Ecology and Environment ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (5): 885-895.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.05.004
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
YAN Mingjuan1( ), CHEN Xianyu2, CAO Rongbin3, LIN Cheng1, WU Yiqun1, HUANG Dingyi1, WU Hailing1, CHEN Zicong1,*(
), CHEN Xianyu2, CAO Rongbin3, LIN Cheng1, WU Yiqun1, HUANG Dingyi1, WU Hailing1, CHEN Zicong1,*( )
)
Received:2022-02-23
Online:2022-05-18
Published:2022-07-12
Contact:
CHEN Zicong
颜明娟1( ), 陈贤玉2, 曹榕彬3, 林诚1, 吴一群1, 黄丁一1, 吴海玲1, 陈子聪1,*(
), 陈贤玉2, 曹榕彬3, 林诚1, 吴一群1, 黄丁一1, 吴海玲1, 陈子聪1,*( )
)
通讯作者:
陈子聪
作者简介:颜明娟(1969年生),女,副研究员,主要从事茶园土壤养分运移研究。E-mail: yanmj163@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
YAN Mingjuan, CHEN Xianyu, CAO Rongbin, LIN Cheng, WU Yiqun, HUANG Dingyi, WU Hailing, CHEN Zicong. The Distribution Characteristics of Soil Mn and Zn in Typical White Tea Plantation in Fujian Province[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(5): 885-895.
颜明娟, 陈贤玉, 曹榕彬, 林诚, 吴一群, 黄丁一, 吴海玲, 陈子聪. 福建典型白茶产区茶园土壤锰锌形态特征及其影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 885-895.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.05.004
| 指标 Indexs | pH | w(SOM)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(TN)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(AN)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(AP)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(AK)/ (mg∙kg-1) | CEC/ (cmol∙kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 均值 Mean | 4.3 | 28.2 | 1.5 | 138.4 | 33.4 | 89.6 | 11.5 |
| 标准差 SD | 0.3 | 12.8 | 0.1 | 57.7 | 45.2 | 40.0 | 2.7 |
| 最大值Max | 4.8 | 66.8 | 3.4 | 318.7 | 194 | 204 | 19.6 |
| 最小值Min | 3.7 | 6.7 | 0.4 | 15.1 | 2.3 | 40 | 6.7 |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 6.5 | 45.2 | 43.3 | 41.7 | 135.4 | 44.7 | 23.8 |
| 高产茶园标准 Indices of high yield tea plantation | 4.5-5.5 | >20 | >1.0 | >100 | >20 | >100 | |
| 低于高产茶园标准比例 The proportion of under indices of high yield tea plantation/% | 84.38 | 31.25 | 21.88 | 18.75 | 59.38 | 65.63 |
Table 1 Physical and chemical properties of the tea garden soil
| 指标 Indexs | pH | w(SOM)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(TN)/ (g∙kg-1) | w(AN)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(AP)/ (mg∙kg-1) | w(AK)/ (mg∙kg-1) | CEC/ (cmol∙kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 均值 Mean | 4.3 | 28.2 | 1.5 | 138.4 | 33.4 | 89.6 | 11.5 |
| 标准差 SD | 0.3 | 12.8 | 0.1 | 57.7 | 45.2 | 40.0 | 2.7 |
| 最大值Max | 4.8 | 66.8 | 3.4 | 318.7 | 194 | 204 | 19.6 |
| 最小值Min | 3.7 | 6.7 | 0.4 | 15.1 | 2.3 | 40 | 6.7 |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 6.5 | 45.2 | 43.3 | 41.7 | 135.4 | 44.7 | 23.8 |
| 高产茶园标准 Indices of high yield tea plantation | 4.5-5.5 | >20 | >1.0 | >100 | >20 | >100 | |
| 低于高产茶园标准比例 The proportion of under indices of high yield tea plantation/% | 84.38 | 31.25 | 21.88 | 18.75 | 59.38 | 65.63 |
| 指标 Indexs | 全锰质量分数 w(total Mn)/(mg∙kg-1) | 有效锰质量分数 w(available Mn)/(mg∙kg-1) | 活化率 Activating rates/% | 全锌质量分数 w(total Zn)/(mg∙kg-1) | 有效锌质量分数 w(available Zn)/(mg∙kg-1) | 活化率 Activating rates/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 均值 Mean | 394.84 | 49.41 | 11.89 | 101.58 | 3.34 | 2.98 |
| 标准差 SD | 343.43 | 41.81 | 5.06 | 57.65 | 2.64 | 0.93 |
| 最大值Max | 1362.41 | 171.00 | 3.73 | 306.53 | 10.60 | 4.95 |
| 最小值Min | 114.61 | 4.27 | 20.47 | 45.56 | 0.79 | 1.73 |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 86.98 | 84.62 | 42.56 | 56.75 | 79.10 | 31.11 |
| Ⅰ比例 Proportion/% | 59.38 (>30) | 65.63 (>2) | ||||
| Ⅱ比例 Proportion/% | 12.50 (15-30) | 34.38 (0.5-2) | ||||
| Ⅲ比例 Proportion/% | 28.13 (<15) | <0.5 |
Table 2 Total content of Mn and Zn in the tea garden soil
| 指标 Indexs | 全锰质量分数 w(total Mn)/(mg∙kg-1) | 有效锰质量分数 w(available Mn)/(mg∙kg-1) | 活化率 Activating rates/% | 全锌质量分数 w(total Zn)/(mg∙kg-1) | 有效锌质量分数 w(available Zn)/(mg∙kg-1) | 活化率 Activating rates/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 均值 Mean | 394.84 | 49.41 | 11.89 | 101.58 | 3.34 | 2.98 |
| 标准差 SD | 343.43 | 41.81 | 5.06 | 57.65 | 2.64 | 0.93 |
| 最大值Max | 1362.41 | 171.00 | 3.73 | 306.53 | 10.60 | 4.95 |
| 最小值Min | 114.61 | 4.27 | 20.47 | 45.56 | 0.79 | 1.73 |
| 变异系数 CV/% | 86.98 | 84.62 | 42.56 | 56.75 | 79.10 | 31.11 |
| Ⅰ比例 Proportion/% | 59.38 (>30) | 65.63 (>2) | ||||
| Ⅱ比例 Proportion/% | 12.50 (15-30) | 34.38 (0.5-2) | ||||
| Ⅲ比例 Proportion/% | 28.13 (<15) | <0.5 |
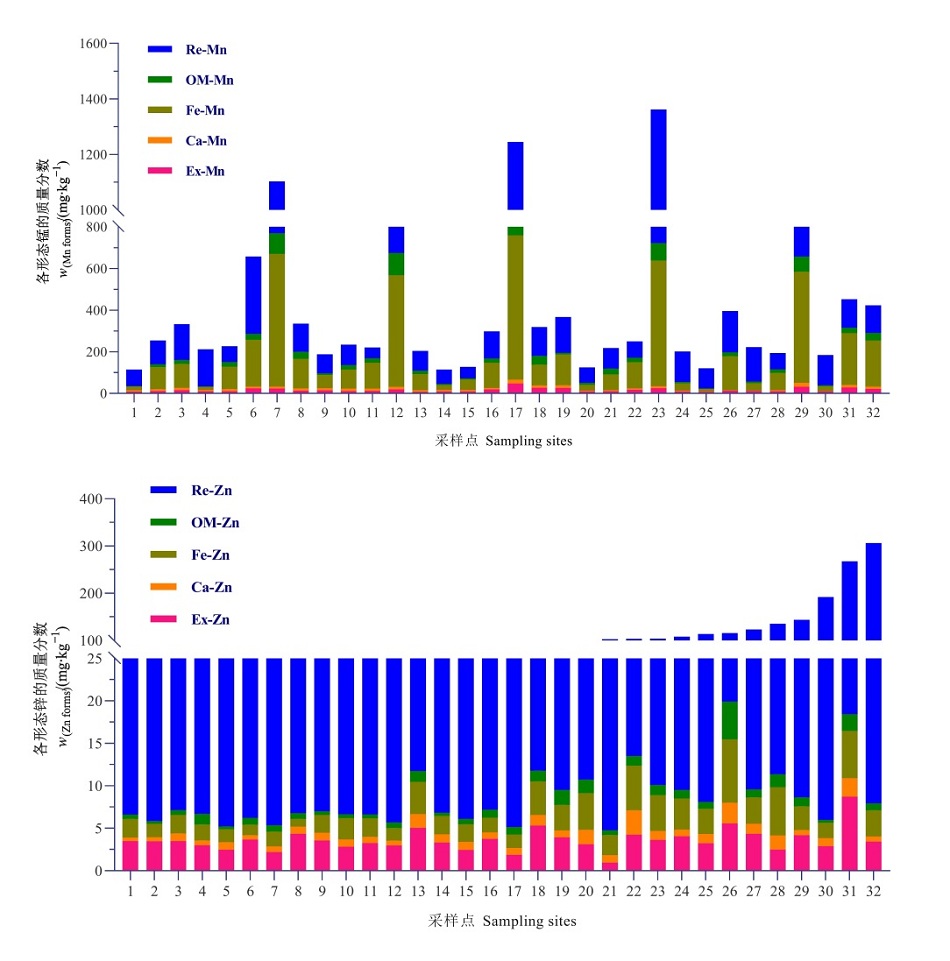
Figure 2 Contents of Mn and Zn forms in tea garden soil Ex-Mn: exchangeable form; Ca-Mn: Carbonate form; Fe-Mn: Fe/Mn oxides form; OM-Mn: organic matter form; Re-Mn: residual form; Ex-Zn: exchangeable form; Ca-Zn: Carbonate form; Fe-Zn: Fe/Mn oxides form; OM-Zn: organic matter form; Re-Zn: residual form. The same below
| 元素 Elements | 指标 Indexs | 离子交换态 Exchangeable | 碳酸盐结合态 Carbonate-bound | 铁锰结合态 Iron and manganese oxides | 有机结合态 Organic-bound | 残渣态 Residuals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 锰 Mn | 均值 | 5.19 | 2.86 | 37.10 | 6.59 | 48.26 |
| 标准差 | 1.77 | 1.70 | 14.91 | 3.34 | 16.85 | |
| 最大值 | 8.03 | 6.68 | 59.32 | 13.18 | 84.74 | |
| 最小值 | 1.79 | 0.38 | 6.92 | 0.75 | 23.68 | |
| 变异系数 | 34.13 | 59.45 | 40.19 | 50.68 | 34.92 | |
| 锌 Zn | 均值 | 4.11 | 1.15 | 3.06 | 1.06 | 90.62 |
| 标准差 | 1.70 | 0.53 | 1.26 | 0.68 | 3.32 | |
| 最大值 | 7.61 | 2.80 | 6.45 | 3.84 | 97.41 | |
| 最小值 | 0.92 | 0.20 | 0.95 | 0.27 | 82.77 | |
| 变异系数 | 41.28 | 45.87 | 41.26 | 64.33 | 3.66 |
Table 3 Relative proportions of different forms of Mn and Zn in tea garden soil %
| 元素 Elements | 指标 Indexs | 离子交换态 Exchangeable | 碳酸盐结合态 Carbonate-bound | 铁锰结合态 Iron and manganese oxides | 有机结合态 Organic-bound | 残渣态 Residuals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 锰 Mn | 均值 | 5.19 | 2.86 | 37.10 | 6.59 | 48.26 |
| 标准差 | 1.77 | 1.70 | 14.91 | 3.34 | 16.85 | |
| 最大值 | 8.03 | 6.68 | 59.32 | 13.18 | 84.74 | |
| 最小值 | 1.79 | 0.38 | 6.92 | 0.75 | 23.68 | |
| 变异系数 | 34.13 | 59.45 | 40.19 | 50.68 | 34.92 | |
| 锌 Zn | 均值 | 4.11 | 1.15 | 3.06 | 1.06 | 90.62 |
| 标准差 | 1.70 | 0.53 | 1.26 | 0.68 | 3.32 | |
| 最大值 | 7.61 | 2.80 | 6.45 | 3.84 | 97.41 | |
| 最小值 | 0.92 | 0.20 | 0.95 | 0.27 | 82.77 | |
| 变异系数 | 41.28 | 45.87 | 41.26 | 64.33 | 3.66 |
| 指标 Indexs | T-Mn | Ex-Mn | Ca-Mn | Fe-Mn | OM-Mn | Re-Mn | pH | SOM | TN | AN | AP | AK | CEC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-Mn | 1 | 0.574** | 0.411** | 0.932** | 0.813** | 0.794** | 0.323** | -0.014 | 0.03 | -0.007 | 0.103 | 0.104 | -0.062 |
| Ex-Mn | 1 | 0.603** | 0.563** | 0.748** | 0.290* | 0.088 | 0.295* | 0.334** | 0.303** | 0.057 | 0.469** | 0.138 | |
| Ca-Mn | 1 | 0.402** | 0.366** | 0.222 | 0.314** | 0.227 | 0.226 | 0.143 | -0.036 | 0.274* | 0.141 | ||
| Fe-Mn | 1 | 0.843** | 0.529** | 0.203 | -0.014 | 0.026 | 0.002 | 0.067 | 0.094 | -0.107 | |||
| OM-Mn | 1 | 0.429** | 0.091 | 0.242* | 0.287* | 0.266* | 0.177 | 0.231 | 0.137 | ||||
| Re-Mn | 1 | 0.431** | -0.097 | -0.061 | -0.105 | 0.109 | 0.016 | -0.036 |
Table 4 Pearson correlation coefficient for Mn forms and soil physicochemical properties in in tea garden of studied area
| 指标 Indexs | T-Mn | Ex-Mn | Ca-Mn | Fe-Mn | OM-Mn | Re-Mn | pH | SOM | TN | AN | AP | AK | CEC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-Mn | 1 | 0.574** | 0.411** | 0.932** | 0.813** | 0.794** | 0.323** | -0.014 | 0.03 | -0.007 | 0.103 | 0.104 | -0.062 |
| Ex-Mn | 1 | 0.603** | 0.563** | 0.748** | 0.290* | 0.088 | 0.295* | 0.334** | 0.303** | 0.057 | 0.469** | 0.138 | |
| Ca-Mn | 1 | 0.402** | 0.366** | 0.222 | 0.314** | 0.227 | 0.226 | 0.143 | -0.036 | 0.274* | 0.141 | ||
| Fe-Mn | 1 | 0.843** | 0.529** | 0.203 | -0.014 | 0.026 | 0.002 | 0.067 | 0.094 | -0.107 | |||
| OM-Mn | 1 | 0.429** | 0.091 | 0.242* | 0.287* | 0.266* | 0.177 | 0.231 | 0.137 | ||||
| Re-Mn | 1 | 0.431** | -0.097 | -0.061 | -0.105 | 0.109 | 0.016 | -0.036 |
| 指标 Indexs | T-Zn | Ex-Zn | Ca-Zn | Fe-Zn | OM-Zn | Re-Zn | pH | SOM | TN | AN | AP | AK | CEC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-Zn | 1 | 0.439** | -0.124 | 0.084 | 0.025 | 0.998** | 0.258* | -0.033 | -0.026 | -0.029 | -0.058 | -0.03 | -0.072 |
| Ex-Zn | 1 | -0.041 | 0.15 | 0.232* | 0.414** | 0.078 | 0.383** | 0.398** | 0.362** | 0.102 | 0.189 | 0.367** | |
| Ca-Zn | 1 | 0.823** | 0.563** | -0.167 | 0.278* | -0.296* | -0.318** | -0.371** | -0.187 | -0.254* | -0.258* | ||
| Fe-Zn | 1 | 0.748** | 0.033 | 0.388** | -0.059 | -0.068 | -0.151 | -0.145 | -0.107 | -0.091 | |||
| OM-Zn | 1 | -0.02 | 0.204 | 0.299* | 0.289* | 0.174 | 0.145 | -0.061 | 0.184 | ||||
| Re-Zn | 1 | 0.241* | -0.039 | -0.032 | -0.03 | -0.057 | -0.028 | -0.077 |
Table 5 Pearson correlation coefficient for Zn forms and soil physicochemical properties in tea garden of studied area
| 指标 Indexs | T-Zn | Ex-Zn | Ca-Zn | Fe-Zn | OM-Zn | Re-Zn | pH | SOM | TN | AN | AP | AK | CEC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-Zn | 1 | 0.439** | -0.124 | 0.084 | 0.025 | 0.998** | 0.258* | -0.033 | -0.026 | -0.029 | -0.058 | -0.03 | -0.072 |
| Ex-Zn | 1 | -0.041 | 0.15 | 0.232* | 0.414** | 0.078 | 0.383** | 0.398** | 0.362** | 0.102 | 0.189 | 0.367** | |
| Ca-Zn | 1 | 0.823** | 0.563** | -0.167 | 0.278* | -0.296* | -0.318** | -0.371** | -0.187 | -0.254* | -0.258* | ||
| Fe-Zn | 1 | 0.748** | 0.033 | 0.388** | -0.059 | -0.068 | -0.151 | -0.145 | -0.107 | -0.091 | |||
| OM-Zn | 1 | -0.02 | 0.204 | 0.299* | 0.289* | 0.174 | 0.145 | -0.061 | 0.184 | ||||
| Re-Zn | 1 | 0.241* | -0.039 | -0.032 | -0.03 | -0.057 | -0.028 | -0.077 |
| 指标 Indexs | Mn | Zn | 水浸出物 Water extract | 咖啡碱 Caffeine | 氨基酸 Amino acid content | 茶多酚 Tea polyphenol | 酚氨比 TP/AA ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-Mn | 0.369* | 0.264 | 0.357* | -0.052 | 0.017 | -0.068 | |
| Ex-Mn | 0.381* | 0.237 | 0.374* | 0.121 | 0.059 | -0.001 | |
| Ca-Mn | 0.261 | 0.003 | 0.267 | 0.088 | -0.154 | 0.107 | |
| Fe-Mn | 0.401* | 0.246 | 0.381* | -0.042 | -0.005 | -0.048 | |
| OM-Mn | 0.326 | 0.192 | 0.370* | -0.03 | -0.049 | -0.009 | |
| Re-Mn | 0.263 | 0.272 | 0.251 | -0.082 | 0.069 | -0.114 | |
| T-Zn | 0.374* | 0.095 | 0.336 | 0.053 | 0.017 | -0.083 | |
| Ex-Zn | 0.053 | -0.149 | 0.057 | -0.145 | -0.032 | -0.081 | |
| Ca-Zn | 0.008 | 0.007 | 0.141 | -0.123 | 0.107 | -0.227 | |
| Fe-Zn | 0.085 | 0.096 | 0.219 | -0.165 | 0.083 | -0.216 | |
| OM-Zn | 0.111 | -0.014 | 0.173 | -0.268 | 0.274 | -0.376* | |
| Re-Zn | 0.245 | 0.099 | 0.333 | 0.013 | 0.012 | -0.069 |
Table 6 Pearson correlation coefficient of soil Mn (Zn) forms and Mn (Zn) contents of tea leaves and tea quality
| 指标 Indexs | Mn | Zn | 水浸出物 Water extract | 咖啡碱 Caffeine | 氨基酸 Amino acid content | 茶多酚 Tea polyphenol | 酚氨比 TP/AA ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-Mn | 0.369* | 0.264 | 0.357* | -0.052 | 0.017 | -0.068 | |
| Ex-Mn | 0.381* | 0.237 | 0.374* | 0.121 | 0.059 | -0.001 | |
| Ca-Mn | 0.261 | 0.003 | 0.267 | 0.088 | -0.154 | 0.107 | |
| Fe-Mn | 0.401* | 0.246 | 0.381* | -0.042 | -0.005 | -0.048 | |
| OM-Mn | 0.326 | 0.192 | 0.370* | -0.03 | -0.049 | -0.009 | |
| Re-Mn | 0.263 | 0.272 | 0.251 | -0.082 | 0.069 | -0.114 | |
| T-Zn | 0.374* | 0.095 | 0.336 | 0.053 | 0.017 | -0.083 | |
| Ex-Zn | 0.053 | -0.149 | 0.057 | -0.145 | -0.032 | -0.081 | |
| Ca-Zn | 0.008 | 0.007 | 0.141 | -0.123 | 0.107 | -0.227 | |
| Fe-Zn | 0.085 | 0.096 | 0.219 | -0.165 | 0.083 | -0.216 | |
| OM-Zn | 0.111 | -0.014 | 0.173 | -0.268 | 0.274 | -0.376* | |
| Re-Zn | 0.245 | 0.099 | 0.333 | 0.013 | 0.012 | -0.069 |
| [1] |
ANTUNES P M C, KREAGER N J, 2015. Lead toxicity to Lemna minor predicted using a metal speciation chemistry approach[J]. Environmental Toxicology Chemistry, 33(10): 2225-2233.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
CHEN Y L, JIA Z, LIU K, et al., 2017. Response of exogenous zinc availability and transformation to maize straw as affected by soil organic matter[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 81(4): 814-827.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
GAO X P, FLATEN D N, TENUTA M, et al., 2011. Soil solution dynamics and plant uptake of cadmium and zinc by durum wheat following phosphate fertilization[J]. Plant and Soil, 338(1-2): 423-434.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
HAMILTON J G, FARRELL R E, NING C, et al., 2016. Characterizing zinc speciation in soils from a smelter affected boreal forest ecosystem[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 45(2): 684-692.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
HE M M, TIAN G M, LIANG X Q, 2009. Phytotoxicity and speciation of copper, zinc and lead during the aerobic composting of sewage sludge[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 163(2-3): 671-677.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
LATRILLE C, DENAIX L, LAMY I, 2010. Interaction of copper and zinc with allophane and organic matter in the B horizon of an Andosol[J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 54(2): 357-364.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
LI B Q, CHEN D, YANG Y P, et al., 2019. Effects of soil properties on accumulation characteristics of copper, manganese, zinc, and cadmium in Chinese turnip[J]. Plant Diversity, 41(5): 340-346.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
LI X, ZHANG Z W, LI P W, et al., 2013. Determination for major chemical contaminants in tea (Camellia sinensis) matrices: A review[J]. Food Research International, 53(2): 649-658.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
MAKSIMOVI J, PIVI R, STANOJKOVI-SEBIA, et al., 2021. Influence of soil type on the reliability of the prediction model for bioavailability of Mn, Zn, Pb, Ni and Cu in the soils of the republic of serbia[J]. Agronomy, 11(1): 141.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
MISHIMA S I, TANIGUCHI S, KAWASAKI A, et al., 2010. Estimation of zinc and copper balance in japanese farmland soil associated with the application of chemical fertilizers and livestock excreta[J]. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 51(3): 437-442.
DOI URL |
| [11] | RANDHAWA B S, SINGH S P, 1997. Distribution of Manganese Fractions in Alluvium-Derived Soils in Different Agro-climatic Zones of Punjab[J]. Journal of the Indian Society of Soil Science, 45(1): 53-57. |
| [12] |
RODELLA A A, CHIOU D G, 2009. Copper, Zinc, and Manganese Mobilization in a Soil Contaminated by a Metallurgy Waste used as Micronutrient Source[J]. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 40(9): 1634-1644.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
SONG X D, ZHANG G L, LIU F, et al., 2016. Characterization of the spatial variability of soil available zinc at various sampling densities using grouped soil type information[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188(11): 1-15.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
STEPHAN C H, COURCHESNE F, HENDERSHOT W H, et al., 2008. Speciation of zinc in contaminated soils[J]. Environmental Pollution, 155(2): 208-216.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
TESSIER A, CAMPBELL P G C, BISSON M P, et al., 1979. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 51(7): 844-851.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
YU F M, LI C M, DAI C L, et al., 2020. Phosphate Coupling the functions of fertilization and passivation in phytoremediation of manganese- contaminated soil by Polygonum pubescens Blume[J]. Chemosphere, DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127651.
DOI |
| [17] |
YUAN G, LAVKULICH L M, 1997. Sorption behavior of copper, zinc, and cadmium in response to simulated changes in soil properties[J]. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 28(6-8): 571-587.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
ZHANG X Y, LI Q H, XU W L, et al., 2020. Identification of MTP gene family in tea plant (Camellia sinensis L.) and characterization of CsMTP8.2 in manganese toxicity[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, DOI: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110904.
DOI |
| [19] |
ZHAO B Z, MAEDA M, ZHANG J B, et al., 2006. Accumulation and chemical fractionation of heavy metals in Andisols after 6-year different fertilization management[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 13(2): 90-97.
DOI URL |
| [20] | 陈振金, 陈春秀, 刘用清, 等, 1992. 福建省土壤环境背景值研究[J]. 环境科学, 13(4): 70-75. |
| CHEN Z J, CHEN C X, LIU Y Q, et al., 1992. Study on soil environmental background values in Fujian Province[J]. Journal of Environmental Science, 13(4): 70-75. | |
| [21] | 陈青松, 2020. 贵州山区主要土壤类型剖面钙镁锰形态特征[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学. |
| CHENG Q S, 2020. Profile characteristics of calcium, magnesium and manganese in main soil types in Guizhou mountainous area[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University. | |
| [22] | 陈艳龙, 贾舟, 师江澜, 等, 2018. 秸秆还田对石灰性土壤Zn扩散迁移及形态转化的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 55(3):721-733. |
| CHEN Y L, JIA Z, SHI J L, et al., 2018. Effect of straw return on diffusion, translocation and transformation of zinc in calcareous soil[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 55(3): 721-733. | |
| [23] | 丁维新, 1995. 土壤中锰赋存形态的地域性差异研究[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 4(1): 38-44. |
| DING W X, 1995. Regional differences of occurrence forms of medium manganese in soil[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 4(1): 38-44. | |
| [24] | 段小华, 陈淑芳, 2017. 外源锌对茶叶锌积累及主要化学品质成分的影响[J]. 江西师范大学学报 (自然版), 41(4): 438-440. |
| DUAN X H, CHEN S F, 2017. The effects of exogenous zinc on zinc accumulation and main chemical qualities of tea leaves[J]. Journal of Jiangxi Normal University (Natural Sciences Edition), 41(4): 438-440. | |
| [25] | 郭海彦, 周卫军, 张杨珠, 等, 2007. 湖南省主要茶园土壤锌的形态及其有效性[J]. 土壤, 39(4): 556-560. |
| GUO H Y, ZHOU W J, ZHANG Y Z, et al., 2007. Forms and availability of zinc in tea garden soils[J]. Soils, 39(4): 556-560. | |
| [26] | 郭雅玲, 许璐璐, 葛宏力, 等, 2012. 福建省铁观音茶园锌素状况[J]. 福建农林大学学报 (自然科学版), 41(3): 232-237. |
| GUO Y L, XU L L, GE H L, et al., 2012. The nutritional situation ofzinc in Tieguanyin tea plantations in Fujian province[J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 41(3): 232-237. | |
| [27] | 韩文炎, 阮建云, 林智, 等, 2002. 茶园土壤主要营养障碍因子及系列茶树专用肥的研制[J]. 茶叶科学, 22(1): 70-74. |
| HAN W Y, RUAN J Y, LIN Z, et al., 2002. The major nutritional limiting factors in tea soils and development of tea speciality fertilizer series[J]. Journal of Tea Science, 22(1): 70-74. | |
| [28] | 黄意欢, 徐仲溪, 王淦, 等, 1992. 茶树六种无机元素含量年周期动态研究[J]. 湖南农业大学学报 (自然科学版), 18(2):270-278. |
| HUANG Y H, XU Z X, WANG G, et al., 1992. Yearly changes of the contents of six minerals in tea plant[J]. Journal of Hunan Agricultural University (Natural Sciences), 18(2): 270-278. | |
| [29] | 江嵩鹤, 胡恭任, 于瑞莲, 等, 2016. 安溪铁观音茶园土壤重金属赋存形态及生态风险评价[J]. 地球与环境, 44(3): 359-369. |
| JIANG S H, HU G R, YU R L, et al., 2016. Speciation and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in soil from Anxi Tieguanyin Tea Garden[J]. Earth and Environment, 44(3): 359-369. | |
| [30] | 李张伟, 张敏, 徐桂崧, 2011. 粤东凤凰山茶区土壤锰、锌赋存形态特征及对茶叶的有效性[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 27(5): 7-12. |
| LI Z W, ZHANG M, XU G S, 2011. Chemical speciation and availability of Mn and Zn to tea in soils of the Fenghuangshan Tea Belt, east Guangdong[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 27(5): 7-12. | |
| [31] | 刘义, 邵树勋, 2010. 凤冈富硒富锌茶园土壤中的锌及其形态分析[J]. 地球与环境, 38(3): 328-332. |
| LIU Y, SHAO S X, 2010. The concentrations and fractional analysis of zinc in Fenggang zinc-and selenium-enriched tea garden soils[J]. Earth and Environment, 38(3): 328-332. | |
| [32] | 鲁如坤, 2000. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社. |
| LU R K, 2000. Analytical methods for soil agro-chemistry[M]. Beijing: Chinese Agricultural Science and Technology Press. | |
| [33] | 马立锋, 石元值, 韩文炎, 2004. 浙江省茶园土壤锰含量状况研究[J]. 土壤通报, 35(2): 203-206. |
| MA L F, SHI Y Z, HAN W Y, 2004. Manganese concentrations in tea garden soil of Zhejiang province[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 35(2): 203-206. | |
| [34] | 汤帆, 尹兰果, 王瑞, 等, 2013. 两种亚热带土壤中铁锰的淋溶淀积及其对Pb和Cd的吸附特征[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 32(3): 579-586. |
| TANG F, YIN L G, WANG R, et al., 2013. Leaching and deposition of fe and Mn in two subtropical soils and their adsorption characteristics of Pb and Cd[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 32(3): 579-586. | |
| [35] | 谭和平, 陈能武, 黄苹, 等, 2006. 四川茶区土壤营养元素背景值研究[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 12(6): 784-788. |
| TAN H P, CHENG N W, HUANG P, et al., 2006. Background of nutrition elements in tea garden soils in Sichuan province[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 12(6): 784-788. | |
| [36] | 王昌全, 李冰, 龚斌, 等, 2010. 西昌市土壤Fe、Mn、Cu、Zn有效性评价及其影响因素分析[J]. 土壤通报, 41(2): 447-451. |
| WANG C Q, LI B, GONG B, et al., 2010. Study on the bioavailability and impact factors of Fe, Mn, Cu and Zn in the soils of Xichang city[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 41(2): 447-451. | |
| [37] | 魏复盛, 陈静生, 吴燕玉, 等, 1991. 中国土壤环境背景值研究[J]. 环境科学, 12(4): 12-19. |
|
WEI F S, CHENG J S, WU Y Y, et al., 1991. Study on the background contents on 61 elements of soils in China[J]. Environmental Science, 12(4): 12-19.
DOI URL |
|
| [38] | 肖厚军, 何佳芳, 芶久兰, 等, 2013. 贵州省中部黄壤锰形态及其影响因素研究[J]. 土壤通报, 44(5): 1113-1117. |
| XIAO H J, HE G F, GOU J L, et al., 2013. Manganese Form and Its Influencing Factors in Yellow Soils in Guizhou[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 44(5): 1113-1117. | |
| [39] | 谢忠雷, 董德明, 李忠华, 等, 2004. 茶园土壤pH值对茶叶从土壤中吸收锰的影响[J]. 地理科学, 21(3): 278-281. |
| XIE Z L, DONG D M, LI Z H, et al., 2004. Effects of soil pH on the uptake of Mn from soil into the tea leaves[J]. Geographical Science, 21(3): 278-281. | |
| [40] | 谢忠雷, 郭平, 刘鹏, 等, 2007. 茶园土壤锰的形态分布及其影响因素[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 26(2): 645-650. |
| XIE Z L, GUO P, LIU P, et al., 2007. Fractionation and its affecting factors of manganese in tea garden soils[J]. Journal of Agro- Environment Science, 26(2): 645-650. | |
| [41] | 谢学锦, 任天祥, 孙焕振, 2012. 中国地球化学图集[M]. 北京: 地质出版社:135. |
| XIE X J, REN T X, SUN H Z, 2012. Geochemical atlas of China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House:135. | |
| [42] | 谢忠雷, 杨佰玲, 包国章, 等, 2005. 茶园土壤锌的形态分布及其影响因素[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 25(z1): 32-36. |
| XIE Z L, YANG B L, BAO G Z, et al., 2005. Distribution of forms of zinc and its affecting factors in tea garden soils[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 25(z1): 32-36. | |
| [43] | 徐秋桐, 鲍陈燕, 张莉, 等, 2014. 施用富铜锌猪粪对低丘茶园土壤及茶叶重金属积累的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 28(5): 204-208, 214. |
| XU Q T, BAO C Y, ZHANG L, et al., 2014. Effects of copper and zinc-rich pig manure application on accumulation of heavy metals in soil and tea plant of hilly tea garden[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 28(5): 204-208, 214. | |
| [44] | 许泉, 芮雯奕, 刘家龙, 等, 2006. 我国农田土壤碳氮耦合特征的区域差异[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 22(3): 57-60. |
| XU Q, RUI W Y, LIU J L, et al., 2006. Spatial variation of coupling characteristics of soil carbon and nitrogen in farmland of China[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 22(3): 57-60. | |
| [45] | 叶宏萌, 李国平, 郑茂钟, 等, 2017. 武夷山茶园土壤铜、铅和锰形态及茶叶有效性特征[J]. 土壤通报, 48(1): 202-207. |
| YE H M, LI G P, ZHENG M Z, et al., 2017. Fraction distribution and tea bioavailability of Cu, Pb, Mn in soil from Wuyishan Tea Garden[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 48(1): 202-207. | |
| [46] | 于保港, 秦丽, 湛方栋, 等, 2018. 间作对莎草与蚕豆体内铅镉锌化学形态分布的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 37(4): 621-631. |
| YU B G, QIN L, ZHAN F D, et al., 2018. Effects of intercropping on Pb, Cd, and Zn compounds in Cyperus glomeratus and Vicia faba[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 37(4): 621-631. | |
| [47] | 袁程, 王月, 韩晓日, 等, 2012. 长期定位施肥对土壤铁、锰形态及剖面分布的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 18(1): 115-122. |
| YUAN C, WANG Y, HAN X R, et al., 2012. Effects of long-term fertilization on forms of Fe and Mn and their distributions in soil profiles[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 18(1): 115-122. | |
| [48] | 张敏, 陈海, 史琴琴, 等, 2019. 黄土丘陵沟壑区耕层土壤重金属空间分异及影响因素[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 38(11): 2465-2475. |
| ZHANG M, CHENG H, SHI Q Q, et al., 2019. Spatial heterogeneity of heavy metals and influencing factors in the surface cultivated soil of the loesshilly-gully region, China[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 38(11): 2465-2475. | |
| [49] | 赵建, 师华定, 吴啸, 等, 2019. 遵义市土壤锌空间分布特征研究[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 36(3): 298-303. |
| ZHAO J, SHI H D, WU X, et al., 2019. Study on spatial distribution of zinc in soils in Zunyi City, China[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 36(3): 298-303. | |
| [50] | 赵维钧, 2006. 云南土壤锰元素背景值及其特征初探[J]. 中国环境监测, 22(5): 91-94. |
| ZHAO W J, 2006. Preliminary research on background value and characteristics of manganses element in Yunnan Province[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 22(5): 91-94. |
| [1] | YAN Xuejun, HAO Saimei, ZHANG Rongrong, QIN Hua, GAO Sulian, WANG Feng, JIN Xianzhong, SUN Youmin, ZHANG Guiqin. Composition Spectrum and Emission Estimation of VOCs from Furniture Malls [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(6): 1070-1077. |
| [2] | DU Dandan, GAO Ruizhong, FANG Lijing, XIE Longmei. Spatial Variation of Soil Heavy Metals and Their Responses to Physicochemical Factors of Salt Lake Basin in Arid Area [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(6): 1123-1132. |
| [3] | LI Chuanfu, ZHU Taochuan, MING Yufei, YANG Yuxuan, GAO Shu, DONG Zhi, LI Yongqiang, JIAO Shuying. Effect of Organic Fertilizer and Desulphurized Gypsum on Soil Aggregates and Organic Carbon and Its Fractions Contents in the Saline-alkali Soil of the Yellow River Delta [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 878-888. |
| [4] | WANG Chao, YANG Qiannan, ZHANG Chi, LIU Tongxu, ZHANG Xialong, CHEN Jing, LIU Kexue. The Characteristics of Soil Phosphorus Fractions and Their Availability under Different Land Use Types in Danxia Mountain [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 889-897. |
| [5] | CHEN Junfang, WU Xian, LIU Xiaolin, LIU Juan, YANG Jiarong, LIU Yu. Shaping Characteristics of Elemental Stoichiometry on Microbial Diversity under Different Soil Water Contents [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 898-909. |
| [6] | DONG Zhijin, ZHANG Chengchun, ZHAN Xiuli, ZHANG Weifu. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Soil Nutrients of Biological Soil Crusts and Their Underlying Soil of Sandy Land in the East of Yellow River in Ningxia [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 910-919. |
| [7] | XU Xiaoyun, RAO Zhihan, JIANG Hongbin, ZHANG Wei, CHEN Chao, YANG Yongan, HU Yanli, WEI Haichuan. Pollution Characteristics and Formation Potential for O3 and SOA of Ambient VOCs in Suining Industrial Zone in Summer [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 956-968. |
| [8] | ZHOU Qinyuan, DONG Quanmin, Wang Fangcao, LIU Yuzhen, FENG Bin, YANG Xiaoxia, YU Yang, ZHANG Chunping, CAO Quan, LIU Wenting. Effects of Mixed Grazing on Aggregates and Organic Carbon in Rhizosphere Soil of Stellera chamaejasme in Alpine Grassland [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 660-667. |
| [9] | PAN Yuling, QU Xiangning, LI Qing, WANG Lei, WANG Xiaoping, TAN Peng, CUI Geng, AN Yu, TONG Shouzheng. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Soil Physicochemical Factors and Their Response to Microtopography in a Typical Beach Wetland of the Yellow River in Ningxia [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 668-677. |
| [10] | ZHAO Weibin, TANG Li, WANG Song, LIU Lingling, WANG Shufeng, XIAO Jiang, CHEN Guangcai. Improvement Effect of Two Biochars on Coastal Saline-Alkaline Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 678-686. |
| [11] | FENG Shuna, LÜ Jialong, HE Hailong. Effect of KI Leaching on the Hg (Ⅱ) Removal of Loess Soil and the Physicochemical Properties of the Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 776-783. |
| [12] | CHEN Minyi, ZHU Hanghai, SHE Weiduo, YIN Guangcai, HUANG Zuzhao, YANG Qiaoling. Health Risk Assessment and Source Apportionment of Soil Heavy Metals at A Legacy Shipyard Site in Pearl River Delta [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 794-804. |
| [13] | XIA Meijun, LI Jian, YAN Yongcan. Spatial-temporal Patterns and Evolution Characteristics of Ecological Well-being Performance in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 814-824. |
| [14] | ZHANG Lin, QI Shi, ZHOU Piao, WU Bingchen, ZHANG Dai, ZHANG Yan. Study on Influencing Factors of Soil Organic Carbon Content in Mixed Broad-leaved and Coniferous Forests Land in Beijing Mountainous Areas [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 450-458. |
| [15] | QIN Hao, LI Mengai, GAO Jin, CHEN Kailong, ZHANG Yinbo, ZHANG Feng. Composition and Diversity of Soil Bacterial Communities in Shrub at Different Altitudes in Luya Mountain [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 459-468. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
