Ecology and Environment ›› 2021, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (5): 1017-1022.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.05.014
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Kai1,2( ), GUO Ziwei1,2, WANG Qian1,2, HAN Ya1,2, LI Kuangjia3, ZHANG Zhongshuai1,2
), GUO Ziwei1,2, WANG Qian1,2, HAN Ya1,2, LI Kuangjia3, ZHANG Zhongshuai1,2
Received:2020-12-09
Online:2021-05-18
Published:2021-08-06
张凯1,2( ), 郭紫微1,2, 王倩1,2, 韩雅1,2, 李贶家3, 张中帅1,2
), 郭紫微1,2, 王倩1,2, 韩雅1,2, 李贶家3, 张中帅1,2
作者简介:张凯(1987年生),男,讲师,博士,研究方向为环境微生物。E-mail:kaizhang1014@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
ZHANG Kai, GUO Ziwei, WANG Qian, HAN Ya, LI Kuangjia, ZHANG Zhongshuai. Distribution Pattern of Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria in Water Supply Reservoirs of Central China[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(5): 1017-1022.
张凯, 郭紫微, 王倩, 韩雅, 李贶家, 张中帅. 华中地区水库型水源地抗生素抗性细菌的赋存特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(5): 1017-1022.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2021.05.014
| 抗生素类别 Category | 名称 Name | ρ/(mg∙L-1) | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 磺胺类 Sulfonamides | 磺胺甲恶唑 Sulfamethoxazole | 50 | Gao et al., |
| β-内酰胺类 β-lactem | 氨苄西林 Ampicillin | 32 | Harthug et al., |
| 四环素类 Tetracycline | 四环素 Tetracycline | 16 | Harnisz et al., |
| 喹诺酮类 Quinolone | 诺氟沙星 Norfloxacin | 10 | Lin et al., |
| 氨基糖苷类 Aminoglycosides | 链霉素 Streptomycin | 30 | Luo et al., |
Table 1 Related information of antibiotic concentration in this study
| 抗生素类别 Category | 名称 Name | ρ/(mg∙L-1) | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 磺胺类 Sulfonamides | 磺胺甲恶唑 Sulfamethoxazole | 50 | Gao et al., |
| β-内酰胺类 β-lactem | 氨苄西林 Ampicillin | 32 | Harthug et al., |
| 四环素类 Tetracycline | 四环素 Tetracycline | 16 | Harnisz et al., |
| 喹诺酮类 Quinolone | 诺氟沙星 Norfloxacin | 10 | Lin et al., |
| 氨基糖苷类 Aminoglycosides | 链霉素 Streptomycin | 30 | Luo et al., |
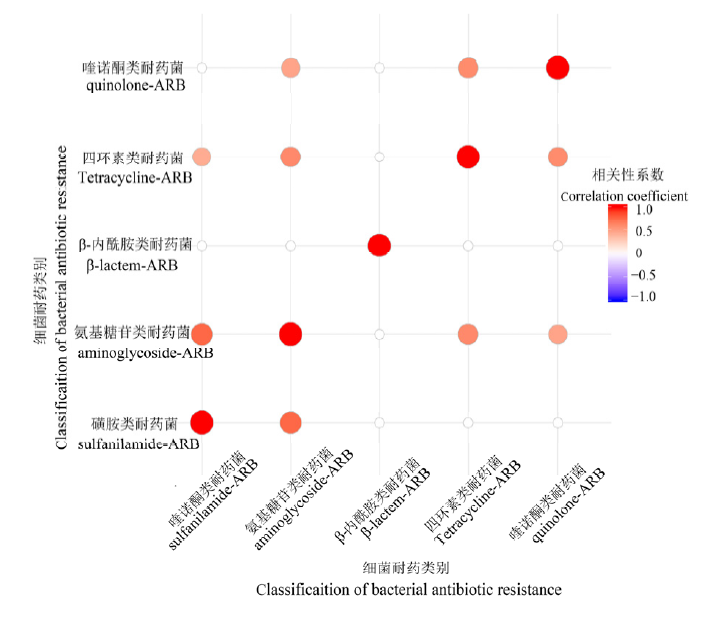
Fig. 3 Co-occurrence patterns among different ARB typesThe correlation coefficient with statistical significance (P<0.05) was selected to conduct the correlation analysis in this study. The correlation coefficient was regarded as 0 if P>0.05.
| 水库 Reservoir | 水样 Water/(CFUs∙mL-1) | 沉积物 Sediment/(CFUs∙g-1) |
|---|---|---|
| HN1 | 9.00×103 | 8.33×104 |
| HN2 | 4.25×103 | 3.67×105 |
| HN3 | 1.88×103 | 8.33×105 |
| HN4 | 5.93×103 | 1.34×105 |
| HB1 | 3.37×103 | 9.33×104 |
| HB2 | 3.95×103 | 1.10×105 |
| HB3 | 2.75×103 | 9.33×104 |
| HU1 | 2.50×103 | 1.28×105 |
| HU2 | 1.18×103 | 1.18×105 |
| HU3 | 3.50×103 | 3.57×104 |
| HU4 | 4.87×103 | 7.00×105 |
Table 2 Total heterotrophic bacteria count of water supply reservoirs in central China
| 水库 Reservoir | 水样 Water/(CFUs∙mL-1) | 沉积物 Sediment/(CFUs∙g-1) |
|---|---|---|
| HN1 | 9.00×103 | 8.33×104 |
| HN2 | 4.25×103 | 3.67×105 |
| HN3 | 1.88×103 | 8.33×105 |
| HN4 | 5.93×103 | 1.34×105 |
| HB1 | 3.37×103 | 9.33×104 |
| HB2 | 3.95×103 | 1.10×105 |
| HB3 | 2.75×103 | 9.33×104 |
| HU1 | 2.50×103 | 1.28×105 |
| HU2 | 1.18×103 | 1.18×105 |
| HU3 | 3.50×103 | 3.57×104 |
| HU4 | 4.87×103 | 7.00×105 |
| [1] |
ALLEN H, DONATO J, WANG H, et al., 2010. Call of the wild: Antibiotic resistance genes in natural environments[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 8(4): 251-259.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
BOYD L B, MAYNARD M J, MORGAN-LINNELL S K, et al., 2009. Relationships among ciprofloxacin, gatifloxacin, levofloxacin, and norfloxacin MICs for fluoroquinolone-resistant Escherichia coli clinical isolates[J]. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 53(1): 229-234.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
CHEN Y H, SU J Q, ZHANG J Y, et al., 2019. High-throughput profiling of antibiotic resistance gene dynamic in a drinking water river-reservoir system[J]. Water Research, 149: 179-189.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
DANG C Y, XIA Y, ZHENG M S, et al., 2020. Metagenomic insights into the profile of antibiotic resistomes in a large drinking water reservoir[J]. Environment International, 136: 105449.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
GARCÍA J, GARCÍA-GALÁN M, DAY J, et al., 2020. A review of emerging organic contaminants (EOCs), antibiotic resistant bacteria (ARB), and antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) in the environment: Increasing removal with wetlands and reducing environmental impacts[J]. Bioresource Technology, DOI:10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123228.
DOI |
| [6] | GAO P, MUNIR M, IRENE X, 2012. Correlation of tetracycline and sulfonamide antibiotics with corresponding resistance genes and resistant bacteria in a conventional municipal wastewater treatment plant[J]. Science of Total Environment, 421-422: 173-183. |
| [7] |
HAN Z M, AN W, YANG M, et al., 2020. Assessing the impact of source water on tap water bacterial communities in 46 drinking water supply systems in China[J]. Water Research, DOI:10.1016/j.watres.2020. 115469.
DOI |
| [8] |
HARNISZ M, KORZENIEWSKA M, GOLAS I, 2015. The impact of a freshwater fish farm on the community of river resistant bacteria and the structure of tetracycline resistance genes in water tetra cycline resistant bacteria and the structure of tetracycline resistance genes in river water[J]. Chemosphere, 128(1): 134-141.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
HARTHUG S, JUREEN R, MOHN S C, et al., 2002. The prevalence of faecal carriage of ampicillin-resistant and high-level gentamicin-resistant enterococci among inpatients at 10 major Norwegian hospitals[J]. Journal of Hospital Infection, 50(2): 145-154.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
JIANG H Y, ZHOU R J, YANG Y, et al., 2018. Characterizing the antibiotic resistance genes in a river catchment: Influence of anthropogenic activities[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 69(7): 125-132.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
LIN M, LIANG J J, ZHANG X, et al., 2015. Genetic diversity of three classes of integrons in antibiotic-resistant bacteria isolated from Jiulong River in southern China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22(15): 11930-11939.
DOI URL |
| [12] | LUO Y, WANG Q, LU Q, et al., 2014. An ionic liquid facilitates the proliferation of antibiotic resistance genes mediated by class I integrons[J]. Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 1(5): 266-270. |
| [13] |
NNADOZIE C, ODUME O, 2019. Freshwater environments as reservoirs of antibiotic resistant bacteria and their role in the dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes[J]. Environmental Pollution, DOI:10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113067.
DOI |
| [14] | PANG Y C, XI J Y, LI G Q, et al., 2015. Prevalence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in a lake for the storage of reclaimed water before and after usage as cooling water[J]. Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts, 17(6): 1182-1189. |
| [15] | QIAO M, YING G G, SINGER A C, et al., 2018. Review of antibiotic resistance in China and its environment[J]. Environment International, 10(16): 160-172. |
| [16] |
QIU J R, ZHAO T, LIU Q Y, et al., 2006. Residual veterinary antibiotics in pig excreta after oral administration of sulfonamides[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 38(2): 549-556.
DOI URL |
| [17] | IWANE T, URASE T, YAMAMOTO K, 2001. Possible impact of treated wastewater discharge on incidence of antibiotic resistant bacteria in river water[J]. Water Science and Technology, 43(2): 91-99. |
| [18] |
YANG Y, ZHOU R J, CHEN B W, et al., 2018. Characterization of airborne antibiotic resistance genes from typical bioaerosol emission sources in the urban environment using metagenomic approach[J]. Chemosphere, 213: 463-471.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
ZHANG K, NIU Z G, LV Z W, et al., 2017. Occurrence and distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in water supply reservoirs in Jingjinji area, China[J]. Ecotoxicology, 26(9): 1284-1292.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
ZHANG K, XIN R, ZHAO Z, et al., 2020. Antibiotic Resistance Genes in drinking water of China: Occurrence, distribution and influencing factors[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, DOI:10.1016/ j.ecoenv.2019.109837.
DOI |
| [21] |
ZHANG Q Q, YING G, PAN C G, et al., 2015. Comprehensive Evaluation of Antibiotics Emission and Fate in the River Basins of China: Source Analysis, Multimedia Modeling, and Linkage to Bacterial Resistance[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 49(11): 6772-6782.
DOI URL |
| [22] | 姜春霞, 黎平, 李森楠, 等, 2019. 海南东寨港海水和沉积物中抗生素抗性基因污染特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(1): 132-139. |
| JIANG C X, LIN P, LI S N, et al., 2019. Pollution characteristics of antibiotic resistance genes in seawater and sediment of Dongzhai Harbor, Hainan Province[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 28(1): 128-135. | |
| [23] | 廖杰, 魏晓琴, 肖燕琴, 等, 2020. 莲花水库水体中抗生素污染特征及生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 41(9): 4081-4087. |
| LIAO J, WEI X Q, XIAO Y Q, et al., 2020. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of antibiotics in Lianhua reservoir[J]. Environmental Science, 41(9): 4081-4087. | |
| [24] | 刘珊珊, 杨栋, 张坤明, 等, 2018. 天津市某地区自来水中抗生素耐药菌及其相关基因的调查[J]. 环境与健康杂志, 35(2): 166-169. |
| LIU S S, YANG D, ZHANG K M, et al., 2018. Antibiotic resistance bacterias and related genes in tap water in an area in Tianjin[J]. Journal of Environment and Health, 35(2): 166-169. | |
| [25] | 陆桂华, 马倩, 2009. 太湖水域“湖泛”及其成因研究[J]. 水科学进展, 20(3): 130-134. |
| LU G H, MA Q, 2009. Research on “Lake Flooding” of Taihu Lake and the related reasons[J]. Advances in Water Sciences, 20(3): 130-134. | |
| [26] | 孟磊, 杨兵, 薛南冬, 2015. 氟喹诺酮类抗生素环境行为及其生态毒理研究进展[J]. 生态毒理学报, 10(2): 76-88. |
| MENG L, YANG B, XUE N D, 2015. A review on environmental behaviors and ecotoxicology of fluoroquinolone antibiotics[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 10(2): 76-88. | |
| [27] | 缪羽晨, 刘尧成, 2019. 我国华中地区区域经济发展差异比较研究[J]. 经济视角, 279(6): 73-79. |
| MIAO Y C, LIU Y C, 2019. A comparative study on the differences of regional economic development in central China[J]. Economic Vision, 279(6): 73-79. | |
| [28] | 彭佳雯, 黄贤金, 钟太洋, 等, 2011. 中国经济增长与能源碳排放的脱钩研究[J]. 资源科学, 33(4): 34-41. |
| PENG J W, HUANG X J, ZHONG T Y, et al., 2011. Research on the decoupling of China’s economic growth and energy carbon emissions[J]. Resource Science, 33(4): 34-41. | |
| [29] | 钱岩, 满江红, 王先良, 等, 2013. 山东主要河湖地表水微生物学指标调查[J]. 环境与健康杂志, 30(3): 241-243. |
| QIAN Y, MAN J H, WANG X L, et al., 2013. Microbial pollution evaluation of main surface water in Shandong[J]. Journal of Environment and Health, 30(3): 241-243. | |
| [30] | 孙增灵, 范喜梅, 阮嘉玲, 等, 2011. 金银湖水质细菌学检测与分析[J]. 安徽农业科学, 39(34): 21238-21239. |
| SUN Z L, FAN X M, RUAN J L, et al., 2011. Bacteriological detection and analysis of water quality of Jinyin Lake[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 39(34): 21238-21239. | |
| [31] | 叶繁, 冯时欢, 吴佳佳, 2019. 养殖虾塘常见耐药菌的分离鉴定与耐药基因检测[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(9): 135-141. |
| YE F, FENG S H, WU J J, et al., 2019. Antibiotic resistant bacterial isolation and identification from shrimp ponds and their antibiotic resistance genes detection[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 28(9): 1843-1849. | |
| [32] | 伊丽丽, 焦文涛, 陈卫平, 2013. 不同抗生素在剖面土壤中的吸附特征[J]. 环境化学, 32(12): 2357-2363. |
| YI L L, JIAO W T, CHEN W P, 2013. Adsorption characteristics of different antibiotics in soil profile[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 32(12): 2357-2363. | |
| [33] | 张皓清, 贾永刚, 王凯歌, 等, 2020. 水体沉积物中内源污染物释放研究进展[J]. 应用化工, 49(337): 228-232. |
| ZHANG H Q, JIA Y G, WANG K G, et al., 2020. Research progress on release of endogenous pollutants in water sediments[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 49(337): 228-232. | |
| [34] | 朱永官, 陈青林, 苏建强, 等, 2018. 环境中抗生素与抗性基因组的研究[J]. 科学观察, 12(6): 60-63. |
| ZHU Y G, CHEN Q L, SU J Q, et al., 2018. Research on antibiotics and antibiotic resisomes in the environment[J]. Science Focus, 12(6): 60-63. |
| [1] | YANG Chunliang, LIU Minxia, WANG Qianyue, MIAO Lele, XIAO Yindi, WANG Min. Spatial Pattern and Correlation of Populations of Anemone rivularis and Kobresia myosuroides under Single-household Management and Multi-household Management Grazing Patterns [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 651-659. |
| [2] | HAO Jinhu, WEI Wei, LI Shengnan, MA Muyuan, LI Xiaoxia, YANG Hongguo, JIANG Qiyu, CHAI Peidong. GEE Based Evaluation of the Spatial-temporal Pattern and Drivers of Long-term Water Body in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 556-566. |
| [3] | ZHANG Guangyi, ZHANG Jiatao, WANG Xiaowei. Phosphorus Speciation Distribution and Release in Lake Sediment Microbial Fuel Cells [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 590-598. |
| [4] | YANG Qili, DOU Weili, LIU Zhiwen, GUO Jing, LÜ Gang. Analysis of Petroleum Hydrocarbon Pollution Characteristics and Influencing Factors Based on N-alkanes Tracing in the River Channel of Fuxin Xihe River [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 599-608. |
| [5] | YANG Nie, SUN Xiaoxun, KONG Tianle, SUN Weimin, CHEN Quanyuan, GAO Pin. Response of Microbial Communities to Changes in Antimony Pollution Concentrations in Fluvial Sediment [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 609-618. |
| [6] | XIANG Xing, MAN Baiying, ZHANG Junzhong, LUO Yang, MAO Xiaotao, ZHANG Chao, SUN Binghua, WANG Xi. Vertical Distribution of Bacterial Community and Functional Groups Mediating Nitrogen Cycling in Mount Huangshan, Anhui, China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(1): 56-69. |
| [7] | JI Bingjing, LIU Yi, WU Yang, GAO Shutao, ZENG Xiangying, YU Zhiqiang. Occurrence, Source and Potential Ecological Risk of Parent and Oxygenated Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Sediments of Yangtze River Estuary and Adjacent East China Sea [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(7): 1400-1408. |
| [8] | KE Qihua, ZHANG Keli. Scale Effect on Water and Soil Loss in China: A Bibliometric Analysis [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(7): 1489-1498. |
| [9] | ZHU Li'an, ZHANG Huihua, CHENG Jiong, LI Ting, LIN ZI, LI Junjie. Potential Ecological Risk Pattern Analysis of Heavy Metals in Soil of Forestry Land in The Pearl River Delta [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(6): 1253-1262. |
| [10] | WEN Zhifeng, WEI Shiguang, LI Lin, YE Wanhui, LIAN Juyu. Spatial Distribution Patterns and Spatial Associations of Evergreen Broad-leaved Forest Plants in Tropical South Asia at Different Taxonomic Levels [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 440-450. |
| [11] | REN Lijiang, ZHANG Yan, ZHANG Xin, SHAN Zexuan, ZHANG Chengqian. Pollution Characteristics and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Surface Water in Guanzhong Section of the Weihe River Basin [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(1): 131-141. |
| [12] | SUN Xuejiao, LI Jimei, ZHANG Yutao, LI Xiang, LU Jianjiang, SHE Fei. Characteristics and Influence of Runoff and Sediment Yield in Mountain Forest on the North Slope of Tianshan Mountains [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(9): 1821-1830. |
| [13] | LI Qiaoyu, ZHANG Xiaojing, CHEN Juan, LIU Yuan, LIU Jinchun, TAO Jianping. Landscape Distribution Pattern of Subalpine Color-leaved Forests and the Influence of Topographic Factors in Western Sichuan [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(8): 1581-1588. |
| [14] | KONG Pan, XIA Sujing, ZHANG Haiwei, ZHU Jianqiang. Effects of Tillage Methods on Ammonia Volatilization of Early Season Rice-ratooning Rice Fields [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(8): 1627-1633. |
| [15] | BAO Yufei, HU Mingming, WANG Dianchang, WU Xinghua, WANG Yuchun, LI Shanze, WANG Qiwen, WEN Jie. Distribution and Pollution Assessment of Nutrients and Heavy Metals in Sediments of the Cascade Reservoirs in Huangbai River [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(5): 1005-1016. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
