Ecology and Environment ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (3): 583-592.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.03.0017
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Guangxuan1( ), SHI An1, ZHANG Liming1,2, XING Shihe1,2, YANG Wenhao1,2,*(
), SHI An1, ZHANG Liming1,2, XING Shihe1,2, YANG Wenhao1,2,*( )
)
Received:2021-08-02
Online:2022-03-18
Published:2022-05-25
Contact:
YANG Wenhao
李光炫1( ), 石岸1, 张黎明1,2, 邢世和1,2, 杨文浩1,2,*(
), 石岸1, 张黎明1,2, 邢世和1,2, 杨文浩1,2,*( )
)
通讯作者:
杨文浩
作者简介:李光炫(1992年生),女,硕士研究生,主要从事于土壤生态修复研究。E-mail: liguangxuan5996@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
LI Guangxuan, SHI An, ZHANG Liming, XING Shihe, YANG Wenhao. Effects of Biochar with Different Particle Sizes on Soil Heavy Metal Immobilization and Bacterial Community[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2022, 31(3): 583-592.
李光炫, 石岸, 张黎明, 邢世和, 杨文浩. 不同粒径生物质炭对土壤重金属钝化及细菌群落的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(3): 583-592.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.jeesci.com/EN/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2022.03.0017
| 材料类型 Material type | pH | 全氮 Total nitrogen/ (mg∙kg-1) | 全碳 Total carbon/ (mg∙kg-1) | 全磷 Total phosphorus/ (mg∙kg-1) | 全钾 Total potassium/ (mg∙kg-1) | 比表面 Specific surface area/ (m2∙g-1) | 微孔面积Micropore area/ (m2∙g-1) | 微孔体积 Micropore volume/ (cm3∙g-1) | 平均孔径 Average aperture/ (10-10 m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 海鲜菇 Seafood mushroom | 9.34 | 2.38 | 43.4 | 1.35 | 0.13 | 19.80 | 41.51 | 0.01 | 95.15 |
| 秀珍菇 Xiuzhen mushroom | 9.68 | 2.29 | 40.0 | 1.30 | 0.15 | 20.01 | 30.73 | 0.02 | 98.28 |
Table 1 Basic physicochemical properties of biochars
| 材料类型 Material type | pH | 全氮 Total nitrogen/ (mg∙kg-1) | 全碳 Total carbon/ (mg∙kg-1) | 全磷 Total phosphorus/ (mg∙kg-1) | 全钾 Total potassium/ (mg∙kg-1) | 比表面 Specific surface area/ (m2∙g-1) | 微孔面积Micropore area/ (m2∙g-1) | 微孔体积 Micropore volume/ (cm3∙g-1) | 平均孔径 Average aperture/ (10-10 m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 海鲜菇 Seafood mushroom | 9.34 | 2.38 | 43.4 | 1.35 | 0.13 | 19.80 | 41.51 | 0.01 | 95.15 |
| 秀珍菇 Xiuzhen mushroom | 9.68 | 2.29 | 40.0 | 1.30 | 0.15 | 20.01 | 30.73 | 0.02 | 98.28 |
| 处理 Treatments | pH | w(DOC)/(mg∙kg-1) | w(Available nitrogen)/(mg∙kg-1) | w(Available phosphorus)/(mg∙kg-1) | w(Available potassium)/(mg∙kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 6.12±0.02f | 47.45±2.70e | 60.48±5.80e | 25.19±3.36d | 155.50±9.51d |
| HC | 7.61±0.10e | 84.95±10.38d | 77.92±2.98d | 35.22±7.67cd | 436.63±10.66c |
| HM | 7.88±0.07d | 125.14±17.10c | 85.38±5.51cd | 46.06±7.64bc | 446.27±11.10bc |
| HF | 8.12±0.20ab | 182.43±10.84a | 89.30±6.97bc | 57.38±4.90ab | 451.07±9.33bc |
| XC | 8.02±0.25c | 130.35±6.43c | 81.86±6.13cd | 43.49±4.69c | 473.82±18.90b |
| XM | 8.09±0.26bc | 165.15±4.40b | 96.61±7.20ab | 49.47±5.55bc | 568.39±17.03a |
| XF | 8.20±0.05a | 160.81±9.18b | 103.25±5.52a | 64.75±12.40a | 567.89±40.51a |
Table 2 Correlation Analysis of Soil pH and Available Nutrient Content under Different Particle Size of Biochar
| 处理 Treatments | pH | w(DOC)/(mg∙kg-1) | w(Available nitrogen)/(mg∙kg-1) | w(Available phosphorus)/(mg∙kg-1) | w(Available potassium)/(mg∙kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 6.12±0.02f | 47.45±2.70e | 60.48±5.80e | 25.19±3.36d | 155.50±9.51d |
| HC | 7.61±0.10e | 84.95±10.38d | 77.92±2.98d | 35.22±7.67cd | 436.63±10.66c |
| HM | 7.88±0.07d | 125.14±17.10c | 85.38±5.51cd | 46.06±7.64bc | 446.27±11.10bc |
| HF | 8.12±0.20ab | 182.43±10.84a | 89.30±6.97bc | 57.38±4.90ab | 451.07±9.33bc |
| XC | 8.02±0.25c | 130.35±6.43c | 81.86±6.13cd | 43.49±4.69c | 473.82±18.90b |
| XM | 8.09±0.26bc | 165.15±4.40b | 96.61±7.20ab | 49.47±5.55bc | 568.39±17.03a |
| XF | 8.20±0.05a | 160.81±9.18b | 103.25±5.52a | 64.75±12.40a | 567.89±40.51a |
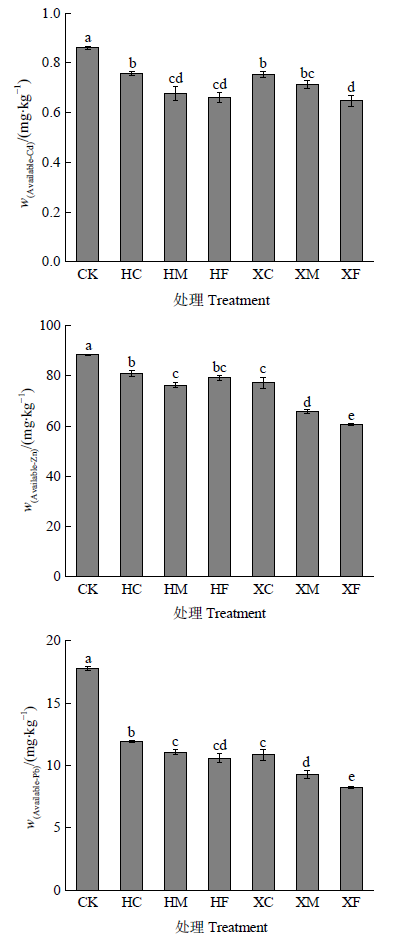
Figure 1 The mass fraction of soil available Cd, Zn and Pb under different particle sizes of biochar treatment (1) The values in the table are mean (n=3)±standard deviation. Different lowercase letters (a, b, c, d, e) in the same column indicate that the corresponding values have significant differences at the level of P<0.05, the same below. (2) CK: no addition control treatment, HC, HM, HF: coarse, medium and fine particle size biochar treatment of waste mushroom sticks, XC, XM, XF: coarse, medium and fine particle size biochar treatment of waste mushroom sticks, same below
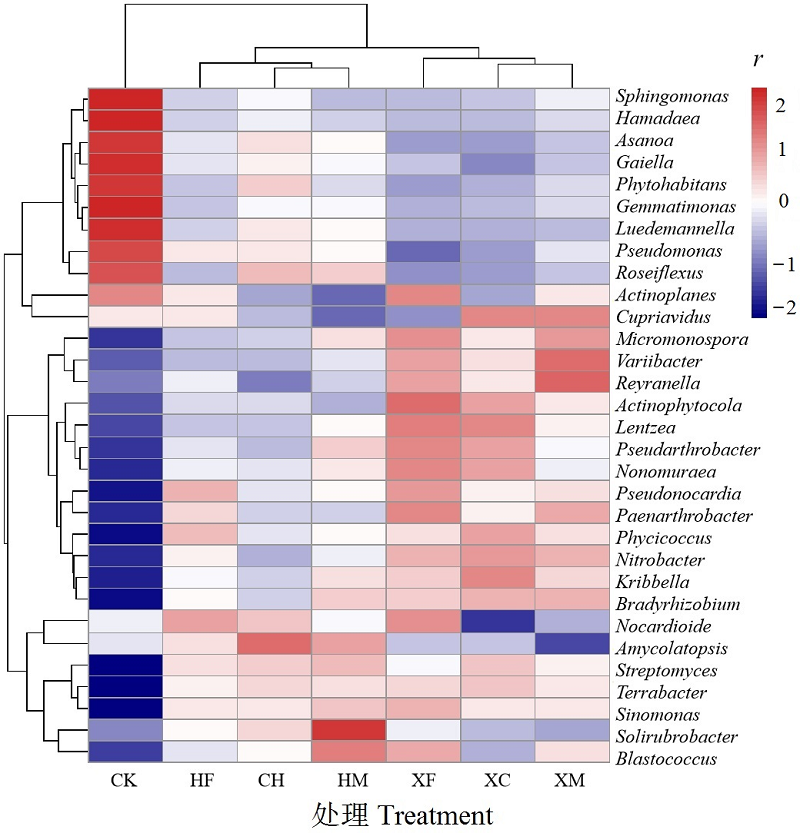
Figure 5 Changes of bacterial community in soil samples under different treatments at genus level Figure r in the table indicates the relative abundance values of-2 to 2, red indicates the increase of relative abundance value, blue indicates the decrease of relative abundance value, and the deeper the color is, the greater the increase (decrease) degree of relative differentiation is
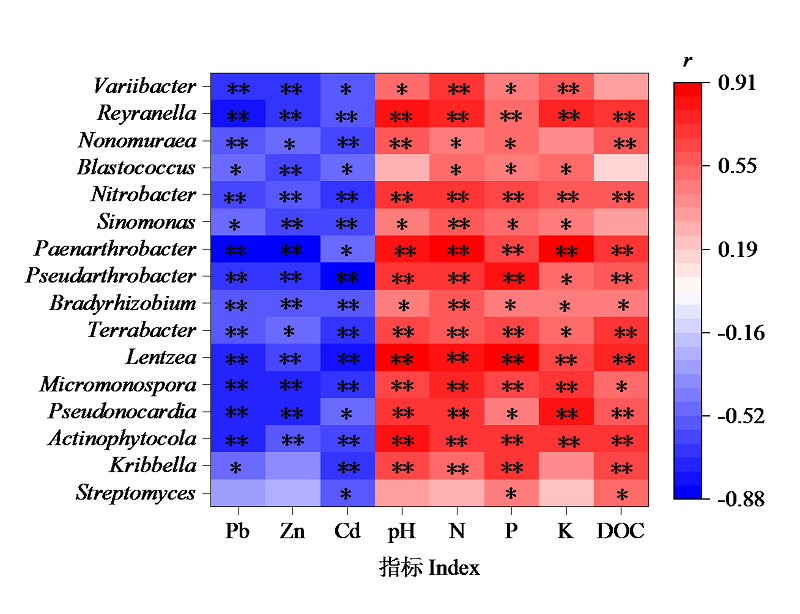
Figure 6 Spearman analysis of environmental factors and bacterial community composition at genus level (1) * Significantly correlated at 0.05 level (bilateral); ** Significantly correlated at 0.01 level (bilateral). (2) Graph r indicates the correlation between -0.88 and 0.19, red indicates positive correlation, blue indicates negative correlation, and the deeper the color, the greater the positive (negative) correlation. (3) Pb: available Pb; Zn: available Zn; Cd: available Cd; pH : acid-base; N: available N; P: available P; K: available K; DOC: dissolved organic carbon
| [1] |
AMELOOT N, GRABER E R, VERHEIJEN F G A, et al., 2013. Interactions between biochar stability and soil organisms: review and research needs[J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 64(4): 379-390.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
BAKER A, TIPPING E S A, THACKER S A, et al., 2008. Relating dissolved organic matter fluorescence and functional properties[J]. Chemosphere, 73(11): 1765-1772.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
CAO X D, HARRIS W, 2010. Properties of dairy-manure-derived biochar pertinent to its potential use in remediation[J]. Bioresource Technology, 101(14): 5222-5228.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
HOSSAIN M Z, BAHAR M M, SARKER B, et al., 2020. Biochar and its importance on nutrient dynamics in soil and plant[J]. Biochar, 2(4): 1-42.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
RUBAB S, YANG W H, WANG S S, et al., 2020. Short term effects of biochar with different particle sizes on phosphorous availability and microbial communities[J]. Chemosphere, DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126862.
DOI |
| [6] |
TANG J F, LI X H, LUO Y, et al., 2016. Spectroscopic characterization of dissolved organic matter derived from different biochars and their polyeylic aromatic hyd rocarbons (PAHs) binding affinity[J]. Chemosphere, 152: 399-406.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
WILLIAMS P N, LEI M, SUN G X, et al., 2009. Occurrence and partitioning of cadmium, arsenic and lead in mine impacted paddy rice: Hunan, China[J]. Environmental science & technology, 43(3): 637-42.
DOI URL |
| [8] | ZARATE A, DORADOR C, VALDES J, et al., 2021. Benthic microbial diversity trends in response to heavy metals in an oxygen-deficient eutrophic bay of the Humboldt current system offshore the Atacama Desert[J]. Environmental Pollution, 286: 117-281. |
| [9] | 包建平, 袁根生, 董方圆, 等, 2020. 生物质炭与秸秆施用对红壤有机碳组分和微生物活性的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 57(3): 721-729. |
| BAO J P, YUAN G S, DONG Y Y, et al., 2020. Effects of biochar and straw application on organic carbon fractions and microbial activities in red soil[J]. Soil Science, 57(3): 721-729. | |
| [10] | 鲍士旦, 2000. 土壤农化分析[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社: 25-440. |
| BAO S D, 2000. Soil agrochemical analysis[M]. Three editions. Beijing: China Agricultural Publishing House: 25-440. | |
| [11] | 陈能场, 郑煜基, 何晓峰, 等, 2017. 《全国土壤污染状况调查公报》探析[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 36(9): 1689-1692. |
| CHEN N C, ZHENG Y J, HE X F, et al., 2017. Analysis of the bulletin of national soil pollution survey[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 36(9): 1689-1692. | |
| [12] | 陈越渠, 刘庆珍, 李立梅, 等, 2021. 杨树溃疡病拮抗链霉菌的筛选及鉴定[J]. 林业科学, 57(7): 92-100. |
| CHEN Y Q, LIU Q Z, LI L M, et al., 2021. Screening and identification of antagonistic Streptomyces to poplar canker[J]. Forestry science, 57(7): 92-100. | |
| [13] | 董达, 王宇婕, 姜培坤, 等, 2021. 炭基肥和竹炭对土壤氮素淋失和微生物的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 35(2): 144-151. |
| DONG D, WANG Y J, JIANG P K, et al., 2021. Effects of carbon-based fertilizer and bamboo charcoal on soil nitrogen leaching and microorganisms[J]. Journal of soil and Water Conservation, 35(2): 144-151. | |
| [14] | 高天一, 李娜, 彭靖, 等, 2019. 连续施用生物炭对棕壤磷素形态及有效性的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 25(9): 1451-1460. |
| GAO T Y, LI N, PENG J, et al., 2019. Effects of continuous application of biochar on the form and availability of phosphorus in brown soil[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 25(9): 1451-1460. | |
| [15] | 苟帅帅, 王明强, 谢飞, 等, 2020. 活性土壤生态修复技术在废弃矿山复绿中的应用[J]. 世界有色金属 (23): 215-216. |
| GOU S S, WANG M Q, XIE F, et al., 2020. Application of active soil ecological remediation technology in green restoration of abandoned mines[J]. World Nonferrous Metals (23): 215-216. | |
| [16] | 关松荫, 1986. 土壤酶及其研究法[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社: 88-250. |
| GUAN S Y, 1986. Soil enzyme and its research method[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Publishing House: 88-250. | |
| [17] | 韩志旺, 赵志华, 张艳利, 等, 2021. 生物炭对农田土壤中酶活性和细菌群落结构的影响研究[J]. 四川环境, 40(4): 26-34. |
| HAN Z W, ZHAO Z H, ZHANG Y L, et al., 2021. Effects of biochar on enzyme activity and bacterial community structure in farmland soil[J]. Sichuan environment, 40(4): 26-34. | |
| [18] | 何绪生, 耿增超, 余雕, 等, 2011. 生物炭生产与农用的意义及国内外动态[J]. 农业工程学报, 27(2): 1-4. |
| HE X S, GENG Z C, YU D, et al., 2011. Significance of biochar production and agricultural use and domestic and foreign developments[J]. Journal of Agricultural Engineering, 27(2): 1-4. | |
| [19] | 胡华英, 殷丹阳, 曹升, 等, 2019. 生物炭对杉木人工林土壤养分、酶活性及细菌性质的影响[J]. 生态学报, 39(11): 4138-4148. |
| HU H Y, YIN D Y, CAO S, et al., 2019. Effects of biochar on soil nutrients, enzyme activities and bacterial properties of Chinese firplantations[J]. Ecology, 39(11): 4138-4148. | |
| [20] | 姬文秀, 李虎林, 冷雪, 等, 2019. 产ACC脱氨酶人参内生细菌的分离和促生特性分析[J]. 吉林农业大学学报, 41(2): 168-174. |
| JI W X, LI H L, LENG X, et al., 2019. Isolation and growth-promoting characteristics of endophytic bacteria producing ACC deaminase from Panax ginseng[J]. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 41(2): 168-174. | |
| [21] | 吉春阳, 何云华, 孙小飞, 等, 2021. 强还原与生物炭对土壤酶活性和温室气体排放的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 41(2): 974-982. |
| JI C Y, HE Y H, SUN X F, et al., 2021. Effects of strong reduction and biochar on soil enzyme activity and greenhouse gas emission[J]. China Environmental Science, 41(2): 974-982. | |
| [22] | 李佳轶, 2019. 不同粒径生物炭对植烟土壤性状及烟株生长的影响[D]. 郑州: 河南农业大学: 35-39. |
| LI J T, 2019. Effects of biochar with different particle sizes on soil properties and growth of tobacco plants[D]. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University: 35-39. | |
| [23] | 李江遐, 吴林春, 张军, 等, 2015. 生物炭修复土壤重金属污染的研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 24(12): 2075-2081. |
| LI J C, WU L C, ZHANG J, et al., 2015. Research Progresses in Remediation of Heavy Metal Contaminated Soils by Biochar[J]. Journal of Ecological Environment, 24(12): 2075-2081. | |
| [24] | 李艳春, 2017. 不同宿根年限铁观音茶园酸化土壤微生物群落特征及改良措施研究[D]. 福州: 福建农林大学: 82-93. |
| LI Y C, 2017. Study on microbial community characteristics and improvement measures of acidified soil in Tie guanyin Tea Garden with different persistent Root years[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian University of Agriculture and Forestry: 82-93. | |
| [25] | 刘冰冰, 郭书贤, 陈兴, 等, 2020. 烤烟K326与香料植物间作模式下根际土可培养细菌多样性及功能[J]. 微生物学通报, 47(8): 2436-2449. |
| LIU B B, GUO S X, CHEN X, et al., 2020. The diversity and function of culturable bacteria in rhizosphere soil under the intercropping mode of flue-cured tobacco K326 and spice plants[J]. Microbiological notification, 47(8): 2436-2449. | |
| [26] | 刘悦畅, 李保珍, 王涛, 等, 2020. 种菌联合修复农田土壤镉污染的研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 34(4): 364-369. |
| LIU Y C, LI B Z, WANG T, et al., 2020. Study on combined remediation of cadmium pollution in farmland soil by two kinds of bacteria[J]. Journal of soil and Water Conservation, 34(4): 364-369. | |
| [27] | 徐建明, 孟俊, 刘杏梅, 等, 2018. 我国农田土壤重金属污染防治与粮食安全保障[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 33(2): 153-159. |
| XU J M, MENG J, LIU X M, et al., 2018. Control of Heavy Metal Pollution in Farmland of China in Terms of Food Security[J]. Journal of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 33(2): 153-159. | |
| [28] | 徐婧婧, 赵科理, 叶正钱, 2019. 重金属污染土壤原位钝化修复材料的最新研究进展[J]. 环境污染与防治, 41(7): 852-855. |
| XU J J, ZHAO K L, YE Z Q, 2019. Recent research progress in in situ passivation remediation materials for heavy metal contaminated soils[J]. Environmental pollution and prevention, 41(7): 852-855. | |
| [29] | 杨萌, 邢海, 闻秀娟, 等, 2020. 生物质炭对土壤重金属污染修复作用的研究进展[J]. 贵州农业科学, 48(4): 153-160. |
| YANG M, XING H, WEN X J, et al., 2020. Research progress on remediation of heavy metal pollution in soil by biomass charcoal[J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, Volume, 48(4): 153-160. | |
| [30] | 袁仁文, 刘琳, 张蕊, 等, 2020. 植物根际分泌物与土壤微生物互作关系的机制研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 36(2): 26-35. |
| YUAN R W, LIU L, ZHANG R, et al., 2020. Research progress on the mechanism of interaction between plant rhizosphere secretions and soil microorganisms[J]. China Agricultural Journal, 36(2): 26-35. | |
| [31] | 张祥, 王典, 姜存仓, 等, 2013. 生物炭对我国南方红壤和黄棕壤理化性质的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 21(8): 979-984. |
| ZHANG X, WANG D, JIANG C C, et al., 2013. Effects of biochar on physical and chemical properties of red soil and yellow-brown soil in southern China[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecological Agriculture, 21(8): 979-984. | |
| [32] | 张志军, 高奕珏, 束蒋成, 等, 2020. 生物炭的环境效应及其修复土壤的研究进展[J]. 广东化工, 47(9): 131-140. |
| ZHANG Z J, GAO Y J, SHU J C, et al., 2020. Environmental effects of biochar and its research progress on soil remediation[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 47(9): 131-140. | |
| [33] | 郑华楠, 宋晴, 朱义, 等, 2019. 芦苇生物炭复合载体固定化微生物去除水中氨氮[J]. 环境工程学报, 13(2): 310-318. |
| ZHENG H N, SONG Q, ZHU Y, et al., 2019. Cui Xinhong. Removal of ammonia nitrogen from water by immobilized microorganisms on Reed biochar composite carrier[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 13(2): 310-318. | |
| [34] | 周春海, 张振强, 黄志红, 等, 2020. 不同钝化剂对酸性土壤中重金属的钝化修复研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 36(33): 71-79. |
| ZHOU C H, ZHANG Z Q, HUANG Z H, et al., 2020. Passivation and Remediation of Heavy Metals in Acid Soil with Different Passivators A Research Progress[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 36(33): 71-79. | |
| [35] | 周显勇, 刘鸿雁, 刘艳萍, 等, 2019. 植物修复重金属和抗生素复合污染土壤微生物数量和酶活性的变化[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 38(6): 1248-1255. |
| ZHOU X Y, LIU H Y, LIU Y P, et al., 2019. Changes in microbial quantity and enzyme activity in phytoremediation of heavy metals and antibiotics contaminated soils[J]. Journal of Agricultural Environmental Sciences, 38(6): 1248-1255. | |
| [36] | 邹小玲, 余江涛, 2019. 改性生物质炭对重金属Cd的吸附作用研究进展[J]. 应用化工, 48(10): 2495-2498. |
| ZOU X L, YU J T, 2019. Research progress on adsorption of heavy metal Cd by modified biomass carbon[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 48(10): 2495-2498. |
| [1] | DU Dandan, GAO Ruizhong, FANG Lijing, XIE Longmei. Spatial Variation of Soil Heavy Metals and Their Responses to Physicochemical Factors of Salt Lake Basin in Arid Area [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(6): 1123-1132. |
| [2] | LI Chuanfu, ZHU Taochuan, MING Yufei, YANG Yuxuan, GAO Shu, DONG Zhi, LI Yongqiang, JIAO Shuying. Effect of Organic Fertilizer and Desulphurized Gypsum on Soil Aggregates and Organic Carbon and Its Fractions Contents in the Saline-alkali Soil of the Yellow River Delta [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 878-888. |
| [3] | CHEN Junfang, WU Xian, LIU Xiaolin, LIU Juan, YANG Jiarong, LIU Yu. Shaping Characteristics of Elemental Stoichiometry on Microbial Diversity under Different Soil Water Contents [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 898-909. |
| [4] | DONG Zhijin, ZHANG Chengchun, ZHAN Xiuli, ZHANG Weifu. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Soil Nutrients of Biological Soil Crusts and Their Underlying Soil of Sandy Land in the East of Yellow River in Ningxia [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(5): 910-919. |
| [5] | ZHOU Qinyuan, DONG Quanmin, Wang Fangcao, LIU Yuzhen, FENG Bin, YANG Xiaoxia, YU Yang, ZHANG Chunping, CAO Quan, LIU Wenting. Effects of Mixed Grazing on Aggregates and Organic Carbon in Rhizosphere Soil of Stellera chamaejasme in Alpine Grassland [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 660-667. |
| [6] | PAN Yuling, QU Xiangning, LI Qing, WANG Lei, WANG Xiaoping, TAN Peng, CUI Geng, AN Yu, TONG Shouzheng. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Soil Physicochemical Factors and Their Response to Microtopography in a Typical Beach Wetland of the Yellow River in Ningxia [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 668-677. |
| [7] | ZHAO Weibin, TANG Li, WANG Song, LIU Lingling, WANG Shufeng, XIAO Jiang, CHEN Guangcai. Improvement Effect of Two Biochars on Coastal Saline-Alkaline Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 678-686. |
| [8] | FENG Shuna, LÜ Jialong, HE Hailong. Effect of KI Leaching on the Hg (Ⅱ) Removal of Loess Soil and the Physicochemical Properties of the Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 776-783. |
| [9] | CHEN Minyi, ZHU Hanghai, SHE Weiduo, YIN Guangcai, HUANG Zuzhao, YANG Qiaoling. Health Risk Assessment and Source Apportionment of Soil Heavy Metals at A Legacy Shipyard Site in Pearl River Delta [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(4): 794-804. |
| [10] | ZHANG Lin, QI Shi, ZHOU Piao, WU Bingchen, ZHANG Dai, ZHANG Yan. Study on Influencing Factors of Soil Organic Carbon Content in Mixed Broad-leaved and Coniferous Forests Land in Beijing Mountainous Areas [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 450-458. |
| [11] | QIN Hao, LI Mengai, GAO Jin, CHEN Kailong, ZHANG Yinbo, ZHANG Feng. Composition and Diversity of Soil Bacterial Communities in Shrub at Different Altitudes in Luya Mountain [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 459-468. |
| [12] | TANG Haiming, SHI Lihong, WEN Li, CHENG Kaikai, LI Chao, LONG Zedong, XIAO Zhiwu, LI Weiyan, GUO Yong. Effects of Different Long-term Fertilizer Managements on Rhizosphere Soil Nitrogen in the Double-cropping Rice Field [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 492-499. |
| [13] | LIU Kanghan, ZHENG Liugen, ZHANG Liqun, DING Dan, SHAN Shifeng. Effect of Complex Plant Derived Activator on the Remediation of As Contaminated Soil by Pteris vittata [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 635-642. |
| [14] | FAN Huilin, ZHANG Jiamin, LI Huan, WANG Yanling. Study on the Profile Storage Pattern and Loss Risk of Phosphorus in Sloping Paddy Red Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(2): 283-291. |
| [15] | SONG Xiaoshuai, DING Wuquan, LIU Xinmin, LI Tingzhen. Study on the Mechanism of Ion Specificity Effect on the Pore Condition of Purple Soil [J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(2): 292-298. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2021 Editorial Office of ACTA PETROLEI SINICA
Address:No. 6 Liupukang Street, Xicheng District, Beijing, P.R.China, 510650
Tel: 86-010-62067128, 86-010-62067137, 86-010-62067139
Fax: 86-10-62067130
Email: syxb@cnpc.com.cn
Support byBeijing Magtech Co.ltd, E-mail:support@magtech.com.cn
