Ecology and Environment ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (3): 470-477.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.03.005
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2021-09-01
Online:2022-03-18
Published:2022-05-25
Contact:
MA Zhiliang
通讯作者:
马志良
作者简介:刘美(1983年生),女,讲师,博士,主要研究方向为高寒灌丛土壤生态过程。E-mail: xhliumei@126.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
LIU Mei, MA Zhiliang. Effects of Warming and Plant Removal on Soil Nitrogen Contents in An Alpine Shrubland of Eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 470-477.
刘美, 马志良. 增温和植物去除对青藏高原东部高寒灌丛土壤不同形态氮的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 470-477.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.03.005
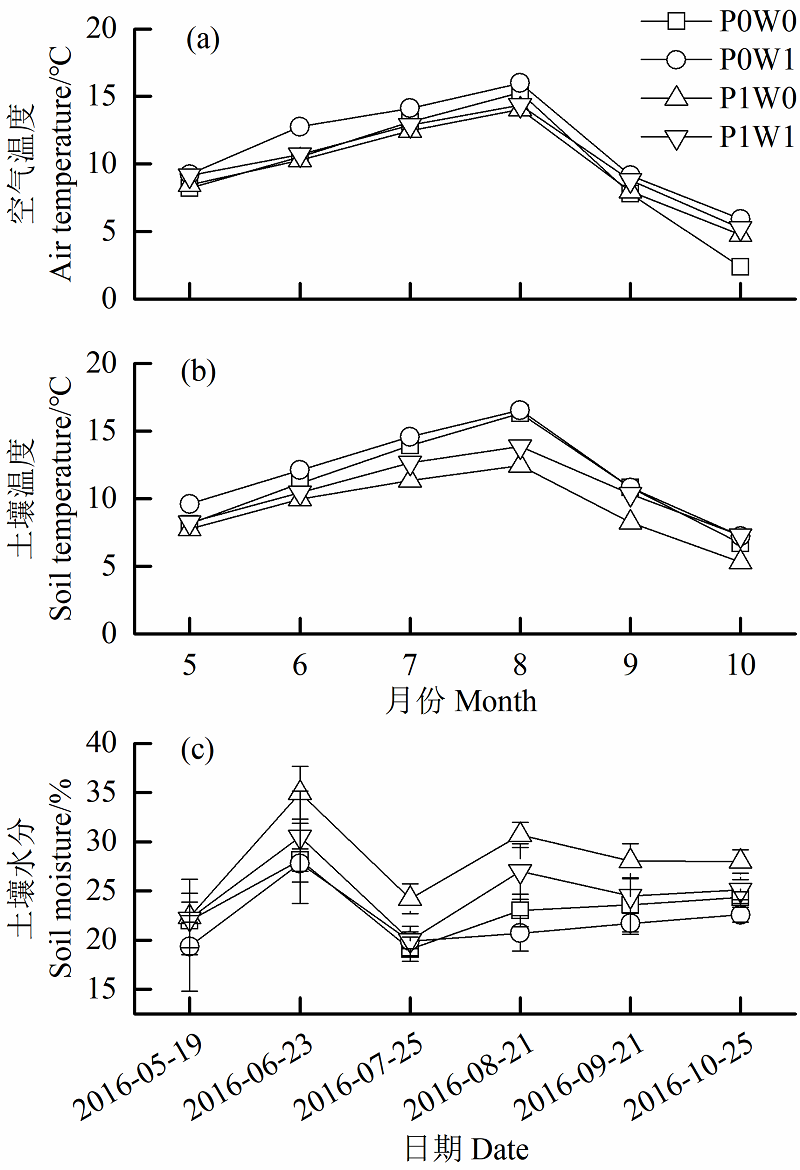
Figure 1 Dynamics of daily mean air temperature at 70 cm above the ground (a), daily mean soil temperature in 0-5 cm soil layer (b) and soil moisture in 0-5 cm soil layer (c) relative to treatment P0W0: removal-plant+control; P0W1: removal-plant+ warming; P1W0: unremoval-plant+control; P1W1: unremoval- plant+warming. The same below
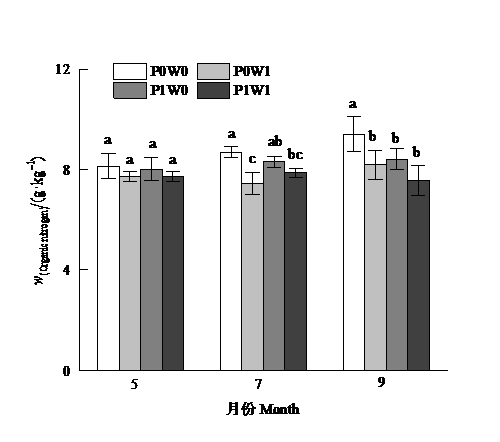
Figure 2 Seasonal dynamics of the soil total nitrogen content relative to treatment Different lower case letters indicated significant differences between the different treatments at 0.05 level. The same below
| 因子 Factor | D | D×P | D×W | D×P×W | P | W | P×W |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | 0.019 | 0.043 | 0.116 | 0.551 | 0.018 | <0.001 | 0.056 |
| 有机氮 Organic nitrogen | 0.020 | 0.037 | 0.125 | 0.563 | 0.018 | <0.001 | 0.058 |
| 无机氮 Inorganic nitrogen | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.002 | 0.605 | 0.122 | 0.208 |
| 微生物生物量氮 Microbial biomass nitrogen | <0.001 | 0.011 | 0.011 | <0.001 | 0.020 | 0.004 | 0.050 |
Table 1 ANOVA of the repeated measurements of different forms of soil N relative to treatment and sampling date
| 因子 Factor | D | D×P | D×W | D×P×W | P | W | P×W |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全氮 Total nitrogen | 0.019 | 0.043 | 0.116 | 0.551 | 0.018 | <0.001 | 0.056 |
| 有机氮 Organic nitrogen | 0.020 | 0.037 | 0.125 | 0.563 | 0.018 | <0.001 | 0.058 |
| 无机氮 Inorganic nitrogen | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.002 | 0.605 | 0.122 | 0.208 |
| 微生物生物量氮 Microbial biomass nitrogen | <0.001 | 0.011 | 0.011 | <0.001 | 0.020 | 0.004 | 0.050 |
| 回归方程 Regression equation | R2 |
|---|---|
| yTN=7.114-0.214xAT+0.216xST | 0.207* |
| yON=7.105-0.215xAT+0.213xST | 0.206* |
| yIN=9.432+0.850xAT+2.396xST+1.185xSM | 0.355** |
| yMBN=1055.641+32.654xAT-67.752xST-21.941xSM | 0.707** |
Table 2 Regression analysis of soil nitrogen contents with air temperature, soil temperature and soil moisture content
| 回归方程 Regression equation | R2 |
|---|---|
| yTN=7.114-0.214xAT+0.216xST | 0.207* |
| yON=7.105-0.215xAT+0.213xST | 0.206* |
| yIN=9.432+0.850xAT+2.396xST+1.185xSM | 0.355** |
| yMBN=1055.641+32.654xAT-67.752xST-21.941xSM | 0.707** |
| [1] |
ALATALO J M, JÄGERBRABD A K, JUHANSON J, et al., 2017. Impacts of twenty years of experimental warming on soil carbon, nitrogen, moisture and soil mites across alpine/subarctic tundra communities[J]. Scientific Reports, 7(1): 44489.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
BRIN L D, GOYER C, ZEBARTH B J, et al., 2018. Changes in snow cover alter nitrogen cycling and gaseous emissions in agricultural soils[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 258: 91-103.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
BUCHKOWSKI R W, SCHMITZ O J, BRADFORD M A, 2015. Microbial stoichiometry overrides biomass as a regulator of soil carbon and nitrogen cycling[J]. Ecology, 96(4): 1139-1149.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
BUTLER S M, MELILLO J M, JOHNSON J E, et al., 2012. Soil warming alters nitrogen cycling in a New England forest: Implications for ecosystem function and structure[J]. Oecologia, 168(3): 819-828.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
CHEN Q Y, LEI T Z, WU Y Q, et al., 2019. Comparison of soil organic matter transformation processes in different alpine ecosystems in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. JGR: Biogeosciences, 124(1): 33-45.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
DAWES M A, SCHLEPPI P, HAGEDORN F, 2017a. The fate of nitrogen inputs in a warmer alpine treeline ecosystem: A 15N labelling study[J]. Journal of Ecology, 105(6): 1723-1737.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
DAWES M A, SCHLEPPI P, HÄTTENSCHWILER S, et al., 2017b. Soil warming opens the nitrogen cycle at the alpine treeline[J]. Global Change Biology, 23(1): 421-434.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
DENG B L, LI Z Z, ZHANG L, et al., 2016. Increases in soil CO2 and N2O emissions with warming depend on plant species in restored alpine meadows of Wugong Mountain, China[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 16(3): 777-784.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
DU E Z, TERRER C, PELLEGRINI A F A, et al., 2020. Global patterns of terrestrial nitrogen and phosphorus limitation[J]. Nature Geoscience, 13(3): 221-226.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
HU X, SUN G, YIN P, et al., 2018. Effects of nutrient input on soil nitrogen cycle in winter in the alpine zone[J]. Journal of Biobased Materials and Bioenergy, 12: 129-133.
DOI URL |
| [11] | IPCC(Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change), 2013. Climate change 2013: The physical science basis[M]. New York: Cambridge University Press. |
| [12] |
LIU J G, GOU X H, GUNINA A, et al., 2020. Soil nitrogen pool drives plant tissue traits in alpine treeline ecotones[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 477(1): 118490.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
LIU Y, HE N, WEN X, et al., 2016. Patterns and regulating mechanisms of soil nitrogen mineralization and temperature sensitivity in Chinese terrestrial ecosystems[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 215: 40-46.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
LIU M, WEN J H, CHEN Y M, et al., 2021. Warming increases soil carbon input in a Sibiraea angustata-dominated alpine shrub ecosystem[J]. Journal of Plant Ecology, Doi: 10.1093/jpe/rtab101.
DOI |
| [15] |
LIU Y, HE N P, WEN X F, et al., 2016. Patterns and regulating mechanisms of soil nitrogen mineralization and temperature sensitivity in Chinese terrestrial ecosystems[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 215: 40-46.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
MA Z L, ZHAO W Q, ZHAO C Z, et al., 2018. Plants regulate the effects of experimental warming on the soil microbial community in an alpine scrub ecosystem[J]. PLoS One, 13(4): e0195079.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
MILLER A E, BOWMAN W D, 2003. Alpine plants show species-level differences in the uptake of organic and inorganic nitrogen[J]. Plant and Soil, 250(2): 283-292.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
MIEHE G, SCHLEUSS M P, SEEBER E, et al., 2018. The Kobresia pygmaea ecosystem of the Tibetan Highlands-Origin, functioning and degradation of the world's largest pastoral alpine ecosystem[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 648: 754-771.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
NIE X Q, XIONG F, YANG L C, et al., 2017. Soil nitrogen storage, distribution, and associated controlling factors in the northeast Tibetan Plateau shrublands[J]. Forests, 8(11): 416.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
PENG Y F, PENG Z P, ZENG X T, et al., 2019. Effects of nitrogen-phosphorus imbalance on plant biomass production: A global perspective[J]. Plant and Soil, 436(1-2): 245-252.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
PREVÉY J, VELLEND M, RÜGER N, et al., 2017. Greater temperature sensitivity of plant phenology at colder sites: Implications for convergence across northern latitudes[J]. Global Change Biology, 23(7): 2660-2671.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
STEINAUER K, TILMAN D, WRAGG P D, et al., 2015. Plant diversity effects on soil microbial functions and enzymes are stronger than warming in a grassland experiment[J]. Ecology, 96(1): 99-112.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
YAN Y, TIAN L L, DU Z Y, et al., 2019. Carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus stocks differ among vegetation patch types in a degraded alpine steppe[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 19(4): 1809-1819.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
YIN L M, DIJKSTRA F A, WANG P, et al., 2018. Rhizosphere priming effects on soil carbon and nitrogen dynamics among tree species with and without intraspecific competition[J]. New Phytologist, 218(3): 1036-1048.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
ZHAO L, WU X D, WANG Z W, et al., 2018. Soil organic carbon and total nitrogen pools in permafrost zones of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Scientific Reports, 8(1): 3656.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
ZHU P, CHEN R, SONG Y, et al., 2015. Effects of land cover conversion on soil properties and soil microbial activity in an alpine meadow on the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Environmental Earth Science, 74(5): 4523-4533.
DOI URL |
| [27] | 刘美, 马志良, 2021. 模拟增温对青藏高原东部高寒灌丛土壤氮转化的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 32(6): 2045-2052. |
| LIU M, MA Z L, 2021. Effects of experimental warming on soil nitrogen transformation in alpine scrubland of eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 32(6): 2045-2052. | |
| [28] | 马彩霞, 李洪杰, 郑海峰, 等, 2019. 川西高山林线土壤活性碳、氮对短期增温的响应[J]. 应用生态学报, 30(3): 718-726. |
| MA C X, LI H J, ZHENG H F, et al., 2019. Responses of soil active carbon and nitrogen to short-term warming in alpine treeline of west Sichuan, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 30(3): 718-726. | |
| [29] | 马志良, 赵文强, 赵春章, 等, 2018a. 青藏高原东缘窄叶鲜卑花灌丛生长季土壤无机氮对增温和植物去除的响应[J]. 植物生态学报, 42(1): 86-94. |
|
MA Z L, ZHAO W Q, ZHAO C Z, et al., 2018a. Responses of soil inorganic nitrogen to increased temperature and plant removal during the growing season in a Sibiraea angustata scrub ecosystem of eastern Qinghai-Xizang Plateau[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 42(1): 86-94.
DOI URL |
|
| [30] | 马志良, 赵文强, 刘美, 等, 2018b. 高寒灌丛生长季土壤转化酶与脲酶活性对增温和植物去除的响应[J]. 应用生态学报, 29(7): 2211-2216. |
| MA Z L, ZHAO W Q, LIU M, et al., 2018b. Responses of soil invertase and urease activities to warming and plant removal during the growing season in an alpine scrub ecosystem[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 29(7): 2211-2216. | |
| [31] |
唐波, 杨欢, 尹春英, 等, 2016. 夜间增温对亚高山针叶林主要树种无机氮吸收的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 40(6): 543-553.
DOI |
|
TANG B, YANG H, YIN C Y, et al., 2016. Effects of night warming obn the uptake of inorganic nitrogen by two dominant species in subalpine coniferous forests[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 40(6): 543-553.
DOI |
|
| [32] | 冶民生, 吴斌, 关文彬, 等, 2009. 岷江上游植物群落稳定性研究[J]. 水土保持研究, 16(1): 259-263. |
| YE M S, WU B, GUAN W B, et al., 2009. Plant community stability in the upper reaches of Minjiang River[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 16(1): 259-263. |
| [1] | LIU Zhendi, SONG Yanyu, WANG Xianwei, TAN Wenwen, ZHANG Hao, GAO Jinli, GAO Siqi, DU Yu. Effects of Simulated Warming on Plant Growth and Carbon and Nitrogen Characteristics in Permafrost Peatland [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(9): 1765-1772. |
| [2] | CHEN Lijuan, ZHOU Wenjun, YI Yanyun, SONG Qinghai, ZHANG Yiping, LIANG Naishen, LU Zhiyun, WEN Handong, MOHD Zeeshan, SHA Liqing. Characteristics of Soil CH4 Flux in the Subtropical Evergreen Broad-leaved Forest in Ailao Mountain, Yunnan, Southwest China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(5): 949-960. |
| [3] | LI Chengwei, LIU Zhangyong, GONG Songling, YANG Wei, LI Shaoqiu, ZHU Bo. Effects of Changing Rice Cropping Patterns on CH4 and N2O Emissions from Paddy Fields [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(5): 961-968. |
| [4] | LIANG Lei, MA Xiuzhi, HAN Xiaorong, LI Changsheng, ZHANG Zhijie. Effects of Litter on Soil Greenhouse Gas Flux of Pinus tabulaeformis Plantation in Daqing Mountain under Simulated Warming [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 478-486. |
| [5] | YAO Shiting, LU Guangxin, DENG Ye, DANG Ning, WANG Yingcheng, ZHANG Haijuan, YAN Huilin. Effects of Simulated Warming on Soil Fungal Community Composition and Diversity [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(7): 1404-1411. |
| [6] | CHEN Si, WANG Can, LI Xiang, Li Mingrui, ZHAN Fangdong, LI Yuan, ZU Yanquan, HE Yongmei. Effects of Different UV-B Radiation Levels on Soil Enzyme Activities, Active Organic Carbon Content and Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Paddy Fields [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(6): 1260-1268. |
| [7] | SHE Yandi, ZHOU Huakun, ZHANG Zhonghua, MA Li, ZHOU Bingrong, SONG Minghua, SUN Jian, DENG Yanfang, XU Wenhua, WANG Fang, YAO Buqing, MA Zhen, HUANG Xiaotao. Suitable Distribution of Notopterygium incisum in the Three Rivers Headwater Region under Climate Change [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(10): 2033-2041. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn

