Ecology and Environment ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (3): 524-534.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.03.011
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Wei1,2,*( ), CHENG Xinyue1
), CHENG Xinyue1
Received:2021-10-21
Online:2022-03-18
Published:2022-05-25
Contact:
WANG Wei
通讯作者:
王薇
作者简介:王薇(1975年生),女,教授,博士,研究方向为建筑技术和人居环境。E-mail: vivi.gan@126.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
WANG Wei, CHENG Xinyue. Analysis of Temporal and Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of PM2.5 and PM10 in Different Functional Street Canyons in Hefei City[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 524-534.
王薇, 程歆玥. 合肥市不同功能街道峡谷PM2.5和PM10时空分布特征及影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 524-534.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.03.011
| 街道峡谷 Street canyon | 商业型 Commerciality | 居住型 Residential | 办公型 Office | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 监测日期 Monitoring date | 2021-08-01 | 2021-08-02 | 2021-08-03 | 2021-08-07 | 2021-08-08 | 2021-08-09 | 2021-08-11 | 2021-08-12 | 2021-08-13 | ||
| 监测地点 Monitoring location | 蜀山区三里庵街道长江西路 | 包河区同安街道马鞍山路 | 庐阳区亳州路街道北一环 | ||||||||
| 长宽比 Aspect ratio | 3.7 | 9.4 | 15 | ||||||||
| 周边建筑 Surrounding buildings | 包括国购广场、之心城、 旺城大厦、官亭路步行街等 | 包括珠光花园、新里海顿公馆、 万振逍遥苑、金地国际城等 | 包括庐阳区政府、置地财富 广场、金鼎国际广场等 | ||||||||
Table 1 Information table of measurement points in different functional streets and canyons
| 街道峡谷 Street canyon | 商业型 Commerciality | 居住型 Residential | 办公型 Office | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 监测日期 Monitoring date | 2021-08-01 | 2021-08-02 | 2021-08-03 | 2021-08-07 | 2021-08-08 | 2021-08-09 | 2021-08-11 | 2021-08-12 | 2021-08-13 | ||
| 监测地点 Monitoring location | 蜀山区三里庵街道长江西路 | 包河区同安街道马鞍山路 | 庐阳区亳州路街道北一环 | ||||||||
| 长宽比 Aspect ratio | 3.7 | 9.4 | 15 | ||||||||
| 周边建筑 Surrounding buildings | 包括国购广场、之心城、 旺城大厦、官亭路步行街等 | 包括珠光花园、新里海顿公馆、 万振逍遥苑、金地国际城等 | 包括庐阳区政府、置地财富 广场、金鼎国际广场等 | ||||||||
| 空气质量指数 Air quality index | 空气质量级别 Air quality grade | 空气质量水平 Air quality level |
|---|---|---|
| AQI≤50 | 一级 | 优 |
| 50<AQI≤100 | 二级 | 良 |
| 100<AQI≤150 | 三级 | 轻度污染 |
| 150<AQI≤200 | 四级 | 中度污染 |
| 200<AQI≤300 | 五级 | 重度污染 |
| AQI>300 | 六级 | 严重污染 |
Table 2 Evaluation standards for air pollutant concentration levels
| 空气质量指数 Air quality index | 空气质量级别 Air quality grade | 空气质量水平 Air quality level |
|---|---|---|
| AQI≤50 | 一级 | 优 |
| 50<AQI≤100 | 二级 | 良 |
| 100<AQI≤150 | 三级 | 轻度污染 |
| 150<AQI≤200 | 四级 | 中度污染 |
| 200<AQI≤300 | 五级 | 重度污染 |
| AQI>300 | 六级 | 严重污染 |
| 空气质量指数 Air quality index | ρ/(μg∙m-3) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0 |
| 50 | 35 |
| 100 | 75 |
| 150 | 115 |
| 200 | 150 |
| 300 | 250 |
| 400 | 350 |
| 500 | 500 |
Table 3 Air quality index limit and mass concentration limit of PM2.5
| 空气质量指数 Air quality index | ρ/(μg∙m-3) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0 |
| 50 | 35 |
| 100 | 75 |
| 150 | 115 |
| 200 | 150 |
| 300 | 250 |
| 400 | 350 |
| 500 | 500 |
| PM2.5质量浓度 PM2.5 mass concentration | PM10质量浓度 PM10 mass concentration | 空气温度 Air temperature | 相对湿度 relative humidity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 相关系数Correlation coefficient | 0.993** | -0.289** | 0.407** |
Table 4 Correlation coefficient between the mass concentration of PM2.5 and PM10 in the street canyon and the environmental factor Person
| PM2.5质量浓度 PM2.5 mass concentration | PM10质量浓度 PM10 mass concentration | 空气温度 Air temperature | 相对湿度 relative humidity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 相关系数Correlation coefficient | 0.993** | -0.289** | 0.407** |
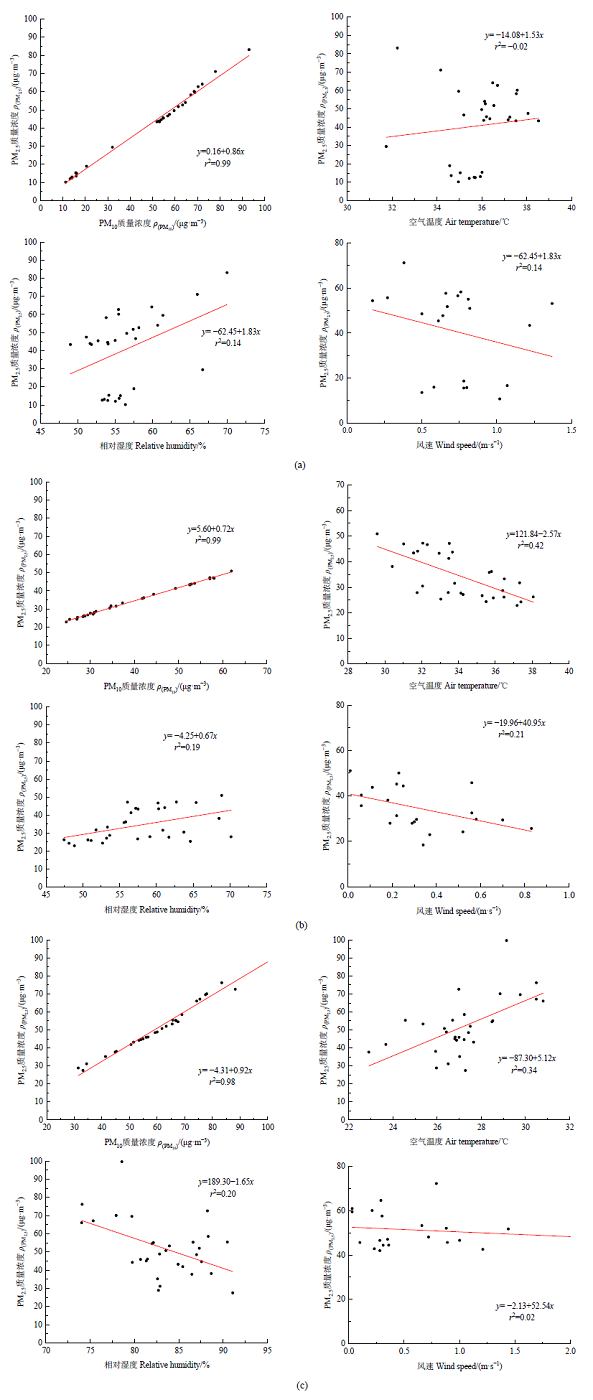
Figure 6 Correlation analysis of PM2.5 and PM10 mass concentrations and environmental factors in commercial (a), residential (b) and office street canyons (c)
| 街道峡谷类型 Street canyon type | 选点位置 Select point position | PM2.5 | PM10 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ρ(PM2.5)/ (μg∙m-3) | AQI | 空气质量水平 Air quality level | 空气质量级别 Air quality grade | ρ(PM10)/ (μg∙m-3) | AQI | 空气质量水平 Air quality level | 空气质量级别 Air quality grade | |||
| 办公型 Office | A | 39.28 | 55.35 | 良 | 二级 | 46.15 | 63.94 | 良 | 二级 | |
| B | 40.38 | 56.73 | 良 | 二级 | 46.92 | 64.90 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| C | 41.42 | 58.03 | 良 | 二级 | 49.63 | 68.29 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| D | 49.38 | 67.98 | 良 | 二级 | 55.10 | 75.13 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| E | 42.48 | 59.35 | 良 | 二级 | 49.54 | 68.18 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| F | 39.45 | 55.56 | 良 | 二级 | 43.70 | 60.88 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| G | 33.18 | 47.40 | 优 | 一级 | 40.43 | 56.79 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| 平均 | 40.80 | 57.25 | 良 | 二级 | 47.35 | 65.44 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| 居住型 Residential | A | 32.16 | 45.94 | 优 | 一级 | 37.01 | 52.51 | 良 | 二级 | |
| B | 42.38 | 59.23 | 良 | 二级 | 51.20 | 70.25 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| C | 34.81 | 49.73 | 优 | 一级 | 40.71 | 57.14 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| D | 37.42 | 53.03 | 良 | 二级 | 42.84 | 59.80 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| E | 33.62 | 48.03 | 优 | 一级 | 38.79 | 54.74 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| F | 33.98 | 48.54 | 优 | 一级 | 37.47 | 53.09 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| G | 26.47 | 37.81 | 优 | 一级 | 30.98 | 44.26 | 优 | 一级 | ||
| 平均 | 34.41 | 49.16 | 优 | 一级 | 39.86 | 56.08 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| 商业型 Commerciality | A | 50.91 | 69.89 | 良 | 二级 | 60.49 | 81.86 | 良 | 二级 | |
| B | 51.87 | 71.09 | 良 | 二级 | 60.45 | 81.81 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| C | 50.66 | 62.53 | 良 | 二级 | 59.36 | 80.45 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| D | 53.76 | 73.45 | 良 | 二级 | 61.90 | 83.63 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| E | 55.90 | 76.13 | 良 | 二级 | 65.39 | 87.99 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| F | 49.79 | 68.49 | 良 | 二级 | 58.45 | 79.31 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| G | 45.91 | 63.64 | 良 | 二级 | 56.76 | 77.20 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| 平均 | 51.26 | 70.33 | 良 | 二级 | 60.40 | 81.75 | 良 | 二级 | ||
Table 5 Evaluation of air quality in different functional streets and valleys
| 街道峡谷类型 Street canyon type | 选点位置 Select point position | PM2.5 | PM10 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ρ(PM2.5)/ (μg∙m-3) | AQI | 空气质量水平 Air quality level | 空气质量级别 Air quality grade | ρ(PM10)/ (μg∙m-3) | AQI | 空气质量水平 Air quality level | 空气质量级别 Air quality grade | |||
| 办公型 Office | A | 39.28 | 55.35 | 良 | 二级 | 46.15 | 63.94 | 良 | 二级 | |
| B | 40.38 | 56.73 | 良 | 二级 | 46.92 | 64.90 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| C | 41.42 | 58.03 | 良 | 二级 | 49.63 | 68.29 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| D | 49.38 | 67.98 | 良 | 二级 | 55.10 | 75.13 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| E | 42.48 | 59.35 | 良 | 二级 | 49.54 | 68.18 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| F | 39.45 | 55.56 | 良 | 二级 | 43.70 | 60.88 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| G | 33.18 | 47.40 | 优 | 一级 | 40.43 | 56.79 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| 平均 | 40.80 | 57.25 | 良 | 二级 | 47.35 | 65.44 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| 居住型 Residential | A | 32.16 | 45.94 | 优 | 一级 | 37.01 | 52.51 | 良 | 二级 | |
| B | 42.38 | 59.23 | 良 | 二级 | 51.20 | 70.25 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| C | 34.81 | 49.73 | 优 | 一级 | 40.71 | 57.14 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| D | 37.42 | 53.03 | 良 | 二级 | 42.84 | 59.80 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| E | 33.62 | 48.03 | 优 | 一级 | 38.79 | 54.74 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| F | 33.98 | 48.54 | 优 | 一级 | 37.47 | 53.09 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| G | 26.47 | 37.81 | 优 | 一级 | 30.98 | 44.26 | 优 | 一级 | ||
| 平均 | 34.41 | 49.16 | 优 | 一级 | 39.86 | 56.08 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| 商业型 Commerciality | A | 50.91 | 69.89 | 良 | 二级 | 60.49 | 81.86 | 良 | 二级 | |
| B | 51.87 | 71.09 | 良 | 二级 | 60.45 | 81.81 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| C | 50.66 | 62.53 | 良 | 二级 | 59.36 | 80.45 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| D | 53.76 | 73.45 | 良 | 二级 | 61.90 | 83.63 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| E | 55.90 | 76.13 | 良 | 二级 | 65.39 | 87.99 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| F | 49.79 | 68.49 | 良 | 二级 | 58.45 | 79.31 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| G | 45.91 | 63.64 | 良 | 二级 | 56.76 | 77.20 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| 平均 | 51.26 | 70.33 | 良 | 二级 | 60.40 | 81.75 | 良 | 二级 | ||
| [1] |
AHMADI M, MIRJALILY S, OLOOMI S, 2020. Simulation of pollutant dispersion in urban street canyons using hybrid rans-les method with two-phase model[J]. Computers and Fluids, DOI: 10.1016/j.compfluid.2020.104676.
DOI |
| [2] |
HUANG M H, HUANG Y, CAO J J, et al., 2021. Study on mitigation of automobile exhaust pollution in an urban street canyon: Emission reduction and air cleaning street lamps[J]. Building and Environment, DOI: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2021.107651.
DOI |
| [3] | MESZAROS D, MARKOS J, FITZGERALD D G, et al., 2015. An observational study of PM10 and hospital admissions for acute exacerbations of chronic respiratory disease in Tasmania, Australia 1992-2002 [J]. BMJ Open Respiratory Research, 2(1): 1-8. |
| [4] |
MIAO C P, YU S, HU Y M, et al., 2020. How the morphology of urban street canyons affects suspended particulate matter concentration at the pedestrian level: An in-situ investigation[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, DOI: /10.1016/j.scs.2020.102042.
DOI |
| [5] | NICHOLSON S E, 1975. A pollution model for street-level air[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 9(1): 19-31. |
| [6] |
RUAN T C, RIM D Y, 2019. Indoor air pollution in office buildings in mega-cities: Effects of filtration efficiency and outdoor air ventilation rates[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, DOI: 10.1016/j.scs.2019.101609.
DOI |
| [7] |
SHE Q N, CHOI M, BELLE J, et al., 2020. Satellite-based estimation of hourly PM2.5 levels during heavy winter pollution episodes in the Yangtze River Delta, China[J]. Chemosphere, DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124678.
DOI |
| [8] | 安永碳中和课题组, 2021. 一本书读懂碳中和[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社: 124-131. |
| Ernst & Young Carbon Neutrality Research Group, 2021. Understanding Carbon Neutrality in a Book[M]. Beijing: Machinery Industry Press: 124-131. | |
| [9] | 陈岚琪, 夏铧, 张习文, 等, 2020. 郑州市道路网络结构特征对大气颗粒物污染的影响及尺度效应[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(3): 562-568. |
| CHEN L Q, XIA H, ZHANG X W, et al., 2020. Scale-dependent effects of structural characteristics of road network on particulate matters pollution in Zhengzhou[J]. Journal of Ecological Environment, 29(3): 562-568. | |
| [10] | 邓寄豫, 郑炘, 2017. 街区层峡几何形态与微气候的关联性研究[J]. 建筑与文化, 14(5): 212-213. |
| DENG J Y, ZHENG X, 2017. Research on the correlation between the geometric forms of the strata and the microclimate in the block[J]. Architecture and Culture, 14(5): 212-213. | |
| [11] | 刁贝娣, 丁镭, 成金华, 2021. 不同类型城市的PM2.5健康风险及影响因素差异[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 31(8): 90-100. |
| DIAO B D, DING L, CHENG J H, 2021. PM2.5 health risks and influencing factors differences in different types of cities[J]. China Population·Resources and Environment, 31(8): 90-100. | |
| [12] | 高嵩, 田蓉, 郭彬, 等, 2018. 长三角典型城市PM2.5浓度变化特征及与气象要素的关系[J]. 科学技术与工程, 18(9): 142-155. |
| GAO S, TIAN R, GUO B, et al., 2018. The characteristics of PM2.5 concentration changes in typical cities in the Yangtze River Delta and its relationship with meteorological elements[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 18(9): 142-155. | |
| [13] | 葛晓燕, 2018. 城市典型街谷道路中污染物扩散特征模拟[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学: 29-56. |
| GE X Y, 2018. Simulation of the diffusion characteristics of pollutants in typical urban street-valley roads[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology:29-56. | |
| [14] | 合肥市生态环境局, 2021. 2020年合肥市环境状况公报[N/OL]. (2021-06-04) [2021-06-04]. http://sthjj.hefei.gov.cn/hbzx/gsgg/18085969.html. |
| Hefei Ecological Environment Bureau, 2021.2020 Hefei Environmental Status Bulletin[N/OL]. (2021-06-04) [2021-06-04]. http://sthjj.hefei.gov.cn/hbzx/gsgg/18085969.html. | |
| [15] | 黄润秋, 2021. 生态环境部部长黄润秋国新办新闻发布会答记者问[N/OL].(2021-08-18) [2021-08-18]. http://www.mee.gov.cn/ywdt/zbft/202108/t20210818_858184.shtml. |
| HUANG R Q, 2021. Minister of the Ministry of Ecology and Environment Huang Runqiu answered reporters' questions at the press conference of the new office[N/OL].(2021-08-18) [2021-08-18]. http://www.mee.gov.cn/ywdt/zbft/202108/t20210818_858184.shtml. | |
| [16] | 李克强, 2021. 2021年政府工作报告[N/OL].(2021-03-05) [2021-03-05]. http://www.gov.cn/zhuanti/2021lhzfgzbg/index.htm. |
| LI K Q, 2021. 2021 Government Work Report[N/OL].(2021-03-05) [2021-03-05]. http://www.gov.cn/zhuanti/2021lhzfgzbg/index.htm. | |
| [17] | 李绥, 杨二东, 石铁矛, 等, 2014. 商业街区可吸入颗粒物空间分布及其气象要素的相关性[J]. 沈阳建筑大学学报 (自然科学版), 30(5): 923-930. |
| LI S, YANG E D, SHI T M, et al., 2014. The spatial distribution of inhalable particulate matter in commercial blocks and the correlation between meteorological factors[J]. Journal of Shenyang Jianzhu University (Natural Science Edition), 30(5): 923-930. | |
| [18] | 刘超, 金梦怡, 朱星航, 等, 2021. 多尺度时空PM2.5分布特征、影响要素、方法演进的综述及城市规划展望[J]. 西部人居环境学刊, 36(4): 9-18. |
| LIU C, JIN M Y, ZHU X H, et al., 2021. A review of multi-scale spatiotemporal PM2.5 distribution characteristics, influencing factors, method evolution and urban planning prospects[J]. Western Human Settlements and Environment Journal, 36(4): 9-18. | |
| [19] | 刘晴, 高鹏, 李成, 等, 2019. 泰安市典型生态功能区空气负离子的时空分布及影响因素分析[J]. 环境化学, 38(1): 169-176. |
| LIU Q, GAO P, LI C, et al., 2019. Spatial-temporal distribution and influencing factors of negative air ions in typical ecological function areas in Tai'an City[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 38(1): 169-176. | |
| [20] | 生态环境部, 2018. 关于发布《环境空气质量标准》(GB 3095-2012)修改单的公告[N/OL].(2021-06-04) [2021-06-04]. http://www.mee.gov.cn/gkml/sthjbgw/sthjbgg/201808/t20180815_451398.htm. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment, 2018. Announcement on the issuance of amendments to “Ambient Air Quality Standards” (GB 3095-2012)[N/OL].(2021-06-04) [2021-06-04]. http://www.mee.gov.cn/gkml/sthjbgw/sthjbgg/201808/t20180815_451398.htm. | |
| [21] | 孙金龙, 黄润秋, 2021. 坚持以习近平生态文明思想为指引深入打好污染防治攻坚战[J]. 环境保护, 49(23): 8-9. |
| SUN J L, HUANG R Q, 2021. Adhere to Xi Jinping's ecological civilization thought as the guide to fight the tough battle of pollution prevention and control[J]. Environmental Protection, 49(23): 8-9. | |
| [22] | 王宝民, 柯咏东, 桑建国, 2005. 城市街谷大气环境研究进展[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 41(1): 146-153. |
| WANG B M, KE Y D, SANG J G, 2005. Research progress of atmospheric environment in urban street canyons[J]. Journal of Peking University (Natural Science Edition), 41(1): 146-153. | |
| [23] | 王佳佳, 夏晓圣, 程先富, 等, 2020. 合肥市PM2.5浓度时空分布特征及影响因素分析[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 29(6): 1413-1421. |
| WANG J J, XIA X S, CHENG X F, et al., 2020. Analysis of the temporal and spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of PM2.5 concentration in Hefei City[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 29(6): 1413-1421. | |
| [24] | 王薇, 程歆玥, 2021a. 室内垂直绿墙对环境因子时空分布特征影响[J]. 中国城市林业, 19(5): 53-59, 82. |
| WANG W, CHENG X Y, 2021. Influence of indoor vertical green walls on spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of environmental factors[J]. China Urban Forestry, 19(5): 53-59, 82. | |
| [25] | 王薇, 程歆玥, 胡春, 等, 2021b. 城市街道峡谷PM2.5时空分布特征与空气质量评价--以合肥市长淮街道为例[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(11): 2157-2164. |
| WANG W, CHENG X Y, HU C, et al., 2021. Spatio-temporal distribution characteristics of PM2.5 and air quality evaluation in urban street canyons: Take Changhuai street in Hefei as an example[J]. Journal of Ecological Environment, 30(11): 2157-2164. | |
| [26] | 王薇, 夏斯涵, 张蕾, 2021c. 基于ENVI-met的高密度城市住区空间PM2.5分布模拟研究[J]. 住宅科技, 41(11): 29-34. |
| WANG W, XIA S H, ZHANG L, 2021. Simulation of PM2.5 distribution in high-density urban residential areas based on ENVI-met[J]. Housing Science and Technology, 41(11): 29-34. | |
| [27] | 王薇, 张蕾, 2021d. 基于CiteSpace的城市环境中细颗粒物研究进展的可视化分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(6): 1321-1332. |
| WANG W, ZHANG L, 2021. Visual analysis of research progress of fine particles in urban environment based on CiteSpace[J]. Journal of Ecological Environment, 30(6): 1321-1332. | |
| [28] | 吴凌云, 谢军飞, 张欣, 2021. 冬季采暖优化对北京地区空气质量的影响[J]. 气候与环境研究, 26(4): 391-402. |
| WU L Y, XIE J F, ZHANG X, 2021. The influence of winter heating optimization on air quality in Beijing[J]. Climatic and Environmental Research, 26(4): 391-402. | |
| [29] | 夏斯涵, 2021. 基于细颗粒物模拟的高层高密度城市住区空间形态研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽建筑大学. |
| XIA S H, 2021. Research on the spatial morphology of high-rise and high-density urban settlements based on simulation of fine particles[D]. Hefei: Anhui University of Architecture and Architecture. | |
| [30] | 闫秀婧, 2009. 青岛市森林与湿地负离子水平时空分布研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学: 13-14. |
| YAN X J, 2009. Research on the temporal and spatial distribution of negative ion levels in forests and wetlands in Qingdao[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University: 13-14. | |
| [31] | 于洋, 刘晓宇, 田达睿, 等, 2020. 街道峡谷几何形态规划要素对太阳能潜力的影响研究[J]. 工业建筑, 50(7): 137-142. |
| YU Y, LIU X Y, TIAN D R, et al., 2020. Research on the influence of street canyon geometry planning elements on solar energy potential[J]. Industrial Architecture, 50(7): 137-142. | |
| [32] | 张丹龙, 方凤满, 姚有如, 等, 2016. 淮南市不同功能区叶面尘和地表灰尘中重金属分布特征、来源及健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学学报, 36(9): 3322-3332. |
| ZHANG D L, FANG F M, YAO Y R, et al., 2016. Distribution characteristics, sources and health risk assessment of heavy metals in leaf dust and surface dust in different functional areas of Huainan City[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 36(9): 3322-3332. | |
| [33] | 周洪昌, 杨佩昆, 高延令, 1994. 城市街道汽车排放物扩散过程的风洞试验[J]. 同济大学学报 (自然科学版), 39(3): 306-311. |
| ZHOU H C, YANG P K, GAO Y L, 1994. Wind tunnel test on the diffusion process of vehicle emissions from urban streets[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science Edition), 39(3): 306-311. |
| [1] | DONG Jiefang, DENG Chun, ZHANG Zhongwu. Spatio-temporal Evolution and Population Exposure Risk to PM2.5 in the Weihe River Basin [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(6): 1078-1088. |
| [2] | LI Jianhui, DANG Zheng, CHEN Lin. Spatial-temporal Characteristics of PM2.5 and Its Influencing Factors in the Yellow River Jiziwan Metropolitan Area [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 697-705. |
| [3] | ZHANG Li, LI Cheng, TAN Haoze, WEI Jiayi, CHENG Jiong, PENG Guixiang. Reduction Effect and Influencing Factors of Typical Urban Woodlands on Atmospheric Particulate Matter in Guangzhou [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(2): 341-350. |
| [4] | JIANG Ming, ZHANG Ziyang, LI Tingting, LIN Boji, ZHANG Zhengen, LIAO Tong, YUAN Luan, PAN Suhong, LI Jun, ZHANG Gan. Source Apportionment of Ammonium in Atmospheric PM2.5 in the Pearl River Delta Based on Nitrogen Isotope [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(9): 1840-1848. |
| [5] | WEI Xiaofeng, HAN Hong, YAN Xuejun, WANG Zaifeng, LI Shengzeng, TIAN Yong, LIANG Di, MA Mingliang, ZHANG Guiqin. Source Apportionment of PM2.5 during Heavy Pollution Process in Ji'nan Based on Satellite Remote Sensing and CMB Model [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(6): 1175-1183. |
| [6] | HAO Yongpei, SONG Xiaowei, ZHAO Wenjun, XIANG Famin. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Air Pollution and Correlation Factors in Fenwei Plain [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 512-523. |
| [7] | ZHAO Rui, ZHAN Liping, ZHOU Liang, ZHANG Junke. Identification of Driving Factors of PM2.5 Based on Geographic Detector Combined with Geographically Weighted Ridge Regression [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(2): 307-317. |
| [8] | JIANG Bin, CHEN Duohong, ZHANG Tao, YUAN Luan, ZHOU Yan, SHEN Jing, ZHANG Chunlin, WANG Boguang. Characteristics and Sources of Carbonaceous Aerosols during the Crop Straw Burning Seasons in Southern China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(12): 2358-2366. |
| [9] | XING Ran, SHEN Guofeng, CHENG Hefa, TAO Shu. Changes of Residential Energy Structure and Regional Pollutant Emissions in Rural Areas of Northeast China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(12): 2367-2373. |
| [10] | WU Zhaoliang, JIN Min. Review and Evidence of the Impacts of Air Pollution on Social Economic Behaviors of Chinese Residents [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(11): 2251-2262. |
| [11] | LI Shengzeng, HAO Saimei, TAN Luyao, ZHANG Huaicheng, XU Biao, GU Shumao, PAN Guang, WANG Shuyan, YAN Huaizhong, ZHANG Guiqin. Characteristics of Spatiotemporal Variation, and Factors Influencing Secondary Components in PM2.5 in Ji'nan [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(1): 100-109. |
| [12] | WANG Wei, CHENG Xinyue, HU Chun, XIA Sihan, WANG Tian. Spatio-temporal Distribution Characteristics of PM2.5 and Air Quality Evaluation in Urban Street Canyons: Take Changhuai Street in Hefei as An Example [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(11): 2157-2164. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
