生态环境学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 1276-1285.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.06.019
张军1,2( ), 高煜1, 王国兰1, 金梓函1, 杨明航1
), 高煜1, 王国兰1, 金梓函1, 杨明航1
收稿日期:2021-01-26
出版日期:2021-06-18
发布日期:2021-09-10
作者简介:张军(1974年生),男,副教授,博士,硕士研究生导师,主要研究方向为区域重金属污染控制与风险评价。E-mail: zhangjun1190@126.com
基金资助:
ZHANG Jun1,2( ), GAO Yu1, WANG Guolan1, JING Zihan1, YANG Minghang1
), GAO Yu1, WANG Guolan1, JING Zihan1, YANG Minghang1
Received:2021-01-26
Online:2021-06-18
Published:2021-09-10
摘要:
探析典型河谷城市土壤重金属空间污染特征及其影响因素,对城市污染防治具有重要意义。采集宝鸡市区62份表层土壤,使用电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS)测定8种重金属(As、Cd、Cr、Cu、Mn、Ni、Pb、Zn)含量,基于地统计空间插值与地理探测器方法,以地理、环境、气象等11种因子为自变量,各元素含量为因变量,探析典型河谷城市土壤重金属含量的空间分异及其影响因素。结果表明,宝鸡市区土壤8种重金属元素均超过陕西省土壤背景值,其中Cd和Zn质量分数均值达0.77、261.17 mg∙kg-1,为陕西省土壤背景值的8.19倍和3.76倍;Cd、Zn、As、Cu污染较严重,其分布主要集中在潘家湾立交桥、滨河路及马家坡,在空间上呈现一定的聚集性;降水对Cd的空间分布影响最大,而其他重金属主要受海拔高程影响。降水因子对Cd空间分布具有最强解释力(因子解释力PD, H达0.188),除Cd外,DEM(高程)对其余7种重金属含量空间分布均具有最强解释力;此外,交互作用的PD, H值均高于单个因素,表明复杂的环境条件加剧了土壤中重金属的积累。重金属的空间分布差异显著,这与研究区的环境和气象条件密切相关。
中图分类号:
张军, 高煜, 王国兰, 金梓函, 杨明航. 典型河谷城市土壤重金属含量空间分异及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1276-1285.
ZHANG Jun, GAO Yu, WANG Guolan, JING Zihan, YANG Minghang. Spatial Differentiation and Influencing Factors of Heavy Metal Content in Soils of Typical River Valley City[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(6): 1276-1285.
| 交互作用 Interaction | 解释力 Explanation |
|---|---|
| 非线性减弱 Nonlinear reduction | PD, H (x∩y)<Min[PD, H (x) PD, H (y)] |
| 单因子减弱 Single factor reduction | Min[PD, H (x) PD, H (y)]<PD, H (x∩y)<Max[PD, H (x) PD, H (y)] |
| 相互独立 Independent | PD, H (x∩y)=PD, H (x)+PD, H (y) |
| 双因子增强 Double factor enhancement | PD, H (x∩y)>Max[PD, H (x) PD, H (y)] |
| 非线性增强 Non-linear enhancement | PD, H (x∩y)>PD, H (x)+PD, H (y) |
表1 交互作用结果划分
Table 1 Interaction result partitioning
| 交互作用 Interaction | 解释力 Explanation |
|---|---|
| 非线性减弱 Nonlinear reduction | PD, H (x∩y)<Min[PD, H (x) PD, H (y)] |
| 单因子减弱 Single factor reduction | Min[PD, H (x) PD, H (y)]<PD, H (x∩y)<Max[PD, H (x) PD, H (y)] |
| 相互独立 Independent | PD, H (x∩y)=PD, H (x)+PD, H (y) |
| 双因子增强 Double factor enhancement | PD, H (x∩y)>Max[PD, H (x) PD, H (y)] |
| 非线性增强 Non-linear enhancement | PD, H (x∩y)>PD, H (x)+PD, H (y) |
| 元素 Element | Cd | Zn | As | Cu | Ni | Pb | Cr | Mn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 均值 Mean value/(mg∙kg-1) | 0.77 | 261.17 | 17.03 | 40.52 | 30.52 | 16.75 | 49.18 | 331.23 | |
| 最小值 Minimum value/(mg∙kg-1) | 0.14 | 22.9 | 2.9 | 4.7 | 6.73 | 未检出 No detection | 8.4 | 未检出 No detection | |
| 最大值 Maximum value/(mg∙kg-1) | 5.5 | 1882 | 67.93 | 214 | 198 | 49.2 | 249 | 614 | |
| 变异系数 Coefficient of variation | 1.34 | 1.14 | 1.08 | 1.18 | 0.82 | 0.67 | 0.72 | 0.65 | |
| 陕西省土壤背景值 Soil background values in Shaanxi Province/(mg∙kg-1) | 0.094 | 69.4 | 11.2 | 21.4 | 28.8 | 21.4 | 62.5 | 557 | |
| 与陕西省土壤背景值比值 Ratio of soil background value to Shaanxi Province | 8.19 | 3.76 | 1.52 | 1.89 | 1.05 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.59 | |
表2 土壤重金属描述统计
Table 2 Descriptive statistics of soil heavy metal
| 元素 Element | Cd | Zn | As | Cu | Ni | Pb | Cr | Mn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 均值 Mean value/(mg∙kg-1) | 0.77 | 261.17 | 17.03 | 40.52 | 30.52 | 16.75 | 49.18 | 331.23 | |
| 最小值 Minimum value/(mg∙kg-1) | 0.14 | 22.9 | 2.9 | 4.7 | 6.73 | 未检出 No detection | 8.4 | 未检出 No detection | |
| 最大值 Maximum value/(mg∙kg-1) | 5.5 | 1882 | 67.93 | 214 | 198 | 49.2 | 249 | 614 | |
| 变异系数 Coefficient of variation | 1.34 | 1.14 | 1.08 | 1.18 | 0.82 | 0.67 | 0.72 | 0.65 | |
| 陕西省土壤背景值 Soil background values in Shaanxi Province/(mg∙kg-1) | 0.094 | 69.4 | 11.2 | 21.4 | 28.8 | 21.4 | 62.5 | 557 | |
| 与陕西省土壤背景值比值 Ratio of soil background value to Shaanxi Province | 8.19 | 3.76 | 1.52 | 1.89 | 1.05 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.59 | |
| 元素 Element | 因子Factor | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DEM | NDVI | 降水Precipitation | 大气温度Atmospheric temperature | 土地利用Land use type | 土壤类型Soil type | 土壤质地 Soil texture | 距公路距离Distance from road | 距河流距离Distance from river | 距工厂距离Distance from factory | 距铁路距离Distance from railway | ||
| Cd | 0.141 | 0.058 | 0.188 | 0.187 | 0.005 | 0.159 | 0.021 | 0.006 | 0.001 | 0.039 | 0.016 | |
| Zn | 0.203 | 0.007 | 0.009 | 0.01 | 0.077 | 0.029 | 0.003 | 0.005 | 0.006 | 0.017 | 0.002 | |
| As | 0.355 | 0.066 | 0.093 | 0.093 | 0.092 | 0.133 | 0.009 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.042 | 0.024 | |
| Cu | 0.082 | 0.047 | 0.012 | 0.011 | 0.036 | 0.04 | 0.002 | 0.013 | 0.021 | 0.045 | 0.003 | |
| Ni | 0.279 | 0.015 | 0.054 | 0.054 | 0.076 | 0.032 | 0.006 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.007 | |
| Pb | 0.142 | 0.001 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.039 | 0.009 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.003 | |
| Cr | 0.095 | 0.054 | 0.037 | 0.036 | 0.052 | 0.025 | 0.003 | 0.007 | 0.019 | 0.053 | 0.004 | |
| Mn | 0.305 | 0.091 | 0.204 | 0.204 | 0.068 | 0.066 | 0.012 | 0.001 | 0.007 | 0.044 | 0.033 | |
表3 影响因子探测值(PD, H)
Table 3 Detection (PD, H) of geographical environment factor
| 元素 Element | 因子Factor | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DEM | NDVI | 降水Precipitation | 大气温度Atmospheric temperature | 土地利用Land use type | 土壤类型Soil type | 土壤质地 Soil texture | 距公路距离Distance from road | 距河流距离Distance from river | 距工厂距离Distance from factory | 距铁路距离Distance from railway | ||
| Cd | 0.141 | 0.058 | 0.188 | 0.187 | 0.005 | 0.159 | 0.021 | 0.006 | 0.001 | 0.039 | 0.016 | |
| Zn | 0.203 | 0.007 | 0.009 | 0.01 | 0.077 | 0.029 | 0.003 | 0.005 | 0.006 | 0.017 | 0.002 | |
| As | 0.355 | 0.066 | 0.093 | 0.093 | 0.092 | 0.133 | 0.009 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.042 | 0.024 | |
| Cu | 0.082 | 0.047 | 0.012 | 0.011 | 0.036 | 0.04 | 0.002 | 0.013 | 0.021 | 0.045 | 0.003 | |
| Ni | 0.279 | 0.015 | 0.054 | 0.054 | 0.076 | 0.032 | 0.006 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.007 | |
| Pb | 0.142 | 0.001 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.039 | 0.009 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.003 | |
| Cr | 0.095 | 0.054 | 0.037 | 0.036 | 0.052 | 0.025 | 0.003 | 0.007 | 0.019 | 0.053 | 0.004 | |
| Mn | 0.305 | 0.091 | 0.204 | 0.204 | 0.068 | 0.066 | 0.012 | 0.001 | 0.007 | 0.044 | 0.033 | |
| 交互探测 Interaction Detection | Cd | Zn | As | Cu | Ni | Pb | Cr | Mn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第一主因子 First principal factor | 降水 Precipitation | DEM | DEM | DEM | DEM | DEM | DEM | DEM |
| PD, H | 0.188 | 0.203 | 0.355 | 0.082 | 0.279 | 0.142 | 0.095 | 0.305 |
| 交互作用1 Interaction Function 1 | 降水∩土壤类型Precipitation ∩ Soil type | DEM ∩大气温度 DEM ∩ Atmospheric temperature | DEM ∩降水 DEM ∩ Precipitation | DEM ∩降水 DEM ∩ Precipitation | DEM ∩ 土地利用 DEM ∩ Land use type | DEM ∩ 土壤类型 DEM ∩ Soil type | DEM ∩降水 DEM ∩ Precipitation | DEM ∩降水 DEM ∩ Precipitation |
| PD, H | 0.307 | 0.298 | 0.441 | 0.251 | 0.331 | 0.227 | 0.244 | 0.424 |
| 交互作用2 Interaction Function 2 | 降水∩土壤质地Precipitation ∩ Soil texture | DEM ∩降水 DEM ∩ Precipitation | DEM ∩ 大气温度 DEM ∩ Atmospheric temperature | DEM ∩ 大气温度 DEM ∩ Atmospheric temperature | DEM ∩ 大气温度 DEM ∩ Atmospheric temperature | DEM ∩降水 DEM ∩ Precipitation | DEM ∩ 大气温度 DEM ∩ Atmospheric temperature | DEM ∩ 大气温度 DEM ∩ Atmospheric temperature |
| PD, H | 0.251 | 0.298 | 0.439 | 0.251 | 0.324 | 0.213 | 0.243 | 0.422 |
| 交互作用3 Interaction Function 3 | 降水∩ 土地利用Precipitation ∩ Land use type | DEM ∩ NDVI | DEM ∩ 土壤类型 DEM ∩ Soil type | DEM ∩ 土壤类型 DEM ∩ Soil type | DEM ∩降水 DEM ∩ Atmospheric temperature | DEM ∩大气温度 DEM ∩ Atmospheric temperature | DEM ∩ 土壤类型 DEM ∩ Soil type | DEM ∩ 土壤类型 DEM ∩ Soil type |
| PD, H | 0.222 | 0.273 | 0.417 | 0.201 | 0.331 | 0.213 | 0.184 | 0.363 |
表4 因子交互作用
Table 4 Factor interaction
| 交互探测 Interaction Detection | Cd | Zn | As | Cu | Ni | Pb | Cr | Mn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第一主因子 First principal factor | 降水 Precipitation | DEM | DEM | DEM | DEM | DEM | DEM | DEM |
| PD, H | 0.188 | 0.203 | 0.355 | 0.082 | 0.279 | 0.142 | 0.095 | 0.305 |
| 交互作用1 Interaction Function 1 | 降水∩土壤类型Precipitation ∩ Soil type | DEM ∩大气温度 DEM ∩ Atmospheric temperature | DEM ∩降水 DEM ∩ Precipitation | DEM ∩降水 DEM ∩ Precipitation | DEM ∩ 土地利用 DEM ∩ Land use type | DEM ∩ 土壤类型 DEM ∩ Soil type | DEM ∩降水 DEM ∩ Precipitation | DEM ∩降水 DEM ∩ Precipitation |
| PD, H | 0.307 | 0.298 | 0.441 | 0.251 | 0.331 | 0.227 | 0.244 | 0.424 |
| 交互作用2 Interaction Function 2 | 降水∩土壤质地Precipitation ∩ Soil texture | DEM ∩降水 DEM ∩ Precipitation | DEM ∩ 大气温度 DEM ∩ Atmospheric temperature | DEM ∩ 大气温度 DEM ∩ Atmospheric temperature | DEM ∩ 大气温度 DEM ∩ Atmospheric temperature | DEM ∩降水 DEM ∩ Precipitation | DEM ∩ 大气温度 DEM ∩ Atmospheric temperature | DEM ∩ 大气温度 DEM ∩ Atmospheric temperature |
| PD, H | 0.251 | 0.298 | 0.439 | 0.251 | 0.324 | 0.213 | 0.243 | 0.422 |
| 交互作用3 Interaction Function 3 | 降水∩ 土地利用Precipitation ∩ Land use type | DEM ∩ NDVI | DEM ∩ 土壤类型 DEM ∩ Soil type | DEM ∩ 土壤类型 DEM ∩ Soil type | DEM ∩降水 DEM ∩ Atmospheric temperature | DEM ∩大气温度 DEM ∩ Atmospheric temperature | DEM ∩ 土壤类型 DEM ∩ Soil type | DEM ∩ 土壤类型 DEM ∩ Soil type |
| PD, H | 0.222 | 0.273 | 0.417 | 0.201 | 0.331 | 0.213 | 0.184 | 0.363 |
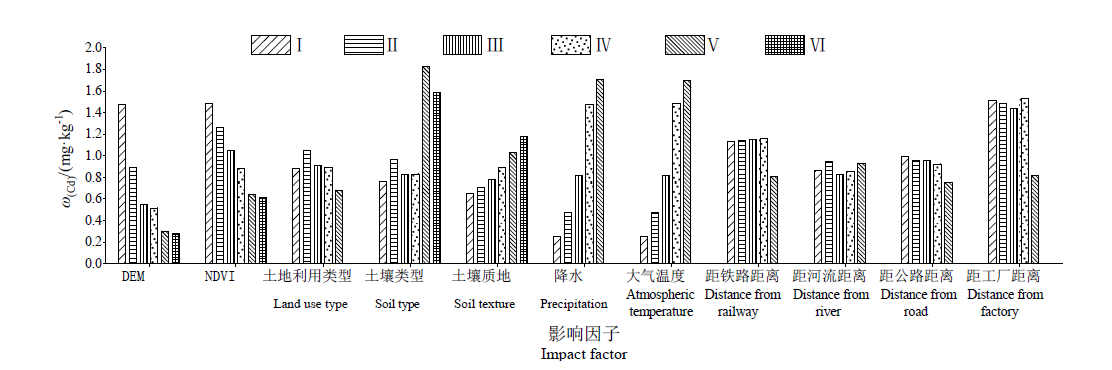
图4 重金属Cd含量风险探测 Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ、Ⅴ、Ⅵ为分类种类。DEM、NDVI、土壤类型、土壤质地为六类,其余影响因子均为五类,下同
Fig. 4 Risk detection of Cd content I, II, III, IV, V, VI are classified. DEM, NDVI, soil type, soil texture are six categories, the other factors are five categories, the same below
| [1] |
BRESSI M, SCIARE J, GHERSI V, et al., 2014. Sources and geographical origins of fine aerosols in Paris (France)[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 14(16): 8813-8839.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
JIANG Y X, CHAO S H, LIU J W, et al., 2016. Source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil for a township in Jiangsu Province, China[J]. Chemosphere, 168: 1658-1668.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
JIANG Y X, CHAO S H, LIU J W, et al., 2017. Source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil for a township in Jiangsu Province, China[J]. Chemosphere, 168: 1658-1668.
DOI URL |
| [4] | LI X P, FENG L N, 2012. Multivariate and geostatistical analyzes of metals in urban soil of Weinan industrial areas, Northwest of China[J]. Atmosp Heric Environment, 47: 58-65. |
| [5] |
NATALIA E K, DMITRY V V, ILYA D K, et al., 2018. Contamination of urban soils with heavy metals in Moscow as affected by building development[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 636(15): 854-863.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
WANG J F, HU Y, 2012. Environmental health risk detection with GeogDetector[J]. Environmental Modelling and Software, 33: 114-115.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
WANG J F, LL X H, CHRISTAKOS G, et al, 2010. Geographical detectors-based health risk assessment and its application in the neural tube defects study of the Heshun region, China[J]. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 24(1): 107-127.
DOI URL |
| [8] | WANG J F, WU Q M, HU W Y, 2018. Using multi-medium factors analysis to assess heavy metal health risks along the Yangtze River in Nanjing, Southeast China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 243(Part B): 1047-1056. |
| [9] |
WANG Y, WANG S J, LL G D, et al., 2017. Identifying the determinants of housing prices in China using spatial regression and the geographical detector technique[J]. Applied Geography, 79: 26-36.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
XUN W, WEI Y, CHE J L, et al., 2019. Climate and vegetation as primary drivers for global mercury storage in surface soil Environ[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 53(18): 10665-10675.
DOI URL |
| [11] | 艾东升, 2011. 上海市大气降水化学组成特征及物源解析[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学. |
| AI D S, 2011. Chemical composition and source analysis of atmospheric precipitation in Shanghai[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University. | |
| [12] | 艾建超, 王宁, 杨净, 2014. 基于UNMIX模型的夹皮沟金矿区土壤重金属源解析[J]. 环境科学, 35(9): 3530-3536. |
| AI J C, WANG N, YANG J, 2014. Source apportionment of soil heavy metals in Jiapigou goldmine based on the UNMIX model[J]. Environmental Science, 35(9): 3530-3536. | |
| [13] | 白秀玲, 马建华, 孙艳丽, 等, 2018. 开封城市土壤磷素组成特征及流失风险[J]. 环境科学, 39(2): 909-915. |
| BAI X L, MA Y H, SUN Y Y, et al., 2018. Characterization of phosphorus in urban surface soils in Kaifeng city and its risk of loss[J]. Environmental Science, 39(2): 909-915. | |
| [14] | 柴立立, 崔邢涛, 2019. 保定城市土壤重金属污染及潜在生态危害评价[J]. 安全与环境学报, 19(2): 607-614. |
| CHAL L L, CUI X T, 2019. Evaluation of soil heavy metal pollution and potential ecological hazards in Baoding city[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 19(2): 607-614. | |
| [15] | 戴彬, 吕建树, 战金成, 等, 2015. 山东省典型工业城市土壤重金属来源、空间分布及潜在生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 36(2): 507-515. |
| DAI B, LU J S, ZHAN J C, et al., 2015. Source, spatial distribution and potential ecological risk assessment of soil heavy metals in typical industrial cities in Shandong province[J]. Environmental Science, 36(2): 507-515. | |
| [16] | 耿雅妮, 梁青芳, 杨宁宁, 等, 2019. 宝鸡市城区灰尘重金属空间分布、来源及健康风险[J]. 地球与环境, 47(5): 696-706. |
| GENG Y N, LING Q F, YANG N N, et al., 2019. Spatial distribution, sources and health risks of dust and heavy metals in urban areas of Baoji city[J]. Earth and Environment, 47(5): 696-706. | |
| [17] | 顾济沧, 赵娟, 2010. 云南省土壤重金属污染现状及治理技术研究[J]. 环境科学导刊, 29(5): 68-71. |
| GU J C, ZHAI J, 2010. Study on soil heavy metal pollution status and treatment technology in Yunnan province[J]. Environmental Science Guide, 29(5): 68-71. | |
| [18] | 谷阳光, 高富代, 2017. 我国省会城市土壤重金属含量分布与健康风险评价[J]. 环境化学, 36(1): 62-71. |
| GU Y G, GAO F D, 2017. Spatial distribution and health risk assessment of heavy metals in provincial capital cities, China[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 36(1): 62-71. | |
| [19] | 吕建树, 张祖陆, 刘洋, 等, 2012. 日照市土壤重金属来源解析及环境风险评价[J]. 地理学报, 67(7): 971-984. |
| LV J S, ZHANG Z L, LIU Y, et al., 2012. Source analysis and environmental risk assessment of soil heavy metals in Rizhao city[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 67(7): 971-984. | |
| [20] | 黄顺生, 吴新民, 颜朝阳, 等, 2007. 南京城市土壤重金属含量及空间分布特征[J]. 城市环境与城市生态, 20(2): 1-4. |
| HUNG S S, WU X M, YAN C Y, et al., 2007. Content and spatial distribution of heavy metals in urban soil in Nanjing[J]. Urban Environment and Urban Ecology, 20(2): 1-4. | |
| [21] | 李锋, 刘思源, 李艳, 等, 2019. 工业发达城市土壤重金属时空变异与源解析[J]. 环境科学, 40(2): 934-944. |
| LI F, LIU S Y, LI Y, et al., 2019. Spatiotemporal variation and source analysis of heavy metals in soil in developed cities[J]. Environmental Science, 40(2): 934-944. | |
| [22] | 李雨, 韩平, 任东, 等, 2017. 基于地理探测器的农田土壤重金属影响因子分析[J]. 中国农业科学, 50(21): 4138-4148. |
| LI Y, HAN P, REN D, et al., 2017. Impact factor analysis of heavy metals in farmland soil based on geographic detector[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 50(21): 4138-4148. | |
| [23] | 林静, 张健, 杨万勤, 等, 2016. 岷江下游五通桥段小型集水区大气降水中pH值对重金属含量的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 36(4): 1419-1427. |
| LIN J, ZHANG J, YANG W Q, et al., 2016. Influence of pH value on heavy metal content in atmospheric precipitation of small catchment area in the lower reaches of Minjiang River[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Science, 36(4): 1419-1427. | |
| [24] | 吕建树, 何华春, 2018. 江苏海岸带土壤重金属来源解析及空间分布[J]. 环境科学, 39(6): 2853-2864. |
| LV J S, HE H C, 2018. Source analysis and spatial distribution of soil heavy metals in coastal zone of Jiangsu province[J]. Environmental Science, 39(6): 2853-2864. | |
| [25] | 罗松英, 王嘉琦, 周敏, 等, 2018. 湛江东海岛红树林湿地表层土壤重金属空间分布特征及生态风险评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 27(8): 1547-1555. |
| LUO S Y, WANG J P, ZHOU M, et al., 2018. Spatial distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the surface soils of mangrove wetland in Donghai Island, Zhanjiang[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 27(8): 1547-1555. | |
| [26] | 邵莉, 肖化云, 吴代赦, 等, 2012. 交通源重金属污染研究进展[J]. 地球与环境, 40(3): 445-459. |
| SHAO L, XIAO H Y, WU D J, et al., 2012. Research progress of heavy metal pollution from traffic sources[J]. Earth and Environment, 40(3): 445-459. | |
| [27] | 王利军, 卢新卫, 雷凯, 等, 2011. 宝鸡市街尘重金属元素含量、来源及形态特征[J]. 环境科学, 32(8): 2470-2476. |
| WANG L J, LU X W, LEI K, et al., 2011. Contents, sources and morphological characteristics of heavy metal elements in street dust of Baoji city[J]. Environmental Science, 32(8): 2470-2476. | |
| [28] | 王洪涛, 张俊华, 丁少峰, 等, 2016. 开封城市河流表层沉积物重金属分布、污染来源及风险评[J]. 环境科学学报, 36(12): 4520-4530. |
| WANG H T, ZHANG J H, DING S F, et al., 2016. Distribution, pollution sources and risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of urban rivers in Kaifeng[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Science, 36(12): 4520-4530. | |
| [29] | 吴涛, 伍钧, 2008. 铜、铅单一及其复合污染对鱼腥草吸收累积铜和铅的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 39(3): 670-674. |
| WU T, WU J, 2008. Effects of single and combined pollution of copper and lead on absorption and accumulation of copper and lead in herba cordata[J]. Soil Bulletin, 39(3): 670-674. | |
| [30] | 徐福银, 胡艳燕, 2014. 重庆市不同功能区城市绿地土壤重金属分布特征与评价[J]. 土壤通报, 45(1): 227-231. |
| XU F Y, HU Y Y, 2014. Distribution characteristics and evaluation of soil heavy metals in urban green space in different functional areas of chongqing[J]. Soil bulletin, 45(1): 227-231. | |
| [31] | 徐蕾, 肖昕, 马玉, 等, 2019. 徐州农田土壤重金属空间分布及来源分析[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 35(11): 1453-1459. |
| XU L, XIAO X, MA Y, et al., 2019. Sources and spatial distributions of heavy metals in Xuzhou farmland soils[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 35(11): 1453-1459. | |
| [32] | 姚桂华, 徐海舟, 朱林刚, 等, 2015. 不同有机物料对东南景天修复重金属污染土壤效率的影响[J]. 环境科学, 36(11): 4268-4276. |
| YAO G H, XU H Z, ZHU L G, et al., 2015. Effects of different kinds of organic materials on soil heavy metal phytoremediation efficiency by sedum alfredii hance[J]. Environmental Science, 36(11): 4268-4276. | |
| [33] | 易文利, 董奇, 杨飞, 等, 2018. 宝鸡市不同功能区土壤重金属污染特征、来源及风险评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 27(11): 2142-2149. |
| YI W L, DONG Q, YANG F, et al., 2018. Pollution characteristics, sources analysis and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in different functional zones of Baoji city[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 27(11): 2142-2149. | |
| [34] | 于元赫, 吕建树, 王亚梦, 2018. 黄河下游典型区域土壤重金属来源解析及空间分布[J]. 环境科学, 39(6): 2866-2874. |
| YU Y H, LU J S, WANG Y M, 2018. Analysis and spatial distribution of soil heavy metals in typical areas of the lower Yellow River[J]. Environmental Science, 39(6): 2866-2874. | |
| [35] | 张军, 董洁, 梁青芳, 等, 2019. 宝鸡市区土壤重金属污染影响因子探测及其源解析[J]. 环境科学, 40(8): 3774-3784. |
| ZHANG J, DONG J, LIANG Q F, et al., 2019. Heavy Metal Pollution Characteristics and Influencing Factors in Baoji Arban Soils[J]. Environmental Science, 40(8): 3774-3784. | |
| [36] | 张善红, 李堆淑, 2017. 基于GIS的土壤重金属污染评价研究进展[J]. 现代农业科技 (22): 151-153. |
| ZHANG S H, LL D S, 2017. Research progress on soil heavy metal pollution evaluation based on GIS[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology (22): 151-153. | |
| [37] | 赵科理, 傅伟军, 叶正钱, 等, 2016. 电子垃圾拆解区土壤重金属空间异质性及分布特征[J]. 环境科学, 37(8): 3151-3159. |
| ZHAO K L, FU W J, YE Z Q, et al., 2016. Spatial Variation of Soil Heavy Metals in an E-waste Dismantling Area and Their Distribution Characteristics[J]. Environmental Science, 37(8): 3151-3159. | |
| [38] | 赵文杰, 李翠梅, 2013. 大气降水中重金属的研究[J]. 环境科学与管理, 38(10): 76-79. |
| ZHAO W J, LI C M, 2013. Study of heavy metal pollutants in precipitation[J]. Environmental Science and Management, 38(10): 76-79. | |
| [39] | 周雪明, 郑乃嘉, 李英红, 等, 2017. 2011—2012北京大气PM2.5中重金属的污染特征与来源分析[J]. 环境科学, 38(10): 4054-4060. |
| ZHOU X M, ZHENG N J, LL Y H, et al., 2017. Analysis of pollution characteristics and sources of heavy metals in PM2.5 from 2011 to 2012 in Beijing[J]. Environmental Science, 38(10): 4054-4060. | |
| [40] | 周永超, 孙慧兰, 陈学刚, 等, 2019. 绿洲城市伊宁市表层土壤重金属污染特征及其生态风险评价[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 33(2): 127-133. |
| ZHOU Y C, SUN H L, CHEN X G, et al., 2019. Characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in surface soil of Yining in Oasis city[J]. Resources and Environment in Arid Areas, 33(2): 127-133. |
| [1] | 杜丹丹, 高瑞忠, 房丽晶, 谢龙梅. 旱区盐湖盆地土壤重金属空间变异及对土壤理化因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1123-1132. |
| [2] | 王琳, 卫伟. 黄土高原典型县域生态系统服务变化特征及驱动因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1140-1148. |
| [3] | 董智今, 张呈春, 展秀丽, 张维福. 宁夏河东沙地生物土壤结皮及其下伏土壤养分的空间分布特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(5): 910-919. |
| [4] | 杨春亮, 刘旻霞, 王千月, 苗乐乐, 肖音迪, 王敏. 单户与联户放牧经营下草玉梅与嵩草种群空间格局及其关联性[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 651-659. |
| [5] | 李建辉, 党争, 陈琳. 黄河几字弯都市圈PM2.5时空特征及影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 697-705. |
| [6] | 冯树娜, 吕家珑, 何海龙. KI淋洗对黄绵土汞污染的去除效果及土壤理化性状的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 776-783. |
| [7] | 陈敏毅, 朱航海, 佘伟铎, 尹光彩, 黄祖照, 杨巧玲. 珠三角某遗留造船厂场地土壤重金属人体健康风险评估及源解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 794-804. |
| [8] | 王成武, 罗俊杰, 唐鸿湖. 基于InVEST模型的太行山沿线地区生态系统碳储量时空分异驱动力分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(2): 215-225. |
| [9] | 付蓉, 武新梅, 陈斌. 城市地表温度空间分异及驱动因子差异性分析——以合肥市为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 110-122. |
| [10] | 肖洁芸, 周伟, 石佩琪. 土壤重金属含量高光谱反演[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 175-182. |
| [11] | 吴胜义, 王飞, 徐干君, 马浩, 党禹杰, 吴菲. 川西北高山峡谷区森林碳储量及空间分布研究--以四川洛须自然保护区为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1735-1744. |
| [12] | 黄宏, 郑欣芸, 李迎东, 赵旭, 俞锦辰, 汪振华. 大陈岛海域不同年龄褐菖鲉对重金属富集作用研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1885-1891. |
| [13] | 马闯, 王雨阳, 周通, 吴龙华. 污染土壤颗粒态有机质镉锌富集特征及其解吸行为研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1892-1900. |
| [14] | 李秀华, 赵玲, 滕应, 骆永明, 黄标, 刘冲, 刘本乐, 赵其国. 贵州汞矿区周边农田土壤汞镉复合污染特征空间分布及风险评估[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1629-1636. |
| [15] | 陶玲, 黄磊, 周怡蕾, 李中兴, 任珺. 污泥-凹凸棒石共热解生物炭对矿区土壤重金属生物有效性和环境风险的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1637-1646. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
