, LI B Q, et al., 2020. Bacterial response to sharp geochemical gradients caused by acid mine drainage intrusion in a terrace: Relevance of C, N, and S cycling and metal resistance[J]. Environment International, 138: 105601.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
SUN W M, XIAO E Z, HAGGBLOM M, et al., 2018. Bacterial survival strategies in an alkaline tailing site and the physiological mechanisms of dominant phylotypes as revealed by metagenomic analyses[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 52(22): 13370-13380.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
SUN X L, LI C A, KUIPER K F, et al., 2016. Human impact on erosion patterns and sediment transport in the Yangtze River[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 143: 88-99.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
SUN X X, KONG T L, HAGGBLOM M M, et al., 2020. Chemolithoautotropic diazotrophy dominates the nitrogen fixation process in mine tailings[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 54(10): 6082-6093.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
SUN X X, SONG B R, XU R, et al., 2021. Root-associated (rhizosphere and endosphere) microbiomes of the Miscanthus sinensis and their response to the heavy metal contamination[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 104(6): 387-398.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
TITUS J H, BISHOP J G, 2014. Propagule limitation and competition with nitrogen fixers limit conifer colonization during primary succession[J]. Journal of Vegetation Science, 25(4): 990-1003.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
WANG J, LIU G N, WU H, et al., 2018. Temporal-spatial variation and partitioning of dissolved and particulate heavy metal(loid)s in a river affected by mining activities in Southern China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(10): 9828-9839.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
XIAO E Z, CUI J L, SUN W M, et al., 2021. Root microbiome assembly of As-hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata and its efficacy in arsenic requisition[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 23(4): 1959-1971.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
ZHAN J, SUN Q Y, 2012. Diversity of free-living nitrogen-fixing microorganisms in the rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere of pioneer plants growing on wastelands of copper mine tailings[J]. MIcrobiological Research, 167(3): 157-165.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | 程蓉, 廖祥文, 舒荣波, 等, 2018. 一种降低高硫煤矸石可燃性的方法[J]. 矿产综合利用 (4): 104-108. |
| CHENG R, LIAO X W, SHU R B, et al., 2018. Technology for reducing the flammability of high-sulfur coal gangue[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources (4): 104-108. | |
| [26] | 董子阳, 胡佳杰, 胡宝兰, 2019. 微生物铁载体转运调控机制及其在环境污染修复中的应用[J]. 生物工程学报, 35(11): 2189-2200. |
| DONG Z Y, HU J J, HU B L, 2019. Regulation of microbial siderophore transport and its application in environmental remediation[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 35(11): 2189-2200. | |
| [27] | 康贻军, 程洁, 梅丽娟, 等, 2010. 植物根际促生菌作用机制研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 21(1): 232-238. |
| KANG Y J, CHENG J, MEI L J, et al., 2021. Action mechanisms of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR): A review[J]. The Journal of Applied Ecology, 21(1): 232-238. | |
| [28] | 李自刚, 彭爱娟, 屈凌波, 2009. 微生物修复茵剂对复垦金尾矿土壤微生物群落的影响[J]. 湖南农业科学 (5): 46-49. |
| LI Z G, PENG A J, QU L B, 2009. Effects of microbial remendiation inocula on microbial community in gold-tailings soil with secondary tillage[J]. Hunan Agricultural Sciences (5): 46-49. | |
| [29] | 龙婉婉, 王金凤, 廖永辉, 等, 2020. 一株硫酸铵耐性菌株的分离鉴定及其特征研究[J]. 井冈山大学学报 (自然科学版), 41(6): 33-39. |
| LONG W W, WANG J F, LIAO Y H, et al., 2020. Isolation, identification, and characteristization of an ammonium sulfate bacterial strain[J]. Journal of Jinggangshan University (Natural Sciences Edition), 41(6): 33-39. | |
| [30] | 栾敏, 胡江, 杨兴明, 等, 2009. 土壤叶杆菌和红球菌菌株的分离鉴定及其自生固氮作用[J]. 土壤学报, 46(3): 541-546. |
| LUAN M, HU J, YANG X M, et al., 2009. Isolation and identification of phyllobacterium and rhodococcus strains from soils and their free living nitrogen-fixation[J]. Journal of Soil Science, 46(3): 541-546. | |
| [31] | 谭志远, 傅琴梅, 彭桂香, 等, 2012. 青香茅和五节芒内生固氮菌多样性及促生作用[C]// 中国土壤学会第十二届全国会员代表大会暨第九届海峡两岸土壤肥料学术交流研讨会论文集. 成都: 840-851. |
| TAN Z Y, FU Q M, PENG G X, et al., 2012. Diversity and plant growth promotion of endophytic diazotrophs isolated from Cymbopogon caesius and Miscanthus[C]// Proceedings of the 12th National Congress of the Soil Society of China and the 9th Cross-Strait Soil and Fertilizer Symposium. Chengdu: 840-851. | |
| [32] | 赵兴青, 李成祥, 王汝成, 等, 2009. 安徽铜陵尾矿堆中三价砷抗性菌株的分离、鉴定及16S rDNA分析[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 28(6): 513-519. |
| ZHAO X Q, LI C X, WANG R C, et al., 2009. Isolation, identification and 16S rDNA sequences analysis of arsenic-resisting bacteria from mine tailing dumps of Tongling in Anhui Province[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogiaca, 28(6): 513-519. | |
| [33] | 周德明, 李蓉, 2012. 杉木根际固氮菌筛选及其溶磷性与分泌IAA特性研究[J]. 四川师范大学学报 (自然科学版), 35(4): 562-566. |
| ZHOU D M, LI R, 2012. Screening of nitrogen-fixing bacteria in rhizosphere of Cunninghaimia lanceolata and investigation on their properties of phosphate-solubilizing and IAA-producing[J]. Journal of Sichuan Normal University (Natural Science), 35(4): 562-566. | |
| [34] | 朱建平, 乐红志, 朱俊阁, 等, 2021. 黄金尾矿材料及环境属性研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 40(10): 3457-3463. |
| ZHU J P, LE H Z, ZHU J G, et al., 2021. Research on material and environmental properties of gold tailings[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 40(10): 3457-3463. |
| [1] | 冯树娜, 吕家珑, 何海龙. KI淋洗对黄绵土汞污染的去除效果及土壤理化性状的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 776-783. |
| [2] | 杨瑞, 孙蔚旻, 李永斌, 郭丽芳, 焦念元. 尾矿先锋植物根际溶磷菌的分离鉴定与其促生研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 166-174. |
| [3] | 马闯, 王雨阳, 周通, 吴龙华. 污染土壤颗粒态有机质镉锌富集特征及其解吸行为研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1892-1900. |
| [4] | 古琛, 贾志清, 杜波波, 何凌仙子, 李清雪. 中国退化草地生态修复措施综述与展望[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1465-1475. |
| [5] | 刘祥宏, 尹勤瑞, 辛建宝, 刘伟, 许秀泉, 黄占斌, 安如意. 生态植被自然修复及其人工促进技术研究进展与展望[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1476-1488. |
| [6] | 邢树文, 许佳敏, 黄彬, 高锦婷, 韩丽. 钨尾矿重金属污染对茶园土壤动物群落结构及多样性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(9): 1903-1915. |
| [7] | 王卫红, 高双全, 杜衍红, 李志丰, 窦飞, 曾晓舵. 镉污染菜地叶面阻隔剂对不同品种辣椒镉积累影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1751-1756. |
| [8] | 牛学奎, 吴学勇, 王薇, 艾志敏, 王舒婷, 侯娟, 周涛. 典型鼓风炉铅冶炼废渣堆场周边优势植物重金属富集特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1293-1298. |
| [9] | 李锋民, 陈琳, 姜晓华, 李晨光, 赵莎莎, 种云霄, 胡洪营, 高帅强. 水质净化与生态修复的水生植物优选指标体系构建[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(12): 2411-2422. |
| [10] | 赵其国, 沈仁芳, 滕应, 李秀华. 中国重金属污染区耕地轮作休耕制度试点进展、问题及对策建议[J]. 生态环境学报, 2017, 26(12): 2003-2007. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
