Ecology and Environment ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (3): 512-523.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.03.010
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
HAO Yongpei1,2( ), SONG Xiaowei1,*(
), SONG Xiaowei1,*( ), ZHAO Wenjun3, XIANG Famin4
), ZHAO Wenjun3, XIANG Famin4
Received:2021-11-14
Online:2022-03-18
Published:2022-05-25
Contact:
SONG Xiaowei
郝永佩1,2( ), 宋晓伟1,*(
), 宋晓伟1,*( ), 赵文珺3, 向发敏4
), 赵文珺3, 向发敏4
通讯作者:
宋晓伟
作者简介:郝永佩(1986年生),女,讲师,博士,研究方向为区域污染防治。E-mail: haoyongpei@sxufe.edu.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
HAO Yongpei, SONG Xiaowei, ZHAO Wenjun, XIANG Famin. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Air Pollution and Correlation Factors in Fenwei Plain[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 512-523.
郝永佩, 宋晓伟, 赵文珺, 向发敏. 汾渭平原大气污染时空分布及相关因子分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 512-523.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.03.010
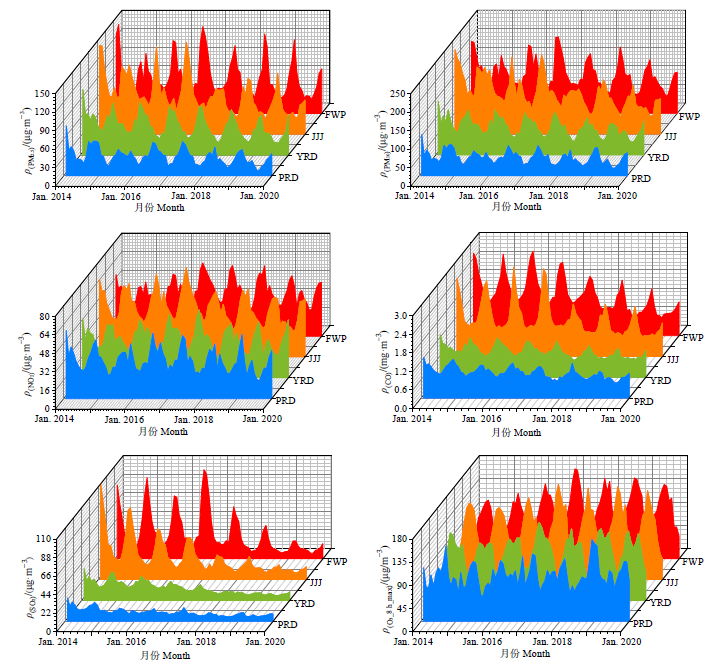
Figure 5 Monthly variations of air pollutants in four regions of China in 2014-2020 PRD, YRD, JJJ, and FWP represents Pearl River Delta, Yangtze River Delta, Jing-Jin-Ji, and Fenwei Plain, respectively
| 年份 Year | 莫兰指数 Moran's I | T值 T value | 热点 Hot spot | 冷点 Cold spot |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 0.289 | 3.214 | ||
| 2015 | 0.391 | 4.412 | 洛阳 | |
| 2016 | 0.587 | 6.723 | 咸阳、西安 | 宝鸡 |
| 2017 | 0.761 | 8.042 | 西安、咸阳、临汾 | 宝鸡、铜川 |
| 2018 | 0.714 | 8.665 | 西安、咸阳、临汾 | 宝鸡、铜川 |
| 2019 | 0.703 | 4.574 | 西安、咸阳、临汾 | 宝鸡、铜川、吕梁 |
| 2020 | 0.698 | 4.051 | 西安、咸阳、临汾 | 宝鸡、铜川、吕梁 |
Table 1 AQI spatial autocorrelation analysis of Fenwei Plain in different years
| 年份 Year | 莫兰指数 Moran's I | T值 T value | 热点 Hot spot | 冷点 Cold spot |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 0.289 | 3.214 | ||
| 2015 | 0.391 | 4.412 | 洛阳 | |
| 2016 | 0.587 | 6.723 | 咸阳、西安 | 宝鸡 |
| 2017 | 0.761 | 8.042 | 西安、咸阳、临汾 | 宝鸡、铜川 |
| 2018 | 0.714 | 8.665 | 西安、咸阳、临汾 | 宝鸡、铜川 |
| 2019 | 0.703 | 4.574 | 西安、咸阳、临汾 | 宝鸡、铜川、吕梁 |
| 2020 | 0.698 | 4.051 | 西安、咸阳、临汾 | 宝鸡、铜川、吕梁 |
| 气象因子 Meteorological factors | PM2.5 | PM10 | NO2 | CO | SO2 | O3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 气温 Air temperature | -0.455** | -0.384** | -0.435** | -0.439** | -0.424** | 0.728** |
| 相对湿度 Relative humidity | 0.073** | -0.119** | -0.114** | 0.011* | -0.251** | -0.175** |
| 气压 Air pressure | 0.191** | 0.181** | 0.179** | 0.247** | 0.142** | -0.247** |
| 降水 Precipitation | -0.109** | -0.167** | -0.171** | -0.073** | -0.129** | -0.036** |
| 风速 Wind velocity | -0.131** | -0.069** | 0.003* | -0.105** | 0.000* | 0.201** |
| 日照时数 Sunshine duration | -0.069** | -0.035** | -0.011* | -0.043** | 0.015* | 0.025** |
Table 2 Correlations of main pollutants with meteorological factors in Fenwei Plain
| 气象因子 Meteorological factors | PM2.5 | PM10 | NO2 | CO | SO2 | O3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 气温 Air temperature | -0.455** | -0.384** | -0.435** | -0.439** | -0.424** | 0.728** |
| 相对湿度 Relative humidity | 0.073** | -0.119** | -0.114** | 0.011* | -0.251** | -0.175** |
| 气压 Air pressure | 0.191** | 0.181** | 0.179** | 0.247** | 0.142** | -0.247** |
| 降水 Precipitation | -0.109** | -0.167** | -0.171** | -0.073** | -0.129** | -0.036** |
| 风速 Wind velocity | -0.131** | -0.069** | 0.003* | -0.105** | 0.000* | 0.201** |
| 日照时数 Sunshine duration | -0.069** | -0.035** | -0.011* | -0.043** | 0.015* | 0.025** |
| [1] |
ADAME J A, NOTARIO A, VILLANUEVA F, et al., 2012. Application of cluster analysis to surface ozone, NO2 and SO2 daily patterns in an industrial area in Central-Southern Spain measured with a DOAS system[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 429: 281-291.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
FAN H, ZHAO C F, YANG Y K, 2020. A comprehensive analysis of the spatio-temporal variation of urban air pollution in China during 2014-2018 [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 220: 117066.
DOI URL |
| [3] | KAISE R J, 2005. Epidemiology: Mounting evidence indicts fine-particle pollution[J]. Science, 307(5717): 1858-1861. |
| [4] |
LEE B K, LEE H K, JUN N Y, 2006. Analysis of regional and temporal characteristics of PM10 during an Asian dust episode in Korea[J]. Chemosphere, 63(7): 1106-1115.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
LEE H L, GU M J, KIM Y J, et al., 2012. First-time remote sensing of NO2 vertical distributions in an urban street canyon using Topographic Target Light scattering Differential Optical Absorption Spectroscopy (ToTaL-DOAS)[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 54: 519-528.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
LI L, LU C, CHAN P W, et al., 2020. Tower observed vertical distribution of PM2.5, O3 and NOx in the Pearl River Delta[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 220: 117083.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
MA X Y, JIA H L, SHA T, et al., 2019. Spatial and seasonal characteristics of particulate matter and gaseous pollution in China: Implications for control policy[J]. Environmental Pollution, 248: 421-428.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
MENG Z Y, XU X B, WANG T, et al., 2010. Ambient sulfur dioxide,nitrogen dioxide, and ammonia at ten background and rural sites in China during 2007-2008 [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 44(21-22): 2625-2631.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
SHAO M, TANG X Y, ZHANG Y H, et al., 2006. City clusters in China: Air and surface water pollution[J]. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 4(7): 353-361.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
WANG Y G, YING Q, HU J L, et al., 2014. Spatial and temporal variations of six criteria air pollutants in 31 provincial capital cities in China during 2013-2014 [J]. Environment International, 73: 413-422.
DOI URL |
| [11] | XU W J, ZENG Z T, XU Z Y, et al., 2020. Public health benefits of optimizing urban industrial land layout - The case of Changsha, China[J]. Environment International, 263(Part B): 114388. |
| [12] |
ZHAO H, ZHENG Y F, LI C, 2018. Spatiotemporal distribution of PM2.5 and O3 and their interaction during the summer and winter seasons in Beijing, China[J]. Sustainability, 10(12): 4519.
DOI URL |
| [13] | 曹宁, 黄学敏, 祝颖, 等, 2019. 西安冬季重污染过程PM2.5理化特征及来源解析[J]. 中国环境科学, 39(1): 32-39. |
| CAO N, HUANG X M, ZHU Y, et al., 2019. Pollution characteristics and source apportionment of fine particles during a heavy pollution in winter in Xi'an City[J]. China Environmental Science, 39(1): 32-39. | |
| [14] | 贺冉冉, 朱兰保, 周开胜, 2017. 基于时间序列模型残差的中国东部地区空气质量指数 (AQI) 空间自相关特征分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 37(7): 2459-2467. |
| HE R R, ZHU L B, ZHOU K S, 2017. Spatial autocorrelation analysis of air quality index (AQI) in eastern China based on residuals of time series models[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 37(7): 2459-2467. | |
| [15] | 胡琳, 程路, 王琦, 等, 2021. 西安近地面臭氧浓度特征及关键气象因子分析[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 35(6): 102-109. |
| HU L, CHENG L, WANG Q, et al., 2021. Analysis of ozone concentration characteristics and key meteorological factors in Xi' an[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 35(6): 102-109. | |
| [16] | 环境保护部, 国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 2012. 环境空气质量标准: GB 3095-2012[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社. |
| Ministry of Environmental Protection, General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine, 2012. Ambient air quality standards: GB 309-2012[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Press. | |
| [17] | 黄晓军, 祁明月, 李艳雨, 等, 2020. 关中地区PM2.5时空演化及人口暴露风险[J]. 环境科学, 41(12): 5245-5255. |
|
HUANG X J, QI M Y, LI Y Y, et al., 2020. Spatio-temporal evolution and population exposure risk to PM2.5 in the Guanzhong area[J]. Environmental Science, 41(12): 5245-5255.
DOI URL |
|
| [18] | 贾小芳, 颜鹏, 孟昭阳, 等, 2019. 2016年11-12月北京及周边重污染过程PM2.5特征[J]. 应用气象学报, 30(3): 302-315. |
| JIA X F, YAN P, MENG Z Y, et al., 2019. Characteristics of PM2.5 in heavy pollution events in Beijing and surrounding areas from November to December in 2016[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 30(3): 302-315. | |
| [19] | 蒋超, 龚建周, 孙家仁, 等, 2018. 2013-2016年珠三角地区PM2.5分布时空演变[J]. 生态环境学报, 27(9): 1698-1705. |
| JIANG C, GONG J Z, SUN J R, et al., 2018. Spatial-temporal evolution of PM2.5 distribution in Pearl River Delta Region in 2013-2016 [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 27(9): 1698-1705. | |
| [20] | 刘超, 花丛, 康志明, 2017. 2014-2015年上海地区冬夏季大气污染特征及其污染源分析[J]. 气象, 43(7): 823-830. |
| LIU C, HUA C, KANG Z M, 2017. Characteristics of air pollution and its resources during winter and summer seasons of 2014 and 2015 in Shanghai[J]. Meteorological Minthly, 43(7): 823-830. | |
| [21] | 宁贵财, 2018. 四川盆地西北部城市群冬季大气污染气象成因及其数值模拟研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学. |
| NING G C, 2018. Meteorological causes of air pollution in the northwest urban agglomeration of Sichuan basin in winter and their numerical simulation[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University. | |
| [22] | 彭玏, 赵媛媛, 赵吉麟, 等, 2019. 京津冀大气污染传输通道区大气污染时空格局研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 39(2): 449-458. |
| PENG L, ZHAO Y Y, ZHAO J L, et al., 2019. Spatiotemoral patterns of air pollution in air pollution transmission channel of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei from 2000 to 2015 [J]. China Environmental Science, 39(2): 449-458. | |
| [23] | 秦卓凡, 廖宏, 陈磊, 等, 2021. 汾渭平原空气质量及气象要素对其日变化和年际变化的影响[J]. 大气科学, 45(6): 1273-1291. |
| QIN Z F, LIAO H, CHEN L, et al., 2021. Fenwei Plain air quality and the dominant meteorological parameters for its daily and interannual variations[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 45(6): 1273-1291. | |
| [24] | 沈楠驰, 周丙锋, 李珊珊, 等, 2020. 2015-2019年天津市大气污染物时空变化特征及成因分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(9): 1862-1873. |
| SHEN N C, ZHOU B F, LI S S, et al., 2020. Temporal and spatial variation characteristics and origin analysis of air pollutants in Tianjin from 2015 to 2019 [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 29(9): 1862-1873. | |
| [25] | 谢蓉, 2017. 中国大气环境PM2.5健康影响的时空变化趋势研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学. |
| XIE R, 2017. Study on the long-term trend and spatial pattern of Premature deaths attributable to ambient PM2.5 in China[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University. | |
| [26] | 解淑艳, 霍晓芹, 曾凡刚, 等, 2021. 2015-2019年汾渭平原臭氧污染状况分析[J]. 中国环境监测, 37(1): 49-57. |
| XIE S Y, HUO X Q, ZENG F G, et al., 2021. Analysis of ozone pollution in Fenwei Plain from 2015 to 2019 [J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 37(1): 49-57. | |
| [27] | 谢杨, 戴瀚程, 花岡達也, 等, 2016. PM2.5污染对京津冀地区人群健康影响和经济影响[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 26(11): 19-27. |
| XIE Y, DAI H C, HANAOKA T, et al., 2016. Health and economic impacts of PM2.5 pollution in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Area[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 26(11): 19-27. | |
| [28] | 徐维超, 2012. 相关系数研究综述[J]. 广东工业大学学报, 29(3): 12-17. |
| [29] | XU W C, 2012. A review on correlation coefficients[J]. Journal of Guangdong University of Technology, 29(3): 12-17. |
| [30] | 张晶, 朱兆洲, 李绪威, 等, 2019. 煤改气后天津市采暖期大气污染特征的时空分布研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(2): 324-331. |
| ZHANG J, ZHU Z Z, LI X W, et al., 2019. Spatial and temporal distribution of atmospheric pollutants in Tianjin during winter heating period after the “coal to gas” project[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 28(2): 324-331. | |
| [31] | 张小娟, 李莉, 王红丽, 等, 2019. 2010-2016年上海城区臭氧长时间序列变化特征初探[J]. 环境科学学报, 39(1): 86-94. |
| ZHANG X J, LI L, WANG H L, et al., 2019. Preliminary study on the long-term trends of ozone in urban Shanghai from 2010 to 2016 [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 39(1): 86-94. | |
| [32] | 赵辉, 郑有飞, 张誉馨, 等, 2020. 京津冀大气污染的时空分布与人口暴露[J]. 环境科学学报, 40(1): 1-12. |
| ZHAO H, ZHENG Y F, ZHANG Y X, et al., 2020. Spatiotemporal distribution and population exposure of air pollution in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 40(1): 1-12. | |
| [33] | 周骥, 孙庆华, 许建明, 等, 2018. 上海地区不同PM2.5污染过程对炎症应激影响的差异性[J]. 气象, 44(12): 1612-1617. |
| ZHOU J, SUN Q H, XU J M, et al., 2018. Effects of different PM2.5 pollution processes on inflammatory stress in Shanghai area[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 44(12): 1612-1617. |
| [1] | DU Caiyan, YANG Peng, FENG Shuxian, MAO Yanting, TAO Qiong, CI Zhulamu, PENG Huiping, HE Jianmei, LI Weilin. Correlation between Quality and Ecological Factors of Weixi Glutinous Yam in Different Ecological Regions [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(6): 1053-1061. |
| [2] | DONG Jiefang, DENG Chun, ZHANG Zhongwu. Spatio-temporal Evolution and Population Exposure Risk to PM2.5 in the Weihe River Basin [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(6): 1078-1088. |
| [3] | ZHANG Lu, HE Yufei, CHEN Tan, YANG Ting, ZHANG Bing, JIN Jun. The Spatial and Temporal Pattern Evolution of Carbon Footprint of Farmland Ecosystem in Fenwei Plain from 2011 to 2020 [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(6): 1149-1162. |
| [4] | ZHANG Shanwen, YANG Ran, HOU Wenxing, WANG Lili, LIU Shuang, SONG Hanyang, ZHAO Wenji, LI Lingjun. Analysis of Fractional Vegetation Cover Changes and Driving Forces on Both Banks of Yongding River Before and After Ecological Water Replenishment [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(2): 264-273. |
| [5] | WANG Wei, CHENG Xinyue. Analysis of Temporal and Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of PM2.5 and PM10 in Different Functional Street Canyons in Hefei City [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 524-534. |
| [6] | WU Zhaoliang, JIN Min. Review and Evidence of the Impacts of Air Pollution on Social Economic Behaviors of Chinese Residents [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(11): 2251-2262. |
| [7] | CHEN Yang, ZHANG Jinpu, QIU Xiaonuan, JU Hong, HUANG Jun. Characteristic of Ozone Pollution and Meteorological Factors Analysis in Guangzhou in 2021 [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(10): 2028-2038. |
| [8] | DENG Yujiao, WANG Jiechun, XU Jie, WU Yongqi, CHEN Jingyang. Spatiotemporal Variation of Vegetation Carbon Sequestration and Its Meteorological Contribution in Guangdong Province [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(1): 1-8. |
| [9] | LI Shengzeng, HAO Saimei, TAN Luyao, ZHANG Huaicheng, XU Biao, GU Shumao, PAN Guang, WANG Shuyan, YAN Huaizhong, ZHANG Guiqin. Characteristics of Spatiotemporal Variation, and Factors Influencing Secondary Components in PM2.5 in Ji'nan [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(1): 100-109. |
| [10] | ZOU Xudong, CAI Fu, LI Rongping, MI Na, ZHAO Hujia, WANG Xiaoying, ZHANG Yunhai, WANG Hongyu, JIA Qingyu. Study on Water and Heat Flux and Energy Change of Maize Field [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(8): 1642-1653. |
| [11] | DENG Huiying, CHEN Lixin, YU Yongjiang, WANG Hong. Characteristics of Ozone Pollution Distribution and Its Correlation Analysis with Meteorological Factors in Wuyishan [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(7): 1428-1435. |
| [12] | LIU Qiang, YANG Zhongyang, CHEN Yiqing, LEI Jinrui, CHEN Zongzhu, CHEN Xiaohua. Multi-scenario Simulation of Land Use Change and Its Eco-environmental Effect in Hainan Island Based on CA-Markov Model [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(7): 1522-1531. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
