Ecology and Environment ›› 2024, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (9): 1406-1415.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.09.008
• Research Article [Ecology] • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHU Ling( ), WEI Tianxing*(
), WEI Tianxing*( ), YU Huan, WANG Xian, FAN Dehui, ZHAO Yuqi
), YU Huan, WANG Xian, FAN Dehui, ZHAO Yuqi
Received:2024-05-13
Online:2024-09-18
Published:2024-10-18
Contact:
WEI Tianxing
朱玲( ), 魏天兴*(
), 魏天兴*( ), 于欢, 王仙, 范德卉, 赵雨琪
), 于欢, 王仙, 范德卉, 赵雨琪
通讯作者:
魏天兴
作者简介:朱玲(1998年生),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为生态环境地理。E-mail: 2211430263@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
ZHU Ling, WEI Tianxing, YU Huan, WANG Xian, FAN Dehui, ZHAO Yuqi. Allelopathic Potential of Robinia pseudoacacia Root System and Rhizosphere Soil on 7 Species of Arbor, Shrub, and Grass Plants[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(9): 1406-1415.
朱玲, 魏天兴, 于欢, 王仙, 范德卉, 赵雨琪. 刺槐根系和根际土对7种乔灌草植物的化感潜力[J]. 生态环境学报, 2024, 33(9): 1406-1415.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2024.09.008
| 样地编号 | 树种 | 海拔/ m | 坡度/ (°) | 坡向 | 郁闭度/% | 平均胸径/cm | 平均 高度/m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 刺槐 R. pseudoacacia | 1159 | 22 | SE13° | 80 | 7.58 | 8.46 |
| 2 | 刺槐 R. pseudoacacia | 1148 | 26 | SE32° | 82 | 11.31 | 9.24 |
| 3 | 刺槐 R. pseudoacacia | 1186 | 23 | NW24° | 85 | 14.53 | 10.15 |
Table 1 Basic overview of sample plots
| 样地编号 | 树种 | 海拔/ m | 坡度/ (°) | 坡向 | 郁闭度/% | 平均胸径/cm | 平均 高度/m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 刺槐 R. pseudoacacia | 1159 | 22 | SE13° | 80 | 7.58 | 8.46 |
| 2 | 刺槐 R. pseudoacacia | 1148 | 26 | SE32° | 82 | 11.31 | 9.24 |
| 3 | 刺槐 R. pseudoacacia | 1186 | 23 | NW24° | 85 | 14.53 | 10.15 |
| 影响因素 | 发芽率 | 发芽势 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | p | F | p | ||
| 不同浸提液 | 0.444 | 0.506 | 0.889 | 0.347 | |
| 质量浓度 | 10.216 | <0.001 | 23.311 | <0.001 | |
| 受体植物 | 705.233 | <0.001 | 1617.928 | <0.001 | |
| 不同浸提液×质量浓度 | 0.498 | 0.778 | 7.180 | <0.001 | |
| 不同浸提液×受体植物 | 6.201 | <0.001 | 23.027 | <0.001 | |
| 质量浓度×受体植物 | 11.127 | <0.001 | 20.755 | <0.001 | |
| 不同浸提液×质量浓度×受体植物 | 0.881 | 0.648 | 5.541 | <0.001 | |
Table 2 Variance analysis of three factors affecting allelopathy on seed germination
| 影响因素 | 发芽率 | 发芽势 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | p | F | p | ||
| 不同浸提液 | 0.444 | 0.506 | 0.889 | 0.347 | |
| 质量浓度 | 10.216 | <0.001 | 23.311 | <0.001 | |
| 受体植物 | 705.233 | <0.001 | 1617.928 | <0.001 | |
| 不同浸提液×质量浓度 | 0.498 | 0.778 | 7.180 | <0.001 | |
| 不同浸提液×受体植物 | 6.201 | <0.001 | 23.027 | <0.001 | |
| 质量浓度×受体植物 | 11.127 | <0.001 | 20.755 | <0.001 | |
| 不同浸提液×质量浓度×受体植物 | 0.881 | 0.648 | 5.541 | <0.001 | |
| 影响因素 | 胚芽鲜质量 | |
|---|---|---|
| F | p | |
| 不同浸提液 | 0.348 | 0.556 |
| 质量浓度 | 3.900 | 0.002 |
| 受体植物 | 121.781 | <0.001 |
| 不同浸提液×质量浓度 | 0.103 | 0.991 |
| 不同浸提液×受体植物 | 0.492 | 0.814 |
| 质量浓度×受体植物 | 1.181 | 0.250 |
| 不同浸提液×质量浓度×受体植物 | 0.106 | 1.000 |
Table 3 Three-factor variance analysis of allelopathy on the fresh weight of seedling germ
| 影响因素 | 胚芽鲜质量 | |
|---|---|---|
| F | p | |
| 不同浸提液 | 0.348 | 0.556 |
| 质量浓度 | 3.900 | 0.002 |
| 受体植物 | 121.781 | <0.001 |
| 不同浸提液×质量浓度 | 0.103 | 0.991 |
| 不同浸提液×受体植物 | 0.492 | 0.814 |
| 质量浓度×受体植物 | 1.181 | 0.250 |
| 不同浸提液×质量浓度×受体植物 | 0.106 | 1.000 |
| 质量浓度/ (mg∙mL−1) | 胚芽鲜质量/mg | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 冰草 A. cristatum | 侧柏 P. orientalis | 刺槐 R. pseudoacacia | 胡枝子 L. bicolor | 绣线菊 S. salicifolia | 油松 P. tabuliformis | 紫花苜蓿 M. sativa | |
| 0 | 4.26±0.55b | 30.02±3.16ab | 77.22±10.67a | 6.92±0.96b | 12.42±1.71a | 71.13±19.34a | 14.96±2.07ab |
| 0.5 | 4.46±0.57b | 30.73±3.21ab | 80.01±11.05a | 7.32±1.00ab | 13.60±1.89a | 74.78±20.37a | 15.48±2.14ab |
| 1.0 | 6.11±0.79a | 33.97±3.54a | 87.61±12.12a | 8.35±1.15ab | 15.32±2.12a | 79.90±21.77a | 16.82±2.33a |
| 3.0 | 4.86±0.64ab | 31.48±3.29a | 76.82±10.62a | 10.83±1.52a | 13.08±1.81a | 109.78±29.90a | 16.14±2.23ab |
| 5.0 | 2.90±0.38bc | 28.12±3.07ab | 74.33±10.28a | 10.96±1.51a | 11.84±1.64a | 78.73±21.44a | 13.69±1.89ab |
| 7.0 | 2.02±0.26c | 25.65±2.79ab | 74.61±10.33a | 9.92±1.37ab | 10.69±1.48a | 63.83±7.38a | 12.00±1.66ab |
| 10.0 | 1.38±0.18c | 21.84±2.39b | 62.60±8.65a | 9.04±1.25ab | 9.68±1.34a | 54.12±14.73a | 10.46±1.45b |
Table 4 Effects of different mass concentrations of extracts on fresh quality of seedling germ
| 质量浓度/ (mg∙mL−1) | 胚芽鲜质量/mg | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 冰草 A. cristatum | 侧柏 P. orientalis | 刺槐 R. pseudoacacia | 胡枝子 L. bicolor | 绣线菊 S. salicifolia | 油松 P. tabuliformis | 紫花苜蓿 M. sativa | |
| 0 | 4.26±0.55b | 30.02±3.16ab | 77.22±10.67a | 6.92±0.96b | 12.42±1.71a | 71.13±19.34a | 14.96±2.07ab |
| 0.5 | 4.46±0.57b | 30.73±3.21ab | 80.01±11.05a | 7.32±1.00ab | 13.60±1.89a | 74.78±20.37a | 15.48±2.14ab |
| 1.0 | 6.11±0.79a | 33.97±3.54a | 87.61±12.12a | 8.35±1.15ab | 15.32±2.12a | 79.90±21.77a | 16.82±2.33a |
| 3.0 | 4.86±0.64ab | 31.48±3.29a | 76.82±10.62a | 10.83±1.52a | 13.08±1.81a | 109.78±29.90a | 16.14±2.23ab |
| 5.0 | 2.90±0.38bc | 28.12±3.07ab | 74.33±10.28a | 10.96±1.51a | 11.84±1.64a | 78.73±21.44a | 13.69±1.89ab |
| 7.0 | 2.02±0.26c | 25.65±2.79ab | 74.61±10.33a | 9.92±1.37ab | 10.69±1.48a | 63.83±7.38a | 12.00±1.66ab |
| 10.0 | 1.38±0.18c | 21.84±2.39b | 62.60±8.65a | 9.04±1.25ab | 9.68±1.34a | 54.12±14.73a | 10.46±1.45b |
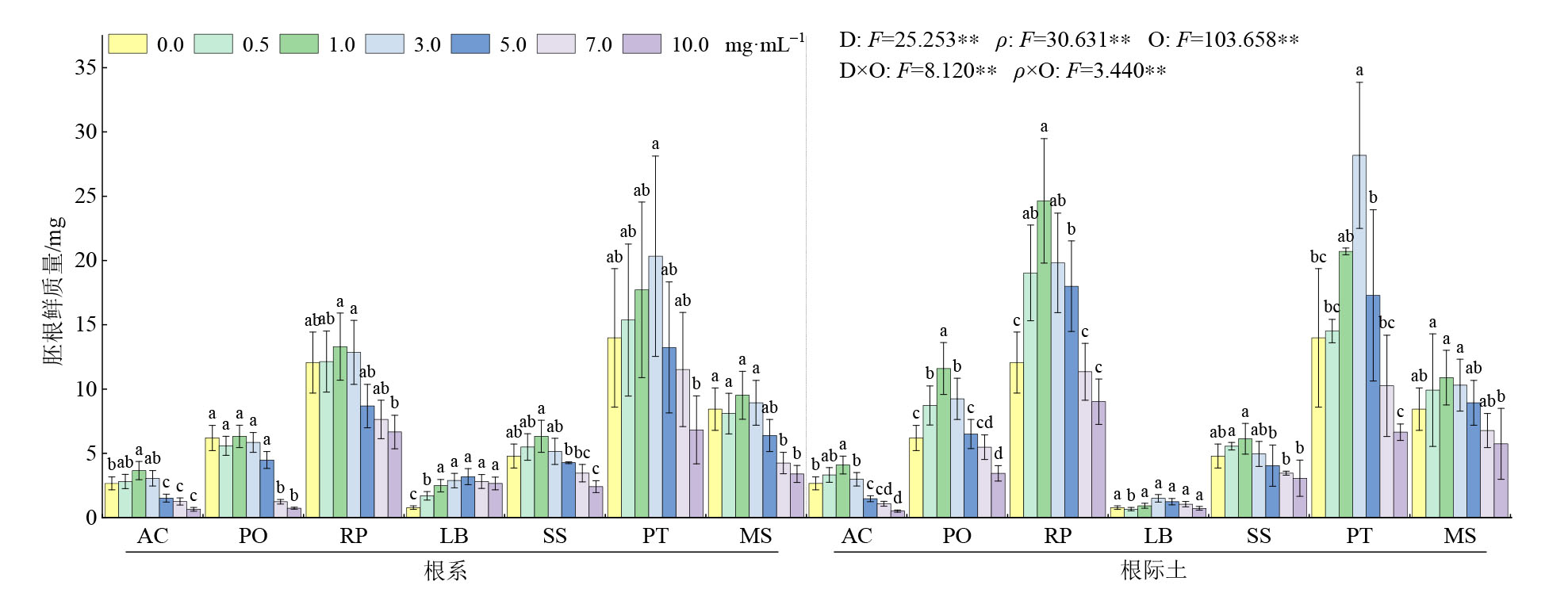
Figure 2 Effects of different mass concentrations of extracts from R. pseudoacacia root and rhizosphere soil on the fresh quality of seedlings radicle
| 不同浸提液 | 受体植物 | 综合化感效应指数 (SE) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 浸提液质量浓度/(mg∙mL−1) | |||||||
| 0.5 | 1.0 | 3.0 | 5.0 | 7.0 | 10.0 | ||
| 根系 | 冰草A. cristatum | 0.092 | 0.211 | 0.174 | −0.050 | −0.083 | −0.363 |
| 侧柏P. orientalis | 0.085 | 0.336 | 0.170 | −0.086 | −0.158 | −0.605 | |
| 刺槐 R. pseudoacacia | 0.140 | 0.193 | 0.235 | 0.268 | 0.298 | 0.323 | |
| 胡枝子L. bicolor | 0.528 | 0.516 | 0.369 | −0.106 | −0.483 | −0.660 | |
| 绣线菊S. salicifolia | 0.167 | 0.294 | 0.287 | 0.374 | 0.388 | 0.418 | |
| 油松P. tabuliformis | 0.215 | 0.083 | 0.334 | 0.417 | 0.353 | −0.138 | |
| 紫花苜蓿M. sativa | 0.032 | 0.127 | 0.106 | −0.022 | −0.099 | −0.178 | |
| 根际土 | 冰草A. cristatum | 0.268 | 0.406 | 0.346 | 0.160 | −0.203 | −0.333 |
| 侧柏P. orientalis | 0.270 | 0.452 | 0.031 | 0.257 | 0.174 | −0.605 | |
| 刺槐 R. pseudoacacia | 0.077 | 0.154 | 0.215 | 0.296 | 0.325 | 0.403 | |
| 胡枝子L. bicolor | 0.495 | 0.558 | 0.356 | −0.316 | −0.150 | −0.446 | |
| 绣线菊S. salicifolia | −0.048 | 0.152 | 0.228 | 0.315 | 0.347 | 0.316 | |
| 油松P. tabuliformis | 0.494 | 0.606 | 0.497 | 0.420 | 0.317 | −0.135 | |
| 紫花苜蓿M. sativa | 0.047 | 0.122 | −0.034 | −0.073 | −0.153 | −0.480 | |
Table 5 Allelopathic response index of different mass concentrations of extracts from R. pseudoacacia locust roots and rhizosphere soil on seed germination
| 不同浸提液 | 受体植物 | 综合化感效应指数 (SE) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 浸提液质量浓度/(mg∙mL−1) | |||||||
| 0.5 | 1.0 | 3.0 | 5.0 | 7.0 | 10.0 | ||
| 根系 | 冰草A. cristatum | 0.092 | 0.211 | 0.174 | −0.050 | −0.083 | −0.363 |
| 侧柏P. orientalis | 0.085 | 0.336 | 0.170 | −0.086 | −0.158 | −0.605 | |
| 刺槐 R. pseudoacacia | 0.140 | 0.193 | 0.235 | 0.268 | 0.298 | 0.323 | |
| 胡枝子L. bicolor | 0.528 | 0.516 | 0.369 | −0.106 | −0.483 | −0.660 | |
| 绣线菊S. salicifolia | 0.167 | 0.294 | 0.287 | 0.374 | 0.388 | 0.418 | |
| 油松P. tabuliformis | 0.215 | 0.083 | 0.334 | 0.417 | 0.353 | −0.138 | |
| 紫花苜蓿M. sativa | 0.032 | 0.127 | 0.106 | −0.022 | −0.099 | −0.178 | |
| 根际土 | 冰草A. cristatum | 0.268 | 0.406 | 0.346 | 0.160 | −0.203 | −0.333 |
| 侧柏P. orientalis | 0.270 | 0.452 | 0.031 | 0.257 | 0.174 | −0.605 | |
| 刺槐 R. pseudoacacia | 0.077 | 0.154 | 0.215 | 0.296 | 0.325 | 0.403 | |
| 胡枝子L. bicolor | 0.495 | 0.558 | 0.356 | −0.316 | −0.150 | −0.446 | |
| 绣线菊S. salicifolia | −0.048 | 0.152 | 0.228 | 0.315 | 0.347 | 0.316 | |
| 油松P. tabuliformis | 0.494 | 0.606 | 0.497 | 0.420 | 0.317 | −0.135 | |
| 紫花苜蓿M. sativa | 0.047 | 0.122 | −0.034 | −0.073 | −0.153 | −0.480 | |
| 不同浸提液 | 受体植物 | 综合化感效应指数 (SE) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 浸提液质量浓度/(mg∙mL−1) | |||||||
| 0.5 | 1.0 | 3.0 | 5.0 | 7.0 | 10.0 | ||
| 根系 | 冰草A. cristatum | 0.035 | 0.044 | −0.050 | −0.319 | −0.439 | −0.632 |
| 侧柏P. orientalis | 0.010 | 0.111 | 0.014 | −0.150 | −0.385 | −0.573 | |
| 刺槐 R. pseudoacacia | 0.045 | 0.142 | 0.063 | −0.123 | −0.240 | −0.362 | |
| 胡枝子L. bicolor | 0.357 | 0.475 | 0.599 | 0.595 | 0.567 | 0.495 | |
| 绣线菊 S. salicifolia | 0.129 | 0.268 | 0.071 | −0.083 | −0.264 | −0.475 | |
| 油松 P. tabuliformis | 0.002 | 0.126 | 0.267 | −0.075 | −0.227 | −0.442 | |
| 紫花苜蓿 M. sativa | −0.034 | −0.032 | −0.093 | −0.226 | −0.338 | −0.423 | |
| 根际土 | 冰草A. cristatum | 0.126 | 0.281 | 0.102 | −0.282 | −0.493 | −0.691 |
| 侧柏P. orientalis | 0.121 | 0.252 | 0.135 | −0.073 | −0.241 | −0.485 | |
| 刺槐 R. pseudoacacia | 0.139 | 0.273 | 0.150 | −0.025 | −0.192 | −0.338 | |
| 胡枝子L. bicolor | 0.085 | 0.326 | 0.535 | 0.453 | 0.337 | 0.089 | |
| 绣线菊 S. salicifolia | −0.196 | −0.019 | 0.069 | −0.134 | −0.282 | −0.431 | |
| 油松 P. tabuliformis | 0.113 | 0.248 | 0.298 | 0.047 | −0.198 | −0.347 | |
| 紫花苜蓿 M. sativa | 0.027 | 0.147 | 0.085 | −0.166 | −0.359 | −0.517 | |
Table 6 Allelopathic response index of different mass concentrations of extracts from R. pseudoacacia roots and rhizosphere soil on seedling growth
| 不同浸提液 | 受体植物 | 综合化感效应指数 (SE) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 浸提液质量浓度/(mg∙mL−1) | |||||||
| 0.5 | 1.0 | 3.0 | 5.0 | 7.0 | 10.0 | ||
| 根系 | 冰草A. cristatum | 0.035 | 0.044 | −0.050 | −0.319 | −0.439 | −0.632 |
| 侧柏P. orientalis | 0.010 | 0.111 | 0.014 | −0.150 | −0.385 | −0.573 | |
| 刺槐 R. pseudoacacia | 0.045 | 0.142 | 0.063 | −0.123 | −0.240 | −0.362 | |
| 胡枝子L. bicolor | 0.357 | 0.475 | 0.599 | 0.595 | 0.567 | 0.495 | |
| 绣线菊 S. salicifolia | 0.129 | 0.268 | 0.071 | −0.083 | −0.264 | −0.475 | |
| 油松 P. tabuliformis | 0.002 | 0.126 | 0.267 | −0.075 | −0.227 | −0.442 | |
| 紫花苜蓿 M. sativa | −0.034 | −0.032 | −0.093 | −0.226 | −0.338 | −0.423 | |
| 根际土 | 冰草A. cristatum | 0.126 | 0.281 | 0.102 | −0.282 | −0.493 | −0.691 |
| 侧柏P. orientalis | 0.121 | 0.252 | 0.135 | −0.073 | −0.241 | −0.485 | |
| 刺槐 R. pseudoacacia | 0.139 | 0.273 | 0.150 | −0.025 | −0.192 | −0.338 | |
| 胡枝子L. bicolor | 0.085 | 0.326 | 0.535 | 0.453 | 0.337 | 0.089 | |
| 绣线菊 S. salicifolia | −0.196 | −0.019 | 0.069 | −0.134 | −0.282 | −0.431 | |
| 油松 P. tabuliformis | 0.113 | 0.248 | 0.298 | 0.047 | −0.198 | −0.347 | |
| 紫花苜蓿 M. sativa | 0.027 | 0.147 | 0.085 | −0.166 | −0.359 | −0.517 | |
| [1] | AN G Q, LI J M, LU H F, et al., 2022. Nitrogen-dependent luteolin effect on Microcystis growth and microcystin-pollution risk-Novel mechanism insights unveiled by comparative proteomics and gene expression[J]. Environmental Pollution, 311(10): 119848. |
| [2] | ANH L H, QUAN N V, NGHIA L T, et al., 2021. Phenolic allelochemicals: Achievements, limitations, and prospective approaches in weed management[J]. Weed Biology and Management, 21(2): 37-67. |
| [3] |
BRUCE WILLIAMSON G, RICHARDSON D, 1988. Bioassays for allelopathy: Measuring treatment responses with independent controls[J]. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 14(1): 181-187.
DOI PMID |
| [4] | CHON S, COUTTS J H, NELSON C J, 2000. Effects of light, growth media, and seedling orientation on bioassays of alfalfa autotoxicity[J]. Agronomy Journal, 92(4): 715-720. |
| [5] | CHON S, NELSON C J, COUTTS J H, 2004. Osmotic and Autotoxic effects of leaf extracts on germination and seedling growth of alfalfa[J]. Agronomy Journal, 96(6): 1673-1679. |
| [6] | LI Q, ZHAO G, CAO G, et al., 2020. Non-additive effects of leaf litter mixtures from Robinia pseudoacacia and ten tree species on soil properties[J]. Journal of Sustainable Forestry, 39(8): 771-784. |
| [7] | SILVIA M V, ALVARO A, MARIA E P C, et al., 2017. Allelopathic potentials of exotic invasive and native trees over coexisting understory species: The soil as modulator[J]. Plant Ecology, 218(5): 579-594. |
| [8] | SHEKARI F, SHEKARI F, NAJAFI J, et al., 2022. Phytotoxic effects of catnip (Nepeta meyeri Benth) on early growth stages development and infection potential of field dodder (Cuscuta campestris Yunck)[J]. Plants-Basel, 11(19): 2629. |
| [9] | SU Z X, ZHU X Y, WANG Y B, et al., 2022. Litter C and N losses at different decomposition stages of Robinia pseudoacacia: The weaker effects of soil enzyme activities compared with those of litter quality and the soil environment[J]. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 10(11): 956309. |
| [10] | VIATOR R P, Johnson R M, Grimm C C, et al., 2006. Allelopathic, Autotoxic, and Hormetic effects of Postharvest sugarcane Residue[J]. Agronomy Journal, 98(6): 1526-1531. |
| [11] | WANG X Q, ZHANG R Q, WANG J X, et al., 2021. The effects of leaf extracts of four tree species on Amygdalus pedunculata seedlings growth[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 11(1): 587579. |
| [12] | WYMAN C L, WALLER G R, JURZYSTA M, et al., 1991. Biological activity and chemical isolation of root saponins of six cultivars of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L)[J]. Plant and Soil, 135(1): 83-94. |
| [13] | ZHANG X X, LIU Z W, ZHU Z H, et al., 2016. Impacts of mixed litter decomposition from Robinia pseudoacacia and other tree species on C loss and nutrient release in the Loess Plateau of China[J]. Journal of Forestry Research, 27(3): 525-532. |
| [14] | ZHAO J C, YANG Z Y, ZOU J Q, et al., 2022. Allelopathic effects of sesame extracts on seed germination of moso bamboo and identification of potential allelochemicals[J]. Scientific Reports, 12(1): 6661. |
| [15] | ZHAO W Y, WEN M X, ZHAO C T, et al., 2023. Warm temperature increments strengthen the crosstalk between roots and soil in the rhizosphere of soybean seedlings[J]. Plants-Basel, 12(24): 4135. |
| [16] | 陈雪冬, 唐明, 张新璐, 等, 2017. 黄土高原刺槐纯林的土壤-菌根关系及随林龄的变化[J]. 林业科学, 53(12): 84-92. |
| CHEN X D, TANG M, ZHANG X L, et al., 2017 Variation of the relationships between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and soil properties with different stand Age of Robinia pseudoacacia plantations on the loess plateau[J]. Scientla Sylvae Sinicae, 53(12): 84-92. | |
| [17] | 段文艳, 李鑫, 李晴, 等, 2023. 黄土高原草地和刺槐根际AM真菌对刺槐和侧柏生长、土壤性质及叶片光合特性的影响[J]. 西北农业学报, 32(9): 1422-1436. |
| DUAN W Y, LI X, LI Q, et al., 2023. Effects of AM Fungi in grassland and rhizosphere of black locust on loess plateau on growth status, leaf photosynthesis characteristic sand soil properties of black locust and oriental arborvitae[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 32(9): 1422-1436. | |
| [18] | 葛杰克, 叶雨蒙, 楼雪怡, 等, 2023. 酚酸化感作用对栝楼生理特性及根际微生态的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 37(3): 258-266, 272. |
| GE J K, YE Y M, LOU X Y, et al., 2023. Effects of phenolic acidification on physiological characteristics and rhizosphere microecology of Trichosanthes kirilowii Maxim[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 37(3): 258-266, 272. | |
| [19] | 郭钟惠, 李洁明, 张明霞, 2023. 不同类型化感物质抑制蓝藻效益比较及联合抑藻效应评述[J]. 水生生物学报, 47(1): 177-194. |
| GUO Z H, LI J M, ZHANG M X, 2023. A review on antialgal effectiveness among distinct allelochemicals and joint inhibitory effects on Cyanobacterial growth[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 47(1): 177-194. | |
| [20] | 何斐, 崔鸣, 孙娅, 等, 2021. 刺槐凋落叶腐解液对3种作物的化感效应[J]. 西北林学院学报, 36(2): 116-122. |
| HE F, CUI M, SUN Y, et al., 2021. Allelopathic effect of decomposed liquid of Robinia pseudoacacia leaf litter on three crops[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 36(2): 116-122. | |
| [21] | 胡缓, 何松林, 张晋瑞, 等, 2023. 小蓬草水浸液对2种花卉种子萌发及幼苗生长的化感作用[J]. 西北植物学报, 43(9): 1528-1536. |
| HU H, HE S L, ZHANG J R, et al., 2023. Allelopathic effects of aqueous extract from Conyza canadensis on seed germination and seedling growth of two herbaceous flower species[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 43(9): 1528-1536. | |
| [22] |
黄良嘉, 刘增文, 朱博超, 等, 2014. 小叶杨和刺槐纯林腐殖质土壤对9种常见灌草植物的化感效应[J]. 草地学报, 22(1): 150-157.
DOI |
| HUANG L J, LIU Z W, ZHU B C, et al., 2014. Allelopathic effects of the humus soil of Populus simonii and Robinia pseudoacacia on tested common shrubs and grasses[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 22(1): 150-157. | |
| [23] | 计怀峰, 林辰壹, 卓马别克吾塔尼别克, 等, 2024. 丛枝菌根真菌对实葶葱生长及化感作用的影响[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 52(6): 1-11. |
| JI H F, LIN C Y, ZHUOMABIEKE U, et al., 2024. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on growth and allelopathy of Allium galanthum[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 52(6): 1-11. | |
| [24] | 荆蓉, 彭祚登, 李云, 等, 2023. 刺槐林下凋落物浸提液对刺槐种子萌发和胚生长的化感作用[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 40(1): 97-106. |
| JING R, PENG Z D, LI Y, et al., 2023. Allelopathy of the litter extracts from Robinia pseudoacacia forest on its seed germination and embryo growth[J]. Journal of Zhejiang A & F University, 40(1): 97-106. | |
| [25] | 孔垂华, 胡飞, 王朋, 2016. 植物化感 (相生相克) 作用[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社: 3-4. |
| KONG C H, HU F, WANG P, 2016. Plant allelopathic effect[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press: 3-4. | |
| [26] | 李轲, 杨柳, 2019. 刺槐根际土壤水浸提液对5种常见园林植物种子萌发及幼苗生长的化感作用[J]. 种子, 38(6): 115-120. |
| LI K, YANG L, 2019. Allelopathic effects of aqueous extracts from rhizosphere soil of Robinia pseudoacacia linn on seed germination and seedling growth of five kinds of common garden plants[J]. Seed, 38(6): 115-120. | |
| [27] |
李彦飞, 初晓辉, 李嘉懿, 等, 2022. 大狼毒对紫花苜蓿种子萌发及幼苗生长的化感效应研究[J]. 草地学报, 30(2): 394-402.
DOI |
| LI Y F, CHU X H, LI J Y, et al., 2022. Allelopathic effects of Euphorbia jolkinii on seed germination and seedling growth of alfalfa[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 30(2): 394-402. | |
| [28] | 宋亮, 潘开文, 王进闯, 等, 2006. 酚酸类物质对苜蓿种子萌发及抗氧化物酶活性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 26(10): 3393-3403. |
| SONG L, PAN K W, WANG J C, et al., 2006. Effects of phenolic acids on seed germination and seedling antioxidant enzyme activity of alfalfa[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 26(10): 3393-3403. | |
| [29] | 汪琼, 辛培尧, 闻永慧, 2023. 两种乔木落叶浸提液对高羊茅幼苗生长和根际土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 草业科学, 40(12): 1-11. |
| WANG Q, XIN P Y, WEN Y H, 2023. Effects of two kinds of tree deciduous extracts on Festuca arundinacea growth and enzyme activity in rhizosphere soil[J]. Pratacultural Science, 40(12): 1-11. | |
| [30] | 王博恒, 卢佶, 王丹, 等, 2024. 基于熵值法的人工林林木邻体结构优化方法[J]. 西北林学院学报, 41(1): 1-7. |
| WANG B H, LU J, WANG D, et al., 2024. Entropy based optimization method of neighborhood structure for the individual plantation tree[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 41(1): 1-7. | |
| [31] | 王仙, 魏天兴, 朱金兆, 等, 2015. 黄土丘陵区油松根系化感效应研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 37(4): 82-89. |
| WANG X, WEI T X, ZHU J Z, et al., 2015. Allelopathic effect of Pinus tabuliformis root in loess hilly area[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 37(4): 82-89. | |
| [32] | 王小雪, 刘芸, 邵呈龙, 等, 2011. 5种经济植物对幼龄尾巨桉叶片提取液的化感敏感性[J]. 林业科学, 47(11): 188-193. |
| WANG X X, LIU Y, SHAO C L, et al., 2011. Allelopathic sensitivity of five economic species to aqueous leaf extract of Eucalyptus urophylla×E. grandis with different ages[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 47(11): 188-193. | |
| [33] | 袁娜, 刘增文, 祝振华, 等, 2012. 黄土高原主要人工林树种对几种豆科牧草的化感作用[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 40(1): 87-92. |
| YUAN N, LIU Z W, ZHU Z H, et al., 2012. Study on allelopathic effects of main planted forest trees in the Loess Plateau on some legumes[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 40(1): 87-92. | |
| [34] | 张静, 温仲明, 李鸣雷, 等, 2018. 外来物种刺槐对土壤微生物功能多样性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 38(14): 4964-4974. |
| ZHANG J, WEN Z M, LI M L, et al., 2018. Effects of the exotic black locust on the functional diversity of soil microorganisms[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(14): 4964-4974. | |
| [35] | 朱美秋, 刘春鹏, 邓明静, 等, 2015. 臭椿根系水浸提液的化感效应[J]. 森林环境学报, 35(3): 284-288. |
| ZHU M Q, LIU C P, DENG M J, et al., 2015. Allelopathy of aqueous extracts obtained from roots of Ailanthus altissima[J]. Journal of Forest and Environment, 35(3): 284-288. |
| [1] | LI Yanlin, CHEN Yangyang, YANG Shuangrong, LIU Jumei. Study on the Effects of Organic Acids in Plant Root Exudates on Soil Organic Carbon and Nitrogen Mineralization [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(9): 1362-1371. |
| [2] | LIN Dandan, BI Huaxing, ZHAO Danyang, GUAN Ning, HAN Jindan, GUO Yanjie. Soil Organic Carbon Fractions and Carbon Pool Characteristics of Robinia pseudoacacia Forests with Different Densities in the Loess Region of Western Shanxi Province [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(3): 379-388. |
| [3] | LIANG Yan, LIU Jiaqi, XIAO Fan, PAN Minping, WEI Kaiwen, ZHANG Chuwen, DUAN Min. Effects of Nitrogen Deposition Forms on Sources of Soil Available Phosphorus in Karst Forest of Southwest China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2024, 33(2): 192-201. |
| [4] | HUANG Shicong, CHEN Like, ZHANG Zhengjie, CHEN Kehua, CHEN Chengyu, ZENG Qiaoyun. Toxicity Thresholds of Tetracycline to Varieties of Vegetables and Its Species Sensitivity Distributions [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(11): 1988-1995. |
| [5] | LI Chengtao, WU Wanqing, CHEN Chen, ZHANG Yong, ZHANG Kai. Effects of Biodegradable PBAT Microplastics on Soil Physical and Chemical Properties and Physiological Indicators of Brassica chinensis [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(11): 1964-1977. |
| [6] | YANG Rui, SUN Weimin, LI Yongbin, GUO Lifang, JIAO Nianyuan. Isolation, Identification and Plant Growth Promotion of Rhizosphere Phosphorus-dissolving Bacteria from Tailings Pioneer Plants [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(1): 166-174. |
| [7] | YOU Hongjian, ZHANG Wenwen, LAN Zhengfang, MA Lan, ZHANG Baodi, MU Xiaokun, LI Wenhui, CAO Yune. Effects of Earthworm in-situ Composting and Biochar on Cucumber Root-knot Nematodes and Rhizosphere Microorganisms [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(1): 99-109. |
| [8] | CUI Yuanyuan, ZHANG Zhengyun, LIU Peng, ZHANG Yunchun, ZHANG Qiaoying. Morphological Characteristics and Fractal Dimension of Brassia chinensis Root System under Cadmium and Polyethylene Microplastic Stress [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(1): 158-165. |
| [9] | LI Ying, ZHANG Zhou, YANG Gaoming, ZU Yanqun, LI Bo, CHEN Jianjun. The Relationship between the Radial Oxygen Loss and the Iron Plaque on Root Surfaces to Wetland Plants Absorb Heavy Metals [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(8): 1657-1666. |
| [10] | LIU Xiaohong, LIU Liuqingqing, LI Min, LIU Qiang, CAO Dongdong, ZHENG Hao, LUO Xianxiang. Effects of Polyethylene Microplastics with Different Particle Sizes on Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Maize and Cucumber [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(6): 1263-1271. |
| [11] | FU Yuhong, ZHANG Daijie, XIANG Jiao, ZHOU Yan, HUANG Zongsheng, YU Lifei. Topological Structure of Plant Roots of Different Underground Habitat Profiles in Karst Areas [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(5): 865-874. |
| [12] | LU Hui, LÜ Gang, LIU Jianhua, ZHANG Zhuo, WANG Fengbai. Study on Soil Priority Flow Characteristics of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica Plantation at Different Ages in Wind Sandy Land of Northwest Liaoning Province [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(12): 2350-2357. |
| [13] | CHEN Fuqiuxue, TANG Siqi, YUAN Hao, MA Zixuan, CHEN Tan, YANG Ting, ZHANG Bing, LIU Ying. Impacts of Polystyrene Microplastics on Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Typical Crops [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(12): 2382-2392. |
| [14] | GAO Ge, GE Xiaogai, ZHOU Jungang, ZHOU Benzhi, LI Zhengcai, YANG Nan. Effect of Drought Stress and Nitrogen Addition on the Biomass and Root Morphology of Cunninghamia lanceolata and Cyclobalanopsis glauca Seedlings [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(12): 2292-2301. |
| [15] | SONG Xianchong, CAI Xuemei, CHEN Tao, PAN Wen, SHI Yuanyuan, TANG Jian, CAO Jizhao. Variation Characteristics of Rhizosphere and Non-rhizosphere Soil Nutrient in Successive Eucalyptus Plantation [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2021, 30(9): 1814-1820. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
