生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (10): 1990-1998.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.10.006
王丽霞( ), 史园莉*, 张宏伟, 毕晓玲, 申文明, 马万栋
), 史园莉*, 张宏伟, 毕晓玲, 申文明, 马万栋
收稿日期:2021-04-26
出版日期:2021-10-18
发布日期:2021-12-21
通讯作者:
*作者简介:王丽霞(1976年生),女,高级工程师,硕士,主要从事生态环境监测评估与修复方面的工作。E-mail: wanglixia20034@163.com
基金资助:
WANG Lixia( ), SHI Yuanli*, ZHANG Hongwei, BI Xiaoling, SHEN Wenming, MA Wandong
), SHI Yuanli*, ZHANG Hongwei, BI Xiaoling, SHEN Wenming, MA Wandong
Received:2021-04-26
Online:2021-10-18
Published:2021-12-21
摘要:
中国北方农牧交错区是种植业和草地畜牧业交错的生态过渡区,也是生态脆弱和生态敏感带,在中国生态环境保护中具有重要战略地位。为探讨2000—2020年中国北方农牧交错区植被生态功能变化趋势及其驱动因子,以北方农牧交错区的植被生态功能为研究对象,利用卫星遥感和气象观测数据,选择植被净初级生产力(NPP)、水源涵养能力和水土保持等指标来量化植被生态功能,采用空间叠加分析、趋势分析和相关分析等方法探索了植被生态功能长期变化趋势,分析气候和人为活动对植被生态功能变化的驱动作用。结果显示,2000—2020年北方农牧交错区95%以上区域的植被生态功能呈现变好趋势。其中,NPP、水土保持和水源涵养能力的提升幅度分别为57.1%、57.3%和86.7%。植被NPP由2000年的502.6 g∙m-2∙a-1(以C计,下同)增加到2020年的789.6 g∙m-2∙a-1;水土保持量由2000年的473.5 t∙hm-2∙a-1增加到2020年的744.9 t∙hm-2∙a-1;水源涵养能力指数由2000年的42.7增加到2020年的79.7。NPP、水土保持功能和水源涵养能力指数明显提高预示该区域生态系统向良性发展。其中,年降水量增加是驱动植被生态功能变化的关键气候因素。人类的生态保护措施使林地和草地等生态用地面积大幅度上升是促进生态功能提高的主要人为因素。
中图分类号:
王丽霞, 史园莉, 张宏伟, 毕晓玲, 申文明, 马万栋. 2000—2020年北方农牧交错区植被生态功能变化及驱动因子分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(10): 1990-1998.
WANG Lixia, SHI Yuanli, ZHANG Hongwei, BI Xiaoling, SHEN Wenming, MA Wandong. Analysis of Vegetation Ecological Function Changes and Driving Factors in Farming-pastoral Ecotone in Northern China from 2000 to 2020[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(10): 1990-1998.
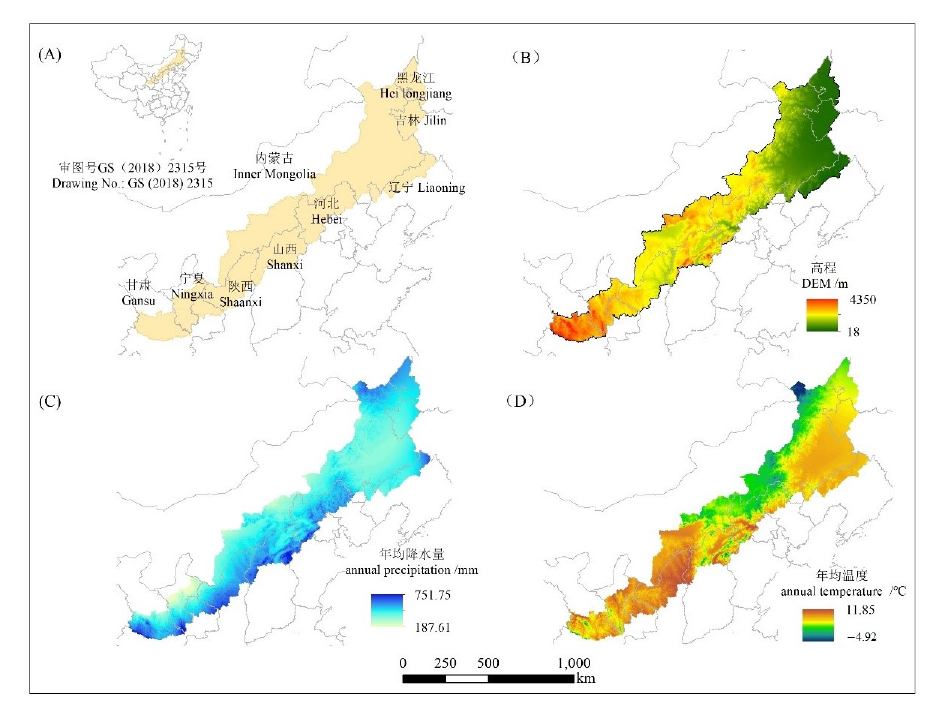
图1 研究区地理位置(A)、地形特征(B)、年降水(C)和年均气温(D)分布图
Fig. 1 Location (A), geomorphological features (B), annual precipitation (C) and annual average temperature (D) of study area
| 区域 Zone | 范围 Region | 反演公式 Inversion formula |
|---|---|---|
| 东北草地区 Northeast grass | 黑龙江、辽宁、吉林和内蒙古东部 Heilongjiang, Liaoning, Jilin and Eastern Inner Mongolia | Y=385.362×e3.813×NDVI |
| 西北草地区 Northwest grass | 内蒙古大部、甘肃、宁夏 Most of Inner Mongolia, Gansu and Ningxia | Y=6381.86×NDVI-521.52 |
| 黄土草地区 Loess grass area | 河北、山西、陕西 Hebei, Shanxi and Shaanxi | Y=18377×NDVI2.0233 |
表1 三大草地区的鲜草质量计算公式1)
Table 1 Formula of fresh grass mass in three grass areas
| 区域 Zone | 范围 Region | 反演公式 Inversion formula |
|---|---|---|
| 东北草地区 Northeast grass | 黑龙江、辽宁、吉林和内蒙古东部 Heilongjiang, Liaoning, Jilin and Eastern Inner Mongolia | Y=385.362×e3.813×NDVI |
| 西北草地区 Northwest grass | 内蒙古大部、甘肃、宁夏 Most of Inner Mongolia, Gansu and Ningxia | Y=6381.86×NDVI-521.52 |
| 黄土草地区 Loess grass area | 河北、山西、陕西 Hebei, Shanxi and Shaanxi | Y=18377×NDVI2.0233 |

图2 2000—2020年研究区平均的NPP(A)、水土保持(C)和水源涵养能力指数(E)及变化(B,D,F)分布图
Fig. 2 Distribution of the average NPP (A), soil and water conservation (C) and water conservation capacity index (E) and their changes (B, D, F) from 2000 to 2020 in the study area
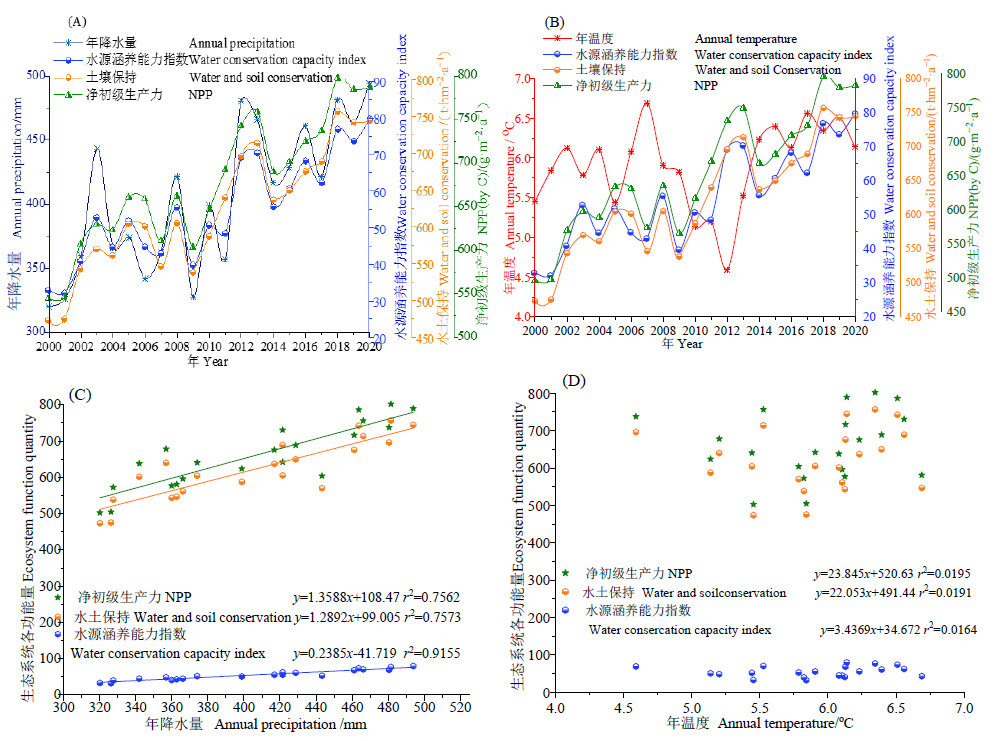
图3 2000-2020年研究区NPP、水土保持和水源涵养能力指数与年均降水(A)和年均气温(B)变化趋势图和相关关系图(C,D)
Fig. 3 Trend (A, B) of NPP, soil and water conservation, water conservation capacity index, average annual precipitation and average annual temperature, and their correlations (C, D) in the study area from 2000 to 2020
| 年份 Year | 林地 Forest | 草地 Grass land | 湿地 Wet land | 未利用地 Unused land | 耕地 Farmland | 建设用地 Construction land |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 82373.9 | 253701.0 | 12488.3 | 48372.7 | 208567.0 | 15035.0 |
| 2010 | 85497.4 | 250335.0 | 12228.1 | 49434.1 | 206810.0 | 16231.2 |
| 2018 | 85627.9 | 246440.9 | 11394.2 | 49200.3 | 207516.5 | 20378.0 |
表2 2000—2018年研究区土地利用面积
Table 2 Land use area from 2000 to 2018 in the study area km2
| 年份 Year | 林地 Forest | 草地 Grass land | 湿地 Wet land | 未利用地 Unused land | 耕地 Farmland | 建设用地 Construction land |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 82373.9 | 253701.0 | 12488.3 | 48372.7 | 208567.0 | 15035.0 |
| 2010 | 85497.4 | 250335.0 | 12228.1 | 49434.1 | 206810.0 | 16231.2 |
| 2018 | 85627.9 | 246440.9 | 11394.2 | 49200.3 | 207516.5 | 20378.0 |
| 2018 | 2000 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 耕地 Farm land | 林地 Forest | 草地 Grass | 湿地 Wet land | 建设用地 Construction land | 未利用地 Unused land | ||
| 耕地 Farm land | 191838.41 | 3863.75 | 7516.88 | 752.81 | 3603.81 | 1003.75 | |
| 林地 Forest | 2011.00 | 77444.7 | 2125.50 | 109.81 | 492.69 | 180.75 | |
| 草地 Grass | 9724.44 | 3710.63 | 232873.66 | 383.13 | 2199.25 | 4831.63 | |
| 水域 Water body | 886.75 | 122.50 | 404.56 | 9551.69 | 112.00 | 1422.38 | |
| 建设用地 Construction land | 945.94 | 132.13 | 302.56 | 38.94 | 13543.38 | 79.56 | |
| 未利用地 Unused land | 2115.69 | 345.69 | 3214.94 | 578.50 | 448.88 | 41672.38 | |
表3 2000—2018年研究区土地利用转移矩阵
Table 3 Land use transfer matrix from 2000 to 2018 in the study area km2
| 2018 | 2000 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 耕地 Farm land | 林地 Forest | 草地 Grass | 湿地 Wet land | 建设用地 Construction land | 未利用地 Unused land | ||
| 耕地 Farm land | 191838.41 | 3863.75 | 7516.88 | 752.81 | 3603.81 | 1003.75 | |
| 林地 Forest | 2011.00 | 77444.7 | 2125.50 | 109.81 | 492.69 | 180.75 | |
| 草地 Grass | 9724.44 | 3710.63 | 232873.66 | 383.13 | 2199.25 | 4831.63 | |
| 水域 Water body | 886.75 | 122.50 | 404.56 | 9551.69 | 112.00 | 1422.38 | |
| 建设用地 Construction land | 945.94 | 132.13 | 302.56 | 38.94 | 13543.38 | 79.56 | |
| 未利用地 Unused land | 2115.69 | 345.69 | 3214.94 | 578.50 | 448.88 | 41672.38 | |
| [1] |
CHEN X, JIANG L, ZHANG G L, et al., 2021. Green-depressing cropping system: A referential land use practice for fallow to ensure a harmonious human-land relationship in the farming-pastoral ecotone of Northern China[J]. Land Use Policy, DOI: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2020.104917.
DOI |
| [2] |
CHEN W, LI A J, HU Y G, et al., 2021. Exploring the long-term vegetation dynamics of different ecological zones in the farming-pastoral ecotone in northern China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(22):27914-27932.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
HUANG L, XIAO T, ZHAO Z P, et al., 2013. Effects of grassland restoration programs on ecosystems in arid and semiarid China[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 117:268-275.
DOI URL |
| [4] | JI Y H, ZHOU G S, LUO T X, et al., 2020. Variation of net primary productivity and its drivers in China’s forests during 2000-2018[J]. Forest Ecosystems, 7(2):190-200. |
| [5] |
JIAO Y, XU Z, ZHAO J H, 2009. Effects of grassland conversion to cropland and forest on soil organic carbon and dissolved organic carbon in the farming-pastoral ecotone of Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 29(3):150-154.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
LI S J, SUN Z G, TAN M H, et al., 2018. Changing patterns in farming-pastoral ecotones in China between 1990 and 2010[J]. Ecological Indicators, 89:110-117.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
LIU J H, GAO J X, LV SH H, et al., 2011. Shifting farming-pastoral ecotone in China under climate and land use changes[J]. Journal of Arid Environments, 75(3):298-308.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
LIU M Z, JIA Y G, ZHAO J J, et al., 2021. Revegetation projects significantly improved ecosystem service values in the agro-pastoral ecotone of northern China in recent 20 years[J]. Science of the Total Environment, DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147756.
DOI |
| [9] |
LIU Z L, LIU Y S, LI Y R, 2018. Anthropogenic contributions dominate trends of vegetation cover changeover the farming-pastoral ecotone of Northern China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 95(1):370-378.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
LU W, JIA G S, 2013. Fluctuation of farming-pastoral ecotone in association with changing east Asia monsoon climate[J]. Climatic Change, 119(3-4):747-760.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
PEI H W, LIU M Z, JIA Y G, et al., 2021. The trend of vegetation greening and its drivers in the agro-pastoral ecotone of northern China, 2000-2020[J]. Ecological Indicators, 129:108004.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
SU W, YU D Y, SUN Z P, et al., 2016. Vegetation changes in the agricultural-pastoral areas of Northern China from 2001 to 2013[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 15(5):1145-1156.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
WANG F, PAN X B, CYNTHIA G S, et al., 2019. Vegetation testoration in Northern China: A contrasted picture[J]. Land Degration & Development, DOI: 10.1002/ldr.3314.
DOI |
| [14] |
WANG X Y, LI Y Q, CHEN Y P, et al., 2018. Temporal and spatial variation of extreme temperatures in an agropastoral ecotone of northern China from 1960 to 2016[J]. Scientific Reports, DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-27066-0.
DOI |
| [15] |
XU H J, WANG X P, ZHAO CH Y, et al., 2018. Diverse responses of vegetation growth to meteorological drought across climate zones and land biomes in Northern China from 1981 to 2014[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 262:1-13.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
YUAN W P, PIAO S L, QIN D H, et al., 2018. Influence of vegetation growth on the enhanced seasonality of atmospheric CO2[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 32(1):32-41.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
ZHU Y H, ZHANG S, LUO P P, et al., 2021. Assessing ecohydrological factors variations and their relationships at different spatio-temporal scales in semiarid area, northwestern China[J]. Advances in Space Research, 67(8):2368-2381.
DOI URL |
| [18] | 高吉喜, 吴丹, 张琨 等, 2019. 基于供体受体关系的大尺度水源涵养生态保护红线划定技术方法及应用[J]. 环境生态学, 1(4):1-14. |
| GAO J X, WU D, ZHANG K et al., 2019. Technical methods and applications of large scale ecological conservation redline delimitation of water conservation based on donor-receptor theory[J]. Environmental Ecology, 1(4):1-14. | |
| [19] | 何立环, 董贵华, 王伟民 等, 2014. 中国北方农牧交错带2000—2010年生态环境状况分析[J]. 中国环境监测, 30(5):63-68. |
| HE L H, DONG G H, WANG W M, et al., 2014. Ecosystem status and change assessment of agro-pastoral ecotone of North China in 2000-2010[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 30(5):63-68. | |
| [20] | 环境保护部, 2015. 生态环境状况评价技术规范: HJ 192—2015[S]. |
| Ministry of the Environmental Protection, 2015. Technical criterion for ecosystem status evaluation: HJ 192—2015[S]. | |
| [21] | 环境保护部办公厅, 国家发展和改革委员会办公厅, 2017. 生态保护红线划定指南: 环办生态[2017]48号[政府文件]. |
| Executive office of the Ministry of the Environmental Protection, Executive Office of the National Development and Reform Commission, 2017. Guidelines for delimitation of ecological protection red line: Environmental Protection Office [2017] 48 [Government documents]. | |
| [22] |
李萌, 王传胜, 张雪飞, 2019. 国土空间规划中水源涵养功能生态保护红线备选区的识别[J]. 地理研究, 38(10):2447-2457.
DOI |
| LI M, WANG C S, ZHANG F X, 2019. Identification of the candidate areas of ecological protection red lines based on water conservation function in territory spatial planning[J]. Geographical Research, 38(10):2447-2457. | |
| [23] | 廖国藩, 贾幼陵, 1996. 中国草地资源[M]. 北京: 中国科学技术出版社: 353-358. |
| LIAO G F, JIA Y L, 1996. Rangeland resources of China [M]. Beijing: China Science and Technology Press: 353-358. | |
| [24] | 刘婵, 刘冰, 赵文智, 等, 2020. 中亚地区植被净初级生产力时空动态及其与气候因子关系[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 35(4):924-933. |
| LIU C, LIU B, ZHAO W Z, et al., 2020. Temporal-spatial variation analysis of net primary productivity and its relationship with climate in central Asia[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 35(4):924-933. | |
| [25] | 孟庆涛, 张文海, 常学礼, 2003. 我国北方农牧交错区形成的原因[J]. 内蒙古环境保护, 15(1):16-19. |
| MENG Q T, ZHANG W H, CHANG X L, 2003. The forming reasons of the farming- pastoral zone in the northern part of China[J]. Inner Mongolia Environmental Protection, 15(1):16-19. | |
| [26] |
史文娇, 刘奕婷, 石晓丽, 2017. 气候变化对北方农牧交错带界线变迁影响的定量探测方法研究[J]. 地理学报, 72(3):407-419.
DOI |
| SHI W J, LIU Y T, SHI X L, 2017. Quantitative methods for detecting the impacts of climate change on the fluctuation of farming-pastoral ecotone boundaries in Northern China[J]. Acta Georgaphica Sinica, 72(3):407-419. | |
| [27] | 王一帆, 徐涵秋, 2020. 利用MODIS EVI时间序列数据分析福建省植被变化 (2000—2017年)[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 35(1):245-254. |
| WANG Y F, XU H Q, 2020. Analysis of vegetation changes in Fujian province using MODIS EVI time series data (2000-2017)[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 35(1):245-254. | |
| [28] | 魏学, 2018. 内蒙古农牧交错区草地植被指数及其对气候的响应[J]. 草业科学, 35(10):2389-2394. |
| WEI X, 2018. Response of natural grassland NDVI to climate factors in a farming-pastoral area of Inner Mongolia[J]. Prata cultural Science, 35(10):2389-2394. | |
| [29] | 徐斌, 杨秀春, 陶伟国, 等, 2007. 中国草原产草量遥感监测[J]. 生态学报, 27(2):405-413. |
| XU B, YANG X CH, TAO W G, et al., 2007. Remote sensing monitoring upon the grass production in China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 27(2):405-413. | |
| [30] | 袁宏霞, 乌兰图雅, 郝强, 2014. 北方农牧交错带界定的研究进展[J]. 内蒙古林业科技, 40(2):38-43. |
| YUAN H X, WU L T Y, HAO Q, 2014. Research progress of definition of farming-pastoral zone in Northern China[J]. Journal of Inner Mongolia Forestry Science & Technology, 40(2):38-43. | |
| [31] | 郑圆圆, 郭思彤, 苏筠, 2014. 我国北方农牧交错带的气候界线及其变迁[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 35(3):6-13. |
| ZHENG Y Y, GUO S T, SU Y, 2014. The climate boundary and its change in farming-pastoral econtone of Northern China[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 35(3):6-13. | |
| [32] | 周立华, 侯彩霞, 2019. 北方农牧交错区草原利用与禁牧政策的关键问题研究[J]. 干旱区地理, 42(2):354-362. |
| ZHOU L H, HOU C X, 2019. Key problems of grassland utilization and the graze ban policy in farming-pastoral ecotone of Northern China[J]. Arid Land Geography, 42(2):354-362. |
| [1] | 王成武, 罗俊杰, 唐鸿湖. 基于InVEST模型的太行山沿线地区生态系统碳储量时空分异驱动力分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 215-225. |
| [2] | 付蓉, 武新梅, 陈斌. 城市地表温度空间分异及驱动因子差异性分析——以合肥市为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 110-122. |
| [3] | 易浪, 孙颖, 尹少华, 魏晓. 生态安全格局构建:概念、框架与展望[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(4): 845-856. |
| [4] | 石智宇, 王雅婷, 赵清, 张连蓬, 朱长明. 2001-2020年中国植被净初级生产力时空变化及其驱动机制分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2111-2123. |
| [5] | 刘佩伶, 刘效东, 冯英杰, 苏宇乔, 甘先华, 张卫强. 新丰江水库库区水源涵养林土壤饱和导水率特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(10): 1993-2001. |
| [6] | 胡瑞, 房焕英, 肖胜生, 段剑, 张杰, 刘洪光, 汤崇军. 南方红壤典型花岗岩侵蚀区主要治理模式的土壤碳汇效应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(8): 1617-1626. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
