生态环境学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (3): 635-642.DOI: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.03.021
• 研究论文 •
上一篇
刘抗旱1,2( ), 郑刘根1,2,*(
), 郑刘根1,2,*( ), 张理群1,2, 丁丹3, 单士锋3
), 张理群1,2, 丁丹3, 单士锋3
收稿日期:2022-12-12
出版日期:2023-03-18
发布日期:2023-06-02
通讯作者:
*郑刘根(1972年生),男,教授,博士,研究方向为矿山生态地质环境治理。E-mail: lgzheng@ustc.edu.cn作者简介:刘抗旱(1998年生),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为矿区土壤重金属修复。E-mail: 1546677262@qq.com
基金资助:
LIU Kanghan1,2( ), ZHENG Liugen1,2,*(
), ZHENG Liugen1,2,*( ), ZHANG Liqun1,2, DING Dan3, SHAN Shifeng3
), ZHANG Liqun1,2, DING Dan3, SHAN Shifeng3
Received:2022-12-12
Online:2023-03-18
Published:2023-06-02
摘要:
长期的人类活动导致砷(As)在土壤中大量积累,对生态环境和人体健康构成严重威胁,迫切需要修复。通过将谷氨酸二乙酸四钠(GLDA,10%)、蜈蚣草水提取物(10%)和茶皂素(4%)以不同比例混合形成复合型植物源活化剂作为试验材料,以As污染的尾矿区土壤作为研究对象,根据土壤模拟和盆栽试验,研究不同配比方案的复合型植物源活化剂对土壤中As的生物有效态含量、供试植物蜈蚣草(Pteris vittata)生物量和提取As的影响,筛选出复合型植物源活化剂最佳的配比方案。研究结果表明,在土壤模拟试验中,复合型植物源活化剂处理土壤中残渣态As的质量分数显著降低,而生物有效态As质量分数显著升高,将残渣态转化为生物有效态,在GST7(7:12:1)处理条件下,生物有效态As的质量分数达到最大,较对照组(CK)提高了40.80%。盆栽试验中,复合型植物源活化剂处理蜈蚣草生物量随GLDA比例升高和茶皂素比例降低,呈现先升高后降低的趋势,在GST6(6:12:2)处理时达到最大,为3.58 g·plant-1,较CK提高了45.21%。蜈蚣草中As的质量分数显著升高,且随GLDA比例升高和茶皂素比例降低逐渐升高,在GST7处理时蜈蚣草地上部和根部As的质量分数达到最大,为738.30 mg·kg-1和281.20 mg·kg-1,较CK提高了40.17%和22.63%。蜈蚣草对As的提取量和去除率变化趋势与其生物量变化一致,呈现先升高后降低的趋势,在GST6处理时达到最大,其值为1795.10 μg·plant-1和0.59%,是CK的1.85倍和1.90倍。综合表明复合型植物源活化剂的配比方案为GST6(6:12:2)时蜈蚣草的修复效果最佳,可作为一种新的As污染土壤的植物修复策略。
中图分类号:
刘抗旱, 郑刘根, 张理群, 丁丹, 单士锋. 复合型植物源活化剂强化蜈蚣草修复砷污染土壤的效应研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 635-642.
LIU Kanghan, ZHENG Liugen, ZHANG Liqun, DING Dan, SHAN Shifeng. Effect of Complex Plant Derived Activator on the Remediation of As Contaminated Soil by Pteris vittata[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2023, 32(3): 635-642.
| 处理 | 浓度 | 提取量/(mg·kg-1) | 提取率/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| EDTA | 3 mmol·L-1 | 13.50±0.03e | 13.26±0.29e |
| ST | 10% | 17.70±0.06d | 17.39±0.58d |
| GLDA | 1% | 26.40±0.03c | 25.89±0.26c |
| 5% | 33.40±0.07b | 32.81±0.66b | |
| 10% | 42.00±0.10a | 41.20±0.99a | |
| TS | 2% | 3.26±0.01f | 3.21±0.09g |
| 4% | 6.02±0.02g | 5.92±0.16f | |
| 6% | 4.18±0.03f | 4.11±0.30g |
表1 不同浓度活化剂从土壤中提取As
Table 1 Extraction of As from soil with different concentrations of activators
| 处理 | 浓度 | 提取量/(mg·kg-1) | 提取率/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| EDTA | 3 mmol·L-1 | 13.50±0.03e | 13.26±0.29e |
| ST | 10% | 17.70±0.06d | 17.39±0.58d |
| GLDA | 1% | 26.40±0.03c | 25.89±0.26c |
| 5% | 33.40±0.07b | 32.81±0.66b | |
| 10% | 42.00±0.10a | 41.20±0.99a | |
| TS | 2% | 3.26±0.01f | 3.21±0.09g |
| 4% | 6.02±0.02g | 5.92±0.16f | |
| 6% | 4.18±0.03f | 4.11±0.30g |
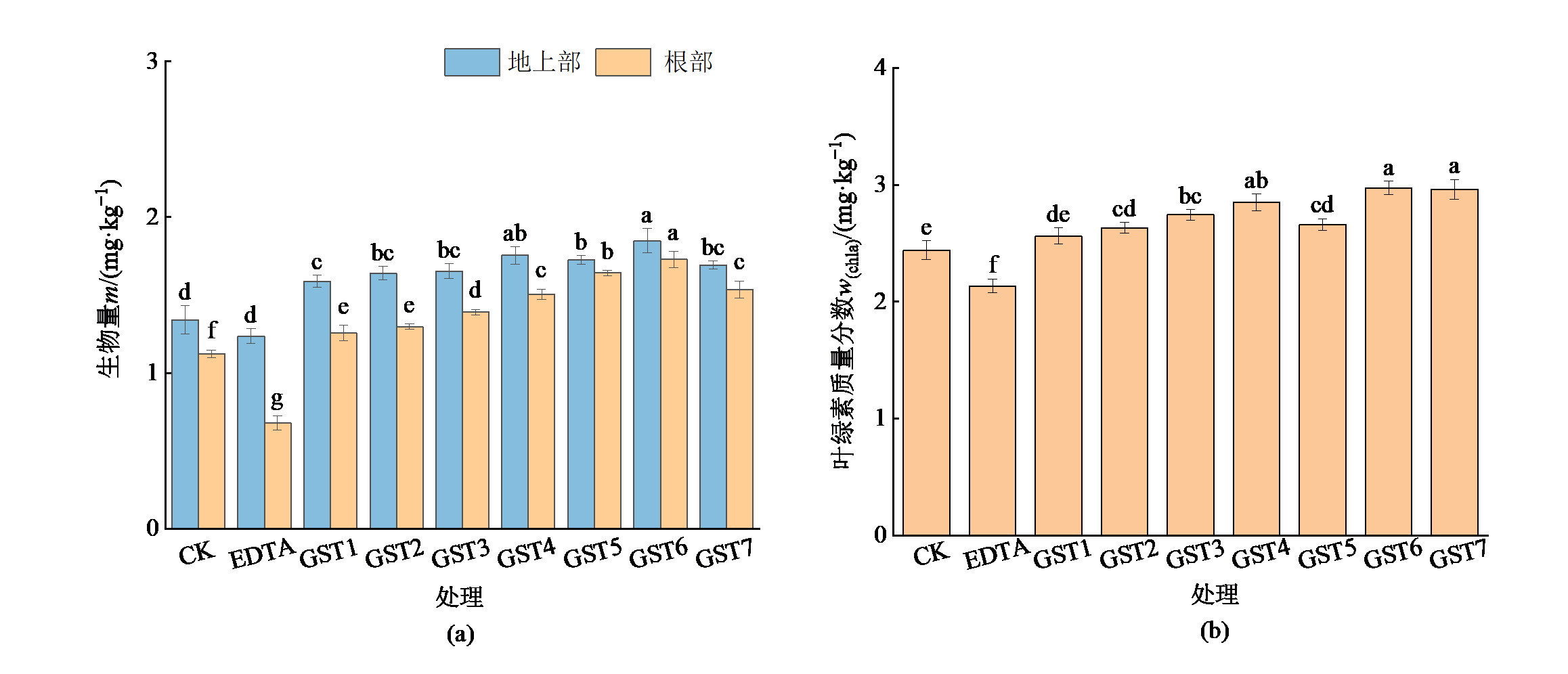
图3 复合型植物源活化剂对蜈蚣草生物量和叶绿素质量分数的影响 不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05),下同
Figure 3 Effects of complex plant derived activators on biomass and chlorophyll content of Pteris vittata
| 处理 | 生物富集系数 (B) | 转移系数 (T) | 提取量/ (μg·plant-1) | 去除率/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地上部 | 根部 | ||||
| CK | 5.20±0.14g | 2.20±0.05f | 2.30±0.12b | 963.93±68f | 0.31±0.02f |
| EDTA | 6.99±0.09c | 2.71±0.11bcd | 2.58±0.08a | 1002.15±36f | 0.33±0.01f |
| GST1 | 5.85±0.13f | 2.40±0.12ef | 2.44±0.15ab | 1198.13±34e | 0.39±0.01e |
| GST2 | 6.20±0.07e | 2.51±0.09de | 2.47±0.10ab | 1281.58±43e | 0.42±0.01de |
| GST3 | 6.65±0.10d | 2.60±0.09de | 2.56±0.06a | 1383.33±24d | 0.45±0.01d |
| GST4 | 6.95±0.10c | 2.69±0.13cd | 2.59±0.09a | 1534.22±8c | 0.50±0c |
| GST5 | 7.45±0.15b | 2.86±0.09abc | 2.61±0.14a | 1644.60±19b | 0.54±0.01bc |
| GST6 | 7.74±0.16a | 2.93±0.11ab | 2.67±0.15a | 1795.10±65a | 0.59±0.02a |
| GST7 | 7.94±0.18a | 3.02±0.11a | 2.63±0.06a | 1681.64±64b | 0.55±0.02b |
表2 不同处理条件下蜈蚣草的植物修复参数
Table 2 Phytoremediation parameters of Pteris vittata under different treatment conditions
| 处理 | 生物富集系数 (B) | 转移系数 (T) | 提取量/ (μg·plant-1) | 去除率/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地上部 | 根部 | ||||
| CK | 5.20±0.14g | 2.20±0.05f | 2.30±0.12b | 963.93±68f | 0.31±0.02f |
| EDTA | 6.99±0.09c | 2.71±0.11bcd | 2.58±0.08a | 1002.15±36f | 0.33±0.01f |
| GST1 | 5.85±0.13f | 2.40±0.12ef | 2.44±0.15ab | 1198.13±34e | 0.39±0.01e |
| GST2 | 6.20±0.07e | 2.51±0.09de | 2.47±0.10ab | 1281.58±43e | 0.42±0.01de |
| GST3 | 6.65±0.10d | 2.60±0.09de | 2.56±0.06a | 1383.33±24d | 0.45±0.01d |
| GST4 | 6.95±0.10c | 2.69±0.13cd | 2.59±0.09a | 1534.22±8c | 0.50±0c |
| GST5 | 7.45±0.15b | 2.86±0.09abc | 2.61±0.14a | 1644.60±19b | 0.54±0.01bc |
| GST6 | 7.74±0.16a | 2.93±0.11ab | 2.67±0.15a | 1795.10±65a | 0.59±0.02a |
| GST7 | 7.94±0.18a | 3.02±0.11a | 2.63±0.06a | 1681.64±64b | 0.55±0.02b |
| [1] |
ANH B T K, MINH N N, HA N T H, et al., 2018. Field Survey and comparative study of Pteris vittata and Pityrogramma calomelanos grown on arsenic contaminated lands with different soil pH[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 100(5): 720-726.
DOI |
| [2] |
CAY S, 2016. Enhancement of cadmium uptake by Amaranthus caudatus, an ornamental plant, using tea saponin[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188(6): 320.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
DITUSA S F, FONTENOT E B, WALLACE R W, et al., 2016. A member of the Phosphate transporter 1 (Pht1) family from the arsenic-hyperaccumulating fern Pteris vittata is a high-affinity arsenate transporter[J]. New Phytologist, 209(2): 762-772.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
GUO X F, ZHANG G X, WEI Z B, et al., 2018. Mixed chelators of EDTA, GLDA, and citric acid as washing agent effectively remove Cd, Zn, Pb, and Cu from soils[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 18(3): 835-844.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
HAN R, DAI H P, GUO B, et al., 2021b. The potential of medicinal plant extracts in improving the phytoremediation capacity of Solanum nigrum L. for heavy metal contaminated soil[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 220: 112411.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
HAN R, DAI H P, SKUZA L, et al., 2021a. Comparative study on different organic acids for promoting Solanum nigrum L. hyperaccumulation of Cd and Pb from the contaminated soil[J]. Chemosphere, 278: 130446.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
HAN R, DAI H P, TWARDOWSKA I, et al., 2020. Aqueous extracts from the selected hyperaccumulators used as soil additives significantly improve accumulation capacity of Solanum nigrum L. for Cd and Pb[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 394: 122553.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
HE Z Y, YAN H L, CHEN Y S, et al., 2016. An aquaporin PvTIP4;1 from Pteris vittata may mediate arsenite uptake[J]. New Phytologist, 209(2): 746-761.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
KALYVAS G, GASPARATOS D, LIZA C A, et al., 2020. Single and combined effect of chelating, reductive agents, and agro-industrial by-product treatments on As, Pb, and Zn mobility in a mine-affected soil over time[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(5): 5536-5546.
DOI |
| [10] |
KAMRAN M A, XU R K, LI J Y, et al., 2018. Effect of different phosphorus sources on soybean growth and arsenic uptake under arsenic stress conditions in an acidic ultisol[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 165: 11-18.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
KHANNA K, KOHLI S K, KUMAR P, et al., 2022. Arsenic as hazardous pollutant: perspectives on engineering remediation tools[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 838(Part 2): 155870.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
LAN J C, ZHANG S R, LIN H C, et al., 2013. Efficiency of biodegradable EDDS, NTA and APAM on enhancing the phytoextraction of cadmium by Siegesbeckia orientalis L. grown in Cd-contaminated soils[J]. Chemosphere, 91(9): 1362-1367.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
LI F L, QIU Y H, XU X Y, et al., 2020. EDTA-enhanced phytoremediation of heavy metals from sludge soil by Italian ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.)[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 191: 110185.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
LI T Q, DI Z Z, HAN X, et al., 2012. Elevated CO2 improves root growth and cadmium accumulation in the hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii[J]. Plant and Soil, 354(1-2): 325-334.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
LIANG Y Q, WANG X H, GUO Z H, et al., 2019. Chelator-assisted phytoextraction of arsenic, cadmium and lead by Pteris vittata L. and soil microbial community structure response[J]. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 21(10): 1032-1040.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
LIANG Y Q, XIAO X Y, GUO Z H, et al., 2021. Co-application of indole-3-acetic acid/gibberellin and oxalic acid for phytoextraction of cadmium and lead with Sedum alfredii Hance from contaminated soil[J]. Chemosphere, 285: 131420.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
LIAO Q H, WANG J H, YANG G J, et al., 2013. Comparison of spectral indices and wavelet transform for estimating chlorophyll content of maize from hyperspectral reflectance[J]. Journal of applied remote sensing, 7(1): 073575.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
LINGUA G, TODESCHINI V, GRIMALDI M, et al., 2014. Polyaspartate, a biodegradable chelant that improves the phytoremediation potential of poplar in a highly metal-contaminated agricultural soil[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 132: 9-15.
DOI PMID |
| [19] |
LUO J P, LIANG J B, SONG Y C, et al., 2021. Compounded chelating agent derived from fruit residue extracts effectively enhances Cd phytoextraction by Sedum alfredii[J]. Soil Ecology Letters, 3(3): 253-265.
DOI |
| [20] |
MA L Q, KOMAR M K, TU C, et al., 2021. A fern that hyperaccumulates arsenic[J]. Nature, 409(6820): 579.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
PANDEY S K, BHATTACHARYA T, CHAKRABORTY S, 2016. Metal phytoremediation potential of naturally growing plants on fly ash dumpsite of patratu thermal power station, Jharkhand, India[J]. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 18(1): 87-93.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | SHAHID M, AUSTRUY A, ECHEVARRIA G, et al., 2014. EDTA-enhanced phytoremediation of heavy metals: A review[J]. Soil & sediment contamination, 23(4): 389-416. |
| [23] |
SUN Y B, ZHOU Q X, AN J, et al., 2009. Chelator-enhanced phytoextraction of heavy metals from contaminated soil irrigated by industrial wastewater with the hyperaccumulator plant (Sedum alfredii Hance)[J]. Geoderma, 150(1-2): 106-112.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
SUN Z C, LIU Y G, HUANG Y Q, et al., 2014. Effects of indole-3-acetic, kinetin and spermidine assisted with EDDS on metal accumulation and tolerance mechanisms in ramie (Boehmeria nivea (L.) Gaud.)[J]. Ecological Engineering, 71: 108-112.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
TAO Q, LI J X, LIU Y K, et al., 2020. Ochrobactrum intermedium and saponin assisted phytoremediation of Cd and B[a]P co-contaminated soil by Cd-hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii[J]. Chemosphere, 245: 125547.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
WANG A G, LUO C L, YANG R X, et al., 2012. Metal leaching along soil profiles after the EDDS application: A field study[J]. Environmental Pollution, 164: 204-210.
DOI URL |
| [27] | WANG G Y, ZHANG S R, XU X X, et al., 2016. Heavy metal removal by GLDA washing: optimization, redistribution, recycling, and changes in soil fertility[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 569-570: 557-568. |
| [28] |
WEI Z H, VAN LE Q., PENG W X, et al., 2021. A review on phytoremediation of contaminants in air, water and soil[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 403: 123658.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
WENZEL W W, KIRCHBAUMER N, PROHASKA T, et al., 2001. Arsenic fractionation in soils using an improved sequential extraction procedure[J]. Analytica chimica acta, 436(2): 309-323.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
WILLSCHER S, JABLONSKI L, FONA Z, et al., 2017. Phytoremediation experiments with Helianthus tuberosus under different pH and heavy metal soil concentrations[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 168: 153-158.
DOI URL |
| [31] | WUANA R A, OKIEIMEN F E, IMBORVUNGU J A, 2010. Removal of heavy metals from a contaminated soil using organic chelating acids[J]. International Journal of Environmental Science & Technology, 7: 485-496. |
| [32] |
XIA H L, CHI X Y, YAN Z J, et al., 2009. Enhancing plant uptake of polychlorinated biphenyls and cadmium using tea saponin[J]. Bioresource Technology, 100(20): 4649-4653.
DOI PMID |
| [33] |
XIANG D F, LIAO S J, TU S X, et al., 2020. Surfactants enhanced soil arsenic phytoextraction efficiency by Pteris vittata L[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 104(2): 259-264.
DOI |
| [34] | XIAO K M, LI Y Z, SUN Y, et al., 2017. Remediation performance and mechanism of heavy metals by a bottom up activation and extraction system using multiple biochemical materials[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 9(36): 30448-30457. |
| [35] |
XU J, XING Y, WANG J, et al., 2022. Effect of poly-γ-glutamic acid on the phytoremediation of ramie (Boehmeria nivea L.) in the Hg-contaminated soil[J]. Chemosphere, 312(Part 1): 137280.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
YANG Q, YANG C, YU H, et al., 2021. The addition of degradable chelating agents enhances maize phytoremediation efficiency in Cd-contaminated soils[J]. Chemosphere, 269: 129373.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
YANG X X, CHEN H, DAI X J, et al., 2009. Evidence of vacuolar compartmentalization of arsenic in the hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 54(22): 4229-4233.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
ZHENG C J, WANG X, LIU J, et al., 2019. Biochar-assisted phytoextraction of arsenic in soil using Pteris vittata L.[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(36): 36688-36697.
DOI |
| [39] |
ZHU G X, XIAO H Y, GUO Q J, et al., 2018. Heavy metal contents and enrichment characteristics of dominant plants in wasteland of the downstream of a lead-zinc mining area in Guangxi, Southwest China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 151: 266-271.
DOI PMID |
| [40] | 黄玉梅, 张杨雪, 刘庆林, 等, 2015. 孔雀草水浸提液对4种园林植物化感作用的研究[J]. 草叶学报, 24(6): 150-158. |
| HUANG Y M, ZHANG Y X, LIU Q L, et al., 2015. Research on allelopathy of aqueous extract from Taget espatula to four garden plants[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 24(6): 150-158. | |
| [41] | 邱亚群, 李益华, 彭佩钦, 等, 2021. 螯合剂添加对蜈蚣草修复砷污染土壤效果的影响分析[J]. 环境工程, 39(3): 204-209. |
| QIU Y Q, LI Y H, PENG P Q, et al., 2021. Effect of chelating agent on Pteris vittata for remediation of arsenic-contaminated soil[J]. Environmental Engineering, 39(3): 204-209. | |
| [42] |
史广宇, 余志强, 施维林, 2021. 植物修复土壤重金属污染中外源物质的影响机制和应用研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 30(3): 655-666.
DOI |
| SHI G Y, YU Z Q, SHI W L, 2021. Research progress on mechanism and application of exogenous substances in phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soil[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 30(3): 655-666. | |
| [43] | 向冬芳, 廖水姣, 涂书新, 等, 2019. 三聚磷酸钠与柠檬酸复合强化蜈蚣草修复砷污染土壤[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 38(8): 1973-1981. |
| XIANG D F, LIAO S J, TU S X, et al., 2019. Effect of a sodium tripolyphosphate and citric acid composite on arsenic bioaccumulation caused by arsenic-contaminated soil in Pteris vittata L[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 38(8): 1973-1981. | |
| [44] | 熊国焕, 潘义宏, 何艳明, 等, 2012. 螯合剂对大叶井口边草Pb、Cd、As吸收性影响研究[J]. 土壤, 44(2): 282-289. |
| XIONG G H, PAN Y H, HE Y M, et al., 2012. Chelate assisted uptake of heavy metal of lead, cadmium and arsenic from soil with Pteris cretica var.nervosa[J]. Soil, 44(2): 282-289. | |
| [45] | 熊俊娟, 丁利君, 2011. 蜈蚣草有效成分的定性分析及紫外光谱研究[J]. 时珍国医国药, 22(11): 2623-2625. |
| XIONG J J, DING L J, 2011. Qualitative analysis on effective constituents of Pteris vittata and its Ultraviolet Spectrophotometry[J]. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research, 22(11): 2623-2625. | |
| [46] | 杨树深, 杨军, 杨俊兴, 等, 2017. 土壤添加剂对蜈蚣草吸收转运铅、镉的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 36(6): 1650-1657. |
| YANG S S, YANG J, YANG J X, et al., 2017. Effects of soil additives on the uptake and translocation of lead and cadmium by Pteris vittata L.[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 36(6): 1650-1657. | |
| [47] |
朱光旭, 肖化云, 郭庆军, 等, 2016. 锌冶炼渣堆场优势植物的重金属累积特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 25(8): 1395-1400.
DOI |
| ZHU G X, XIAO H Y, GUO Q J, et al., 2016. Accumulation of heavy metals by dominant plants in zinc smelting slag field[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 25(8): 1395-1400. | |
| [48] | 张雅睿, 黄益宗, 保琼莉, 等, 2022. 不同螯合剂和有机酸对苍耳修复镉砷复合污染土壤的影响[J]. 环境科学, 43(8): 4292-4300. |
| ZHANG Y R, HUANG Y Z, BAO Q L, et al., 2022. Effect of chelating agents and organic acids on remediation of cadmium and arsenic complex contaminated soil using Xanthium sibiricum[J]. Enviromental Science, 43(8): 4292-4300. |
| [1] | 赵良侠, 高坤, 黄婷婷, 高也, 琚唐丹, 蒋秋阳, 金珩, 熊蕾, 汤在琳, 高灿红. 玉米籽粒高/低镉积累自交系不同生育期的镉累积特性研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(4): 766-775. |
| [2] | 杨耀东, 陈玉梅, 涂鹏飞, 曾清如. 经济作物轮作模式下镉污染农田修复潜力[J]. 生态环境学报, 2023, 32(3): 627-634. |
| [3] | 高鹏, 高品, 孙蔚旻, 孔天乐, 黄端仪, 刘华清, 孙晓旭. 蜈蚣草根际及内生微生物群落对砷污染胁迫的响应机制研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1225-1234. |
| [4] | 黄敏, 赵晓峰, 梁荣祥, 王鹏忠, 戴安然, 何晓曼. 3种螯合剂对Cd、Cu复合污染土壤淋洗修复的对比研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(6): 1244-1252. |
| [5] | 伍德, 彭鸥, 刘玉玲, 张朴心, 尹雪斐, 黄薪铭, 铁柏清. 螯合剂及组配对伴矿景天修复两种镉污染土壤的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(12): 2414-2421. |
| [6] | 俞龙生, 李卫, 许铭宇, 林泽帆. 赤霉素浸种对2种矿区修复先锋植物种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(11): 2225-2233. |
| [7] | 丛超, 杨宁柯, 王海娟, 王宏镔. 吲哚乙酸和激动素配合施用提高蜈蚣草和龙葵对砷、镉富集的田间试验[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6): 1299-1309. |
| [8] | 李富荣, 王琳清, 李文英, 吴志超, 王旭. 水芹对重金属的吸收累积及其应用研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(12): 2423-2430. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
