Ecology and Environment ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (12): 1849-1861.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.12.003
• Research Article [Ecology] • Previous Articles Next Articles
LUO Xiaoling1( ), LIU Jun1, WANG Qi2, LIU Tongxu2, LIANG Yaojie1, XIE Zhiyi1,*(
), LIU Jun1, WANG Qi2, LIU Tongxu2, LIANG Yaojie1, XIE Zhiyi1,*( ), WANG Zhongwei1, CHEN Duohong1
), WANG Zhongwei1, CHEN Duohong1
Received:2024-10-20
Online:2024-12-18
Published:2024-12-31
Contact:
XIE Zhiyi
罗小玲1( ), 刘军1, 王琦2, 刘同旭2, 梁耀杰1, 谢志宜1,*(
), 刘军1, 王琦2, 刘同旭2, 梁耀杰1, 谢志宜1,*( ), 王中伟1, 陈多宏1
), 王中伟1, 陈多宏1
通讯作者:
谢志宜
作者简介:罗小玲(1982年生),女,高级工程师,硕士,研究方向为土壤环境监测与评价。E-mail: 78086941@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
LUO Xiaoling, LIU Jun, WANG Qi, LIU Tongxu, LIANG Yaojie, XIE Zhiyi, WANG Zhongwei, CHEN Duohong. Temporal and Spatial Changes in pH and Organic Matter and Their Influencing Factors in Soils with Various Land Use Types in Guangdong Province since 2016[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(12): 1849-1861.
罗小玲, 刘军, 王琦, 刘同旭, 梁耀杰, 谢志宜, 王中伟, 陈多宏. 2016年以来广东省不同土地利用类型土壤pH和有机质时空变化及其影响因素分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(12): 1849-1861.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.12.003
| 统计范围 | 点位个数 | 时期 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 均值 | 标准差 | 均值变化量及其显著性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全省 | 2110 | 2016-2018 | 2.70 | 8.94 | 5.41 | 0.97 | 0.05 |
| 2021-2022 | 3.22 | 8.70 | 5.46 | 0.96 | |||
| 耕地 (水田) | 867 | 2016-2018 | 2.70 | 8.56 | 5.40a | 0.78 | 0.12** 2) |
| 2021-2022 | 3.68 | 8.50 | 5.52A | 0.77 | |||
| 耕地 (旱地) | 942 | 2016-2018 | 3.32 | 8.94 | 5.59b | 1.11 | 0.03 |
| 2021-2022 | 3.22 | 8.70 | 5.62B | 1.10 | |||
| 林地 | 173 | 2016-2018 | 3.86 | 7.51 | 4.80c | 0.69 | −0.14*1) |
| 2021-2022 | 3.91 | 7.76 | 4.66C | 0.59 | |||
| 园地 | 53 | 2016-2018 | 3.68 | 7.16 | 4.96c | 0.70 | 0.00 |
| 2021-2022 | 3.78 | 7.43 | 4.96C | 0.77 | |||
| 其他 | 75 | 2016-2018 | 3.85 | 8.40 | 4.86c | 0.80 | 0.04 |
| 2021-2022 | 3.90 | 8.20 | 4.90C | 0.78 |
Table 1 Soil pH changes of different land use types in Guangdong Province
| 统计范围 | 点位个数 | 时期 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 均值 | 标准差 | 均值变化量及其显著性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全省 | 2110 | 2016-2018 | 2.70 | 8.94 | 5.41 | 0.97 | 0.05 |
| 2021-2022 | 3.22 | 8.70 | 5.46 | 0.96 | |||
| 耕地 (水田) | 867 | 2016-2018 | 2.70 | 8.56 | 5.40a | 0.78 | 0.12** 2) |
| 2021-2022 | 3.68 | 8.50 | 5.52A | 0.77 | |||
| 耕地 (旱地) | 942 | 2016-2018 | 3.32 | 8.94 | 5.59b | 1.11 | 0.03 |
| 2021-2022 | 3.22 | 8.70 | 5.62B | 1.10 | |||
| 林地 | 173 | 2016-2018 | 3.86 | 7.51 | 4.80c | 0.69 | −0.14*1) |
| 2021-2022 | 3.91 | 7.76 | 4.66C | 0.59 | |||
| 园地 | 53 | 2016-2018 | 3.68 | 7.16 | 4.96c | 0.70 | 0.00 |
| 2021-2022 | 3.78 | 7.43 | 4.96C | 0.77 | |||
| 其他 | 75 | 2016-2018 | 3.85 | 8.40 | 4.86c | 0.80 | 0.04 |
| 2021-2022 | 3.90 | 8.20 | 4.90C | 0.78 |
| 统计范围 | 点位个数 | 时期 | 最小值/(g∙kg−1) | 最大值/(g∙kg−1) | 均值/(g∙kg−1) | 标准差/(g∙kg−1) | 均值变化量及其显著性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全省 | 2110 | 2016-2018 | 1.22 | 94.40 | 24.07 | 11.78 | −0.84 |
| 2021-2022 | 1.40 | 66.70 | 23.23 | 10.88 | |||
| 耕地 (水田) | 867 | 2016-2018 | 1.22 | 69.90 | 28.36a | 11.98 | −0.93* |
| 2021-2022 | 3.00 | 64.70 | 27.43A | 10.85 | |||
| 耕地 (旱地) | 942 | 2016-2018 | 1.54 | 94.40 | 20.10b | 9.64 | −0.55 |
| 2021-2022 | 1.40 | 66.00 | 19.55B | 9.04 | |||
| 林地 | 173 | 2016-2018 | 1.40 | 61.20 | 27.03a | 13.33 | −3.84** |
| 2021-2022 | 1.46 | 56.50 | 23.20C | 12.47 | |||
| 园地 | 53 | 2016-2018 | 2.30 | 57.50 | 20.87b | 9.59 | −0.27 |
| 2021-2022 | 2.38 | 43.80 | 20.60BC | 8.96 | |||
| 其他 | 75 | 2016-2018 | 3.11 | 76.50 | 19.83b | 12.42 | 2.91 |
| 2021-2022 | 3.80 | 66.70 | 22.74BC | 12.49 |
Table 2 Changes of soil organic matter content in different land use types in Guangdong Province
| 统计范围 | 点位个数 | 时期 | 最小值/(g∙kg−1) | 最大值/(g∙kg−1) | 均值/(g∙kg−1) | 标准差/(g∙kg−1) | 均值变化量及其显著性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全省 | 2110 | 2016-2018 | 1.22 | 94.40 | 24.07 | 11.78 | −0.84 |
| 2021-2022 | 1.40 | 66.70 | 23.23 | 10.88 | |||
| 耕地 (水田) | 867 | 2016-2018 | 1.22 | 69.90 | 28.36a | 11.98 | −0.93* |
| 2021-2022 | 3.00 | 64.70 | 27.43A | 10.85 | |||
| 耕地 (旱地) | 942 | 2016-2018 | 1.54 | 94.40 | 20.10b | 9.64 | −0.55 |
| 2021-2022 | 1.40 | 66.00 | 19.55B | 9.04 | |||
| 林地 | 173 | 2016-2018 | 1.40 | 61.20 | 27.03a | 13.33 | −3.84** |
| 2021-2022 | 1.46 | 56.50 | 23.20C | 12.47 | |||
| 园地 | 53 | 2016-2018 | 2.30 | 57.50 | 20.87b | 9.59 | −0.27 |
| 2021-2022 | 2.38 | 43.80 | 20.60BC | 8.96 | |||
| 其他 | 75 | 2016-2018 | 3.11 | 76.50 | 19.83b | 12.42 | 2.91 |
| 2021-2022 | 3.80 | 66.70 | 22.74BC | 12.49 |
| 2016-2018年 土壤理化指标 | 2016年气象条件 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年平均气温 | 年平均地面温度 | 年日照时数 | 年平均相对湿度 | 年降雨量 | 年降雨日数 | |
| pH | −0.147** 1) | −0.174** | −0.221** | −0.236** | 0.155** | 0.195** |
| 有机质含量 | −0.153** | −0.146** | −0.064** | −0.082** | 0.051* 2) | 0.082** |
Table 3 Correlation analysis between meteorological conditions and main physical and chemical indexes of soil in Guangdong Province from 2016 to 2018
| 2016-2018年 土壤理化指标 | 2016年气象条件 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年平均气温 | 年平均地面温度 | 年日照时数 | 年平均相对湿度 | 年降雨量 | 年降雨日数 | |
| pH | −0.147** 1) | −0.174** | −0.221** | −0.236** | 0.155** | 0.195** |
| 有机质含量 | −0.153** | −0.146** | −0.064** | −0.082** | 0.051* 2) | 0.082** |
| 2021-2022年 土壤理化指标 | 2021年气象条件 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年平均气温 | 年平均地面温度 | 年日照时数 | 年平均相对湿度 | 年降雨量 | 年降雨日数 | |
| pH | −0.155** | −0.169** | −0.216** | −0.176** | 0.029 | 0.038 |
| 有机质含量 | −0.014 | 0.004 | 0.051* | −0.100** | −0.024 | 0.016 |
Table 4 Correlation analysis between meteorological conditions and main physical and chemical indexes of soil in Guangdong Province from 2021 to 2022
| 2021-2022年 土壤理化指标 | 2021年气象条件 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年平均气温 | 年平均地面温度 | 年日照时数 | 年平均相对湿度 | 年降雨量 | 年降雨日数 | |
| pH | −0.155** | −0.169** | −0.216** | −0.176** | 0.029 | 0.038 |
| 有机质含量 | −0.014 | 0.004 | 0.051* | −0.100** | −0.024 | 0.016 |
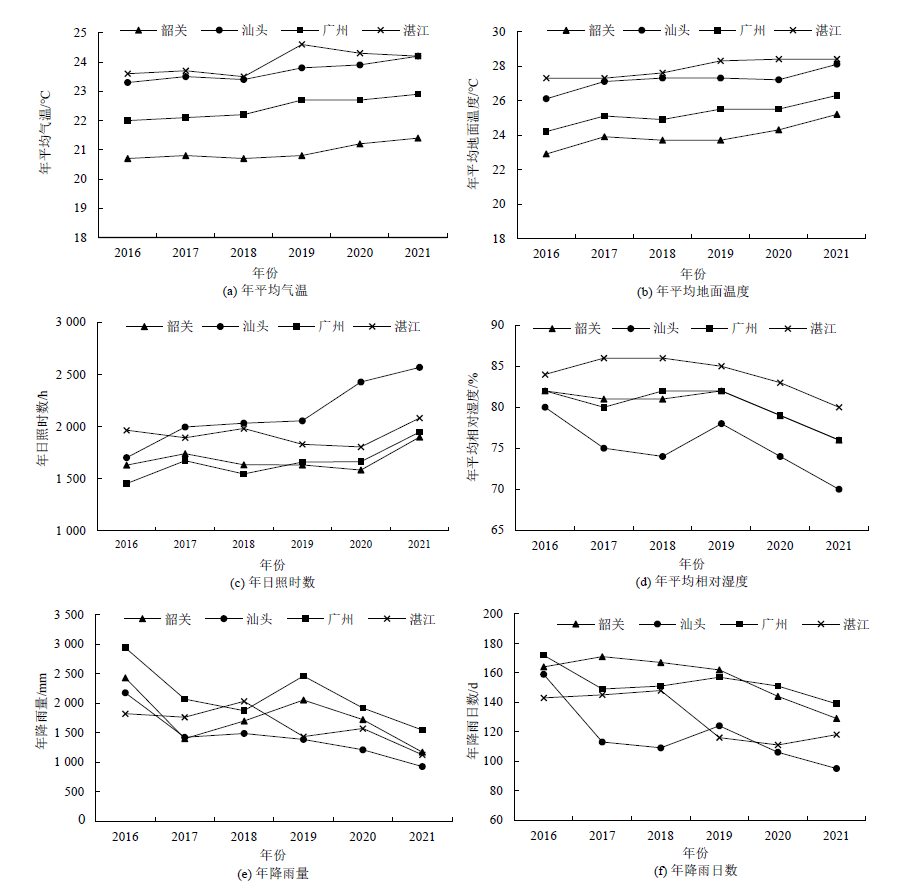
Figure 11 Meteorological conditions over the years during soil sampling of representative cities in East, West, North of Guangdong and Pearl River Delta
| 时间 | 降水pH | 酸雨频率/ % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 均值 | 最大值 | 最小值 | ||
| 2016年 | 5.64 | 7.97 | 3.17 | 26.5 |
| 2021年 | 5.96 | 8.74 | 4.03 | 10.7 |
Table 5 Variation of precipitation pH and frequency of acid rain in Guangdong Province
| 时间 | 降水pH | 酸雨频率/ % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 均值 | 最大值 | 最小值 | ||
| 2016年 | 5.64 | 7.97 | 3.17 | 26.5 |
| 2021年 | 5.96 | 8.74 | 4.03 | 10.7 |
| 时期 | 点位所属县域化肥用使用量/(t∙hm−2∙a−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 氮肥 | 磷肥 | 钾肥 | 复合肥 | ||
| 水田土壤pH | 2016-2018年 | −0.071* 1) | −0.086* | −0.097** 2) | −0.040 |
| 2021-2022年 | 0.034 | −0.007 | −0.002 | 0.021 | |
| 旱地土壤pH | 2016-2018年 | 0.056 | 0.007 | 0.012 | 0.080* |
| 2021-2022年 | 0.020 | 0.018 | 0.018 | 0.000 | |
Table 6 Correlation between soil pH and chemical fertilizer application per unit area in paddy and dry land in Guangdong Province
| 时期 | 点位所属县域化肥用使用量/(t∙hm−2∙a−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 氮肥 | 磷肥 | 钾肥 | 复合肥 | ||
| 水田土壤pH | 2016-2018年 | −0.071* 1) | −0.086* | −0.097** 2) | −0.040 |
| 2021-2022年 | 0.034 | −0.007 | −0.002 | 0.021 | |
| 旱地土壤pH | 2016-2018年 | 0.056 | 0.007 | 0.012 | 0.080* |
| 2021-2022年 | 0.020 | 0.018 | 0.018 | 0.000 | |
| 时期 | 点位所属县区年均化肥总用量/(t∙a−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 氮肥 | 磷肥 | 钾肥 | 复合肥 | ||
| 水田土壤pH | 2016-2018年 | −0.115** | −0.115** | −0.112** | −0.060 |
| 2021-2022年 | −0.061 | −0.115** | −0.080* | −0.066 | |
| 旱地土壤pH | 2016-2018年 | −0.291** | −0.358** | −0.337** | −0.229** |
| 2021-2022年 | −0.201** | −0.286** | −0.208** | −0.169** | |
Table 7 Correlation between soil pH and total amount of chemical fertilizer in paddy field and dry land in Guangdong Province
| 时期 | 点位所属县区年均化肥总用量/(t∙a−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 氮肥 | 磷肥 | 钾肥 | 复合肥 | ||
| 水田土壤pH | 2016-2018年 | −0.115** | −0.115** | −0.112** | −0.060 |
| 2021-2022年 | −0.061 | −0.115** | −0.080* | −0.066 | |
| 旱地土壤pH | 2016-2018年 | −0.291** | −0.358** | −0.337** | −0.229** |
| 2021-2022年 | −0.201** | −0.286** | −0.208** | −0.169** | |
| [1] | BARAK P, JOBE B O, KRUEGER A R, et al., 1997. Effects of long-term soil acidification due to nitrogen fertilizer inputs in Wisconsin[J]. Plant and Soil, 197: 61-69. |
| [2] | HU K L, WANG S Y, LI H, et al., 2014. Spatial scaling effects on variability of soil organic matter and total nitrogen in suburban Beijing[J]. Geoderma, 226-227: 54-63. |
| [3] | LIU D W, WANG Z M, ZHANG B, et al., 2006. Spatial distribution of soil organic carbon and analysis of related factors in croplands of the black soil region, Northeast China[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 113(1-4): 73-81. |
| [4] | LI Q Q, LI A W, YU X L, et al., 2020. Soil acidification of the soil profile across Chengdu Plain of China from the 1980s to 2010s[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 698: 134320. |
| [5] | TIAN D S, NIU S L, 2015. A global analysis of soil acidification caused by nitrogen addition[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 10(2): 24-19. |
| [6] | WANG Z M, ZHANG B, SONG K S, et al., 2010. Spatial variability of soil organic carbon under maize monoculture in the Songnen Plain, Northeast China[J]. Pedosphere, 20(1): 80-89. |
| [7] | YANG Y H, JI C J, MA W H, et al., 2012. Significant soil acidification across northern China’s grasslands during 1980s-2000s[J]. Global Change Biology, 18(7): 2292-2300. |
| [8] | ZHU J X, HE N P, WANG Q F, et al., 2015. The composition, spatial patterns, and influencing factors of atmospheric wet nitrogen deposition in Chinese terrestrial ecosystems[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 511: 777-785. |
| [9] | ZHU Q C, VRIES W D, LIU X J, et al., 2016. The contribution of atmospheric deposition and forest harvesting to forest soil acidification in China since 1980[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 146: 215-222. |
| [10] | 丁俊男, 于少鹏, 史传奇, 等, 2021. 寒区湿地不同土地利用方式对土壤理化性质和团聚体稳定性的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 40(11): 3543-3551. |
|
DING J N, YU S P, SHI C Q, et al., 2021. Effects of land use types on soil physicochemical properties and aggregates stability in cold region wetland[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 40(11): 3543-3551.
DOI |
|
| [11] | 广东省土壤普查办公室, 1993. 广东土壤[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| Guangdong Soil Census Office, 1993. Soil in Guangdong[M]. Beijing: Science Press. | |
| [12] | 国家环境保护局, 1992. 大气降水pH值的测定电极法: GB 13580.4-92[S/OL]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/image20010518/1883.pdf. |
| State Bureau of Environment Pro-tection, 1992. Atmospheric precipitation-Determination of pH-Electrode method: GB 13580.4-92[S/OL]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/image20010518/1883.pdf. | |
| [13] | 国家林业局, 1999. 森林土壤pH值的测定: LY/T 1239—1999[S/OL]. https://www.cnemc.cn/jcgf/trhj/201711/P020181010541051823125.pdf. |
| State Forestry Bureau, 1999. Determination of pH value of forest soil: LY/T 1239—1999[S/OL]. https://www.cnemc.cn/jcgf/trhj/201711/P020181010541051823125.pdf. | |
| [14] | 国家林业局, 1999. 森林土壤有机质的测定及碳氮比的计算: LY/T 1237—1999[S/OL]. https://www.cnemc.cn/jcgf/trhj/201711/W020181008687794710910.pdf. |
| State Forestry Bureau, 1999. Determination of forest soil organic matter and calculation of carbon nitrogen ratio: LY/T 1237—1999[S/OL]. https://www.cnemc.cn/jcgf/trhj/201711/W020181008687794710910.pdf. | |
| [15] | 国家环境保护总局, 2004. 酸沉降监测技术规范: HJ/T 165—2004[S/OL]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/jcffbz/200412/W020110127389246611965.pdf. |
| The State Environmental Protection Administration, 2004. Technical specification for acid deposition monitoring: HJ/T 165—2004[S/OL]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/jcffbz/200412/W020110127389246611965.pdf. | |
| [16] | 杲广文, 汪景宽, 李双异, 等, 2015. 30年来东北主要黑土区耕层土壤有机碳密度与储量动态变化研究[J]. 土壤通报, 46(4): 774-780. |
| GAO G W, WANG J K, LI S Y, et al., 2015. Changes of organic carbon density and storage in northeastern black soil areas in past 30 years[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 46(4): 774-780. | |
| [17] | 广东省林业局, 2020. 2020年广东省林业统计分析报告[R/OL]. https://lyj.gd.gov.cn/government/release/content/post_3350630.html. |
| Guangdong Forestry Bureau, 2020. 2020 Guangdong province forestry statistical analysis report[R/OL]. https://lyj.gd.gov.cn/government/release/content/post_3350630.html. | |
| [18] | 韩天富, 柳开楼, 黄晶, 等, 2020. 近30年中国主要农田土壤pH时空演变及其驱动因素[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 26(12): 2137-2149. |
| HAN T F, LIU K L, HUANG J, et al., 2020. Spatio-temporal evolution of soil pH and its driving factors in the main Chinese farmland during past 30 years[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 26(12): 2137-2149. | |
| [19] | 何孟霓, 孙继光, 徐英德, 等, 2024. 长白山-辽东黑土区耕地土壤有机质时空变异及影响因素[J/OL]. 农业环境科学学报, [2024-06-26]. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/12.1347.S.20240625.1715.006. |
| HE M N, SUN J G, XU Y D, et al., 2024. The spatiotemporal variation of soil organic matter and its influencing factors in the Changbai Mountain-Liaodong black soil region[J/OL]. Journal of Agro- Environment Science, [2024-06-26]. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/12.1347.S.20240625.1715.006. | |
| [20] | 罗世琼, 杨雪鸥, 2013. 烤烟石灰性黄壤肥力状况及其与土壤微生物的关系[J]. 广东农业科学, 40(14): 78-80. |
| LUO S Q, YANG X O, 2013. Relationship between soil fertility and microorganism in calcareous yellow soil of flue-cured tobacco[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Science, 40(14): 78-80. | |
| [21] | 李子君, 李英姿, 王海军, 2023. 鲁中南山地丘陵区土地利用方式对土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 山东农业大学学报(自然科学版), 54(2): 254-266. |
| LI Z J, LI Y Z, WANG H J, 2023. Effects of land use types on soil physical and chemical properties in mountainous and hilly areas in central and southern Shandong Province[J]. Journal of Shandong Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition), 54(2): 254-266. | |
| [22] | 秦诗涵, 孙继光, 常坤, 等, 2024. 松嫩平原黑土区土壤有机质含量时空变化及其影响因素[J/OL]. 农业资源与环境学报, [2024-03-25]. https://doi.org/10.13254/j.jare.2023.0623. |
| QIN S H, SUN J G, CHANG K, et al., 2024. Spatial-temporal variation of soil organic matter content and its influencing factors in the black soil area of Songnen Plain[J/OL]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, [2024-03-25]. https://doi.org/10.13254/j.jare.2023.0623. | |
| [23] | 绍学新, 黄标, 顾志权, 等, 2006. 长三角经济高速发展地区土壤pH时空变化及其影响因素[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 25(2): 114-149. |
| SHAO X X, HUANG B, GU Z Q, et al., 2006. Spatial-temporal variation of pH values of soils in a rapid economic developingarea in the Yangtze River Delta Region and their causing factors[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 25(2): 114-149. | |
| [24] |
邵兴华, 徐金仁, 张建忠, 等, 2011. 长期施肥对旱地红壤肥力和酶活性的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 20(2): 266-269.
DOI |
| SHAO X H, XU J R, ZHANG J Z, et al., 2011. Effects of long-term fertilizer on soil fertility and soil enzyme activities in upland red soils[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 20(2): 266-269. | |
| [25] | 王子龙, 孙建, 姜秋香, 等, 2019. 松嫩平原黑土区有机质空间分布特征及影响因素[J]. 东北农业大学学报, 50(10): 54-62. |
| WANG Z L, SUN J, JIANG Q X, et al., 2019. Spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of organic matter in black soil region of the Songnen Plain[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 50(10): 54-62. | |
| [26] | 熊顺贵, 2001. 基础土壤学[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社. |
| XIONG S G, 2001. Basic soil science[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press. | |
| [27] | 徐影, 于镇华, 李彦生, 等, 2024. 土壤酸化成因及其对农田土壤-微生物-作物系统影响的研究进展[J]. 土壤通报, 55(2): 562-572. |
| XU Y, YU Z H, LI Y S, et al., 2024. Research progresses on soil acidification and its effects on soilmicroorganism-crop systems in agricultural soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 55(2): 562-572. | |
| [28] | 杨皓, 胡继伟, 黄先飞, 等, 2015. 喀斯特地区金刺梨种植基地土壤肥力研究[J]. 水土保持研究, 22(3): 50-55. |
| YANG H, HU J W, HUANG X F, et al., 2015. Study on soil fertility of Rosa sterilis S. D. Shi planting bases located in karst areas[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 22(3): 50-55. | |
| [29] | 余倩, 段雷, 郝吉明, 2021. 中国酸沉降: 来源、影响与控制[J]. 环境科学学报, 41(3): 731-746. |
| YU Q, DUAN L, HAO J M, 2021. Acid deposition in China: Sources, effects and control[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 41(3): 731-746. | |
| [30] | 张桂兰, 苞德俊, 王英, 等, 1999. 长期施用化肥对作物产量和土壤性质的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 30(2): 64-67. |
| ZHANG G L, BAO D J, WANG Y, et al., 1999. Effects of long-term application of chemical ertilizers on crop yield and soil properties[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 30(2): 64-67. | |
| [31] | 中华人民共和国农业部, 2006. 土壤检测第6部分: 土壤有机质的测定:NY/T 1121.6—2006[S/OL]. https://www.nssi.org.cn/standard/detail/73a4a81eca24c0a3dfdf28b7b399c893. |
| Agricultural Ministry of the People’s Republic of China, 2006. Determination of soil organic matter: NY/T 1121.6—2006[S/OL]. https://www.nssi.org.cn/standard/detail/73a4a81eca24c0a3dfdf28b7b399c893. | |
| [32] | 中华人民共和国农业部, 2007. 土壤pH的测定: NY/T 13779—2007[S/OL]. https://www.nssi.org.cn/standard/detail/e45022a959f2efe4271e559fb768e099. |
| Agricultural Ministry of the People’s Republic of China, 2007. Determination of soil pH: NY/T 13779—2007[S/OL]. https://www.nssi.org.cn/standard/detail/e45022a959f2efe4271e559fb768e099. | |
| [33] | 曾招兵, 汤建东, 刘一峰, 等, 2013. 广东耕地土壤有机质的变化趋势及其驱动力分析[J]. 土壤, 45(1): 84-90. |
| ZENG Z B, TANG J D, LIU Y F, et al., 2013. Changes and driving forces of farmland organic matter in Guangdong Province, China[J]. Soil, 45(1): 84-90. | |
| [34] | 曾招兵, 曾思坚, 刘一锋, 等, 2014. 1984 年以来广东水稻土pH变化趋势及影响因素[J]. 土壤, 46(4): 732-736. |
| ZENG Z B, ZENG S J, LIU Y F, et al., 2014. Change tendency of paddy soil pH in Guangdong Province Since 1984 and influential factors[J]. Soil, 46(4): 732-736. | |
| [35] | 生态环境部, 2019. 土壤pH值的测定电位法: HJ962—2018[S/OL]. 北京: 中国环境出版社. https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/jcffbz/201808/W020180815584753007210.pdf. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment, 2019. Determination of soil pH by potentiometric method: HJ962—2018[S/OL]. Beijing, China Environmental Press https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/jcffbz/201808/W020180815584753007210.pdf. | |
| [36] | 郑超, 郭治兴, 袁宇志, 等, 2019. 广东省不同区域农田土壤酸化时空变化及其影响因素[J]. 应用生态学报, 30(2): 593-601. |
|
ZHENG C, GUO Z X, YUAN Y Z, et al., 2019. Spatial and temporal changes of farmland soil acidification and their influencing factors in different regions of Guangdong Province, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 30(2): 593-601.
DOI |
| [1] | HOU Jinlong, MA Zhiqiang, YANG Cheng, GE Shuangshuang, HE Di, DONG Fan. Analysis of Spatio-temporal Variation of Vegetation Carbon Sources and Sinks in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region and Influencing Factors [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(9): 1329-1338. |
| [2] | LI Jianfu, HUANG Zhilin, HE Chengzhong, JIANG Xin, SONG Lin, LIU Jiaxin, CHEN Liding. Spatial Distribution and Key Factors Affecting Soil Organic Carbon Within the Karst Fault Basin in Eastern Yunnan, China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(9): 1339-1352. |
| [3] | LI Yanlin, CHEN Yangyang, YANG Shuangrong, LIU Jumei. Study on the Effects of Organic Acids in Plant Root Exudates on Soil Organic Carbon and Nitrogen Mineralization [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(9): 1362-1371. |
| [4] | SHI Hanzhi, XIONG Zhenqian, CAO Yiran, WU Zhichao, WEN Dian, LI Furong, LI Dongqin, WANG Xu. Effect of Straw Returning to Field on Organic Carbon Fixation in Red Soil and Black Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(9): 1372-1383. |
| [5] | ZHU Leyang, ZHANG Xizhe, TAO Jiang, WANG Xiu, HAN Yanying, YE Yanhui. The Effect of Nitrogen Addition on Soil Respiration in the Abies Georgei var. Smithii Forest of Sygera Mountains [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(9): 1384-1396. |
| [6] | ZHU Ling, WEI Tianxing, YU Huan, WANG Xian, FAN Dehui, ZHAO Yuqi. Allelopathic Potential of Robinia pseudoacacia Root System and Rhizosphere Soil on 7 Species of Arbor, Shrub, and Grass Plants [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(9): 1406-1415. |
| [7] | WU Dongyang, WU Jiahuan, LI Weizhi, HUANG Zhijie, YANG Chunya, CHEN Huojun. Effects of Vermicompost and Pig manure Combined with Chemical Fertilizers on Soil Quality, Growth and Quality of Peppers [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(9): 1416-1425. |
| [8] | WEN Shan, XING Siqi, XIAO Yuxiang, LIU Yun, WU Xu. Study on Pollutant Phosphorus Release Behavior during Dredging Process of Tianfumiao Reservoir Based on Multi-field Coupling Finite Element Method [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(9): 1438-1450. |
| [9] | CONG Xin, ZHANG Huaidi, ZHANG Rong, ZHAO Cen, CHEN Kun, LIU Hanbing. Pollution Characteristics and Risk Analysis of Heavy Metal in Farmland Soils of China in Recent 10 Years Based on Meta Analysis [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(9): 1451-1459. |
| [10] | LIU Dongyi, QU Yonghua, FENG Yaowei, QU Ran. Research on Chromium Ion Content Inversion of GF-5 Satellite Images Based on Grid Search Optimization CatBoost Model [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(9): 1460-1470. |
| [11] | ZHANG Shuhan, JIANG Hailing, YU Hailin, FENG Xinhui. Spatio-temporal Evolution and Driving Force Analysis of Landscape Ecological Risk in Shenyang Modern Metropolitan [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(9): 1471-1481. |
| [12] | PANG Bo, HAI Xiang, ZHANG Haifang, ZHANG Yanjun, WANG Hui, LIU Hongmei, YANG Dianlin. Effects of Spread of Veratrum nigrum on Vegetation Characteristics and Soil Physicochemical Properties in Mountain Meadow Steppe [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(8): 1174-1181. |
| [13] | WANG Wenjing, ZHAI Shuijing, WANG Sai. Distribution Characteristics of Silicon and Its Influencing Factors in the Wetland Soils along the Minjiang River Downstream [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(8): 1182-1191. |
| [14] | WU Yi, MAO Xufeng, LIU Zebi, XIA Liang, JIN Xin, TANG Wenjia, YU Hongyan, DU Kai. Abundance and Community Structure of Methanotrophs in the Sediment of Cascade Reservoirs in the Upper Yellow River [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(8): 1192-1202. |
| [15] | FAN Beibie, DING Shuai, ZHANG Tiantian, ZHANG Shuai, WEI Lulu, CHEN Qing. Simulation Study on Phosphorus Loss Risk with Periodic Flooding-Drying and Straw Incorporation in a Dolomite-Amended Brown Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(8): 1203-1213. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
