Ecology and Environment ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (7): 1455-1469.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.07.015
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
GAO Feng1( ), CHEN Xiaoling2,*(
), CHEN Xiaoling2,*( ), YANG Wenfu3,4, SHI Lijiang1, WANG Wenwen4
), YANG Wenfu3,4, SHI Lijiang1, WANG Wenwen4
Received:2021-05-12
Online:2021-07-18
Published:2021-10-09
Contact:
CHEN Xiaoling
高峰1( ), 陈晓玲2,*(
), 陈晓玲2,*( ), 杨文府3,4, 史利江1, 汪雯雯4
), 杨文府3,4, 史利江1, 汪雯雯4
通讯作者:
陈晓玲
作者简介:高峰(1987年生),男,讲师,博士,主要从事水环境遥感和气候变化方面的研究。E-mail: gaofeng0204@sxufe.edu.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
GAO Feng, CHEN Xiaoling, YANG Wenfu, SHI Lijiang, WANG Wenwen. Study on the Absorption Characteristics of Different Types of Water Particles and CDOM in Summer in Taiyuan[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(7): 1455-1469.
高峰, 陈晓玲, 杨文府, 史利江, 汪雯雯. 太原市不同类型夏季水体颗粒物与CDOM吸收特性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(7): 1455-1469.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.07.015
| 站点 Sites | 经度 Longitude | 纬度 Latitude | 采样时间 Sampling time | 采样位置 Sampling location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 112.50°E | 37.76°N | Aug. 14, 2020 | 晋阳湖 Lake Jinyang |
| A2 | 112.52°E | 37.76°N | Aug. 15, 2020 | 排洪渠 Flood discharge channel |
| A3 | 112.47°E | 37.71°N | Aug. 15, 2020 | |
| A4 | 112.46°E | 37.69°N | Aug. 15, 2020 | |
| A5 | 112.53°E | 37.84°N | Aug. 15, 2020 | |
| A6 | 112.51°E | 37.90°N | Aug. 15, 2020 | |
| A7 | 112.53°E | 37.85°N | Aug. 17, 2020 | 汾河太原城区段 Taiyuan reach of the Fenhe river |
| A8 | 112.54°E | 37.83°N | Aug. 17, 2020 | |
| A9 | 112.53°E | 37.82°N | Aug. 17, 2020 | |
| A10 | 112.53°E | 37.79°N | Aug. 17, 2020 | |
| A11 | 112.53°E | 37.79°N | Aug. 17, 2020 | |
| A12 | 112.53°E | 37.78°N | Aug. 17, 2020 | |
| A13 | 112.51°E | 37.93°N | Aug. 18, 2020 | |
| A14 | 112.51°E | 37.92°N | Aug. 18, 2020 | |
| A15 | 112.53°E | 37.90°N | Aug. 18, 2020 | |
| A16 | 112.53°E | 37.89°N | Aug. 18, 2020 | |
| A17 | 112.53°E | 37.89°N | Aug. 18, 2020 | |
| A18 | 112.53°E | 37.89°N | Aug. 18, 2020 | |
| A19 | 112.54°E | 37.76°N | Aug. 20, 2020 | |
| A20 | 112.53°E | 37.77°N | Aug. 20, 2020 | |
| A21 | 112.53°E | 37.76°N | Aug. 20, 2020 | |
| A22 | 112.53°E | 37.76°N | Aug. 20, 2020 | |
| A23 | 112.54°E | 37.75°N | Aug. 20, 2020 | |
| A24 | 112.54°E | 37.74°N | Aug. 20, 2020 | |
| A25 | 112.37°E | 37.98°N | Aug. 22, 2020 | 汾河二库 Fenhe second reservoir |
| A26 | 112.36°E | 37.98°N | Aug. 22, 2020 | |
| A27 | 112.36°E | 37.97°N | Aug. 22, 2020 | |
| A28 | 112.54°E | 37.74°N | Aug. 23, 2020 | 汾河太原城区段 Taiyuan reach of the Fenhe river |
| A29 | 112.54°E | 37.71°N | Aug. 23, 2020 | |
| A30 | 112.54°E | 37.76°N | Aug. 23, 2020 |
Table 1 Location and time of sample sites
| 站点 Sites | 经度 Longitude | 纬度 Latitude | 采样时间 Sampling time | 采样位置 Sampling location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 112.50°E | 37.76°N | Aug. 14, 2020 | 晋阳湖 Lake Jinyang |
| A2 | 112.52°E | 37.76°N | Aug. 15, 2020 | 排洪渠 Flood discharge channel |
| A3 | 112.47°E | 37.71°N | Aug. 15, 2020 | |
| A4 | 112.46°E | 37.69°N | Aug. 15, 2020 | |
| A5 | 112.53°E | 37.84°N | Aug. 15, 2020 | |
| A6 | 112.51°E | 37.90°N | Aug. 15, 2020 | |
| A7 | 112.53°E | 37.85°N | Aug. 17, 2020 | 汾河太原城区段 Taiyuan reach of the Fenhe river |
| A8 | 112.54°E | 37.83°N | Aug. 17, 2020 | |
| A9 | 112.53°E | 37.82°N | Aug. 17, 2020 | |
| A10 | 112.53°E | 37.79°N | Aug. 17, 2020 | |
| A11 | 112.53°E | 37.79°N | Aug. 17, 2020 | |
| A12 | 112.53°E | 37.78°N | Aug. 17, 2020 | |
| A13 | 112.51°E | 37.93°N | Aug. 18, 2020 | |
| A14 | 112.51°E | 37.92°N | Aug. 18, 2020 | |
| A15 | 112.53°E | 37.90°N | Aug. 18, 2020 | |
| A16 | 112.53°E | 37.89°N | Aug. 18, 2020 | |
| A17 | 112.53°E | 37.89°N | Aug. 18, 2020 | |
| A18 | 112.53°E | 37.89°N | Aug. 18, 2020 | |
| A19 | 112.54°E | 37.76°N | Aug. 20, 2020 | |
| A20 | 112.53°E | 37.77°N | Aug. 20, 2020 | |
| A21 | 112.53°E | 37.76°N | Aug. 20, 2020 | |
| A22 | 112.53°E | 37.76°N | Aug. 20, 2020 | |
| A23 | 112.54°E | 37.75°N | Aug. 20, 2020 | |
| A24 | 112.54°E | 37.74°N | Aug. 20, 2020 | |
| A25 | 112.37°E | 37.98°N | Aug. 22, 2020 | 汾河二库 Fenhe second reservoir |
| A26 | 112.36°E | 37.98°N | Aug. 22, 2020 | |
| A27 | 112.36°E | 37.97°N | Aug. 22, 2020 | |
| A28 | 112.54°E | 37.74°N | Aug. 23, 2020 | 汾河太原城区段 Taiyuan reach of the Fenhe river |
| A29 | 112.54°E | 37.71°N | Aug. 23, 2020 | |
| A30 | 112.54°E | 37.76°N | Aug. 23, 2020 |
| 站点 Sites | ρ(TSM)/ (mg∙L-1) | ρ(Chla)/ (mg∙m-3) | ρ(ISM)/ (mg∙L-1) | ρ(OSM)/ (mg∙L-1) | ρ(TN)/ (mg∙L-1) | ρ(TP)/ (mg∙L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 13.67 | 22.6 | 5 | 8.67 | 1.44 | 0.02 |
| A2 | 24 | 48.55 | 15 | 9 | 3.18 | 0.12 |
| A3 | 41 | 40.36 | 29.5 | 11.5 | 5.8 | 0.25 |
| A4 | 47.5 | 16.01 | 35.5 | 12 | 5.48 | 0.17 |
| A5 | 15 | 9.58 | 10.33 | 4.67 | 4.31 | 0.15 |
| A6 | 27.5 | 50.86 | 18.5 | 9 | 2.88 | 0.2 |
| A7 | 19 | 51.42 | 5 | 14 | 3.17 | 0.12 |
| A8 | 17.5 | 68.89 | 7.5 | 10 | 4.24 | 0.12 |
| A9 | 11 | 13.25 | 7.67 | 3.33 | 2.07 | 0.05 |
| A10 | 18.5 | 32.46 | 5 | 13.5 | 5.44 | 0.2 |
| A11 | 47.5 | 42.85 | 31.5 | 16 | 2.53 | 0.13 |
| A12 | 18.5 | 62.73 | 12 | 6.5 | 3.62 | 0.22 |
| A13 | 37 | 375.95 | 6 | 31 | 3.27 | 0.37 |
| A14 | 29.5 | 27.01 | 18.5 | 11 | 4.36 | 0.14 |
| A15 | 8.5 | 43.2 | 3.5 | 5 | 2.65 | 0.09 |
| A16 | 20.5 | 39.19 | 13 | 7.5 | 3.39 | 0.12 |
| A17 | 41.5 | 33.15 | 35 | 6.5 | 3.17 | 0.1 |
| A18 | 137.14 | 2.55 | 115.71 | 21.43 | 11.06 | 0.34 |
| A19 | 11.67 | 75.46 | 3.67 | 8 | 4.25 | 0.16 |
| A20 | 19 | 60.82 | 10 | 9 | 3.46 | 0.11 |
| A21 | 16.33 | 87.27 | 7.67 | 8.67 | 3.39 | 0.09 |
| A22 | 14.33 | 111.17 | 5.33 | 9 | 3.43 | 0.1 |
| A23 | 24 | 332.71 | 5.33 | 18.67 | 3.72 | 0.26 |
| A24 | 24.33 | 265.71 | 7 | 17.33 | 3.91 | 0.19 |
| A25 | 3.33 | 12.14 | 0.33 | 3 | 1.89 | 0.01 |
| A26 | 4 | 12.98 | 0 | 4 | 1.82 | 0.01 |
| A27 | 4.67 | 14.81 | 0.33 | 4.33 | 1.69 | 0.01 |
| A28 | 14 | 114.27 | 4 | 10 | 3.32 | 0.14 |
| A29 | 15 | 137.98 | 3.33 | 11.67 | 3.41 | 0.17 |
| A30 | 17.33 | 113.89 | 5.67 | 11.67 | 3.08 | 0.42 |
Table 2 Results of water quality parameters for different types of water in Taiyuan City
| 站点 Sites | ρ(TSM)/ (mg∙L-1) | ρ(Chla)/ (mg∙m-3) | ρ(ISM)/ (mg∙L-1) | ρ(OSM)/ (mg∙L-1) | ρ(TN)/ (mg∙L-1) | ρ(TP)/ (mg∙L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 13.67 | 22.6 | 5 | 8.67 | 1.44 | 0.02 |
| A2 | 24 | 48.55 | 15 | 9 | 3.18 | 0.12 |
| A3 | 41 | 40.36 | 29.5 | 11.5 | 5.8 | 0.25 |
| A4 | 47.5 | 16.01 | 35.5 | 12 | 5.48 | 0.17 |
| A5 | 15 | 9.58 | 10.33 | 4.67 | 4.31 | 0.15 |
| A6 | 27.5 | 50.86 | 18.5 | 9 | 2.88 | 0.2 |
| A7 | 19 | 51.42 | 5 | 14 | 3.17 | 0.12 |
| A8 | 17.5 | 68.89 | 7.5 | 10 | 4.24 | 0.12 |
| A9 | 11 | 13.25 | 7.67 | 3.33 | 2.07 | 0.05 |
| A10 | 18.5 | 32.46 | 5 | 13.5 | 5.44 | 0.2 |
| A11 | 47.5 | 42.85 | 31.5 | 16 | 2.53 | 0.13 |
| A12 | 18.5 | 62.73 | 12 | 6.5 | 3.62 | 0.22 |
| A13 | 37 | 375.95 | 6 | 31 | 3.27 | 0.37 |
| A14 | 29.5 | 27.01 | 18.5 | 11 | 4.36 | 0.14 |
| A15 | 8.5 | 43.2 | 3.5 | 5 | 2.65 | 0.09 |
| A16 | 20.5 | 39.19 | 13 | 7.5 | 3.39 | 0.12 |
| A17 | 41.5 | 33.15 | 35 | 6.5 | 3.17 | 0.1 |
| A18 | 137.14 | 2.55 | 115.71 | 21.43 | 11.06 | 0.34 |
| A19 | 11.67 | 75.46 | 3.67 | 8 | 4.25 | 0.16 |
| A20 | 19 | 60.82 | 10 | 9 | 3.46 | 0.11 |
| A21 | 16.33 | 87.27 | 7.67 | 8.67 | 3.39 | 0.09 |
| A22 | 14.33 | 111.17 | 5.33 | 9 | 3.43 | 0.1 |
| A23 | 24 | 332.71 | 5.33 | 18.67 | 3.72 | 0.26 |
| A24 | 24.33 | 265.71 | 7 | 17.33 | 3.91 | 0.19 |
| A25 | 3.33 | 12.14 | 0.33 | 3 | 1.89 | 0.01 |
| A26 | 4 | 12.98 | 0 | 4 | 1.82 | 0.01 |
| A27 | 4.67 | 14.81 | 0.33 | 4.33 | 1.69 | 0.01 |
| A28 | 14 | 114.27 | 4 | 10 | 3.32 | 0.14 |
| A29 | 15 | 137.98 | 3.33 | 11.67 | 3.41 | 0.17 |
| A30 | 17.33 | 113.89 | 5.67 | 11.67 | 3.08 | 0.42 |
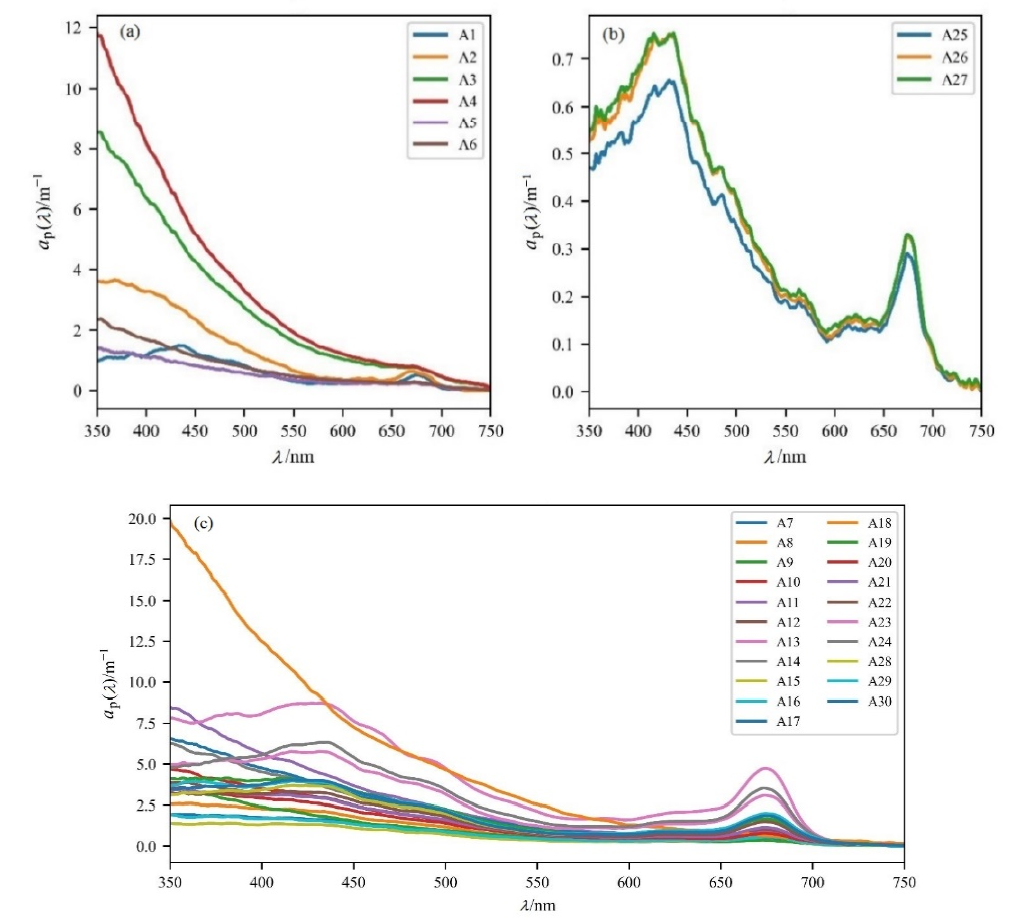
Fig. 2 Spectral curves of the absorption coefficient of total particles for different types of water in Taiyuan city (a) Lake Jinyang and flood discharge channel; (b) Fenhe second reservoir; (c) Taiyuan district section of Fenhe river. The same below
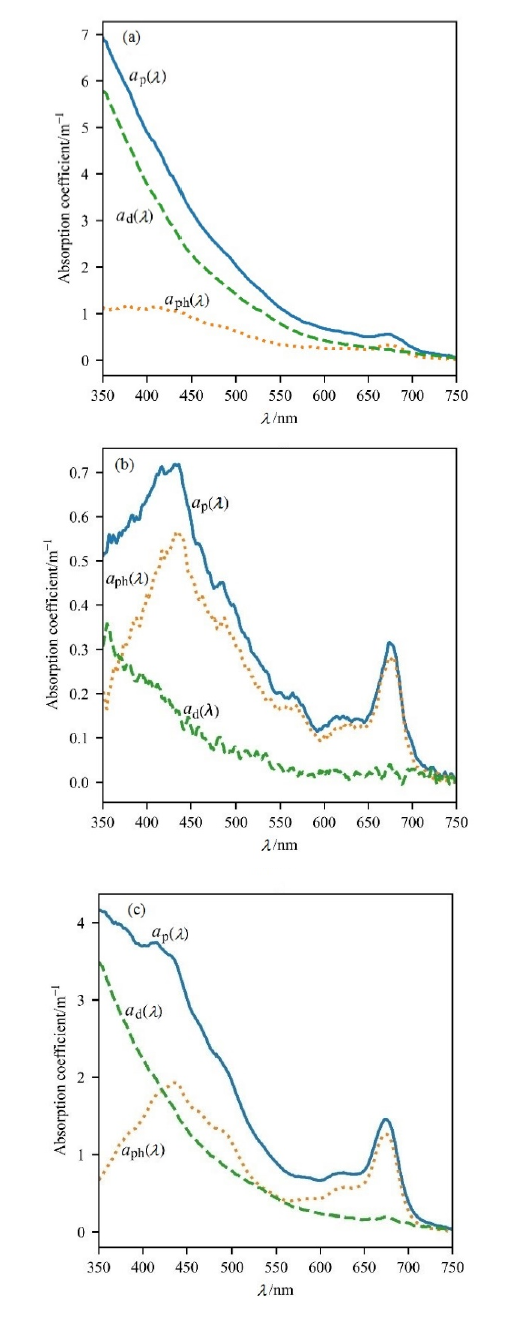
Fig. 3 Average absorption spectral curves of total suspended particles, non-algal particles and phytoplankton for different types of water in Taiyuan city
| 参数 Parameters | ap(440) | ap(675) | ad(440) | ad(675) | aph(440) | aph(675) | ag(440) | Chla | TSM | ISM | OSM | TP | TN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ap(440) | 1.0000 | ||||||||||||
| ap(675) | 0.7058** | 1.0000 | |||||||||||
| ad(440) | 0.7071** | 0.0167 | 1.0000 | ||||||||||
| ad(675) | 0.8405** | 0.3889* | 0.7996** | 1.0000 | |||||||||
| aph(440) | 0.7275** | 0.9815** | 0.0292 | 0.4123* | 1.0000 | ||||||||
| aph(675) | 0.6348** | 0.9941** | -0.0770 | 0.2863 | 0.9720** | 1.0000 | |||||||
| ag(440) | 0.5824** | 0.1778 | 0.6212** | 0.6238** | 0.2206 | 0.1112 | 1.0000 | ||||||
| Chla | 0.5959** | 0.9605** | -0.1033 | 0.2295 | 0.9426** | 0.9718** | 0.1668 | 1.0000 | |||||
| TSM | 0.6821** | 0.0332 | 0.9469** | 0.7118** | 0.0454 | -0.0495 | 0.6296** | -0.0458 | 1.0000 | ||||
| ISM | 0.5312** | -0.1645 | 0.9298** | 0.6355** | -0.1513 | -0.2462 | 0.5850** | -0.2428 | 0.9734** | 1.0000 | |||
| OSM | 0.8600** | 0.7342** | 0.4945** | 0.6022** | 0.7359** | 0.6924** | 0.4493* | 0.6955** | 0.5531** | 0.3474 | 1.0000 | ||
| TP | 0.7354** | 0.5641** | 0.4876** | 0.5722** | 0.5664** | 0.5191** | 0.6232** | 0.5037** | 0.5074** | 0.3740* | 0.7169** | 1.0000 | |
| TN | 0.6132** | 0.0254 | 0.8720** | 0.7247** | 0.0207 | -0.0592 | 0.7009** | -0.0609 | 0.8370** | 0.8191** | 0.4469* | 0.5567** | 1.0000 |
Table 3 Linear relationship between absorption coefficient of particulates and water quality parameters
| 参数 Parameters | ap(440) | ap(675) | ad(440) | ad(675) | aph(440) | aph(675) | ag(440) | Chla | TSM | ISM | OSM | TP | TN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ap(440) | 1.0000 | ||||||||||||
| ap(675) | 0.7058** | 1.0000 | |||||||||||
| ad(440) | 0.7071** | 0.0167 | 1.0000 | ||||||||||
| ad(675) | 0.8405** | 0.3889* | 0.7996** | 1.0000 | |||||||||
| aph(440) | 0.7275** | 0.9815** | 0.0292 | 0.4123* | 1.0000 | ||||||||
| aph(675) | 0.6348** | 0.9941** | -0.0770 | 0.2863 | 0.9720** | 1.0000 | |||||||
| ag(440) | 0.5824** | 0.1778 | 0.6212** | 0.6238** | 0.2206 | 0.1112 | 1.0000 | ||||||
| Chla | 0.5959** | 0.9605** | -0.1033 | 0.2295 | 0.9426** | 0.9718** | 0.1668 | 1.0000 | |||||
| TSM | 0.6821** | 0.0332 | 0.9469** | 0.7118** | 0.0454 | -0.0495 | 0.6296** | -0.0458 | 1.0000 | ||||
| ISM | 0.5312** | -0.1645 | 0.9298** | 0.6355** | -0.1513 | -0.2462 | 0.5850** | -0.2428 | 0.9734** | 1.0000 | |||
| OSM | 0.8600** | 0.7342** | 0.4945** | 0.6022** | 0.7359** | 0.6924** | 0.4493* | 0.6955** | 0.5531** | 0.3474 | 1.0000 | ||
| TP | 0.7354** | 0.5641** | 0.4876** | 0.5722** | 0.5664** | 0.5191** | 0.6232** | 0.5037** | 0.5074** | 0.3740* | 0.7169** | 1.0000 | |
| TN | 0.6132** | 0.0254 | 0.8720** | 0.7247** | 0.0207 | -0.0592 | 0.7009** | -0.0609 | 0.8370** | 0.8191** | 0.4469* | 0.5567** | 1.0000 |
| 水体类型 Water type | M值变化范围 Range of M value | M值均值 Mean of M value | 文献来源 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 本研究 This study | 5.62‒10.74 | 7.01±1.18 | ‒ |
| 太湖 Taihu | 6.94‒9.88 | 8.66±0.088 | 施坤等, (Shi et al., |
| 巢湖 Chaohu | 8.57‒15.22 | 10.6±1.57 | 施坤等, (Shi et al., |
| 滇池 Dianchi | 6.443‒10.238 | 7.678±0.164 | 张红等, 2011 (Zhang et al., 2011) |
| 查干湖 Chagan | 7.5‒15.09 | 11.44±2.00 | 李思佳等, (Li et al., |
| 新立城水库 Xinlicheng | 6.17‒8.89 | 7.53±0.79 | 李思佳等, (Li et al., |
Table 4 Statistic results of M values in different waters
| 水体类型 Water type | M值变化范围 Range of M value | M值均值 Mean of M value | 文献来源 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 本研究 This study | 5.62‒10.74 | 7.01±1.18 | ‒ |
| 太湖 Taihu | 6.94‒9.88 | 8.66±0.088 | 施坤等, (Shi et al., |
| 巢湖 Chaohu | 8.57‒15.22 | 10.6±1.57 | 施坤等, (Shi et al., |
| 滇池 Dianchi | 6.443‒10.238 | 7.678±0.164 | 张红等, 2011 (Zhang et al., 2011) |
| 查干湖 Chagan | 7.5‒15.09 | 11.44±2.00 | 李思佳等, (Li et al., |
| 新立城水库 Xinlicheng | 6.17‒8.89 | 7.53±0.79 | 李思佳等, (Li et al., |
| [1] |
BINDING C E, JEROME J H, BUKATA R P, et al., 2008. Spectral absorption properties of dissolved and particulate matter in Lake Erie[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 112(4): 1702-1711.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
BRICAUD A, BAIN M, MOREL A, 1995. Variability in the chlorophyll specific absorption coefficients of natural phytoplankton: Analysis and parameterization[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 100(C7): 13321-13332.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
BRICAUD A, MOREL A, BABIN M, et al., 1998. Variations of light absorption by suspended particles with chlorophyll a concentration in oceanic (case 1) waters: Analysis and implications for bio-optical models[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 103(C13): 31033-31044.
DOI URL |
| [4] | DAS S, HZARA S, GIRI S, et al., 2017. Light absorption characteristics of chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in the coastal waters of northern Bay of Bengal during winter season[J]. Indian Journal of Geo-Marine Sciences, 46(5): 884-892. |
| [5] |
GUILLERMINA RUIZ M, LUTZ V, FROUIN R, 2017. Spectral absorption by marine chromophoric dissolved organic matter: Laboratory determination and piecewise regression modeling[J]. Marine Chemistry, 194: 10-21.
DOI URL |
| [6] | KIRK J T O, 1994. Light and photosynthesis in aquatic ecosystem[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press: 1-431. |
| [7] |
LEI X, PAN J Y, DEVLIN A, 2019. Characteristics of Absorption Spectra of Chromophoric Dissolved Organic Matter in the Pearl River Estuary in Spring[J]. Remote Sensing, DOI: 10.3390/rs11131533.
DOI |
| [8] |
ZHANG Y L, ZHANG B, WANG X, et al., 2007. A study of absorption characteristics of chromophoric dissolved organic matter and particles in Lake Taihu, China[J]. Hydrobiologia, 592(1): 105-120.
DOI URL |
| [9] | 曹文熙, 杨跃忠, 许晓强, 等, 2003. 珠江口悬浮颗粒物的吸收光谱及区域模式[J]. 科学通报, 48(17): 1876-1882. |
| CAO W X, YANG Y Z, XU X Q, et al., 2003. Absorption spectrum and regional model of suspended particulate matter in the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 48(17): 1876-1882. | |
| [10] | 陈毅忠, 杜尔登, 王聿琳, 等, 2017. 三维荧光组合PARAFAC分析评估城市水体DOM特征分布与来源[J]. 常州大学学报(自然科学版), 29(6): 55-62. |
| CHEN Y Z, DU E D, WANG Y L, et al., 2017. Distribution and source of DOM in urban water bodies by EEMs spectrum and PARAFAC analysis[J]. Journal of Changzhou University (Natural Science Edition), 29(6): 55-62. | |
| [11] | 程艳, 胡霞, 杜加强, 等, 2018. 西北内陆河城区段入河水体CDOM三维荧光光谱特征[J]. 中国环境科学, 38(7): 2680-2690. |
| CHENG Y, HU X, DU J Q, et al., 2018. Characteristics of three-dimensional fluorescence on CDOM of the sewage into city segment of a typical northwest inland river[J]. China Environment Science, 38(7): 2680-2690. | |
| [12] | 戴永宁, 李素菊, 王学军, 2008. 巢湖水体固有光学特性研究[J]. 环境科学研究, 21(5): 173-177. |
| DAI Y N, LI S J, WANG X J, 2008. Inherent optical properties of water body of Chao Lake[J]. Research of Environmental Science, 21(5): 173-177. | |
| [13] | 丁潇蕾, 李云梅, 吕恒, 等, 2018. 城市黑臭水体的吸收特性分析[J]. 环境科学, 39(10): 4519-4529. |
| DING X L, LI Y M, LYN H, et al., 2018. Analysis of absorption characteristics of urban black-odor water[J]. Environmental Science, 39(10): 4519-4529. | |
| [14] | 盖利亚, 刘正军, 张继贤, 2010. 三峡坝区水体吸收系数的特征研究[J]. 遥感学报, 14(2): 313-332. |
| GAI L Y, LIU Z J, ZHANG J X, 2010. Absorption coefficient characteristics of the Three Gorges Dam water[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 14(2): 313-332. | |
| [15] | 郭燕妮, 李元鹏, 石玉, 等, 2020. 大型通江湖泊有色可溶性有机物对不同水文情景的响应[J]. 环境科学, 41(5): 2198-2209. |
| GUO Y N, LI Y P, SHI Y, et al., 2020. Response of chromophoric dissolved organic matter dynamics to different hydrological scenarios in the two largest freshwater lakes connected to the Yangtze River[J]. Environmental Science, 41(5): 2198-2209. | |
| [16] | 黄昌春, 李云梅, 孙德勇, 等, 2009. 太湖CDOM紫外吸收特性及其分子量时空分布特征[J]. 中国环境科学, 29(3): 261-268. |
| HUANG C C, LI Y M, SUN D Y, et al., 2009. Spatial-temporal distribution of CDOM molecular weight and its ultraviolet absorption characteristics in Taihu Lake[J]. China Environmental Science, 29(3): 261-268. | |
| [17] | 雷霞, 郭子祺, 田野, 等, 2013. 官厅水库秋季悬浮颗粒物和CDOM吸收特性[J]. 湖泊科学, 26(6): 883-891. |
| LEI X, GUO Z Q, TIAN Y, et al., 2013. Absorption characteristics of particulates and the CDOM in autumn in Guangting Reservoir[J]. Journal of Lake Science, 26(6): 883-891. | |
| [18] | 李方, 徐京萍, 何艳芬, 等, 2009. 长春市石头口门水库颗粒物光谱吸收特性[J]. 湖泊科学, 21(2):280-287. |
| LI F, XU J P, HE Y F, et al., 2009. Spectral absorption properties of particulate matters in the Shitoukoumen Reservori of Changchun city[J]. Journal of Lake Science, 21(2): 280-287. | |
| [19] | 李佳琦, 李家国, 朱利, 等, 2019. 太原市黑臭水体遥感识别与地面验证[J]. 遥感学报, 23(4): 773-784. |
| LI J Q, LI J G, ZHU L, et al., 2019. Remote sensing identification and validation of urban black and odorous water in Taiyuan city[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 23(4): 773-784. | |
| [20] | 李思佳, 宋开山, 陈智文, 等, 2015. 兴凯湖春季水体悬浮颗粒物和CDOM吸收特性[J]. 湖泊科学, 27(5): 941-952. |
| LI S J, SONG K S, CHEN Z W, et al., 2015. Absorption characteristics of particulaates and CDOM in spring in the Lake Xingkai[J]. Journal of Lake Science, 27(5): 941-952. | |
| [21] | 李思佳, 宋开山, 赵莹, 等, 2016. 查干湖和新立城水库秋季水体悬浮颗粒物和CDOM吸收特性[J]. 环境科学, 37(1): 112-122. |
| LI S J, SONG K S, ZHAO Y, et al., 2016. Absorption characteristics of particulates and CDOM in waters of Chagan Lake and Xinglicheng Reservoir in Autumn[J]. Environmental Science, 37(1): 112-122. | |
| [22] | 刘剑, 李俊生, 申茜, 等, 2015. 昆明湖水体悬浮颗粒物与有色可溶性有机物光谱吸收特性研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 35(4): 1089-1096. |
| LIU J, LI J S, SHEN Q, et al., 2015. Spectral absorption features of suspended particulate and colored dissolved organic matter in Kunming Lake[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiate, 35(4): 1089-1096. | |
| [23] | 刘忠华, 李云梅, 吕恒, 等, 2012. 太湖春季水体固有光学特性及其对遥感反射率变化的影响[J]. 生态学报, 32(2): 438-447. |
| LIU Z H, LI Y M, LYN H, et al., 2012. Analysis of inherent optical properties of Lake Taihu in spring and its influence on the change of remote sensing reflectance[J]. Acta Ecological Sinica, 32(2): 438-447. | |
| [24] | 柳彩霞, 郭子祺, 张宝钢, 等, 2011. 太湖流域坤承湖春季颗粒物和有色可溶性有机物吸收特性[J]. 湖泊科学, 23(5): 773-782. |
| LIU C X, GUO Z Q, ZHANG B G, et al., 2011. Absorption characteristics of particulates and the CDOM in Spring in Lake Kuncheng, Taihu Basin[J]. Journal of Lake Science, 23(5): 773-782. | |
| [25] | 马荣华, 戴锦芳, 张运林, 2005. 东太湖CDOM吸收光谱的影响因素与参数确定[J]. 湖泊科学, 17(2): 120-126. |
|
MA R H, DAI J F, ZHANG Y L, 2005. Influence Factors and slope coefficients of spectral absorption of coloured dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in East Taihu Lake, China[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 17(2): 120-126.
DOI URL |
|
| [26] | 钱伟, 江淼华, 黄佳芳, 等, 2020. 闽江下游有机碳及CDOM的季节动态[J]. 亚热带资源与环境学报, 15(3): 1-8. |
| QIAN W, JIANG M H, HUANG J F, et al., 2020. Seasonal variations of organic carbon and CDOM in the Lower Reaches of Min River[J]. Journal of Subtropical Resources and Environment, 15(3): 1-8. | |
| [27] | 邵田田, 宋开山, 丁智, 等, 2016. 辽河水体光学吸收特性的季节变化[J]. 生态学报, 36(7): 1861-1871. |
| SHAO T T, SONG K S, DING Z, et al., 2016. Absorption characteristics and seasonal variation of optically active water constituents from Liaohe River[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36(7): 1861-1871. | |
| [28] | 施坤, 李云梅, 王桥, 等, 2010. 太湖、巢湖水体CDOM吸收特性和组成的异同[J]. 环境科学, 31(5): 1183-1191. |
| SHI K, LI Y M, WANG Q, et al., 2010. Similarities and differences in absorption characteristics and composition of CDOM between Taihu Lake and Chaohu Lake[J]. Environmental Science, 31(5): 1183-1191. | |
| [29] | 宋开山, 温志丹, 刘阁, 等, 2018. 内陆水体CDOM光学特性与遥感反演研究进展[J]. 吉林师范大学学报(自然科学版), 39(4): 115-125. |
| SONG K S, WEN Z D, LIU G, et al., 2018. The research progress of CDOM optical characteristics and remote sensing retrieval for inland waters[J]. Journal of Jilin Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 39(4): 115-125. | |
| [30] | 魏兰苏, 孙德勇, 李楠, 2018. 东中国海水体悬浮颗粒物的光谱吸收特征研究[J]. 科技视界 (21): 58-61. |
| WEI L S, SUN D Y, LI N, 2018. Research on spectral absorption characteristics of particulates in East China sea[J]. Science & Technology Vision (21): 58-61. | |
| [31] | 张运林, 秦伯强, 2007. 梅梁湾、大太湖夏季和冬季CDOM特征及可能来源分析[J]. 水科学进展, 18(3): 415-423. |
| ZHANG Y L, QIN B Q, 2007. Feature of CDOM and its possible source in Meiliang bay and Da Taihu lake in Taihu lake in summer and winter[J]. Advances in Water Science, 18(3): 415-423. | |
| [32] | 张运林, 秦伯强, 杨龙元, 2006. 太湖梅梁湾水体悬浮颗粒物和CDOM的吸收特性[J]. 生态学报, 26(12): 3969-3979. |
| ZHANG Y L, QIN B Q, YANG L Y, 2006. Spectral absorption coefficients of particulate matter and chromophoric dissolved organic matter in Meiliang Bay of Lake Taihu[J]. Acta Ecology Sinica, 26(12): 3969-3979. | |
| [33] | 张运林, 张恩楼, 刘明亮, 2009. 云南高原湖泊有色可溶性有机物和颗粒物光谱吸收特性[J]. 湖泊科学, 21(2): 255-263. |
| ZHANG Y L, ZHANG E L, LIU M L, 2009. Spectral absorption properties of chromophoric dissolved organic matter and particulate matter in Yunnan Plateau lakes[J]. Journal of Lake Science, 21(2): 255-263. | |
| [34] | 赵巧华, 张运林, 秦伯强, 2006. 太湖梅梁湾水体悬浮颗粒物吸收系数的分离[J]. 湖泊科学, 18(4): 356-362. |
| ZHAO Q H, ZHANG Y L, QIN B Q, 2006. Partitioning spectral absorption of particulate matter in Meiliang Bay of Lake Taihu[J]. Journal of Lake Science, 18(4): 356-362. | |
| [35] | 赵巧华, 秦伯强, 2008. 太湖有色溶解有机质光谱吸收空间的分异特征[J]. 中国环境科学, 28(4): 289-293. |
| ZHAO Q H, QIN B Q, 2008. Mechanisms and characteristics of spatial distribution of colored dissolved organic matter in Taihu Lake between summer and winter[J]. China Environmental Science, 28(4): 289-293. |
| [1] | WANG Jiayi, SUN Tingting, SHA Runyu, CHEN Tinghong, XING Ran, QIN Boqiang, SHI Wenqing. Study on the Synergic Effect of Algae Salvage on Pollution Control and Carbon Emission Reduction in Eutrophic Lakes [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(6): 1108-1114. |
| [2] | DU Dandan, GAO Ruizhong, FANG Lijing, XIE Longmei. Spatial Variation of Soil Heavy Metals and Their Responses to Physicochemical Factors of Salt Lake Basin in Arid Area [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(6): 1123-1132. |
| [3] | CHENG Peng, SUN Mingdong, HAO Shaonan. Water Quality Assessment of Upstream Rivers of Guanting Reservoir Based on the Simplest Water Quality Index [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(2): 372-380. |
| [4] | WANG Zhe, TIAN Shengni, ZHANG Yongmei, ZHANG Heyu, ZHOU Zhongze. Study on the Plant Community Characteristics of the Estuary of Pai River in Chaohu Lake [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(9): 1823-1831. |
| [5] | CHEN Xiaowan, TIAN Huachuan, CHANG Junjun, CHEN Liqiang, SHU Xingquan, FENG Xiuxiang. Purification Efficiency for Polluted River Water and Microbial Community Characteristics of A Surface-flow Wetland Located at Zhonghe River Estuary near Qilu Lake [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(9): 1865-1875. |
| [6] | LÜ Guifang, WU Yingxin, DONG Changxun, LU Yang, ZHOU Yue, ZENG Wenjun, WU Wencheng. Study on the Mass Transfer Regulation in Micro-scale Ni-Fe/PCBs System by Humic Acid and Tween-80 [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(7): 1456-1464. |
| [7] | ZHU Jinfu, HUANG Ruiling, DONG Zhiqiang, MAO Xiaoning, ZHOU Huakun. Response of the Soil Bacterial Community to Nitrogen Addition in Alpine Wetland of Qinghai Lake [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(6): 1101-1109. |
| [8] | JI Xiaoyan, WANG Shanshan, YANG Kai, REN Bei. Temporal and Spatial Variation Characteristics of Total Nitrogen Concentration in Surface Water from 2016 to 2020 in China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(6): 1184-1192. |
| [9] | CUI Jian, DU Yi, DING Chengcheng, LI Jinfeng, GAO Fangshu, CHANG Yajun, ZHANG Jibiao, LIU Xiaojing, YAO Dongrui. Phosphorus Fraction and Abatement of Lakes in China: A Review [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 621-633. |
| [10] | XUE Wenkai, ZHU Pan, DE Ji, GUO Xiaofang. Study on the Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of the Dominant Species of Cultivable Filamentous Fungi in Nam Co Lake [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(12): 2331-2340. |
| [11] | XU Dongxue, LI Xing, WANG Yong, GOU Mangmang. Spatial Distribution Characteristics and the Response of Different Forms of Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Chlorophyll-a in Lake Ulansuhai during the Frozen Period [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(9): 1855-1864. |
| [12] | YUAN Weihao, WANG Hua, XIA Yubao, ZENG Yichuan, DENG Yanqing, LI Yuanyuan, ZHANG Xinyue. Relationship of Chlorophyll A and Water Quality Factors in Poyang Lake Based on GAM Model [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(8): 1716-1723. |
| [13] | ZHOU Dan, ZHANG Juan, LUO Jing, GUO Guang, LI Baohua. Analysis on the Causes of Qinghai Lake Water Level Changes and Prediction of Its Future Trends [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(7): 1482-1491. |
| [14] | BAO Yufei, HU Mingming, WANG Dianchang, WU Xinghua, WANG Yuchun, LI Shanze, WANG Qiwen, WEN Jie. Distribution and Pollution Assessment of Nutrients and Heavy Metals in Sediments of the Cascade Reservoirs in Huangbai River [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(5): 1005-1016. |
| [15] | ZHANG Kai, GUO Ziwei, WANG Qian, HAN Ya, LI Kuangjia, ZHANG Zhongshuai. Distribution Pattern of Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria in Water Supply Reservoirs of Central China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(5): 1017-1022. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
