生态环境学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (8): 1365-1375.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.08.002
王宁1,2( ), 刘效东1, 甘先华2, 苏宇乔2, 吴国章1,2, 黄芳芳2, 张卫强2,*(
), 刘效东1, 甘先华2, 苏宇乔2, 吴国章1,2, 黄芳芳2, 张卫强2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-05-23
出版日期:2023-08-18
发布日期:2023-11-08
通讯作者:
*张卫强。E-mail: 584674651@qq.com作者简介:王宁(1998年生),男,硕士研究生,主要从事森林生态水文研究。E-mail: 13475823960@163.com
基金资助:
WANG Ning1,2( ), LIU Xiaodong1, GAN Xianhua2, SU Yuqiao2, WU Guozhang1,2, HUANG Fangfang2, ZHANG Weiqiang2,*(
), LIU Xiaodong1, GAN Xianhua2, SU Yuqiao2, WU Guozhang1,2, HUANG Fangfang2, ZHANG Weiqiang2,*( )
)
Received:2023-05-23
Online:2023-08-18
Published:2023-11-08
摘要:
森林生态系统在净化空气、截留沉降污染物及改善流域水质等方面具有重要作用。为评价亚热带地区典型森林生态系统对大气降水中氮、磷及重金属离子的截留能力和调控特征,以广东省新丰江库区3种典型林分(常绿阔叶林、针阔混交林、针叶林)为研究对象,分析了大气降水、穿透水、树干茎流、土壤渗透水及溪流水中pH值、总磷(TP)、总氮(TN)、硝酸盐氮(NO3--N)、铵态氮(NH4+-N)及6种重金属(Cd、Cr6+、Pb、Cu、Hg、Mn)含量的变化特征和冠层截留效应。结果表明:观测期间,大气降水经3种林分溪流输出后,均呈中性,常绿阔叶林对酸雨的缓冲能力较强。降水经针叶林后酸化加剧,树干茎流pH值为3.89。大气降水中TN、TP、NH4+-N和NO3--N质量浓度分别为0.977、0.046、0.047和0.173 mg?L-1,Cd、Cr6+、Pb、Hg、Cu和Mn的质量浓度为0.041、8.05、0.512、0.014、1.31和16.9 μg?L-1。降水过程中氮素及重金属浓度多呈先升高后下降的趋势,峰值多现于土壤渗透水中,而Hg浓度呈增加趋势。土壤渗透水中氮素和重金属离子浓度极高,可能与表层凋落物、土壤中养分和重金属本底值含量偏高有关,酸性较强的土壤水环境促进了离子的析出。TN、TP、NH4+-N和NO3--N的大气沉降量分别为13.3、0.83、1.66和2.59 kg?hm-2,Cd、Cr6+、Pb、Hg、Cu和Mn的沉降量为0.82、160.9、10.5、0.28、25.9和363.5 g?hm-2。典型林分冠层吸附或解吸氮、磷物质和重金属沉降的能力有所差异,针阔混交林和针叶林对TN、TP、NH4+-N和Cd有较好的截留净化作用,截留率均高于常绿阔叶林。常绿阔叶林冠层析出了较多的氮、磷物质和重金属元素,能够有效吸纳大气污染并改善空气质量;而针叶林和针阔混交林冠层相对于常绿阔叶林能更好地过滤、净化降水水质。
中图分类号:
王宁, 刘效东, 甘先华, 苏宇乔, 吴国章, 黄芳芳, 张卫强. 亚热带典型林分降水过程中的水质效应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(8): 1365-1375.
WANG Ning, LIU Xiaodong, GAN Xianhua, SU Yuqiao, WU Guozhang, HUANG Fangfang, ZHANG Weiqiang. Water Quality Effect in Precipitation by Typical Forests in Subtropical Region of China[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(8): 1365-1375.
| 森林类型 | 林分密度/ (plant∙hm-2) | 郁闭度/ % | 坡度/ (o) | 坡向 | 优势树种 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 针叶林 | 4476 | 80.7 | 30 | 北 | 杉木 (Cunninghamia lanceolata) |
| 针阔混交林 | 6192 | 75.5 | 30 | 北 | 杉木、木荷 (Schima superba)、五列木 (Pentaphylax euryoides)、马尾松 (Pinus massoniana)、 浙江润楠 (Machilus chekiangensis)、细齿叶柃 (Eurya nitida)、罗浮柿 (Diospyros morrisiana)、黄樟 (Cinnamomum parthenoxylon) |
| 常绿阔叶林 | 6520 | 88.0 | 27 | 西北 | 红锥 (Castanopsis hystrix)、黄果厚壳桂 (Cryptocarya concinna)、厚壳桂 (Cryptocarya chinensis)、鹿角锥 (Castanopsis lamontii)、橄榄 (Canarium album)、木荷、罗浮柿、华润楠 (Machilus chinensis) |
表1 研究样地的基本特征
Table 1 The basic characteristics of sample plots
| 森林类型 | 林分密度/ (plant∙hm-2) | 郁闭度/ % | 坡度/ (o) | 坡向 | 优势树种 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 针叶林 | 4476 | 80.7 | 30 | 北 | 杉木 (Cunninghamia lanceolata) |
| 针阔混交林 | 6192 | 75.5 | 30 | 北 | 杉木、木荷 (Schima superba)、五列木 (Pentaphylax euryoides)、马尾松 (Pinus massoniana)、 浙江润楠 (Machilus chekiangensis)、细齿叶柃 (Eurya nitida)、罗浮柿 (Diospyros morrisiana)、黄樟 (Cinnamomum parthenoxylon) |
| 常绿阔叶林 | 6520 | 88.0 | 27 | 西北 | 红锥 (Castanopsis hystrix)、黄果厚壳桂 (Cryptocarya concinna)、厚壳桂 (Cryptocarya chinensis)、鹿角锥 (Castanopsis lamontii)、橄榄 (Canarium album)、木荷、罗浮柿、华润楠 (Machilus chinensis) |
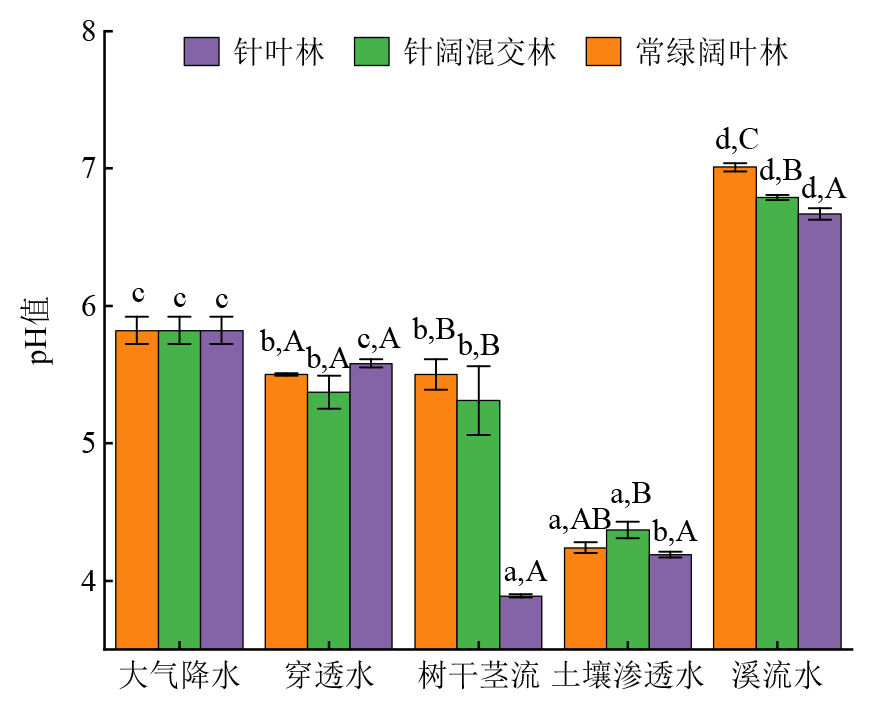
图2 3种典型林分酸化特征 不同小写字母表示同列同一林分各水文分量水质指标差异显著(P<0.05),不同大写字母表示典型林分间同一水文分量水质指标差异显著(P<0.05),n=3;下同
Figure 2 Acidification characteristics of three typical forests
| 林分类型 | 森林降水层次 | TN | TP | NH4+-N | NO3--N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大气降水沉降量/ (kg∙hm-2) | 13.3 | 0.829 | 1.66 | 2.60 | |
| 常绿阔叶林 | 穿透水沉降量/ (kg∙hm-2) | 10.2 | 0.674 | 0.672 | 3.01 |
| 树干茎流沉降量/ (kg∙hm-2) | 1.72 | 1.72 | 0.233 | 0.403 | |
| ΔF截留量/ (kg∙hm-2) | 1.39 | -1.57 | 0.754 | -0.82 | |
| 截留率/% | 10.5 | -189.2 | 45.5 | -31.6 | |
| 针阔混交林 | 穿透水沉降量/ (kg∙hm-2) | 7.66 | 0.38 | 0.795 | 3.71 |
| 树干茎流沉降量/ (kg∙hm-2) | 2.51 | 0.074 | 0.277 | 0.41 | |
| ΔF截留量/ (kg∙hm-2) | 3.11 | 0.375 | 0.587 | -1.53 | |
| 截留率/% | 23.4 | 45.3 | 35.4 | -58.9 | |
| 针叶林 | 穿透水沉降量/ (kg∙hm-2) | 7.88 | 0.573 | 0.544 | 3.00 |
| 树干茎流沉降量/ (kg∙hm-2) | 3.14 | 0.06 | 0.24 | 0.605 | |
| ΔF截留量/ (kg∙hm-2) | 2.26 | 0.20 | 0.88 | -1.02 | |
| 截留率/% | 17.0 | 23.5 | 52.7 | -39.3 |
表2 观测期间典型林分冠层对TN、TP、NH4+-N和NO3--N的截留
Table 2 Canopy interception of TN, TP, NH4+-N and NO3--N in typical forests during the observation period
| 林分类型 | 森林降水层次 | TN | TP | NH4+-N | NO3--N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大气降水沉降量/ (kg∙hm-2) | 13.3 | 0.829 | 1.66 | 2.60 | |
| 常绿阔叶林 | 穿透水沉降量/ (kg∙hm-2) | 10.2 | 0.674 | 0.672 | 3.01 |
| 树干茎流沉降量/ (kg∙hm-2) | 1.72 | 1.72 | 0.233 | 0.403 | |
| ΔF截留量/ (kg∙hm-2) | 1.39 | -1.57 | 0.754 | -0.82 | |
| 截留率/% | 10.5 | -189.2 | 45.5 | -31.6 | |
| 针阔混交林 | 穿透水沉降量/ (kg∙hm-2) | 7.66 | 0.38 | 0.795 | 3.71 |
| 树干茎流沉降量/ (kg∙hm-2) | 2.51 | 0.074 | 0.277 | 0.41 | |
| ΔF截留量/ (kg∙hm-2) | 3.11 | 0.375 | 0.587 | -1.53 | |
| 截留率/% | 23.4 | 45.3 | 35.4 | -58.9 | |
| 针叶林 | 穿透水沉降量/ (kg∙hm-2) | 7.88 | 0.573 | 0.544 | 3.00 |
| 树干茎流沉降量/ (kg∙hm-2) | 3.14 | 0.06 | 0.24 | 0.605 | |
| ΔF截留量/ (kg∙hm-2) | 2.26 | 0.20 | 0.88 | -1.02 | |
| 截留率/% | 17.0 | 23.5 | 52.7 | -39.3 |
| 林分类型 | 森林降水层次 | Cd | Cr6+ | Pb | Hg | Cu | Mn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大气降水沉降量/(g∙hm-2) | 0.823 | 160.9 | 10.5 | 0.275 | 25.9 | 363.5 | |
| 常绿阔叶林 | 穿透水沉降量/(g∙hm-2) | 0.558 | 388.7 | 33.5 | 0.245 | 182.9 | 553.3 |
| 树干茎流沉降量/(g∙hm-2) | 0.071 | 47.7 | 4.74 | 0.036 | 9.38 | 55.7 | |
| ΔF截留量/(g∙hm-2) | 0.194 | -275.5 | -27.7 | -0.007 | -166.3 | -245.5 | |
| 截留率/% | 23.6 | -171.2 | -263.7 | -2.67 | -641.5 | -67.6 | |
| 针阔混交林 | 穿透水沉降量/(g∙hm-2) | 0.369 | 171.5 | 18.4 | 0.284 | 91.2 | 760.7 |
| 树干茎流沉降量/(g∙hm-2) | 0.075 | 35.9 | 7.70 | 0.036 | 38.4 | 109.7 | |
| ΔF截留量/(g∙hm-2) | 0.379 | -46.5 | -15.6 | -0.045 | -103.7 | -506.9 | |
| 截留率/% | 46.1 | -28.9 | -148.0 | -16.6 | -399.8 | -139.5 | |
| 针叶林 | 穿透水沉降量/(g∙hm-2) | 0.463 | 346.3 | 15.8 | 0.133 | 66.1 | 566.0 |
| 树干茎流沉降量/(g∙hm-2) | 0.106 | 77.4 | 16.6 | 0.035 | 75.6 | 131.9 | |
| ΔF截留量/(g∙hm-2) | 0.255 | -263.7 | -21.9 | 0.107 | -115.7 | -334.4 | |
| 截留率/% | 30.9 | -163.2 | -208.3 | 38.8 | -446.3 | -92.0 |
表3 观测期间典型林分冠层对6种重金属的截留
Table 3 Canopy interception of six heavy metals in typical forest during observation period
| 林分类型 | 森林降水层次 | Cd | Cr6+ | Pb | Hg | Cu | Mn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大气降水沉降量/(g∙hm-2) | 0.823 | 160.9 | 10.5 | 0.275 | 25.9 | 363.5 | |
| 常绿阔叶林 | 穿透水沉降量/(g∙hm-2) | 0.558 | 388.7 | 33.5 | 0.245 | 182.9 | 553.3 |
| 树干茎流沉降量/(g∙hm-2) | 0.071 | 47.7 | 4.74 | 0.036 | 9.38 | 55.7 | |
| ΔF截留量/(g∙hm-2) | 0.194 | -275.5 | -27.7 | -0.007 | -166.3 | -245.5 | |
| 截留率/% | 23.6 | -171.2 | -263.7 | -2.67 | -641.5 | -67.6 | |
| 针阔混交林 | 穿透水沉降量/(g∙hm-2) | 0.369 | 171.5 | 18.4 | 0.284 | 91.2 | 760.7 |
| 树干茎流沉降量/(g∙hm-2) | 0.075 | 35.9 | 7.70 | 0.036 | 38.4 | 109.7 | |
| ΔF截留量/(g∙hm-2) | 0.379 | -46.5 | -15.6 | -0.045 | -103.7 | -506.9 | |
| 截留率/% | 46.1 | -28.9 | -148.0 | -16.6 | -399.8 | -139.5 | |
| 针叶林 | 穿透水沉降量/(g∙hm-2) | 0.463 | 346.3 | 15.8 | 0.133 | 66.1 | 566.0 |
| 树干茎流沉降量/(g∙hm-2) | 0.106 | 77.4 | 16.6 | 0.035 | 75.6 | 131.9 | |
| ΔF截留量/(g∙hm-2) | 0.255 | -263.7 | -21.9 | 0.107 | -115.7 | -334.4 | |
| 截留率/% | 30.9 | -163.2 | -208.3 | 38.8 | -446.3 | -92.0 |
| [1] |
BÉJAR PULIDO S J, CANTÚ SILVA I, DOMÍNGUEZ GÓMEZ T G, et al., 2018. Rainfall redistribution and nutrient input Pinus cooperi C.E. Blanco[J]. Revista Mexicana de Ciencias Forestales, 9(50): 94-120.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
CHEN L, ZHOU S L, WU S H, et al., 2019. Concentration, fluxes, risks, and sources of heavy metals in atmospheric deposition in the Lihe River watershed, Taihu region, eastern China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 255: 113301.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
DRAAIJERS G P J, Van EK R, BLEUTEN W, 1994. Atmospheric deposition in complex forest landscapes[J]. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 69(4): 343-366.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
DUAN J C, TAN J H, 2013. Atmospheric heavy metals and Arsenic in China: Situation, sources and control policies[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 74: 93-101.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
EISALOU H K, ŞENGÖNÜL K, GÖKBULAK F, et al., 2013. Effects of forest canopy cover and floor on chemical quality of water in broad leaved and coniferous forests of Istanbul, Turkey[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 289: 371-377.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
HUANG X, HU J, LI C, et al., 2009. Heavy-metal pollution and potential ecological risk assessment of sediments from Baihua Lake, Guizhou, P.R.China[J]. International Journal of Environmental Health Research, 19(6): 405-419.
DOI URL |
| [7] | JIANG J, WANG Y P, YU M X, et al., 2016. Responses of soil buffering capacity to acid treatment in three typical subtropical forests[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 563: 1068-1077. |
| [8] |
LI Y, ZHOU S L, JIA Z Y, et al., 2021. Temporal and spatial distributions and sources of heavy metals in atmospheric deposition in western Taihu Lake, China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 284: 117465.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
LIE Z Y, HUANG W J, ZHOU G Y, et al., 2023. Acidity of soil and water decreases in acid-sensitive forests of tropical China[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 57(30): 11075-11083.
DOI URL |
| [10] | MICHOPOULOS P, BOURLETSIKAS A, KAOUKIS K, et al., 2019. The distribution and variability of heavy metals in a mountainous fir forest ecosystem in two hydrological years[J]. Global Network of Environmental Science and Technology Journal, 20(2): 188-197. |
| [11] |
TAN S Y, ZHAO H R, YANG W Q, et al., 2019. Forest canopy can efficiently filter trace metals in deposited precipitation in a subalpine spruce plantation[J]. Forests, 10(4): 318.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
WANG Y Y, ZHU F F, KANG R H, et al., 2022. Chemical composition and deposition characteristics of precipitation into a typical temperate forest in northeastern China[J]. Forests, 13(12): 2024.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
WILLIAMS M W, BROOKS P D, MOSIER A, et al., 1996. Mineral nitrogen transformations in and under seasonal snow in a high-elevation catchment in the Rocky Mountains, United States[J]. Water Resources Research, 32(10): 3161-3171.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
WU J P, SU Y X, CHEN X Z, et al., 2019. Redistribution characteristics of atmospheric precipitation in different spatial levels of Guangzhou urban typical forests in southern China[J]. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 10(5): 1404-1411.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
ZANG C F, WU M W, ZHANG J M, et al., 2020. Research on the chemical element transport characteristics of the larch forest ecosystem of Greater Xing'an Mountain in China[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C, 120: 102919.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
ZHU J J, YU L Z, XU T L, et al., 2019. Comparison of water quality in two catchments with different forest types in the headwater region of the Hun River, Northeast China[J]. Journal of Forestry Research, 30(2): 565-576.
DOI |
| [17] | 白薇扬, 张成, 赵铮, 等, 2015. 三峡库区长寿湖水体不同形态汞的空间分布特征[J]. 环境科学, 36(8): 2863-2869. |
| BAI W Y, ZHANG C, ZHAO Z, et al., 2015. Spatial distribution characteristics of different species mercury in water body of Changshou Lake in Three Gorges Reservoir region[J]. Environmental Science, 36(8): 2863-2869. | |
| [18] | 陈军, 孟小星, 张卫东, 等, 2009. 重庆四面山森林冠层对降水化学组成的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学, 37(32): 16098-16101. |
| CHEN J, MENG X X, ZHANG W D, et al., 2009. Effects of Chongqing Simian Mountain forest canopy on chemical composition of precipitation[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultura Sciences, 37(32): 16098-16101. | |
| [19] | 陈晓滢, 植秋滢, 杨肖, 等, 2021. 广州市3种典型绿化树冠层降水再分配对重金属元素沉降的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 40(7): 1937-1946. |
| CHEN X Y, ZHI Q Y, YANG X, et al., 2021. The effects of rainfall partitioning on heavy metal deposition for three typical urban tree species in Guangzhou[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 40(7): 1937-1946. | |
| [20] | 杜子璇, 刘荣花, 魏璐, 2010. 郑州市酸雨变化特征及影响因素分析[J]. 气象与环境科学, 33(2): 32-36. |
| DU Z X, LIU R H, WEI L, 2010. Variation characteristic and influencing factor analysis of acid rain in Zhengzhou[J]. Meteorological and Environmental Sciences, 33(2): 32-36. | |
| [21] | 段江飞, 2022. 贵州松桃县某水库锰污染现状及成因分析[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 34(S1): 20-23. |
| DUAN J F, 2022. Analysis on manganese pollution status and cause of a reservoir in Songtao County, Guizhou Province[J]. Coal Geology of China, 34(S1): 20-23. | |
| [22] | 付淑清, 殷学博, 方国祥, 等, 2013. 新丰江上游铁矿区河流沉积剖面微量元素特征[J]. 安全与环境学报, 13(6): 123-127. |
| FU S Q, YIN X B, FANG G X, et al., 2013. Characteristic analysis of the trace elements abundance in the river-bed sediments near the ferris mine area in the upper reach of Xinfengjian[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 13(6): 123-127. | |
| [23] |
葛晓敏, 卢晓强, 陈水飞, 等, 2020. 武夷山常绿阔叶林生态系统降水分配与离子输入特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(2): 250-259.
DOI |
| GE X M, LU X Q, CHEN S F, et al., 2020. Reallocation and chemical characteristics of atmospheric precipitation in a mid-subtropical evergreen broad-leaved Forest in Wuyi Mountains, Fujian province, China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 29(2): 250-259. | |
| [24] | 蒋雨芮, 周蛟, 李晗, 等, 2020. 亚高山森林溪流镉储量与分配的动态变化特征[J]. 生态学报, 40(13): 4436-4444. |
| JIANG Y R, ZHOU J, LI H, et al., 2020. Dynamic characteristics of cadmium storage and distribution in the subalpine forest streams[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(13): 4436-4444. | |
| [25] | 康希睿, 张涵丹, 王小明, 等, 2021. 北亚热带3种森林群落对大气湿沉降重金属的调控[J]. 生态学报, 41(6): 2107-2117. |
| KANG X R, ZHANG H D, WANG X M, et al., 2021. Distribution of heavy metals in precipitation by three forest communities in northern subtropical region of China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41(6): 2107-2117. | |
| [26] | 李佳, 李巍, 侯锦湘, 等, 2010. 贵州地区酸雨作用下典型森林植被冠层淋溶规律研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 30(10): 1297-1302. |
| LI J, LI W, HOU J X, et al., 2010. Typical forests’ leaching characteristics during acid rain in Guizhou[J]. China Environmental Science, 30(10): 1297-1302. | |
| [27] |
李凯, 程金花, 陈仲旭, 2019. 密云水库库滨带不同植被配置下面源污染特征分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 28(6): 1183-1192.
DOI |
|
LI K, CHENG J H, CHEN Z X, 2019. Analysis on the characteristics of non-point source pollution in the bank zone of Miyun Resevoir[J]. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 28(6): 1183-1192.
DOI |
|
| [28] | 李可见, 黄芳芳, 张卫强, 等, 2018. 新丰江水库及库区地表水水质分析与评价[J]. 林业与环境科学, 34(3): 6-13. |
| LI K J, HUANG F F, ZHANG W Q, et al., 2018. Analysis and assessment of surface water quality in Xinfengjiang Reservoir area[J]. Forestry and Environmental Science, 34(3): 6-13. | |
| [29] | 李怡然, 刘素梅, 2019. 河源市新丰江水库可持续发展的环境保护方法研究[J]. 科技资讯, 17(10): 77-78. |
| LI Y R, LIU S M, 2019. A study on environmental protection methods for sustainable development of Xinfengjiang Reservoir in Heyuan[J]. Science & Technology Information, 17(10): 77-78. | |
| [30] | 廖剑宇, 彭秋志, 郑楚涛, 等, 2013. 东江干支流水体氮素的时空变化特征[J]. 资源科学, 35(3): 505-513. |
| LIAO J Y, PENG Q Z, ZHENG C T, et al., 2013. Temporal-Spatial distribution of nitrogen in the Dongjiang River and Its Tributaries[J]. Resources Science, 35(3): 505-513. | |
| [31] | 刘菊秀, 2003. 酸沉降对森林生态系统影响的研究现状及展望[J]. 生态学杂志, 22(5): 113-117. |
| LIU J X, 2003. Current and future study about effects of acid deposition on forest ecosystems[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 22(5): 113-117. | |
| [32] | 刘菊秀, 张德强, 周国逸, 等, 2003. 鼎湖山酸沉降背景下主要森林类型水化学特征初步研究[J]. 应用生态学报, 14(8): 1223-1228. |
| LIU J X, ZHANG D Q, ZHOU G Y, et al., 2003. A preliminary study on the chemical properties of precipitation, throughfall, stemflow and surface run-off in major forest types at Dinghushan under acid deposition[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 14(8): 1223-1228. | |
| [33] |
刘佩伶, 刘效东, 冯英杰, 等, 2022. 新丰江水库库区水源涵养林土壤饱和导水率特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 31(10): 1993-2001.
DOI |
| LIU P L, LIU X D, FENG Y J, et al., 2022. Characteristics of soil saturated hydraulic conductivity of water conservation forests in the Xinfengjiang Reservoir Area[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 31(10): 1993-2001. | |
| [34] | 刘效东, 张卫强, 冯英杰, 等, 2022. 森林生态系统水源涵养功能研究进展与展望[J]. 生态学杂志, 41(4): 784-791. |
| LIU X D, ZHANG W Q, FENG Y J, et al., 2022. Research on water conservation function of forest ecosystem:Progress and prospect[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 41(4): 784-791. | |
| [35] | 刘逸菲, 鲁绍伟, 赵娜, 等, 2021. 森林影响降水水质研究概述[J]. 世界林业研究, 34(5): 14-19. |
| LIU Y F, LU S W, ZHAO N, et al., 2021. Research progress in forests’ influence on precipitation water quality[J]. World Forestry Research, 34(5): 14-19. | |
| [36] | 刘永杰, 党坤良, 王连贺, 等, 2014. 秦岭南坡2种林分类型林冠层对大气降水水质的生态效应[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 42(7): 89-94. |
| LIU Y J, DANG K L, WANG L H, et al., 2014. Ecological effects of canopies of two forest types on rain water quality on the south slope of Qinling Mountains[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 42(7): 89-94. | |
| [37] | 卢晓强, 杨万霞, 丁访军, 等, 2015. 茂兰喀斯特地区森林降水分配的水化学特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 34(8): 2115-2122. |
| LU X Q, YANG W X, DING F J, et al., 2015. Reallocation and chemical characteristics of precipitation in a Maolan karst forest[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 34(8): 2115-2122. | |
| [38] | 钱学诗, 钱壮壮, 王波, 等, 2022. 森林生态系统对降水过程中的重金属影响研究综述[J]. 世界林业研究, 35(3): 8-13. |
| QIAN X S, QIAN Z Z, WANG B, et al., 2022. A Review of the effect of forest ecosystems on heavy metals in precipitation[J]. World Forestry Research, 35(3): 8-13. | |
| [39] | 孙涛, 马明, 王定勇, 2016. 中亚热带典型森林生态系统对降水中铅镉的截留特征[J]. 生态学报, 36(1): 218-225. |
|
SUN T, MA M, WANG D Y, 2016. Interceptive characteristics of lead and cadmium in a representative forest ecosystem in mid-subtropical area in China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36(1): 218-225.
DOI URL |
|
| [40] | 覃芳华, 王彬, 王云琦, 等, 2014. 重庆缙云山三种典型林分穿透水和树干茎流中氮素特征研究[J]. 土壤通报, 45(4): 884-891. |
| TAN F H, WANG B, WANG Y Q, et al., 2014. Nitrogen characteristics in throughfall and stemflow in three typical forests on Jinyun Mountain, Chongqing City[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 45(4): 884-891. | |
| [41] | 田大伦, 2002. 会同广坪林区降雨和杉木林内雨的养分含量[J]. 中南林学院学报, 22(3): 9-13. |
| TIAN D L, 2002. Nutrient contents in the rainfall inside and outside the stands of Guangping forest zone, Huitong[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 22(3): 9-13. | |
| [42] | 温美丽, 杨龙, 方国祥, 等, 2015. 新丰江水库上游氮磷污染的时空变化[J]. 热带地理, 35(1): 103-110. |
| WEN M L, YANG L, FANG G X, et al., 2015. Spatio-Temporal variation of nitrogen and phosphorus pollution in upriver watercourse of the Xinfengjiang Reservoir in Guangdong Province[J]. Tropical Geography, 35(1): 103-110. | |
| [43] | 伍琪, 任世奇, 姜同强, 等, 2020. 南方四种速生树种凋落叶在不同模拟酸雨环境中变化特性研究[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学, 39(4): 1758-1768. |
| WU Q, REN S Q, JIANG T Q, et al., 2020. The Study of variation characteristic of litters of four fast-growing species on simulated acid rain with different acidities[J]. Genomics and Applied Biology, 39(4): 1758-1768. | |
| [44] | 肖以华, 陈步峰, 潘勇军, 等, 2010. 广州帽峰山常绿阔叶林森林生态系统水文环境效应[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 38(3): 78-81. |
| XIAO Y H, CHEN B F, PAN Y J, et al., 2010. Effects of hydrological environment on tropical evergreen broad-leaved forest in Maofengshan Mountain of Guangzhou[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 38(3): 78-81. | |
| [45] | 徐小勤, 于澎涛, 王彦辉, 等, 2023. 六盘山华北落叶松林的结构随林龄变化及其水文影响[J]. 林业科学研究, 36(1): 109-116. |
| XU X Q, YU P T, WANG Y H, et al., 2023. The Variation of stand structure with age and its hydrological effects of larch plantation in Liupan Mountains[J]. Forest Research, 36(1): 109-116. | |
| [46] | 杨丽丽, 邢元军, 王彦辉, 等, 2019. 宁夏六盘山4种典型森林伴随降水的无机氮通量变化特征[J]. 生态学报, 39(8): 2851-2861. |
| YANG L L, XING Y J, WANG Y H, et al., 2019. The spatial variability of inorganic nitrogen flux with precipitation for four typical forests of the Liupan Mountain of Ningxia, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(8): 2851-2861. | |
| [47] | 张楠, 范春楠, 陈思羽, 等, 2019. 次生落叶阔叶林降雨过程中的4种金属元素特征[J]. 南京林业大学学报 (自然科学版), 43(4): 178-184. |
| ZHANG N, FAN C N, CHEN S Y, et al., 2019. Effects of precipitation characteristics on the distribution of four metal elements by rainfalls in a secondary deciduous broad-leaved forest[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 43(4): 178-184. | |
| [48] | 张运, 许仕荣, 卢少勇, 2018. 新丰江水库表层沉积物重金属污染特征与评价[J]. 环境工程, 36(1): 134-141. |
| ZHANG Y, XU S R, LU S Y, 2018. Pollution characteristics and assessment of heavy metals in the surface sediment of Xinfengjiang reservoir[J]. Environmental Engineering, 36(1): 134-141. | |
| [49] | 赵银, 令狐文生, 2020. 铬离子的危害及其处理研究进展[J]. 河南化工, 37(5): 6-8. |
| ZHAO Y, LING H W S, 2020. The Harm of chromium ion and its treatment research progress[J]. Henan Chemical Industry, 37(5): 6-8. | |
| [50] | 赵宇寒, 曹建生, 朱春雨, 等, 2022. 壤中流形成机制及其生态水文效应研究进展[J]. 中国生态农业学报 (中英文), 30(1): 38-46. |
| ZHAO Y H, CAO J S, ZHU C Y, et al., 2022. Research progress on the formation mechanism of subsurface flow and its ecohydrological effects[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 30(1): 38-46. |
| [1] | 刘炳妤, 王一佩, 姚作芳, 杨钙仁, 徐晓楠, 邓羽松, 黄钰涵. 沼液还田下不同种植模式的重金属风险评价及安全消纳量分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(8): 1507-1515. |
| [2] | 杜丹丹, 高瑞忠, 房丽晶, 谢龙梅. 旱区盐湖盆地土壤重金属空间变异及对土壤理化因子的响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(6): 1123-1132. |
| [3] | 冯树娜, 吕家珑, 何海龙. KI淋洗对黄绵土汞污染的去除效果及土壤理化性状的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 776-783. |
| [4] | 陈敏毅, 朱航海, 佘伟铎, 尹光彩, 黄祖照, 杨巧玲. 珠三角某遗留造船厂场地土壤重金属人体健康风险评估及源解析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 794-804. |
| [5] | 肖洁芸, 周伟, 石佩琪. 土壤重金属含量高光谱反演[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(1): 175-182. |
| [6] | 黄宏, 郑欣芸, 李迎东, 赵旭, 俞锦辰, 汪振华. 大陈岛海域不同年龄褐菖鲉对重金属富集作用研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1885-1891. |
| [7] | 马闯, 王雨阳, 周通, 吴龙华. 污染土壤颗粒态有机质镉锌富集特征及其解吸行为研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(9): 1892-1900. |
| [8] | 陶玲, 黄磊, 周怡蕾, 李中兴, 任珺. 污泥-凹凸棒石共热解生物炭对矿区土壤重金属生物有效性和环境风险的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1637-1646. |
| [9] | 李莹, 张洲, 杨高明, 祖艳群, 李博, 陈建军. 湿地植物根系泌氧能力和根表铁膜与根系吸收重金属的关系[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8): 1657-1666. |
| [10] | 罗松英, 李秋霞, 邱锦坤, 邓素炎, 李一锋, 陈碧珊. 南三岛土壤-红树植物系统中重金属形态特征及迁移转化规律[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1409-1416. |
| [11] | 董乐恒, 王旭刚, 陈曼佳, 王子豪, 孙丽蓉, 石兆勇, 吴琪琪. 光照和避光条件下石灰性水稻土Fe氧化还原与Cu活性关系研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(7): 1448-1455. |
| [12] | 彭红丽, 谭海霞, 王颖, 魏建梅, 冯阳. 不同种植模式下土壤重金属形态分布差异与生态风险评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1235-1243. |
| [13] | 黄敏, 赵晓峰, 梁荣祥, 王鹏忠, 戴安然, 何晓曼. 3种螯合剂对Cd、Cu复合污染土壤淋洗修复的对比研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1244-1252. |
| [14] | 朱立安, 张会化, 程炯, 李婷, 林梓, 李俊杰. 珠江三角洲林业用地土壤重金属潜在生态风险格局分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1253-1262. |
| [15] | 施建飞, 靳正忠, 周智彬, 王鑫. 额尔齐斯河流域典型尾矿库区周边土壤重金属污染评价[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(5): 1015-1023. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
