Ecology and Environment ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (11): 2072-2082.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.11.017
• Reviews • Previous Articles
ZHOU Yongkang1,2( ), YU Shengpin3,4, LI Jiale1,2,*(
), YU Shengpin3,4, LI Jiale1,2,*( ), DONG Yihui1,2, WANG Meng1,2, ZHAO Qiling1,2, LI Yeyu1,2
), DONG Yihui1,2, WANG Meng1,2, ZHAO Qiling1,2, LI Yeyu1,2
Received:2023-08-01
Online:2023-11-18
Published:2024-01-17
Contact:
LI Jiale
周永康1,2( ), 余圣品3,4, 李佳乐1,2,*(
), 余圣品3,4, 李佳乐1,2,*( ), 董一慧1,2, 王萌1,2, 赵齐灵1,2, 李烨余1,2
), 董一慧1,2, 王萌1,2, 赵齐灵1,2, 李烨余1,2
通讯作者:
李佳乐
作者简介:周永康(1998年生),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为环境有机污染。E-mail: 1115268271@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
ZHOU Yongkang, YU Shengpin, LI Jiale, DONG Yihui, WANG Meng, ZHAO Qiling, LI Yeyu. Research Progress on Adsorption Behavior and Mechanism of Antibiotics in Soil[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(11): 2072-2082.
周永康, 余圣品, 李佳乐, 董一慧, 王萌, 赵齐灵, 李烨余. 土壤中抗生素的吸附行为与机理研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(11): 2072-2082.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.11.017
| 样品类型 | 采样地点 | 主要污染物 | 检出率/% | 质量分数/(μg∙kg−1) | 参考文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤 | 重庆市开州区 | 四环素类 (TCs) | 土霉素 (OTC) | 46.15 | 0‒42.88 | 方林发等, |
| 喹诺酮类 (FQs) | 诺氟沙星 (NOR) | 100 | 1.75‒32.23 | |||
| 环丙沙星 (CIP) | 66.67 | 1.31‒264.70 | ||||
| 恩诺沙星 (ENR) | 50 | 0‒120.35 | ||||
| 洛美沙星 (LOM) | 25 | 0‒37.41 | ||||
| 诺氟沙星 (NOR) | 50 | 0‒48.63 | ||||
| 浙江省宁波市海曙区 | 四环素类 (TCs) | 金霉素 (CTC) | ‒ | 0‒324.70 | 赵方凯等, | |
| 江苏省、上海市 和云南省 | 四环素类 (TCs) | 四环素 (TC) | 100 | 1.30‒249 | Zhang et al., | |
| 土霉素 (OTC) | 100 | 1‒ | ||||
| 多西环素 (DOC) | 100 | 1.10‒256 | ||||
| 喹诺酮类 (FQs) | 诺氟沙星 (NOR) | 100 | 1.50‒102 | |||
| 恩诺沙星 (ENR) | 100 | 0.20‒92 | ||||
| 珠江三角洲 | 四环素类 (TCs) | 四环素 (TC) | 54 | 0‒90.42 | Gu et al., | |
| 土霉素 (OTC) | 81 | 0‒406.70 | ||||
| 金霉素 (CTC) | 77 | 0‒134.30 | ||||
| 山西省汾河沿岸 | 喹诺酮类 (FQs) | 诺氟沙星 (NOR) | 100 | 0‒27.21 | Zhu et al., | |
| 新加坡 | 大环内酯类 (MLs) | 红霉素 (ERY) | 93 | 18.80‒80.60 | Yi et al., | |
| 河流沉积物 | 丹江口水库 | 磺胺类 (SAs) | ‒ | 7.18 | 0‒8.94 | Li et al., |
| 大环内酯类 (MLs) | ‒ | 54.5 | 0‒4.34 | |||
| 四环素类 (TCs) | ‒ | 13.3 | 0‒12.10 | |||
| 广东省珠江沿岸 | 磺胺类 (SAs) | 磺胺二甲嘧啶 (SMZ) | 78 | 0‒248 | Yang et al., | |
| 四环素类 (TCs) | 土霉素 (OTC) | 71 | 0‒196 | |||
| 喹诺酮类 (FQs) | 诺氟沙星 (NOR) | 57 | 0‒1120 | |||
| 氧氟沙星 (OFL) | 57 | 0‒1560 | ||||
| 大环内酯类 (MLs) | 罗红霉素 (RTM) | 86 | 0‒133 | |||
| 莱州湾东岸 | 磺胺类 (SAs) | 磺胺二甲嘧啶 (SMZ) | ‒ | 0‒1369.61 | Han et al., | |
| 甲氧苄氨嘧啶 (TMP) | ‒ | 0‒4533.83 | ||||
| 喹诺酮类 (FQs) | 氧氟沙星 (OFL) | ‒ | 0‒2007.84 | |||
| 恩诺沙星 (ENR) | ‒ | 0‒1778.12 | ||||
| 环丙沙星 (CIP) | ‒ | 0‒752.11 | ||||
| 波兰海岸波罗的海南部 | 磺胺类 (SAs) | 磺胺甲噁唑 (SMX) | 58 | 0‒419 | Siedlewicz et al., | |
Table 1 Current status of antibiotic pollution in soil environment
| 样品类型 | 采样地点 | 主要污染物 | 检出率/% | 质量分数/(μg∙kg−1) | 参考文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤 | 重庆市开州区 | 四环素类 (TCs) | 土霉素 (OTC) | 46.15 | 0‒42.88 | 方林发等, |
| 喹诺酮类 (FQs) | 诺氟沙星 (NOR) | 100 | 1.75‒32.23 | |||
| 环丙沙星 (CIP) | 66.67 | 1.31‒264.70 | ||||
| 恩诺沙星 (ENR) | 50 | 0‒120.35 | ||||
| 洛美沙星 (LOM) | 25 | 0‒37.41 | ||||
| 诺氟沙星 (NOR) | 50 | 0‒48.63 | ||||
| 浙江省宁波市海曙区 | 四环素类 (TCs) | 金霉素 (CTC) | ‒ | 0‒324.70 | 赵方凯等, | |
| 江苏省、上海市 和云南省 | 四环素类 (TCs) | 四环素 (TC) | 100 | 1.30‒249 | Zhang et al., | |
| 土霉素 (OTC) | 100 | 1‒ | ||||
| 多西环素 (DOC) | 100 | 1.10‒256 | ||||
| 喹诺酮类 (FQs) | 诺氟沙星 (NOR) | 100 | 1.50‒102 | |||
| 恩诺沙星 (ENR) | 100 | 0.20‒92 | ||||
| 珠江三角洲 | 四环素类 (TCs) | 四环素 (TC) | 54 | 0‒90.42 | Gu et al., | |
| 土霉素 (OTC) | 81 | 0‒406.70 | ||||
| 金霉素 (CTC) | 77 | 0‒134.30 | ||||
| 山西省汾河沿岸 | 喹诺酮类 (FQs) | 诺氟沙星 (NOR) | 100 | 0‒27.21 | Zhu et al., | |
| 新加坡 | 大环内酯类 (MLs) | 红霉素 (ERY) | 93 | 18.80‒80.60 | Yi et al., | |
| 河流沉积物 | 丹江口水库 | 磺胺类 (SAs) | ‒ | 7.18 | 0‒8.94 | Li et al., |
| 大环内酯类 (MLs) | ‒ | 54.5 | 0‒4.34 | |||
| 四环素类 (TCs) | ‒ | 13.3 | 0‒12.10 | |||
| 广东省珠江沿岸 | 磺胺类 (SAs) | 磺胺二甲嘧啶 (SMZ) | 78 | 0‒248 | Yang et al., | |
| 四环素类 (TCs) | 土霉素 (OTC) | 71 | 0‒196 | |||
| 喹诺酮类 (FQs) | 诺氟沙星 (NOR) | 57 | 0‒1120 | |||
| 氧氟沙星 (OFL) | 57 | 0‒1560 | ||||
| 大环内酯类 (MLs) | 罗红霉素 (RTM) | 86 | 0‒133 | |||
| 莱州湾东岸 | 磺胺类 (SAs) | 磺胺二甲嘧啶 (SMZ) | ‒ | 0‒1369.61 | Han et al., | |
| 甲氧苄氨嘧啶 (TMP) | ‒ | 0‒4533.83 | ||||
| 喹诺酮类 (FQs) | 氧氟沙星 (OFL) | ‒ | 0‒2007.84 | |||
| 恩诺沙星 (ENR) | ‒ | 0‒1778.12 | ||||
| 环丙沙星 (CIP) | ‒ | 0‒752.11 | ||||
| 波兰海岸波罗的海南部 | 磺胺类 (SAs) | 磺胺甲噁唑 (SMX) | 58 | 0‒419 | Siedlewicz et al., | |
| 抗生素类型 | 化学结构式 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 磺胺类 | 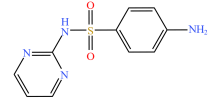 | 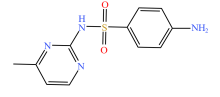 | 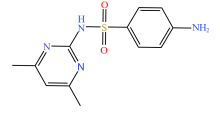 | 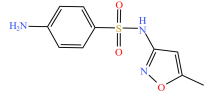 |
| 磺胺嘧啶 | 磺胺甲基嘧啶 | 磺胺二甲嘧啶 | 磺胺甲噁唑 | |
| 四环素类 | 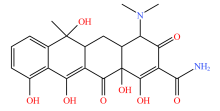 | 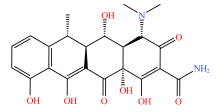 | 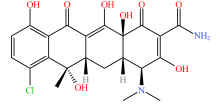 | 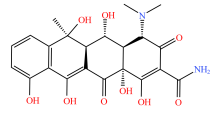 |
| 四环素 | 多西环素 | 金霉素 | 土霉素 | |
| 喹诺酮类 | 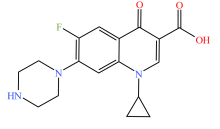 | 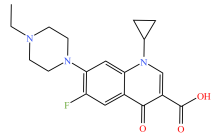 | 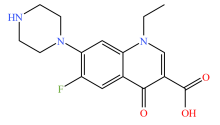 | 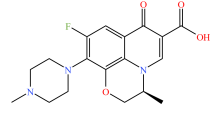 |
| 环丙沙星 | 恩诺沙星 | 诺氟沙星 | 左氧氟沙星 | |
| 大环内酯类 | 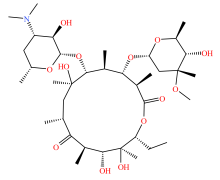 | 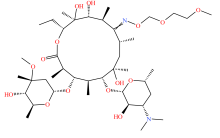 | 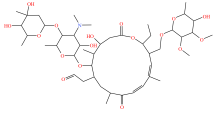 | 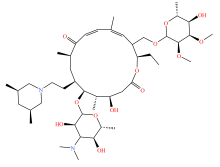 |
| 红霉素 | 罗红霉素 | 泰乐菌素 | 替米考星 | |
Table 2 Types and molecular structure of antibiotics detected in soil
| 抗生素类型 | 化学结构式 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 磺胺类 | 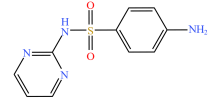 | 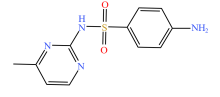 |  |  |
| 磺胺嘧啶 | 磺胺甲基嘧啶 | 磺胺二甲嘧啶 | 磺胺甲噁唑 | |
| 四环素类 |  |  |  |  |
| 四环素 | 多西环素 | 金霉素 | 土霉素 | |
| 喹诺酮类 |  |  |  |  |
| 环丙沙星 | 恩诺沙星 | 诺氟沙星 | 左氧氟沙星 | |
| 大环内酯类 |  |  |  |  |
| 红霉素 | 罗红霉素 | 泰乐菌素 | 替米考星 | |
| 吸附机制 | 主要原子 | 主要官能团 |
|---|---|---|
| H键作用 | N、H、O | -OH、-NH2和C=O |
| π-π相互作用 | C、H | 苯环 |
| 金属离子配位络合作用 | N、H、O | -NH2、-COOH和-OH |
| 去质子化作用 | C、H、O | -COOH |
| 阳离子交换 | N、H、O | -OH、-NH2和-COOH |
Table 3 Adsorption mechanism and the main atoms and functional groups involved
| 吸附机制 | 主要原子 | 主要官能团 |
|---|---|---|
| H键作用 | N、H、O | -OH、-NH2和C=O |
| π-π相互作用 | C、H | 苯环 |
| 金属离子配位络合作用 | N、H、O | -NH2、-COOH和-OH |
| 去质子化作用 | C、H、O | -COOH |
| 阳离子交换 | N、H、O | -OH、-NH2和-COOH |
| 抗生素类型 | 溶解性/ (mg∙L−1) | pKa1 | pKa2 | pKa3 | logKow | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 磺胺类 | 磺胺甲噁唑 (Chen et al., | 610 | 1.7 | 5.6 | ‒ | 0.89 |
| 磺胺嘧啶 (杜鹃, | 77 | 2.0 | 7.0 | ‒ | 0.25 | |
| 磺胺二甲嘧啶 (杜鹃, | 1500 | 2.7 | 7.7 | ‒ | 0.89 | |
| 四环 素类 | 四环素 (Rivera-Utrilla et al., | 22 | 3.3 | 7.8 | 9.6 | −1.30 |
| 土霉素 (Rivera-Utrilla et al., | 17 | 3.2 | 7.5 | 9.0 | −0.90 | |
| 金霉素 (Rivera-Utrilla et al., | 4.2 | 3.3 | 7.6 | 9.3 | −0.62 | |
| 多西环素 (Gao et al., | ‒ | 3.5 | 7.7 | 9.5 | ‒ | |
| 大环 内酯类 | 罗红霉素 (杜鹃, | 0.02 | ‒ | ‒ | 9.1 | 1.7 |
| 红霉素 (杜鹃, | 4.2 | ‒ | ‒ | 8.4 | 2.37 | |
| 喹诺 酮类 | 环丙沙星 (杜鹃, | 30000 | ‒ | 6.1 | 8.7 | 0.28 |
| 恩诺沙星 (杜鹃, | 3430 | ‒ | 5.5 | 8.6 | −0.2 | |
| 诺氟沙星 (杜鹃, | 17800 | ‒ | 6.3 | 8.7 | 0.46 | |
Table 4 Basic properties of antibiotics
| 抗生素类型 | 溶解性/ (mg∙L−1) | pKa1 | pKa2 | pKa3 | logKow | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 磺胺类 | 磺胺甲噁唑 (Chen et al., | 610 | 1.7 | 5.6 | ‒ | 0.89 |
| 磺胺嘧啶 (杜鹃, | 77 | 2.0 | 7.0 | ‒ | 0.25 | |
| 磺胺二甲嘧啶 (杜鹃, | 1500 | 2.7 | 7.7 | ‒ | 0.89 | |
| 四环 素类 | 四环素 (Rivera-Utrilla et al., | 22 | 3.3 | 7.8 | 9.6 | −1.30 |
| 土霉素 (Rivera-Utrilla et al., | 17 | 3.2 | 7.5 | 9.0 | −0.90 | |
| 金霉素 (Rivera-Utrilla et al., | 4.2 | 3.3 | 7.6 | 9.3 | −0.62 | |
| 多西环素 (Gao et al., | ‒ | 3.5 | 7.7 | 9.5 | ‒ | |
| 大环 内酯类 | 罗红霉素 (杜鹃, | 0.02 | ‒ | ‒ | 9.1 | 1.7 |
| 红霉素 (杜鹃, | 4.2 | ‒ | ‒ | 8.4 | 2.37 | |
| 喹诺 酮类 | 环丙沙星 (杜鹃, | 30000 | ‒ | 6.1 | 8.7 | 0.28 |
| 恩诺沙星 (杜鹃, | 3430 | ‒ | 5.5 | 8.6 | −0.2 | |
| 诺氟沙星 (杜鹃, | 17800 | ‒ | 6.3 | 8.7 | 0.46 | |
| [1] |
ADEYINKA G C, MOODLEY B, 2019. Kinetic and thermodynamic studies on partitioning of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) between aqueous solution and modeled individual soil particle grain sizes[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences (China), 76: 100-110.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
ÁLVAREZ-ESMORÍS C, RODRÍGUEZ-LÓPEZ, NÚÑEZ-DELGADO A, et al., 2022. Influence of pH on the adsorption-desorption of doxycycline, enrofloxacin, and sulfamethoxypyridazine in soils with variable surface charge[J]. Environmental Research, 214(Part 4): 114071.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
ALVAREZ-ESMORIS C, CONDE-CID M, FERNANDEZ-CALVINO D, et al., 2020. Adsorption-desorption of doxycycline in agricultural soils: Batch and stirred-flow-chamber experiments[J]. Environmental Research, 186: 109565.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
BADSHA M A H, KHAN M, WU B, et al., 2021. Role of surface functional groups of hydrogels in metal adsorption: From performance to mechanism[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 408: 124463.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
BHATT P, BHANDARI G, BILAL M, 2022. Occurrence, toxicity impacts and mitigation of emerging micropollutants in the aquatic environments: Recent tendencies and perspectives[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 10(3): 107598.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
CHEN J G, ZHU B, ZHANG Y H, 2023. A meta-analysis on the responses of soil microbial biomass and community structure to antibiotics[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 184: 104786.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
CHEN K L, LIU L C, CHEN W R, 2017. Adsorption of sulfamethoxazole and sulfapyridine antibiotics in high organic content soils[J]. Environmental Pollution, 231(Part 1): 1163-1171.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
CHENG J, YE Q, LU Z J, et al., 2021. Quantification of the sorption of organic pollutants to minerals via an improved mathematical model accounting for associations between minerals and soil organic matter[J]. Environmental Pollution, 280: 116991.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
CONDE-CID M, FERREIRA-COELHO G, ARIAS-ESTEVEZ M, et al., 2020. Adsorption/desorption of three tetracycline antibiotics on different soils in binary competitive systems[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 262: 110337.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
CONDE-CID M, FERREIRA-COELHO G, NUNEZ-DELGADO A, et al., 2019. Competitive adsorption of tetracycline, oxytetracycline and chlortetracycline on soils with different pH value and organic matter content[J]. Environmental Research, 178: 108669.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
GAO Y, LI Y, ZHANG L, et al., 2012. Adsorption and removal of tetracycline antibiotics from aqueous solution by graphene oxide[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 368(1): 540-546.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
GONZALEZ-GAYA B, GARCIA-BUENO N, BUELOW E, et al., 2022. Effects of aquaculture waste feeds and antibiotics on marine benthic ecosystems in the Mediterranean Sea[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 806(Part 2): 151190.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
GU J Y, CHEN C Y, HUANG X Y, et al., 2021. Occurrence and risk assessment of tetracycline antibiotics in soils and vegetables from vegetable fields in Pearl River Delta, South China[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 776(4): 145959.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
HACIOSMANOGLU G G, MEJIAS C, MARTIN J, et al., 2022. Antibiotic adsorption by natural and modified clay minerals as designer adsorbents for wastewater treatment: A comprehensive review[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 317: 115397.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
HAIDER F U, WANG X K, ZULFIQAR U, et al., 2022. Biochar application for remediation of organic toxic pollutants in contaminated soils; An update[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 248: 114322.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
HAN Q F, ZHANG X R, XU X Y, et al., 2021. Antibiotics in marine aquaculture farms surrounding Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea: Distribution characteristics considering various culture modes and organism species[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 760: 143863.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
HOMEM V, SANTOS L, 2011. Degradation and removal methods of antibiotics from aqueous matrices: A review[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 92(10): 2304-2347.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
HUI K L, XI B D, TAN W B, et al., 2022. Long-term application of nitrogen fertilizer alters the properties of dissolved soil organic matter and increases the accumulation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons[J]. Environmental Research, 215(Part 2): 114267.
DOI URL |
| [19] | JIA W L, SONG C, HE L Y, et al., 2022. Antibiotics in soil and water: occurrence, fate, and risk[J]. Current Opinion in Environmental Science & Health, 32: 100437. |
| [20] |
JING K, LI Y, YAO C, et al., 2023. Towards the fate of antibiotics and the development of related resistance genes in stream biofilms[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 898: 165554.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
KOOPAL L, TAN W F, AVENA M, 2020. Equilibrium mono- and multicomponent adsorption models: From homogeneous ideal to heterogeneous non-ideal binding[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 280: 102138.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
LI F F, CHEN L J, CHEN W D, et al., 2020. Antibiotics in coastal water and sediments of the East China Sea: Distribution, ecological risk assessment and indicators screening[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 151(1-2): 110810.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
LI J P, LI W, LIU K, et al., 2022a. Global review of macrolide antibiotics in the aquatic environment: Sources, occurrence, fate, ecotoxicity, and risk assessment[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 439: 129628.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
LI M, YANG L, YEN H, et al., 2023. Occurrence, spatial distribution and ecological risks of antibiotics in soil in urban agglomeration[J]. Journal Environmental Sciences (China), 125: 678-690.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
LI S, SHI W Z, LIU W, et al., 2018. A duodecennial national synthesis of antibiotics in China’s major rivers and seas (2005-2016)[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 615: 906-917.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
LI S, SHI W Z, YOU M T, et al., 2019. Antibiotics in water and sediments of Danjiangkou Reservoir, China: Spatiotemporal distribution and indicator screening[J]. Environmental Pollution, 246: 435-442.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
LI Y, WEI M L, LIU L, 2022b. Evaluation on adsorption capacity of low organic matter soil for hydrophobic organic pollutant[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 10(3): 107561.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
LU Y, LI Y L, LIU D Q, et al., 2020. Adsorption of benzene vapor on natural silicate clay minerals under different moisture contents and binary mineral mixtures[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 585: 124072.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
MA W J, XU X Y, AN B Y, et al., 2021. Single and ternary competitive adsorption-desorption and degradation of amphenicol antibiotics in three agricultural soils[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 297: 113366.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
MANGALGIRI K P, IBITOYE T, BLANEY L, 2022. Molar absorption coefficients and acid dissociation constants for fluoroquinolone, sulfonamide, and tetracycline antibiotics of environmental concern[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 835: 155508.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
NOVIKAU R, LUJANIENE G, 2022. Adsorption behaviour of pollutants: Heavy metals, radionuclides, organic pollutants, on clays and their minerals (raw, modified and treated): A review[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 309: 114685.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
OKOYE C O, NYARUABA R, ITA R E, et al., 2022. Antibiotic resistance in the aquatic environment: Analytical techniques and interactive impact of emerging contaminants[J]. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 96: 103995.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
QU C C, CHEN W L, HU X P, et al., 2019. Heavy metal behaviour at mineral-organo interfaces: Mechanisms, modelling and influence factors[J]. Environment International, 131: 104995.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
RATH S, FOSTIER A H, PEREIRA L A, et al., 2019. Sorption behaviors of antimicrobial and antiparasitic veterinary drugs on subtropical soils[J]. Chemosphere, 214: 111-122.
DOI PMID |
| [35] |
RIVERA-UTRILLA J, GOMEZ-PACHECO C V, SANCHEZ-POLO M, et al., 2013. Tetracycline removal from water by adsorption/bioadsorption on activated carbons and sludge-derived adsorbents[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 131: 16-24.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
ROUT D R, JENA H M, BAIGENZHENOV O, et al., 2023. Graphene-based materials for effective adsorption of organic and inorganic pollutants: A critical and comprehensive review[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 863: 160871.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
SHAIKH S M R, NASSER M S, HUSSEIN I, et al., 2017. Influence of polyelectrolytes and other polymer complexes on the flocculation and rheological behaviors of clay minerals: A comprehensive review[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 187: 137-161.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
SHEN C, HE M Y, ZHANG J H, et al., 2023. Effects of the coexistence of antibiotics and heavy metals on the fate of antibiotic resistance genes in chicken manure and surrounding soils[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 263: 115367.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
SIEDLEWICZ G, BORECKA M, BIAŁK-BIELIŃSKA A, et al., 2016. Determination of antibiotic residues in southern Baltic Sea sediments using tandem solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Oceanologia, 58(3): 221-234.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
SRINIVASAN P, SARMAH A K, MANLEY-HARRIS M, 2014. Sorption of selected veterinary antibiotics onto dairy farming soils of contrasting nature[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 472: 695-703.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
TANG J P, WANG S, FAN J J, et al., 2019. Predicting distribution coefficients for antibiotics in a river water-sediment using quantitative models based on their spatiotemporal variations[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 655: 1301-1310.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
TIAN C H, SUN M, QUAN J, 2021. Molecular chirality of Macrolide antibiotics[J]. Chemical Physics, 545: 111120.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
WANG W B, ZHAO W T, ZHANG H, et al., 2021. Mesoporous polymetallic silicate derived from naturally abundant mixed clay: A potential robust adsorbent for removal of cationic dye and antibiotic[J]. Powder Technology, 390: 303-314.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
WANG Y T, YU W F, CHANG Z F, et al., 2022. Effects of dissolved organic matter on the adsorption of norfloxacin on a sandy soil (fraction) from the Yellow River of Northern China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 848: 157495.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
WU M, ZHAO S F, JING R S, et al., 2019. Competitive adsorption of antibiotic tetracycline and ciprofloxacin on montmorillonite[J]. Applied Clay Science, 180: 105175.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
XU L Y, ZHANG H, XIONG P, et al., 2021. Occurrence, fate, and risk assessment of typical tetracycline antibiotics in the aquatic environment: A review[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 753: 141975.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
XU Y F, ZHU L, CHEN S G, et al., 2023. Risk assessment and dissemination mechanism of antibiotic resistance genes in compost[J]. Environment International, 178: 108126.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
YANG H R, DONG H, HUANG Y R, et al., 2022. Interactions of microplastics and main pollutants and environmental behavior in soils[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 821: 153511.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
YANG J F, YING G G, ZHAO J L, et al., 2010. Simultaneous determination of four classes of antibiotics in sediments of the Pearl Rivers using RRLC-MS/MS[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 408(16): 3424-3432.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
YI X Z, LIN C H, ONG E J L, et al., 2019. Occurrence and distribution of trace levels of antibiotics in surface waters and soils driven by non-point source pollution and anthropogenic pressure[J]. Chemosphere, 216: 213-223.
DOI PMID |
| [51] |
ZHANG H B, ZHOU Y, HUANG Y J, et al., 2016. Residues and risks of veterinary antibiotics in protected vegetable soils following application of different manures[J]. Chemosphere, 152: 229-237.
DOI PMID |
| [52] |
ZHAO F K, CHEN L D, YEN H, et al., 2020. An innovative modeling approach of linking land use patterns with soil antibiotic contamination in peri-urban areas[J]. Environment International, 134: 105327.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
ZHAO F K, YANG L, CHEN L D, et al., 2019. Soil contamination with antibiotics in a typical peri-urban area in eastern China: Seasonal variation, risk assessment, and microbial responses[J]. Journal of environmental sciences (China), 79: 200-212.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
ZHAO Y P, TAN Y Y, GUO Y, et al., 2013. Interactions of tetracycline with Cd (II), Cu (II) and Pb (II) and their cosorption behavior in soils[J]. Environmental Pollution, 180: 206-213.
DOI PMID |
| [55] |
ZHI D, YANG D X, ZHENG Y X, et al., 2019. Current progress in the adsorption, transport and biodegradation of antibiotics in soil[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 251: 109598.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
ZHU Y, MIAO J R, WEN H X, et al., 2019. The occurrence and spatial distribution of typical antibiotics in soils along the Fenhe River in Shanxi Province[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 20(2): 889-899.
DOI |
| [57] | 陈宇, 许亚南, 庞燕, 2021. 抗生素赋存、来源及风险评估研究进展[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 11(03): 562-570. |
| CHEN Y, XU Y N, PANG Y, 2021. Advances in research on the occurrence, source and risk assessment of antibiotics[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 11(3): 562-570. | |
| [58] |
丛鑫, 王宇, 李瑶, 等, 2022. 生物炭及氧化石墨烯/生物炭复合材料对水中抗生素吸附性能研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 31(2): 326-334.
DOI |
| CONG X, WANG Y, LI Y, et al., 2022. Adsorption characteristics of biochars and graphene oxide/biochar composites for antibiotics from aqueous solution[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 31(2): 326-334. | |
| [59] | 杜鹃, 2021. 黄渤海部分区域近岸海域中抗生素的分布、分配及释放动力学[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学:18-107. |
| DU J, 2021. Occurence, distribution and desorption kinetics of antibiotics in regional coastal areas of the Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology:18-107. | |
| [60] | 方林发, 叶苹苹, 方标, 等, 2022. 重庆开州区菜地土壤抗生素污染特征及潜在生态环境风险评估[J]. 环境科学, 43(11): 5244-5252. |
| FANG L F, YE P P, FANG B, et al., 2022. Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of antibiotics in vegetable field in Kaizhou District, Chongqing[J]. Environmental Science, 43(11): 5244-5252. | |
| [61] | 郭欣妍, 王娜, 许静, 等, 2013. 5种磺胺类抗生素在土壤中的吸附和淋溶特性[J]. 环境科学学报, 33(11): 3083-3091. |
| GUO X Y, WANG N, XU J, et al., 2013. Adsorption and leaching behavior of five sulfonamide in soil[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 33(11): 3083-3091. | |
| [62] | 黄利玲, 2012. 氮肥施用对紫色土酸化及表面电化学性质的影响研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学:11-55. |
| HUANG L L, 2012. Study on the influence of nitrogen fertilization on purple soil acidification and surface electrochemical Properties[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University:11-55. | |
| [63] | 李佳乐, 王萌, 胡发旺, 等, 2022a. 江西锦江流域抗生素污染特征与生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 43(8): 4064-4073. |
| LI J L, WANG M, HU F W, et al., 2022a. Antibiotic pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment in Jinjiang River Basin, Jiangxi province[J]. Environmental Science, 43(8): 4064-4073. | |
| [64] | 李佳乐, 王瑶, 董一慧, 等, 2022b. 鄱阳湖流域袁河水体典型抗生素分布特征及生态风险评价[J]. 生态毒理学报, 17(4): 563-574. |
| LI J L, WANG Y, DONG Y H, et al., 2022b. Distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of typical antibiotics in Yuanhe River of Poyang Lake Basin[J]. Journal of Ecotoxicology, 17(4): 563-574. | |
| [65] | 李威, 李佳熙, 李吉平, 等, 2020. 我国不同环境介质中的抗生素污染特征研究进展[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 44(1): 205-214. |
| LI W, LI J X, LI J P, et al., 2020. Pollution characteristics of antibiotics in different environment media in China: A review[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 44(1): 205-214. | |
| [66] | 李艳丹, 2017. 典型氟喹诺酮类抗生素在高岭土上吸附特征的实验研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学:13-90. |
| LI Y D, 2017. Sorption behavior of typical fluoroquinolone antibiotics on kaolinite: Batch experiments[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences:13-90. | |
| [67] | 李余杰, 2020. 畜禽粪污中FQs类抗生素的污染水平及在紫色土中迁移转化研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学:14-122. |
| LI Y J, 2020. Pollution of fluoroquinolone antibiotics in livestock and poultry wastes and its migration-transformation in purple soil[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University:14-122. | |
| [68] | 林吟萱, 于娇, 吴玲玲, 2023. 抗生素和重金属复合污染现状及其生态效应研究进展[J]. 应用化工, 52(2): 504-510. |
| LIN Y X, YU J, WU L L, 2023. The status and ecological effects of antibiotics and heavy metals combined pollution: A review[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 52(2): 504-510. | |
| [69] | 秦晓鹏, 刘菲, 王广才, 等, 2015. 抗生素在土壤/沉积物中吸附行为的研究进展[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 42(3): 142-148. |
| QIN X P, LIU F, WANG G C, et al., 2015. Adsorption of antibiotics in soils/sediments: A review[J]. Hydrogeology Engineering Geology, 42(3): 142-148. | |
| [70] | 宋豆豆, 2021. 底泥对磺胺类抗生素的吸附-解吸特性研究[D]. 长春: 吉林农业大学:7-36. |
| SONG D D, 2021. Study on the adsorption-desorption characteristics of sulfonamide antibiotics in sediment[D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University:7-36. | |
| [71] | 提清清, 高增文, 季慧慧, 等, 2017. 抗生素在土壤中的吸附行为研究进展[J]. 土壤, 49(3): 437-445. |
| TI Q Q, GAO Z W, JI H H, et al., 2017. Adsorption of Antibiotics in Soils: A Review[J]. Soil, 49(3): 437-445. | |
| [72] | 王晓洁, 赵蔚, 张志超, 等, 2021. 兽用抗生素在土壤中的环境行为、生态毒性及危害调控[J]. 中国科学: 技术科学, 51(6): 615-636. |
| WANG X J, ZHAO W, ZHANG Z C, et al., 2021. Veterinary antibiotics in soils:Environmental processes, ecotoxicity, and risk mitigation[J]. China Science: Technical Sciences, 51(6): 615-636. | |
| [73] | 王新爽, 2017. 不同类型土壤对磺胺甲恶唑的吸附/解吸特性研究[D]. 长春: 吉林农业大学:8-42. |
| WANG X S, 2017. The characteristic study of different type of soils absorption/desorption for sulfamethoxazole[D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University:8-42. | |
| [74] | 卫承芳, 2022. 典型抗生素在污水塘土壤中的吸附、迁移特性[D]. 南昌: 东华理工大学:13-86. |
| WEI C F, 2022. Adsorption and migration characteristics of typical antibiotics in sewage pond soil[D]. Nanchang: East China University of Technology:13-86. | |
| [75] | 夏敏, 2021. 赤铁矿与黏土矿物相互作用对有机污染物归趋的影响[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学:17-70. |
| XIA M, 2021. Impact of the interaction between hematite and clay on environmental fate of organic pollutants[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology:17-70. | |
| [76] | 张步迪, 2017. 磺胺嘧啶在土壤及组分中的吸附迁移特征及模拟[D]. 青岛: 青岛大学:10-114. |
| ZHANG B D, 2017. Adsorption and migration characteristics and simulation of sulfadiazine in soil and its components[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao University:10-114. | |
| [77] | 张焕军, 王席席, 李轶, 2022. 水体中抗生素污染现状及其对氮转化过程的影响研究进展[J]. 环境化学, 41(4): 1168-1181. |
| ZHANG H J, WANG X X, LI Y, 2022. Progress in current pollution status of antibiotics and their influences on the nitrogen transformation in water[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 41(4): 1168-1181. | |
| [78] | 张平, 2020. 东营凹陷泥页岩中有机质与无机矿物相互作用及孔隙特征研究[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学:11-96. |
| ZHANG P, 2020. Study on the interaction between organic matter and inorganic minerals and pore characteristcs in shale of Dongying depression[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum:11-96. | |
| [79] | 章明奎, 王丽平, 郑顺安, 2008. 两种外源抗生素在农业土壤中的吸附与迁移特性[J]. 生态学报, 28(2): 761-766. |
| ZHANG M K, WANG L P, ZHENG S A, 2008. Adsorption and migration characteristics of two exogenous antibiotics in agricultural soils[J]. Ecology, 28(2): 761-766. | |
| [80] | 赵方凯, 陈利顶, 杨磊, 等, 2017. 长三角典型城郊不同土地利用土壤抗生素组成及分布特征[J]. 环境科学, 38(12): 5237-5246. |
| ZHAO F K, CHEN L D, YANG L, et al., 2017. Composition and distribution of antibiotics in soils with different land use types in a typical peri-urban area of the Yangtze River Delta[J]. Environmental Sciences, 38(12): 5237-5246. | |
| [81] | 周琪琪, 2022. 巢湖流域抗生素的分布、来源、风险评估及其去除方法研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学:17-132. |
| ZHOU Q Q, 2022. Study on the distribution, source, risk assessment and removal methods of antibiotics in Chaohu Lake Basin[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China:17-132. |
| [1] | TANG Zhiwei, WENG Ying, ZHU Xiatong, CAI Hongmei, DAI Wenci, WANG Pengna, ZHENG Baoqiang, LI Jincai, CHEN Xiang. Meta-analysis of Soil Microbial Mass Carbon and Its Influencing Factors in Farmland in China under Straw Return [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(9): 1552-1562. |
| [2] | LI Hang, CHEN Jinping, DING Zhaohua, SHU Yang, WEI Jiangsheng, ZHAO Pengwu, ZHOU Mei, WANG Yuxuan, LIANG Chihao, ZHANG Yichao. Effects of Fire Disturbance on Soil Nitrogen Fractions and Functional Genes of Nitrogen Cycling in Soil of Larix gmelinii Forests [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(9): 1563-1573. |
| [3] | FANG Yuan, LIANG Zhong, ZHANG Yutao, SHI Qingdong, SUN Xuejiao, LI Jimei, LI Xiang, DONG Zhentao. Characteristics of Altitudinal Gradient Changes in Water Retention of Tianshan Spruce Forest Ecosystems [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(9): 1574-1584. |
| [4] | SONG Simeng, LIN Dongmei, ZHOU Hengyu, LUO Zongzhi, ZHANG Lili, YI Chao, LIN Hui, LIN Xingsheng, LIU Bin, SU Dewei, ZHENG Dan, YU Shikui, LIN Zhanxi. Effects of Planting Cenchrus fungigraminus on Plant Species Diversity and Soil Physicochemical Properties in the Ulan Buh Desert [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(9): 1595-1605. |
| [5] | LIANG Xin, HAN Yafeng, ZHENG Ke, WANG Xugang, CHEN Zhihuai, DU Juan. Effects of Fe3O4 on Soil Carbon Mineralization in Paddy Field [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(9): 1615-1622. |
| [6] | LIU Han, WANG Ping, SUN Luyuan, QING Wenjing, CHEN Xiaofen, CHEN Jin, ZHOU Guopeng, LIANG Ting, LIU Jia, LI Yanli. Effects of Winter Green Manure Planting on Soil Microbial Biomass Carbon, Nitrogen, and Enzyme Activity in Red Soil Young Citrus Orchard [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(9): 1623-1631. |
| [7] | NING Jian, CHENG Xiaobo, SU Chaoli, TANG Zeping, YU Zefeng. Analysis of Soil Radioactivity Levels around NORM Facilities in Guangdong Province [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(9): 1692-1699. |
| [8] | JIANG Yishan, SUN Yingtao, ZHANG Gan, LUO Chunling. Pattern and Influencing Factors of Forest Soil Microbial Communities in Different Climate Types in China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(8): 1355-1364. |
| [9] | WANG Yuqin, SONG Meiling, ZHOU Rui, WANG Hongsheng. Effects of Spread of Ligularia virgaurea on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Enzyme Activities in Alpine Meadow [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(8): 1384-1391. |
| [10] | GU Meiying, TANG Guangmu, ZHANG Yunshu, HUANG Jian, ZHANG Zhidong, ZHANG Lijuan, ZHU Jing, TANG Qiyong, CHU Min, XU Wanli. Effects of Organic Fertilizers and Biochar on Microorganism Community Characteristics in Saline-alkali Sandy Soil of Xinjiang [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(8): 1392-1404. |
| [11] | LIU Chen, BAI Xuedong, ZHAO Haichao, HUANG Zhihong, LIU Songtao, LU Haibo, LIU Zigang, LIU Xueling. The Effect Mechanism of Spring Maize Straw Returning Method on Soil DOM Spectral Characteristics in Cold and Arid Regions of China [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(8): 1419-1432. |
| [12] | LI Jiaman, WANG Xiaoming, HU Xinrui, XIE Yingying, WEN Zhen. Effects of Fe-S Ratio on the Microstructure and Cr Adsorption Properties of Schwertmannite [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(8): 1478-1486. |
| [13] | LIU Bingyu, WANG Yipei, YAO Zuofang, YANG Gairen, XU Xiaonan, DENG Yusong, HUANG Yuhan. Risk Assessment and Safe Consumption Analysis of Heavy Metals under Different Planting Patterns of Biogas Slurry [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(8): 1507-1515. |
| [14] | FAN Wanyi, TU Chen, WANG Shunyang, WU Xinyou, LI Xuanzhen, LUO Yongming. Cadmium Accumulation Characteristics and Pollution Reduction Potential of Different Tobacco Species in Lightly Contaminated Farmland Soils [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(8): 1516-1524. |
| [15] | CHEN Dongdong, HUO Lili, ZHAO Liang, CHEN Xin, SHU Min, HE Fuquan, ZHANG Yukun, ZHANG Li, LI Qi. Contribution of Water and Heat Factors to Spatial Variability of Soil Microbial Biomass Carbon and Nitrogen in Qinghai Alpine Grassland: Based on Enhanced Regression Tree Model [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(7): 1207-1217. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
